Enhanced Macrophage and Granulocytic Recruitment with Increased Neo-Angiogenesis in Chicken Embryo Yolk Sac Following In Ovo Probiotic Blend Administration
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Probiotic Preparation and Treatments
2.2. Inoculation Procedure
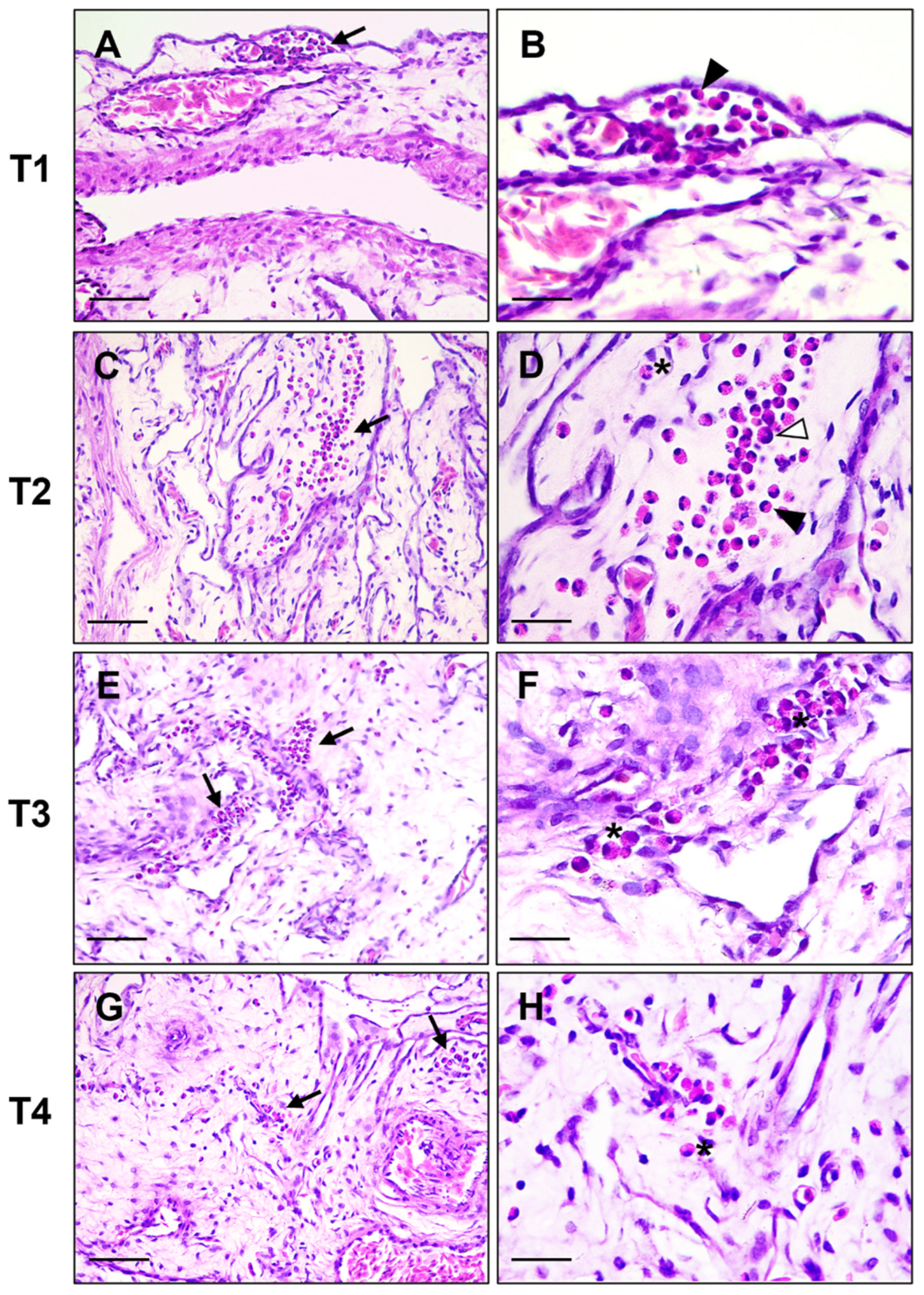
2.3. Sampling and Histological Examination
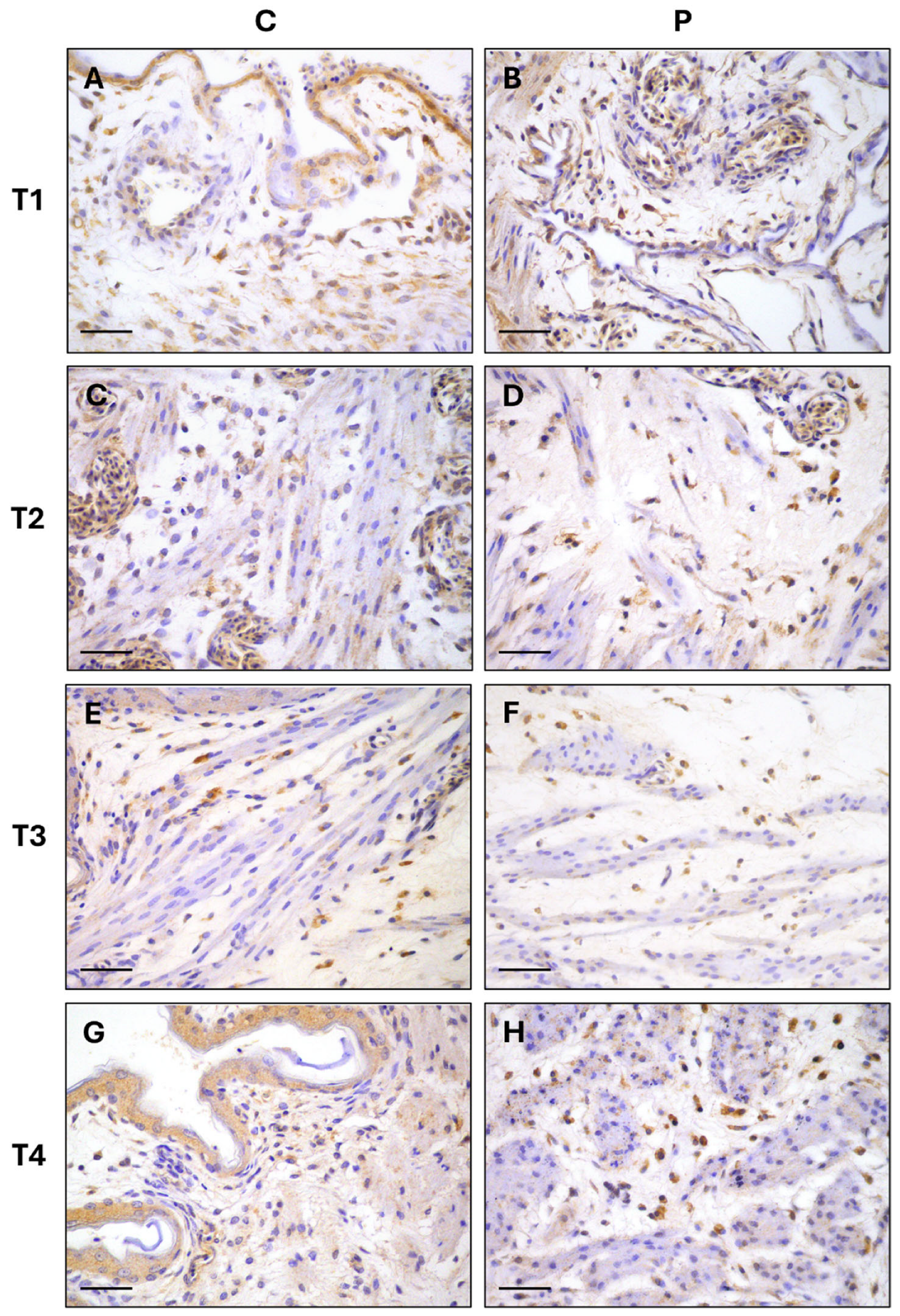
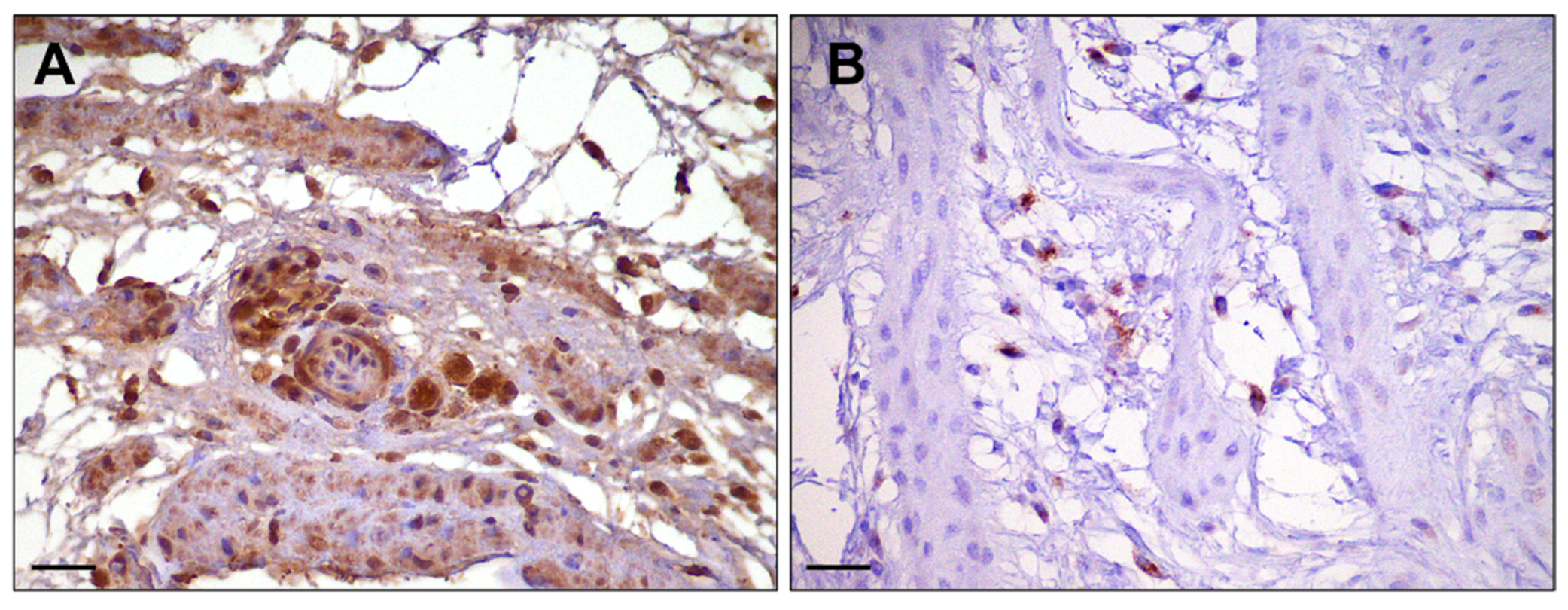
2.4. Immunohistochemical Staining
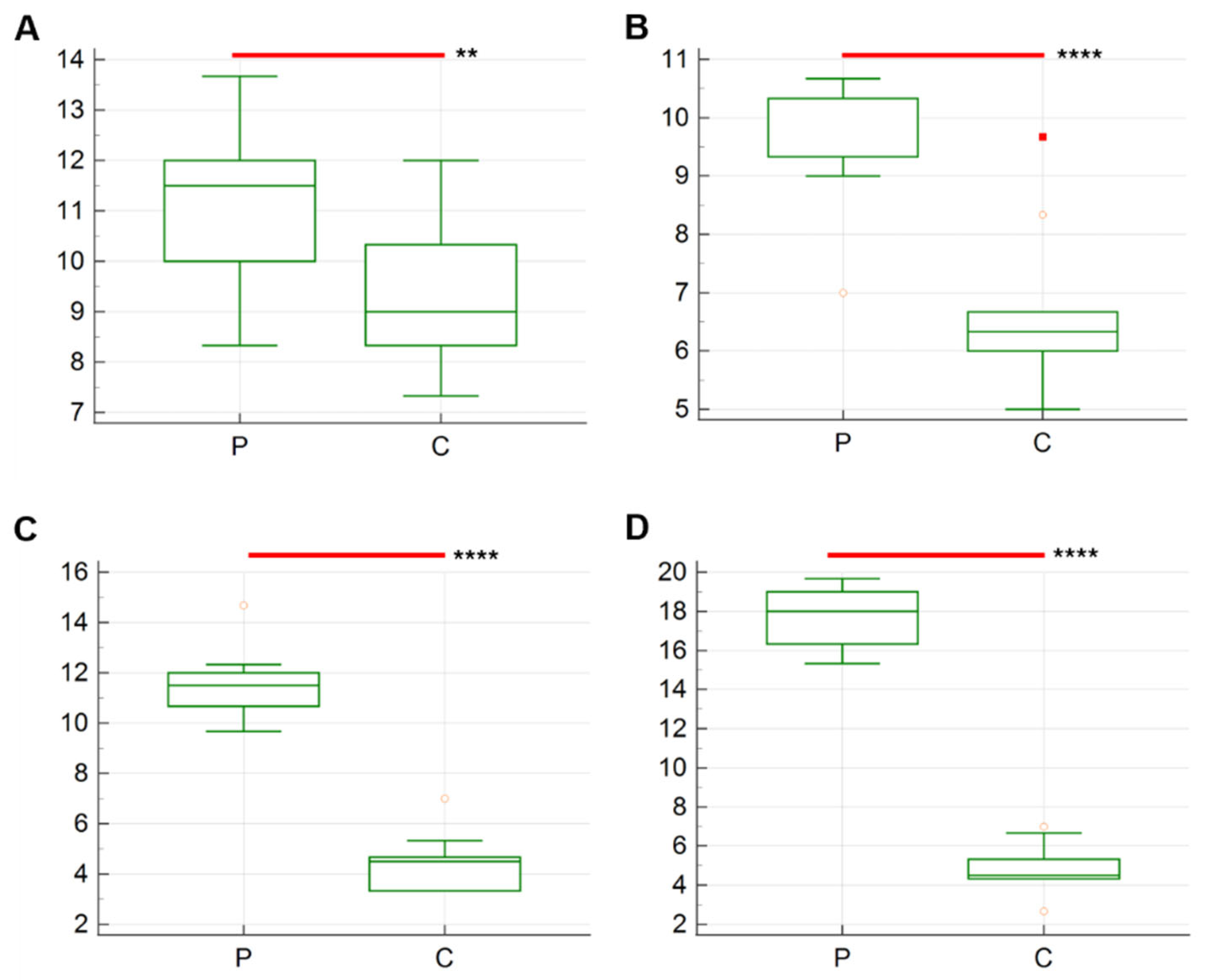
2.5. Statistical Analysis
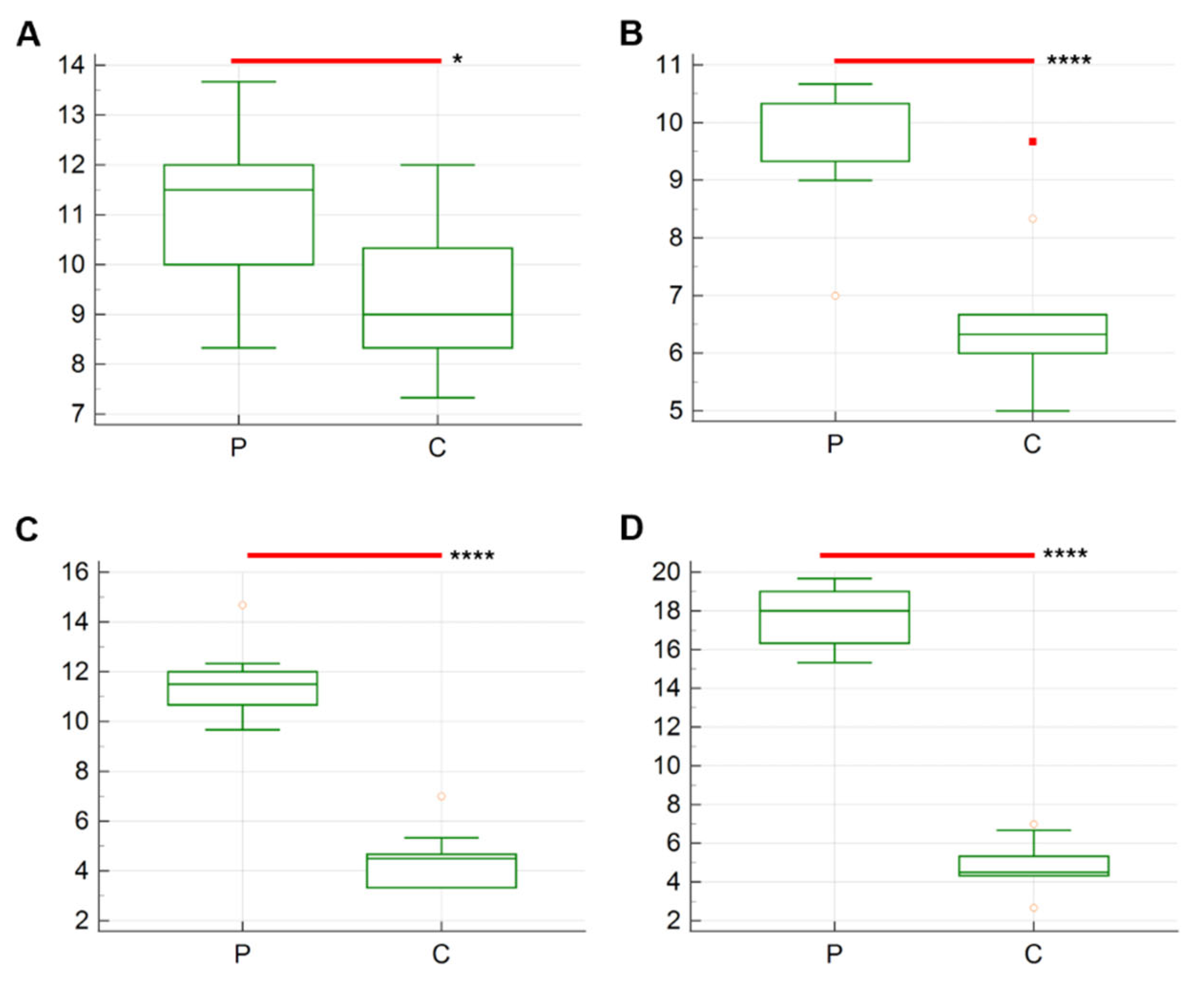
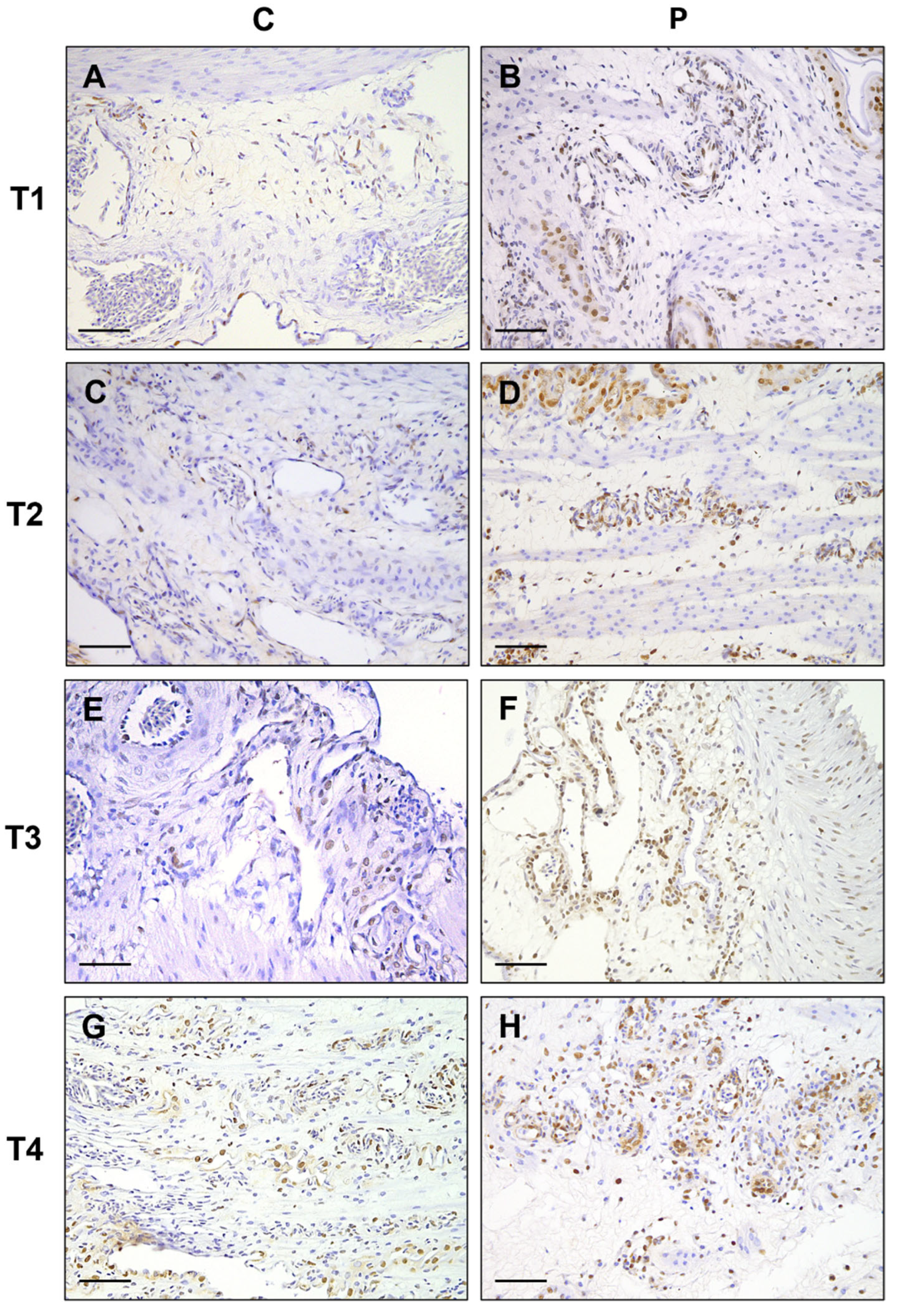
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ED | Embryonic Day |
| YS | Yolk Sac |
| P | Probiotic group |
| C | Control group |
| MALT | Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue |
| GALT | Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| EMPs | Erythro-myeloid Progenitor Cells |
| CFU | Colony Forming Unit |
| BSA-PVP-TBS | 1% bovine serum albumin, 1% polyvinylpyrrolidone, 1% tris-buffered saline |
| Iba1 | Ionized calcium-binding protein molecule 1 |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
References
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate Use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givisiez, P.E.N.; Moreira Filho, A.L.B.; Santos, M.R.B.; Oliveira, H.B.; Ferket, P.R.; Oliveira, C.J.B.; Malheiros, R.D. Chicken Embryo Development: Metabolic and Morphological Basis for In Ovo Feeding Technology. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6774–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roto, S.M.; Kwon, Y.M.; Ricke, S.C. Applications of In Ovo Technique for the Optimal Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract and the Potential Influence on the Establishment of Its Microbiome in Poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uni, Z.; Tako, E.; Gal-Garber, O.; Sklan, D. Morphological, Molecular, and Functional Changes in the Chicken Small Intestine of the Late-Term Embryo. