l-Theanine as a Functional Food Additive: Its Role in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion
Abstract
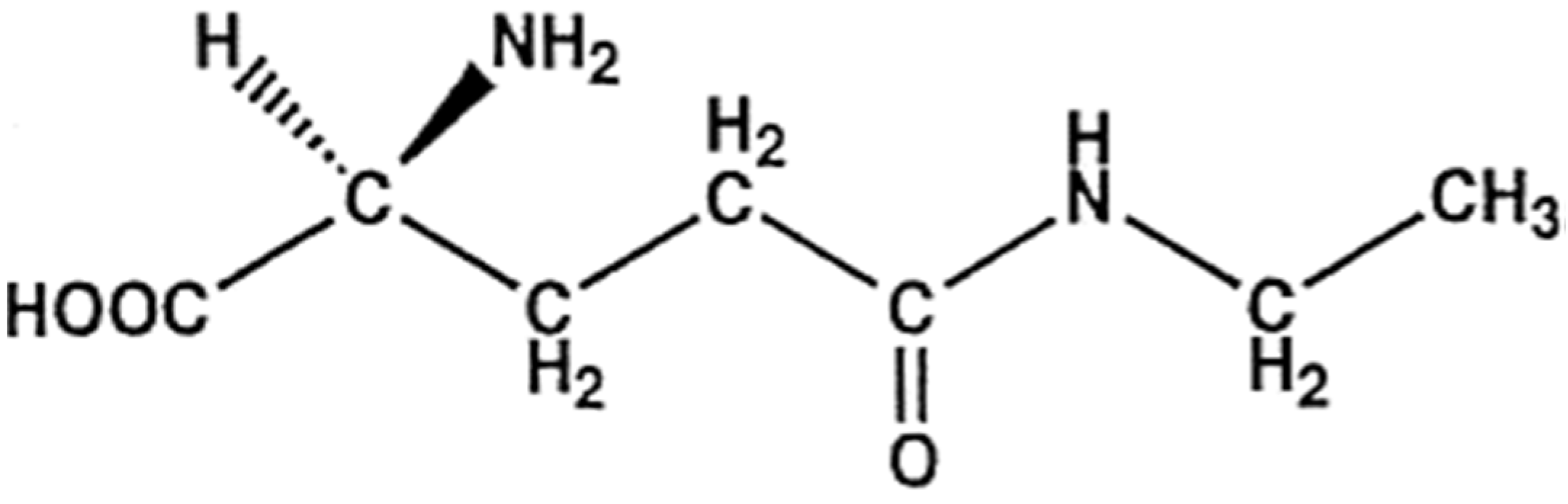
:1. Introduction
2. l-THE in Nature
3. Chemical, Physical and Flavour Properties
4. Extraction and Synthesis of l-THE
4.1. Isolation of l-THE from Tea
4.2. Chemical Synthesis
4.3. Enzymatic Synthesis of Theanine
5. Analytical Methods for the Determination of l-THE Levels
6. Pharmacokinetic Properties of l-THE
7. Animal Toxicity Studies
8. l-THE and the Brain
8.1. Production of Alpha Waves in Brain
8.2. Effect of l-THE on Cognition and Learning Ability
9. Systemic Effects of l-THE
Immune System
10. Cancer
11. Vascular System
12. Applications in Food
13. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| l-THE | l-Theanine |
| MIP | Molecularly imprinted polymer |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| DAD | Diode array detectors |
| ECC | Electrokinetic capillary chromatography |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| IL | Interleukin |
| DOX | doxorubicin |
| GSH | glutathione |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
References
- Graham, H. Green tea composition, consumption, and polyphenol chemistry. Prev. Med. 1992, 21, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yang, H.; Wei, C.; Yu, O.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xia, T.; et al. Deep sequencing of the camellia sinensis transcriptome revealed candidate genes for major metabolic pathways of tea-specific compounds. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yan, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, L. Black and green tea consumption and the risk of coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.S.; Landau, J.M. Effects of tea consumption on nutrition and health. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2409–2412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Juneja, R.; Djong-Chi, C.; Tsutomu, O.; Yukiko, N.; Hidehiko, Y. l-theanine—A unique amino acid of green tea and its relaxation effect in humans. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.N. Protein and Amino Acids in Tea Plant: Varieties and Distribution of Amino Acids in Tea Plant; Chinese Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1984; pp. 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhanga, Z.; Wan, X. A novel colorimetric determination of free amino acids content in tea infusions with 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009, 22, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.V.; Bowyer, M.C.; Roach, P.D. l-Theanine: Properties, synthesis and isolation from tea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakato, Y. The chemical constituents of tea: III A new amide theanine. Nippon Nogei Kagakukaishi 1949, 23, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, N. Preparation of γ-alkylamides of glutamic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1942, 64, 1021–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.W.; Ashihara, H. Occurrence and de novo biosynthesis of caffeine and theanine in seedlings of tea (Camellia sinensis). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.W.; Fei, Y.; Wang, S.; Wan, X.C.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Hu, X.Y. Effect of shade treatment on theanine biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 71, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, K.; Jedlinszki, N.; Csupor, D. Theanine and caffeine content of infusions prepared from commercial tea samples. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eschenauer, G.; Sweet, B.V. Pharmacology and therapeutic uses of theanine. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2006, 63, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldrum, B. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: Review of physiology and pathology. J. Nutr. 2000, 130 (4S Supplement), 1007S–1015S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D. Chemistry and biological properties of theanine, in tea and tea products. In Tea and Tea Products: Chemistry and Health-Promoting Properties; Ho, C., Lin, J., Shahidi, F., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 255–274. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, M.J. The Merck Index—An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 15th ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2013; p. 2708. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S.N.L.o.M. l-Theanine. Available online: http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/L-Theanine#section=Top (accessed on 18 November 2015).
