Simple Summary
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) is a threatening disease rarely occurring in human and animals, mainly caused by microbial toxins, such as lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria and peptidoglycan and exotoxins of Gram-positive bacteria. Bacterial toxins are recognized as potent superantigens causing the release of massive amounts of host inflammatory mediators responsible for the clinical and pathologic features of septic shock (high fever, hypotension, thrombosis, immune activation, multiple organ failure). In this paper, we describe a case of TSS-like caused by mixed bacterial infection predominantly involving Staphylococcus aureus, in an old, male dog, following a biting injury. The most surprising clinical signs were dermatological lesions, which consisted of severe, diffuse and symmetrical skin ulceration on the dorsum concurrent with fever and depression. Routine laboratory and molecular techniques were helpful in the diagnosis. The treatment was challenging because of recurrent infections, but multiple, long-term antibiotic therapies finally led to complete recovery of the patient. Very little is known about the transmission and prevention of this condition. However, the zoonotic potential of the incriminated bacteria, especially Staphylococcus aureus, which is known to be the most versatile colonizer and multiple-host pathogen able to readily cross species barriers and adapt to new hosts, should not be excluded.
Abstract
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a serious, often fatal disease, rarely occurring in dogs via infection with Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. The development of TSS is mainly dependent on the presence of bacterial toxins recognized to be potent superantigens causing the release of massive amounts of host inflammatory cytokines, notably TNF-α, progressing to high fever, hypotension, haemoconcentration, thrombosis and neutrophil and endothelial activation with multiple organ failure. Rarely, TSS is associated with erythematous and exfoliative dermatitis progressing to ulceration with extremely extensive dermo-epidermal detachment, which is often very painful. Like in humans, very little is known about the transmission and prevention of this condition. In our paper, a case of TSS-like caused by a mixed bacterial infection with Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus halichoeri and Dermatophilus spp. has been described in an 11 year-old, cross-breed male dog, most probably following injury due to biting and fighting. Lesions consisted of severe and diffuse ulceration on the dorsum, and bacterial culture/cytology led to the isolation and identification of Gram-positive staphylococci and streptococci associated with an intense neutrophil reaction. Dermatophilus spp. was presumed morphologically based on cytological preps, not by culture or molecular analysis. PCR demonstrated the presence of the nuc thermonucleaze gene (for S. aureus confirmation) together with the genes encoding enterotoxin H (seh), protein A (spa), toxic shock syndrome toxin TSST-1 (tst) and methicillin resistance (mecC); the exfoliative toxins (eta, etb) were detected. Clinical signs, cytology, bacterial culture and the response to systemic antibiotic therapy were compatible with a TSS-like diagnosis. The patient has completely recovered after 1 year of treatment.
1. Introduction
Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci recognized as significant commensal and opportunistic pathogens, commonly responsible for canine pyoderma, especially S. pseudintermedius. S. aureus does not typically colonize dog skin, but occasionally can lead to severe infections and more rarely toxic shock syndrome (TSS) due to sophisticated attack and defence mechanisms [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Surprisingly, S. aureus strains isolated from pets are mainly of human origin and passed between human owners and their animals [1,3,8]. New data highlighted S. aureus as the most versatile colonizer and multiple-host pathogen able to readily cross species barriers and adapt to new hosts and new niches through the acquisition of and/or loss mutations in mobile genetic elements (MGEs) [1,3,9]. S. aureus pathogenicity is based on a combination of toxin-mediated cytotoxicity, invasiveness, immune evasion and antibiotic resistance in correlation with host specific reactivity [2,3,5,6,7,9]. The development of staphylococcal TSS is mainly dependent on the presence of bacterial toxins recognized to be potent superantigens causing the release of massive amounts of host inflammatory cytokines, notably TNF-α. Both S. aureus and S. pseudintermedius are known to produce a number of superantigens, including staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs), staphylococcal exfoliative toxin (ET) and toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) [3,5,10]. These molecules are responsible for the clinical and pathologic features of septic shock, including high fever, hypotension, haemoconcentration, thrombosis, neutrophil and endothelial activation, non-specific T-cell proliferation and multiple organ failure, but also severe exfoliative dermatitis progressing to ulceration with extremely extensive dermo-epidermal detachment, which is often very painful [5,11,12,13,14].
