Metabolic Profiles of Feline Obesity Revealed by Untargeted and Targeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Approaches
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Cohorts
2.2. Participants
2.3. Diagnoses and Classification
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Untargeted and Targeted Metabolomic Analyses
2.5.1. Untargeted Metabolomics
2.5.2. Targeted Metabolomics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Approvals
3. Results
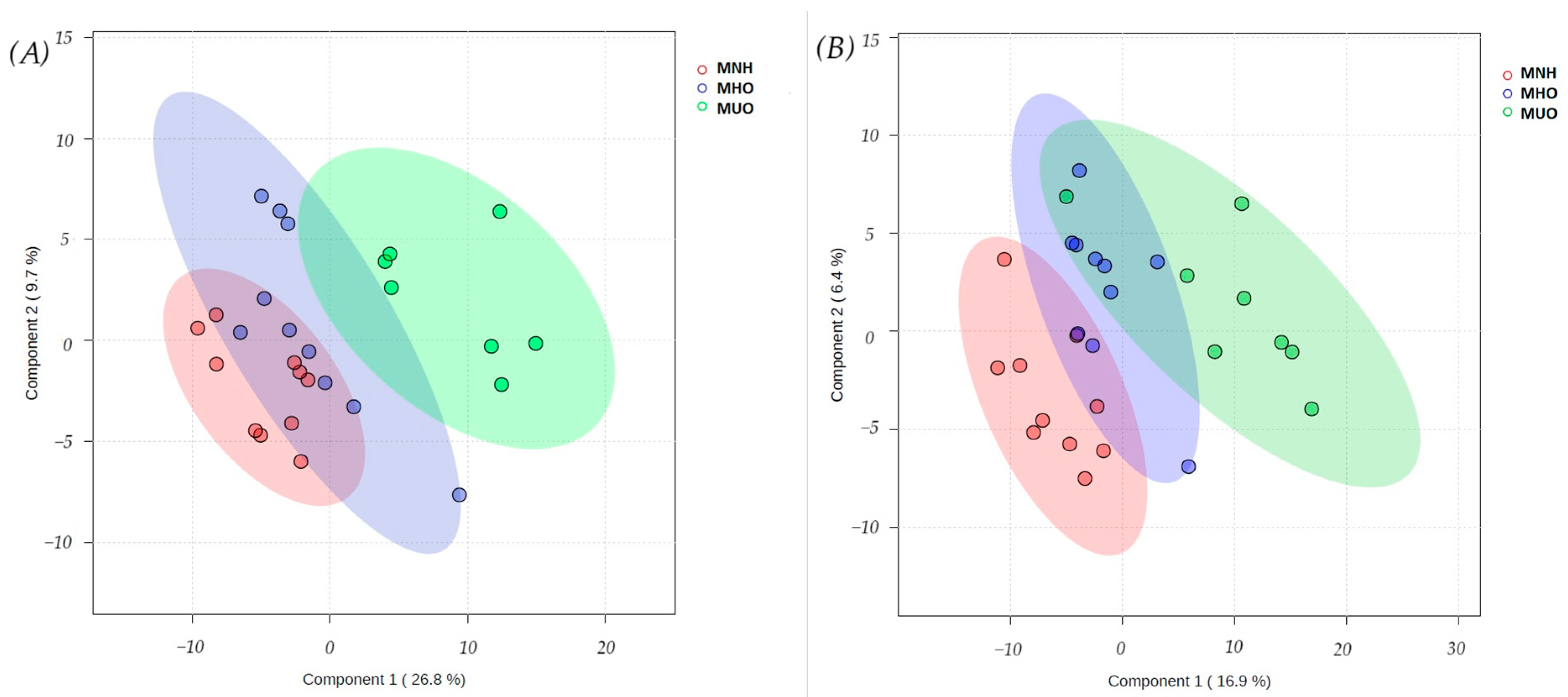
3.1. Data Processing
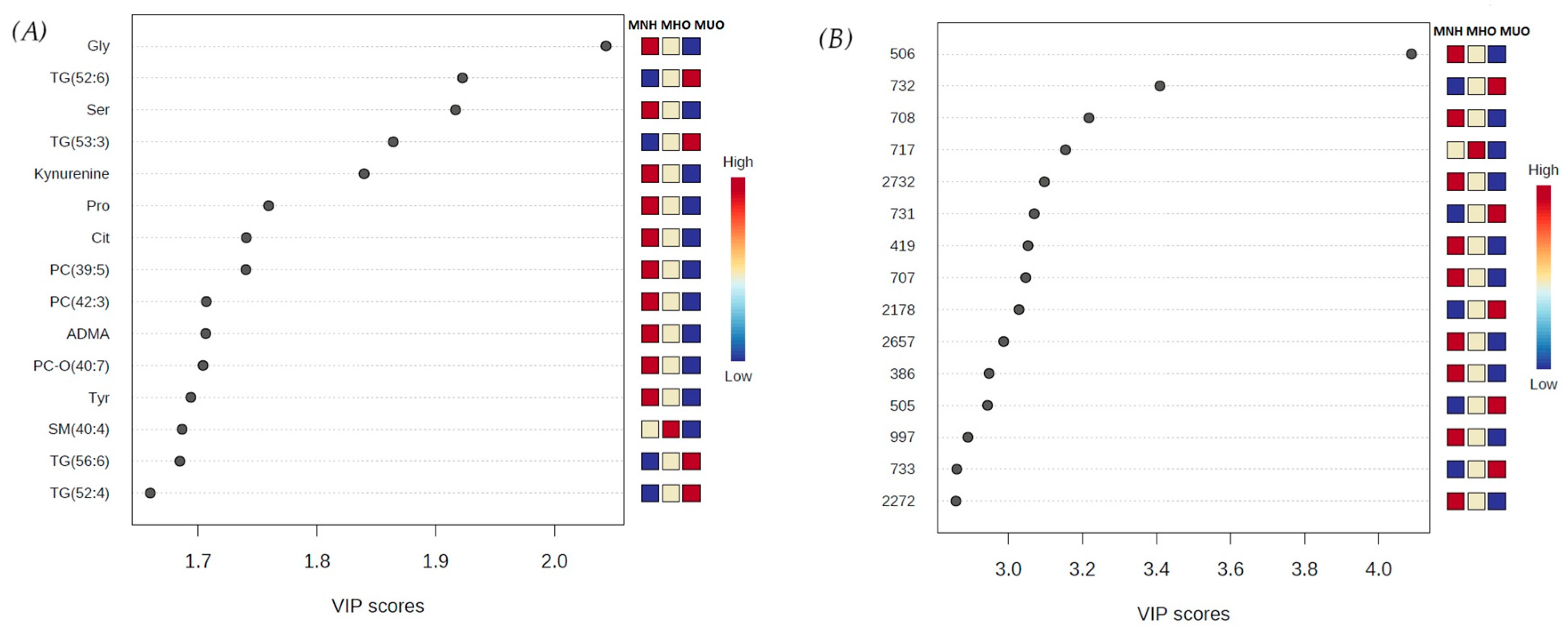
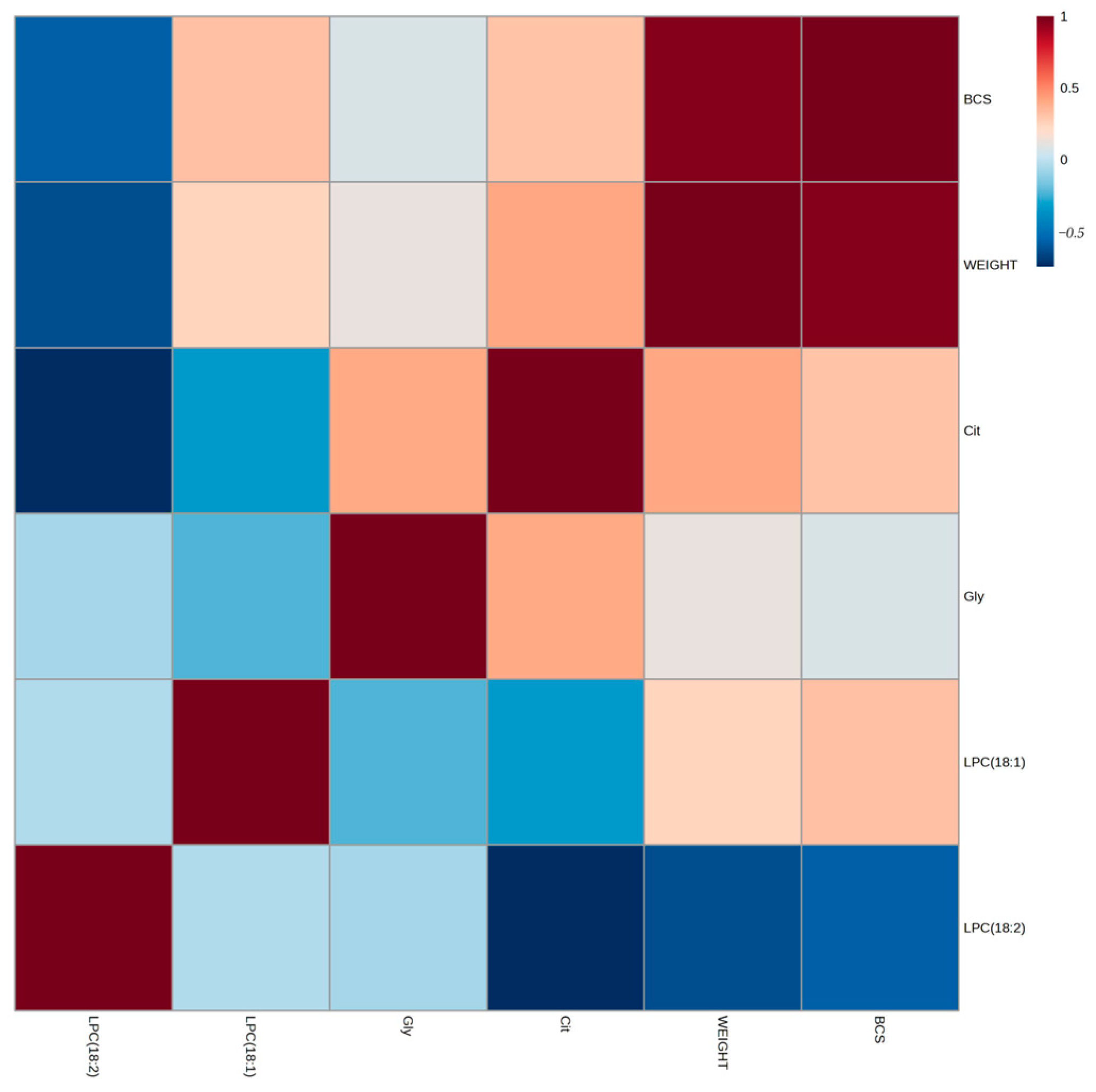
3.2. Discriminant Metabolite Identification
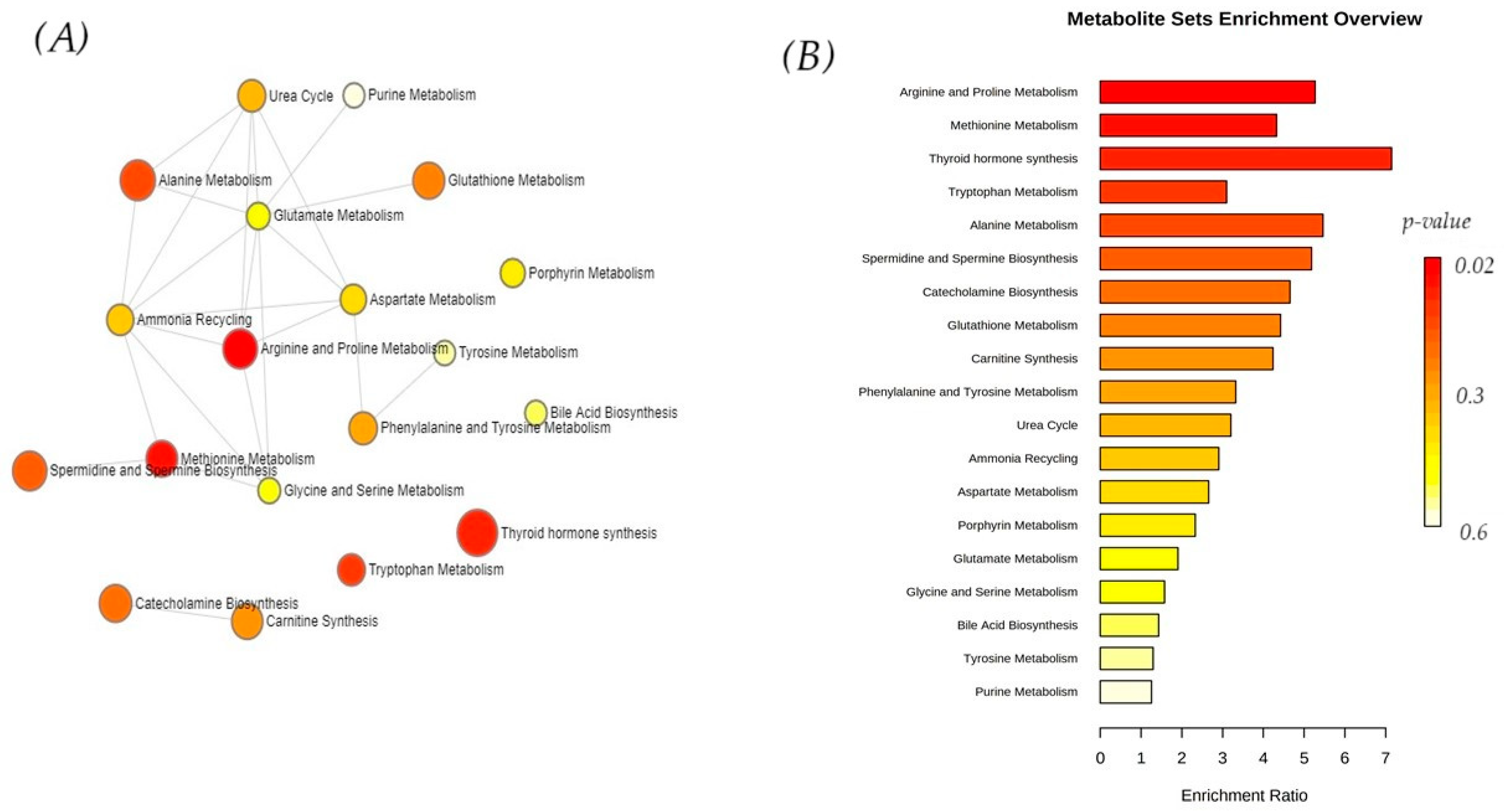
3.3. Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organisation. Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. WHO Consult. 2000, 894, 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- BSAVA. Obesity. 2019. Available online: https://bsava.com/position-statement/obesity/ (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Tarkosova, D.; Story, M.M.; Rand, J.S.; Svoboda, M. Feline obesity–prevalence, risk factors, pathogenesis, associated conditions and assessment: A review. Vet. Med. 2016, 61, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotto, M.R.; Oba, P.M.; de Godoy, M.R.C.; Pappan, K.L.; Buff, P.R.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of Weight Loss and Moderate-Protein, High-Fiber Diet Consumption on the Fasted Serum Metabolome of Cats. Metabolites 2021, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, M.; Palmgren, M.; Holst, B.S. Overweight in adult cats: A cross-sectional study. Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve-Johnson, M.K. Screening for Prediabetes in Senior Cats and Metabolomic Characteristics of Obesity and Burmese Cats. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Veterinary Science, The University of Queensland, Gatton, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gottlieb, S.; Rand, J.; Anderson, S.T.; Morton, J.M.; Dias, D.A.; Boughton, B.A.; Roessner, U.; Ramadan, Z. Metabolic Profiling of Diabetic Cats in Remission. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, Y. The long-term prognosis of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality for metabolically healthy obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2016, 70, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Body Condition Scoring in Cats. Association for Pet Obesity Prevention. 