- Nobre, A.C.; Rao, A.; Owen, G.N. l-Theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R. Green tea and theanine: Health benefits. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narukawa, M.; Toda, Y.; Nakagita, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Misaka, T. l-Theanine elicits umami taste via the T1R1 + T1R3 umami taste receptor. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, Z.; Shi, Z. Preparative isolation and purification of l-theanine by HPLC. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachová, M.; Lehotay, J.; Karasová, G.; Skacáni, I.; Armstrong, D.W. Isolation of l-theanine from plant material using a molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2007, 30, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zheng, Q.Z.; Jiao, Q.C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, G. Enzymatic synthesis of theanine from glutamic acid γ-methyl ester and ethylamine by immobilized escherichia coli cells with γ-glutamyltranspeptidase activity. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagishi, H.; Sugiyama, K. Facile and large-scale synthesis of l-theanine. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.H.; Dufour, J.P.; Meurens, M. Synthesis and characterization of highly pure theanine. Tea Sci. 2003, 23, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J. A practical synthesis of ethyl l-glutamine (l-theanine). Org. Prep. Proc. Int. 2004, 36, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wei, P.; Ouyang, P. Enzymatic synthesis of theanine with l-glutamine-zn(II) complexes. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2012, 17, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachiki, T.; Yamada, T.; Mizuno, K.; Ueda, M.; Shiode, J.; Fukami, H.B.B.B. γ-Glutamyl transfer reactions by glutaminase from pseudomonas nitroreducens IFO 12694 and their application for the syntheses of theanine and γ-glutamylmethylamide. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelian, V.H.; Okubo, T.; Mutoh, K.; Chu, D.C.; Kim, M.; Yamamoto, T. A continuous production method for theanine by immobilized pseudomonas nitroreducens cells. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1993, 76, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Wakayama, M.; Tachiki, T. Theanine production by coupled fermentation with energy transfer employing pseudomonas taetrolens y-30 glutamine synthetase and baker’s yeast cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Wakayama, M.; Tachiki, T. Cloning and expression of methylovorus mays no. 9 gene encoding gamma-glutamylmethylamide synthetase: An enzyme usable in theanine formation by coupling with the alcoholic fermentation system of baker’s yeast. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, X.; Wu, Y.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Mn2+ enhances theanine-forming activity of recombinant glutamine synthetase from bacillus subtilis in escherichia coli. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Izuka, S.; Miyakawa, N.; Kumagai, H. Enzymatic production of theanine, an “umami” component of tea, from glutamine and ethylamine with bacterial γ-glutamyltranspeptidase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 31, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zheng, Q.Z.; Jiao, Q.C.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhao, G.H. Synthesis of theanine from glutamic acid gamma-methyl ester and ethylamine catalyzed by escherichia coli having gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase activity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindal, S.; Gupta, R. l-Theanine synthesis using γ-glutamyl transpeptidase from bacillus licheniformis ER-15. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9151–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.J.; Kim, Y.D.; Jeong, M.J.; Ahn, M.S.; Kim, S.W.; Liu, J.R.; Choi, M.S. Rapid selection of theanine-rich green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) trees and metabolites profiling by fourier transform near-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 9, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xua, R.; Hua, B.; Lia, W.; Suna, Y.; Tub, Y.; Zeng, X. Analysis of free amino acids in Chinese teas and flower of tea plant by high performance liquid chromatography combined with solid-phase extraction. Food Chem. 2010, 124, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wan, X.C.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Li, J.; Shen, Z.J. A novel assay method for theanine synthetase activity by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 819, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancu, G.; Simon, B.; Rusu, A.; Mircia, E.; Gyéresi, Á. Principles of micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography applied in pharmaceutical analysis. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcázar, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Jurado, J.M.; Pablos, F.; Martín, M.J.; Vilches, J.L.; Navalón, A. Differentiation of green, white, black, oolong, and pu-erh teas according to their free amino acids content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5960–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.P.; Jandik, P.; Rocklin, R.D.; Liu, Y.; Avdalovic, N. An integrated amperometry waveform for the direct, sensitive detection of amino acids and amino sugars following anion-exchange chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yu, H.; Mou, S. Direct determination of free amino acids and sugars in green tea by anion-exchange chromatography with integrated pulsed amperometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 982, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Imaoka, M.; Yano, S.; Sawaragi, Y.; Takagi, K.; Wakayama, M. Sensitive enzymatic method for the quantification of theanine, a principal umami component of commercial tea beverages. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 19, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-N.; Liang, C.-M.; Lai, J.-R.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Tsay, J.-S.; Lin, J.-K. Capillary electrophoretic determination of theanine, caffeine, and catechins in fresh tea leaves and oolong tea and their effects on rat neurosphere adhesion and migration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7495–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, H.-Y.; Chen, R.L.C.; Cheng, T.-J. Determination of tea fermentation degree by a rapid micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, L.; Ellinger, S.; Alteheld, B.; Herholz, H.; Ellinger, J.; Henn, T.; Helfrich, H.P.; Stehle, P. Kinetics of l-theanine uptake and metabolism in healthy participants are comparable after ingestion of l-theanine via capsules and green tea. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Pijl, P.C.; Chen, L.; Mulder, T.P.J. Human disposition of l-theanine in tea or aqueous solution. J. Func. Foods 2010, 2, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzelleca, J.F.; Peters, D.; Hall, W. A 13-week dietary toxicity and toxicokinetic study with l-theanine in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, K.; Yasuda, E.; Nagasawa, K.; Fujimoto, S. Altered levels of oxidation and phospholipase c isozyme expression in the brains of theanine-administered rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Schmitz, H.J.; Baumgart, A.; Guédon, D.; Netsch, M.I.; Kreuter, M.H.; Schmidlin, C.B.; Schrenk, D. Toxicity of green tea extracts and their constituents in rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Nagato, Y.; Aoi, N.; Juneja, L.; Kim, M.; Yamamoto, T. Effects of l-theanine on the release of α-brain waves in human volunteers. Nippon Nogei Kagakukaishi 1998, 72, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ramirez, M.; Higgins, B.A.; Rycroft, J.; Owen, G.N.; Mahoney, J.; Shpaner, M.; Foxe, J.J. The deployment of intersensory selective attention: A high-density electrical mapping study of the effects of theanine. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2007, 30, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, M.R.; Kapoor, M.P.; Juneja, L.R. The effects of l-theanine (suntheanine(r)) on objective sleep quality in boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.S.; Jung, J.Y.; Jang, I.S.; Jang, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ha, J.H.; Suk, K.; Lee, M.G. l-Theanine partially counteracts caffeine-induced sleep disturbances in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 101, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, M.; Wakabayashi, C.; Sato, N.; Hori, H.; Hattori, K.; Teraishi, T.; Ozawa, H.; Okubo, T.; Kunugi, H. Effect of l-theanine on glutamatergic function in patients with schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015, 27, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Ozeki, M.; Juneja, L.R.; Ohira, H. l-Theanine reduces psychological and physiological stress responses. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Gray, M.A.; Oliver, C.; Liley, D.T.; Harrison, B.J.; Bartholomeusz, C.F.; Phan, K.; Nathan, J. The acute effects of l-theanine in comparison with alprazolam on anticipatory anxiety in humans. Human Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2004, 19, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashiyama, A.; Htay, H.H.; Ozeki, M.; Juneja, L.R.; Kapoor, M.P. Effects of l-theanine on attention and reaction time response. J. Func. Foods 2011, 3, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, C.F.; Kennedy, D.O.; Milne, A.L.; Wesnes, K.A.; Scholey, A.B. The effects of l-theanine, caffeine and their combination on cognition and mood. Biol. Psychol. 2008, 77, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einöther, S.J.L.; Martens, V.E.G.; Rycroft, J.A.; De Bruin, A. l-Theanine and caffeine improve task switching but not intersensory attention or subjective alertness. Appetite 2010, 54, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.P.; Gomez-Ramirez, M.; Montesi, J.L.; Foxe, J.J. l-Theanine and caffeine in combination affect human cognition as evidenced by oscillatory alpha-band activity and attention task performance. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1572s–1577s. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giesbrecht, T.; Rycroft, J.A.; Rowson, M.J.; De Bruin, E.A. The combination of l-theanine and caffeine improves cognitive performance and increases subjective alertness. Nutr. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, M.; Wakabayashi, C.; Matsuo, J.; Kinoshita, Y.; Hori, H.; Hattori, K.; Sasayama, D.; Teraishi, T.; Obu, S.; Ozawa, H.; et al. Effect of l-theanine on sensorimotor gating in healthy human subjects. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 68, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritsner, M.S.; Miodownik, C.; Ratner, Y.; Shleifer, T.; Mar, M.; Pintov, L.; Lerner, V. l-Theanine relieves positive, activation, and anxiety symptoms in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: An 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2-center study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 72, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakuda, T. Neuroprotective effects of theanine and its preventive effects on cognitive dysfunction. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 64, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, K.; Tanida, N.; Ishii, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Iguchi, K.; Hoshino, M.; Takeda, A.; Ozawa, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Juneja, L.R.; et al. Anti-stress effect of theanine on students during pharmacy practice: Positive correlation among salivary alpha-amylase activity, trait anxiety and subjective stress. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 111, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R. 200 mg of zen: l-Theanine boosts alpha waves, promotes alert relaxation. Altern. Complement. Ther. 2001, 7, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, M.; Kakuda, T.; Takarada, T.; Nakamichi, N.; Fukumori, R.; Kim, Y.H.; Hinoi, E.; Yoneda, Y. Promotion of both proliferation and neuronal differentiation in pluripotent p19 cells with stable overexpression of the glutamine transporter slc38a1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, G.N.; Parnell, H.; De Bruin, E.A.; Rycroft, J.A. The combined effects of l-theanine and caffeine on cognitive performance and mood. Nutr. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, G.M. A calculated response: Control of inflammation by the innate immune system. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, S.; Hiraoka, T.; Akutsu, M.; Sukegawa, E.; Bannai, M.; Shibahara, S. Effects of (l)-cystine and (l)-theanine supplementation on the common cold: A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. J. Amino Acids 2010, 2010, 307475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Kurihara, S.; Titchenal, C.A.; Ohtani, M. Suppression of exercise-induced neutrophilia and lymphopenia in athletes by cystine/theanine intake: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutri. 2010, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, J.F.; Percival, S. l-Theanine intervention enhances human gammadelta T lymphocyte function. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Kurihara, S.; Maeda, A. Co-administration of l-cystine and l-theanine enhances efficacy of influenza vaccination in elderly persons: Nutritional status-dependent immunogenicity. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2008, 8, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyachi, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Oyama, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Abe, N.; Sato, A.; Chiba, Y.; Kurihara, S.; Shibakusa, T.; Mikami, T. Perioperative oral administration of cystine and theanine enhances recovery after distal gastrectomy: A prospective randomized trial. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2013, 37, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Ohtani, M.; Fukusaki, C. Cystine and theanine supplementation restores high-intensity resistance exercise-induced attenuation of natural killer cell activity in well-trained men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Kurihara, S.; Koikawa, N.; Nakamura, A.; Aoki, K.; Yosigi, H.; Sawaki, K.; Ohtani, M. Effects of oral supplementation with cystine and theanine on the immune function of athletes in endurance exercise: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. United States Cancer Statistics: 1999–2011 Incidence and Mortality Web-Based Report; Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and National Cancer Institute: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014.
- Liu, Q.; Duan, H.; Luan, J.; Yagasaki, K.; Zhang, G. Effects of theanine on growth of human lung cancer and leukemia cells as well as migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells. Cytotechnology 2009, 59, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Mackey, B.E.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, I.S.; Lee, K.R.; Lee, S.U.; Kozukue, E.; Kozukue, N. Structure-activity relationships of tea compounds against human cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Zuo, J.; Li, M.; Gu, Q.; Hu, C. Theanine improves the function of dendritic cells via the downregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Ye, X.; Ji, D.; Zhang, H.; Sun, F.; Shang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, E.; Wang, F.; Wu, F.; et al. Inhibition of lung tumor growth by targeting EGFR/VEGFR-Akt/NF-κB pathways with novel theanine derivatives. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8528–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadzuka, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Sonobe, T. Efficacies of tea components on doxorubicin induced antitumor activity and reversal of multidrug resistance. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 114, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Sadzuka, Y. Enhancing effects of green tea components on the antitumor activity of adriamycin against m5076 ovarian sarcoma. Cancer Lett. 1998, 133, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadzuka, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Nagamine, M.; Umegaki, K.; Sonobe, T. Efficacy of theanine is connected with theanine metabolism by any enzyme, not only drug metabolizing enzymes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T.; Noguchi, K.; Ando, S. Increase of body surface temperature and blood flow by theanine. In Proceedings of the first Asian and Oceanic Congress for Radiation Protection (AOCRP-1), Seoul, Korea, 20–24 October 2002.
