Genetic Diversity of Newcastle Disease Virus and Its Implications for Vaccine Development
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
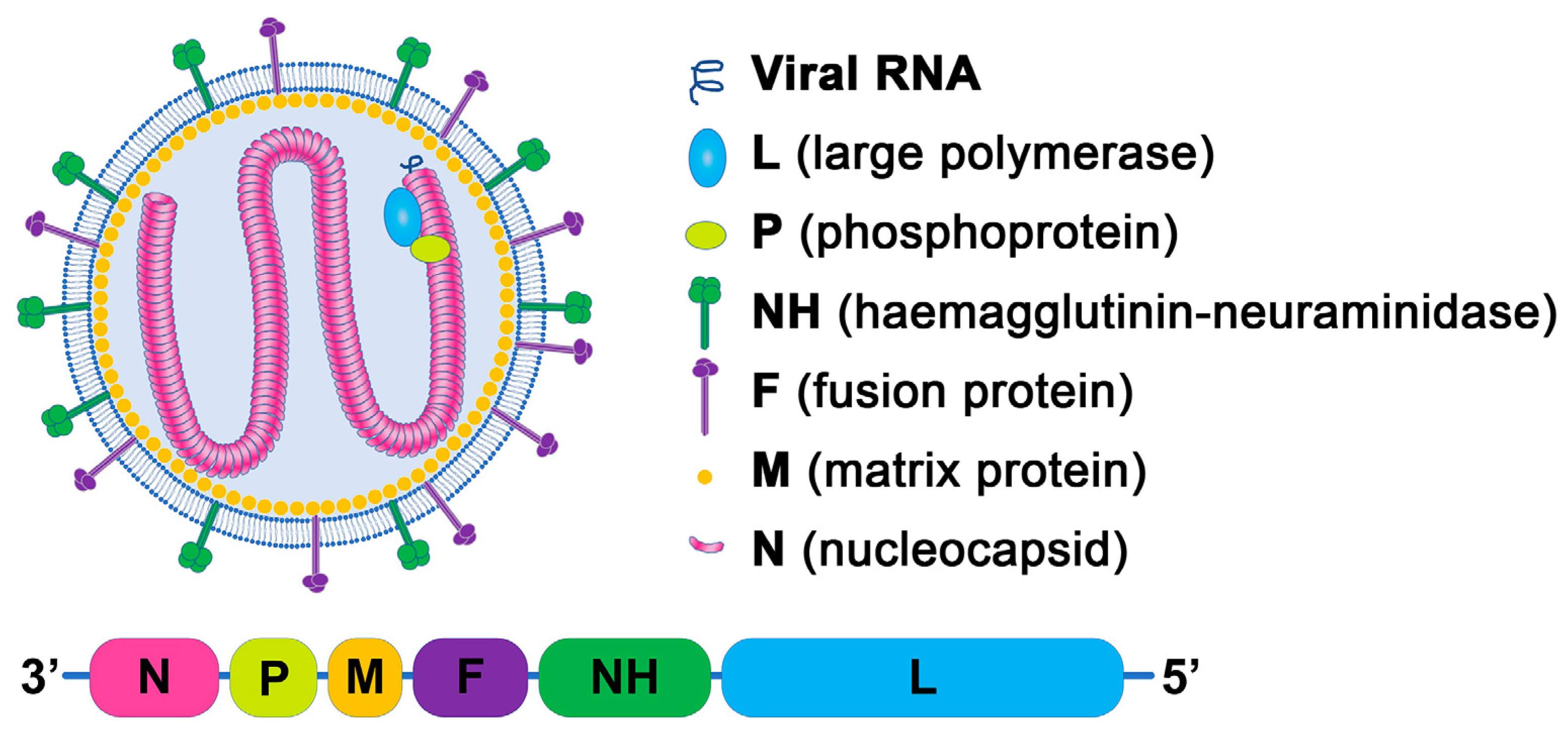
2. Structure of NDV and Functions of Virus-Specific Proteins
3. NDV Taxonomy, Genetic Variability, and Epidemiology
| Continent | Genotype | Subgenotype | Hosts | Pathogenicity for Chicken | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasia | I | I.1.1 | Poultry, wild and migratory waterfowl | Low virulent | [32,33,34,35] |
| I.2 | Wild and domestic waterfowl | ||||
| I.1.2.1 | Wild and migratory waterfowl and landbirds | ||||
| II | - | Gallinaceous poultry and domestic waterfowl, wild birds, peridomestic birds | Low virulent and virulent | [32,35,36,37] | |
| III | - | Chickens and domestic waterfowl | Virulent | [35,38] | |
| IV | - | Poultry | Virulent | [35,39] | |
| V | V.1, V.2 | Poultry, wild birds | Virulent | [32,35,40] | |
| VI | VI.1.1, VI.2.1 VI.1.2.2.2 VI.2.1.1.2.1 VI.2.1.1.2.2. | Wild and domestic pigeons, poultry | Low virulent and virulent | [29,33,35,41,42,43] | |
| VII | VII.1.1 | Poultry, domestic and migratory waterfowl, wild birds, peridomestic birds | Virulent | [29,34,35,36,40,42,44,45,46,47] | |
| VII.1.2 | Chickens, pigeons, wild migratory birds | [29,35,36] | |||
| VII.2 | Chickens, wild birds | [4,7,37,44,48,49,50] | |||
| Vaccinated chicken | 100% mortality | [6] | |||
| VIII | - | Vaccinated chinese game fowl | 100% morbidity and mortality | [3] | |
| IX | - | Poultry, wild birds | Virulent | [51,52] | |
| XII | XII.1, XII.2 | Chickens, domestic geese | Virulent | [35,53,54] | |
| XIII | XIII.1 | Vaccinated chicken | 80% mortality | [2] | |
| XIII.2 XIII.2.1 XIII.2.2 | Chickens | Virulent | [37,55,56,57] | ||
| XIII.2.3 (N.V.) | Chickens | Virulent | [58] | ||
| XX | - | Chickens | Virulent | [59] | |
| - | Pigeons | 80% morbidity and mortality | [60] | ||
| XXI | XXI.1.1 XXI.1.2 | Pigeons | Virulent | [36,37,61] | |
| XXII (N.V.) | XXII.1, XXII.2. | Vaccinated chicken | 90–100% mortality | [5] | |
| Africa | I | N.I. | Chickens, wild and domestic waterfowl | Low virulent | [62,63] |
| I.1 | Chickens | [64] | |||
| II | - | Poultry and wild birds | Low virulent and virulent | [62,63,64] | |
| III | - | Chickens and domestic waterfowl | Virulent | [28] | |
| IV | - | Poultry | Virulent | [62] | |
| V | N.I. | Chickens | Virulent | [62] | |
| V.3 (N.V.) | Chickens | Virulent | [65] | ||
| VI | VI.1.1 | Pigeons and parrot | Low virulent and virulent | [62] | |
| VI.1.2 | Chickens | ||||
| VI.1.2.1.1 | Pigeons and Chickens | ||||
| VI.1.2.1.2 | Pigeons and doves | ||||
| VI.1.2.2.1 | Chickens | ||||
| VII | VII.1.1 | Poultry, wild birds (migratory and non-migratory) | Virulent | [62,66,67,68,69] | |
| VII.2 | Chickens | [62,70,71] | |||
| VIII | - | Chickens | Virulent | [63,72] | |
| XI | - | Poultry | Virulent | [73] | |
| XIII | XIII.1. XIII.2 | Poultry | Virulent | [62] | |
| XIV | XIV.1, XIV.2 | Chickens, village weaver | Virulent | [62] | |
| XVII | - | Poultry | Virulent | [62,74] | |
| XVIII | XVIII.1 XVIII.2 | Chickens, wild birds | Virulent | [62,74] | |
| XX | - | Poultry | Virulent | [62] | |
| XXI | XXI.1.1 XXI.2 | Chickens, pigeons | Virulent | [74,75] | |
| N.V. | Chickens | Virulent | [76] | ||
| North America | I | I.1.2.1 I.2 | Wild and migratory waterfowl and landbird, domestic waterfowl | Low virulent | [32,35] |
| II | - | Poultry and domestic waterfowl, wild birds | Low virulent and virulent | [32,35,77] | |
| V | V; V.I V.2 | Chickens, wild birds | Virulent | [77,78] | |
| VI | VI.1.2.2.1 VI.1.2.1.1.1 VI.2.1.1.1 | Pigeons, doves, chickens and poultry | Low virulent and virulent | [35,77,79,80] | |
| X | - | Wild waterfowl, turkeys | Low virulent | [29,77] | |
| XVI | - | Chickens | Virulent | [27,77] | |
| XIX | - | Cormorant, pelicans, gulls, chickens | Virulent | [77] | |
| South America | I | I.1.1 | Chickens | Low virulent | [81] |
| II | - | Chickens | Low virulent | [81] | |
| V | V.2 | Chickens, wild birds | Virulent | [82,83] | |
| VI | VI.1.1 VI.1.2.1.2 VI.2.1.2 VI.2.1.1.1 | Pigeons | Low virulent and virulent | [83,84] | |
| VII | VII.1.1 | Chickens, fighting cock (Gallus gallus) | Virulent | [81,85,86] | |
| X | - | Wild waterfowl | Low virulent | [35] | |
| XII | XII.1 | Chickens, peacock | Virulent | [81,87,88] | |
| Australia | I | N.I. | Chickens | Virulent | [89] |
| VI | VI. 2.1.1.2.2 | Pigeons | Virulent | [90] |
4. Global Distribution and Panzootics of Newcastle Disease
5. Current Vaccines for Newcastle Disease
6. Vaccines Under Development
6.1. Whole-Virion Vaccines
6.2. Recombinant Virus Vector Vaccines
6.2.1. Herpesvirus Vector Vaccines
6.2.2. Adenovirus Vector Vaccines
6.3. Plasmid DNA Vaccines
6.4. Live Bacterial Vaccine Vectors
6.5. Recombinant Subunit Vaccines
6.5.1. Plant-Based Expression Systems
6.5.2. Bacterial Expression Systems
6.6. Synthetic Peptide Vaccines
6.7. Vaccines Based on Virus-like Particles
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, D.J.; Aldous, E.W.; Fuller, C.M. The Long View: A Selective Review of 40 Years of Newcastle Disease Research. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, A.K.; Munusamy, P.; Kumar, D.; Latheef, S.K.; Singh, S.D.; Singh, R.; Dhama, K. Pathological and Molecular Investigation of Velogenic Viscerotropic Newcastle Disease Outbreak in a Vaccinated Chicken Flocks. Virusdisease 2018, 29, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Deng, Q.; Zhai, G.; He, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, R.; Mo, M.; Huang, T.; Wei, P. Re-Emergence of a Genotype VIII Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated from Chinese Game Fowl after 13 Years. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooruzzaman, M.; Hossain, I.; Begum, J.A.; Moula, M.; Khaled, S.A.; Parvin, R.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Islam, M.R.; Diel, D.G.; Dimitrov, K.M. The First Report of a Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus of Genotype VII.2 Causing Outbreaks in Chickens in Bangladesh. Viruses 2022, 14, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkhowa, T.K.; Zodinpuii, D.; Bhutia, L.D.; Islam, S.J.; Gogoi, A.; Hauhnar, L.; Kiran, J.; Choudhary, O.P. Emergence of a Novel Genotype of Class II New Castle Disease Virus in North Eastern States of India. Gene 2023, 864, 147315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regmi, S.; Bhatta, R.; Pal, P.; Shrestha, A.; Mató, T.; Puri, B.; Paudel, S. Clinicopathological and Molecular Investigation of Newcastle Disease Outbreaks in Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Broiler Chicken Flocks in Nepal. Animals 2024, 14, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.G.; Dong, V.H.; Le, V.T.; Vu, T.N.; Dang, H.A.; Le Huynh, T.M. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus (Subgenotype VII.2) in Broiler Chickens in Northern Vietnam. Vet. World 2023, 16, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusoff, K.; Tan, W.S. Newcastle Disease Virus: Macromolecules and Opportunities. Avian Pathol. 2001, 30, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.; Zhao, L.; Ledda, A.; Liu, W.; Ding, C.; Nair, V.; Ferretti, L. Patterns of RNA Editing in Newcastle Disease Virus Infections. Viruses 2020, 12, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, X. The Multifaceted Interactions between Newcastle Disease Virus Proteins and Host Proteins: A Systematic Review. Virulence 2024, 15, 2299182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, Thirteenth Edition 2024, Chapter 3.3.10 (Newcastle Disease (Infection with Newcastle Disease Virus)). Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/A_summry.htm (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Nagai, Y.; Klenk, H.D.; Rott, R. Proteolytic Cleavage of the Viral Glycoproteins and Its Significance for the Virulence of Newcastle Disease Virus. Virology 1976, 72, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone-Hulslander, J.; Morrison, T.G. Detection of an Interaction between the HN and F Proteins in Newcastle Disease Virus-Infected Cells. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6287–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, B.P.H.; de Leeuw, O.S.; Koch, G.; Gielkens, A.L.J. Rescue of Newcastle Disease Virus from Cloned CDNA: Evidence That Cleavability of the Fusion Protein Is a Major Determinant for Virulence. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5001–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Panda, A.; Elankumaran, S.; Govindarajan, D.; Rockemann, D.D.; Samal, S.K. The Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Protein of Newcastle Disease Virus Determines Tropism and Virulence. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4176–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.; Huang, Z.; Elankumaran, S.; Rockemann, D.D.; Samal, S.K. Role of Fusion Protein Cleavage Site in the Virulence of Newcastle Disease Virus. Microb. Pathog. 2004, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leeuw, O.S.; Koch, G.; Hartog, L.; Ravenshorst, N.; Peeters, B.P.H. Virulence of Newcastle Disease Virus Is Determined by the Cleavage Site of the Fusion Protein and by Both the Stem Region and Globular Head of the Haemagglutinin–Neuraminidase Protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rima, B.; Balkema-Buschmann, A.; Dundon, W.G.; Duprex, P.; Easton, A.; Fouchier, R.; Kurath, G.; Lamb, R.; Lee, B.; Rota, P.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Paramyxoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1593–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICTV Taxonomy Release 2024. Available online: https://ictv.global/taxonomy (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Miller, P.J.; Decanini, E.L.; Afonso, C.L. Newcastle Disease: Evolution of Genotypes and the Related Diagnostic Challenges. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panshin, A.; Shihmanter, E.; Weisman, Y.; Orvell, C.; Lipkind, M. Antigenic Heterogeneity amongst the Field Isolates of Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) in Relation to the Vaccine Strain. Part II: Studies on Viruses Isolated from Domestic Birds in Israel. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 25, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-H.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, T.-E.; Kim, J.-H.; Yoo, H.-S.; Kim, S.-J. Variation of a Newcastle Disease Virus Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Linear Epitope. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, H.-M.; Zhao, J.; Xue, J.; Yang, Y.-L.; Zhang, G.-Z. Antigenic Variation of LaSota and Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) and Their Efficacy against Challenge with Velogenic NDV. Vaccine 2017, 35, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballagi-Pordány, A.; Wehmann, E.; Herczeg, J.; Belák, S.; Lomniczi, B. Identification and Grouping of Newcastle Disease Virus Strains by Restriction Site Analysis of a Region from the F Gene. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeglédi, A.; Ujvári, D.; Somogyi, E.; Wehmann, E.; Werner, O.; Lomniczi, B. Third Genome Size Category of Avian Paramyxovirus Serotype 1 (Newcastle Disease Virus) and Evolutionary Implications. Virus Res. 2006, 120, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diel, D.G.; da Silva, L.H.A.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L. Genetic Diversity of Avian Paramyxovirus Type 1: Proposal for a Unified Nomenclature and Classification System of Newcastle Disease Virus Genotypes. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, S.C.; Susta, L.; Gomez, D.; Hines, N.L.; Pedersen, J.C.; Brown, C.C.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L. Highly Divergent Virulent Isolates of Newcastle Disease Virus from the Dominican Republic Are Members of a New Genotype That May Have Evolved Unnoticed for Over 2 Decades. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, C.J.; Owoade, A.A.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Alkali, B.R.; Okwen, M.P.; Adeyanju, A.T.; Komoyo, G.F.; Nakouné, E.; Le Faou, A.; Muller, C.P. High Genetic Diversity of Newcastle Disease Virus in Poultry in West and Central Africa: Cocirculation of Genotype XIV and Newly Defined Genotypes XVII and XVIII. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2250–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Abolnik, C.; Afonso, C.L.; Albina, E.; Bahl, J.; Berg, M.; Briand, F.-X.; Brown, I.H.; Choi, K.-S.; Chvala, I.; et al. Updated Unified Phylogenetic Classification System and Revised Nomenclature for Newcastle Disease Virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 74, 103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ai, H.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Shi, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, S. Surveillance of Class I Newcastle Disease Virus at Live Bird Markets in China and Identification of Variants with Increased Virulence and Replication Capacity. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0024122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, K. Merck Veterinary Manual. Available online: https://www.merckvetmanual.com/poultry/newcastle-disease-and-other-paramyxovirus-infections/newcastle-disease-in-poultry (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Rahman, A.-U.; Habib, M.; Shabbir, M.Z. Adaptation of Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) in Feral Birds and Their Potential Role in Interspecies Transmission. Open Virol. J. 2018, 12, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-P.; Lee, F.; Cheng, M.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Chiou, C.-J.; Tsai, H.-J. Genetic Diversity of Avian Paramyxoviruses Isolated from Wild Birds and Domestic Poultry in Taiwan between 2009 and 2020. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashkina, T.; Sharshov, K.; Gadzhiev, A.; Petherbridge, G.; Derko, A.; Sobolev, I.; Dubovitskiy, N.; Loginova, A.; Kurskaya, O.; Kasianov, N.; et al. Avian Influenza Virus and Avian Paramyxoviruses in Wild Waterfowl of the Western Coast of the Caspian Sea (2017–2020). Viruses 2024, 16, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Ramey, A.M.; Qiu, X.; Bahl, J.; Afonso, C.L. Temporal, Geographic, and Host Distribution of Avian Paramyxovirus 1 (Newcastle Disease Virus). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 39, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guseva, N.A.; Kolosov, S.N.; Zinyakov, N.G.; Andriyasov, A.V.; Yin, R.; Scherbakova, L.O.; Ovchinnikova, E.V.; Nikonova, Z.B.; Andreychuk, D.B.; Sprygin, A.V.; et al. Analysis of Avian Orthoavulavirus 1 Detected in the Russian Federation between 2017 and 2021. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbir, M.Z.; Mahmood, S.; Ul-Rahman, A.; Banyard, A.C.; Ross, C.S. Genomic Diversity and Evolutionary Insights of Avian Paramyxovirus-1 in Avian Populations in Pakistan. Viruses 2024, 16, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, G.; Shao, H. Genome Sequence of a Virulent Genotype III Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated from Laying Ducks in China. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e01436-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhesara, S.J.; Prasad, V.V.S.P.; Pal, J.K.; Jhala, M.K.; Prajapati, K.S.; Joshi, C.G. Pathotypic and Sequence Characterization of Newcastle Disease Viruses from Vaccinated Chickens Reveals Circulation of Genotype II, IV and XIII and in India. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.J. Newcastle Disease in the European Union 2000 to 2009. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Tu, S.; Sheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Qian, J.; Zou, J.; Zhou, H. Phylogenetic Analysis, Genetic Diversity, and Epidemiology of Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 in China. Arch. Virol. 2024, 169, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mubarak, A.I.A.; Al-Kubati, A.A.G.; Sheikh, A.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Hussen, J.; Kandeel, M.; Falemban, B.; Hemida, M.G. Detection of Avian Orthoavulavirus-1 Genotypes VI.2.1 and VII.1.1 with Neuro-Viscerotropic Tropism in Some Backyard Pigeons (Columbidae) in Eastern Saudi Arabia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1352636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Xie, L.; Xie, Z.; Hua, J.; Huang, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Luo, S.; Li, M.; et al. Analysis of Newcastle Disease Virus Prevalence in Wild Birds Reveals Interhost Transmission of Genotype VI Strains. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0081624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.J.; Haddas, R.; Simanov, L.; Lublin, A.; Rehmani, S.F.; Wajid, A.; Bibi, T.; Khan, T.A.; Yaqub, T.; Setiyaningsih, S.; et al. Identification of New Sub-Genotypes of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus with Potential Panzootic Features. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 29, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouri, F.; Vasfi Marandi, M.; Bashashati, M. Characterization of a Novel VIIl Sub-Genotype of Newcastle Disease Virus Circulating in Iran. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Akhtar, R.W.; Hussain, S.A.; Zhao, K.; Yuan, W. Complete Genome and Molecular Characterization of Genotype VII Velogenic Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated in China. Acta Virol. 2021, 65, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rtishchev, A.; Treshchalina, A.; Shustova, E.; Boravleva, E.; Gambaryan, A. An Outbreak of Newcastle Disease Virus in the Moscow Region in the Summer of 2022. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.; Löndt, B.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Lewis, N.; van Boheemen, S.; Fouchier, R.; Coven, F.; Goujgoulova, G.; Haddas, R.; Brown, I. An Epizootiological Report of the Re-Emergence and Spread of a Lineage of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus into Eastern Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, N.; Ozsemir, C.; Yilmaz, A.; Cizmecigil, U.Y.; Aydin, O.; Bamac, O.E.; Gurel, A.; Kutukcu, A.; Ozsemir, K.; Tali, H.E.; et al. Identification of Newcastle Disease Virus Subgenotype VII.2 in Wild Birds in Turkey. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensels, M.; Van Borm, S.; Mertens, I.; Houdart, P.; Rauw, F.; Roupie, V.; Snoeck, C.J.; Bourg, M.; Losch, S.; Beerens, N.; et al. Molecular and Virological Characterization of the First Poultry Outbreaks of Genotype VII.2 Velogenic Avian Orthoavulavirus Type 1 (NDV) in North-West Europe, BeNeLux, 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Chi, M.; Wen, H.; Zhao, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z. Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Newcastle Disease Virus from China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Sun, Q.; Wu, S.; Dong, L.; Hu, S.; Meng, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Entire Genome Sequence Analysis of Genotype IX Newcastle Disease Viruses Reveals Their Early-Genotype Phylogenetic Position and Recent-Genotype Genome Size. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.T.K.; Doan, H.T.T.; Le, T.H. Molecular Analysis of Newcastle Disease Virus Isolates Reveals a Novel XIId Subgenotype in Vietnam. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 3125–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Chen, R.; Liang, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, Q.; Sun, M.; Kang, Y.; Ding, C.; Liao, M.; Xu, C.; et al. Phylogeny, Pathogenicity and Transmissibility of a Genotype XII Newcastle Disease Virus in Chicken and Goose. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooruzzaman, M.; Mumu, T.T.; Kabiraj, C.K.; Hasnat, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Islam, M.R. Genetic and Biological Characterization of Newcastle Disease Viruses Circulating in Bangladesh during 2010-2017: Further Genetic Diversification of Class II Genotype XIII in Southcentral Asia. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, G.; Deepa, P.M.; Sulficar, S. Epidemiology and Molecular Characterization of Genotype XIII.2.2 of Class II Newcastle Disease Virus from Vaccinated Flocks in Kerala, India. J. Adv. Microbiol. 2024, 24, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, Z.; Tabatabaeizadeh, S.-E.; Toroghi, R.; Farzin, H.; Saffarian, P. First Detection and Characterisation of Sub-Genotype XIII.2.1 Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated from Backyard Chickens in Iran. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 2521–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zereen, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Hossain, M.G.; Alam, J.; Shimada, M.; Rahman, M.T.; Saha, S. First Report of the Emergence of Novel Sub-Genotype XIII.2.3 of Newcastle Disease Virus in Chickens from Selected Regions of Bangladesh. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2025, 130, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umali, D.V.; Ito, H.; Shirota, K.; Katoh, H.; Ito, T. Characterization of Complete Genome Sequence of Genotype VI and VII Velogenic Newcastle Disease Virus from Japan. Virus Genes 2014, 49, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Gao, X.; Feng, L.; Yao, D.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, F. A Novel Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 Isolated from a Sick Racing Pigeon in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China Shows High Virulence in Chickens. Vet. Med. (Praha) 2024, 69, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooruzzaman, M.; Barman, L.R.; Mumu, T.T.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Islam, M.R. A Pigeon-Derived Sub-Genotype XXI.1.2 Newcastle Disease Virus from Bangladesh Induces High Mortality in Chickens. Viruses 2021, 13, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoia, C.F.; Hakizimana, J.N.; Chengula, A.A.; Munir, M.; Misinzo, G.; Weger-Lucarelli, J. Genomic Diversity and Geographic Distribution of Newcastle Disease Virus Genotypes in Africa: Implications for Diagnosis, Vaccination, and Regional Collaboration. Viruses 2024, 16, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolnik, C.; Horner, R.F.; Bisschop, S.P.R.; Parker, M.E.; Romito, M.; Viljoen, G.J. A Phylogenetic Study of South African Newcastle Disease Virus Strains Isolated between 1990 and 2002 Suggests Epidemiological Origins in the Far East. Arch. Virol. 2004, 149, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.N.; Shittu, I.; Abolnik, C.; Solomon, P.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Taylor, T.L.; Williams-Coplin, D.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Meseko, C.A.; Ibu, J.O.; et al. Genomic Comparison of Newcastle Disease Viruses Isolated in Nigeria between 2002 and 2015 Reveals Circulation of Highly Diverse Genotypes and Spillover into Wild Birds. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 2031–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariithi, H.M.; Ferreira, H.L.; Welch, C.N.; Ateya, L.O.; Apopo, A.A.; Zoller, R.; Volkening, J.D.; Williams-Coplin, D.; Parris, D.J.; Olivier, T.L.; et al. Surveillance and Genetic Characterization of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus Subgenotype V.3 in Indigenous Chickens from Backyard Poultry Farms and Live Bird Markets in Kenya. Viruses 2021, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hamid, H.S.; Shafi, M.E.; Albaqami, N.M.; Ellakany, H.F.; Abdelaziz, N.M.; Abdelaziz, M.N.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Taha, A.E.; Alanazi, K.M.; Elbestawy, A.R. Sequence Analysis and Pathogenicity of Avian Orthoavulavirus 1 Strains Isolated from Poultry Flocks during 2015–2019. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.A.M.; Hussein, A.; Hassanin, O.; Elbakrey, R.M.; Daines, R.; Sadeyen, J.-R.; Abdien, H.M.F.; Chrzastek, K.; Iqbal, M. Newcastle Disease Genotype VII Prevalence in Poultry and Wild Birds in Egypt. Viruses 2022, 14, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elfatah, K.S.; Elabasy, M.A.; El-khyate, F.; Elmahallawy, E.K.; Mosad, S.M.; El-Gohary, F.A.; Abdo, W.; Al-Brakati, A.; Seadawy, M.G.; Tahoon, A.E.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Velogenic Newcastle Disease Virus (Sub-Genotype VII.1.1) from Wild Birds, with Assessment of Its Pathogenicity in Susceptible Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihiretu, B.D.; Usui, T.; Chibssa, T.R.; Yamaguchi, T. Genetic and Antigenic Characteristics of Genotype VII.1.1 Newcastle Disease Viruses Currently Circulating in Ethiopian Chickens. Virol. J. 2025, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalonda, A.; Saasa, N.; Kajihara, M.; Nao, N.; Moonga, L.; Ndebe, J.; Mori-Kajihara, A.; Mukubesa, A.N.; Sakoda, Y.; Sawa, H.; et al. Phylogenetic Analysis of Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated from Poultry in Live Bird Markets and Wild Waterfowl in Zambia. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammon, A.; Rammah, E.; Giweli, A.; Monne, I. Molecular Characterization of Newcastle Disease Virus (AOAV-1) Obtained from Western Region of Libya. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herczeg, J.; Wehmann, E.; Bragg, R.R.; Travassos Dias, P.M.; Hadjiev, G.; Werner, O.; Lomniczi, B. Two Novel Genetic Groups (VIIb and VIII) Responsible for Recent Newcastle Disease Outbreaks in Southern Africa, One (VIIb) of Which Reached Southern Europe. Arch. Virol. 1999, 144, 2087–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maminiaina, O.F.; Gil, P.; Briand, F.X.; Albina, E.; Keita, D.; Andriamanivo, H.R.; Chevalier, V.; Lancelot, R.; Martinez, D.; Rakotondravao, R.; et al. Newcastle Disease Virus in Madagascar: Identification of an Original Genotype Possibly De-riving from a Died Out Ancestor of Genotype IV. PLoS ONE. 2010, 5, e13987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeck, C.J.; Adeyanju, A.T.; Owoade, A.A.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Alkali, B.R.; Ottosson, U.; Muller, C.P. Genetic Diversity of Newcastle Disease Virus in Wild Birds and Pigeons in West Africa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7867–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abozaid, K.G.A.; Abdel-Moneim, A.S. Epidemiological Surveillance of Newcastle Disease Virus in Egypt—A 6-Year Cohort Study. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twabela, A.T.; Nguyen, L.T.; Masumu, J.; Mpoyo, P.; Mpiana, S.; Sumbu, J.; Okamatsu, M.; Matsuno, K.; Isoda, N.; Zecchin, B.; et al. A New Variant among Newcastle Disease Viruses Isolated in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 2018 and 2019. Viruses 2021, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.L. Virulence during Newcastle Disease Viruses Cross Species Adaptation. Viruses 2021, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Ferreira, H.L.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Taylor, T.L.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Crossley, B.M.; Killian, M.L.; Bergeson, N.H.; Torchetti, M.K.; Afonso, C.L.; et al. Pathogenicity and Transmission of Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus from the 2018–2019 California Outbreak and Related Viruses in Young and Adult Chickens. Virology 2019, 531, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Marks, D.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Stopak, S.R.; Williams-Coplin, D.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Miller, P.J.; DeLiberto, T.J. Identification of Avian Paramyxovirus Serotype-1 in Wild Birds in the USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Taylor, T.L.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Butt, S.L.; Stanton, J.B.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Fenton, H.; Poulson, R.; Zhang, J.; Brown, C.C.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Genotype VI Newcastle Disease Viruses from Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues from Wild Pigeons Reveals Continuous Evolution and Previously Unrecognized Genetic Diversity in the U.S. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhane, Y.; Hisanaga, T.; Xu, W.; Mosos Campos, N.A.; Kehler, H.; Calderón Parra, C.P.; Pasick, J. Characterization of Colombian Serotype 1 Avian Paramyxoviruses, 2008-2010. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.C.; Varani, A.M.; Lemos, E.G.M.; de Miranda, V.F.O.; Silva, K.R.; Fernando, F.S.; Montassier, M.F.S.; Montassier, H.J. Molecular and Phylogenetic Characterization Based on the Complete Genome of a Virulent Pathotype of Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated in the 1970s in Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 26, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, H.L.; Taylor, T.L.; Absalon, A.E.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Cortés-Espinosa, D.V.; Butt, S.L.; Marín-Cruz, J.L.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Volkening, J.D.; Suarez, D.L.; et al. Presence of Newcastle Disease Viruses of Sub-Genotypes Vc and VIn in Backyard Chickens and in Apparently Healthy Wild Birds from Mexico in 2017. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomazelli, L.M.; Sinhorini, J.A.; Oliveira, D.B.L.; Knöbl, T.; Bosqueiro, T.C.M.; Sano, E.; Costa, G.C.V.; Monteiro, C.; Dorlass, E.G.; Utecht, N.; et al. An Outbreak in Pigeons Caused by the Subgenotype VI.2.1.2 of Newcastle Disease Virus in Brazil. Viruses 2021, 13, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozo, F.; Marcano, R.; Afonso, C.L. Biological and Phylogenetic Characterization of a Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus from Venezuela: Efficacy of Field Vaccination. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1204–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Díaz, M.; Montalván-Avalos, A.; Isasi-Rivas, G.; Villanueva-Pérez, D.; Quiñones-Garcia, S.; Tataje-Lavanda, L.; Rios-Matos, D.; Lulo-Vargas, M.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Guevara-Sarmiento, L.A.; et al. Draft Genome Sequence of an Isolate of Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated from an Outbreak in Fighting Cock in Peru. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e0129322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diel, D.G.; Susta, L.; Cardenas Garcia, S.; Killian, M.L.; Brown, C.C.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L. Complete Genome and Clinicopathological Characterization of a Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus Isolate from South America. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chumbe, A.; Izquierdo-Lara, R.; Tataje, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Cribillero, G.; González, A.E.; Fernández-Díaz, M.; Icochea, E. Pathotyping and Phylogenetic Characterization of Newcastle Disease Viruses Isolated in Peru: Defining Two Novel Subgenotypes Within Genotype XII. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susta, L.; Miller, P.J.; Afonso, C.L.; Brown, C.C. Clinicopathological Characterization in Poultry of Three Strains of Newcastle Disease Virus Isolated From Recent Outbreaks. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.; Bruce, K.; Stevens, V.; Wong, F.; Wang, J.; Johnson, D.; Middleton, D.; O’Riley, K.; McCullough, S.; Williams, D.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of a Pigeon Paramyxovirus Type 1 Isolated from Domestic Pigeons in Victoria, Australia 2011. Viruses 2021, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcastle Disease. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/disease/newcastle-disease/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Dimitrov, K.M.; Afonso, C.L.; Yu, Q.; Miller, P.J. Newcastle Disease Vaccines—A Solved Problem or a Continuous Challenge? Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; He, X.; Deng, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. Current Situation and Future Direction of Newcastle Disease Vaccines. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Sun, Q.; Yao, C.; Dong, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, S.; Liu, X. Full-length genome analysis of two genotype III velogenic Newcastle diseases virus strains reveals their close relationship with vaccine Mukteswar. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2009, 49, 302–308. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Song, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Liu, X. Amino Acid Mutations in Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Enhance the Virulence and Pathogenicity of the Genotype III Newcastle Disease Vaccine Strain After Intravenous Inoculation. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 890657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewidar, A.A.A.; Kilany, W.H.; El-Sawah, A.A.; Shany, S.A.S.; Dahshan, A.-H.M.; Hisham, I.; Elkady, M.F.; Ali, A. Genotype VII.1.1-Based Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccines Afford Better Protection against Field Isolates in Commercial Broiler Chickens. Animals 2022, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, H.A.; Elfeil, W.K.; Nour, A.A.; Tantawy, L.; Kamel, E.G.; Eed, E.M.; El Askary, A.; Talaat, S. Efficacy of the Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII.1.1-Matched Vaccines in Commercial Broilers. Vaccines 2021, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, I.; Subarna, J.F.; Kabiraj, C.K.; Begum, J.A.; Parvin, R.; Martins, M.; Diel, D.G.