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, C.D.; Dittoe, D.K.; Wamsley, K.G.S.; McDaniel, C.D.; Blanch, A.; Sandvang, D.; Kiess, A.S. In Ovo Inoculation of an Enterococcus faecium–Based Product to Enhance Broiler Hatchability, Live Performance, and Intestinal Morphology. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6163–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; La, T.-M.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, I.-S.; Song, C.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Characterization of Microbial Communities in the Chicken Oviduct and the Origin of Chicken Embryo Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, M.H. The Gut Microbiota and Host Innate Immunity: Regulators of Host Metabolism and Metabolic Diseases in Poultry?1. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2013, 22, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, M.U.; Wang, G.; Wang, M. An Updated Review on Probiotics as an Alternative of Antibiotics in Poultry—A Review. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robino, P.; Galosi, L.; Bellato, A.; Vincenzetti, S.; Gonella, E.; Ferrocino, I.; Serri, E.; Biagini, L.; Roncarati, A.; Nebbia, P.; et al. Effects of a Supplemented Diet Containing 7 Probiotic Strains (Honeybeeotic) on Honeybee Physiology and Immune Response: Analysis of Hemolymph Cytology, Phenoloxidase Activity, and Gut Microbiome. Biol. Res. 2024, 57, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławinska, A.; Siwek, M.Z.; Bednarczyk, M.F. Effects of Synbiotics Injected In Ovo on Regulation of Immune-Related Gene Expression in Adult Chickens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 75, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Munyaka, P.; Yitbarek, A.; Echeverry, H.; Rodriguez-Lecompte, J.C. Maternal Antibody Decay and Antibody-Mediated Immune Responses in Chicken Pullets Fed Prebiotics and Synbiotics. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, J.P.; Bednarczyk, M. Effect of In Ovo-Delivered Prebiotics and Synbiotics on the Morphology and Specific Immune Cell Composition in the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheled-Shoval, S.L.; Gamage, N.S.W.; Amit-Romach, E.; Forder, R.; Marshal, J.; Van Kessel, A.; Uni, Z. Differences in Intestinal Mucin Dynamics between Germ-Free and Conventionally Reared Chickens after Mannan-Oligosaccharide Supplementation. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schokker, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Vastenhouw, S.A.; Heilig, H.G.; Smidt, H.; Rebel, J.M.; Smits, M.A. Early-Life Environmental Variation Affects Intestinal Microbiota and Immune Development in New-Born Piglets. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shira, E.; Friedman, A. Development and Adaptations of Innate Immunity in the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Newly Hatched Chick. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Shira, E.; Sklan, D.; Friedman, A. Establishment of Immune Competence in the Avian GALT during the Immediate Post-Hatch Period. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, K.; Balic, A.; Kaspers, B.; Vervelde, L. Chapter 8.1—Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. In Avian Immunology, 3rd ed.; Kaspers, B., Schat, K.A., Göbel, T.W., Vervelde, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 167–195. ISBN 978-0-12-818708-1. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.L.; Powers, C.; Beal, R. The Avian Enteric Immune System in Health and Disease. In Avian Immunology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 303–326. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, P.; Valente, A.J.; Prabhu, S.D.; Venkatesan, B.; Yoshida, T.; Delafontaine, P.; Chandrasekar, B. Angiotensin-II Type 1 Receptor and NOX2 Mediate TCF/LEF and CREB Dependent WISP1 Induction and Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 50, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut Microbiota, Metabolites and Host Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.; Boroviak, T.E. Origin and Function of the Yolk Sac in Primate Embryogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garceau, V.; Balic, A.; Garcia-Morales, C.; Sauter, K.A.; McGrew, M.J.; Smith, J.; Vervelde, L.; Sherman, A.; Fuller, T.E.; Oliphant, T.; et al. The Development and Maintenance of the Mononuclear Phagocyte System of the Chick Is Controlled by Signals from the Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.A.; Uni, Z. Centennial Review: The Chicken Yolk Sac Is a Multifunctional Organ. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, P.T.; de Oliveira, B.C.E.P.D.; Manso, P.P.d.A.; Caputo, L.F.G.; Cotta-Pereira, G.; Pelajo-Machado, M. Histological Analyses Demonstrate the Temporary Contribution of Yolk Sac, Liver, and Bone Marrow to Hematopoiesis during Chicken Development. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadgary, L.; Wong, E.A.; Uni, Z. Temporal Transcriptome Analysis of the Chicken Embryo Yolk Sac. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G. Primitive and Definitive Erythropoiesis in the Yolk Sac: A Bird’s Eye View. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2010, 54, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stremmel, C.; Schuchert, R.; Wagner, F.; Thaler, R.; Weinberger, T.; Pick, R.; Mass, E.; Ishikawa-Ankerhold, H.C.; Margraf, A.; Hutter, S.; et al. Yolk Sac Macrophage Progenitors Traffic to the Embryo during Defined Stages of Development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagini, L.; Galosi, L.; Tambella, A.M.; Roncarati, A.; De Bellis, D.; Pesaro, S.; Attili, A.-R.; Berardi, S.; Rossi, G. Effect of In Ovo Supplementation of Slab51 Probiotic Mixture, Associated with Marek’s Disease Vaccine, on Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology and Eimeria Spp. Infection in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2024, 14, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luise, D.; Correa, F.; Chalvon-Demersay, T.; Galosi, L.; Rossi, G.; Lambert, W.; Bosi, P.; Trevisi, P. Supplementation of Mixed Doses of Glutamate and Glutamine Can Improve the Growth and Gut Health of Piglets during the First 2 Weeks Post-Weaning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, A.P.A.; Alvarenga, R.R.; Zangeronimo, M.G. In Ovo Inoculation of Probiotics for Broiler Chickens: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 280, 115080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, E.D. In Ovo Applications in Poultry: A Review. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2322–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desantis, S.; Galosi, L.; Santamaria, N.; Roncarati, A.; Biagini, L.; Rossi, G. Modulation of Morphology and Glycan Composition of Mucins in Farmed Guinea Fowl (Numida Meleagris) Intestine by the Multi-Strain Probiotic Slab51®. Animals 2021, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starck, J.M. Morphology of the Avian Yolk Sac. J. Morphol. 2021, 282, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wagt, I.; de Jong, I.C.; Mitchell, M.A.; Molenaar, R.; van den Brand, H. A Review on Yolk Sac Utilization in Poultry. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2162–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Mine, Y. Egg Yolk Antibodies for Passive Immunity. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Acero-Lopez, A. Ovotransferrin: Structure, Bioactivities, and Preparation. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, V.M.; Escorcia, M.; Fehervari, T.; Téllez, I.G. Evaluation of an Early Granulocytic Response of Chick Embryos Inoculated with Herpesvirus of Turkeys. Br. Poult. Sci. 2002, 43, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.; He, H.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Hong, W. Immune Responses of Two Recombinant Adenoviruses Expressing VP1 Antigens of FMDV Fused with Porcine Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor. Vaccine 2007, 25, 8209–8219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeshan, B.; Mushtaq, M.H.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Jiang, P. Protective Immune Responses Induced by In Ovo Immunization with Recombinant Adenoviruses Expressing Spike (S1) Glycoprotein of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Fused/Co-Administered with Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.-P.; Ziober, A.; Zhang, P.J.; Bagg, A. Ionized Calcium Binding Adaptor Molecule 1 (IBA1) A Novel, Highly Sensitive, and Specific Marker for Histiocytic, Dendritic, and Monocytic Neoplasms. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 156, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Perdiguero, E.; Klapproth, K.; Schulz, C.; Busch, K.; Azzoni, E.; Crozet, L.; Garner, H.; Trouillet, C.; de Bruijn, M.F.; Geissmann, F.; et al. Tissue-Resident Macrophages Originate from Yolk-Sac-Derived Erythro-Myeloid Progenitors. Nature 2015, 518, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.E.; Erf, G.F.; Higgins, J.P.; Henderson, S.N.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Gaona-Ramirez, G.; Hargis, B.M. Effect of Probiotic Treatment in Broiler Chicks on Intestinal Macrophage Numbers and Phagocytosis of Salmonella Enteritidis by Abdominal Exudate Cells. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pors, S.E.; Olsen, R.H.; Bojesen, A.M. Transmission and Pathogenicity of Gallibacterium Anatis and Escherichia Coli in Embryonated Eggs. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 217, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidro, R.A.; Lopez, A.; Cruz, M.L.; Gonzalez Torres, M.I.; Chompre, G.; Isidro, A.A.; Appleyard, C.B. The Probiotic VSL#3 Modulates Colonic Macrophages, Inflammation, and Microflora in Acute Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid Colitis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2017, 65, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J. Macrophage Polarization Induced by Probiotic Bacteria: A Concise Review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidro, R.A.; Bonilla, F.J.; Pagan, H.; Cruz, M.L.; Lopez, P.; Godoy, L.; Hernandez, S.; Loucil-Alicea, R.Y.; Rivera-Amill, V.; Yamamura, Y.; et al. The Probiotic Mixture VSL#3 Alters the Morphology and Secretion Profile of Both Polarized and Unpolarized Human Macrophages in a Polarization-Dependent Manner. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 5, 1000227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, N.; Verbruggen, S.; Gijbels, M.J.; Post, M.J.; De Winther, M.P.J.; Donners, M.M.P.C. Anti-Inflammatory M2, but Not pro-Inflammatory M1 Macrophages Promote Angiogenesis in Vivo. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Papadopoulos, J.; Wook Kim, S.; Maya, M.; Zhang, F.; He, J.; Fan, D.; Langley, R.; Fidler, I.J. Circulating Monocytes Expressing CD31: Implications for Acute and Chronic Angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-K.; Llewellyn, O.P.C.; Bates, D.O.; Nicholson, L.B.; Dick, A.D. IL-10 Regulation of Macrophage VEGF Production Is Dependent on Macrophage Polarisation and Hypoxia. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusztaszeri, M.P.; Seelentag, W.; Bosman, F.T. Immunohistochemical Expression of Endothelial Markers CD31, CD34, von Willebrand Factor, and Fli-1 in Normal Human Tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Hamidzadeh, K.; Goncalves, R. Macrophages and the Maintenance of Homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Galan, C.; Hill, A.A.; Wu, W.-J.; Fehlner-Peach, H.; Song, H.W.; Schady, D.; Bettini, M.L.; Simpson, K.W.; Longman, R.S.; et al. Critical Role for the Microbiota in CX3CR1+ Intestinal Mononuclear Phagocyte Regulation of Intestinal T Cell Responses. Immunity 2018, 49, 151–163.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, L.J.; Kogut, M.H. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Shaping the Immune System of Chickens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 204, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.P.; Wu, A.M.; Ding, X.M.; Lei, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, K.Y.; Chio, J.S. Effects of Probiotic-Supplemented Diets on Growth Performance and Intestinal Immune Characteristics of Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Antibody | Host | Type | Secondary Antibody | Pre-Treatment | Dilution | Incubation (4°) | Code No. | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Iba1 | Rabbit | P | Goat α Rabbit | Microwave, citrate buffer, pH6 | 1:300 | Overnight | 019-19741 | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Richmond, VA, USA |
| Anti-CD204 | Mouse | M | Goat α Mouse | Microwave, citrate buffer, pH6 | 1:50 | Overnight | KAL-KT022 | TransGenic, Inc., Kobe, Japan |
| Anti-iNOS | Rabbit | P | Goat α Rabbit | Microwave, citrate buffer, pH6 | 1:300 | Overnight | Ab3523 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA |
| Anti-CD31 | Mouse | M | Goat α Mouse | Microwave, citrate buffer, pH6 | 1:100 | Overnight | Ab119339 | Abcam, Boston, MA, USA |
