Detection of Endoparasites in Non-Native Raccoons from Central Italy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Endoparasites Detection
3.2. B. procyonis Identification
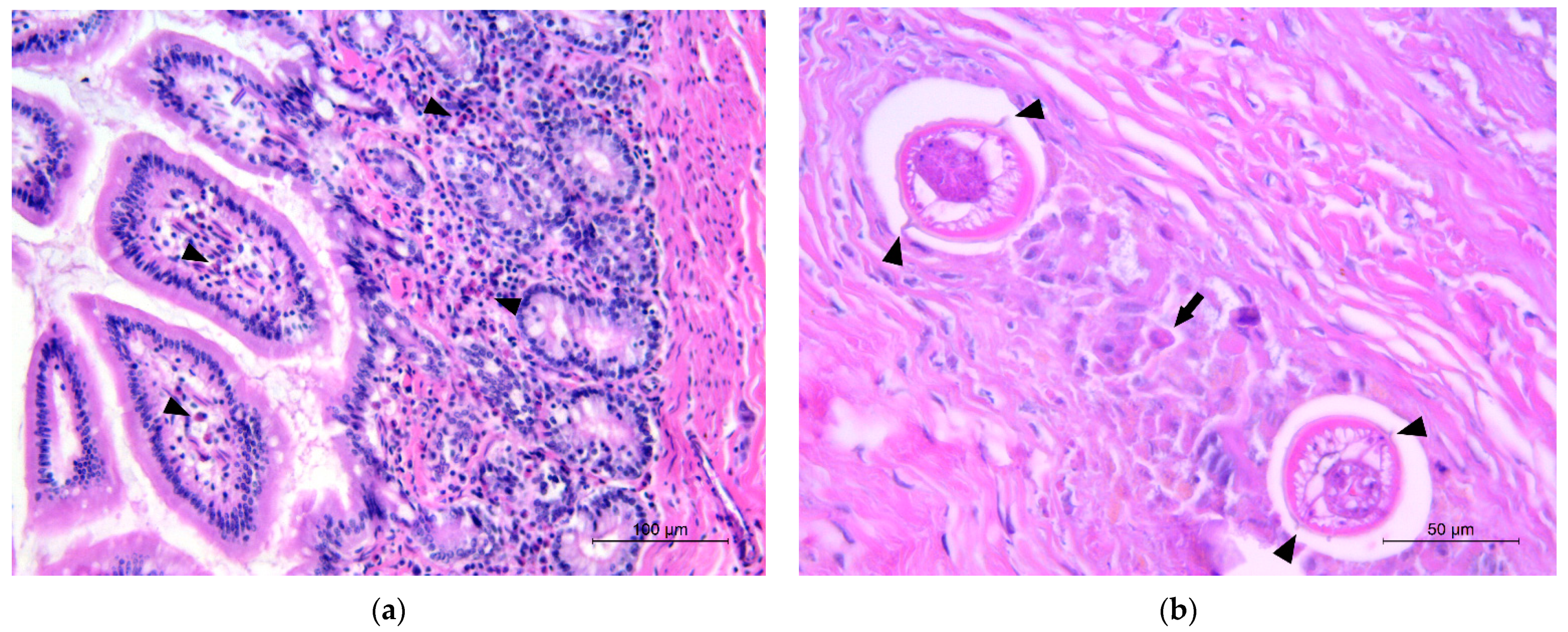
3.3. Pathology and Histopathology
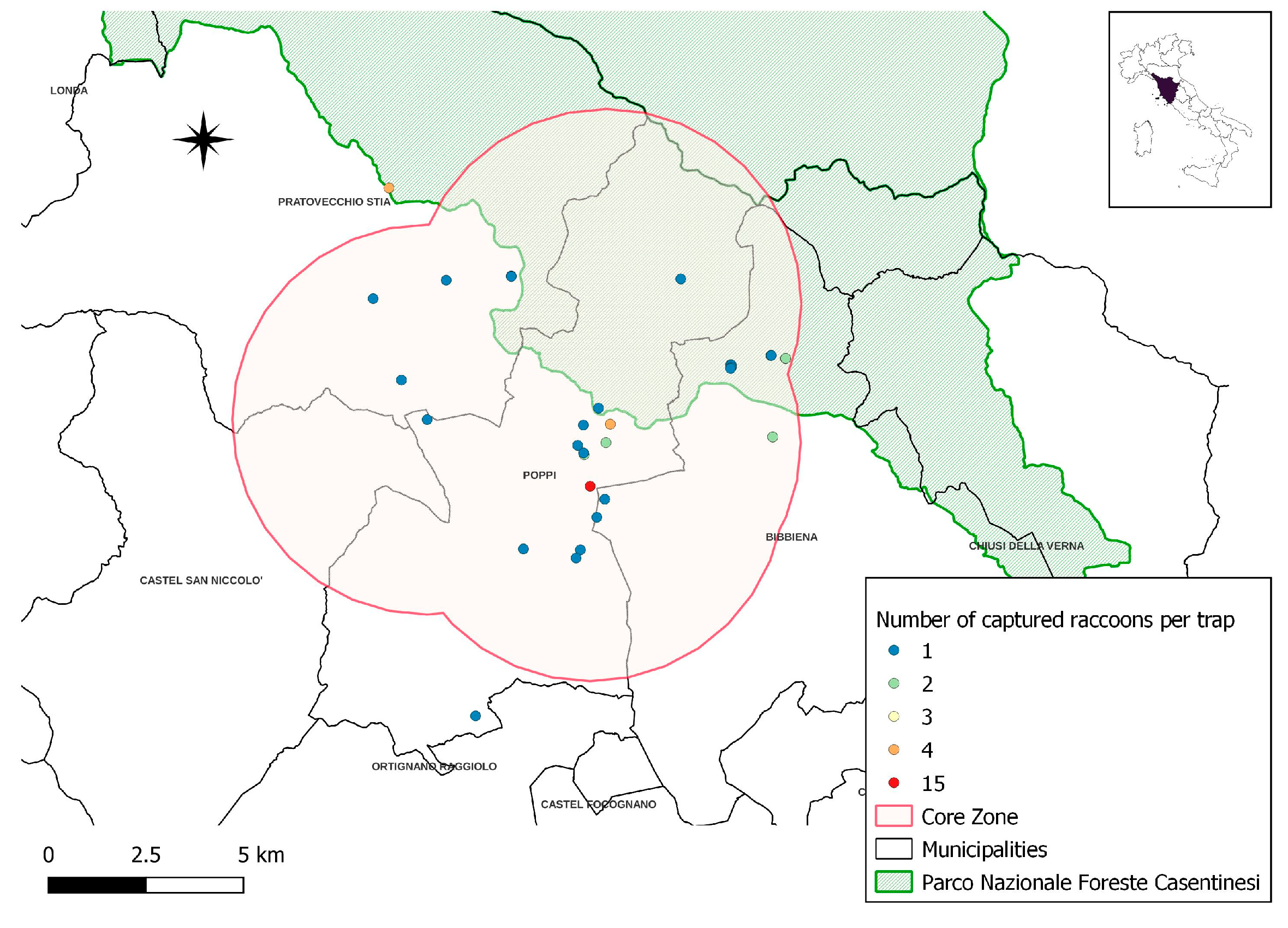
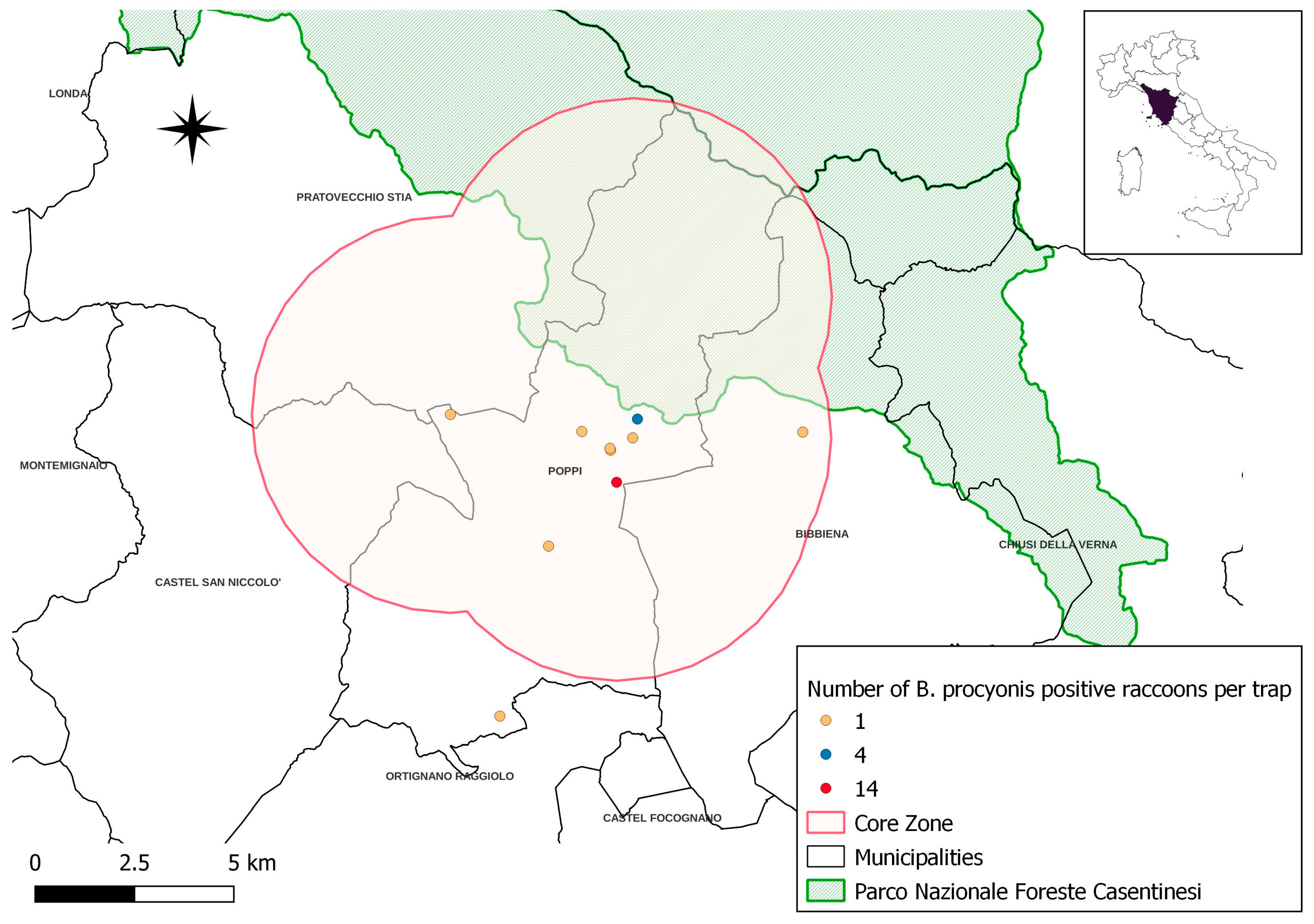
3.4. Spatial Distribution of B. procyonis Positive Raccoons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gehrt, S.D.; Clark, W.R. Raccoons, Coyotes, and Reflections on the Mesopredator Release Hypothesis. Wildl. Soc. Bull. (1973–2006) 2003, 31, 836–842. [Google Scholar]
- Kazacos, K.R. Baylisascaris procyonis and Related Species; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780470377000. [Google Scholar]
- Romeo, C.; Cafiso, A.; Fesce, E.; Martínez-Rondán, F.J.; Panzeri, M.; Martinoli, A.; Cappai, N.; Defilippis, G.; Ferrari, N. Lost and Found: Helminths Infecting Invasive Raccoons Introduced to Italy. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 83, 2020–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consiglio dei Ministri of the Italian Republic. Decreto Legislativo 15 Dicembre 2017, n. 230. Available online: https://www.normattiva.it/uri-res/N2Ls?urn:nir:stato:decreto.legislativo:2017-12-15;230 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Mori, E.; Mazza, G.; Menchetti, M.; Panzeri, M.; Gager, Y.; Bertolino, S.; Di Febbraro, M. The Masked Invader Strikes Again: The Conquest of Italy by the Northern Raccoon. Hystrix 2015, 26, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff-Teixeira, C.; Morassutti, A.L.; Kazacos, K.R. Update on Baylisascariasis, a Highly Pathogenic Zoonotic Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvillo, F.; Ash, L.R.; Berlin, O.G.W.; Yatabe, J.; Degiorgio, C.; Morse, S.A. Baylisascaris procyonis: An Emerging Helminthic Zoonosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabi, M.N.S.; Chriél, M.; Hansen, M.S.; Enemark, H.L. Baylisascaris procyonis in Wild Raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Denmark. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2015, 1–2, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duscher, G.G.; Frantz, A.C.; Kuebber-Heiss, A.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Heddergott, M. A Potential Zoonotic Threat: First Detection of Baylisascaris procyonis in a Wild Raccoon from Austria. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 3034–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamon, J.; Kochanowski, M.; Cencek, T.; Bartoszewicz, M.; Kusyk, P. Gastrointestinal Helminths of Raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Western Poland (Lubuskie Province)-with Particular Regard to Baylisascaris procyonis. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2014, 58, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentería-Solís, Z.; Birka, S.; Schmäschke, R.; Król, N.; Obiegala, A. First Detection of Baylisascaris procyonis in Wild Raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Leipzig, Saxony, Eastern Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3289–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, A.; Brocherel, G.; Donnini, C.; Fichi, G.; Mariacher, A.; Diaconu, E.L.; Carfora, V.; Battisti, A.; Cappai, N.; Mattioli, L.; et al. First Report of the Zoonotic Nematode Baylisascaris procyonis in Non-Native Raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Italy. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulska, A.; Skopek, R.; Kornacka, A.; Popiołek, M.; Piróg, A.; Laskowski, Z.; Moskwa, B. First Detection of Trichinella pseudospiralis Infection in Raccoon (Procyon lotor) in Central Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 254, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kanai, Y.; Ono, Y.; Matoba, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Okamoto, M.; Taniyama, H.; Yagi, K.; Oku, Y.; Katakura, K.; et al. Epidemiology, Histpathology, and Muscle Distribution of Trichinella T9 in Feral Raccoons (Procyon lotor) and Wildlife of Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piróg, A.; Kusmierek, N.; Popiolek, M. The Occurrence of Avian Acanthocephalan Polymorphus Minutus (Goeze, 1782) in Raccoons (Procyon lotor L.) Introduced to Europe. Ann. Parasitol. 2018, 64, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.J.; Conboy, G.A.; Stromberg, B.E.; Hayden, D.W. Pulmonary Trematodosis (Pharyngostomoides sp.) in a Juvenile Raccoon (Procyon lotor). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, E.W.; Beverley-Burton, M. The Taxonomy of Capillaria spp. (Nematoda: Trichuroidea) in Carnivorous Mammals from Ontario, Canada. Syst. Parasitol. 1980, 1, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.E. Indirect Immunofluorescent Detection of Oocysts of Cryptosporidium Parvum in the Feces of Naturally Infected Raccoons (Procyon lotor). Allen Press on Behalf of The American Society of Parasitologists Stable. J. Parasitol. 