Effects and Microbiota Changes Following Oral Lyophilized Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Capsules in Canine with Chronic Enteropathy After Parvovirus Infection: Case Report
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Case Description
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcomes
3.1.1. Hematological Parameters
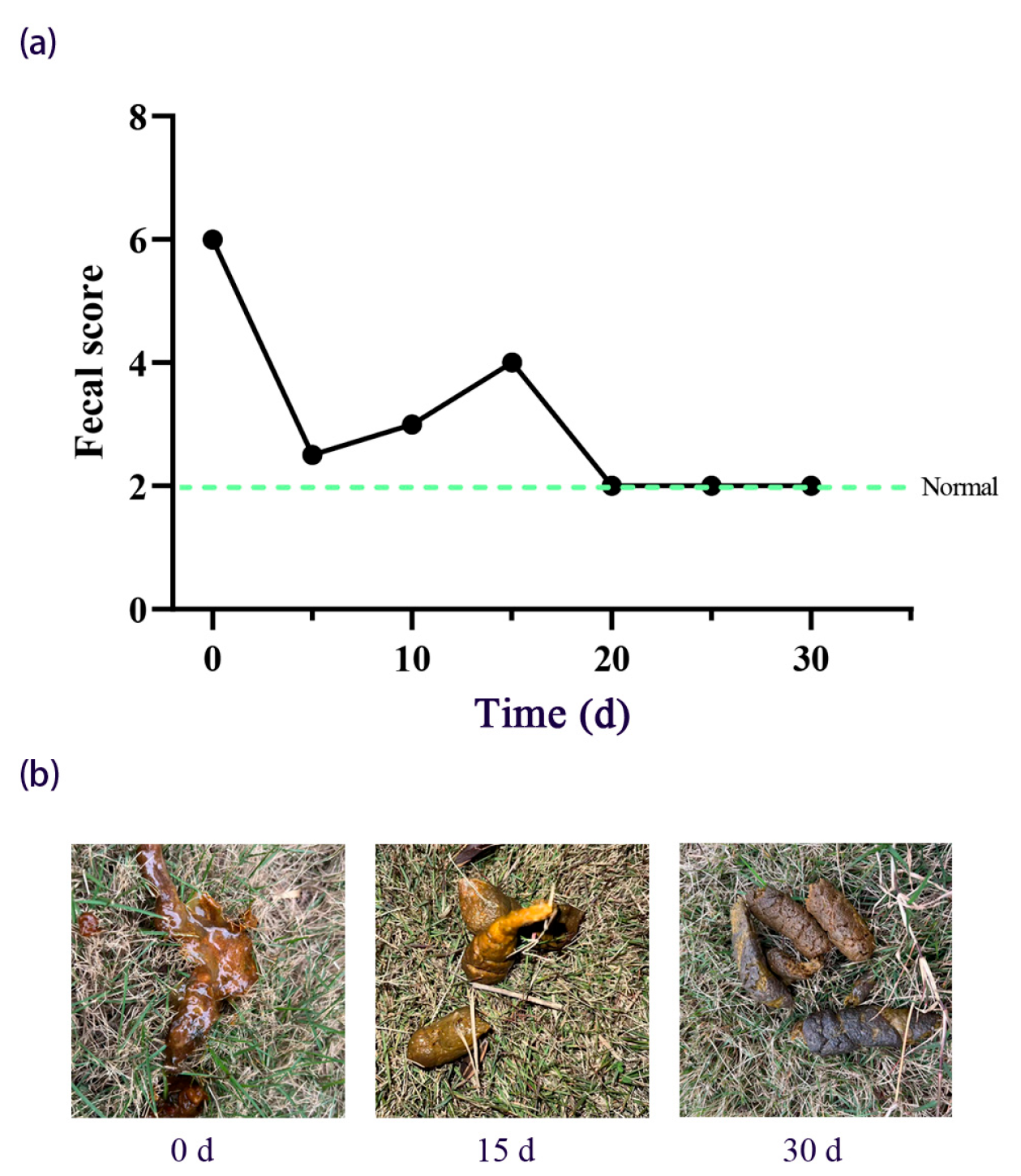
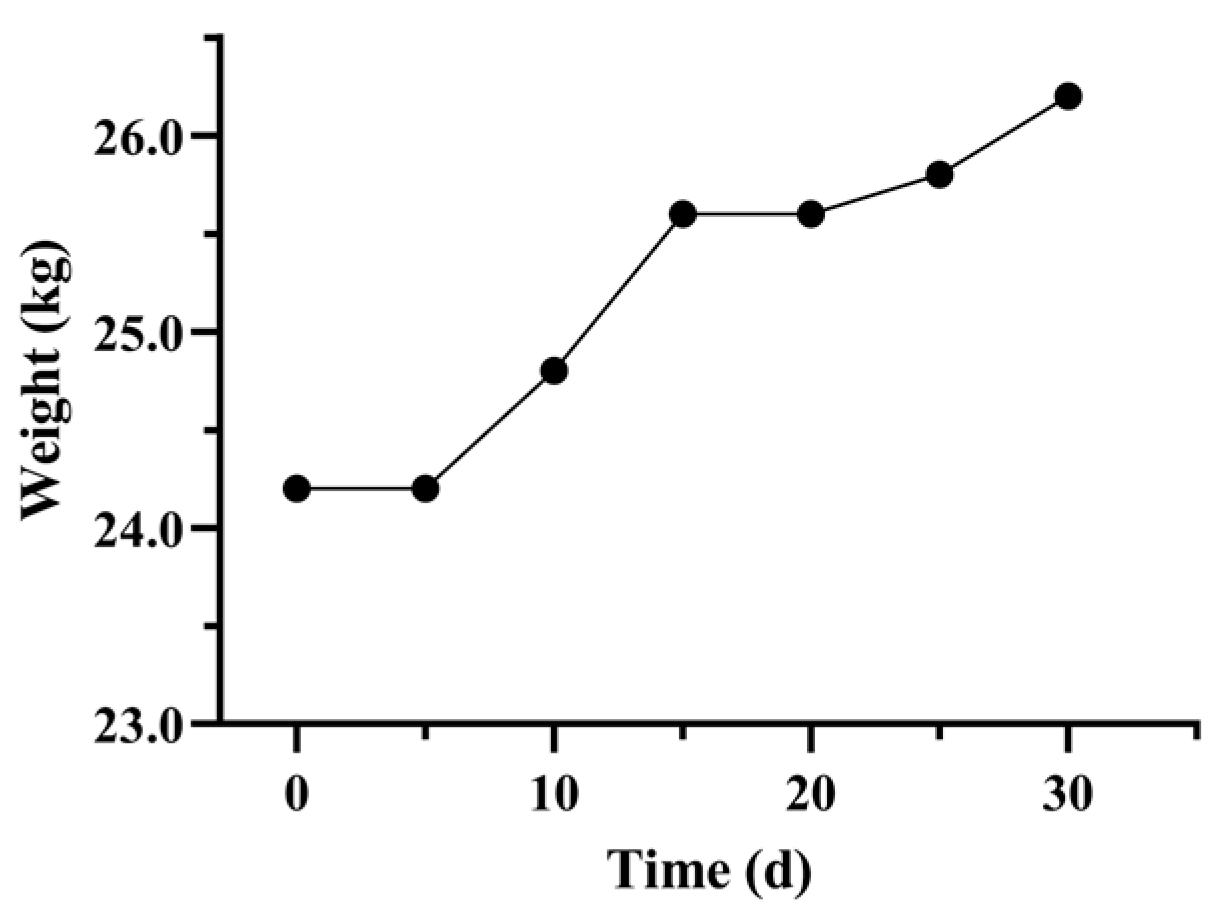
3.1.2. Fecal Score and Body Weight Recovery
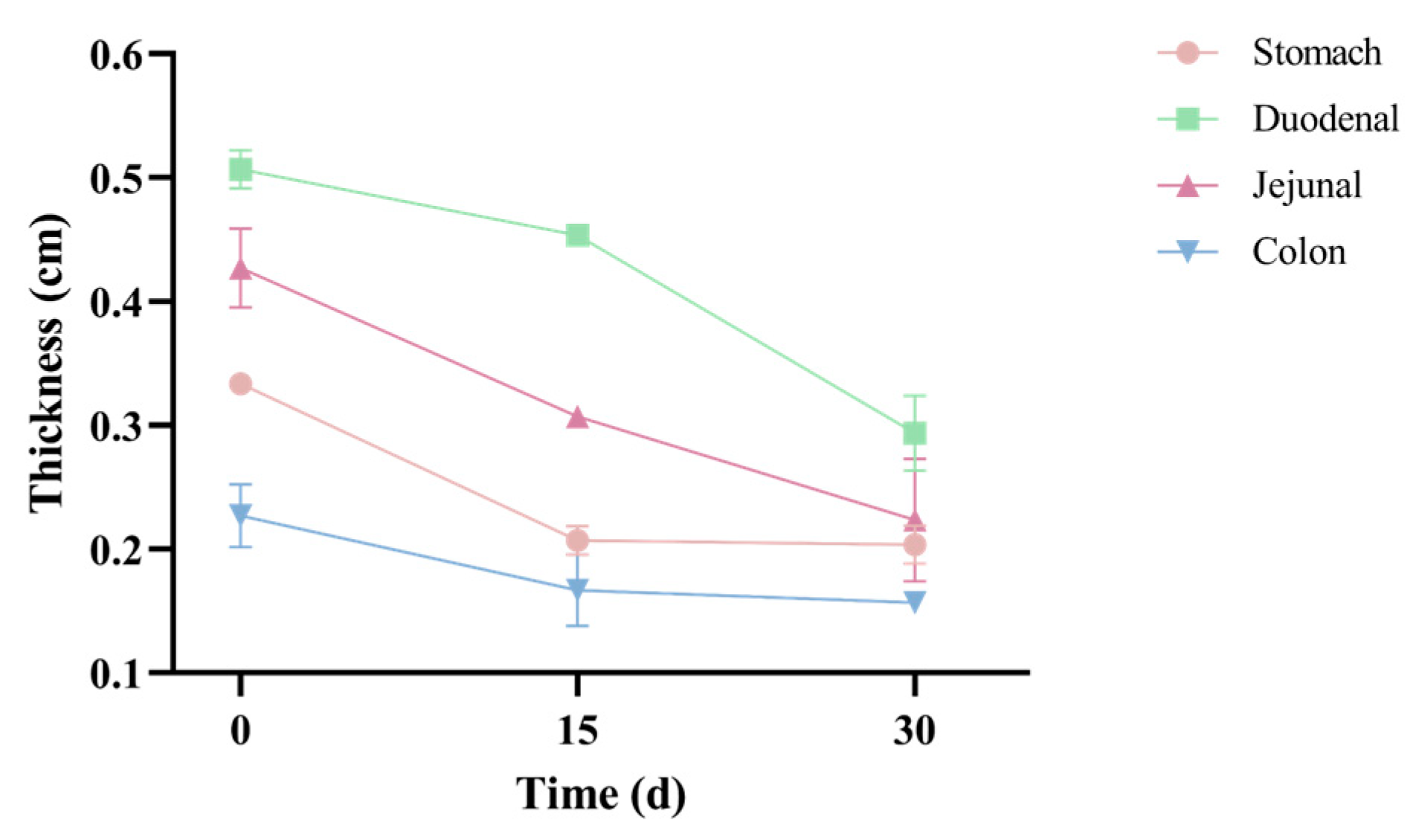
3.1.3. Gastrointestinal Morphology Evaluation
3.2. Effects of FMT on Fecal Microbial Communities
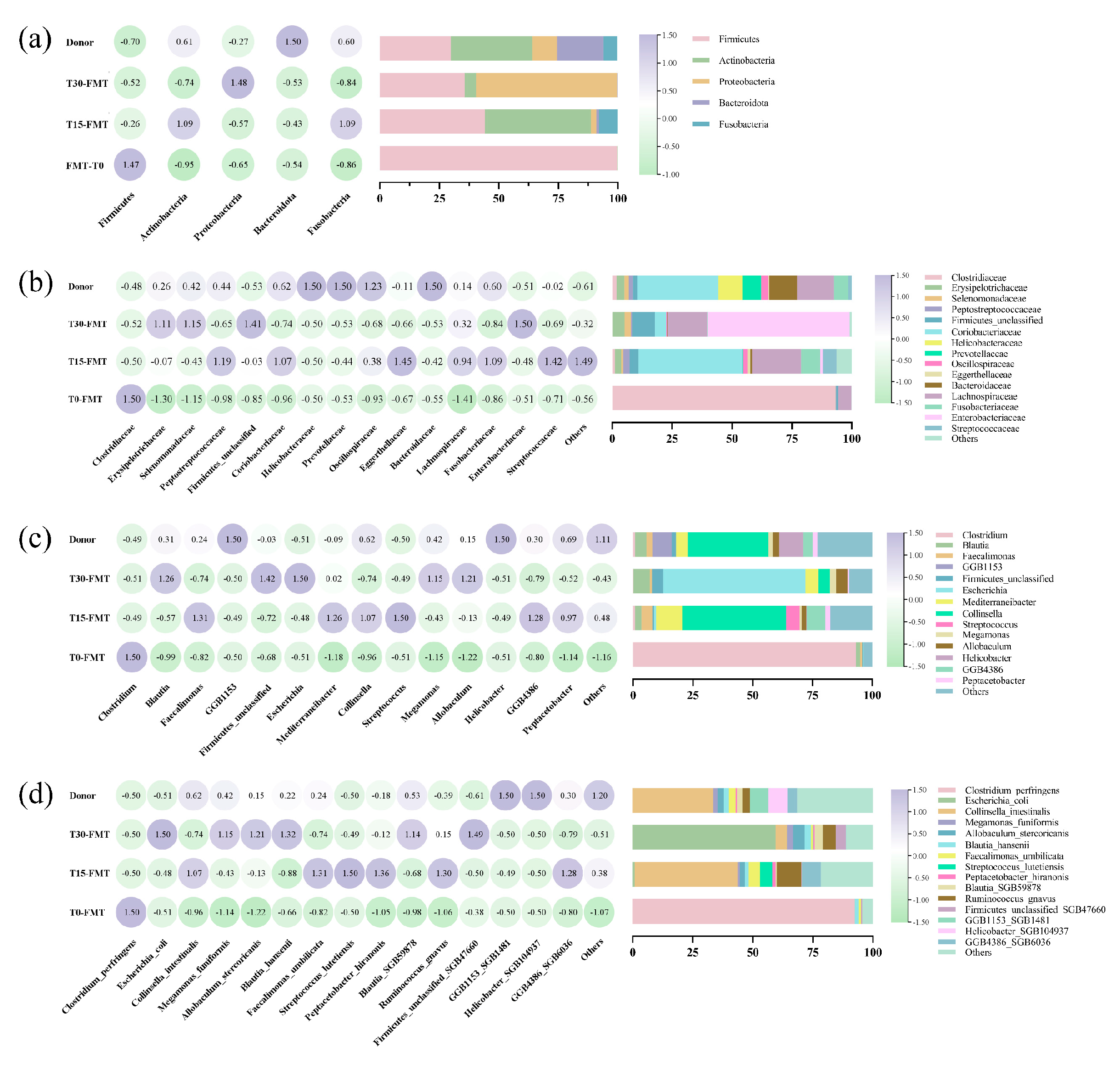
3.2.1. Microbial Composition
3.2.2. Diversity Analysis
3.3. SCFAs and Metagenome Functions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehain, S.O.; Haines, J.M.; Lee, P.M. Platelet indices as biomarkers for characterization and determination of severity in canine chronic enteropathy. Vet. J. 2019, 248, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Martins, R.; Sullivan, M.C.; Friedman, E.S.; Misic, A.M.; El-Fahmawi, A.; De Martinis, E.C.P.; O’Brien, K.; Chen, Y.; Bradley, C.; et al. Diet-induced remission in chronic enteropathy is associated with altered microbial community structure and synthesis of secondary bile acids. Microbiome 2019, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menozzi, A.; Dall’Aglio, M.; Quintavalla, F.; Dallavalle, L.; Meucci, V.; Bertini, S. Rifaximin is an effective alternative to metronidazole for the treatment of chronic enteropathy in dogs: A randomised trial. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Cristóbal, J.I.; Duque, F.J.; Usón-Casaús, J.M.; Ruiz, P.; Nieto, E.L.; Pérez-Merino, E.M. Effects of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Dogs with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treated with and without Corticosteroids. Animals 2021, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, X.; Hu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, G.; Yu, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y. Clinical Efficacy and Microbiome Changes Following Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Children with Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makielski, K.; Cullen, J.; O’Connor, A.; Jergens, A.E. Narrative review of therapies for chronic enteropathies in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Li, P.; Xu, L.; Peng, Z.; Xiang, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ji, G.; Nie, Y.; Wu, K.; et al. Step-up fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) strategy. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taur, Y.; Coyte, K.; Schluter, J.; Robilotti, E.; Figueroa, C.; Gjonbalaj, M.; Littmann, E.R.; Ling, L.; Miller, L.; Gyaltshen, Y.; et al. Reconstitution of the gut microbiota of antibiotic-treated patients by autologous fecal microbiota transplant. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooyottu, S.; Muyyarikkandy, M.S.; Yousefi, F.; Li, G.; Sahin, O.; Burrough, E.; Scaria, J.; Sponseller, B.; Ramirez, A. Fecal microbiota transplantation modulates jejunal host-microbiota interface in weanling piglets. Microbiome 2025, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederwerder, M.C.; Constance, L.A.; Rowland, R.R.R.; Abbas, W.; Fernando, S.C.; Potter, M.L.; Sheahan, M.A.; Burkey, T.E.; Hesse, R.A.; Cino-Ozuna, A.G. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Is Associated with Reduced Morbidity and Mortality in Porcine Circovirus Associated Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcari, S.; Maida, M.; Bibbò, S.; McIlroy, J.; Ianiro, G.; Cammarota, G. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as Emerging Treatment in European Countries 2.0. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1435, 85–99. [Google Scholar]
- Niina, A.; Kibe, R.; Suzuki, R.; Yuchi, Y.; Teshima, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Kataoka, Y.; Koyama, H. Fecal microbiota transplantation as a new treatment for canine inflammatory bowel disease. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2021, 40, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, A.; Barko, P.C.; Biggs, P.J.; Gedye, K.R.; Midwinter, A.C.; Williams, D.A.; Burchell, R.K.; Pazzi, P. One dog’s waste is another dog’s wealth: A pilot study of fecal microbiota transplantation in dogs with acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitman, J.; Ziese, A.L.; Pilla, R.; Minamoto, Y.; Blake, A.B.; Guard, B.C.; Isaiah, A.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Unterer, S.; et al. Fecal Microbial and Metabolic Profiles in Dogs with Acute Diarrhea Receiving Either Fecal Microbiota Transplantation or Oral Metronidazole. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, K.; Yanuma, N.; Ohno, H.; Takahashi, K.; Kawano, K.; Morita, H.; Ohmori, K. Oral faecal microbiota transplantation for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea in a dog: A case report. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.Q.; Gomes, L.A.; Santos, I.S.; Alfieri, A.F.; Weese, J.S.; Costa, M.C. Fecal microbiota transplantation in puppies with canine parvovirus infection. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantas, L.; Goll, R.; Fenton, C.G.; Paulssen, R.H.; Sørum, H. Impact of fecal microbiota transplantation in dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1505226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitman, J.; Gaschen, F. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Dogs. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niina, A.; Kibe, R.; Suzuki, R.; Yuchi, Y.; Teshima, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Kataoka, Y.; Koyama, H. Improvement in Clinical Symptoms and Fecal Microbiome After Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in a Dog with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Vet. Med. 2019, 10, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiwaki, H.; Ito, M.; Hamaguchi, T.; Maeda, T.; Kashihara, K.; Tsuboi, Y.; Ueyama, J.; Yoshida, T.; Hanada, H.; Takeuchi, I.; et al. Short chain fatty acids-producing and mucin-degrading intestinal bacteria predict the progression of early Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Long, X.; Zuo, X.L.; Hou, X.H.; Cong, Y.Z.; Li, Y.Q. Visceral hypersensitive rats share common dysbiosis features with irritable bowel syndrome patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 5211–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takáčová, M.; Bomba, A.; Tóthová, C.; Micháľová, A.; Turňa, H. Any Future for Faecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Novel Strategy for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Human and Veterinary Medicine? Life 2022, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavati Schmitz, S. Observational Study of Small Animal Practitioners’ Awareness, Clinical Practice and Experience with Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Dogs. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2022, 47, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marclay, M.; Dwyer, E.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Gaschen, F.P. Recovery of Fecal Microbiome and Bile Acids in Healthy Dogs after Tylosin Administration with and without Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.A.; Questa, M.; Wanakumjorn, P.; Kol, A.; McLaughlin, B.; Weimer, B.C.; Buono, A.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Marsilio, S. Safety profile and effects on the peripheral immune response of fecal microbiota transplantation in clinically healthy dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024, 38, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerquetella, M.; Marchegiani, A.; Rossi, G.