| P | C | Statistical Data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 5.5 ± 0.30 | 7.9 ± 0.43 | p = 0.003 |
| T2 | 5.1 ± 0.31 | 7.4 ± 0.26 | p < 0.0001 |
| T3 | 5.2 ± 0.35 | 7 ± 0.21 | p = 0.0004 |
| T4 | 3.5 ± 0.22 | 4.9 ± 0.23 | p = 0.0004 |
| P | C | Statistical Data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| iNOS | |||
| T1 | 96.8 ± 0.41 | 9.7 ± 0.51 | p = 0.8820 |
| T2 | 90.5 ± 0.89 | 90.6 ± 0.88 | p = 0.9376 |
| T3 | 86.7 ± 1.25 | 87.0 ± 1.37 | p = 0.8738 |
| T4 | 83.2 ± 1.30 | 86.4 ± 1.06 | p = 0.0739 |
| CD204 | |||
| T1 | 3.8 ± 0.51 | 4 ± 0.39 | p = 0.7642 |
| T2 | 9 ± 0.96 | 9.3 ± 0.91 | p = 0.8241 |
| T3 | 13.5. ± 1.36 | 13.8 ± 1.35 | p = 0.8873 |
| T4 | 13.9 ± 1.06 | 17.1 ± 1.37 | p = 0.0821 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biagini, L.; Pesaro, S.; Galosi, L.; Volpatti, D.; De Bellis, D.; Roncarati, A.; Gavazza, A.; Rossi, G. Enhanced Macrophage and Granulocytic Recruitment with Increased Neo-Angiogenesis in Chicken Embryo Yolk Sac Following In Ovo Probiotic Blend Administration. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090892
Biagini L, Pesaro S, Galosi L, Volpatti D, De Bellis D, Roncarati A, Gavazza A, Rossi G. Enhanced Macrophage and Granulocytic Recruitment with Increased Neo-Angiogenesis in Chicken Embryo Yolk Sac Following In Ovo Probiotic Blend Administration. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090892
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiagini, Lucia, Stefano Pesaro, Livio Galosi, Donatella Volpatti, Danilo De Bellis, Alessandra Roncarati, Alessandra Gavazza, and Giacomo Rossi. 2025. "Enhanced Macrophage and Granulocytic Recruitment with Increased Neo-Angiogenesis in Chicken Embryo Yolk Sac Following In Ovo Probiotic Blend Administration" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090892
APA StyleBiagini, L., Pesaro, S., Galosi, L., Volpatti, D., De Bellis, D., Roncarati, A., Gavazza, A., & Rossi, G. (2025). Enhanced Macrophage and Granulocytic Recruitment with Increased Neo-Angiogenesis in Chicken Embryo Yolk Sac Following In Ovo Probiotic Blend Administration. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090892







