Novel Prion Protein Gene Polymorphisms in Awassi Sheep in Three Regions of the Fertile Crescent
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
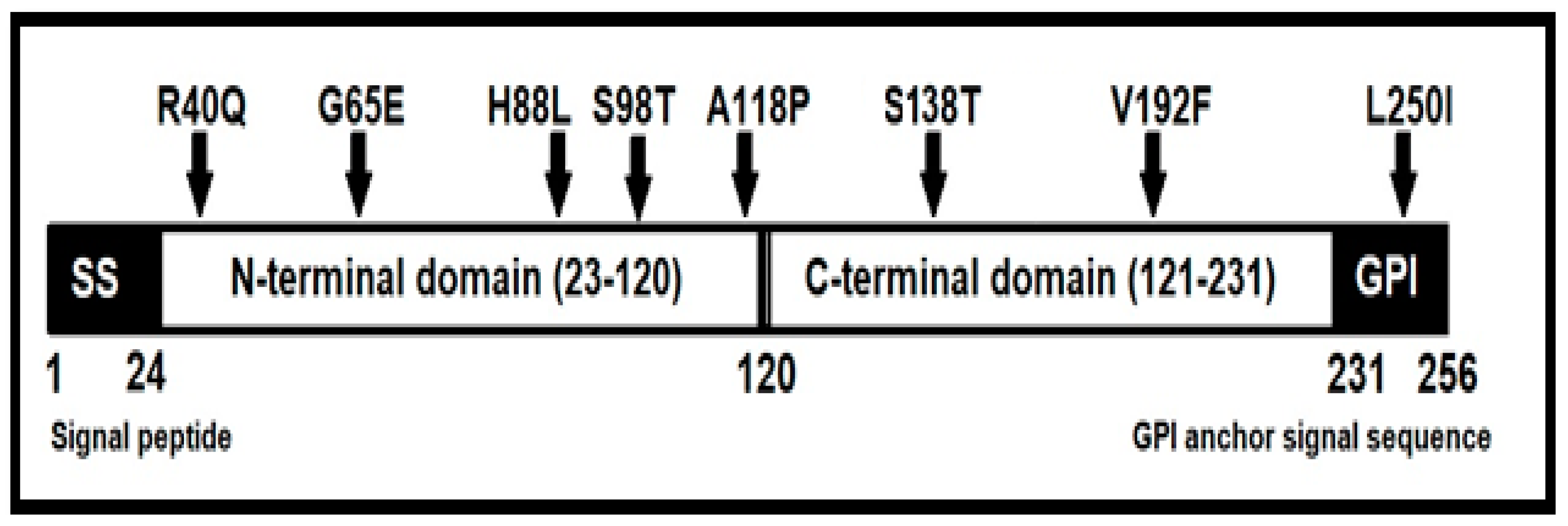
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leopoldt, J.G. Nutzliche und auf die Erfahrung gegrundete Einleitung zu der Land-Wirthschafft; Verlag Nicht Ermittelbar: Sorau, Germany, 1750; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, S.; Morris, C. Genetics of disease resistance in sheep and goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2007, 70, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, N. Scrapie—Uncertainties, biology and molecular approaches. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 2007, 1772, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeder, M.A. Domestication and early agriculture in the Mediterranean Basin: Origins, diffusion, and impact. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11597–11604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Jassim, R.; Aziz, D.; Zorah, K.; Black, J. Effect of concentrate feeding on milk yield and body-weight change of Awassi ewes and the growth of their lambs. Anim. Sci. 1999, 69, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Atiyat, R.M.; Tabbaa, M.J.; Barakeh, F.S.; Awawdeh, F.T.; Baghdadi, S.H. Power of phenotypes in discriminating Awassi sheep to pure strains and from other breeds. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gootwine, E.; Abdulkhaliq, A.; Jawasreh, K.; Zárate, A.V. Screening for polymorphism at the prion protein (PrP) locus (PRNP) in Awassi and Assaf populations in Israel, the Palestinian Authority and Jordan. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 77, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meydan, H.; Yüceer, B.; Degirmenci, R.; Özkan, M.; Yildiz, M. Prion protein gene polymorphism and genetic risk evaluation for scrapie in all Turkish native sheep breeds. Virus Genes 2012, 45, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; DD, D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, W.; Kraus, M.; Schmoll, F.; Achmann, R.; Baumgartner, W. PrP genotyping of Austrian sheep breeds. J. Vet. Med. 2002, 49, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Curcio, L.; Sebastiani, C.; Di Lorenzo, P.; Lasagna, E.; Biagetti, M. A review on classical and atypical scrapie in caprine: Prion protein gene polymorphisms and their role in the disease. Animal 2016, 10, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldmann, W.; Baylis, M.; Chihota, C.; Stevenson, E.; Hunter, N. Frequencies of PrP gene haplotypes in British sheep flocks and the implications for breeding programmes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, N.; Goldmann, W.; Smith, G.; Hope, J. Frequencies of PrP gene variants in healthy cattle and cattle with BSE in Scotland. Vet. Rec. 1994, 135, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chi, T.; Yu, X.; Song, F.; Wang, Z. Allelic variants of PRNP in 16 Chinese local sheep breeds. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2141–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meydan, H.; Özkan, M.; Yildiz, M.; Goldmann, W. Novel polymorphisms in ovine prion protein gene. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teferedegn, E.Y.; Yaman, Y.; Un, C. Five novel PRNP gene polymorphisms and their potential effect on Scrapie susceptibility in three native Ethiopian sheep breeds. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, R.; Liu, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Diao, X.; Guan, H.; Wang, X. Ovine prion protein genotype frequencies in northwestern China. Genet. Mol. Res. 2012, 11, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldmann, W. Classic and atypical scrapie—A genetic perspective. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Puig, B.; Altmeppen, H.; Glatzel, M. The GPI-anchoring of PrP: Implications in sorting and pathogenesis. Prion 2014, 8, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gíslason, M.H.; Nielsen, H.; Armenteros, J.J.A.; Johansen, A.R. Prediction of GPI-anchored proteins with pointer neural networks. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2021, 3, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Gupta, N.; Jethra, G. Genotyping of PRNP coding region for scrapie in Indian sheep. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 15, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Babar, M.; Farid, A.; Benkel, B.; Ahmad, J.; Sajid, I.; Imran, M.; Hussain, T.; Nadeem, A. Genetic variability at seven codons of the prion protein gene in nine Pakistani sheep breeds. J. Genet. 2008, 87, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gombojav, A.; Ishiguro, N.; Horiuchi, M.; Serjmyadag, D.; Byambaa, B.; Shinagawa, M. Amino acid polymorphisms of PrP gene in Mongolian sheep. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frootan, F.; Nikbakht, G.; Özgentürk, N.Ö.; Ün, C. Prion protein coding gene (PRNP) variability in sheep from Turkey and Iran. Biochem. Genet. 2012, 50, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, K.; Namikawa, T.; Sato, K.; Hasnath, M.; Nyunt, M.M.; Rajbandary, H.B.; Loc, C.B.; Zanchiv, T.; Chang, H.; Sun, W. Prion protein polymorphisms and estimation of risk of scrapie in East Asian sheep. Biochem. Genet. 2010, 48, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsayed, O.; Alak, S.E.; Cemal, Ü. Analysis of prion protein coding gene polymorphisms in Palestinian native sheep breeds. Ankara Üniv. Vet. Fak.Derg. 2019, 66, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acín, C.; Martín-Burriel, I.; Goldmann, W.; Lyahyai, J.; Monzon, M.; Bolea, R.; Smith, A.; Rodellar, C.; Badiola, J.J.; Zaragoza, P. Prion protein gene polymorphisms in healthy and scrapie-affected Spanish sheep. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekateriniadou, L.; Kanata, E.; Panagiotidis, C.; Nikolaou, A.; Koutsoukou, E.; Lymberopoulos, A.; Sklaviadis, T. PrP genotypes in scrapie-affected sheep in Greece—The contribution of the AHQ 1 polymorphism. Small Rumin. Res. 2007, 73, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioutsioukis, C.; Papadogiannakis, E.; Palaska, V.; Kontos, V.; Papakostaki, D.; Paraskeva, S.; Vassalou, E. Prion protein gene polymorphisms in classical scrapie-affected flocks of sheep in Central Macedonia. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2018, 69, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martemucci, G.; Iamartino, D.; Blasi, M.; D’Alessandro, A.G. PrP genotype frequencies and risk evaluation for scrapie in dairy sheep breeds from southern Italy. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 122, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongue, S.; Wilesmith, J.; Cook, C. Frequencies of prion protein (PrP) genotypes and distribution of ages in 15 scrapieaffected flocks in Great Britain. Vet. Rec. 2004, 154, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautaniemi, M.; Tapiovaara, H.; Korpenfelt, S.