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; Passamonti, F.; Isidori, M.; Rueca, F. Case Report: Oral Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in a Dog Suffering from Relapsing Chronic Diarrhea-Clinical Outcome and Follow-Up. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 893342. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, B.E.; Saraiya, N.; Poeth, K.; Schwartz, R.M.; Epstein, M.E.; Honig, G. Effectiveness of fecal-derived microbiota transfer using orally administered capsules for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.A.; Entrolezo, Z.; Jarett, J.K.; Jospin, G.; Martin, A.; Ganz, H.H. Microbiome Responses to Oral Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in a Cohort of Domestic Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 42. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 14924.1-2001; Laboratory Animals-General Quality Standard for Formula Feeds. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Sichuan Anaerobic Biotechnology Limited Liability Company. A Lyophilized Protective Agent for Intestinal Flora and Its Application. Patent CN118638635A, 13 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gladwin, N.E.; Penninck, D.G.; Webster, C.R. Ultrasonographic evaluation of the thickness of the wall layers in the intestinal tract of dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 75, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chumpitazi, B.P.; Self, M.M.; Czyzewski, D.I.; Cejka, S.; Swank, P.R.; Shulman, R.J. Bristol Stool Form Scale reliability and agreement decreases when determining Rome III stool form designations. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Do, K.H.; Kim, J.K.; Ham, J.S.; Lee, W.K. Effects of Queso Blanco Cheese Containing Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563 on the Intestinal Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acid in Healthy Companion Dogs. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziese, A.L.; Suchodolski, J.S. Impact of Changes in Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Canine and Feline Digestive Diseases. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.M.; Tolbert, M.K. Harnessing the microbiome: Probiotics, antibiotics and their role in canine and feline gastrointestinal disease. Vet. Rec. 2024, 195, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Yang, R.; Bi, Y.; Xiong, X. The canine gastrointestinal microbiota: Early studies and research frontiers. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, E.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Hartmann, K.; Mueller, R.S.; Wess, G.; Unterer, S. Long-term effects of canine parvovirus infection in dogs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gallego, C.; Junnila, J.; Männikkö, S.; Hämeenoja, P.; Valtonen, E.; Salminen, S.; Beasley, S. A canine-specific probiotic product in treating acute or intermittent diarrhea in dogs: A double-blind placebo-controlled efficacy study. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 197, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Ni, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Xiao, Q.; Hong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Gut microbiota derived from fecal microbiota transplantation enhances body weight of Mimas squabs. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.L.; Lu, J.B.; Chen, Q.Y.; Cui, J.Q.; Ye, C.; Tian, H.L.; Qin, H.L.; Li, N. Clinical effectiveness of fecal microbiota transplantation combined with nutritional support and psychological intervention in patients with “Tetralogy of Tongji”. Zhonghua Wei Chang. Wai Ke Za Zhi 2022, 25, 784–791. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Deng, Z.; Luo, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 759306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, C.; Kelly, C.R.; Brandt, L.J.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Complete Microbiota Engraftment Is Not Essential for Recovery from Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection following Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. mBio 2016, 7, e01965-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanda, M.; Innocente, G.; Simionati, B.; Di Camillo, B.; Facchin, S.; Giron, M.C.; Savarino, E.; Sebastiani, F.; Fiorio, F.; Patuzzi, I. Faecal Microbiome Transplantation as a Solution to Chronic Enteropathies in Dogs: A Case Study of Beneficial Microbial Evolution. Animals 2021, 11, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarden, A.; González, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Weiss, S.; Humphry, G.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Knights, D.; Unno, T.; Bobr, A.; Kang, J.; et al. Dynamic changes in short- and long-term bacterial composition following fecal microbiota transplantation for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Microbiome 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goll, R.; Johnsen, P.H.; Hjerde, E.; Diab, J.; Valle, P.C.; Hilpusch, F.; Cavanagh, J.P. Effects of fecal microbiota transplantation in subjects with irritable bowel syndrome are mirrored by changes in gut microbiome. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1794263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, P.; Tan, S.; Wen, Z.; Lin, L.; He, J.; Wen, J.; Lu, S. Dynamic changes of intestinal flora in patients with irritable bowel syndrome combined with anxiety and depression after oral administration of enterobacteria capsules. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 11885–11897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.R.; Khoruts, A.; Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Abd, M.; Alani, M.; Bakow, B.; Curran, P.; McKenney, J.; Tisch, A.; et al. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Recurrence in Multiply Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuniyazi, M.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N. Canine Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: Current Application and Possible Mechanisms. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullish, B.H.; Merrick, B.; Quraishi, M.N.; Bak, A.; Green, C.A.; Moore, D.J.; Porter, R.J.; Elumogo, N.T.; Segal, J.P.; Sharma, N.; et al. The use of faecal microbiota transplant as treatment for recurrent or refractory Clostridioides difficile infection and other potential indications: Second edition of joint British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and Healthcare Infection Society (HIS) guidelines. Gut 2024, 73, 1052–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godínez-Méndez, L.A.; Gurrola-Díaz, C.M.; Zepeda-Nuño, J.S.; Vega-Magaña, N.; Lopez-Roa, R.I.; Íñiguez-Gutiérrez, L.; García-López, P.M.; Fafutis-Morris, M.; Delgado-Rizo, V. In Vivo Healthy Benefits of Galacto-Oligosaccharides from Lupinus albus (LA-GOS) in Butyrate Production through Intestinal Microbiota. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, A.; Sharshov, K.; Li, Y. Comparative metagenomics of the gut microbiota in wild greylag geese (Anser anser) and ruddy shelducks (Tadorna ferruginea). Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, J.; Pulgar, R.; Mandakovic, D.; Porras, O.; Flores, C.A.; Luco, D.; Trujillo, C.A.; Díaz-Esquivel, B.; Alvarez, C.; Acevedo, A.; et al. Nocturnal Light Pollution Induces Weight Gain in Mice and Reshapes the Structure, Functions, and Interactions of Their Colonic Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 2, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. The role of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal barrier function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and colonic carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Nelson, C.D.; Driver, J.D.; Elzo, M.A.; Peñagaricano, F.; Jeong, K.C. Host genetics exerts lifelong effects upon hindgut microbiota and its association with bovine growth and immunity. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2306–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tai, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hao, J.; Han, D.; Li, J.; Deng, X. Cecum microbiome and metabolism characteristics of Silky Fowl and White Leghorn chicken in late laying stages. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 984654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, H.; Jodai, Y.; Koyama, K.; Omori, T.; Horiguchi, N.; Kamano, T.; Funasaka, K.; Nagasaka, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Shibata, T.; et al. Clinical response and changes in the fecal microbiota and metabolite levels after fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection. Fujita Med. J. 2021, 7, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Garge, N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; O’Connell, T.M.; Bunger, M.K.; Bultman, S.J. The microbiome and butyrate regulate energy metabolism and autophagy in the mammalian colon. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, H.M.; Jonkers, D.; Venema, K.; Vanhoutvin, S.; Troost, F.J.; Brummer, R.J. Review article: The role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, M.; Gao, J.; Rizzo, M.; Harrison, T.; Tiedje, J.M. Diet is a major factor governing the fecal butyrate-producing community structure across Mammalia, Aves and Reptilia. ISME J. 2015, 9, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


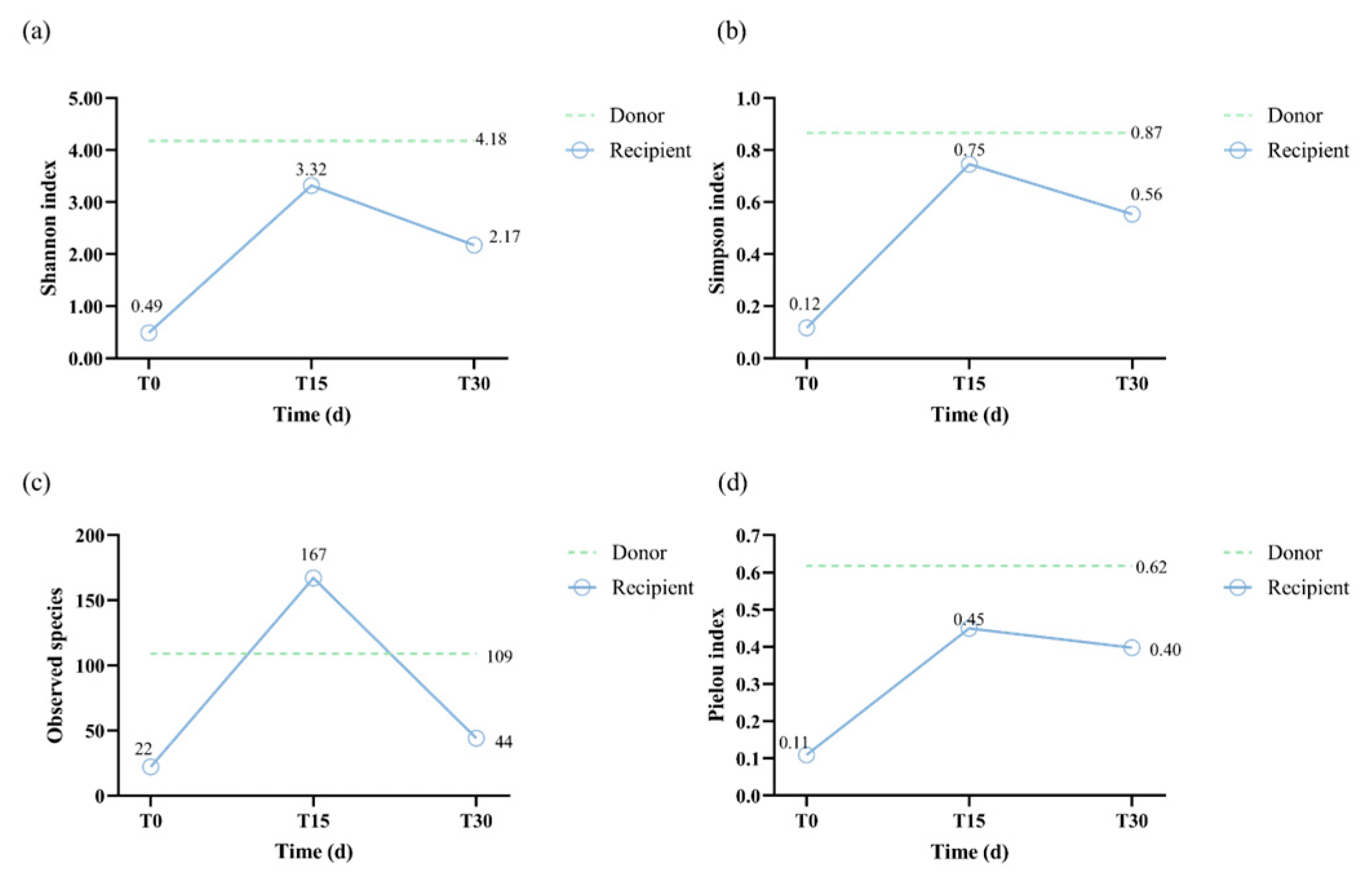
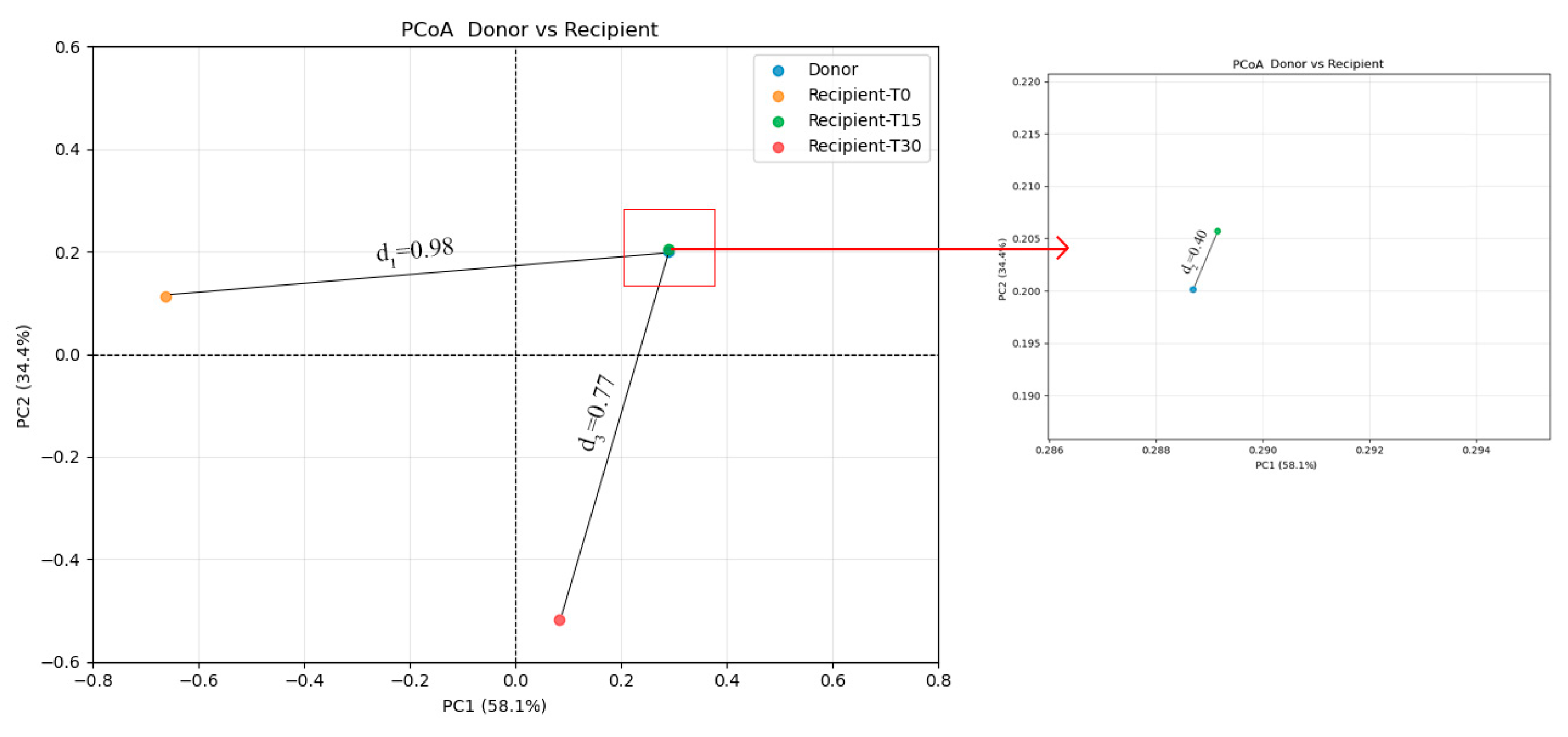

| Indicators | Unit | FMT-T0 | FMT-T15 | FMT-T30 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HGB | g/L | 208 | 192 | 190 | 110–190 |
| HCT | % | 60.6 | 55.1 | 55.7 | 39.0–56.0 |
| WBC | 109/L | 11.1 | 8.4 | 10.5 | 6.0–17.0 |
| Lymph | 109/L | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 0.8–5.1 |
| Mon | 109/L | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.0–1.8 |
| Gran | 109/L | 8.7 | 6.0 | 7.5 | 4.0–12.6 |
| Lymph | % | 16.4 | 23.9 | 21.6 | 12.0–30.0 |
| Mon | % | 5.2 | 5.3 | 6.8 | 2.0–9.0 |
| Gran | % | 78.4 | 70.8 | 71.6 | 60.0–83.0 |
| RBC | 1012/L | 8.18 | 7.53 | 7.58 | 5.50–8.50 |
| MCV | fL | 74.1 | 73.3 | 72.0 | 62.0–72.0 |
| MCH | pg | 25.4 | 25.4 | 25.0 | 20.0–25.0 |