1988, 74, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarczyk, P.; Dabert, M.; Frantz, A.C.; Osten-Sacken, N.; Trzebny, A.; Wojtkowiak-Giera, A.; Heddergott, M. Zoonotic Giardia Duodenalis Sub-Assemblage BIV in Wild Raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Germany and Luxembourg. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.W.; McCleery, R.A.; Forrester, D.J. Intestinal Coccidia of Raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Key Largo, Florida, U.S.A. Comp. Parasitol. 2004, 71, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemming, L.; Jørgensen, A.C.; Nielsen, L.B.; Nielsen, S.T.; Mejer, H.; Chriél, M.; Petersen, H.H. Cardiopulmonary Nematodes of Wild Carnivores from Denmark: Do They Serve as Reservoir Hosts for Infections in Domestic Animals? Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 13, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, J. Predictive Values and Quality Control of Techniques for the Diagnosis of Echinococcus Multilocularis in Definitive Hosts. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cringoli, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Maurelli, M.P.; Utzinger, J. FLOTAC: New Multivalent Techniques for Qualitative and Quantitative Copromicroscopic Diagnosis of Parasites in Animals and Humans. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleni, C.; Mariacher, A.; Grifoni, G.; Cardini, E.; Tonon, S.; Lombardo, A.; Barone, A.; Fichi, G. Pathology of Urinary Bladder in Pearsonema spp. Infected Wildlife from Central Italy. Pathogens 2021, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Gehrt, S.D.; Fritzell, E.K. Sexual Differences in Home Ranges of Raccoons. J. Mammal. 1997, 78, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Donomoto, T.; Manchanayake, T.; Shibahara, T.; Sasai, K.; Matsubayashi, M. First Surveillance and Molecular Identification of the Cryptosporidium Skunk Genotype and Cryptosporidium Parvum in Wild Raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Osaka, Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3669–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popiołek, M.; Szczȩsna-Staśkiewicz, J.; Bartoszewicz, M.; Okarma, H.; Smalec, B.; Zalewski, A. Helminth Parasites of an Introduced Invasive Carnivore Species, the Raccoon (Procyon lotor L.), from the Warta Mouth National Park (Poland). J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, H.H.; Nielsen, S.T.; Larsen, G.; Holm, E.; Chriél, M. Prevalence of Capillaria Plica in Danish Wild Carnivores. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2018, 7, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, M.M.; Minter, L.J.; Flowers, J.R.; Stoskopf, M.K.; Kennedy-Stoskopf, S. Raccoon Roundworm Prevalence (Baylisascaris procyonis) at the North Carolina Zoo, USA. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, N.; Dörge, D.D.; Cunze, S.; Schantz, A.V.; Skaljic, A.; Rueckert, S.; Klimpel, S. Raccoons Contraband—The Metazoan Parasite Fauna of Free-Ranging Raccoons in Central Europe. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 20, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauda, F.; Malandrucco, L.; MacRì, G.; Scarpulla, M.; De Liberato, C.; Terracciano, G.; Fichi, G.; Berrilli, F.; Perrucci, S. Leishmania Infantum, Dirofilaria spp. and Other Endoparasite Infections in Kennel Dogs in Central Italy. Parasite 2018, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.K.; Riley, J.; Darby, B.; Murphy, J.; Turner, L.; Segarra, M.D.; Roellig, D.M. Cryptosporidium Parvum Outbreak Associated with Raccoons at a Wildlife Facility—Virginia, May–June 2019. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddergott, M.; Frantz, A.C.; Pohl, D.; Osten-Sacken, N.; Steinbach, P. Detection of Cryptosporidium spp. Infection in Wild Raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Luxembourg Using an ELISA Approach. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leśniańska, K.; Perec-Matysiak, A.; Hildebrand, J.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K.; Piróg, A.; Popiołek, M. Cryptosporidium spp. and Enterocytozoon Bieneusi in Introduced Raccoons (Procyon lotor)—First Evidence from Poland and Germany. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4535–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentería-Solís, Z.; Meyer-Kayser, E.; Obiegala, A.; Ackermann, F.; Król, N.; Birka, S. Cryptosporidium sp. Skunk Genotype in Wild Raccoons (Procyon lotor) Naturally Infected with Baylisascaris procyonis from Central Germany. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 79, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad Rahimi, H.; Soleimani Jevinani, S.; Nemati, S.; Sharifdini, M.; Mirjalali, H.; Zali, M.R. Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium Skunk Genotype in Raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Iran: Concern for Zoonotic Transmission. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, U.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium Species in Humans and Animals: Current Understanding and Research Needs. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1667–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Ahmadpour, E.; Carmena, D.; Spotin, A.; Bangoura, B.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium Infections in Terrestrial Ungulates with Focus on Livestock: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Lopez, L.; Elwin, K.; Chalmers, R.M.; Enemark, H.L.; Beser, J.; Troell, K. Development of a Gp60-Subtyping Method for Cryptosporidium Felis. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.H.; Levine, N.D.; Todd, K.S. In Raccoons in Illinois’. J. Protoozol. 1981, 28, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Sarcocystis and Other Coccidia in Foxes and Other Wild Carnivores from Montana. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1982, 181, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matoba, Y.; Yamada, D.; Asano, M.; Oku, Y.; Kitaura, K.; Yagi, K.; Tenora, F.; Asakawa, M. Parasitic Helminths from Feral Raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Japan. Helminthologia 2006, 43, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Beck, B.; García, F.J.; Gortázar, C. Raccoons in Europe: Disease Hazards Due to the Establishment of an Invasive Species. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2012, 58, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Inaba, T.; Ihama, Y.; Kamiya, H. Parasitological survey on wild carnivora in Nord-Western Tohoku, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1999, 61, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Suzuki, K. Gastrointestinal Helminths of Feral Raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Wakayama Prefecture, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2006, 68, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.C.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, E.K.; Son, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kang, S.W.; Choi, S.H. Mixed Infection of Toxocara Canis and Ancylostoma Caninum in a Wild Raccoon. RDA J. Agric. Sci. (Korea Repub.) 1996, 1, 857–863. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoszewicz, M.; Okarma, H.; Zalewski, A.; Szczȩsna, J. Ecology of the Raccoon (Procyon lotor) from Western Poland. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 2008, 45, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, E.W.; Beverley Burton, M. Observations on the Prevalence and Intensity of Capillaria spp. (Nematoda: Trichuroidea) in Wild Carnivora from Ontario, Canada. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1981, 48, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, R.A.; Shoop, W.L. Helminths of the Raccoon (Procyon lotor) in Western Kentucky. J. Parasitol. 1987, 73, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.J.; Owen, W.B.; Snyder, D.E. Helminth Parasites of the Raccoon (Procyon lotor) from North-Central Arkansas. J. Parasitol. 1992, 78, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddergott, M.; Müller, F.; Steinbach, P.; Jeschke, D.; Stubbe, M.; Frantz, A.C.; Stubbe, A.; Ansorge, H.; Osten-Sacken, N. First Detection and Low Prevalence of Pearsonema spp. in Wild Raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Central Europe. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 19, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pence, D.B. Capillaria procyonis sp. n.(Trichuridae) from the Esophagus of the Raccoon, Procyon lotor. J. Parasitol. 1975, 61, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synder, D.E. Capillaria Procyonis (Nematoda: Trichuroidea) Eggs from the Tongue of the Raccoon (Procyon lotor). J. Wildl. Dis. 1988, 24, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, D.E. New Information on the Location of Capillaria Procyonis (Nematoda: Trichuroidea) in the Tongue of a Raccoon (Procyon lotor). J. Wildl. Dis. 1989, 25, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare, A.; Castagna, G.; Meloni, S.; Otranto, D.; Traversa, D. Mixed Trichuroid Infestation in a Dog from Italy. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravec, F. Proposal of a New Systematic Arrangement of Nematodes of the Family Capillariidae. Folia Parasitol. 1982, 29, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Rosatte, R.C. Management of Raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Ontario, Canada: Do Human Intervention and Disease Have Significant Impact on Raccoon Populations ? Mammalia 2000, 64, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, K.; Beasley, J.C.; Olson, Z.H.; Smyser, T.J.; Downey, M.; Kellner, K.F.; McCord, S.E.; Egan, T.S.; Rhodes, O.E. Reducing Baylisascaris procyonis Roundworm Larvae in Raccoon Latrines. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Body Weight Class (kg) | Number of Raccoons | % |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0–1.9 | 5/62 | 8.06 |
| 2.0–3.9 | 15/62 | 24.19 |
| 4.0–5.9 | 24/62 | 38.70 |
| 6.0–7.9 | 15/62 | 24.19 |
| ≥8.0 | 4/62 | 6.45 |
| Parasites | Technique | Prevalence | % | Eggs-Oocysts/g (m ± sd) * | Eggs-Oocysts/g (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eimeria sp. | Flotac | 2/62 | 3.2 | 4 ± 1.16 | 2–6 |