S. halichoeri appears to be a member of the skin microbiota in dogs. It is commonly associated with skin infections, but rarely isolated as a monoculture, so its clinical significance remains uncertain. However, the pathogenic potential of S. halichoeri should not be neglected, being reported in severe postoperative infections, abscesses, sinusitis, otitis media and necrotic pyoderma in humans, dogs and other animal species [2,15]. Surprisingly, S. halichoeri isolates from dog and human were found to be genetically similar indicating the zoonotic potential of this bacterium [15,16,17].
By contrast, Dermatophilus spp. is an actinomycete pathogen not found as a normal skin inhabitant in dogs, and it can be transmitted through contact with another carrier animal or via acquisition from the soil. Generally, chronic trauma associated with insect bites, moisture and debilitating diseases may predispose to an individual to dermatophilosis, characterized by crusting, erythematous and suppurative and ulcerative dermatitis in more severe forms. These skin lesions are caused by bacterial phospholipases and extracellular proteases, with a role in epidermal penetration, intense neutrophil infiltration and possibly inactivation of host immune response [18].
In this paper, a case of TSS-like caused by mixed infection with aforementioned bacterial species has been described in an 11 year-old, cross-breed intact male dog, most probably following injury to the dog due to biting and fighting.
2. Materials and Method
Case presentation: The patient was an 11 year-old, cross-breed intact male dog with an aggressive behaviour. History data suggested a previous injury caused by biting and fighting with another dog from the country habitat. The patient was found to be expressing clinical signs of shock, such as hypotension, weakness, depression, anorexia and fever concurrently with dermatological lesions. These consisted of severe and diffuse ulceration on the dorsum with symmetrical extension to the anterior limbs with gangrenous areas (Figure 1). Under supportive therapy with Duphalyte and enrofloxacin, the patient had become relatively recovered before our investigation.
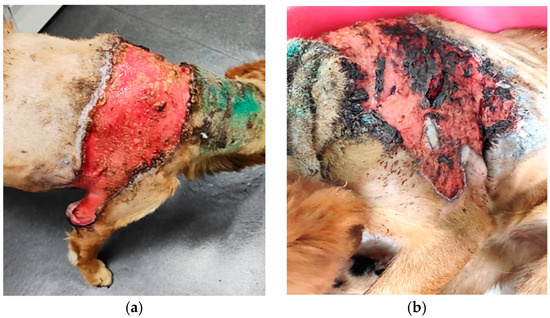
Figure 1.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis: (a) severe and diffuse ulceration on the dorsum; (b) skin lesions on anterior limbs with gangrenous areas.
Cytology: Skin samples were collected with sterile cotton swabs from different affected areas, and multiple smears were prepared and stained using May Grünwald-Giemsa and Gram stains. Microscopic examination identified intense neutrophil infiltration with the presence of free and phagocytized Gram-positive cocci.
Bacterial culture and antimicrobial susceptibility testing: Skin exudates were sampled using eSwabs®-Copan (Copan, Brescia, Italy) in Amies liquid. Samples were inoculated in duplicate on 5% sheep Blood and MacConkey Agar (HiMedia Laboratories GmbH, Einhausen, Germany) and incubated aerobically at 37 °C for 24–48 h. A significant mixed culture with haemolytic and non-haemolytic colonies of Gram-positive cocci was observed only on a Blood Agar (BA) plate.
The antimicrobial susceptibility of clinical isolates was determined by performing the Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion method using the protocol specified in the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [CLSI]. The sensitivity pattern of the isolates was determined against 15 antibiotics: oxacillin, methicillin, cefalexin, cefuroxime, amoxyclave, spectinomycin, lincomycin, rifampicin, clarithromycin, doxycycline, oxytetracycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, vancomycin, enrofloxacin and levofloxacin.