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Islam, M.R.; Nooruzzaman, M. A Booster with a Genotype-Matched Inactivated Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) Vaccine Candidate Provides Better Protection against a Virulent Genotype XIII.2 Virus. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensels, M.; Soldan, C.; Rauw, F.; Roupie, V.; Lambrecht, B. Protective Efficacy of Classical Vaccines and Vaccination Protocols against an Exotic Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII.2 in Belgian Layer and Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, B.; Wu, S. Molecular Characterization of a Virulent Genotype VIId Strain of Newcastle Disease Virus from Farmed Chickens in Shanghai. Avian Dis. 2011, 55, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, D.A.; Holland, J.J. Rapid Evolution of RNA Viruses. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1987, 41, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramey, A.M.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Hicks, J.T.; Dimitrov, K.M.; Poulson, R.L.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Bahl, J.; Afonso, C.L. Assessment of Contemporary Genetic Diversity and Inter-Taxa/Inter-Region Exchange of Avian Paramyxovirus Serotype 1 in Wild Birds Sampled in North America. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, R.; Koopman, R.; García, M.; Armour, N.; Dunn, J.R.; Barbosa, T.; Martinez, A. Review of Poultry Recombinant Vector Vaccines. Avian Dis. 2021, 65, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Ni, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X. Newcastle Disease Virus as a Vaccine Vector for 20 Years: A Focus on Maternally Derived Antibody Interference. Vaccines 2020, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wen, G.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, M.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Y.; Song, C.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y.; Shao, H.; et al. Development of a Recombinant Thermostable Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) Vaccine Express Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV) Multiple Epitopes for Protecting against IBV and NDV Challenges. Vaccines 2020, 8, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Spatz, S.; Dunn, J.R.; Yu, Q. Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) Recombinant Expressing Marek’s Disease Virus (MDV) Glycoprotein B Significantly Protects Chickens against MDV and NDV Challenges. Vaccine 2023, 41, 5884–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.Y.; Cao, X.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Guo, X.C.; Liu, J.M.; Xue, Z.Q.; Li, H.J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.T.; Li, Q.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a Bivalent Vaccine Based on Recombinant Newcastle Disease Virus Expressing Infectious Bursal Disease Virus VP2L-CH3-CH4 in SPF Chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 288, 109950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wei, L.; Du, X.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; Jiang, M.; Liu, J.; Xue, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Development and evaluation of Newcastle disease—Avian influenza bivalent vector vaccines in commercial chickens. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Song, S.U.; Lee, H.; Cho, A.Y.; Hyeon, J.Y.; et al. Efficacy of live and inactivated recombinant Newcastle disease virus vaccines expressing clade 2.3.4.4b H5 hemagglutinin against H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza in SPF chickens, Broilers, and domestic ducks. Vaccine 2024, 42, 3756–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Yang, W.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Lu, X.; Gao, R.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Spray vaccination with a safe and bivalent H9N2 recombinant chimeric NDV vector vaccine elicits complete protection against NDV and H9N2 AIV challenge. Vet. Res. 2025, 56, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lardinois, A.; Vandersleyen, O.; Steensels, M.; Desloges, N.; Mast, J.; van den Berg, T.; Lambrecht, B. Stronger Interference of Avian Influenza Virus–Specific Than Newcastle Disease Virus–Specific Maternally Derived Antibodies with a Recombinant NDV-H5 Vaccine. Avian Dis. 2016, 60, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, S.; Meng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X. Generation of a Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Candidate with High Yield in Embryonated Chicken Eggs. Avian Dis. 2011, 55, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Nayak, B.; Samuel, A.; Paldurai, A.; Kanabagattebasavarajappa, M.; Prajitno, T.Y.; Bharoto, E.E.; Collins, P.L.; Samal, S.K. Correction: Generation by Reverse Genetics of an Effective, Stable, Live-Attenuated Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Based on a Currently Circulating, Highly Virulent Indonesian Strain. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-M.; Cheng, J.-L.; Yu, X.-H.; Qin, Z.-M.; Tian, F.-L.; Zhang, G.-Z. Generation by Reverse Genetics of an Effective Attenuated Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Based on a Prevalent Highly Virulent Chinese Strain. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, T.; Du, Y.; Cui, X.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Q. A Novel Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Candidate Generated by Mutation in the L and F Genes Confers Improved Protection in Chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 216, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.B.; Mahamud, S.N.A.; Yusoff, K.; Ideris, A.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Peeters, B.P.H.; Omar, A.R. Development of an Effective and Stable Genotype-Matched Live Attenuated Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Based on a Novel Naturally Recombinant Malaysian Isolate Using Reverse Genetics. Vaccines 2020, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, R.; Wang, J.; Su, J.; Gu, C.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W. Establishment of Reverse Genetics for Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus and Altering the Cell Tropism by Inserting TMPRSS2 into the Viral Genome. Virus Genes 2023, 59, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.W.; Yang, H.M.; Jin, J.H.; Zhao, J.; Xue, J.; Zhang, G.Z. Recombinant Newcastle disease virus (NDV) La Sota expressing the haemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein of genotype VII NDV shows improved protection efficacy against NDV challenge. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Lara, R.; Chumbe, A.; Calderón, K.; Fernández-Díaz, M.; Vakharia, V.N. Genotype-matched Newcastle disease virus vaccine confers improved protection against genotype XII challenge: The importance of cytoplasmic tails in viral replication and vaccine design. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Bo, Z.; Ruan, B.; Guo, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Construction of Novel Thermostable Chimeric Vaccine Candidates for Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus. Viruses 2022, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah Mouhamed, A.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.H.; Song, C.S. Comparative protective efficacy of a newly generated live recombinant thermostable highly attenuated vaccine rK148/GVII-F using a single regimen against lethal NDV GVII.1.1. Avian Pathol. 2024, 53, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, W.; Lu, X.; Gao, R.; Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Gu, M.; Hu, J.; Hu, S.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Chimeric Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Vaccine: Overcoming Maternal Antibody Interference and Spray Administration. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Veterinary Pharmacopoeia; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000.
