Transcriptome RNA Sequencing Reveals That Circular RNAs Are Abundantly Expressed in Embryonic Breast Muscle of Duck
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples for Circular RNA Sequencing
2.2. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Annotation of Duck circRNAs and Differential Expression Analysis between E13 and E19
2.4. Enrichment Analysis of the Differentially Expressed circRNAs
2.5. cDNA Synthesis and qRT-PCR
2.6. Validation of circRNAs
2.7. Overexpression Plasmid Construction and siRNA Synthesis
2.8. Cell Isolation, Culture, and Electroporation
2.9. Flow Cytometry of Cell Cycle Analysis
2.10. Cell-Counting Assay
3. Results
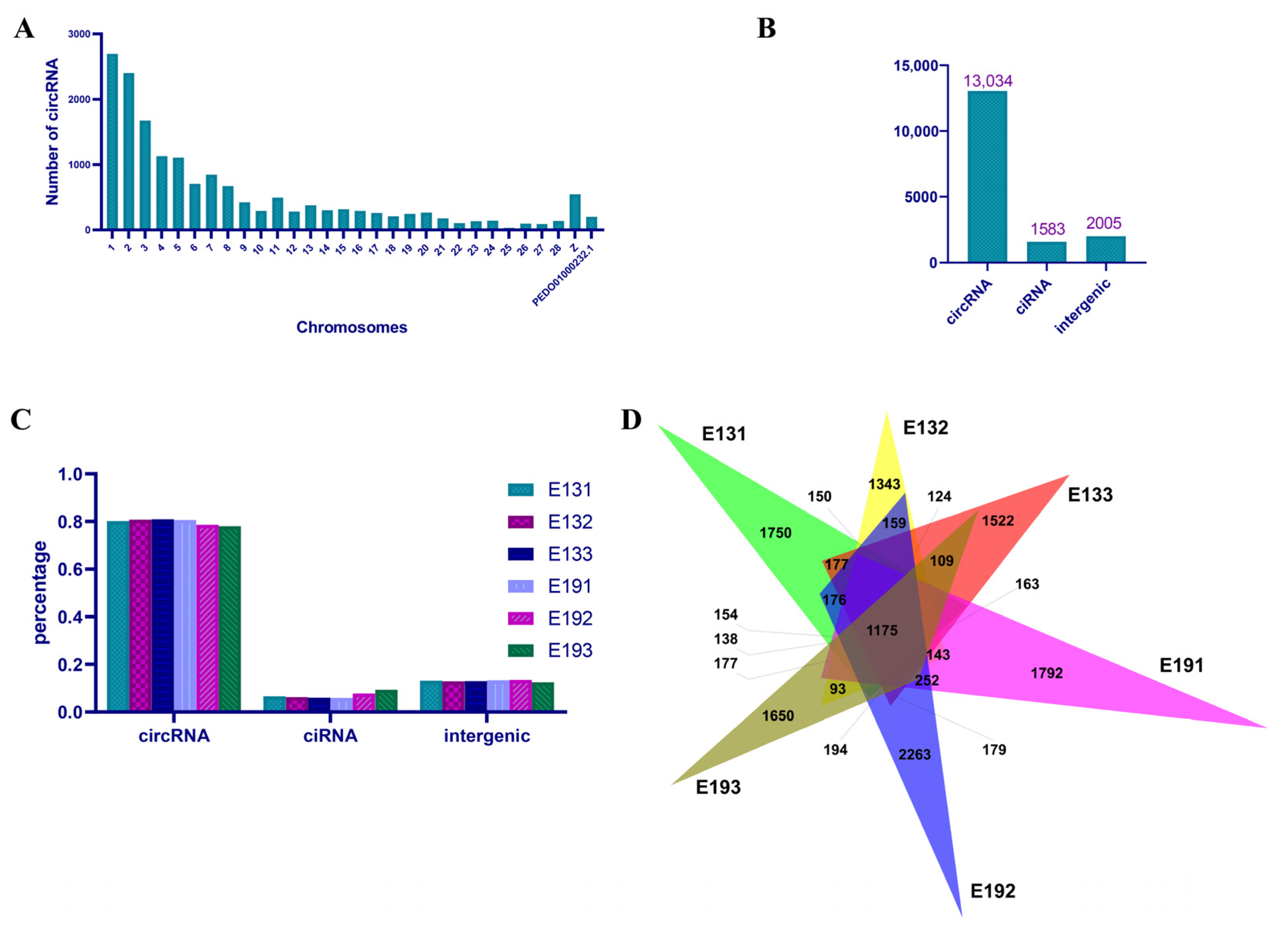
3.1. Overview of RNA Sequencing Data and Identification of Duck Circular RNA
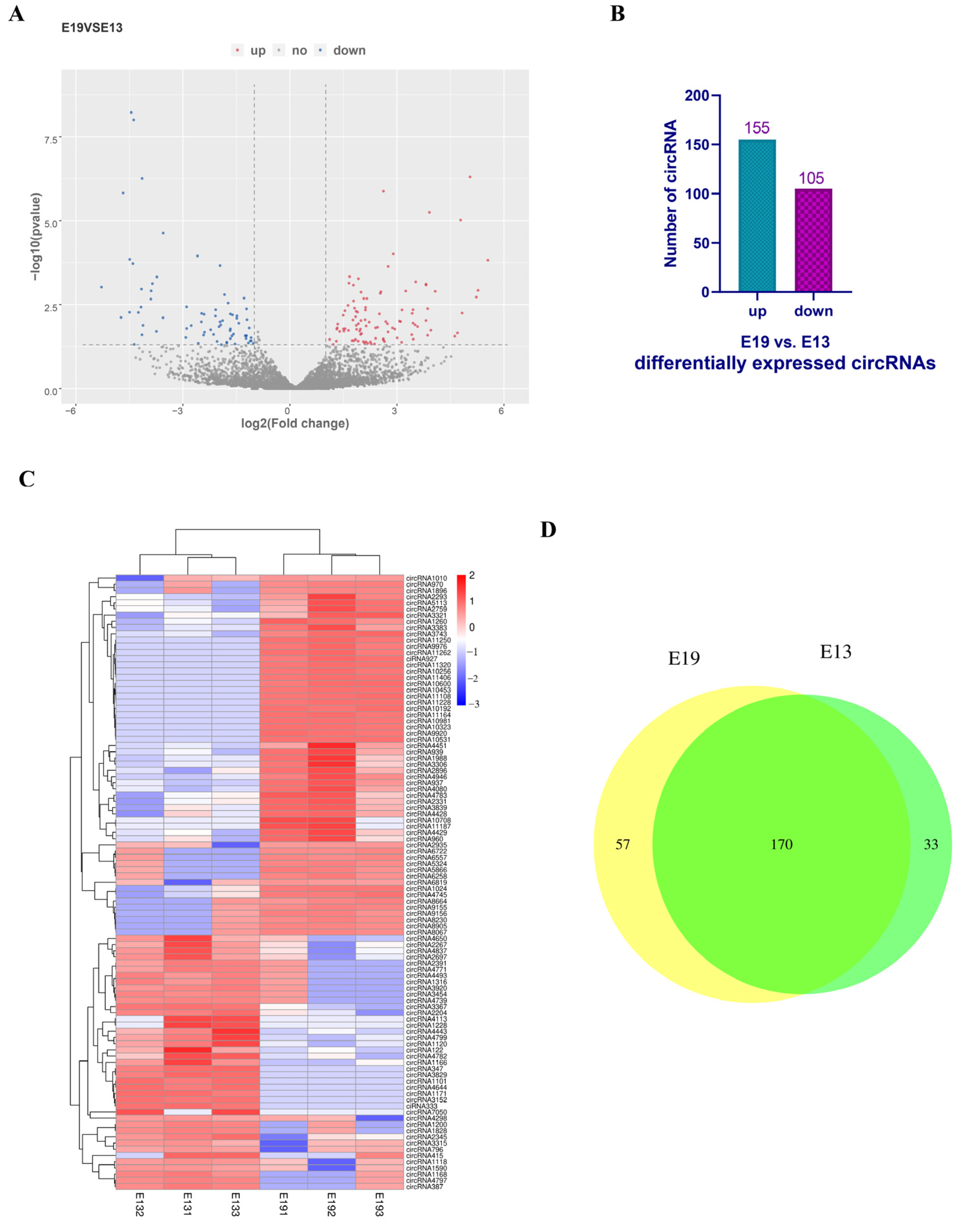
3.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs
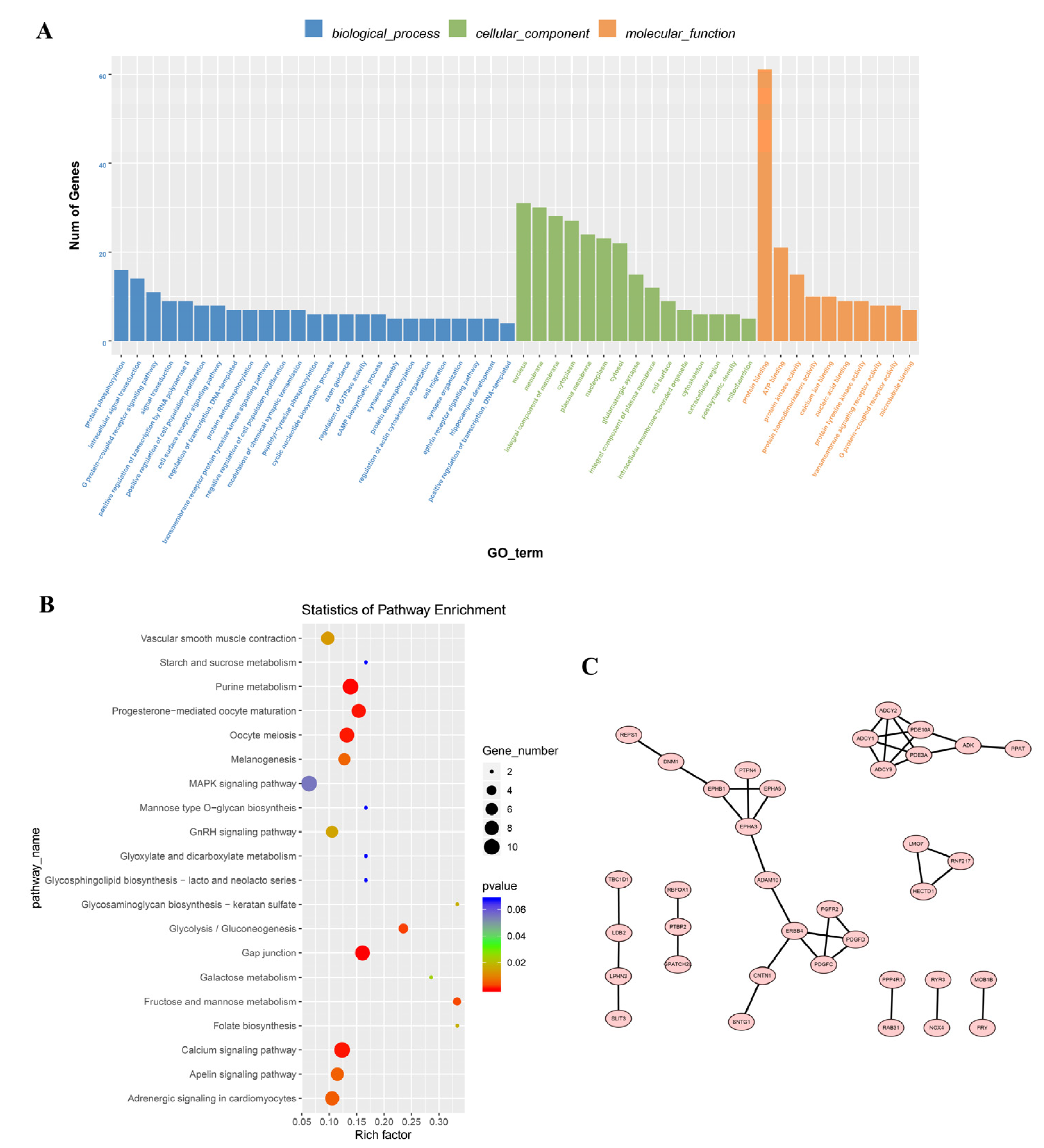
3.3. Enrichment Analysis of the Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs
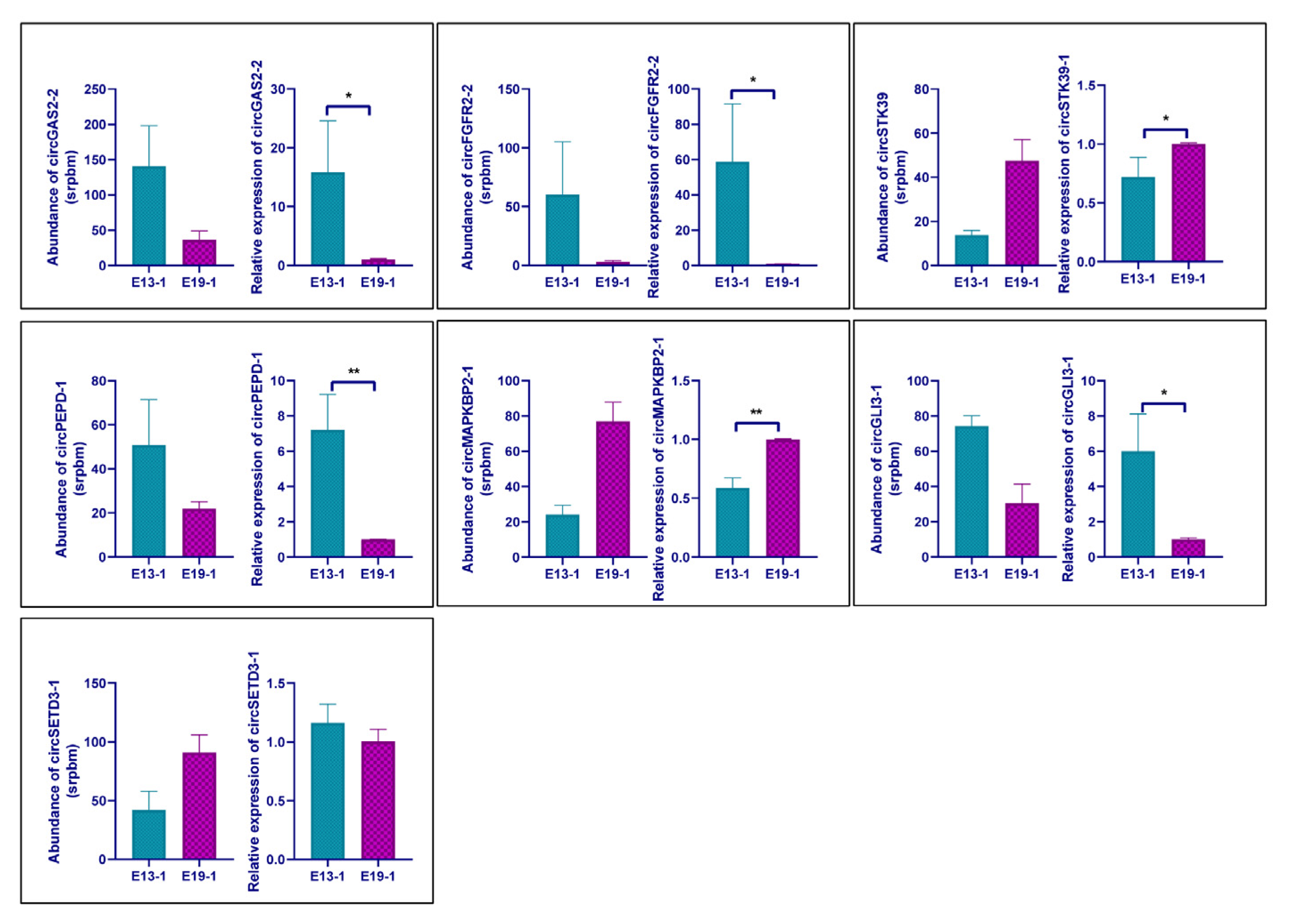
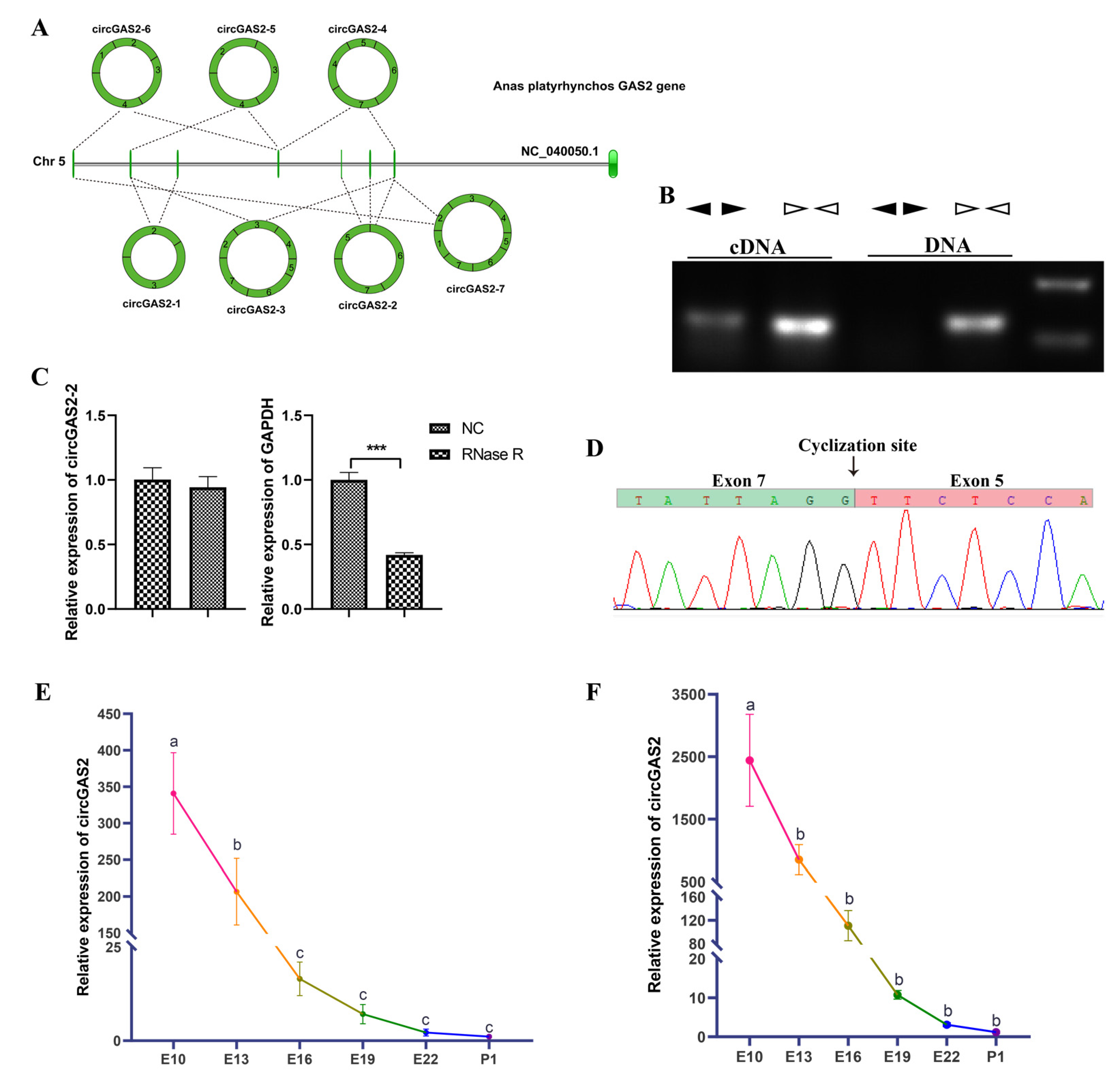
3.4. Verification of the Differential Expression Circular RNAs
3.5. Experimental Validation and Spatiotemporal Expression of circGAS2-2
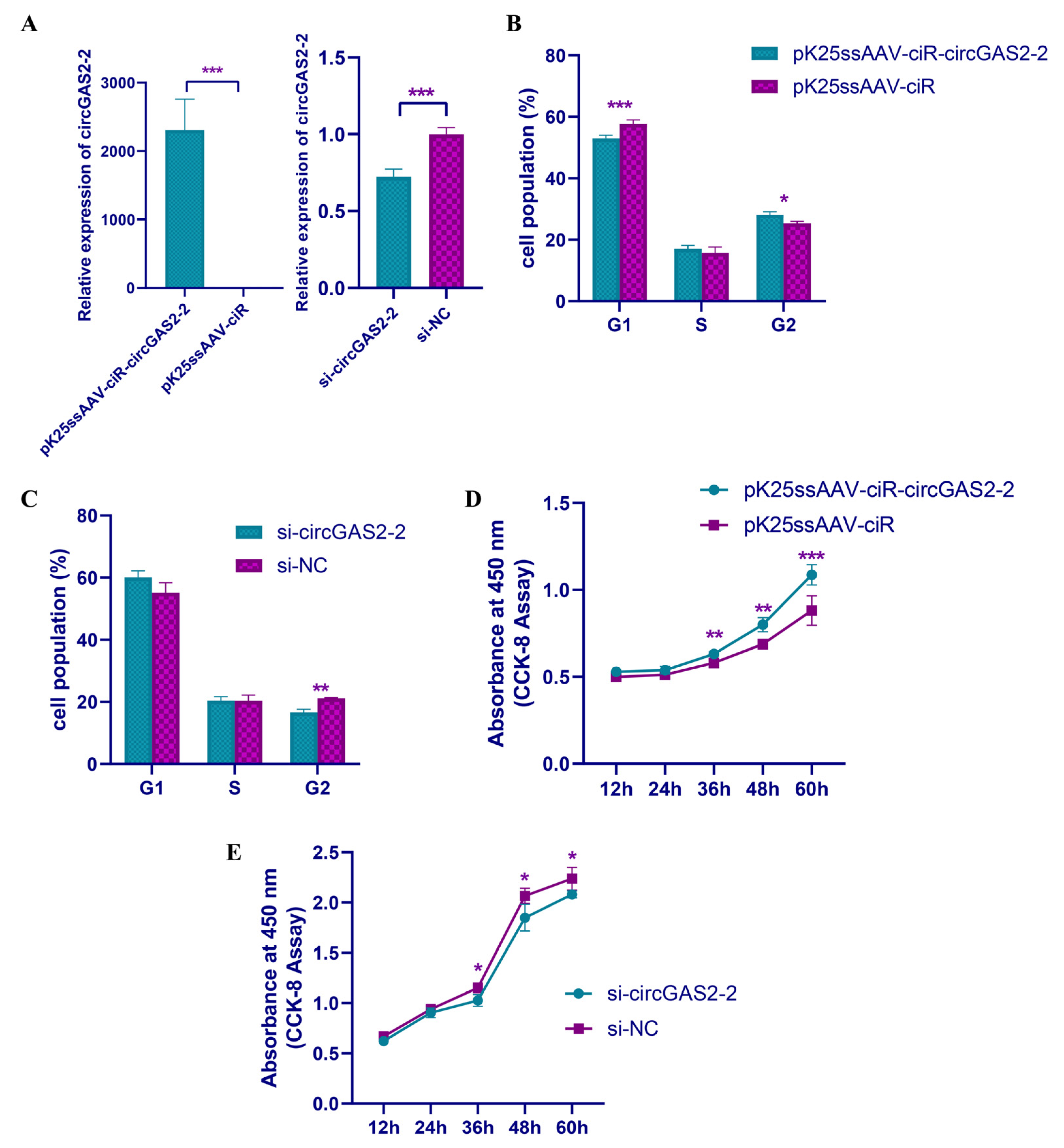
3.6. circGAS2-2 Promotes the Proliferation of Duck Breast Primary Myoblasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scanes, C.G.; Harvey, S.; Marsh, J.A.; King, D.B. Hormones and Growth in Poultry. Poult. Sci. 1984, 63, 2062–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Nie, Q. A Novel Circular RNA Generated by FGFR2 Gene Promotes Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation by Sponging MiR-133a-5p and MiR-29b-1-5p. Cells 2018, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Gautel, M. Transcriptional Mechanisms Regulating Skeletal Muscle Differentiation, Growth and Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abmayr, S.M.; Pavlath, G.K. Myoblast Fusion: Lessons from Flies and Mice. Development 2012, 139, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M. Skeletal Muscle Formation in Vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wu, H.; Ye, Y.; Li, Z.; Hao, S.; Kong, L.; Zheng, X.; Lin, S.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, X. The Transient Expression of MiR-203 and Its Inhibiting Effects on Skeletal Muscle Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cai, B.; Abdalla, B.A.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, M.; Han, P.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, X. LncIRS1 Controls Muscle Atrophy via Sponging MiR-15 Family to Activate IGF1-PI3K/AKT Pathway. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Ren, X.; Cheng, T.; Lu, S.; Lawal, R.A.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hanotte, O. C-Myc Inhibits Myoblast Differentiation and Promotes Myoblast Proliferation and Muscle Fibre Hypertrophy by Regulating the Expression of Its Target Genes, MiRNAs and LincRNAs. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs Are a Large Class of Animal RNAs with Regulatory Potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yuan, Y.; He, Z.; Li, D.; Zeng, B.; Ni, Q.; Yang, M.; Yang, D. The Regulatory Functions of Circular RNAs in Digestive System Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ding, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Han, Q.; Li, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Circular RNA Regulation of Myogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, E.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, T.; Pan, M.; Bai, Y.; Ge, Q. Transcriptomic Profiling of Circular RNA in Different Brain Regions of Parkinson’s Disease in a Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legnini, I.; Di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M.; et al. Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA That Can Be Translated and Functions in Myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamudurti, N.R.; Bartok, O.; Jens, M.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Stottmeister, C.; Ruhe, L.; Hanan, M.; Wyler, E.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Ramberger, E.; et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 9–21.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-L. The Expanding Regulatory Mechanisms and Cellular Functions of Circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-Intron Circular RNAs Regulate Transcription in the Nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Han, F. Back-Spliced RNA from Retrotransposon Binds to Centromere and Regulates Centromeric Chromatin Loops in Maize. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A CeRNA Hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a Hidden RNA Language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Liu, E.; Yang, Z.; Dhaliwal, P.; Yang, B.B. Foxo3 Circular RNA Retards Cell Cycle Progression via Forming Ternary Complexes with P21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2846–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Du, W.W.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Awan, F.M.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Yee, A.; et al. A Circular RNA Binds To and Activates AKT Phosphorylation and Nuclear Localization Reducing Apoptosis and Enhancing Cardiac Repair. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3842–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.-Q. Structure, Regulation, and Function of Linear and Circular Long Non-Coding RNAs. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs Are Abundant, Conserved, and Associated with ALU Repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dori, M.; Bicciato, S. Integration of Bioinformatic Predictions and Experimental Data to Identify CircRNA-MiRNA Associations. Genes 2019, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, Z.; Cao, X.; He, H.; Han, S.; Chen, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Circular RNA Profiling Identified an Abundant Circular RNA CircTMTC1 That Inhibits Chicken Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation by Sponging MiR-128-3p. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2265–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, H.; Li, R.; Wu, W.; Chao, Z.; Li, C.; Xia, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. Assessment of Myoblast Circular RNA Dynamics and Its Correlation with MiRNA during Myogenic Differentiation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 99, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Yang, Y.; Niu, G.; Tang, Z.; Li, K. Genome-Wide Profiling of Sus Scrofa Circular RNAs across Nine Organs and Three Developmental Stages. DNA Res. 2017, 24, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Jia, X.; Li, Z.; Luo, W.; Abdalla, B.A.; Jebessa, E.; Nie, Q.; et al. Circular RNAs Are Abundant and Dynamically Expressed during Embryonic Muscle Development in Chickens. DNA Res. 2017, 25, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C. A Zfp609 Circular RNA Regulates Myoblast Differentiation by Sponging MiR-194-5p. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.H.; Xu, T.S.; Huang, W.; Xie, M.; Shi, W.B.; Sun, S.D.; Hou, S.S. Developmental Characteristics of Pectoralis Muscle in Pekin Duck Embryos. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 6733–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, T.; Zhou, M.; Hu, X.; Mao, H.; Liu, S. Profiling Analysis of N6-Methyladenosine MRNA Methylation Reveals Differential M6A Patterns during the Embryonic Skeletal Muscle Development of Ducks. Animals 2022, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Song, C.; Ji, G.; Liu, H.; Xu, W.; Ding, J. A New Primer for Sex Identification of Ducks and a Minimally Invasive Technique for Sampling of Allantoic Fluid to Detect Sex during Bird Embryo Development. Sex. Dev. 2015, 9, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kechin, A.; Boyarskikh, U.; Kel, A.; Filipenko, M. CutPrimers: A New Tool for Accurate Cutting of Primers from Reads of Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2017, 24, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate Alignment of Transcriptomes in the Presence of Insertions, Deletions and Gene Fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat-Fusion: An Algorithm for Discovery of Novel Fusion Transcripts. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-O.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.-L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Diverse Alternative Back-Splicing and Alternative Splicing Landscape of Circular RNAs. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F. CIRI: An Efficient and Unbiased Algorithm for de Novo Circular RNA Identification. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-O.; Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Complementary Sequence-Mediated Exon Circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and Integrative Analysis of Large Gene Lists Using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING Database in 2021: Customizable Protein–Protein Networks, and Functional Characterization of User-Uploaded Gene/Measurement Sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs Are the Predominant Transcript Isoform from Hundreds of Human Genes in Diverse Cell Types. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Agarwal, V.; Guo, H.; Bartel, D.P. Expanded Identification and Characterization of Mammalian Circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Yao, Y.; You, S.; Wang, D.; Quan, R.; Hou, X.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Circular RNAs in Prenatal and Postnatal Pituitary Glands of Sheep. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liu, J.; Fang, X.; Chen, H. Circular RNA of Cattle Casein Genes Are Highly Expressed in Bovine Mammary Gland. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4750–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Li, T.; Zhang, G.; Wu, P.; Chen, F.; Lou, Q.; Chen, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J. Dynamic Expression and Functional Analysis of CircRNA in Granulosa Cells during Follicular Development in Chicken. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Pi, J.; Zhang, H.; Pan, A.; Pu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Shen, J.; Du, J. The Circular RNA Aplacirc_13267 Upregulates Duck Granulosa Cell Apoptosis by the Apla-MiR-1-13/THBS1 Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5750–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi Tahrir, F.; Gupta, M.; Myers, V.; Gordon, J.; Cheung, J.Y.; Feldman, A.M.; Khalili, K. Role of Bcl2-Associated Athanogene 3 in Turnover of Gap Junction Protein, Connexin 43, in Neonatal Cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, T.B.; Egli, M. Calcium’s Role in Mechanotransduction during Muscle Development. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gu, L.; Schachtschneider, K.M.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Xie, M.; Hou, S. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Breast Muscle and Skin Fat of Postnatal Pekin Duck. PLoS One 2014, 9, e107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, P.; Reverter, A.; Fortes, M.R.S.; Weikard, R.; Suhre, K.; Hammon, H.; Albrecht, E.; Kuehn, C. A Systems Biology Approach Using Metabolomic Data Reveals Genes and Pathways Interacting to Modulate Divergent Growth in Cattle. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-J.; Li, J.-H.; Chen, H.-F.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Liu, S.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Zheng, L.-L.; et al. Inhibition of the JNK/MAPK Signaling Pathway by Myogenesis-Associated MiRNAs Is Required for Skeletal Muscle Development. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, H.; Dhindsa, S.; Batra, M.; Green, K.; Abuaysheh, S.; Kuhadiya, N.D.; Makdissi, A.; Chaudhuri, A.; Dandona, P. Effect of Testosterone on FGF2, MRF4, and Myostatin in Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: Relevance to Muscle Growth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, X. Circular RNA CircSVIL Promotes Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation by Sponging MiR-203 in Chicken. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Hao, D.; Dong, D.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Plath, M.; Lei, C.; Lin, F.; et al. Circular RNA Profiling Reveals an Abundant CircLMO7 That Regulates Myoblasts Differentiation and Survival by Sponging MiR-378a-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Cui, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, X. Growth Arrest–Specific 2 Protein Family: Structure and Function. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Tian, H.; Hai, Y. GAS2 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion and Suppresses Apoptosis in Pediatric T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Activates Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.