Effects of a Multimodal Approach Using Buprenorphine with/without Meloxicam on Food Intake, Body Weight, Nest Consolidating Behavior, Burrowing Behavior, and Gastrointestinal Tissues in Postoperative Male Mice
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
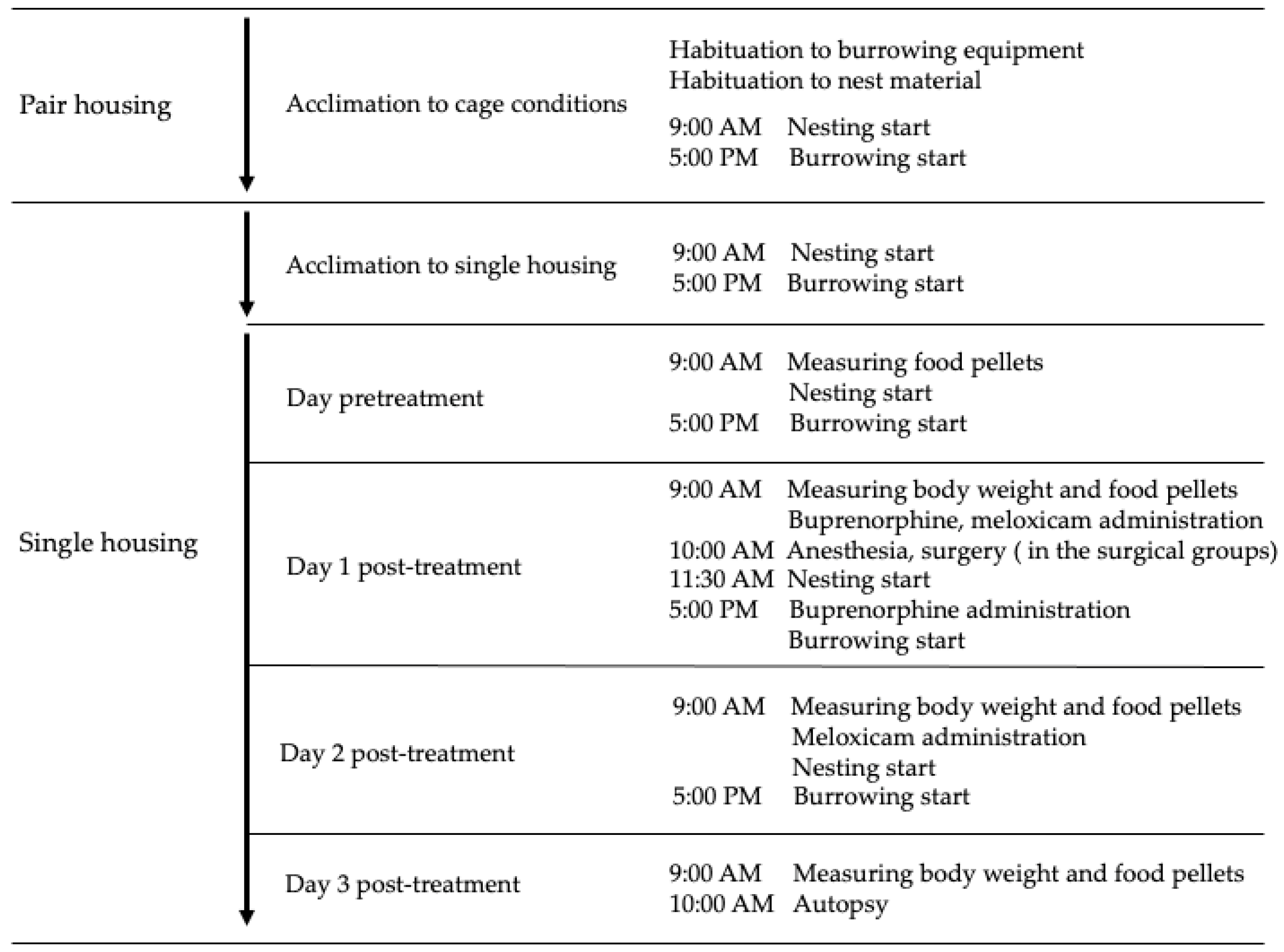
2.1. Animals and Experimental Setup
2.2. Treatment Groups
2.3. Surgery and Perioperative Care
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Food Intake
2.4.2. Body Weight
2.4.3. Nest Consolidating Behavior
2.4.4. Burrowing Behavior
2.5. Histological Assessment of the Stomach, Duodenum, and Jejunum
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
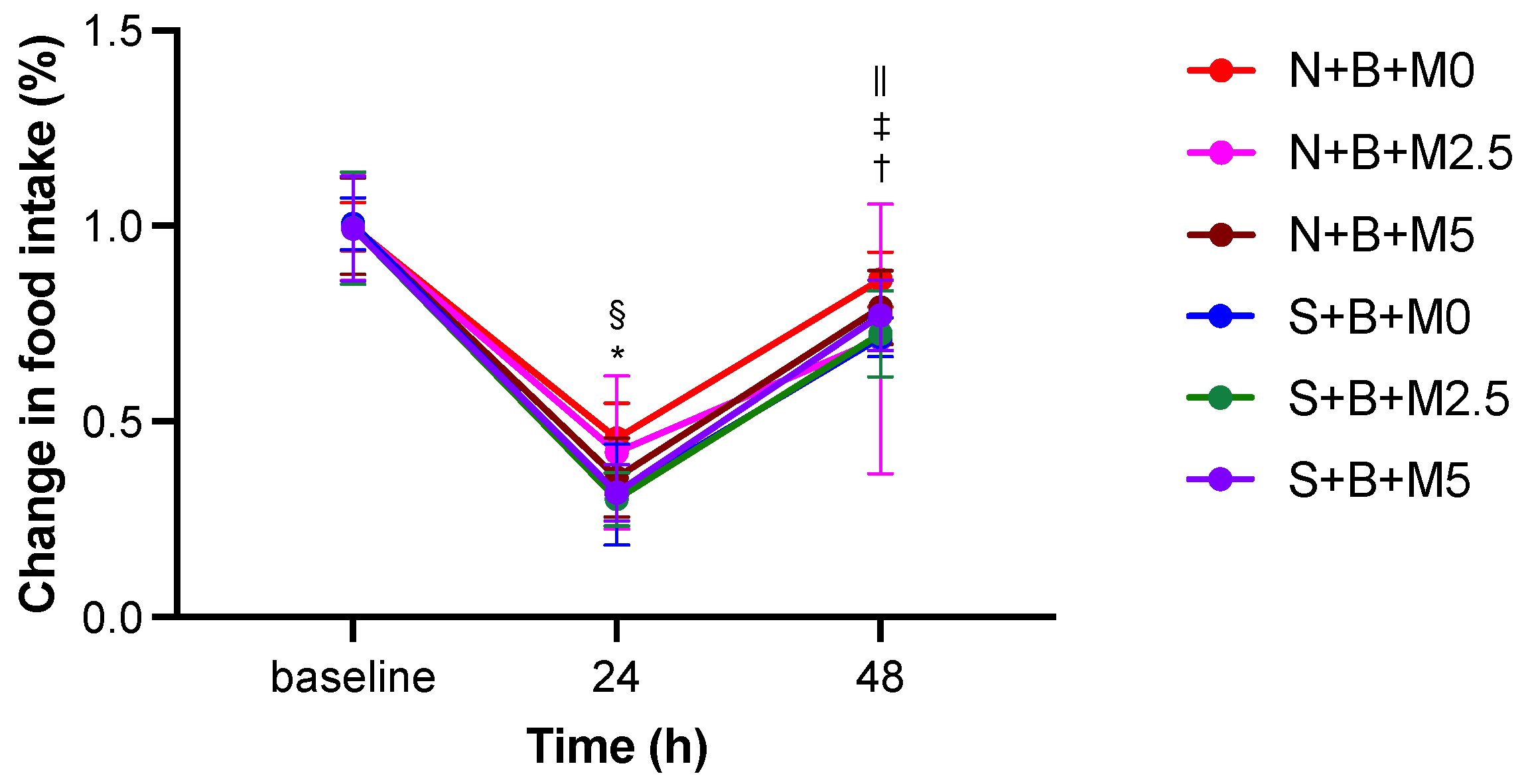
3.1. Changes in Food Intake
3.2. Changes in Body Weight
3.3. Nest Consolidating Behavior
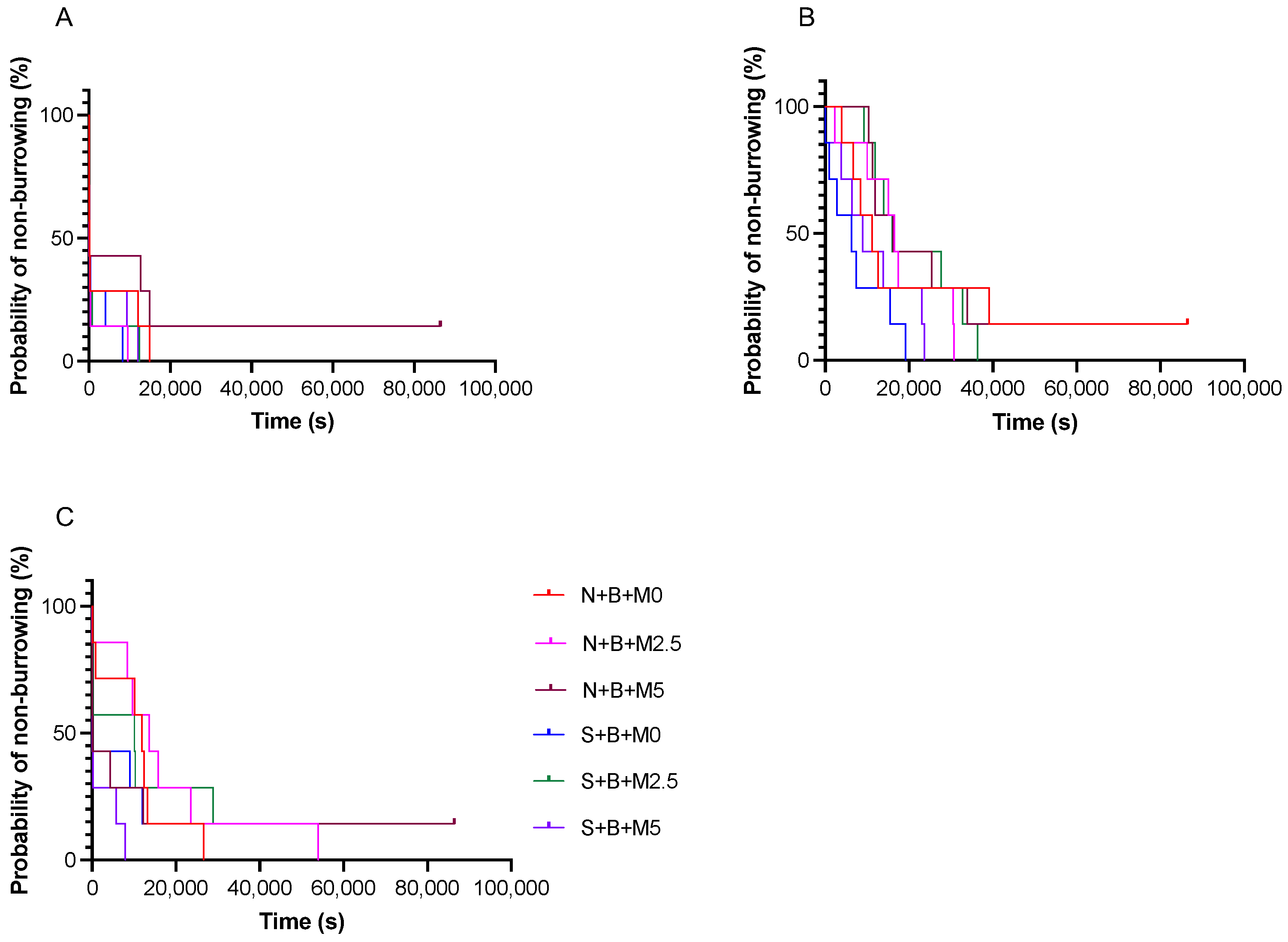
3.4. Burrowing Behavior
3.5. Histological Assessment of the Stomach, Duodenum, and Jejunum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jirkof, P. Side effects of pain and analgesia in animal experimentation. Lab Anim. 2017, 46, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, L.; Austin, J. Pain and laboratory animals: Publication practices for better data reproducibility and better animal welfare. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute for Laboratory Animal Research. Veterinary Care. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 105–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hellyer, P.W.; Robertson, S.A.; Fails, A.D. Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia, 4th ed.; Tranquilli, W.J., Thurmon, J.C., Grimm, K.A., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780781754712. [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk, E.S.; Mariano, E.R. Designing the ideal perioperative pain management plan starts with multimodal analgesia. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 71, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, P.L.; Kendall, L.V.; Turner, P.V. Clinical Management of Pain in Rodents. Comp. Med. 2019, 69, 468–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaha, M.D.; Leon, L.R. Effects of indomethacin and buprenorphine analgesia on the postoperative recovery of mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2008, 47, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, V.L.; Thurston, S.E.; Lofgren, J.L. Using cageside measures to evaluate analgesic efficacy in mice (Mus Musculus) after surgery. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2018, 57, 186–201. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, J.M.; Austin, J.; Wilkerson, J.; Carbone, L. Effects of multimodal analgesia on the success of mouse embryo transfer surgery. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Dueñas, V.; Poveda, R.; Sánchez, S.; Ciruela, F. Synergistic interaction between fentanyl and a tramadol:Paracetamol combination on the inhibition of nociception in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 118, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, H.F.; Pinardi, G. Lack of effect of naltrindole on the spinal synergism of morphine and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tubbs, J.T.; Kissling, G.E.; Travlos, G.S.; Goulding, D.R.; Clark, J.A.; King-Herbert, A.P.; Blankenship-Paris, T.L. Effects of buprenorphine, meloxicam, and flunixin meglumine as postoperative analgesia in mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2011, 50, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Furumoto, K.; Ogita, K.; Kamisaka, T.; Kawasumi, A.; Takata, K.; Maeta, N.; Itoi, T.; Nohara, M.; Saeki, K.; Kanda, T. Effects of multimodal analgesic protocol, with buprenorphine and meloxicam, on mice well-being: A dose finding study. Animals 2021, 11, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskill, B.N.; Karas, A.Z.; Garner, J.P.; Pritchett-Corning, K.R. Nest building as an indicator of health and welfare in laboratory mice. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2013, 82, 51012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P. Burrowing and nest building behavior as indicators of well-being in mice. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 234, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjendal, K.; Ottesen, J.L.; Olsson, I.A.S.; Sørensen, D.B. Effect of Repeated Exposure to Isoflurane on Nest Building and Burrowing in Mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. JAALAS 2020, 59, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arras, M.; Rettich, A.; Cinelli, P.; Kasermann, H.P.; Burki, K. Assessment of post-laparotomy pain in laboratory mice by telemetric recording of heart rate and heart rate variability. BMC Vet. Res. 2007, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P.; Cesarovic, N.; Rettich, A.; Nicholls, F.; Seifert, B.; Arras, M. Burrowing behavior as an indicator of post-laparotomy pain in mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R. Assessing burrowing, nest construction, and hoarding in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 59, e2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, L.A.; Nicholson, J.R.; Doods, H.; Pekcec, A. Deficits in spontaneous burrowing behavior in the rat bilateral monosodium iodoacetate model of osteoarthritis: An objective measure of pain-related behavior and analgesic efficacy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, T.; Goto, T.; Toyoda, A. Assessing nest-building behavior of mice using a 3D depth camera. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 251, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.V.; Pang, D.S.J.; Lofgren, J.L.S. A Review of Pain Assessment Methods in Laboratory Rodents. Comp. Med. 2019, 69, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, S.E.; Rohr, S.; Dufour, B.D.; Gaskill, B.N.; Pajor, E.A.; Garner, J.P. Home improvement: C57BL/6J mice given more naturalistic nesting materials build better nests. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2008, 47, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P.; Cesarovic, N.; Rettich, A.; Fleischmann, T.; Arras, M. Individual housing of female mice: Influence on postsurgical behaviour and recovery. Lab. Anim. 2012, 46, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumiya, L.C.; Sorge, R.E.; Sotocinal, S.G.; Tabaka, J.M.; Wieskopf, J.S.; Zaloum, A.; King, O.D.; Mogil, J.S. Using the mouse grimace scale to reevaluate the efficacy of postoperative analgesics in laboratory mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2012, 51, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jirkof, P.; Tourvieille, A.; Cinelli, P.; Arras, M. Buprenorphine for pain relief in mice: Repeated injections vs sustained-release depot formulation. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, L.V.; Wegenast, D.J.; Smith, B.J.; Dorsey, K.M.; Kang, S.; Lee, N.Y.; Hess, A.M. Efficacy of sustained-release buprenorphine in an experimental laparotomy model in female mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2016, 55, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wright-Williams, S.L.; Courade, J.P.; Richardson, C.A.; Roughan, J.V.; Flecknell, P.A. Effects of vasectomy surgery and meloxicam treatment on faecal corticosterone levels and behaviour in two strains of laboratory mouse. Pain 2007, 130, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlbaum, K.; Bert, B.; Dietze, S.; Palme, R.; Fink, H.; Thöne-Reineke, C. Severity classification of repeated isoflurane anesthesia in C57BL/6JRj mice—Assessing the degree of distress. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfaty, A.E.; Zeiss, C.J.; Willis, A.D.; Harris, J.M.; Smith, P.C. Concentration-dependent toxicity after subcutaneous administration of meloxicam to C57BL/6N mice (Mus musculus). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2018, 58, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, T.W.; Kendall, L.V.; Goss, S.; Grayson, K.; Tourna, C.; Palme, R.; Chen, J.Q.; Borowsky, A.D. Assessment of carprofen and buprenorphine on recovery of mice after surgical removal of the mammary fat pad. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2010, 49, 610–616. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, R.M.J. Burrowing in rodents: A sensitive method for detecting behavioral dysfunction. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, M.S.; Arras, M.; Palme, R.; Talbot, S.R.; Jirkof, P. Lidocaine and buprenorphine as part of multimodal pain management in a C57BL/6J laparotomy mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourque, S.L.; Adams, M.A.; Nakatsu, K.; Winterborn, A. Comparison of buprenorphine and meloxicam for postsurgical analgesia in rats: Effects on body weight, locomotor activity, and hemodynamic parameters. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2010, 49, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.M.; Hagman, B.; Codita, A.; Van Loo, P.L.P.; Strömmer, L.; Baumans, V. Housing environment influences the need for pain relief during post-operative recovery in mice. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 99, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loo, P.L.P.; Kuin, N.; Sommer, R.; Avsaroglu, H.; Pham, T.; Baumans, V. Impact of “living apart together” on postoperative recovery of mice compared with social and individual housing. Lab. Anim. 2007, 41, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufiange, M.; Leung, V.S.Y.; Simpson, K.; Pang, D.S.J. Pre-warming following premedication limits hypothermia before and during anesthesia in Sprague-Dawley rats (Rattus Norvegicus). Can. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 85, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Celeste, N.A.; Emmer, K.M.; Bidot, W.A.; Perret-Gentil, M.I.; Malbrue, R.A. Effects of Cling Film Draping Material on Body Temperature of Mice during Surgery. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2021, 60, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, M.; Bernardo, A.; Linga, N.; Pérez-Romero, C.A.; Guillou, J.L.; Sibille, E.; Prevot, T.D. Handling techniques to reduce stress in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 2021, e62593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, K. Tunnel use facilitates handling of ICR mice and decreases experimental variation. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.L.; West, R.S. Taming anxiety in laboratory mice. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.J.; Dani, B.; Serrano, E.M.N.; Smulders, T.V.; Roughan, J.V. Benefits of tunnel handling persist after repeated restraint, injection and anaesthesia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, K.; Hurst, J.L. Reducing Mouse Anxiety during Handling: Effect of Experience with Handling Tunnels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudeck, J.; Vogl, S.; Heinl, C.; Steinfath, M.; Fritzwanker, S.; Kliewer, A.; Schulz, S.; Schönfelder, G.; Bert, B. Analgesic treatment with buprenorphine should be adapted to the mouse strain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 191, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Treatment | N + B + M0 S + B + M0 | N + B + M2.5 S + B + M2.5 | N + B + M5 S + B + M5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 post-treatment | Buprenorphine | 0.1 mg/kg (SC) 2 times | 0.1 mg/kg (SC) 2 times | 0.1 mg/kg (SC) 2 times |
| Meloxicam | Sterile water for injection (SC) | 2.5 mg/kg (SC) | 5 mg/kg (SC) | |
| Bupivacaine | N + B + M0: None S + B + M0: 0.5% (drop) | N + B + M2.5: None S + B + M2.5: 0.5% (drop) | N + B + M5: None S + B + M5: 0.5% (drop) | |
| Day 2 post-treatment | Meloxicam | Sterile water for injection (SC) | 2.5 mg/kg (SC) | 5 mg/kg (SC) |
| Treatment | N + B + M0 | N + B + M2.5 | N + B + M5 | S + B + M0 | S + B + M2.5 | S + B + M5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day pre-treament | 2 h | 5 (4–5) * | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) | 4 (4–5) | 4 (2–5) | 4 (3–5) |
| 4 h | 5 (5–5) | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | 5 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | |
| 6 h | 5 (5–5) | 4 (4–5) | 4 (3–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (3–5) | 4 (4–5) | |
| 8 h | 5 (5–5) | 4 (4–5) | 4 (4–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
| 12 h | 5 (5–5) | 4 (4–5) | 4 (4–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
| 16 h | 5 (5–5) | 5 (5–5) | 4 (4–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (3–5) | 5 (5–5) | |
| 24 h | 5 (5–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (3–5) | 5 (5–5) | |
| Day 1 post-treatment | 2 h | 1 (1–1) | 1 (1–1) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) |
| 4 h | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–1) | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | |
| 6 h | 2 (1–3) | 1 (1–3) | 1 (1–2) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–3) | |
| 8 h | 2 (2–3) | 1 (1–3) | 1 (1–2) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (2–3) | |
| 12 h | 3 (2–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (2–4) | 2 (2–3) | 3 (2–4) | |
| 16 h | 3 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (3–4) | 5 (4–5) | |
