Establishment and Application of PDCoV Antibody Indirect ELISA Detection Method Based on N Protein
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses, Experimental Animals, PDCoV Strain, Inactivated Vaccine and Serum, and Clinical Samples
2.2. Recombinant Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.3. PDCoV N Protein Recombinant Expression
2.4. Positive and Negative Serum Preparation
2.5. Cross-Reactivity Detection of Three Porcine Intestinal Coronavirus N Proteins
2.6. Optimization of ELISA Method
2.7. Analysis of ROC Curve of ELISA
2.8. Assessment of Reproducibility and Specificity of ELISA Method
2.9. Validation with Clinical Samples
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. IFA
3. Results
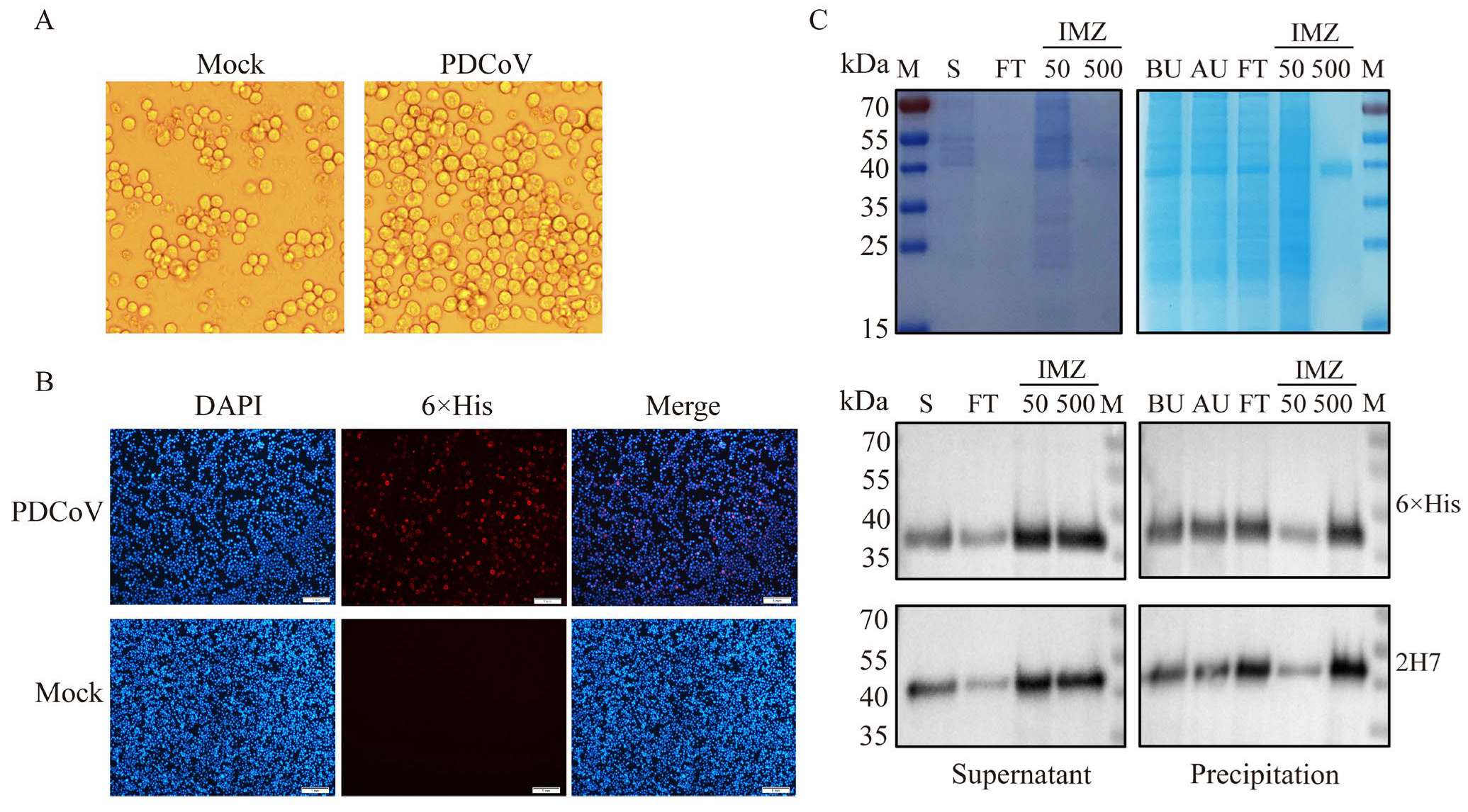
3.1. Induction of Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins
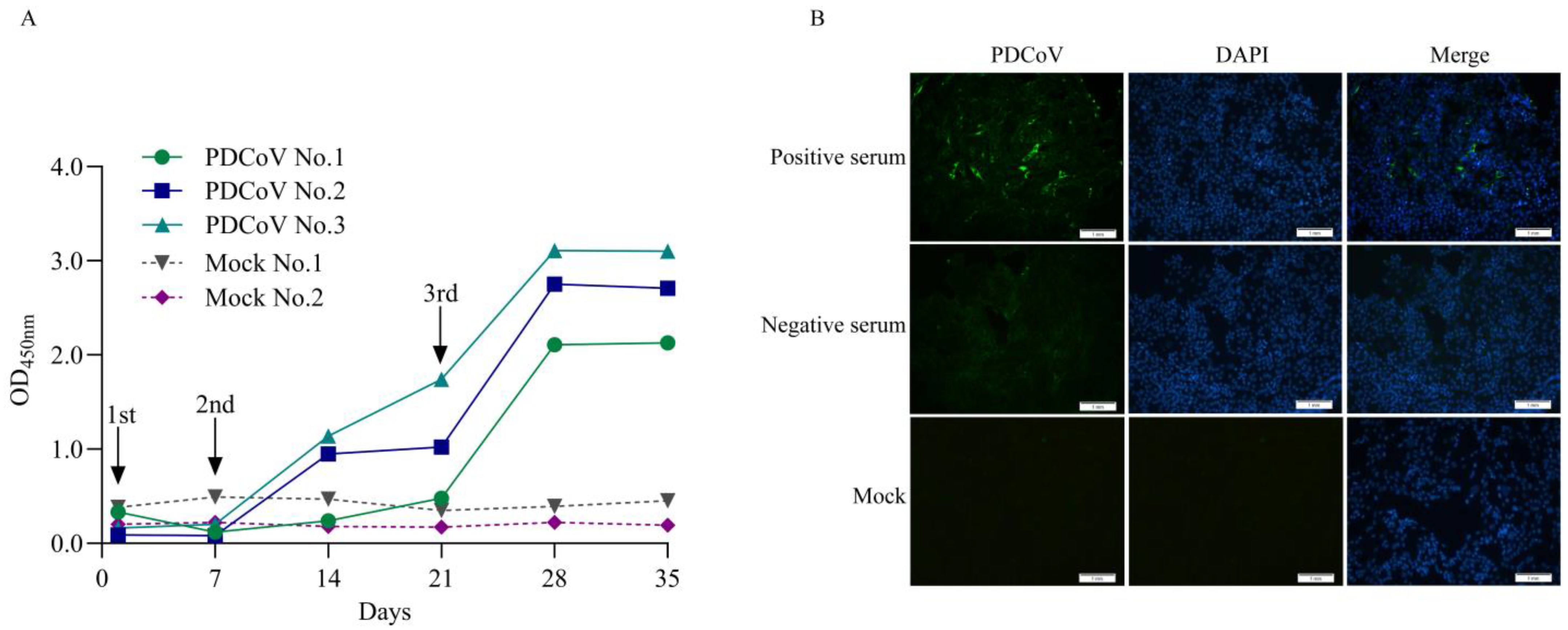
3.2. Preparation of PDCoV Antibody-Positive and -Negative Control Serum
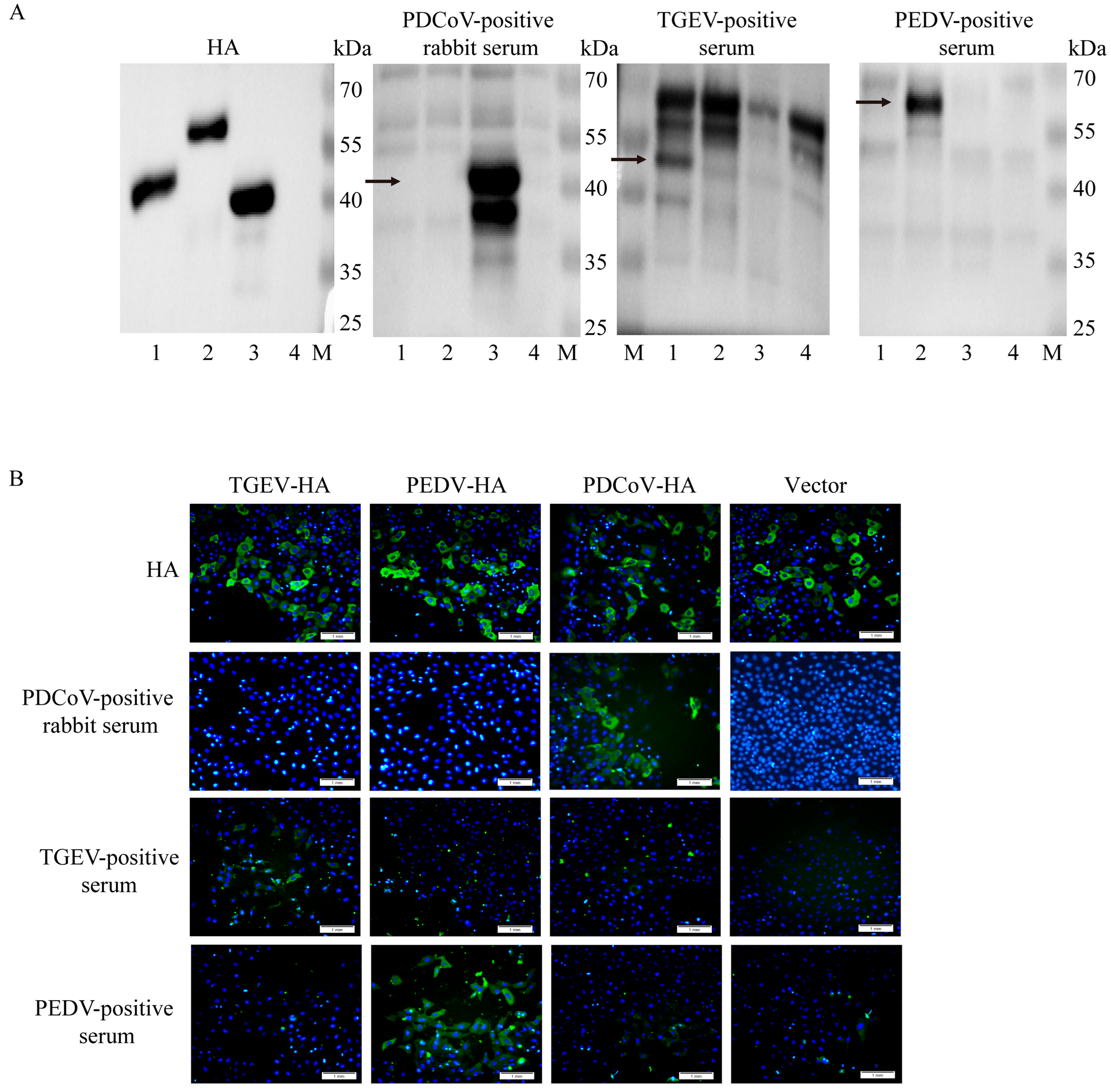
3.3. Analysis of the Cross-Reactivity of Porcine Intestinal Coronavirus N Proteins
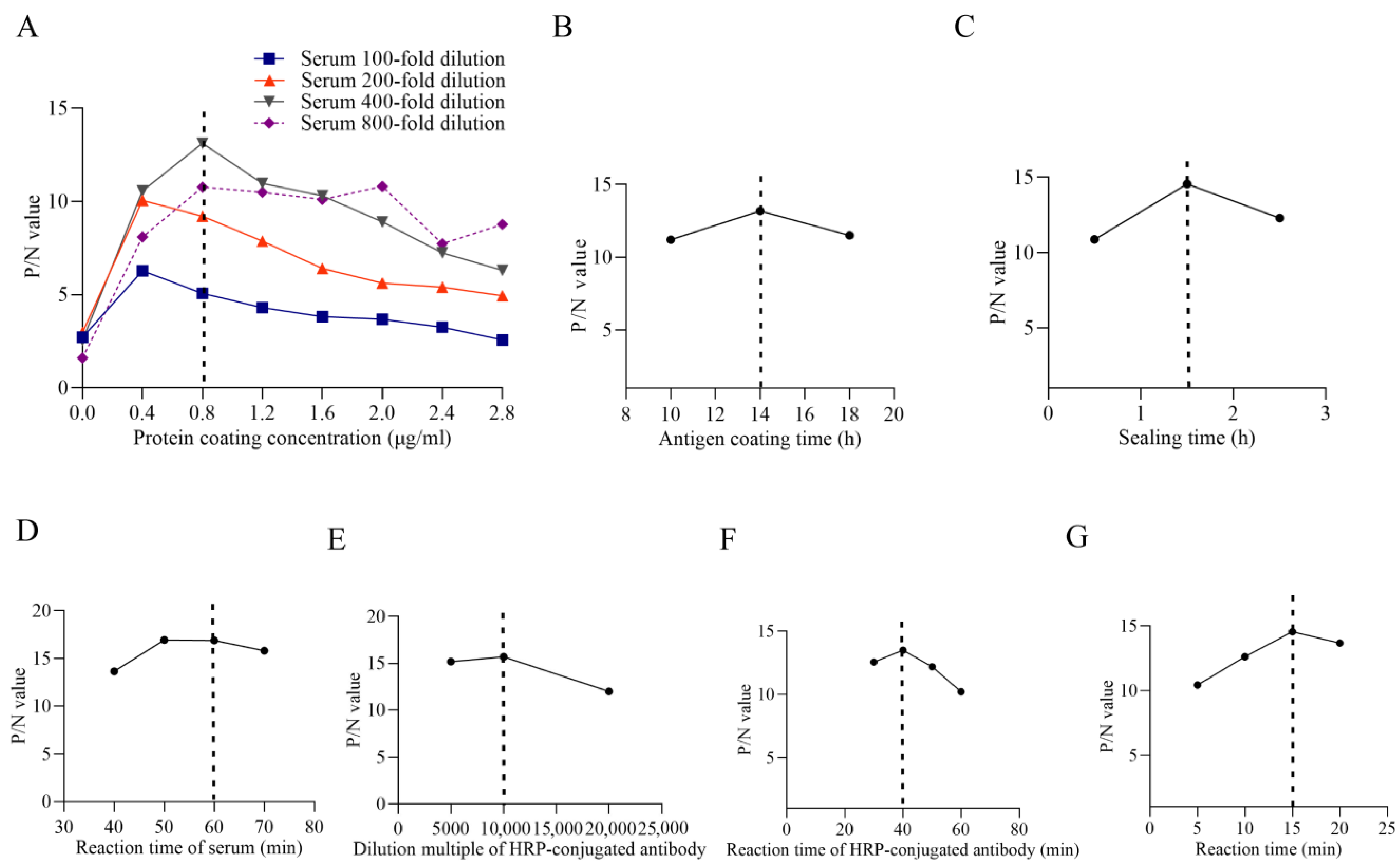
3.4. Establishment of Indirect ELISA Method and Optimization of Conditions
3.4.1. Optimization of Antigen Coating Concentration and Serum Dilution
3.4.2. Determination of the Cut-Off Value of ELISA
3.5. Analysis of the Reproducibility and Specificity of ELISA
3.6. Clinical Samples Detection by ELISA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Lau, J.H.N.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.L.; Tsang, C.C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C. An Updated Review of Porcine Deltacoronavirus in Terms of Prevalence, Pathogenicity, Pathogenesis and Antiviral Strategy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 811187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Chung, H.C.; Nguyen, V.G.; Moon, H.J.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, G.E.; Park, B.K. Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Porcine Deltacoronavirus in Korean Swine Farms, 2015. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madapong, A.; Saeng-Chuto, K.; Lorsirigool, A.; Temeeyasen, G.; Srijangwad, A.; Tripipat, T.; Wegner, M.; Nilubol, D. Complete Genome Sequence of Porcine Deltacoronavirus Isolated in Thailand in 2015. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00408-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorsirigool, A.; Saeng-Chuto, K.; Temeeyasen, G.; Madapong, A.; Tripipat, T.; Wegner, M.; Tuntituvanont, A.; Intrakamhaeng, M.; Nilubol, D. The first detection and full-length genome sequence of porcine deltacoronavirus isolated in Lao PDR. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2909–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.P.; Song, S.; An, B.-H.; Park, G.-N.; Pham, N.T.; Le, D.Q.; Nguyen, V.T.; Vu, T.T.H.; Kim, K.-S.; Choe, S.; et al. A novel strain of porcine deltacoronavirus in Vietnam. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rivera, C.; Ramírez-Mendoza, H.; Mendoza-Elvira, S.; Segura-Velázquez, R.; Sánchez-Betancourt, J.I. First report and phylogenetic analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus in Mexico. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Fang, L.; Zeng, S.; Sun, Q.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S. Porcine Deltacoronavirus in Mainland China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2254–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, T.; Zhang, T.; Li, A.; Huang, D.; Wu, Q.; et al. Newly Emerged Porcine Deltacoronavirus Associated With Diarrhoea in Swine in China: Identification, Prevalence and Full-Length Genome Sequence Analysis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Lou, F.; Oglesbee, M.; Krakowka, S.; Li, J. Origin, evolution, and virulence of porcine deltacoronaviruses in the United States. mBio 2015, 6, e00064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Porcine deltacoronavirus: Overview of infection dynamics, diagnostic methods, prevalence and genetic evolution. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Shan, F.; Hou, J.; Guo, D.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wei, Z. Establishment and application of PDCoV antigen-specific DAS-ELISA detection method. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W. FBXW8 suppresses PDCoV proliferation via the NPD52-dependent autophagic degradation of a viral nucleocapsid protein. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1457255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhao, G.; Lin, Y.; Chan, C.; He, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wu, C.; Jin, D.-Y.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Priming with rAAV encoding RBD of SARS-CoV S protein and boosting with RBD-specific peptides for T cell epitopes elevated humoral and cellular immune responses against SARS-CoV infection. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, R.; van Zyl, M.; Fielding, B.C. The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein. Viruses 2014, 6, 2991–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthaler, D.; Raymond, L.; Jiang, Y.; Collins, J.; Rossow, K.; Rovira, A. Rapid detection, complete genome sequencing, and phylogenetic analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Fan, M.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X. Establishment and Application of a Triplex Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Differentiation of PEDV, PoRV, and PDCoV. Viruses 2023, 15, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Yu, T.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Cheng, G.; Wei, L.; Ni, L.; et al. Establishment and application of a quadruplex real-time RT-qPCR assay for differentiation of TGEV, PEDV, PDCoV, and PoRVA. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 191, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okda, F.; Lawson, S.; Liu, X.; Singrey, A.; Clement, T.; Hain, K.; Nelson, J.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E.A. Development of monoclonal antibodies and serological assays including indirect ELISA and fluorescent microsphere immunoassays for diagnosis of porcine deltacoronavirus. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, O.H.; Heinzel, T. Phosphorylation–acetylation switch in the regulation of STAT1 signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 315, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Feng, L. Development of an indirect ELISA for detecting porcine deltacoronavirus IgA antibodies. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thachil, A.; Gerber, P.F.; Xiao, C.-T.; Huang, Y.-W.; Opriessnig, T. Development and application of an ELISA for the detection of porcine deltacoronavirus IgG antibodies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Hu, H.; Eyerly, B.; Lu, Z.; Chepngeno, J.; Saif, L.J. Pathogenicity of 2 porcine deltacoronavirus strains in gnotobiotic pigs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Li, C.; Guo, D.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Geng, Y.; Yao, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, E.; Zhao, X.; et al. A recombinant nucleocapsid protein-based indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect antibodies against porcine deltacoronavirus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Development of a Nucleocapsid Protein-Based Blocking ELISA for the Detection of Porcine Deltacoronavirus Antibodies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Fan, B.; Zhang, X.; Guo, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Li, B. Development of a Novel Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA for Quantitative Detection of Porcine Deltacoronavirus Antigen. Viruses 2021, 13, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Li, T.; Xue, W.; Zhang, S.; Cui, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Gu, Y.; Xia, N.; et al. Genetic engineering of baculovirus-insect cell system to improve protein production. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 994743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Xu, J.; Yue, M.; Fang, W.; Li, X. Utility Evaluation of Porcine Enteroids as PDCoV Infection Model in vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnette, W.N. “Western blotting”: Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 112, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Wang, N.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Yan, Y. Porcine deltacoronavirus nucleocapsid protein species-specifically suppressed IRF7-induced type I interferon production via ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 250, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Qu, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. Prevalence and potential risk factors of PDCoV in pigs based on publications during 2015–2021 in China: Comprehensive literature review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 179, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckow, V.A.; Summers, M.D. High level expression of nonfused foreign genes with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology 1989, 170, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, A.C.; Aksular, M.; Graves, L.P.; Irons, S.L.; Possee, R.D.; King, L.A. Overview of the Baculovirus Expression System. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2018, 91, 5.4.1–5.4.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yu, L.; Teng, F.; Wang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L. Expression of recombinant allergen, Der f 1, Der f 2 and Der f 4 using baculovirus-insect cell systems. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2018, 14, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irons, S.L.; Chambers, A.C.; Lissina, O.; King, L.A.; Possee, R.D. Protein Production Using the Baculovirus Expression System. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2018, 91, 5.5.1–5.5.22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Fang, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Du, T.; Fang, P.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S. Isolation, genomic characterization, and pathogenicity of a Chinese porcine deltacoronavirus strain CHN-HN-2014. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 196, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Sue, S.-C.; Yu, T.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Tsai, C.-K.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Lee, S.; Hsiao, H.; Wu, W.-J.; Chang, W.-L.; et al. Modular organization of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Gao, X.; Oka, T.; Vlasova, A.N.; Esseili, M.A.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J. Antigenic relationships among porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and transmissible gastroenteritis virus strains. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3332–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarrineh, M.; Mashhadi, I.S.; Farhadpour, M.; Ghassempour, A. Mechanism of antibodies purification by protein A. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 609, 113909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
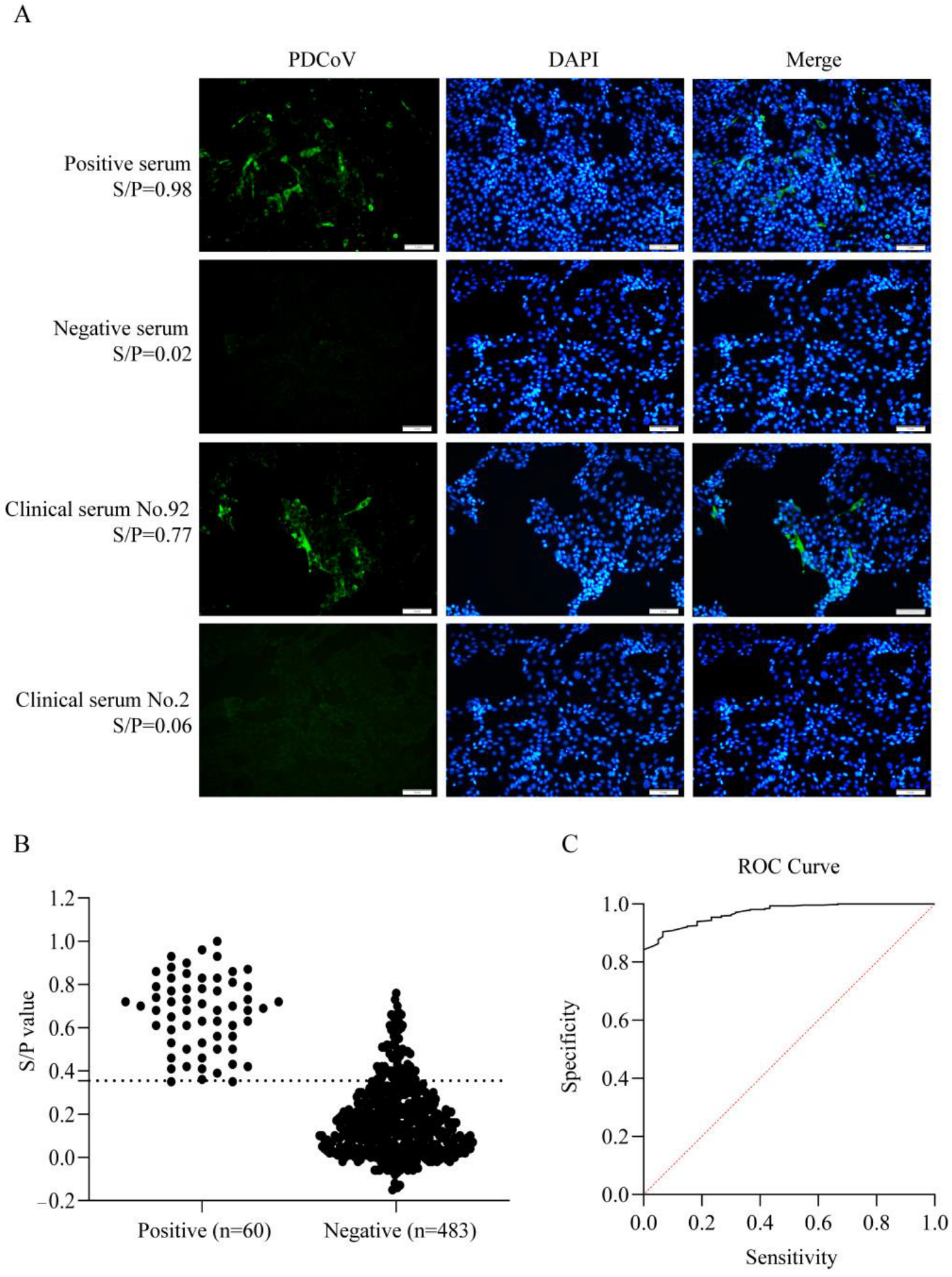
| Number | Days | Mean | SD (%) | CV (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 1 | 0.791 | 0.809 | 0.769 | 0.790 | 2.00 | 2.54 |
| 2 | 0.073 | 0.065 | 0.078 | 0.072 | 0.66 | 9.11 |
| 3 | 1.606 | 1.579 | 1.589 | 1.591 | 1.37 | 0.86 |
| 4 | 0.114 | 0.117 | 0.109 | 0.113 | 0.40 | 3.57 |
| 5 | 0.061 | 0.056 | 0.059 | 0.059 | 0.25 | 4.29 |
| 6 | 0.082 | 0.093 | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.55 | 6.31 |