-X.; Cheng, A.S.L.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Yang, D.-Y.; Seto, W.-K. Growth Arrest-Specific Gene 2 Suppresses Hepatocarcinogenesis by Intervention of Cell Cycle and P53-Dependent Apoptosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4715–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgorbissa, A.; Benetti, R.; Marzinotto, S.; Schneider, C.; Brancolini, C. Caspase-3 and Caspase-7 but Not Caspase-6 Cleave Gas2 in Vitro: Implications for Microfilament Reorganization during Apoptosis. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 4475–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Mao, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, B. Transcriptome RNA Sequencing Reveals That Circular RNAs Are Abundantly Expressed in Embryonic Breast Muscle of Duck. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020075
Liu J, Liu S, Zhang W, Hu X, Mao H, Liu S, Chen B. Transcriptome RNA Sequencing Reveals That Circular RNAs Are Abundantly Expressed in Embryonic Breast Muscle of Duck. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(2):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020075
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jing, Shuibing Liu, Wentao Zhang, Xiaolong Hu, Huirong Mao, Sanfeng Liu, and Biao Chen. 2023. "Transcriptome RNA Sequencing Reveals That Circular RNAs Are Abundantly Expressed in Embryonic Breast Muscle of Duck" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 2: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020075
APA StyleLiu, J., Liu, S., Zhang, W., Hu, X., Mao, H., Liu, S., & Chen, B. (2023). Transcriptome RNA Sequencing Reveals That Circular RNAs Are Abundantly Expressed in Embryonic Breast Muscle of Duck. Veterinary Sciences, 10(2), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020075