- Dodd, F.L.; Kennedy, D.O.; Riby, L.M.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effects of caffeine and l-theanine both alone and in combination on cerebral blood flow, cognition and mood. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 2563–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoto, A.; Motoki, M.; Murao, S.; Yokogoshi, H. Effects of l-theanine or caffeine intake on changes in blood pressure under physical and psychological stresses. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2012, 31, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, P.J.; Smith, J.E.; Heatherley, S.V.; Pleydell-Pearce, C.W. Time for tea: Mood, blood pressure and cognitive performance effects of caffeine and theanine administered alone and together. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 2008, 195, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siamwala, J.H.; Dias, P.M.; Majumder, S.; Joshi, M.K.; Sinkar, V.P.; Banerjee, G.; Chatterjee, S. l-Theanine promotes nitric oxide production in endothelial cells through eNOS phosphorylation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, C.; Ross, P.R.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Sinderen, D.V. Fermented functional foods based on probiotics and their biogenic metabolites. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siró, I.; Kápolna, E.; Kápolna, B.; Lugasi, A. Functional food. Product development, marketing and consumer acceptance—A review. Appetite 2008, 51, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, M.V.S.R.; Wald, N.; Sneddon, J.; Densem, J.; Frost, C.; Stone, R. Prevention of neural tube defects: Results of the medical research council vitamin study. Lancet 1991, 338, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bower, C.; Stanley, F.J. Dietary folate as a risk factor for neural-tube defects: Evidence from a case-control study in western australia. Med. J. Aust. 1989, 150, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, K.; Chen, R.; Gianesini, T. What Is So Smart about Neurogum. Available online: http://neurogum.com/pages/the-science (accessed on 1 April 2016).
- White, D.J.; de Klerk, S.; Woods, W.; Gondalia, S.; Noonan, C.; Scholey, A.B. Anti-stress, behavioural and magnetoencephalography effects of an l-theanine-based nutrient drink: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Nutrients 2016, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montopoli, M.; Stevens, L.; Smith, C.J.; Montopoli, G.; Passino, S.; Brown, S.; Camou, L.; Carson, K.; Maaske, S.; Knights, K.; et al. The acute electrocortical and blood pressure effects of chocolate. NeuroRegulation 2015, 2, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culetu, A.; Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Ullate, M.; del Castillo, M.D.; Andlauer, W. Effect of theanine and polyphenols enriched fractions from decaffeinated tea dust on the formation of maillard reaction products and sensory attributes of breads. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Di, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Y.; Liang, Y.; et al. The cessation and detoxification effect of tea filters on cigarette smoke. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- l-Theanine (98%) Food Usage Conditions for General Recognition of Safety. Food and Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety & Appiled Nutrition. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/ucm/groups/fdagov-public/@fdagov-foods-gen/documents/document/ucm269524.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2016).
- Tang, J.E.; Moore, D.R.; Kujbida, G.W.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: Effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Impact on | Pure Theanine Treatment | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| α-Wave production | Administration of l-THE (50–200 mg) in 6 female participants displayed an increase in alpha wave production observed 40 min after oral ingestion. This presented a relaxing effect without causing drowsiness due to unchanged θ-waves. | [5] |
| α-Wave production | Ingestion of l-THE (50 mg) enhanced α-wave production in young participants. | [19] |
| α-Wave production | Administration of l-THE (200 mg) in 8 females enhanced the generation of α-wave production. | [52] |
| Relaxation | Administration of l-THE (200 mg) may increase relaxation under resting conditions. | [58] |
| Relaxation | Administration of l-THE (200 mg) resulted in a reduction in heart rate and salivary immunoglobulin A (s-IgA) in response to an acute stress task. | [57] |
| Improved sleep quality | Administration of l-THE (400 mg) may improve sleep quality in boys diagnosed with ADHD. | [54] |
| Improved sleep quality | Treatment of diagnosed schizophrenia patients (8 weeks) with l-THE (250 mg) was effective in improving sleep quality. | [56] |
| Impact on | Proposed Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Learning ability | Co-treatment of l-THE (250 mg) and caffeine (150 mg) enhanced reaction time, working memory and sentence verification accuracy. | [60] |