| 7 | 0.093 | 0.109 | 0.099 | 0.100 | 0.81 | 8.06 |
| 8 | 0.175 | 0.174 | 0.170 | 0.173 | 0.26 | 1.53 |
| 9 | 0.314 | 0.313 | 0.307 | 0.311 | 0.38 | 1.22 |
| 10 | 0.096 | 0.084 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.60 | 6.67 |
| 11 | 0.156 | 0.133 | 0.143 | 0.144 | 1.15 | 8.01 |
| 12 | 0.146 | 0.122 | 0.132 | 0.133 | 1.21 | 9.04 |
| 13 | 0.696 | 0.703 | 0.700 | 0.700 | 0.35 | 0.50 |
| 14 | 0.423 | 0.448 | 0.427 | 0.433 | 1.34 | 3.10 |
| 15 | 0.141 | 0.141 | 0.139 | 0.140 | 0.12 | 0.82 |
| 16 | 0.111 | 0.099 | 0.100 | 0.103 | 0.67 | 6.44 |
| Number | Batches | Mean | SD (%) | CV (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 1 | 0.612 | 0.649 | 0.607 | 0.623 | 2.29 | 3.68 |
| 2 | 0.521 | 0.490 | 0.535 | 0.515 | 2.30 | 4.47 |
| 3 | 0.562 | 0.560 | 0.520 | 0.547 | 2.37 | 4.33 |
| 4 | 0.729 | 0.701 | 0.781 | 0.737 | 4.06 | 5.51 |
| 5 | 0.520 | 0.545 | 0.551 | 0.539 | 1.64 | 3.05 |
| 6 | 0.735 | 0.703 | 0.776 | 0.738 | 3.66 | 4.96 |
| 7 | 0.386 | 0.369 | 0.342 | 0.366 | 2.22 | 6.07 |
| 8 | 0.631 | 0.589 | 0.579 | 0.600 | 2.76 | 4.60 |
| 9 | 0.388 | 0.346 | 0.352 | 0.362 | 2.27 | 6.28 |
| 10 | 0.309 | 0.300 | 0.347 | 0.319 | 2.49 | 7.83 |
| 11 | 0.683 | 0.658 | 0.730 | 0.690 | 3.66 | 5.30 |
| 12 | 0.067 | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.065 | 0.17 | 2.66 |
| 13 | 1.257 | 1.159 | 1.241 | 1.219 | 5.26 | 4.31 |
| 14 | 0.132 | 0.140 | 0.159 | 0.144 | 1.39 | 9.65 |
| 15 | 0.080 | 0.083 | 0.085 | 0.083 | 0.25 | 3.04 |
| 16 | 0.161 | 0.169 | 0.151 | 0.160 | 0.90 | 5.62 |
| Serum | PDCoV | PEDV | TGEV | PRRSV | CSFV | PCV2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S/P | 0.98 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.12 |
| Result | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| Year | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | ||||||
| Hangzhou | 16 | 32 | 18 | - | 66 | |
| Jinhua | 16 | 40 | 18 | 33 | 107 | |