-L.; Sihvonen, L. Genotyping and surveillance for scrapie in Finnish sheep. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianella, P.; McManus, C.; Caetano, A.; Paiva, S. PRNP haplotype and genotype frequencies in Brazilian sheep: Issues for conservation and breeding programs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acutis, P.; Martucci, F.; Mazza, M.; Peletto, S.; Iulini, B.; Corona, C.; Bozzetta, E.; Casalone, C.; Caramelli, M. A case of scrapie in a sheep carrying the lysine-171 allele of the prion protein gene. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, A.; Dalvit, C.; Caldon, M.; Colamonico, R.; Barberio, A.; Mutinelli, F. PRNP gene polymorphism in native Italian sheep breeds undergoing in situ conservation. Small Rumin. Res. 2013, 113, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijas, J.W.; Lenstra, J.A.; Hayes, B.; Boitard, S.; Porto Neto, L.R.; San Cristobal, M.; Servin, B.; McCulloch, R.; Whan, V.; Gietzen, K. Genome-wide analysis of the world’s sheep breeds reveals high levels of historic mixture and strong recent selection. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Region | Sample Size | Location/Herd |
|---|---|---|
| Türkiye | 50 | Şanlıurfa (n = 25) Gaziantep (n = 25) |
| Palestinian Authority | 50 | Jenin (n = 15) Jericho (n = 15) Hebron (n = 20) |
| Saudi Arabia | 50 | Riyadh (n = 25) Taif (n = 25) |
| Variation | Breed | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA | Codon | Protein | Palestinian Authority | S. Arabia | Türkiye | Total |
| 119G → A | CGA/CAA | R40Q* | 5 | 10 | - | 15 |
| 153C → T | CGC/CGT | Silent | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| 194G → A | GGA/GAA | G65E* | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| 263A → T | CAT/CTT | H88L* | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| 293G → C | AGC/ACC | S98T* | 4 | 9 | - | 13 |
| 304T → G | TGG/GGG | W102G | 5 | 11 | - | 16 |
| 342T → G | CAT/CAG | H114Q | 6 | 7 | - | 13 |
| 347A → G | GCA/GAA | A116E | - | 3 | - | 3 |
| 352G → C | GCT/CCT | A118P* | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| 379G → A | GGC/AGC | G127S | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 |
| 380G → T | GGC/GTC | G127V | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 407C → T | GCC/GTC | A136V | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| 409A → G | ATG/GTG | M137V | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| 413G → C | AGC/ACC | S138T* | 2 | 3 | - | 5 |
| 428A → G | CAT/CGT | H143R | - | - | 2 | 2 |
| 433G → A | GGC/AGC | G145S | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| 437A → G | AAT/AGT | N146S | 1 | 3 | 11 | 15 |
| 445G → A | GAG/AAG | E149K | 1 | 1 | - | 2 |
| 459T → C | TAT/TAC | Silent | 2 | - | - | 2 |
| 461G → A | CGT/CAT | R154H | 4 | - | - | 4 |
| 500G → A | AGA/AAA | R167K | 5 | 8 | - | 13 |
| 506T → G | GTG/GGG | V169G | 3 | 6 | - | 9 |
| 511C → A | CAG/AAG | Q171K | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| 512A → G | CAG/CGG | Q171R | 24 | 20 | 12 | 56 |
| 513G → T | CAG/CAT | Q171H | 20 | 34 | 21 | 75 |
| 511C → A 513G → T | CAG/AAT | Q171N | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| 525G → A | CAG/CAA | Silent | 4 | 2 | - | 6 |