Species confirmation was performed using biochemical and molecular testing: catalase, mannitol fermentation, coagulase, latex agglutination, detection of the nuc thermonucleaze gene via real–time PCR methods for S. aureus identification [19] and Whole Genome Sequencing with metagenomic analysis for S. halichoeri identification. Additionally, the S. aureus strain was checked for 10 enterotoxin genes (sea, seb, sec, sed, seg, seh, sei, sej, ser, sep) using a multiplex real-time PCR method [19], but also for the genes causing methicillin resistance (mecA, mecC), protein A (spa) [20], toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (tst) and exfoliative toxins (eta, etb) using a conventional PCR method [21,22,23]. Unfortunately, Dermatophilus spp. was presumed only morphologically in cytological preps and not through culturing, probably being inhibited by polymicrobial competition.
The therapeutic protocol began with shock therapy including Duphalyte and Enroxil, 10 mg/kg intravenously, every 24 h, for 5 days. Topically, Chlorhexidine solution 2% was used for cleaning the wound. We decided to interrupt the enrofloxacin administration after S. canis suspicion based on cytology because of the high risk of pathogen emergence caused by superantigen expression through the enrofloxacin-lysis of S. canis [14]. The treatment continued with clindamycin 10 mg/kg for 60 days with good clinical recovery. At 30 days after therapy discontinuation, clinical relapse occurred and the treatment was changed to the oral administration of trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole 17 mg/kg, for 60 days.
Unfortunately, we could not perform therapy monitoring regularly according to standard protocols (every 2–3 weeks), but only after clinical relapse, depending on the owner’s motivation. Finally, several cycles of antibiotic therapy were necessary to complete clinical recovery.
3. Results
History and clinical signs were consistent with toxic shock syndrome-like, including hypotension, weakness, depression, anorexia and fever concurrent with severe and diffuse ulcerative dermatitis on the dorsum with symmetrical extension to anterior limbs with gangrenous areas (Figure 1). Dermatological lesions led us to suspicions of thermal or chemical burn, drug reactions, epitheliotropic lymphoma or deep fungal infection.
Skin cytology from different affected areas was useful for diagnosis, showing intense neutrophil infiltration, with hyper segmented and degenerate neutrophils, some of them entrapped in a fibrin matrix, containing phagocytized cocci (Figure 2).
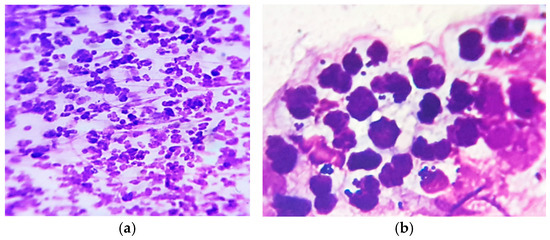
Figure 2.
Skin cytology: (a) high cellular infiltrate with degenerate neutrophils (MGG stain, ×200); (b) some neutrophils with phagocytized cocci (MGG stain, ×1000).
In MGG-stained smears, we also detected abundant clusters and rows of small coccoid cells of presumptive Dermatophilus spp., occasionally with a “railroad track” appearance (Figure 3), as well as numerous cocci chains (Figure 4).
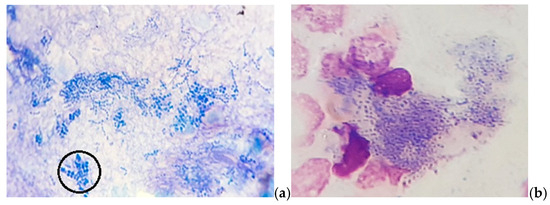
Figure 3.
Skin cytology: (a) abundant free small coccoid cells with a “railroad track” appearance (in the circle); (b) phagocytized small coccoid cells of presumptive Dermatophilus spp. (MGG stain, ×1000).
