Exogenous L-Serine Alleviates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Inflammation by Reprogramming the Transcription and Metabolism of Macrophages
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
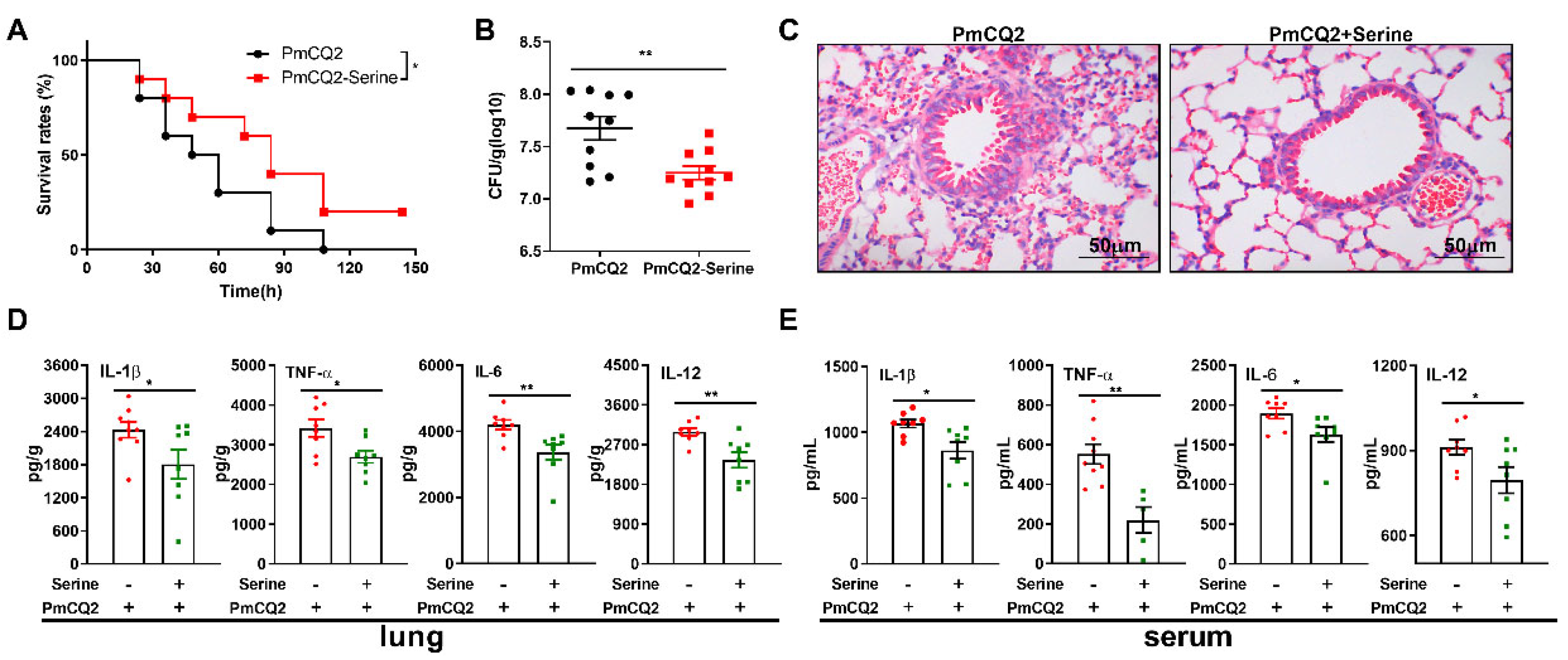
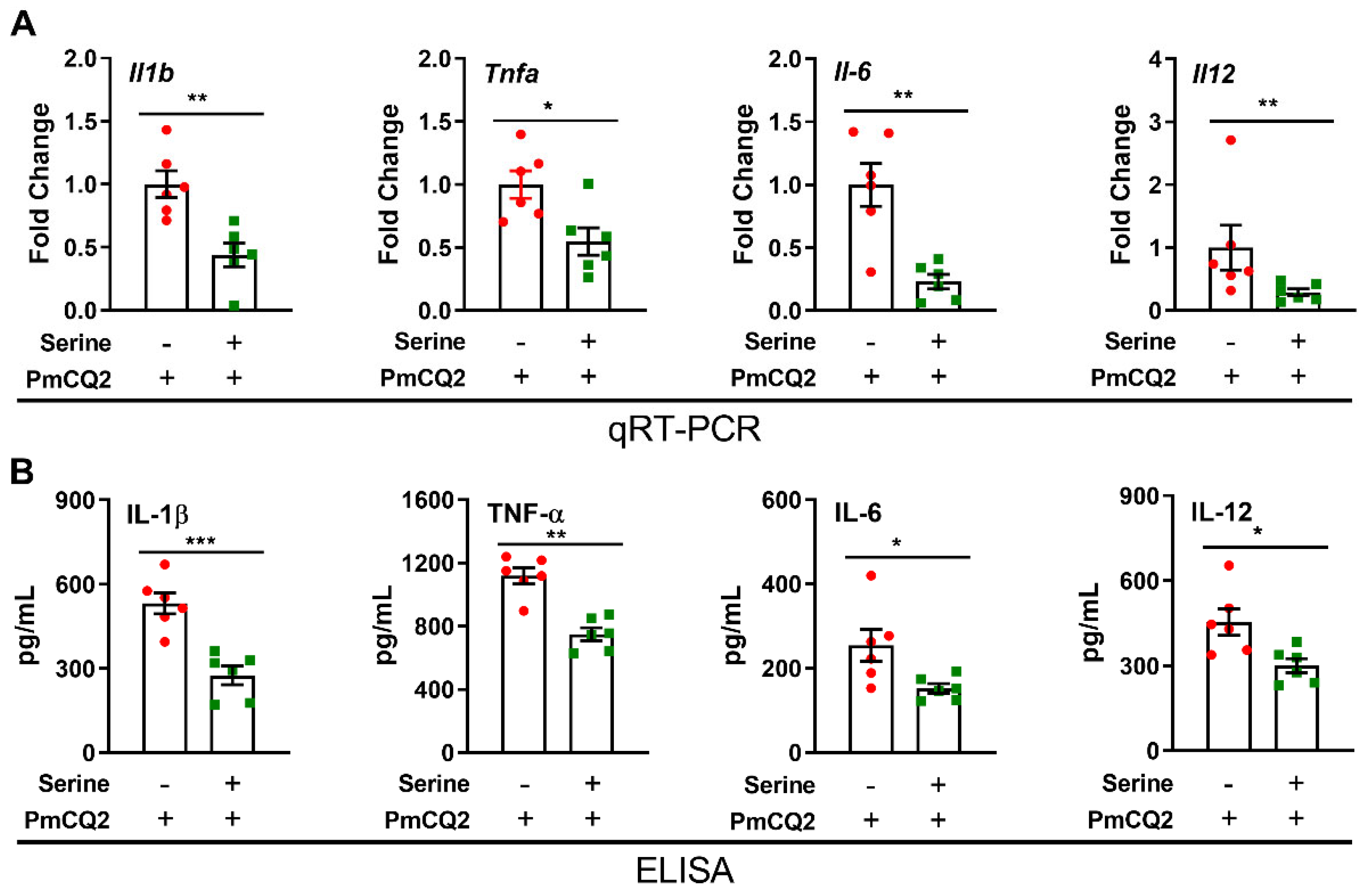
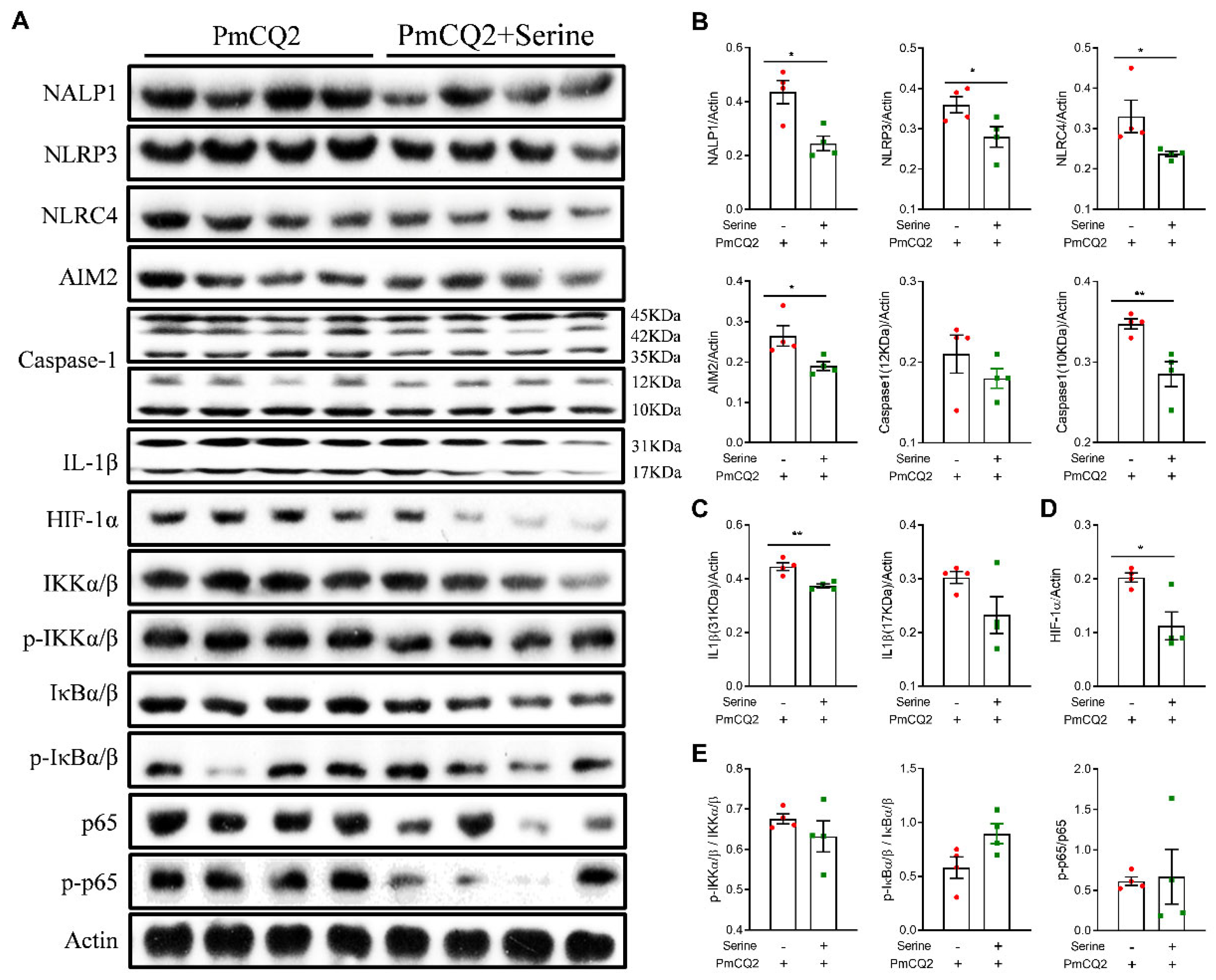
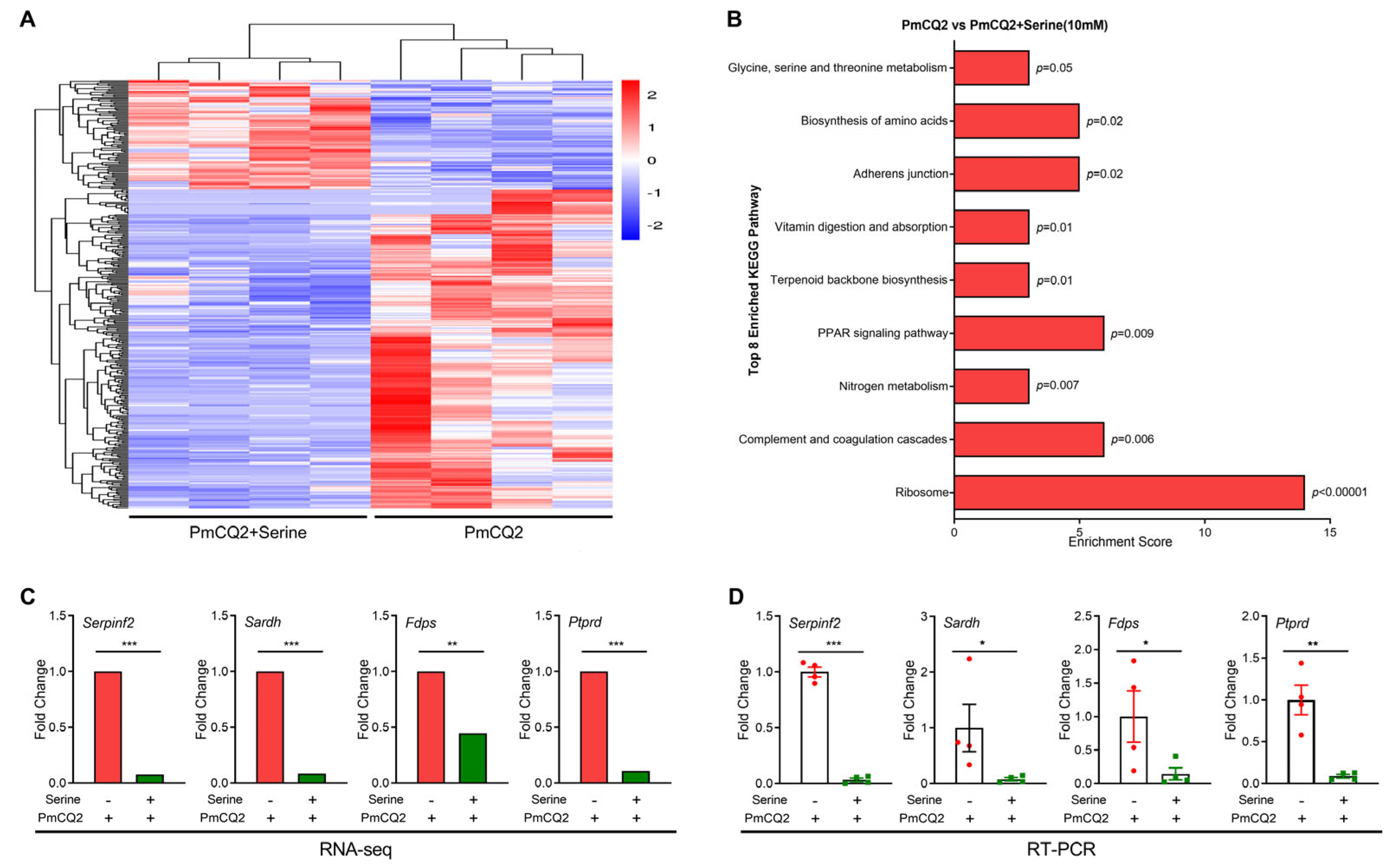
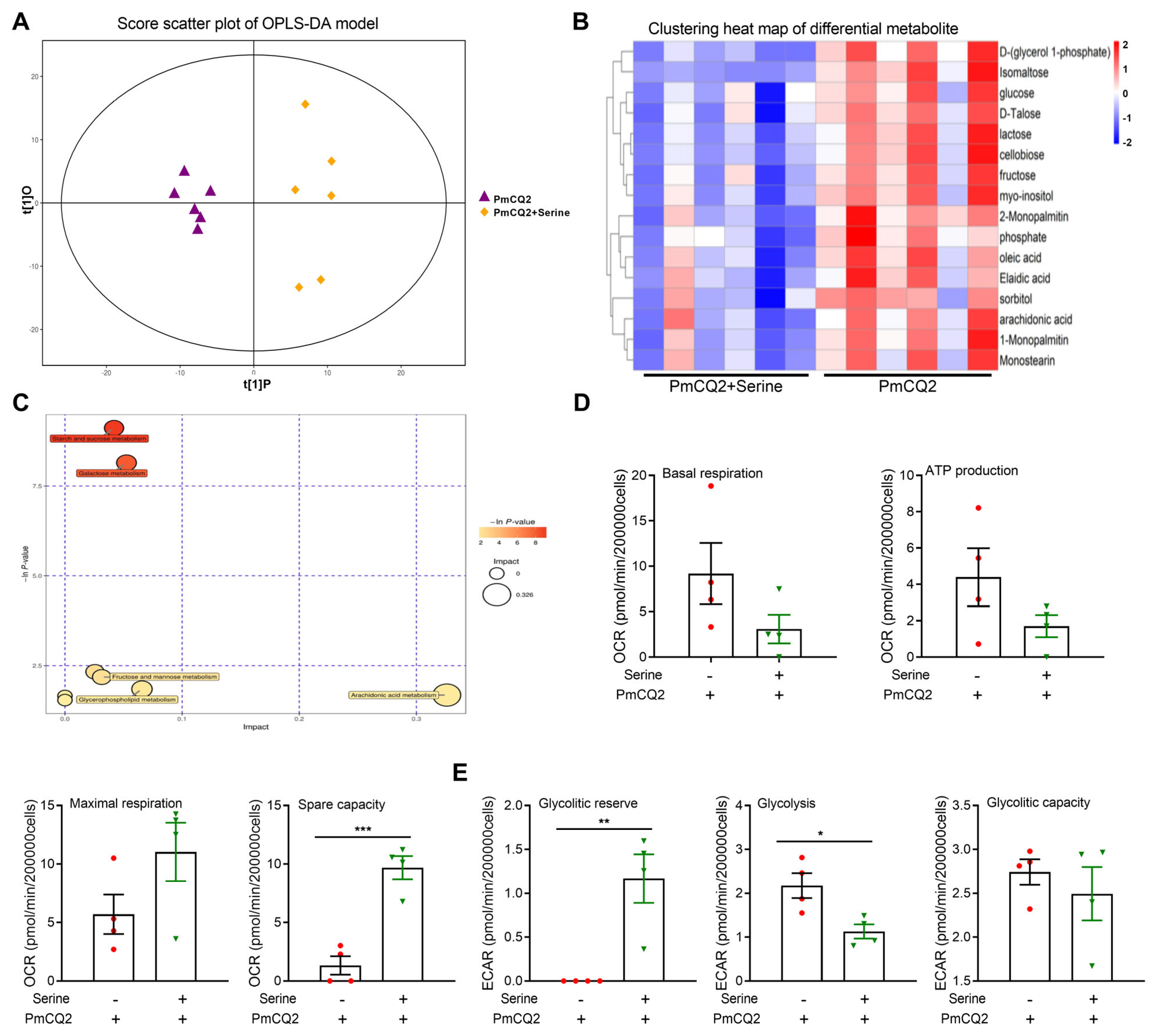
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortés, M.; Brischetto, A.; Martinez-Campanario, M.; Ninfali, C.; Domínguez, V.; Fernández, S.; Celis, R.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Lozano, J.; Sidorova, J.; et al. Inflammatory macrophages reprogram to immunosuppression by reducing mitochondrial translation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locati, M.; Curtale, G.; Mantovani, A. Diversity, mechanisms, and significance of macrophage plasticity. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Du, H.; Lei, G.; Liu, Y.; Feng, S.; Ye, C.; Li, N.; Peng, Y. NLRP3 inflammasome plays an important role in caspase-1 activation and IL-1β secretion in macrophages infected with Pasteurella multocida. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 231, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Lei, G.; Jiang, J.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Z.; Ye, C.; Li, N.; Peng, Y. High- and low-virulent bovine Pasteurella multocida induced differential NLRP3 inflammasome activation and subsequent IL-1β secretion. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, 108646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tang, Y.; Dan, R.; Xie, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.; He, F.; Li, N.; Peng, Y. Pasteurella multocida activates apoptosis via the FAK-AKT-FOXO1 axis to cause pulmonary integrity loss, bacteremia, and eventually a cytokine storm. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, C.H.; Lei, M.; Zeng, Q.; Li, L.; Tang, H.; Zhang, N. Metabolic regulation of the immune system in health and diseases: Mechanisms and interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G.; Riquelme, S.; Prince, A.; Avraham, R. Immunometabolic crosstalk during bacterial infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Rajendran, R.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, B.; Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Zhu, G.; Peng, Y.; Huang, X.; Deng, J.; et al. Amino acids as mediators of metabolic cross talk between host and pathogen. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbuagu, N.E.; Ayo, J.O.; Aluwong, T.; Akor-Dewu, M.B. Effect of L-serine on circadian variation of cloacal and body surface temperatures in broiler chickens subjected to feed restriction during the hot-dry season. J. Therm. Biol. 2023, 112, 103445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, G. L-Serine, an endogenous amino acid, is a potential neuroprotective agent for neurological disease and injury. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 726665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Hornemann, T.; Štefanić, S.; Schraner, E.; Zuellig, R.; Reding, T.; Malagola, E.; Henstridge, D.; Hills, A.; Graf, R.; et al. Serine administration as a novel prophylactic approach to reduce the severity of acute pancreatitis during diabetes in mice. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Peng, S.; Ye, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, H.; Luo, Q.; He, M.; Wang, G. Neuroinflammation aggravated by traumatic brain injury at high altitude is reversed by l-serine via NFAT1-mediated microglial polarization. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1152392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.E.; Ducker, G.S.; Billingham, L.K.; Martinez, C.A.; Mainolfi, N.; Suri, V.; Friedman, A.; Manfredi, M.G.; Weinberg, S.E.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; et al. Serine metabolism supports macrophage il-1β production. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1003–1011.e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yin, Z.; Wu, C.; Xia, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, N.; Zhu, G.; et al. L-Serine lowers the inflammatory responses during Pasteurella multocida infection. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, G.; Hardeland, R.; et al. Melatonin inhibits Gram-negative pathogens by targeting citrate synthase. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Xiong, P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, G.; Li, N.; Peng, Y. Attenuated vaccine PmCQ2Δ4555-4580 effectively protects mice against Pasteurella multocida infection. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; He, F.; Wu, X.; Tan, B.; Chen, S.; Liao, Y.; Qi, M.; Chen, S.; Peng, Y.; Yin, Y.; et al. GABA transporter sustains IL-1β production in macrophages. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe9274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Qin, X.; Li, P.; Pan, T.; Ren, W.; Li, N.; Peng, Y. Transcriptomic analysis on responses of murine lungs to Pasteurella multocida infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, X.; Xia, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Zhang, R.; Fang, R.; Li, N.; et al. Slc6a13 deficiency attenuates Pasteurella multocida infection-induced inflammation via glycine-inflammasome signaling. J. Innate Immun. 2023, 15, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP: Short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Erreni, M.; Allavena, P.; Porta, C. Macrophage polarization in pathology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4111–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.D. Anatomy of a discovery: M1 and M2 macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, R.C.; Schroder, K. Inflammasome components as new therapeutic targets in inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 25, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, J.; Jiang, B.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Tong, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Major vault protein suppresses obesity and atherosclerosis through inhibiting IKK-NF-κB signaling mediated inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonina, I.S.; Zhong, Z.; Karin, M.; Beyaert, R. Limiting inflammation-the negative regulation of NF-κB and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettrick, A.F.; O’Neill, L.A. NLRP3 and IL-1β in macrophages as critical regulators of metabolic diseases. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15 (Suppl 3), 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, F.; Liu, B.; Wu, X.; Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Duan, J.; Ren, W. Interaction between intestinal mycobiota and microbiota shapes lung inflammation. iMeta 2024, 3, e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Li, N.; He, F.; Peng, Y. Pasteurella multocida activates Rassf1-Hippo-Yap pathway to induce pulmonary epithelial apoptosis. Vet. Res. 2024, 55, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhao, G.; Tang, T.; He, F.; Liu, X.; Li, N.; Peng, Y. Avian Pasteurella multocida induces chicken macrophage apoptosis by inhibiting the Zyxin-FAK-AKT-FoxO1/NF-κB axis. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Hu, P.; Ni, L.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Cui, Y.; Guo, M.; Wang, H.; Ran, L.; et al. Serine metabolism orchestrates macrophage polarization by regulating the IGF1-p38 axis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Gao, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yao, L.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S. Salvianolic acid B inhibits RAW264.7 cell polarization towards the M1 phenotype by inhibiting NF-κB and Akt/mTOR pathway activation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xu, X.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Hoque, M.; Li, G.; Lian, Q.; Long, K.; Zhou, T.; Piao, H.; et al. MDM2 induces pro-inflammatory and glycolytic responses in M1 macrophages by integrating iNOS-nitric oxide and HIF-1α pathways in mice. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.; Yao, L.; et al. The transcription factor KLF14 regulates macrophage glycolysis and immune function by inhibiting HK2 in sepsis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaete, P.V.; Nieves-Barreto, L.D.; Guatibonza-García, V.; Losada-Barragán, M.; Vargas-Sánchez, K.; Mendivil, C.O. Medium-chain fatty acids modify macrophage expression of metabolic and inflammatory genes in a PPAR β/δ-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Name | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Bases | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC Content (%) | Uniquely Mapped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control1 | 5,359,8470 | 52,766,552 | 7.91G | 97.2 | 92.73 | 51.78 | 45,933,660 (87.05%) |
| Control2 | 56,675,122 | 55,129,440 | 8.27G | 98 | 94.79 | 52.38 | 46,941,892 (85.15%) |
| Control3 | 58,821,956 | 56,695,884 | 8.5G | 98 | 94.62 | 52.18 | 48,879,328 (86.21%) |
| Control4 | 49,940,592 | 49,166,168 | 7.37G | 97.4 | 92.92 | 51.83 | 42,542,372 (86.53%) |
| Ser9 | 49,807,792 | 48,215,352 | 7.23G | 98 | 94.66 | 52.62 | 41,203,396 (85.46%) |
| Ser10 | 54,377,336 | 52,357,056 | 7.85G | 98 | 94.77 | 52.02 | 45,177,015 (86.29%) |
| Ser11 | 55,734,868 | 54,474,590 | 8.17G | 98.1 | 94.86 | 52.15 | 47,368,843 (86.96%) |