| 566A → T | CAA/CTA | Q189L | - | - | 5 | 5 |
| 574G → T | GTC/TTC | V192F* | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| 691C → A | AGG/CGG | Silent | 4 | 8 | - | 12 |
| 711C → G | CTC/CTG | Silent | 4 | 8 | - | 12 |
| 748C → A | CTC/ATC | L250I* | 5 | 7 | - | 12 |
| NSP * | Palestinian Authority n = 50 | Saudi Arabia n = 50 | Türkiye n = 50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype frequency | ||||
| R1 | ARR/ARR | 0.20 (10) | 0 | 0.06 (3) |
| R2 | ARR/AHQ | 0.08 (4) | 0 | 0 |
| R2 | ARR/ARH | 0 | 0.16 (8) | 0.10 (5) |
| R2 | ARR/ARQ | 0.20 (10) | 0.24 (12) | 0.08 (4) |
| R3 | ARH/ARH | 0 | 0 | 0.16 (8) |
| R3 | ARQ/ARH | 0.34 (17) | 0.48 (24) | 0.16 (8) |
| R3 | ARQ/ARQ | 0.12 (6) | 0.08 (4) | 0.40 (20) |
| R5 | VRQ/ARQ | 0 | 0 | 0.02 (1) |
| ** | ARH/ARK | 0.04 (2) | 0.04 (2) | 0 |
| ** | ARQ/ARK | 0 | 0 | 0.02 (1) |
| ** | ARH/ARN | 0.02 (1) | 0 | 0 |
| Allele frequency | ||||
| ARR | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.15 | |
| AHQ | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | |
| ARQ | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.54 | |
| ARH | 0.20 | 0.34 | 0.29 | |
| VRQ | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| ARK | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| ARN | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | |
| Variations | Haplotypes Based on Codons 136/154/171 |
|---|---|
| R40Q | ARQ/ARQ, ARQ/ARH, ARR/AHQ, ARH/ARN |
| G65E | ARQ/ARQ, ARR/ARQ |
| H88L | ARQ/ARQ, ARR/ARQ |
| S98T | ARQ/ARQ, ARQ/ARH, ARR/AHQ, ARR/ARH |
| W102G | ARQ/ARQ, ARQ/ARH, ARR/ARQ, ARH/ARK, ARR/ARH, |
| H114Q | ARQ/ARQ, ARR/ARR, ARQ/ARH, ARR/ARQ, ARH/ARK, ARH/ARN |
| A116E | ARR/ARQ |
| A118P | ARQ/ARQ |
| G127S | ARQ/ARH, ARR/ARQ |
| G127V | ARQ/ARH, ARH/ARH |
| M137V | ARQ/ARQ |
| S138T | ARR/ARR, ARQ/ARH, ARR/ARQ, ARR/ARH |
| H143R | ARQ/ARH |
| G145S | ARQ/ARQ |
| N146S | ARQ/ARQ, ARQ/ARH, ARH/ARH, ARR/ARQ |
| E149K | ARH/ARK, ARQ/ARH |
| R167K | ARQ/ARH, ARH/ARK, ARR/ARQ, ARR/ARH |
| V169G | ARQ/ARH, ARR/ARQ, ARR/ARH |
| Q189L | ARQ/ARQ, ARR/ARH, ARH/ARH, ARQ/ARH |
| V192F | ARR/ARQ |
| L250I | ARQ/ARQ, ARR/ARQ, ARQ/ARH, ARR/ARH |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashaydeh, F.S.; Yildiz, M.A.; Alharthi, A.S.; Al-Baadani, H.H.; Alhidary, I.A.; Meydan, H. Novel Prion Protein Gene Polymorphisms in Awassi Sheep in Three Regions of the Fertile Crescent. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100597
Rashaydeh FS, Yildiz MA, Alharthi AS, Al-Baadani HH, Alhidary IA, Meydan H. Novel Prion Protein Gene Polymorphisms in Awassi Sheep in Three Regions of the Fertile Crescent. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(10):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100597
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashaydeh, Faisal S., Mehmet A. Yildiz, Abdulrahman S. Alharthi, Hani H. Al-Baadani, Ibrahim A. Alhidary, and Hasan Meydan. 2023. "Novel Prion Protein Gene Polymorphisms in Awassi Sheep in Three Regions of the Fertile Crescent" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 10: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100597
APA StyleRashaydeh, F. S., Yildiz, M. A., Alharthi, A. S., Al-Baadani, H. H., Alhidary, I. A., & Meydan, H. (2023). Novel Prion Protein Gene Polymorphisms in Awassi Sheep in Three Regions of the Fertile Crescent. Veterinary Sciences, 10(10), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100597