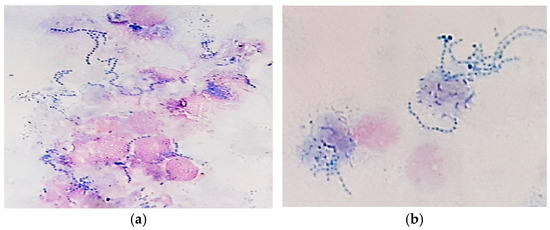
Figure 4.
Skin cytology: (a) free and phagocytized streptococci (MGG stain, ×1000); (b) phagocytized streptococci—detailed image (MGG stain, ×1000).
Gram-stained smears from skin lesions showed abundant free and phagocytized Gram-positive cocci, but only in a few examined fields (Figure 5).
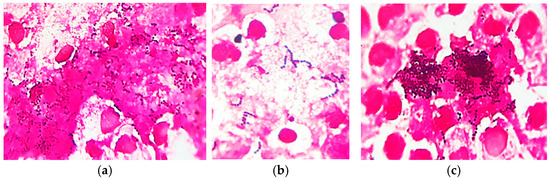
Figure 5.
Skin cytology: (a) free and phagocytized Gram-positive cocci (Gram stain, ×1000); (b) short chains of streptococci (Gram stain, ×1000); (c) clusters of intense Gram-positive cocci (Gram stain, ×1000).
Bacterial culture from skin exudates indicated, only on Blood Agar (BA) plate, a significant mixed culture with cream-yellow smooth, medium α-β haemolytic colonies and whitish-grey, pin-points umbonate, non-haemolytic colonies. Each colony type was picked-up for Gram’s staining and subcultured into Brain-Heart-Infusion (HiMedia Laboratories GmbH, Einhausen, Germany), Blood Agar (Figure 6a,b), Mannitol Salt Agar and Hichrome UTI-Agar (HiMedia Laboratories GmbH, Germany) for presumptive bacterial identification. Gram staining from agars showed intense Gram-positive cocci, in clusters and short chains, but substantial chaining was revealed when pin-point colonies were grown in BHI, an important feature for the streptococci group. On MSA-Agar, our staphylococcal isolate showed mannitol-positive golden yellow colonies. On the chromogenic UTI agar, our streptococci revealed βeta-glucuronidase (βGRU)-positive colonies with a turquoise pigment, resembling those of enterococci (Figure 6c) Additionally, our strain gave a positive agglutination reaction with the Group B Lancefield antisera (Pastorex Strep, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA)—Figure 6d. Finally, we considered our isolate to be of the non-haemolytic Streptococcus Group B. Taken together, the colony morphology, double-haemolysis, catalase, mannitol fermentation and coagulase-positive tests and strong agglutination with the Prolex Staph Latex Kit (Pro-Lab Diagnostics, Richmond Hill, ON, Canada) were significant for S. aureus identification.
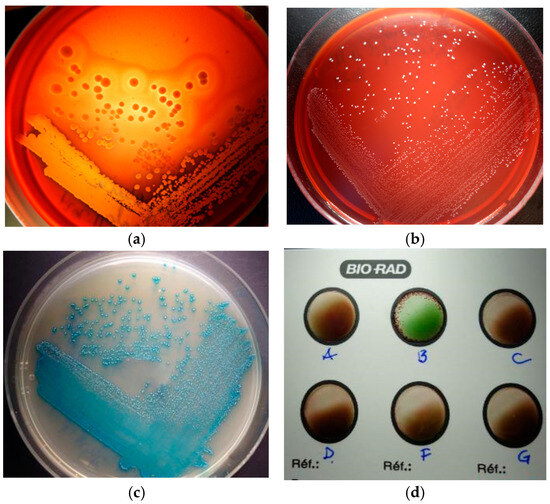
Figure 6.
Bacterial culture: (a) double-haemolysis of S. aureus colonies; (b) non-haemolytic colonies of S. halichoeri; (c) βGRU-positive colonies of S. halichoeri; (d) S. halichoeri—positive agglutination with the Group B Lancefield.
