A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Specific Detection of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains of Virus, Bacteria Strains, and Clinical Samples
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Primers and Probes Design
2.4. Generation of Standard DNA
2.5. Real-Time RPA Assay
2.6. Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity Test
2.7. Validation of Performance Using Clinical Samples
3. Results
3.1. Primer and Probe Selection
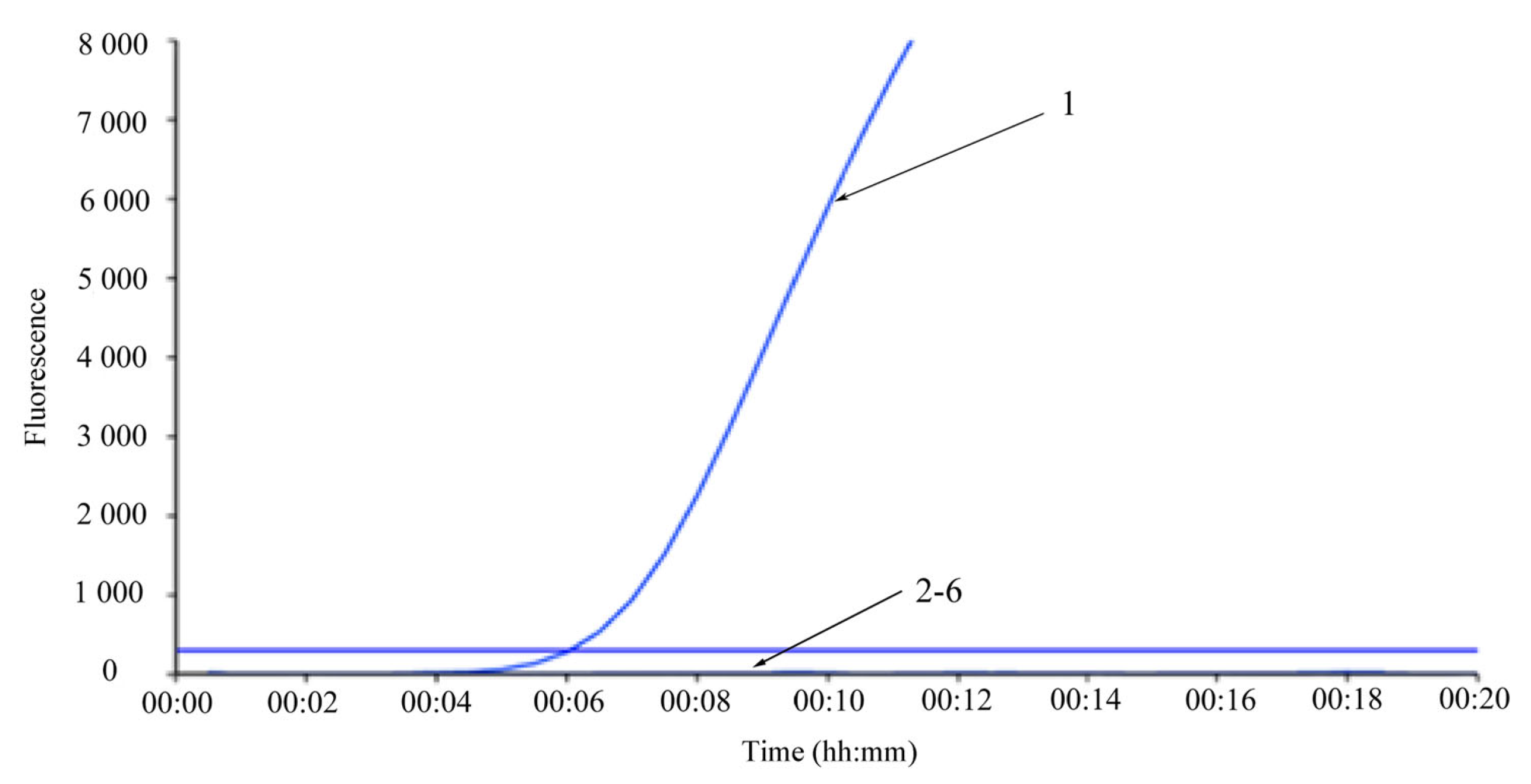
3.2. Analytical Sensitivity and Specificity Analysis
3.3. Qualitative Agreement Test between the Real-Time RPA Assay and WOAH Real-Time PCR Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tulman, E.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genome of lumpy skin disease virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7122–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulman, E.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Sur, J.H.; Sandybaev, N.T.; Kerembekova, U.Z.; Zaitsev, V.L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. The genomes of sheeppox and goatpox viruses. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6054–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Noyce, R.S.; Babiuk, L.A.; Lung, O.; Bulach, D.M.; Bowden, T.R.; Boyle, D.B.; Babiuk, S.; Evans, D.H. Extended sequencing of vaccine and wild-type capripoxvirus isolates provides insights into genes modulating virulence and host range. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tageldin, M.H.; Wallace, D.B.; Gerdes, G.H.; Putterill, J.F.; Greyling, R.R.; Phosiwa, M.N.; Al, B.R.; Al, I.S. Lumpy skin disease of cattle: An emerging problem in the Sultanate of Oman. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2014, 46, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiuk, S.; Bowden, T.R.; Boyle, D.B.; Wallace, D.B.; Kitching, R.P. Capripoxviruses: An emerging worldwide threat to sheep, goats and cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2008, 55, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.L.; Sun, M.F.; Xu, Z.H.; Li, C.L.; Wang, G.; Zheng, C.; Liao, M. Two important poxviruses that originated in Africa, are spreading rapidly in other continents: Why? New Microbes New Infect. 2022, 49–50, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuppurainen, E.S.; Oura, C.A. Review: Lumpy skin disease: An emerging threat to Europe, the Middle East and Asia. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2012, 59, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, P.M. Lumpy skin disease: A direct threat to Europe. Vet. Rec. 2016, 178, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, Y.; Shao, J.; Sun, M.; He, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q. Genomic characterization of a lumpy skin disease virus isolated in southeast China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, 2788–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chander, Y.; Kumar, R.; Khandelwal, N.; Riyesh, T.; Chaudhary, K.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, M.K.; et al. Isolation and characterization of lumpy skin disease virus from cattle in India. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0241022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasib, F.M.Y.; Islam, M.S.; Das, T.; Rana, E.A.; Uddin, M.H.; Bayzid, M.; Nath, C.; Hossain, M.A.; Masuduzzaman, M.; Das, S.; et al. Lumpy skin disease outbreak in cattle population of Chattogram, Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariya, L.; Paungpin, W.; Chaiwattanarungruengpaisan, S.; Thongdee, M.; Nakthong, C.; Jitwongwai, A.; Taksinoros, S.; Sutummaporn, K.; Boonmasawai, S.; Kornmatitsuk, B. Molecular detection and characterization of lumpy skin disease viruses from outbreaks in Thailand in 2021. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2145–e2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.D.; Tran, L.H.; Nguyen, H.D.; Hoang, T.T.; Nguyen, G.H.; Tran, K.V.D.; Nguyen, H.X.; Van Dong, H.; Bui, A.N.; Bui, V.N. Characterization of Lumpy skin disease virus isolated from a giraffe in Vietnam. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e3268–e3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutarbush, S.M.; Ababneh, M.M.; Al Zoubi, I.G.; Al Sheyab, O.M.; Al Zoubi, M.G.; Alekish, M.O.; Al Gharabat, R.J. Lumpy Skin Disease in Jordan: Disease Emergence, Clinical Signs, Complications and Preliminary-associated Economic Losses. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubinga, J.C.; Tuppurainen, E.S.; Mahlare, R.; Coetzer, J.A.; Stoltsz, W.H.; Venter, E.H. Evidence of transstadial and mechanical transmission of lumpy skin disease virus by Amblyomma hebraeum ticks. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuppurainen, E.; Dietze, K.; Wolff, J.; Bergmann, H.; Beltran-Alcrudo, D.; Fahrion, A.; Lamien, C.E.; Busch, F.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Conraths, F.J.; et al. Review: Vaccines and Vaccination against Lumpy Skin Disease. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gari, G.; Abie, G.; Gizaw, D.; Wubete, A.; Kidane, M.; Asgedom, H.; Bayissa, B.; Ayelet, G.; Oura, C.A.; Roger, F.; et al. Evaluation of the safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of three capripoxvirus vaccine strains against lumpy skin disease virus. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3256–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Xie, J.; Luo, J.; Shao, R.; Jia, K.; Li, S. Lumpy skin disease outbreaks in China, since 3 August 2019. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abutarbush, S.M. Adverse reactions to field vaccination against lumpy skin disease in cattle. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 45, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Detection of pseudorabies virus with a real-time recombinase-aided amplification assay. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2266–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, T.R.; Babiuk, S.L.; Parkyn, G.R.; Copps, J.S.; Boyle, D.B. Capripoxvirus tissue tropism and shedding: A quantitative study in experimentally infected sheep and goats. Virology 2008, 371, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, J.L.; Levin, B.; Paik, M.C. Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Yao, K.; Wang, S.; Yin, J.; Ma, X.; Yin, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Understanding the research advances on lumpy skin disease: A comprehensive literature review of experimental evidence. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1065894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, M.A.; El-Deeb, A.; El-Tholoth, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Czerny, C.P.; Hufert, F.T.; Weidmann, M.; Abd El Wahed, A. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of lumpy skin disease virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Tao, D.; Geng, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, B.; Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Chen, H.; Xie, S.; Guo, A. Sensitive and Specific Detection of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus in Cattle by CRISPR-Cas12a Fluorescent Assay Coupled with Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. Genes 2022, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestova, Y.; Byadovskaya, O.; Kononov, A.; Sprygin, A. A real time high-resolution melting PCR assay for detection and differentiation among sheep pox virus, goat pox virus, field and vaccine strains of lumpy skin disease virus. Mol. Cell Probes 2018, 41, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidanovic, D.; Tesovic, B.; Sekler, M.; Debeljak, Z.; Vaskovic, N.; Matovic, K.; Koltsov, A.; Krstevski, K.; Petrovic, T.; De Leeuw, I.; et al. Validation of TaqMan-Based Assays for Specific Detection and Differentiation of Wild-Type and Neethling Vaccine Strains of LSDV. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agianniotaki, E.I.; Chaintoutis, S.C.; Haegeman, A.; Tasioudi, K.E.; De Leeuw, I.; Katsoulos, P.D.; Sachpatzidis, A.; De Clercq, K.; Alexandropoulos, T.; Polizopoulou, Z.S.; et al. Development and validation of a TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR method for the differentiation of wild type lumpy skin disease virus from vaccine virus strains. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 249, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Probe-Based Real-Time qPCR Assays for a Reliable Differentiation of Capripox Virus Species. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, W.; Gong, M.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Qu, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wu, X.; et al. A novel triplex real-time PCR assay for the differentiation of lumpy skin disease virus, goatpox virus, and sheeppox virus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1175391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Sequence 5′–3′ | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| LSD-F | TATAMTGGTCTATTTTTAACTTTTTTATGCAAT | 176 |
| LSD-R | GAYAACAACACTTTTTCCTTATCTAAAGAGYC | |
| LSD-Pro | TAATTCACTTTTAACTTTTTTATTAT/i6FAMdT/A/idSp/A/iBHQ1dT/CCATCGATACATGTA-C3 Spacer |
| Reaction Times | 15 Copies/μL | 10 Copies/μL | 5 Copies/μL | 1 Copy/μL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TT Value (min) | Result | TT Value (min) | Result | TT Value (min) | Result | TT Value (min) | Result | |
| 1 | 00:11:04 | + | 00:14:42 | + | 00:17:44 | + | Unde | - |
| 2 | 00:10:16 | + | 00:14:46 | + | 00:17:58 | + | Unde | - |
| 3 | 00:10:31 | + | 00:17:19 | + | 00:18:13 | + | Unde | - |
| 4 | 00:13:16 | + | 00:14:26 | + | 00:16:38 | + | Unde | - |
| 5 | 00:09:51 | + | 00:15:21 | + | 00:15:38 | + | Unde | - |
| 6 | 00:09:47 | + | 00:14:52 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 7 | 00:10:37 | + | 00:15:35 | + | 00:15:56 | + | Unde | - |
| 8 | 00:08:43 | + | 00:13:37 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 9 | 00:09:27 | + | 00:11:25 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 10 | 00:08:47 | + | 00:14:24 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 11 | 00:08:25 | + | 00:12:44 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 12 | 00:11:27 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 13 | 00:08:51 | + | 00:14:40 | + | 00:18:01 | + | Unde | - |
| 14 | 00:10:05 | + | 00:12:28 | + | 00:17:12 | + | Unde | - |
| 15 | 00:08:57 | + | 00:14:00 | + | 00:17:34 | + | Unde | - |
| 16 | 00:09:17 | + | Unde | - | 00:16:33 | + | Unde | - |
| 17 | 00:08:18 | + | 00:09:04 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 18 | 00:08:17 | + | 00:14:28 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 19 | 00:09:03 | + | 00:12:02 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| 20 | 00:10:44 | + | 00:13:48 | + | Unde | - | Unde | - |
| Real-Time RPA | Diagnostic Sensitivity | Diagnostic Specificity | Kappa Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | |||||
| WOAH method | Positive | 31 | 1 | 32 | 96.88% | 100% | 0.94 |
| Negative | 0 | 11 | 11 | ||||
| Total | 31 | 12 | 43 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Q.; Zhou, X.; Du, L.; Yang, N.; Lou, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, S. A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Specific Detection of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100625
Zhai Q, Zhou X, Du L, Yang N, Lou Y, Liu J, Zhai S. A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Specific Detection of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(10):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100625
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Qi, Xia Zhou, Liyin Du, Nan Yang, Yakun Lou, Jianying Liu, and Shaolun Zhai. 2023. "A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Specific Detection of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 10: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100625
APA StyleZhai, Q., Zhou, X., Du, L., Yang, N., Lou, Y., Liu, J., & Zhai, S. (2023). A Real-Time Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Specific Detection of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus. Veterinary Sciences, 10(10), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100625