- Haque, M.A.; Haque, M.E.; Parvin, M.K.; Kamal, M.M.; Islam, T.R.; Sadekuzzaman, M.; Islam, M.A.; Khatun, M.M.; Hossain, M.T.; Uddin, M.A.; et al. Determination of Immunogenicity of an Inactivated ND-Vaccine Developed Experimentally with Newcastle Disease Virus (Genotype VII.2) Local Isolates of Bangladesh. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1482314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.A.; Sadekuzzaman, M.; Haque, M.E.; Parvin, M.K.; Kamal, M.M.; Hayat, S.; Islam, M.A.; Khatun, M.M.; Siddique, M.P.; Nahar, S.S.; et al. Characterization of the Dominant Strain (G-VII) of Newcastle Disease Viruses Isolated from Commercial Chickens in Bangladesh during Recent Outbreaks. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2024, 11, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananda Kumar, B.S.; Panickan, S.; Bindu, S.; Kumar, V.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Saxena, S.; Shrivastava, S.; Dandapat, S. Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of an Inactivated Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Encapsulated in Poly-(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeik, M.E.; Awad, A.M.; El-Shall, N.A. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination programs against Newcastle disease virus genotype VII in chickens. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 87, 101836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Teng, Q.; Xue, J.; Zhang, G. Construction and immune efficacy of a recombinant turkey herpesvirus vaccine strain expressing fusion protein of genotype VII Newcastle disease virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 268, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, K.; Rojas-Neyra, A.; Carbajal-Lévano, B.; Luján-Valenzuela, L.; Ticona, J.; Isasi-Rivas, G.; Montalvan, A.; Criollo-Orozco, M.; Huaccachi-Gonzáles, E.; Tataje-Lavanda, L.; et al. A recombinant Turkey herpesvirus expressing the F protein of newcastle disease virus genotype XII generated by NHEJ-CRISPR/Cas9 and Cre-LoxP systems confers protection against genotype XII challenge in chickens. Viruses 2022, 14, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Yang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Qian, K.; Shao, H.; Xu, M.; Qin, A. Long-Term Protection against Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) in Chickens Immunized with a Single Dose of Recombinant Turkey Herpesvirus Expressing NDV F Protein. Vaccines 2024, 12, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, H.L.; Miller, P.J.; Suarez, D.L. Protection against Different Genotypes of Newcastle Disease Viruses (NDV) Afforded by an Adenovirus-Vectored Fusion Protein and Live NDV Vaccines in Chickens. Vaccines 2021, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, F.E.A.; Zhao, X.; Guan, Z.; Chang, Z.; Thrusfield, M.; Lu, K.; El Tigani-Asil, E.T.A.; Terab, A.M.A.; Ismael, M.; Tong, L.; et al. Simultaneous Expression of Chicken Granulocyte Monocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor and the Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Epitope of the Virulent Newcastle Disease Virus Genotype VII C22 Strain in a Functional Synthetic Recombinant Adenovirus as a Genotype-Matched Vaccine with potential antiviral activity. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0402422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xiong, T.; Xie, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Lv, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Construction and Evaluation of the Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of Recombinant Replication-Deficient Human Adenovirus-5 Expressing Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus F Protein and Infectious Bursal Disease Virus VP2 Protein. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnós, O.; Gelaye, E.; Trabelsi, K.; Bernier, A.; Subramani, K.; Kallel, H.; Yami, M.; Kamenm, A.A. Establishing a Robust Manufacturing Platform for Recombinant Veterinary Vaccines: An Adenovirus-Vector Vaccine to Control Newcastle Disease Virus Infections of Poultry in Sub-Saharan Africa. Vaccines 2020, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnós, O.; Martins Fernandes Paes, B.C.; Getachew, B.; Rourou, S.; Chaabene, A.; Gelaye, E.; Tefera, T.A.; Kamen, A.A. Intranasally Delivered Adenoviral Vector Protects Chickens against Newcastle Disease Virus: Vaccine Manufacturing and Stability Assessments for Liquid and Lyophilized Formulations. Vaccines 2023, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Hu, J. DNA Vaccines: Their Formulations, Engineering and Delivery. Vaccines 2024, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ji, H.; Peng, L.; Gao, X.; Jiang, S. Development of PLGA-PEG-PLGA Hydrogel Delivery System for Enhanced Immunoreaction and Efficacy of Newcastle Disease Virus DNA Vaccine. Molecules 2020, 25, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Xiang, B.; Lin, Q.; Jin, J.; Ding, C.; Xu, C.; Ren, T. Immune Effect of a Newcastle Disease Virus DNA Vaccine with IL-12 as a Molecular Adjuvant Delivered by Electroporation. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoia, C.F.; Chengula, A.A.; Hakizimana, J.N.; Wambura, P.N.; Munir, M.; Misinzo, G.; Weger-Lucarelli, J. Development of a Genotype-Matched Newcastle Disease DNA Vaccine Candidate Adjuvanted with IL-28b for the Control of Targeted Velogenic Strains of Newcastle Disease Virus in Africa. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 49, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellagostin, O.A.; Borsuk, S.; Oliveira, T.L.; Seixas, F.K. Auxotrophic Mycobacterium Bovis BCG: Updates and Perspectives. Vaccines 2022, 10, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, A.; Duan, A.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xue, L.; Ma, X.; Luan, W.; Yang, S. The Construction of Recombinant Lactobacillus Casei Expressing Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Protein and Its Immune Response in Chickens. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xu, K.; Yang, G.; Shi, C.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Kang, Y.; et al. Construction of a Novel DNA Vaccine Candidate Targeting F Gene of Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus and Chicken IL-18 Delivered by Salmonella. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, P.Y.; Kotani, E.; Liew, M.W.O. Progress and Challenges in Production of Recombinant Newcastle Disease Virus Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Subunit Vaccine. Process Biochem. 2023, 132, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudainazarova, N.S.; Granovskiy, D.L.; Kondakova, O.A.; Ryabchevskaya, E.M.; Kovalenko, A.O.; Evtushenko, E.A.; Arkhipenko, M.V.; Nikitin, N.A.; Karpova, O. V Prokaryote- and Eukaryote-Based Expression Systems: Advances in Post-Pandemic Viral Antigen Production for Vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusibov, V.; Streatfield, S.J.; Kushnir, N. Clinical Development of Plant-Produced Recombinant Pharmaceuticals: Vaccines, Antibodies and Beyond. Hum. Vaccin. 2011, 7, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, E.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.; Ou, J.; Yin, H.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Niu, X.; et al. A Plant-Produced Recombinant Fusion Protein-Based Newcastle Disease Subunit Vaccine and Rapid Differential Diagnosis Platform. Vaccines 2020, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Andrade, O.; Loza-Rubio, E.; Olivera-Flores, T.; Fehérvári-Bone, T.; Gómez-Lim, M.A. Expression of the Newcastle Disease Virus Fusion Protein in Transgenic Maize and Immunological Studies. Transgenic Res. 2006, 15, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroujeni, N.A.; Khatouni, S.B.; Motamedi, M.J.; Afraz, S.; Jafari, M.; Salmanian, A.-H. Root-Preferential Expression of Newcastle Virus Glycoproteins Driven by NtREL1 Promoter in Tobacco Hairy Roots and Evaluation of Oral Delivery in Mice. Transgenic Res. 2022, 31, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamedi, M.J.; Ebrahimi, M.M.; Shahsavandi, S.; Amani, J.; Kazemi, R.; Jafari, M.; Salmanian, A.-H. The Immunogenicity of a Novel Chimeric Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase-Fusion Antigen from Newcastle Disease Virus by Oral Delivery of Transgenic Canola Seeds to Chickens. Mol. Biotechnol. 2020, 62, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lai, H.; Hurtado, J.; Stahnke, J.; Leuzinger, K.; Dent, M. Agroinfiltration as an Effective and Scalable Strategy of Gene Delivery for Production of Pharmaceutical Proteins. Adv. Tech. Biol. Med. 2013, 1, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurzijah, I.; Elbohy, O.A.; Kanyuka, K.; Daly, J.M.; Dunham, S. Development of Plant-Based Vaccines for Prevention of Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease in Poultry. Vaccines 2022, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahriari, A.G.; Niazi, A.; Habibi-Pirkoohi, M. Transient Expression of Fusion and Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Epitopes of Newcastle Disease Virus in Maize as a Potent Candidate Vaccine. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2021, 10, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Tan, W.S.; Omar, A.R.; Tan, C.S.; Yusoff, K. Immunogenic Properties of Recombinant Ectodomain of Newcastle Disease Virus Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Protein Expressed in Escherichia Coli. Acta Virol. 2009, 53, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Huang, J.-P.; Hong, L.-S.; Shu, S.-F.; Yu, C.; Chu, C.-Y. Prokaryotic Recombinant Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Protein Enhances the Humoral Response and Efficacy of Commercial Newcastle Disease Vaccines in Chickens. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N.; Rao, A.Q.; Ahad, A.; Gul, A.; Latif, A.; Azam, S.; Shahid, M.; Akhtar, S.; Shahid, A.A.; Husnain, T.E. Coli Expression and Immunological Assessment of Expressed Recombinant Newcastle Disease Virus Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Protein in Chickens. Acta Virol. 2020, 64, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, M.J.; Amani, J.; Shahsavandi, S.; Salmanian, A.H. In Silico Design of Multimeric HN-F Antigen as a Highly Immunogenic Peptide Vaccine Against Newcastle Disease Virus. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2014, 20, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, M.J.; Shahsavandi, S.; Amani, J.; Kazemi, R.; Takrim, S.; Jafari, M.; Salmanian, A.H. Immunogenicity of the Multi-Epitopic Recombinant Glycoproteins of Newcastle Disease Virus: Implications for the Serodiagnosis Applications. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, e1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, A.; Amani, J.; Shahsavandi, S.; Hatef Salmanian, A. A Novel Multi-Epitope Edible Vaccine Candidate for Newcastle Disease Virus: In Silico Approach. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, e3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, A.; Rahmani, M.; Yasini Nasab, Y.; Shahsavandi, S.; Jafari, M.; Salmanian, A.H. The Heterologous Expression of Novel Recombinant Protein Composed of HN and F Moieties of Newcastle Disease Virus and Immunogenicity Evaluation in Mouse Model. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2024, 16, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Mozafari, A.; Jafari, M.; Salmanian, A.H. The Heat-Labile Enterotoxin B Subunit Bio-Adjuvant Linked to Newcastle Disease Virus Recombinant Hemagglutinin Neuraminidase Elicited a Humoral Immune Response in the Animal Model. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, A.O.; Ryabchevskaya, E.M.; Evtushenko, E.A.; Manukhova, T.I.; Kondakova, O.A.; Ivanov, P.A.; Arkhipenko, M.V.; Gushchin, V.A.; Nikitin, N.A.; Karpova, O.V. Vaccine Candidate Against COVID-19 Based on Structurally Modified Plant Virus as an Adjuvant. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 845316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovskiy, D.L.; Khudainazarova, N.S.; Evtushenko, E.A.; Ryabchevskaya, E.M.; Kondakova, O.A.; Arkhipenko, M.V.; Kovrizhko, M.V.; Kolpakova, E.P.; Tverdokhlebova, T.I.; Nikitin, N.A.; et al. Novel Universal Recombinant Rotavirus A Vaccine Candidate: Evaluation of Immunological Properties. Viruses 2024, 16, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakova, O.A.; Ivanov, P.A.; Baranov, O.A.; Ryabchevskaya, E.M.; Arkhipenko, M.V.; Skurat, E.V.; Evtushenko, E.A.; Nikitin, N.A.; Karpova, O.V. Novel Antigen Panel for Modern Broad-Spectrum Recombinant Rotavirus A Vaccine. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2021, 10, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, M.T.; Dumont, E.; Khan, M.T.; Shehzadi, A.; Ahmad, I. Multi-Epitopic Peptide Vaccine Against Newcastle Disease Virus: Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experimental Validation. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantua, H.D.; McGinnes, L.W.; Peeples, M.E.; Morrison, T.G. Requirements for the Assembly and Release of Newcastle Disease Virus-Like Particles. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11062–11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnes, L.W.; Pantua, H.; Laliberte, J.P.; Gravel, K.A.; Jain, S.; Morrison, T.G. Assembly and Biological and Immunological Properties of Newcastle Disease Virus-Like Particles. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4513–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Ding, J.; Yin, R.; Sun, Y.; Xue, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, C.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Newcastle Disease Virus-like Particles Induce Dendritic Cell Maturation and Enhance Viral-Specific Immune Response. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ding, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Cong, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, J.; et al. A Genotype VII Newcastle Disease Virus-like Particles Confer Full Protection with Reduced Virus Load and Decreased Virus Shedding. Vaccine 2019, 37, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzamandi, M.; Helan, J.A.; Moeini, H.; Soleimanian, A.; Khatemeh, S.; Hosseini, S.D. Developing a Vaccine against Velogenic Sub-Genotype Seven of Newcastle Disease Virus Based on Virus-like Particles. AMB Express 2023, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; O’Kennedy, M.M.; Ross, C.S.; Lewis, N.S.; Abolnik, C. The Production of Newcastle Disease Virus-like Particles in Nicotiana Benthamiana as Potential Vaccines. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1130910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Xue, C.; Lv, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. Assembly and Immunological Properties of a Bivalent Virus-like Particle (VLP) for Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhai, X.; Lai, Y.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, X.; Xiang, R.; Kang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H. Construction and Immunogenicity of Novel Chimeric Virus-Like Particles Bearing Antigens of Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Newcastle Disease Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcano, V.C.; Cardenas-Garcia, S.; Diel, D.G.; Antoniassi da Silva, L.H.; Gogal, R.M., Jr.; Miller, P.J.; Brown, C.C.; Butt, S.L.; Goraichuk, I.V.; Dimitrov, K.M.; et al. A Novel Recombinant Newcastle Disease Vaccine Improves Post- In Ovo Vaccination Survival with Sustained Protection against Virulent Challenge. Vaccines 2021, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boravleva, E.; Treshchalina, A.; Gordeeva, D.; Gambaryan, A.; Belyakova, A.; Gafarova, I.; Prilipov, A.; Sadykova, G.; Adams, S.; Timofeeva, T.; et al. Genotype I Newcastle Disease Virus, Isolated from Wild Duck, Can Protect Chickens Against Newcastle Disease Caused by Genotype VII. Pathogens 2025, 14, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, M.S.; Shahid, N.; Ajmal, S.; Shakoor, S.; Khursheed, Z.; Salisu, I.B.; Ahmad, S.; Azam, S.; Yasmeen, A.; Latif, A.; et al. Investigation of the toxicity and safety concerns of transgenic maize seeds expressing immunogenic F and HN protein genes against Newcastle disease virus. Toxicol Res 2024, 13, tfae143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xu, Q.; Wang, A.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Ou, J.; Li, R.; Yin, H.; et al. A universal design of restructured dimer antigens: Development of a superior vaccine against the paramyxovirus in transgenic rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2305745121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lan, Q.; Zong, X.; Zhu, G.; Yang, R.; Yang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, H.; Shi, C.; et al. Protection against genotype VII Newcastle disease virus by a mucosal subunit vaccination based on bacterium-like particles bearing the F or HN antigen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khulape, S.A.; Maity, H.K.; Pathak, D.C.; Ramamurthy, N.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Chellappa, M.M.; Dey, S. Evaluation of a fusion gene-based DNA prime-protein boost vaccination strategy against Newcastle disease virus. Trop. Anim. Health. Prod. 2019, 51, 2529–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, E.; Escarmís, C.; Sevilla, N.; Moya, A.; Elena, S.F.; Quer, J.; Novella, I.S.; Holland, J.J. Basic Concepts in RNA Virus Evolution. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1996, 10, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, V.A.; Fearns, R. How Does the Polymerase of Non-Segmented Negative Strand RNA Viruses Commit to Transcription or Genome Replication? J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0033224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Panzootic | NDV Genotype (Subgenotype) | Years |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GII, GIII, GIV | 1926–1960 |