Susceptibility testing showed the sensitivity of our S. aureus strain to lincosamides, sulphonamides, fluoroquinolones, rifampicin and vancomycin, but the resistance to all beta-lactam antibiotics and tetracyclines. The Streptococcus isolate was sensitive to all antimicrobials tested.
Molecular testing of the clinical isolate confirmed the diagnostic through the detection of the nuc thermonucleaze gene using the real-time PCR method (for S. aureus confirmation) and Whole Genome Sequencing with metagenomic analysis (for S. halichoeri confirmation). Additionally, PCR analyses of our S. aureus strain demonstrated the presence of the genes for enterotoxin H (seh), protein A (spa), toxic shock syndrome toxin TSST-1 (tst) and methicillin resistance (mecC), but the lack of genes for exfoliative toxins (eta, etb).
Therapeutic protocol: The patient fully recovered after several cycles of antibiotic therapy lasting for about one year, with periodical relapse (Figure 7).
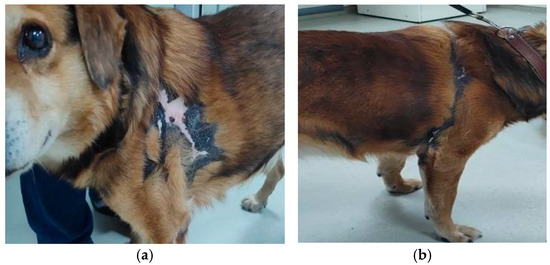
Figure 7.
Complete clinical recovery, (a)—left and (b)—right side, after 1 year of therapy.
Surprisingly, after two cycles of antibiotic therapy, we identified, via the cytological examination of chronic skin wounds, the presence of neutrophils with a particular morphology (Figure 8), which we assumed was suggestive of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). These are defined as extruded chromatin coated with antibacterial molecules and enzymes, which can kill microorganisms even when the neutrophils have died [2]. NETs are usually abundant at sites of infection, indicating the activation of antimicrobial innate immunity.
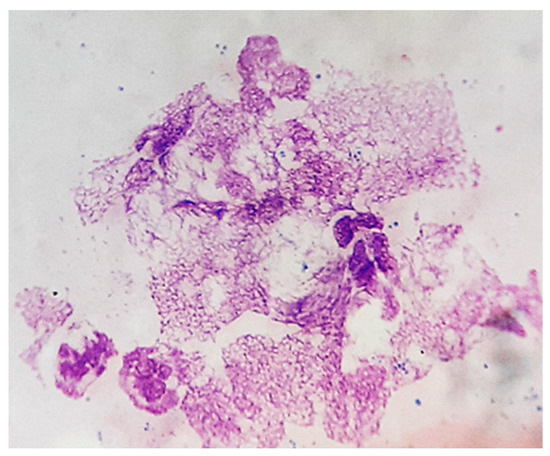
Figure 8.
Skin cytology. Particular morphology of neutrophils with nuclear networks (MGG stain, ×1000).
However, excessive NET formation may amplify inflammation and tissue damage leading to delayed wound healing (Figure 9a–c) due to their toxic components, such as histones, myeloperoxidase, matrix metalloproteinases, etc. [24].
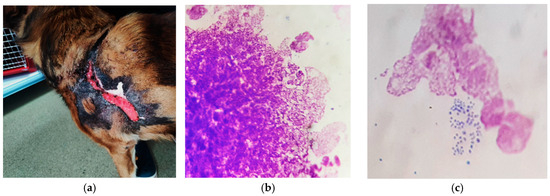
Figure 9.
(a) Delayed wound healing; (b) excessive neutrophil nuclear networks (MGG stain, ×1000); (c) persistent bacterial colonization, after 6 months of therapy (MGG stain, ×1000).