| Quzhou | 16 | - | 32 | 37 | 85 | |
| Lishui | 16 | 35 | 18 | 20 | 89 | |
| Shaoxing | 17 | - | 27 | - | 44 | |
| Wenzhou | 19 | - | 36 | 30 | 85 | |
| Huzhou | 46 | - | - | - | 46 | |
| Taizhou | - | - | 25 | - | 25 | |
| Ningbo | - | - | 38 | 15 | 53 | |
| Total | 146 | 107 | 212 | 135 | 600 | |
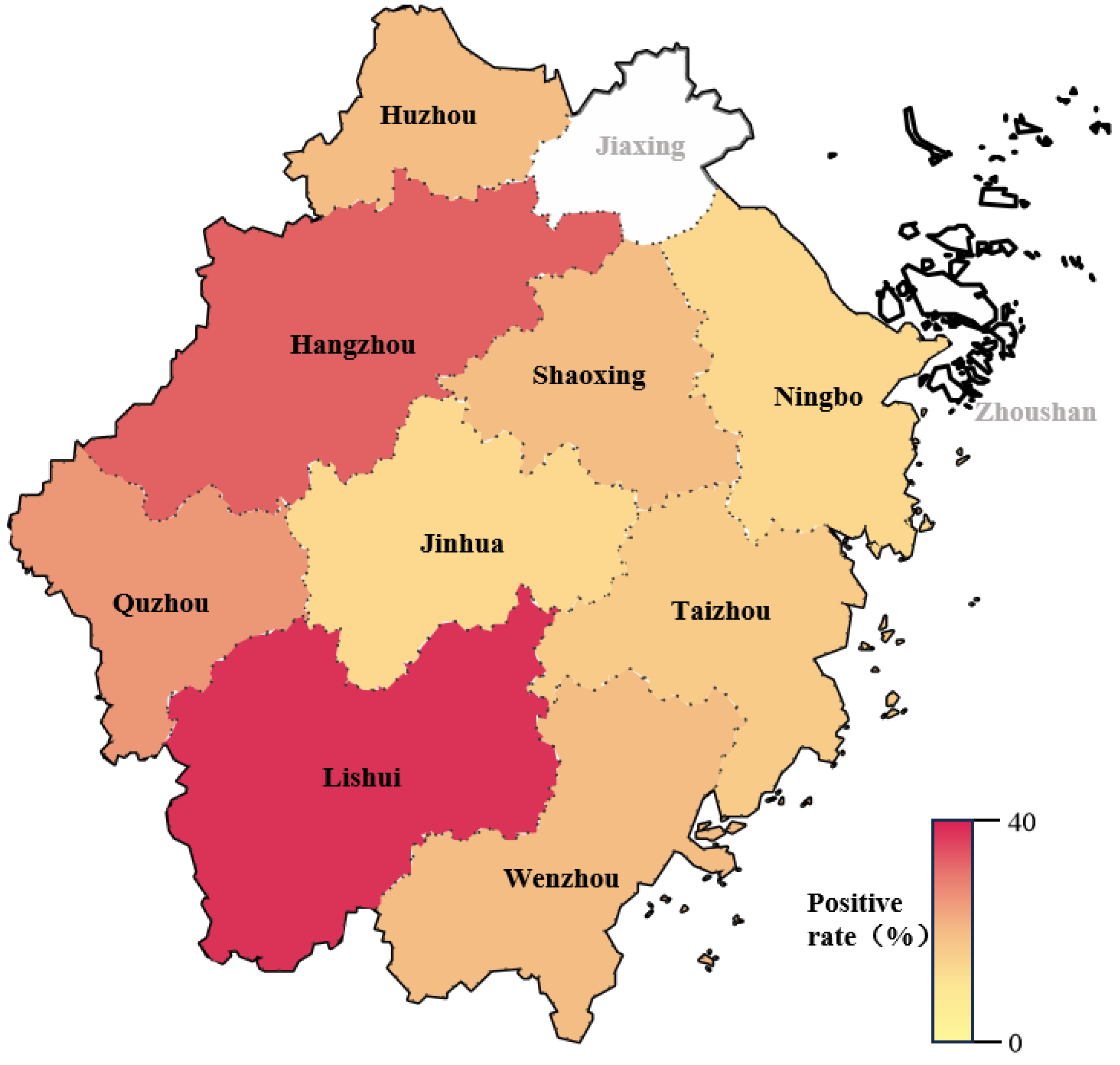
| Cities | Serum Number | Positive Number | Positive Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hangzhou | 66 | 20 | 30.3 |
| Jinhua | 107 | 11 | 10.3 |
| Quzhou | 85 | 18 | 21.2 |
| Lishui | 89 | 38 | 42.7 |
| Shaoxing | 44 | 5 | 11.4 |
| Wenzhou | 85 | 13 | 15.3 |
| Taizhou | 25 | 2 | 8.0 |
| Huzhou | 46 | 5 | 10.8 |
| Ningbo | 53 | 4 | 7.5 |
| Total | 600 | 116 | 19.3 |
| Year | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum count | 146 | 107 | 212 | 135 |
| Positive number | 26 | 33 | 21 | 36 |
| Positive rate (%) | 17.8 | 30.8 | 9.9 | 26.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Gao, Q.; Shan, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Establishment and Application of PDCoV Antibody Indirect ELISA Detection Method Based on N Protein. Vet. Sci. 2026, 13, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010012
Xiao Y, Zhou L, Gao Q, Shan Y, Xu J, Li X. Establishment and Application of PDCoV Antibody Indirect ELISA Detection Method Based on N Protein. Veterinary Sciences. 2026; 13(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yuting, Lei Zhou, Qin Gao, Ying Shan, Jidong Xu, and Xiaoliang Li. 2026. "Establishment and Application of PDCoV Antibody Indirect ELISA Detection Method Based on N Protein" Veterinary Sciences 13, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010012
APA StyleXiao, Y., Zhou, L., Gao, Q., Shan, Y., Xu, J., & Li, X. (2026). Establishment and Application of PDCoV Antibody Indirect ELISA Detection Method Based on N Protein. Veterinary Sciences, 13(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010012






