Cognitive Bias in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A Systematic Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
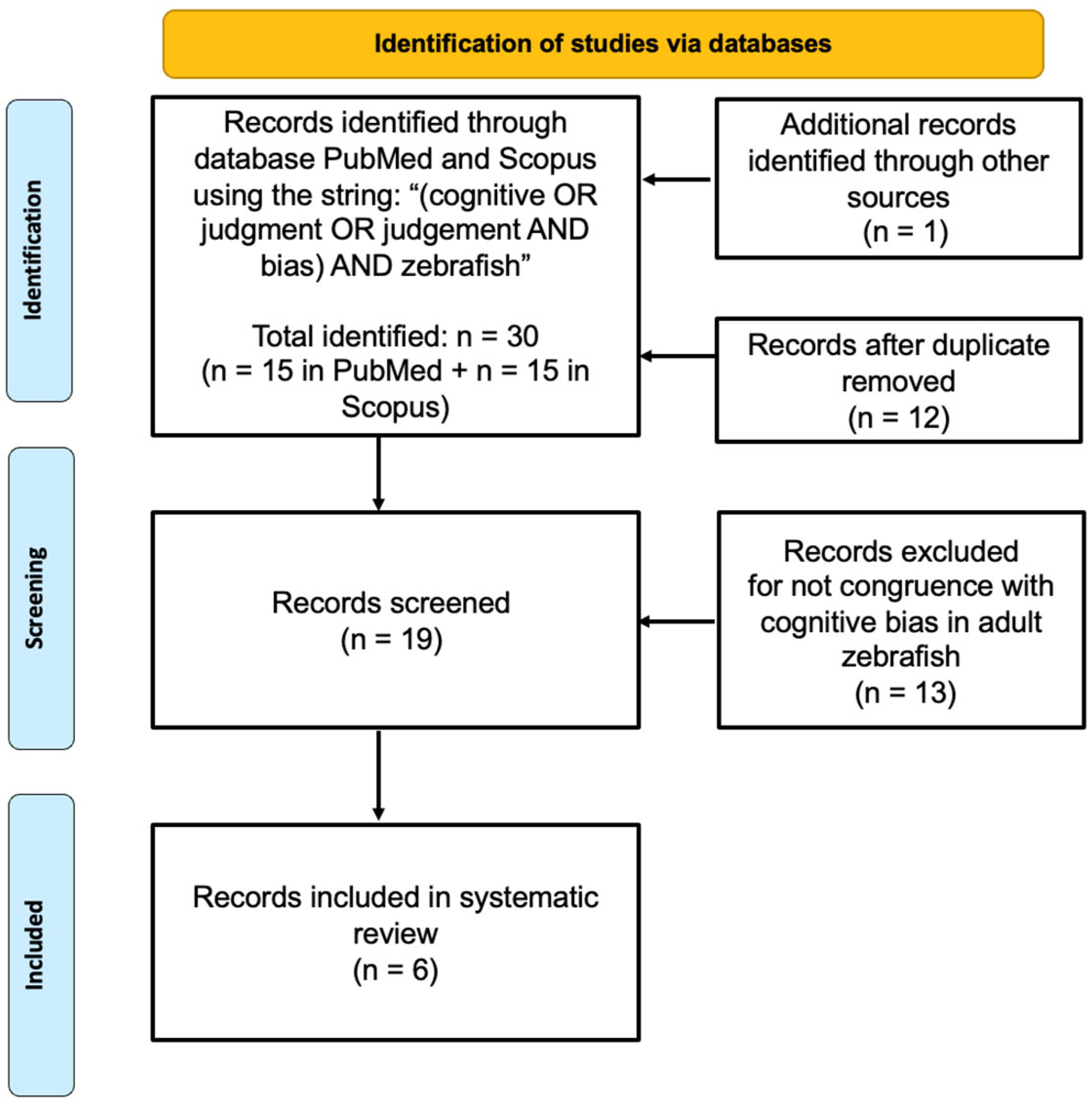
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
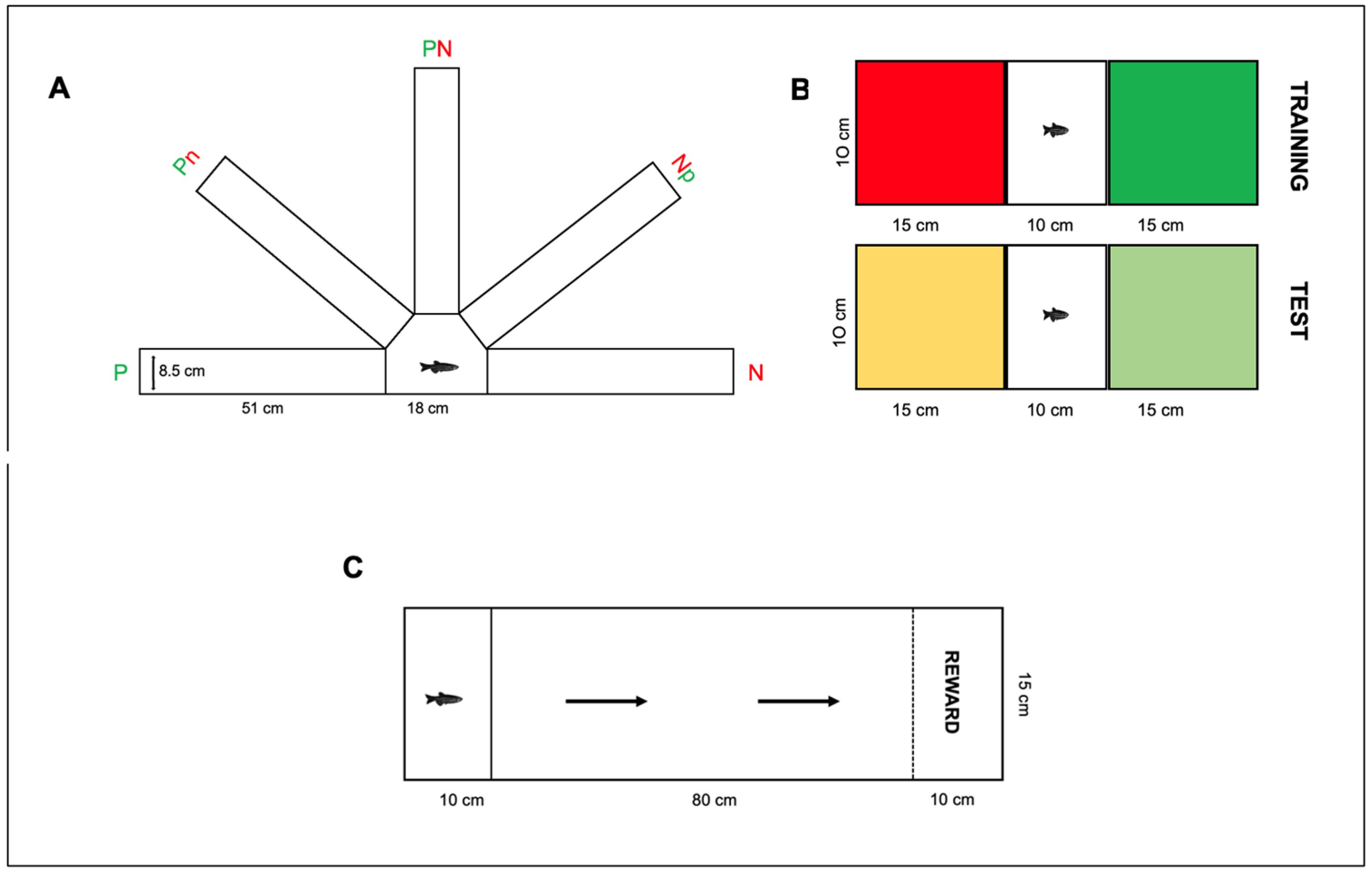
How to Test Cognitive Bias
4. Purpose of Using Cognitive Bias
4.1. Correlate Between the Affective State and the Life-History Strategies
4.2. Evaluation of the Relation Between the Environmental and the Affective State
4.3. Effects of Emotional State on Cognitive Abilities
4.4. Reporting Quality and Risk of Bias Assessment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.J.; Paull, G.C.; Tyler, C.R. Improving Zebrafish Laboratory Welfare and Scientific Research through Understanding Their Natural History. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 1038–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.H.; Reed, B.T.; Hawkins, P. Enrichment for Laboratory Zebrafish—A Review of the Evidence and the Challenges. Animals 2021, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrinalini, R.; Tamilanban, T.; Naveen Kumar, V.; Manasa, K. Zebrafish—The Neurobehavioural Model in Trend. Neuroscience 2023, 520, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzano, V.; Di Filippo, M.; Licitra, R.; Ogi, A.; Fronte, B.; Curadi, M.C.; Gazzano, A. Rearing in a Physically Enriched Environment Affects Shoaling and Stress Responses of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Exposed to Novel Conditions. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, H.S.; Carder, G.; Cornish, A.R. Searching for Animal Sentience: A Systematic Review of the Scientific Literature. Animals 2013, 3, 882–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendl, M.; Burman, O.H.P.; Parker, R.M.A.; Paul, E.S. Cognitive Bias as an Indicator of Animal Emotion and Welfare: Emerging Evidence and Underlying Mechanisms. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 118, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Désiré, L.; Boissy, A.; Veissier, I. Emotions in Farm Animals: A New Approach to Animal Welfare in Applied Ethology. Behav. Process. 2002, 60, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, J.P.; Meehan, C.L.; Mench, J.A. Stereotypies in Caged Parrots, Schizophrenia and Autism: Evidence for a Common Mechanism. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 145, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, E.S.; Harding, E.J.; Mendl, M. Measuring Emotional Processes in Animals: The Utility of a Cognitive Approach. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 469–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herry, C.; Bach, D.R.; Esposito, F.; Di Salle, F.; Perrig, W.J.; Scheffler, K.; Lüthi, A.; Seifritz, E. Processing of Temporal Unpredictability in Human and Animal Amygdala. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5958–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uccheddu, S.; Mariti, C.; Sannen, A.; Vervaecke, H.; Arnout, H.; Gutierrez Rufo, J.; Gazzano, A.; Haverbeke, A. Behavioral and Cortisol Responses of Shelter Dogs to a Cognitive Bias Test after Olfactory Enrichment with Essential Oils. Dog Behav. 2018, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecorps, B.; Weary, D.M.