| 24 h | 5 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | 4 (2–5) | 5 (2–5) | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
| Day 2 post-treatment | 2 h | 2 (2–2) | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 2 (2–3) | 3 (2–4) | 4 (3–5) † |
| 4 h | 2 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–4) | 4 (2–5) | 4 (4–5) | |
| 6 h | 4 (3–4) | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–5) | 3 (2–4) | 4 (2–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
| 8 h | 4 (3–4) | 3 (3–4) | 3 (3–5) | 3 (2–4) | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
| 12 h | 4 (3–4) | 3 (3–4) | 4 (3–5) | 3 (2–5) | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
| 16 h | 4 (4–5) | 4 (3–4) | 5 (4–5) | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
| 24 h | 5 (4–5) | 4 (4–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (3–5) | 5 (5–5) | 5 (4–5) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furumoto, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Nohara, M.; Takenaka, N.; Maeta, N.; Kanda, T. Effects of a Multimodal Approach Using Buprenorphine with/without Meloxicam on Food Intake, Body Weight, Nest Consolidating Behavior, Burrowing Behavior, and Gastrointestinal Tissues in Postoperative Male Mice. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110589
Furumoto K, Sasaki Y, Nohara M, Takenaka N, Maeta N, Kanda T. Effects of a Multimodal Approach Using Buprenorphine with/without Meloxicam on Food Intake, Body Weight, Nest Consolidating Behavior, Burrowing Behavior, and Gastrointestinal Tissues in Postoperative Male Mice. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(11):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110589
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurumoto, Kayo, Yuka Sasaki, Masakatsu Nohara, Nagisa Takenaka, Noritaka Maeta, and Teppei Kanda. 2022. "Effects of a Multimodal Approach Using Buprenorphine with/without Meloxicam on Food Intake, Body Weight, Nest Consolidating Behavior, Burrowing Behavior, and Gastrointestinal Tissues in Postoperative Male Mice" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 11: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110589
APA StyleFurumoto, K., Sasaki, Y., Nohara, M., Takenaka, N., Maeta, N., & Kanda, T. (2022). Effects of a Multimodal Approach Using Buprenorphine with/without Meloxicam on Food Intake, Body Weight, Nest Consolidating Behavior, Burrowing Behavior, and Gastrointestinal Tissues in Postoperative Male Mice. Veterinary Sciences, 9(11), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110589