| MCHC | g/L | 343 | 348 | 341 | 300–380 |
| RDW | % | 12.4 | 12.6 | 12.1 | 11.0–15.5 |
| PLT | 201 | 178 | 192 | 117–460 | |
| MPV | fL | 8.3 | 8.6 | 8.3 | 7.0–12.9 |
| PDW | 109/L | 16.6 | 17.0 | 16.6 | |
| PCT | % | 0.166 | 0.153 | 0.159 | |
| Eos% | % | 4.3 | 8.3 | 3.7 |
| Indicators | Unit | FMT-T0 | FMT-T15 | FMT-T30 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLU | mmol/L | 5.82 | 5.75 | 6.06 | 4.11–7.95 |
| CREA | μmol/L | 167.0 | 119.0 | 121.0 | 44–159 |
| UREA | mmol/L | 11.9 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 2.5–9.6 |
| BUN/CREA | 18 | 14 | 14 | ||
| TP | g/L | 68 | 66 | 66 | 52–82 |
| ALB | g/L | 35 | 33 | 33 | 23–40 |
| GLOB | g/L | 34 | 33 | 34 | 25–45 |
| ALB/GLOB | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| ALT | U/L | 51 | 46 | 46 | 10–125 |
| ALKP | U/L | 44 | 46 | 50 | 23–212 |
| CRP | mg/L | 4.5 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 0.0–10.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhou, B.; Liu, L.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, G.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Effects and Microbiota Changes Following Oral Lyophilized Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Capsules in Canine with Chronic Enteropathy After Parvovirus Infection: Case Report. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090909
Liu S, Zhou B, Liu L, Zhong J, Zhang X, Jiang W, Liu H, Zhou Z, Peng G, Zhong Y, et al. Effects and Microbiota Changes Following Oral Lyophilized Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Capsules in Canine with Chronic Enteropathy After Parvovirus Infection: Case Report. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090909
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Siyu, Baihui Zhou, Lei Liu, Jialai Zhong, Xinyan Zhang, Wenting Jiang, Haifeng Liu, Ziyao Zhou, Guangneng Peng, Yalin Zhong, and et al. 2025. "Effects and Microbiota Changes Following Oral Lyophilized Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Capsules in Canine with Chronic Enteropathy After Parvovirus Infection: Case Report" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090909
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhou, B., Liu, L., Zhong, J., Zhang, X., Jiang, W., Liu, H., Zhou, Z., Peng, G., Zhong, Y., Zhang, K., & Zhong, Z. (2025). Effects and Microbiota Changes Following Oral Lyophilized Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Capsules in Canine with Chronic Enteropathy After Parvovirus Infection: Case Report. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090909