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Negative expectations and vulnerability to stressors in animals. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 130, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenhombre, J.; Daza-Cardona, E.A.; Mota-Rojas, D.; Domínguez-Oliva, A.; Rivera, A.; Medrano-Galarza, C.; De Tarso, P.; Cajiao-Pachón, M.N.; Vargas, F.; Pedraza-Toscano, A.; et al. Trait Sensitivity to Stress and Cognitive Bias Processes in Fish: A Brief Overview. Personal. Neurosci. 2024, 7, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorbjørnsen, S.H.; Moland, E.; Villegas-Ríos, D.; Bleeker, K.; Knutsen, H.; Olsen, E.M. Selection on Fish Personality Differs between a No-Take Marine Reserve and Fished Areas. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabegalov, K.N.; Kolesnikova, T.O.; Khatsko, S.L.; Volgin, A.D.; Yakovlev, O.A.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Friend, A.J.; Bao, W.; Alekseeva, P.A.; Lakstygal, A.M.; et al. Understanding Zebrafish Aggressive Behavior. Behav. Process. 2019, 158, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, S.; Gerlai, R. Individual Differences in Activity Levels in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 257, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, A.; Licitra, R.; Naef, V.; Marchese, M.; Fronte, B.; Gazzano, A.; Santorelli, F.M. Social Preference Tests in Zebrafish: A Systematic Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 590057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishfaq, M.; Nazir, M.S.; Qamar, M.A.J.; Usman, M. Cognitive Bias and the Extraversion Personality Shaping the Behavior of Investors. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 556506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loong, S.; Tan, T. Cognitive Bias as an Indicator of Emotional State and Welfare in Captive Zebrafish. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer, P.C. Optimistic and Realistic Perspectives on Cognitive Biases. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 12, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareklas, K.; Oliveira, R.F. Emotional Contagion and Prosocial Behaviour in Fish: An Evolutionary and Mechanistic Approach. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 163, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinello, C.; Yang, Y.; Macrì, S.; Porfiri, M. Zebrafish Adjust Their Behavior in Response to an Interactive Robotic Predator. Front. Robot. AI 2019, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.I.M.; Galhardo, L.; Noble, C.; Damsgård, B.; Spedicato, M.T.; Zupa, W.; Beauchaud, M.; Kulczykowska, E.; Massabuau, J.C.; Carter, T.; et al. Behavioural Indicators of Welfare in Farmed Fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; Korte, S.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Van Der Vegt, B.J.; Van Reenen, C.G.; Hopster, H.; De Jong, I.C.; Ruis, M.A.W.; Blokhuis, H.J. Coping Styles in Animals: Current Status in Behavior and Stress-Physiology. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1999, 23, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øverli, Ø.; Sørensen, C.; Pulman, K.G.T.; Pottinger, T.G.; Korzan, W.; Summers, C.H.; Nilsson, G.E. Evolutionary Background for Stress-Coping Styles: Relationships between Physiological, Behavioral, and Cognitive Traits in Non-Mammalian Vertebrates. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.R.; Wong, R.Y. Contextual Fear Learning and Memory Differ between Stress Coping Styles in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carere, C.; Locurto, C. Interaction between Animal Personality and Animal Cognition. Curr. Zool. 2011, 57, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Buwalda, B.; Van Reenen, K. Individual Variation in Coping with Stress:A Multidimensional Approach of Ultimate and Proximate Mechanisms. Brain Behav. Evol. 2007, 70, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, E.J.; Paul, E.S. Cognitive Bias And Affective State. Nature 2004, 427, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgunay, S.; Murray, J.K.; Rowe, E.; Gee, N.R.; Bartholomeus, M.; Casey, R. Cognitive and Composite Behavioural Welfare Assessments of Pet Cats between the Ages of 9–22 Months, Living in Single and Multi-Cat Households. Animals 2021, 11, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.A.T.; Guo, C.; Homberg, J.R. Cognitive Bias Under Adverse and Rewarding Conditions: A Systematic Review of Rodent Studies. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košťál, Ľ.; Skalná, Z.; Pichová, K. Use of Cognitive Bias as a Welfare Tool in Poultry. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, S63–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, R.; Mainau, E.; Rodriguez, P.; Llonch, P.; Dalmau, A.; Manteca, X.; Velarde, A. Cognitive Bias in Pigs: Individual Classification and Consistency over Time. J. Vet. Behav. 2015, 10, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagisz, M.; Zidar, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Neville, V.; Sorato, E.; Paul, E.S.; Bateson, M.; Mendl, M.; Løvlie, H. Optimism, Pessimism and Judgement Bias in Animals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabane, L.; Thomas, T.; Ye, C.; Paul, J. Posing the Research Question: Not so Simple. Can. J. Anesth. 2009, 56, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; De Vries, R.B.M.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s Risk of Bias Tool for Animal Studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espigares, F.; Martins, R.R.; Oliveira, R.F. A Behavioural Assay to Investigate Judgment Bias in Zebrafish. Bio-Protocol 2022, 12, e4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espigares, F.; Alvarado, M.V.; Faísca, P.; Abad-Tortosa, D.; Oliveira, R.F. Pessimistic Cognitive Bias Is Associated with Enhanced Reproductive Investment in Female Zebrafish. Biol. Lett. 2022, 18, 20220232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espigares, F.; Abad-Tortosa, D.; Varela, S.A.M.; Ferreira, M.G.; Oliveira, R.F. Short Telomeres Drive Pessimistic Judgement Bias in Zebrafish. Biol. Lett. 2021, 17, 20200745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtas, K.; Przemyslaw, P.C.; Roman, K. Cognitive Bias Test as a Tool for Accessing Fish Welfare. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenhombre, J.; Daza-Cardona, E.A.; Sousa, P.; Gouveia, A.; Cajiao-Pachón, M.N. Structural Environmental Enrichment and the Way It Is Offered Influence Cognitive Judgement Bias and Anxiety-like Behaviours in Zebrafish. Anim. Cogn. 2023, 26, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.L.T.; Handasyde, K.A.; Rault, J.L.; Mendl, M. Insensitivity to Reward Shifts in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Implications for Assessing Affective States. Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, P.; Lau, B.; Guo, S. Conditioned Place Preference Behavior in Zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chen, B. Bin An Evolutionary Life History Approach to Understanding Mental Health. Gen. Psychiatry 2020, 33, e100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.J.; Lukaszewski, A.W.; Grant, D.M.M.; Sng, O. Human Life History Strategies: Calibrated to External or Internal Cues? Evol. Psychol. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusi-Heikkilä, S.; Salonen, J.K.; Karjalainen, J.S.; Väisänen, A.; Hippeläinen, J.; Hämärvuo, T.; Kuparinen, A. Fish with Slow Life-History Cope Better with Chronic Manganese Exposure than Fish with Fast Life-History. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz Koç, N.; Aytekin, Y.; Yüce, R. Ovary maturation stages and histological investigation of ovary of the Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2008, 51, 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Greiveldinger, L.; Veissier, I.; Boissy, A. Behavioural and Physiological Responses of Lambs to Controllable vs. Uncontrollable Aversive Events. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piato, A.L.; Capiotti, K.M.; Tamborski, A.R.; Oses, J.P.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Bogo, M.R.; Lara, D.R.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Unpredictable Chronic Stress Model in Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Behavioral and Physiological Responses. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, B.M.; van den Bos, R.; Pijlman, F.T.A. A Concept of Welfare Based on Reward Evaluating Mechanisms in the Brain: Anticipatory Behaviour as an Indicator for the State of Reward Systems. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2001, 72, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino, A.I.; Oliveira, G.A.; Oliveira, R.F. Linking Appraisal to Behavioral Flexibility in Animals: Implications for Stress Research. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moors, A.; Ellsworth, P.C.; Scherer, K.R.; Frijda, N.H. Appraisal Theories of Emotion: State of the Art and Future Development. Emot. Rev. 2013, 5, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellaneda, M.; Serafini, M.; Kamenetzky, G. Consummatory Successive Positive Contrast with Aversive Solutions in Infant Rats: Replication and Generalization to a Higher Concentration of a Bitter Solution. Behav. Process. 2022, 202, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, S.L.H.; Riemer, S.; Thompson, H.; Burman, O.H.P. Assessing the External Validity of Successive Negative Contrast-Implications for Animal Welfare. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2019, 23, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzik, V.; Cavalli, C.; Iglesias, M.; Bentosela, M. Do Dogs Experience Frustration? New Contributions on Successive Negative Contrast in Domestic Dogs (Canis familiaris). Behav. Process. 