4. Discussion
In dogs, S. aureus and Dermatophilus spp. are not recognized as usual pathogens of the skin, but occasionally can cause severe ulcerative pyoderma leading to death. S. halichoeri, as a skin inhabitant in dogs, may be associated with abscesses and cellulitis, but is most frequently isolated in polymicrobial culture [14]. Particularly, S. aureus is known as the most versatile pathogen, able to readily cross species barriers and adapt to new hosts and niches via sophisticated attack and defence mechanisms, including toxin-mediated cytotoxicity, invasiveness, immune evasion and antibiotic resistance in correlation with host specific reactivity [2,3,5,6,7,9]. In our patient, we can speculate that S. aureus infection was transmitted from another carrier dog after biting trauma, while Dermatophilus spp. might have been secondarily acquired from the soil.
Both S. aureus and S. pseudintermedius are known to produce a number of potent superantigens, including staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs), staphylococcal exfoliative toxin (ET) and toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST-1), which are able to cause the release of massive amounts of host inflammatory cytokines, notably TNF-α. These molecules are responsible for the clinical and pathologic features of septic shock, including high fever, hypotension, haemoconcentration, thrombosis, neutrophil and endothelial activation, non-specific T-cell proliferation and multiple organ failure [2,5,12,13,14,24]. In our case, the immunological response profile associated with TSS was not assessed, and no cytokine profiling (e.g., TNF-α) or protein-level confirmation of toxin production was conducted. Other bacteria reported to be responsible for TSS and invasive infections in dogs, cats, domestic animals and humans are Streptococcus canis and Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus. Both streptococci are opportunistic pathogens often found as inhabitants of the skin and mucosal surfaces, with zoonotic potential. Additionally, human toxic shock caused by S. pyogenes resembles the canine TSS, and these streptococci are rarely transferable to dogs [25].
In the skin, staphylococcal superantigens can mediate epidermal necrolysis via multiple mechanisms, such as keratinocyte activation, vascular endothelial activation and innate and adaptive immunity activation (neutrophil, monocytes, infiltrating lymphocytes) [2,5,10]. Staphylococcal toxins can also be responsible for direct cytotoxicity toward keratinocytes, even in the absence of immune mechanisms [26]. Thus, significant differences have been shown in the action of staphylococcal toxins on human keratinocytes. For example, staphylococcal exfoliative toxin (ET) is able to cause the intercellular separation of granular-layer keratinocytes, independent of super antigenic properties. Alpha-toxin (α-haemolysin) was shown to induce more significant cytotoxic damage to human keratinocytes, in contrast to super antigenic toxins (TSST-1, ET, enterotoxins SEA, SEB) [10]. It is also reported that alpha-toxin plays an important role in gangrene generation by inducing ischemic coagulative necrosis in affected adjacent tissue [18], as it can be seen in our patient (Figure 1a,b). Additionally, alpha-toxin and staphylococcal protein A of S. aureus isolates from a patient with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis were found to be able to induce direct proinflammatory effects via TNF-α release from keratinocytes [10]. In other experimental studies, S. aureus enterotoxins and alpha-toxin were demonstrated to promote apoptosis in different cell types, like T cells, neutrophils, epithelial cells and endothelial cells [27].
The recruitment of neutrophils observed in cytological preps was shown to be critical for the clearing of S. aureus infection but also for the significant adhesion of S. aureus to keratinocytes and skin colonization, independent of staphylococcal virulence factors [2,9,12,28]. Besides its antimicrobial role, neutrophil overactivation in the initial stage of shock syndrome can be responsible for the induction of a compensatory anti-inflammatory response characterized by decreased macrophage activity and T-cell anergy with an increasing risk of secondary infections [13,29]. The survival of our patient after the initial stage of shock could be explained by this compensatory mechanism. Moreover, the detection of particular neutrophils (NETs) in the smears from chronic skin wounds could be interpreted as a mechanism of enhancing bactericidal activity and preventing bacterial dissemination [2,27,28,30]. On the other hand, skin inflammation associated with the release of NETs was shown to be significantly correlated with increased colonization, as well as the persistence of S. aureus in mouse skin [4,28,30]. Indeed, in our patient, poor wound healing with extensive hyperpigmentation, hair loss and focal vitiligo and scars was associated with increased neutrophil nuclear networks and remaining bacterial colonization after long-term antibiotic therapy (Figure 9a–c). Of note, the early diagnosis of TSS and prompt shock and multiple-antimicrobial therapy (penicillin G, clindamycin, lincomycin, erythromycin, potentiated sulfas, etc.) are essential for patient recovery, and still, there is always a questionable antibiotic therapy (Appendix A).