2023. Available online: https://www.petobesityprevention.org/catbcs (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Okada, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sawamura, M.; Arai, T. Comparison of Visceral Fat Accumulation and Metabolome Markers among Cats of Varying BCS and Novel Classification of Feline Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleš, J.; Rubić, I.; Beer Ljubić, B.; Bilić, P.; Barić Rafaj, R.; Brkljačić, M.; Burchmore, R.; Eckersall, D.; Mrljak, V. Combined Untargeted and Targeted Metabolomics Approaches Reveal Urinary Changes of Amino Acids and Energy Metabolism in Canine Babesiosis with Different Levels of Kidney Function. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 715701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rubić, I.; Weidt, S.; Burchmore, R.; Kovačević, A.; Kuleš, J.; Eckersall, P.D.; Torti, M.; Jović, I.; Kovačić, M.; Gotić, J.; et al. Metabolome Profiling in the Plasma of Dogs with Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A Multiplatform Mass-Spectrometry-Based Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gloaguen, Y.; Smith, R.; Parker, C.E.; Jude, C.; Dunn, W.B.; Viant, M.R.; Goodacre, R. PiMP my metabolome: An integrated, web-based tool for LC-MS metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 4007–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, J.D.; Tabb, D.L.; Mallick, P. Employing ProteoWizard to Convert Raw Mass Spectrometry Data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 46, 13.24.1–13.24.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, G.; Favero, C.; Savino, D.; Mercadante, R.; Albetti, B.; Dioni, L.; Vigna, L.; Bollati, V.; Pesatori, A.C.; Fustinoni, S. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling in 1391 Subjects with Overweight and Obesity from the SPHERE Study. Metabolites 2021, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, W.E.; Pieper, C.F.; Huffman, K.M.; Thompson, D.K.; Kraus, V.B.; Morey, M.C.; Cohen, H.J.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Association of plasma small-molecule intermediate metabolites with age and body mass index across six diverse study populations. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, C.B.; An, J.; Bain, J.R.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Lien, L.F.; Haqq, A.M.; Shah, S.H.; Arlotto, M.; Slentz, C.A.; et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmnäs, M.S.A.; Kopciuk, K.A.; Shaykhutdinov, R.A.; Robson, P.J.; Mignault, D.