2019, 162, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.O.; Gaviria, J.; Haigh, A.; Millington, M.E.; Brown, V.J.; Combe, F.J.; Brennan, C.H. Discrimination Reversal and Attentional Sets in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 232, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, S.; Froc, C.; Pontiggia, A.; Yamamoto, K. Existence of Working Memory in Teleosts: Establishment of the Delayed Matching-to-Sample Task in Adult Zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 370, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baciadonna, L.; McElligott, A.G. The Use of Judgement Bias to Assess Welfare in Farm Livestock. Anim. Welf. 2015, 24, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N | Title | Authors | Bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cognitive bias test as a tool for assessing fish welfare. | Wojtas et al., 2015 | [41] |
| 2 | Insensitivity to reward shifts in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and implications for assessing affective states. | Tan et al., 2020 | [43] |
| 3 | Short telomeres drive pessimistic judgement bias in zebrafish. | Espigares et al., 2021 | [40] |
| 4 | A behavioral assay to investigate judgment bias in zebrafish. | Espigares et al., 2022a | [38] |
| 5 | Pessimistic cognitive bias is associated with enhanced reproductive investment in female zebrafish. | Espigares et al., 2022b | [39] |
| 6 | Structural environmental enrichment and the way it is offered influence cognitive judgement bias and anxiety-like behaviors in zebrafish | Buenhombre et al., 2023 | [42] |
| Authors | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wojtas et al., 2015 [41] | N | NC | N | NC | N | NC | NC | NC | N | N |
| Tan et al., 2020 [43] | NC | N | N | NC | N | NC | NC | Y | Y | Y |
| Espigares et al., 2021 [40] | NC | Y | NC | NC | N | NC | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Espigares et al., 2022a [38] | N | NC | Y | NC | Y | NC | NC | NC | Y | N |
| Espigares et al., 2022b [39] | NC | Y | N | NC | N | Y | NC | Y | Y | Y |
| Buenhombre et al., 2023 [42] | NC | Y | N | NC | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gazzano, V.; Ogi, A.; Cecchi, F.; Curadi, M.C.; Marchese, M.; Gazzano, A. Cognitive Bias in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A Systematic Review. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12010071
Gazzano V, Ogi A, Cecchi F, Curadi MC, Marchese M, Gazzano A. Cognitive Bias in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A Systematic Review. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleGazzano, Valentina, Asahi Ogi, Francesca Cecchi, Maria Claudia Curadi, Maria Marchese, and Angelo Gazzano. 2025. "Cognitive Bias in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A Systematic Review" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12010071
APA StyleGazzano, V., Ogi, A., Cecchi, F., Curadi, M. C., Marchese, M., & Gazzano, A. (2025). Cognitive Bias in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A Systematic Review. Veterinary Sciences, 12(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12010071