| 2 | GV | 1960–1970 |
| 3 | GVI | 1978–present |
| 4 | GVII (GVII.1.1) | 1985–present |
| 5 | GVII (GVII.2). | 2009–present |
| Antigen(s) | Approach/Expression System | Adjuvant | Delivery Route | Developers | Development Stage | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live vaccine | ||||||
| NDV structural proteins | Reverse Genetics-Based attenuated strain | No | OC | FARVET S.A.C., Peru; University of Maryland, USA | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [119] |
| NDV structural proteins | Reverse Genetics-Based attenuated strain | No | ON | University Putra Malaysia, Malaysia | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [116] |
| NDV structural proteins | Chimeric vaccine, HN gene alteration in an existing vaccine strain | No | ON | China Agricultural University, China | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [118] |
| NDV structural proteins | Chimeric vaccine, modification of an existing attenuated strain | No | IO | US National Poultry Research Center, USA | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [173] |
| NDV structural proteins | Chimeric vaccine, HN and F genes alteration in an existing vaccine strain | No | OC | Beni-Suef University and Animal Health Research Institute, Egypt | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [96] |
| NDV structural proteins | Chimeric vaccine, F gene alteration in an existing virulent strain and attenuation | No | ON | Yangzhou University, China | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [120] |
| NDV structural proteins | Chimeric vaccine, HN and F genes alteration in an existing attenuated strain | No | IN, OC | Yangzhou University, China | Immunogenicity, HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [122] |
| NDV structural proteins | Strain isolated from a wild duck | No | PO | Group of institutes, Russia | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [174] |
| Inactivated vaccine | ||||||
| NDV structural proteins | Inactivation of a virulent strain | Montanide ISA 70 | SC | Bangladesh Agricultural University, Bangladesh; Cornell University, Ithaca, USA | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [98] |
| NDV structural proteins | Inactivation of a virulent strain | PLGA | IM | ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute, India | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [126] |
| NDV structural proteins | Inactivation of a virulent strain | Incomplete Freund’s adjuvant | SC | Bangladesh Agricultural University, Bangladesh | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [124] |
| HVT-vectored vaccine | ||||||
| F protein | HVT-vectored vaccine expressing F protein | No | SC | FARVET S.A.C., Peru; The Pirbright Institute, UK | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [129] |
| F protein | HVT-vectored vaccine expressing F protein | No | SC | Yangzhou University, China; | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken, virus neutralizing activity of chicken serum in vitro | [130] |
| Adenovirus-vectored vaccine | ||||||
| F protein | Adenovirus (Ad5) vectored vaccine expressing F protein | No | NI | US National Poultry Research Center, USA | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [131] |
| F protein | Adenovirus (Ad5) vectored vaccine expressing F protein | No | IM, SC, IN | McGill University, Canada; National Veterinary Institute, Ethiopia; Université Tunis El Manar, Tunisia | Protective efficacy in chicken | [135] |
| HN protein | Adenovirus (Ad5) vectored vaccine expressing HN and ChGM-CSF | ChGM-CSF | IM | Northwest A&F University, China | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [132] |
| F protein | Adenovirus (Ad5) vectored vaccine expressing F protein | No | IM | Zhaoqing Branch of Guangdong Laboratory of Lingnan Modern Agricultural Science and Technology and College of Veterinary Medicine, China | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [133] |
| Subunit recombinant vaccine | ||||||
| F protein | Transgenic rice seeds | Montanide™ ISA 71 VG | IM | Northwest A&F University; Wuhan Healthgen Biotechnology Corp., China | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [146] |
| HN and F proteins | Tobacco hairy roots | No | PO | National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Iran | Immunogenicity in mice | [148] |
| HN-F protein | Transgenic canola seeds | No | PO | National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Iran | HI serum titers in chicken | [149] |
| HN and F proteins | Transgenic maize seeds | No | PO | University of the Punjab, Pakistan | Safety in rats | [175] |
| HN protein dimer | Expression in transgenic rice seeds | ISA 71VG | NI | Henan Agricultural University and Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences China; | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [176] |
| F and HN proteins | Transient expression in maize | Chitosan | IP | Shiraz University, Higher Education Center of Eghlid and Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Iran | Immunogenicity in rabbits | [152] |
| HN protein | E. coli | No adjuvant and Freund’s adjuvant | SC | CEMB University of the Punjab, Pakistan | Immunogenicity in chicken | [155] |
| HN protein | E. coli | LTB and Freund’s adjuvant | IP | National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Iran | Immunogenicity in mice | [160] |
| HN and F proteins | E. coli | LTB and Freund’s adjuvant | IP | National Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Iran | Immunogenicity in mice | [159] |
| F and HN proteins | Lactococcus lactis bacterial-like particles | No | IN | Jilin Agricultural University, China | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [177] |
| VLP vaccine | ||||||
| M, HN and F protein | Expression in insect cells | Incomplete Freund’s adjuvant | NI | University of Tabriz, Iran | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [169] |
| HN and F protein | Transient expression in N. benthamiana | Emulsigen®-P adjuvantant | IM | University of Pretoria, Gauteng, Pretoria, South Africa | Immunogenicity in chicken, virus neutralizing activity of chicken serum in vitro | [170] |
| Bivalent VLPs: F protein NDV, IBV S1 and M protein | Expression in insect cells | No | NI | Sichuan University, China | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [172] |
| Peptide vaccine | ||||||
| F and HN proteins | Chemical peptide synthesis | Alum | SC | Khyber Medical University, Pakistan | HI serum titers in mice and chicken | [164] |
| Live bacterial vaccine vector | ||||||
| F protein | S. typhimurium χ11246 | chIL-18 | PO | Jilin Agricultural University, China | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken | [142] |
| HN protein | L. casei | No | PO | Jilin Agricultural University, China | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [141] |
| DNA-vaccine | ||||||
| F protein | Plasmid-based expression | No | IM | Indian Veterinary Research Institute, India | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken, virus neutralizing activity of chicken serum in vitro | [178] |
| F protein | Plasmid-based expression | IL-12 | IM or electroporation | South China Agricultural University, China | Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in chicken, virus neutralizing activity of chicken serum in vitro | [138] |
| F and HN proteins | Plasmid-based expression | IL-28b | IM or OC | Sokoine University of Agriculture, Tanzania; Virginia Tech, USA. | HI serum titers and protective effectiveness in chicken | [139] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondakova, O.A.; Agranovsky, A.A.; Ryabchevskaya, E.M.; Umarova, E.P.; Granovskiy, D.L.; Toropov, S.E.; Evtushenko, E.A.; Nikitin, N.A.; Karpova, O.V. Genetic Diversity of Newcastle Disease Virus and Its Implications for Vaccine Development. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090858
Kondakova OA, Agranovsky AA, Ryabchevskaya EM, Umarova EP, Granovskiy DL, Toropov SE, Evtushenko EA, Nikitin NA, Karpova OV. Genetic Diversity of Newcastle Disease Virus and Its Implications for Vaccine Development. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090858
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondakova, Olga A., Alexey A. Agranovsky, Ekaterina M. Ryabchevskaya, Elizaveta P. Umarova, Dmitriy L. Granovskiy, Stepan E. Toropov, Ekaterina A. Evtushenko, Nikolai A. Nikitin, and Olga V. Karpova. 2025. "Genetic Diversity of Newcastle Disease Virus and Its Implications for Vaccine Development" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090858
APA StyleKondakova, O. A., Agranovsky, A. A., Ryabchevskaya, E. M., Umarova, E. P., Granovskiy, D. L., Toropov, S. E., Evtushenko, E. A., Nikitin, N. A., & Karpova, O. V. (2025). Genetic Diversity of Newcastle Disease Virus and Its Implications for Vaccine Development. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090858