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Vogel, H.J.; Csizmadi, I. Serum Metabolomics of Activity Energy Expenditure and its Relation to Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashina, C.; Tsujino, I.; Watanabe, T.; Sakaue, S.; Ikeda, D.; Yamada, A.; Sato, T.; Ohira, H.; Otsuka, Y.; Oyama-Manabe, N.; et al. Associations among the plasma amino acid profile, obesity, and glucose metabolism in Japanese adults with normal glucose tolerance. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Aama, J.; Al Mahdi, H.B.; Salama, M.A.; Bakur, K.H.; Alhozali, A.; Mosli, H.H.; Bahirji, S.M.; Babhieldin, A.; Willmitzer, L.; Edris, S. Detection of Secondary Metabolites as Biomarkers for the Early Diagnosis and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2675–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetenyi, G., Jr.; Anderson, P.J.; Raman, M.; Ferrarotto, C. Gluconeogenesis fromglycine and serine in fasted normal and diabetic rats. Biochem. J. 1988, 253, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okekunle, A.P.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Du, S.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, J.; Sun, C.; Feng, R. Abnormal circulating amino acid profiles in multiple metabolic disorders. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 132, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, N.D.; Stevens, R.D.; Antinozzi, P.A.; Anderson, A.; Bergmann, R.N.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Newgard, C.B.; Bowden, D.W. Metabolomic profile associated with insulin resistance and conversion to diabetes in the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Jackson, M.I.; Vondran, J.C.; Vanchina, M.A.; Jewell, D.E. Comparison of circulating metabolite concentrations in dogs and cats when allowed to freely choose macronutrient intake. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio036228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayol, M.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Ferrari, P.; Zamora-Ros, R.; Achaintre, D.; Stepien, M.; Schmidt, J.A.; Travis, R.C.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; et al. Blood Metabolic Signatures of Body Mass Index: A Targeted Metabolomics Study in the EPIC Cohort. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favennec, M.; Hennart, B.; Caiazzo, R.; Leloire, A.; Yengo, L.; Verbanck, M.; Arredouani, A.; Marre, M.; Pigeyre, M.; Bessede, A.; et al. The kynurenine pathway is activated in human obesity and shifted toward kynurenine monooxygenase activation. Obesity 2015, 23, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.E.; Larson, M.G.; Ghorbani, A.; Cheng, S.; Chen, M.H.; Keyes, M.; Rhee, E.P.; Clish, C.B.; Vasan, R.S.; Gerszten, R.E.; et al. Metabolomic profiles of body mass index in the framingham heart study reveal distinct cardiometabolic phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.T.; Fu, X.Y.; Xu, B.; Zuo, L.L.; Ma, H.B.; Wang, S.R. Untargeted metabolomics approach (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) explores the biomarkers of serum and urine in overweight/obese young men. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 1067–1076. Available online: https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/ielapa.898530530553980 (accessed on 5 May 2025). [PubMed]
- Piro, M.C.; Tesauro, M.; Lena, A.M.; Gentileschi, P.; Sica, G.; Rodia, G.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Rovella, V.; Cardillo, C.; Melino, G.; et al. Free-amino acid metabolic profiling of visceral adipose tissue from obese subjects. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Djazayery, A.; Farzadfar, F.; Qi, L.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Aslibekyan, S.; Chamari, M.; Hassani, H.; Koletzko, B.; Uhl, O. Plasma metabolomic profiling of amino acids and polar lipids in Iranian obese adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, O.Y.; Ham, B.M.; Kim, H.-J.; Kwon, D.Y.; Jang, Y.; Lee, J.H. Metabolic profiling of plasma in overweight/obese and lean men using ultra performance liquid chromatography and Q-TOF mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF MS). J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4368–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, S.; Yu, Z.; Kleber, M.; Singmann, P.; Holzapfel, C.; He, Y.; Mittelstrass, K.; Polonikov, A.; Prehn, C.; Römisch-Margl, W.; et al. Childhood Obesity Is Associated with Changes in the Serum Metabolite Profile. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.; Mirza, I.; Morsy, M.; Mostafa, A.; Hassan, C.; Masrur, M.; Bianco, F.M.; Papasani, S.; Levitan, I.; Mahmoud, A.M. Comparison of Adiposomal Lipids between Obese and Non-Obese Individuals. Metabolites 2024, 14, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Beyene, H.B.; Olshansky, G.; Giles, C.; Huynh, K.; Cinel, M.; Mellett, N.A.; Smith, A.A.T.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J.; Meikle, P.J. Lipidomic Signatures of Changes in Adiposity: A Large Prospective Study of 5849 Adults from the Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study. Metabolites 2021, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rauschert, S.; Uhl, O.; Koletzko, B.; Hellmuth, C. Metabolomic biomarkers for obesity in humans: A short review. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 64, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenig, M. The cat as a model for human obesity and diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, E.; Kley, S.; Le, N.-A.; Waldron, M.; Hoenig, M. Dyslipidemia in obese cats. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2008, 35, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, L.; Boronat, M.; Melián, C.; Brito-Casillas, Y.; Wägner, A.M. Kidney function and glucose metabolism in overweight and obese cats. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedini, S.; Fermo, I.; Caumo, A.; Terruzzi, I.; Luzi, L. Plasma Citrulline: A New Marker of Gut Epithelium Alteration in Obese Patients? J. Diabetes Mellit. 2015, 5, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.R.; Boyle, K.E.; Koves, T.R.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; Muoio, D.M.; Houmard, J.A.; Friedman, J.E. Metabolomic analysis reveals altered skeletal muscle amino acid and fatty acid handling in obese humans. Obesity 2015, 23, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalande, C.; Drouin-Chartier, J.P.; Tremblay, A.J.; Couture, P.; Veilleux, A. Plasma biomarkers of small intestine adaptations in obesity-related metabolic alterations. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyram, R.; Kansara, A.; Banerji, M.A.; Loney-Hutchinson, L. Chronic kidney disease and diabetes. Maturitas 2012, 71, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillaert, A.; Liu, D.J.X.; Daminet, S.; Broeckx, B.J.G.; Stock, E.; Paepe, D.; Hesta, M.; Vanderperren, K. Serum symmetric dimethylarginine shows a relatively consistent long-term concentration in healthy dogs with a significant effect of increased body fat percentage. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laville, M. Renal consequences of obesity. Nephrol. Ther. 2011, 7, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, E. Metabolic syndrome and kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2008, 26, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickman, C.; Kramer, H. Obesity and kidney disease: Potential mechanisms. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barić Rafaj, R.; Kuleš, J.; Turković, V.; Rebselj, B.; Mrljak, V.; Kučer, N. Prospective hematologic and biochemical evaluation of spontaneously overweight and obese dogs. Vet. Arh. 2016, 86, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- García-Solís, P.; García, O.P.; Hernández-Puga, G.; Sánchez-Tusie, A.A.; Sáenz-Luna, C.E.; Hernández-Montiel, H.L.; Solis-S, J.C. Thyroid hormones and obesity: A known but poorly understood relationship. Endokrynol. Pol. 2018, 69, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, K.; Sieminska, L. Obesity and Thyroid Axis. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 18, 9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, M.A.; MacInnis, R.J.; Canfell, K.; Shaw, J.E.; Magliano, D.J.; Banks, E.; Giles, G.G.; Byles, J.E.; Gill, T.K.; Mitchell, P.; et al. Thyroid cancers potentially preventable by reducing overweight and obesity in Australia: A pooled cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| MHN | MHO | MUO | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Unit | MEAN | MIN | MAX | MEAN | MIN | MAX | MEAN | MIN | MAX |
| BCS | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7.0 | 6 | 9 | 7.0 | 6 | 8 | |
| BUN | mmol/L | 7.8 | 3.9 | 11 | 6.9 | 4.5 | 8.6 | 9.7 | 7.2 | 15 |
| CRE | µmol/L | 97 | 74 | 142 | 100 | 62 | 188 | 98 | 72 | 153 |
| PRO | g/L | 73 | 64 | 85 | 73 | 57 | 87 | 81 | 72 | 88 |
| ALB | g/L | 27 | 23 | 30 | 27 | 24 | 30 | 28 | 25 | 31 |
| BIL | µmol/L | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 4.9 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 4.4 |
| GLU | mmol/L | 5.3 | 4.2 | 6.6 | 4.8 | 1.9 | 6.4 | 13 | 7.7 | 25 |
| AST | IU/L, 37 °C | 19 | 10 | 37 | 21 | 9.0 | 42 | 30 | 8.0 | 98 |
| ALT | IU/L, 37 °C | 56 | 34 | 149 | 61 | 36 | 112 | 78 | 40 | 153 |
| AP | IU/L, 37 °C | 65 | 24 | 135 | 48 | 20 | 104 | 42 | 22 | 60 |
| TG | mmol/L | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 5.4 |
| CHOL | mmol/L | 2.9 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 5.9 | 4.8 | 8.8 |
| ADP | µg/mL | 4.2 | 1.0 | 7.5 | 2.4 | 1.3 | 4.6 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 2.5 |
| Metabolite | p | FDR | Post Hoc Significance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kynurenine | 2.90 × 10−6 | 0.000577 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| Gly | 9.84 × 10−6 | 0.000979 | MHN/MHO | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO |
| TG (52:6) | 1.73 × 10−5 | 0.000985 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | MUO/MHO |