| Cryptosporidium sp. | IF | 2/62 | 3.2 | - | - |
| Baylisascaris procyonis | Flotac | 24/62 | 38.7 | 3852.30 ± 7355.30 | 2–28,320 |
| Capillariidae | Flotac | 6/62 | 9.6 | 4.7 ± 17.55 | 2–96 |
| Ancylostomatidae | Flotac | 2/62 | 3.2 | 2.5 ± 2.82 | 2–10 |
| Pearsonema sp. | Urine centrifugation/NaCl flotation | 6/62 | 9.6 | - | - |
| B. procyonis Load Range | Frequency (Number of Raccoons) | % |
|---|---|---|
| 1–10 | 5/25 | 20 |
| 20–30 | 6/25 | 24 |
| 30–40 | 4/25 | 16 |
| 40–50 | 3/25 | 12 |
| 50–60 | 2/25 | 8 |
| >100 | 5/25 * | 20 |
| Number of Captured Raccoons Per Trap | Number of Traps | Total Number of Captured Raccoons |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 | 22 |
| 2 | 6 | 12 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 | 8 |
| 15 | 1 | 15 |
| Total | 32 | 60 |
| Variables | Test | p |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Χ2 (1, N = 62) = 0.47683 | p = 0.4899 |
| Age | Χ2 (1, N = 62) = 0.01242 | p = 0.9113 |
| Seasonality | Χ2 (3, N = 62) = 2.9039 | p = 0.4067 |
| Weight | Χ2 (3, N = 62) = 1.2647 | p = 0.7375 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lombardo, A.; Diano, M.; Brocherel, G.; Palmerini, L.; Giovannini, S.; Mezher, Z.; Iurescia, M.; Cerci, T.; Caprioli, A.; Eleni, C.; et al. Detection of Endoparasites in Non-Native Raccoons from Central Italy. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020171
Lombardo A, Diano M, Brocherel G, Palmerini L, Giovannini S, Mezher Z, Iurescia M, Cerci T, Caprioli A, Eleni C, et al. Detection of Endoparasites in Non-Native Raccoons from Central Italy. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(2):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020171
Chicago/Turabian StyleLombardo, Andrea, Marco Diano, Giuseppina Brocherel, Lucia Palmerini, Serena Giovannini, Ziad Mezher, Manuela Iurescia, Tamara Cerci, Andrea Caprioli, Claudia Eleni, and et al. 2023. "Detection of Endoparasites in Non-Native Raccoons from Central Italy" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 2: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020171
APA StyleLombardo, A., Diano, M., Brocherel, G., Palmerini, L., Giovannini, S., Mezher, Z., Iurescia, M., Cerci, T., Caprioli, A., Eleni, C., Raso, C., Mariacher, A., Del Lesto, I., Cappai, N., Mattioli, L., De Liberato, C., & Fichi, G. (2023). Detection of Endoparasites in Non-Native Raccoons from Central Italy. Veterinary Sciences, 10(2), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020171