5. Conclusions
The correlation of the history, clinical signs, cytology, bacterial culture and response to systemic antibiotic therapy was suggestive of a TSS-like diagnosis with the major involvement of S. aureus and presumptive role of Dermatophilus spp. and S. halichoeri.
In this case, toxic shock symptoms, multidrug resistance and clinical relapse were correlated with the presence of the genes for enterotoxin H (seh), protein A (spa), toxic shock syndrome toxin TSST-1 (tst) and methicillin resistance (mecC), but a lack of genes for the exfoliative toxins responsible for staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome (eta, etb) in our S. aureus clinical isolate. However, the detection of tst and seh genes is not, by itself, sufficient to support a TSS-syndrome. Staphylococcal enterotoxins, TSST-1 and protein A are recognized as having an important role in the pathogenesis of invasive staphylococcal infection, preventing a protective immune response and recurrent/persistent infection even with antibiotic and surgical therapy.
In polymicrobial infections, like in our case, the pathogenic role of each species remains uncertain due to potential microbial interactions and host factors that may influence disease expression.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.N., V.N. and L.M.C.; methodology, C.N. and L.M.C.; validation, C.N., V.N. and V.C.; formal analysis, C.N. and L.M.C.; investigation, C.N.; resources, C.N. and L.M.C.; data curation, C.N.; writing—original draft preparation, V.N. and V.C.; writing—review and editing, C.N. and L.M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no external financial support for the research. Financial publication of this article was supported by University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the Declaration on the granting of consent for the processing of personal data for activities provided by free practice veterinarian doctors within the “Prof. Univ. dr. Alin Birțoiu University Emergency Veterinary Hospital”.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Appendix A. Challenge Question
What would be the clinical benefits of combined systemic Enroxil plus Clindamicin plus Trimetoprim sulphonamide in the treatment of canine toxic shock syndrome caused by an MRSA strain of S. aureus?
A. Good penetrability into deep pyoderma lesions and accelerated clinical resolution of infection.
B. Under-expression of bacterial superantigens (toxins) in the skin surface and reducing inflammation.
C. Preventing the selection of intracellular pathogenic variants of S. aureus more resistant to antibiotics and host defence and therefore the clinical management of relapses of skin microbiota and barrier functions, and therefore the prevention of blood stream infections.
D. All of the above.
References
- Haag, A.F.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Penades, J.R. Staphylococcus aureus in animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, P.B.; Imai, A. The immunopathogenesis of staphylococcal skin infections—A review. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 49, 8–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howden, B.P.; Giulieri, S.G.; Lung, T.W.F.; Baines, S.L.; Sharkey, L.K.; Lee, J.Y.H.; Hachani, A.; Monk, I.R.; Stinear, T.P. Staphylococcus aureus host interactions and adaptation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Ali, T.; Alkasir, R.; Yin, J.; Liu, G.; Han, B. Staphylococcal enterotoxin H induced apoptosis of bovine mammary epithelial cells in vitro. Toxins 2014, 6, 3552–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negoiţă, C.; Negoiţă, V. Ear Cytology—A key test in the diagnosis and management of canine otitis externa. Sci. Works Ser. C Vet. Med. 2022, 68, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Peetermans, M.; Vanassche, T.; Liesenborghs, L.; Claes, J.; Vande Velde, G. Kwiecinksi, J.; Jin, T.; De Geest, B.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Lijnen, R.H.; et al. Plasminogen activation by staphylokinase enhances local spreading of S. aureus in skin infections. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Phukan, U.J. Interaction of host and Staphylococcus aureus protease-system regulates virulence and pathogenicity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus secreted toxins and extracellular enzymes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 7, 10-1128. [Google Scholar]