| Learning ability | Intake of a combination of l-THE (97 mg) and caffeine (40 mg) improved attention on an inter-sensory attention switch task. | [61] |
| Learning ability | Administration of l-THE (250 mg) enhanced α-wave activity over the parieto-occipital scalp during the inter-sensory attentional cuing task. | [53] |
| Learning ability | Co-administration of l-THE (100 mg) and caffeine (50 mg) increased speed and accuracy of performance of an attention-switching task. | [70] |
| Cognition | Co-administration of l-THE (100 mg) and caffeine (50 mg) enhanced tonic apportionment of attentional resources to visuospatial attentional deployment. | [62] |
| Cognition | Co-intake of l-THE (97 mg) and caffeine (40 mg) improved cognitive performance and increased subjective alertness in young adults. | [63] |
| Cognition | Administration of l-THE (200–400 mg) increased sensorimotor gating. | [64] |
| Memory loss | Ingestion of l-THE (47.5 mg) showed a lower decline in cognitive function in elderly patients. | [66] |
| Impact on | Proposed Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Immune function | Co-administration of l-THE (280 mg) and cysteine (700 mg) attenuated an increase in neutrophil count and a reduction in lymphocyte count during exercise (in 16 athletes). | [73] |
| Immune function | Supplementation with l-THE (200 mg) decreases the incidence of cold and flu symptoms through enhancement of human γ and δ T lymphocyte function. | [74] |
| Immune function | Co-administration of l-THE (280 mg) and cysteine (700 mg) before vaccination enhanced immune responses to influenza vaccine in elderly subjects with low serum total protein or haemoglobin. | [75] |
| Immune function | Co-treatment of l-THE (280 mg) and cysteine (700 mg) for 2 weeks restored the attenuation of natural killer cell activity in well trained men | [77] |
| Immune function | Co-administration of l-THE (70 mg) and cysteine (175 mg) in 176 subjects correlated with a lower incidence in development of the common cold | [72] |
| Preventative immune function | Co-administration of l-THE (280 mg) and cysteine (700 mg) reduced neutrophil counts, maintained high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) levels and prevented a decrease in lymphocytes post endurance training compared with placebo. | [78] |
| Post-operative recovery | Co-administration of l-THE (280 mg) and cysteine (700 mg) during a randomised, single blind, parallel-group trial alleviated post-gastrectomy inflammation in patients that have undertaken distal gastrectomy for cancer. | [76] |
| Study Type | Proposed Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Ex Vivo/In Vitro | ||
| Cancer suppression | Administration of l-THE (400 μg/mL) was found to induce cell death of four cancer cell lines: breast 23 (MCF-7), colon (HT-29), hepatoma (HepG2), and prostate (PC-3) as well as normal human liver cells in vitro or ex vivo. | [81] |
| Tumour growth | Dendritic cells were purified with l-THE solution (200 μmol/L) that resulted in partial recovery of dendritic cell function, promoted the differentiation of T cells and activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. | [82] |
| Cancer suppression | Four theanine derivatives (methyl coumarin-3-carboxylyl l-theanine, ethyl coumarin-3-carboxylyl l-theanine, ethyl 6-fluorocoumarin- 3-carboxylyl l-theanine, and ethyl 6-nitrocoumarin-3-carboxylyl l-theanine) significantly inhibited lung cancer cell migration, growth of lung cancer and leukemia in in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo models of human and mouse cancers. | [83] |
| Cancer suppression | 48-h l-THE treatment induced in vitro and ex vivo growth of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 and leukemia K562 cell lines in dose- and time-dependant manners | [80] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, J.; Kellett, J.; Roach, P.D.; McKune, A.; Mellor, D.; Thomas, J.; Naumovski, N. l-Theanine as a Functional Food Additive: Its Role in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Beverages 2016, 2, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages2020013
Williams J, Kellett J, Roach PD, McKune A, Mellor D, Thomas J, Naumovski N. l-Theanine as a Functional Food Additive: Its Role in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Beverages. 2016; 2(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages2020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Jackson, Jane Kellett, Paul Daniel Roach, Andrew McKune, Duane Mellor, Jackson Thomas, and Nenad Naumovski. 2016. "l-Theanine as a Functional Food Additive: Its Role in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion" Beverages 2, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages2020013
APA StyleWilliams, J., Kellett, J., Roach, P. D., McKune, A., Mellor, D., Thomas, J., & Naumovski, N. (2016). l-Theanine as a Functional Food Additive: Its Role in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Beverages, 2(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages2020013