| SM (40:4) | 2.34 × 10−5 | 0.000985 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (53:3) | 2.48 × 10−5 | 0.000985 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| PC (42:3) | 5.10 × 10−5 | 0.001615 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| Ser | 5.68 × 10−5 | 0.001615 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (54:7) | 0.000154 | 0.00384 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| SM (31:1) | 0.00021 | 0.00465 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (54:6) | 0.00029 | 0.005767 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| ADMA | 0.000375 | 0.006493 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (52:4) | 0.000392 | 0.006493 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| TG (56:6) | 0.000481 | 0.007365 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| Tyr | 0.00054 | 0.007673 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (51:3) | 0.000602 | 0.007988 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| TG (56:7) | 0.000676 | 0.008048 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| Pro | 0.000687 | 0.008048 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| PC (33:0) | 0.000896 | 0.009132 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| Cit | 0.000913 | 0.009132 | MHN/MHO | MHN/MUO | |
| PC (39:5) | 0.000918 | 0.009132 | MHN/MHO | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO |
| TG (52:5) | 0.001179 | 0.011175 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| PC-O (40:7) | 0.001288 | 0.011648 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| PC (37:5) | 0.001403 | 0.011905 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (54:5) | 0.001472 | 0.011905 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| LPC (18:1) | 0.001496 | 0.011905 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (53:4) | 0.002004 | 0.014842 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| PC (34:5) | 0.002032 | 0.014842 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| Cer (34:0) | 0.002088 | 0.014842 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (52:2) | 0.002237 | 0.01535 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| TG (50:4) | 0.002529 | 0.016257 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| PC (24:0) | 0.002555 | 0.016257 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (51:2) | 0.002614 | 0.016257 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| TG (52:3) | 0.002812 | 0.016958 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| Creatinine | 0.003092 | 0.018095 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| Trp | 0.003213 | 0.018265 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| LPC (18:2) | 0.003337 | 0.018406 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| SDMA | 0.003509 | 0.018406 