- Thammavongsa, V.; Kim, H.K.; Missiakas, D.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcal manipulation of host immune responses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Hauk, P.; Strickland, I.; Travers, J.B.; Norris, D.A. The role of superantigens in human diseases: Therapeutic implications for the treatment of skin diseases. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 139, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futagawa-Saito, K.; Makino, S.; Sunaga, F.; Kato, Y.; Sakurai-Komada, N.; Ba-Thein, W.; Fukuyasu, T. Identification of first exfoliative toxin in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 301, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaguere, E.; Prelaud, P.; Craig, M. Staphyloccocal toxic shock syndrome. In Practical Guide to Canine Dermatology; Kalianxis: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- McGavin, M.D.; Zachary, J.F. Stages and progression of shock. In Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease; Mosby Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.; Srivastava, M.K.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, R. Canine streptococcal toxic shock syndrome associated with necrotizing fasciitis: An overview. Vet. World 2012, 5, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, M.; Aaltonen, K.; Sironen, T.; Raunio-Saarnisto, M.; Grönthal, T.; Nordgren, H.; Pitkälä, A.; Vapalahti, O.; Rantala, M. Comparison of Streptococcus halichoeri isolates from canine and fur animal infections: Biochemical patterns, molecular characteristics and genetic relatedness. Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Center for Food Security & Public Health, Institute for International Cooperation in Animal Biologics, Iowa State University, World Organisation for Animal Health. Zoonotic Streptococcosis (Monograph Online). Available online: www.cfsph.iastate.edu (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Shakir, S.M.; Gill, R.; Salberg, J.; Slechta, E.S.; Feldman, M.; Fritsche, T.; Clarridge, J.; Sharp, S.E.; Fisher, M.A. Clinical laboratory perspective on Streptococcus halichoeri, an unusual nonhemolytic, Lancefield group B Streptococcus causing human infetions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songer, J.G.; Post, K.W. The genus Staphylococcus and the genera Dermatophilus and Nocardia. In Veterinary Microbiology-Bacterial and Fungal Agents of Animal Disease; Elsevier Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ANSES/LSAliments/LSA-INS-1294. In Identification of Staphylococcus Aureus Species and Detection of Genes Encoding S.aureus Enterotoxins by Real-Time PCR; Laboratory for Food Safety National Reference Laboratory for Coagulase Positive Staphylococci: Maisons-Alfort, France, 2017.
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Aerts, M.; Battisti, A.; Hendriksen, R.; Larsen, J.; Nilsson, O.; Abrahantes, J.C.; Guerra, B.; Papanikolaou, A.; Beloeil, P.A. Technical specifications for a baseline survey on the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in pigs. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Rincon, N.; Wood, D.E.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Pockrandt, C.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L.; Steinegger, M. Metagenome analysis using the Kraken software suite. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 2815–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, M.; Wang, G.; Johnson, W.M. Multiplex PCR for detection of genes for Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin1 and methicillin resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.E.; Salzberg, S.L. Kraken: Ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Ling, X.; Jin, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Miao, C.; et al. The emerging roles of neutrophil extracellular traps in wound healing. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.L.; Sohn, M.; Woeller, C.F.; Wozniak, R.A.F. Staphylococcal enterotoxins promote virulence in bacterial keratitis. Invest. Ophtalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Rao, X. Apoptosis induced by Staphylococcus aureus toxins. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 205, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitschar, K.; Staudenmaier, L.; Klink, L.; Focken, J.; Sauer, B.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Herster, F.; Bittner, Z.; Bleul, L.; Schaller, M.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus skin colonization is enhanced by the interaction of neutrophil extracellular traps with keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E. Neutrophil extracellular traps: A strategic tactic to defeat pathogens with potential consequences for the host. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, F.V.S.; Kubes, P. Neutrophils and NETs in modulating acute and chronic inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Lee, J.H.; Liu, R.; Lawhon, S.D.; Yang, C.; Otto, M. Methicilin resistance elements in the canine pathogen Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and their association with the peptide toxin PSM-mec. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).