| Ser12 | 5,6845,112 | 55,463,248 | 8.32G | 98.1 | 94.78 | 52.23 | 47,843,443 (86.26%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, F.; Lang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Xiong, P.; Li, N.; Zhao, G.; Peng, Y. Exogenous L-Serine Alleviates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Inflammation by Reprogramming the Transcription and Metabolism of Macrophages. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030254
He F, Lang Z, Huang Y, Qiu Y, Xiong P, Li N, Zhao G, Peng Y. Exogenous L-Serine Alleviates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Inflammation by Reprogramming the Transcription and Metabolism of Macrophages. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(3):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030254
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Fang, Zhengchun Lang, Yanlan Huang, Yangyang Qiu, Pan Xiong, Nengzhang Li, Guangfu Zhao, and Yuanyi Peng. 2025. "Exogenous L-Serine Alleviates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Inflammation by Reprogramming the Transcription and Metabolism of Macrophages" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 3: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030254
APA StyleHe, F., Lang, Z., Huang, Y., Qiu, Y., Xiong, P., Li, N., Zhao, G., & Peng, Y. (2025). Exogenous L-Serine Alleviates Pasteurella multocida-Induced Inflammation by Reprogramming the Transcription and Metabolism of Macrophages. Veterinary Sciences, 12(3), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030254