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| PC-O (26:1) | 0.003515 | 0.018406 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| PC (37:7) | 0.003745 | 0.018724 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| PC (44:10) | 0.003764 | 0.018724 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| PC (36:5) | 0.00447 | 0.021252 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| Putrescine | 0.004485 | 0.021252 | MHN/MUO | MHO/MUO | |
| TG (54:4) | 0.004875 | 0.022559 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| TG (50:3) | 0.005183 | 0.02344 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| TG (56:8) | 0.007278 | 0.032184 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
| PC (37:2) | 0.008218 | 0.035549 | MHN/MUO | ||
| PC (42:7) | 0.009626 | 0.040756 | MHN/MHO | MHN/MUO | |
| TG (54:3) | 0.011436 | 0.047411 | MUO/MHN | MUO/MHO | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barić Rafaj, R.; Rubić, I.; Kuleš, J.; Prišćan, D.; Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Gotić, J.; Ećimović, L.; Kučer, N.; Samardžija, M.; Kovačić, M.; et al. Metabolic Profiles of Feline Obesity Revealed by Untargeted and Targeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Approaches. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080697
Barić Rafaj R, Rubić I, Kuleš J, Prišćan D, Muñoz-Prieto A, Gotić J, Ećimović L, Kučer N, Samardžija M, Kovačić M, et al. Metabolic Profiles of Feline Obesity Revealed by Untargeted and Targeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Approaches. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(8):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080697
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarić Rafaj, Renata, Ivana Rubić, Josipa Kuleš, Dominik Prišćan, Alberto Muñoz-Prieto, Jelena Gotić, Luka Ećimović, Nada Kučer, Marko Samardžija, Mislav Kovačić, and et al. 2025. "Metabolic Profiles of Feline Obesity Revealed by Untargeted and Targeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Approaches" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 8: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080697
APA StyleBarić Rafaj, R., Rubić, I., Kuleš, J., Prišćan, D., Muñoz-Prieto, A., Gotić, J., Ećimović, L., Kučer, N., Samardžija, M., Kovačić, M., & Mrljak, V. (2025). Metabolic Profiles of Feline Obesity Revealed by Untargeted and Targeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Approaches. Veterinary Sciences, 12(8), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080697







