Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis Using High-Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for the Comparison of Volatile and Non-Volatile Compounds in Hot and Cold Brew Coffee
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparing Coffee
2.3. Analysis of Non-Volatile Compounds
2.4. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
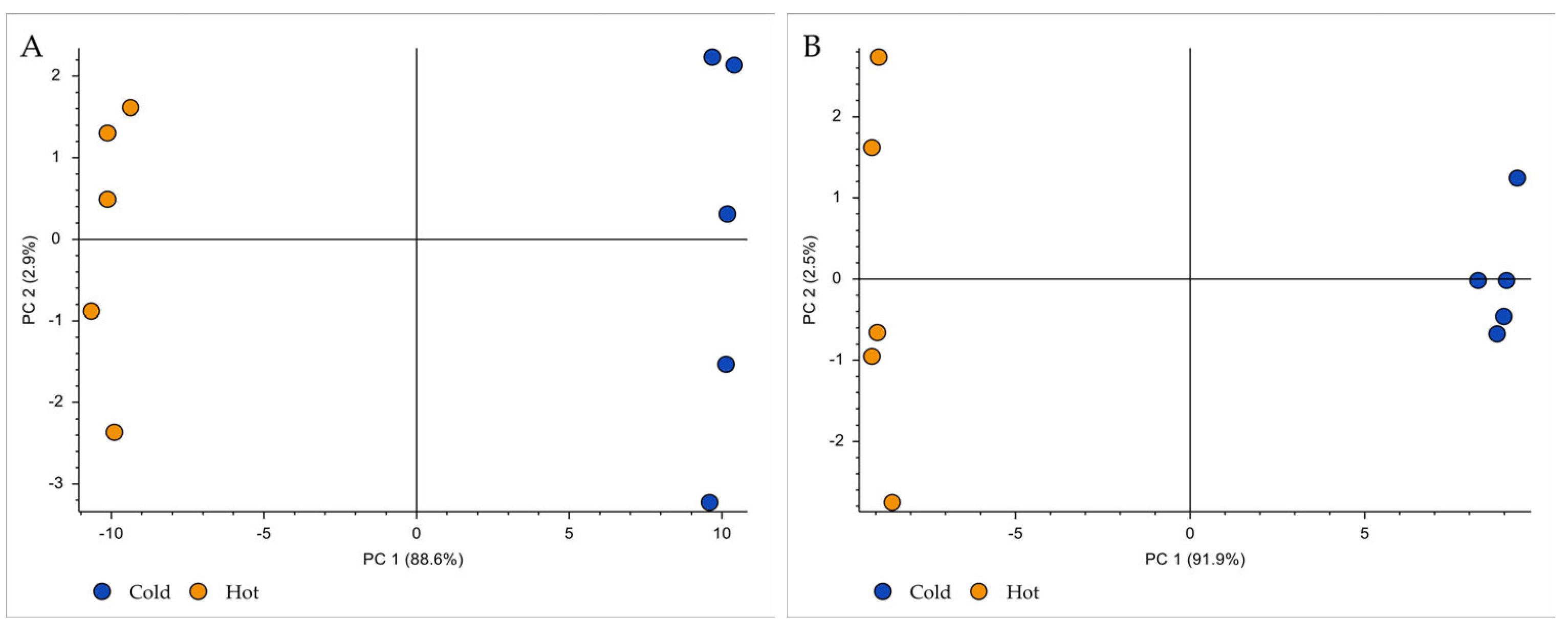
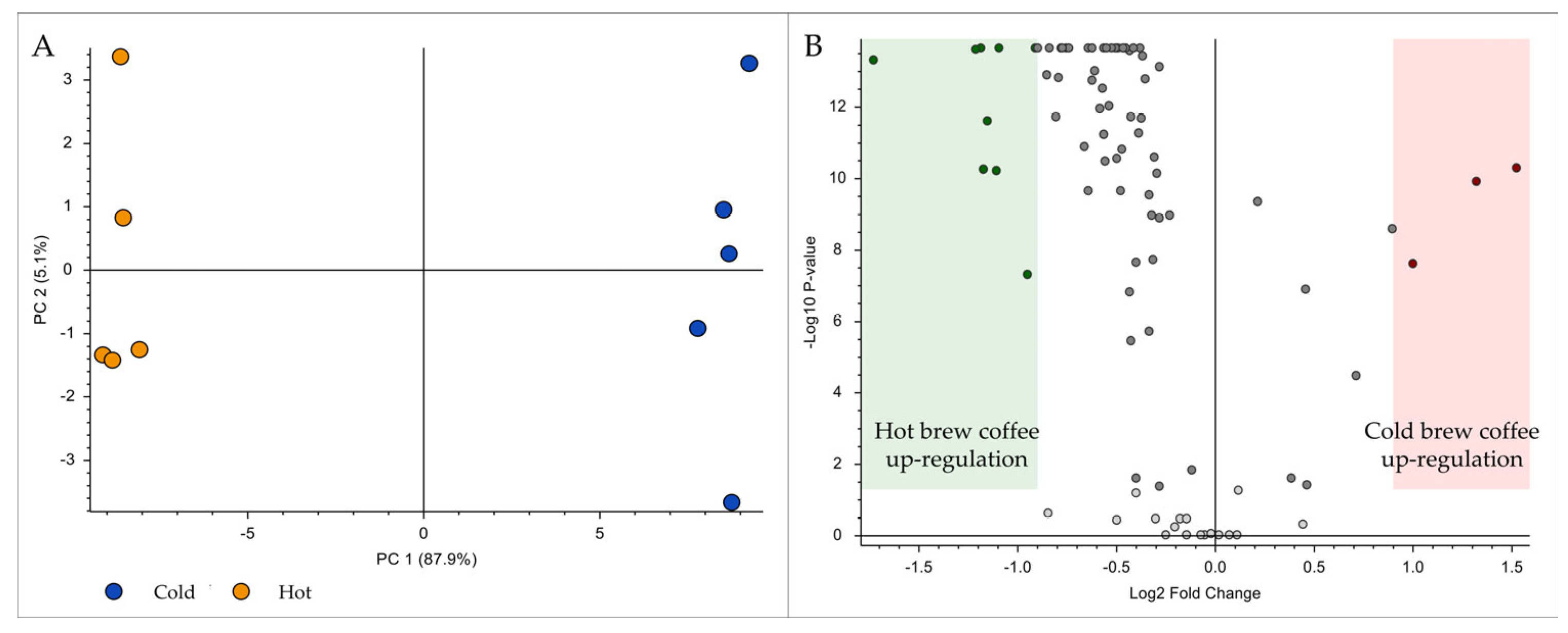
2.5. Data Processing and Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Non-Volatile Compounds in Hot and Cold Brew Coffee
3.2. Volatile Compounds in Hot and Cold Brew Coffee
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coffee: World Markets and Trade. Available online: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/coffee-world-markets-and-trade (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Ludwig, I.A.; Clifford, M.N.; Lean, M.E.; Ashihara, H.; Crozier, A. Coffee: Biochemistry and potential impact on health. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1695–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Coffee, caffeine, and health. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socała, K.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Poleszak, E.; Wlaź, P. Neuroprotective Effects of Coffee Bioactive Compounds: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarharum, W.B.; Williams, D.J.; Smyth, H.E. Complexity of coffee flavor: A compositional and sensory perspective. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzberger, C.S.G.; dos Santos Scholz, M.B.; de Toledo Benassi, M. Bioactive compounds content in roasted coffee from traditional and modern Coffea arabica cultivars grown under the same edapho-climatic conditions. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.M.M.; Batista, N.N.; Miguel, M.G.d.C.P.; Simão, J.B.P.; Soares, J.R.; Schwan, R.F. Coffee growing altitude influences the microbiota, chemical compounds and the quality of fermented coffees. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordoba, N.; Fernandez-Alduenda, M.; Moreno, F.L.; Ruiz, Y. Coffee extraction: A review of parameters and their influence on the physicochemical characteristics and flavour of coffee brews. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 96, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloess, A.N.; Schönbächler, B.; Klopprogge, B.; DAmbrosio, L.; Chatelain, K.; Bongartz, A.; Strittmatter, A.; Rast, M.; Yeretzian, C. Comparison of nine common coffee extraction methods: Instrumental and sensory analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 236, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batali, M.E.; Lim, L.X.; Liang, J.; Yeager, S.E.; Thompson, A.N.; Han, J.; Ristenpart, W.D.; Guinard, J.-X. Sensory analysis of full immersion coffee: Cold brew is more floral, and less bitter, sour, and rubbery than hot brew. Foods 2022, 11, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilyuk, O.; Braaten, T.; Skeie, G.; Weiderpass, E.; Dumeaux, V.; Lund, E. High coffee consumption and different brewing methods in relation to postmenopausal endometrial cancer risk in the Norwegian women and cancer study: A population-based prospective study. BMC Women’s Health 2014, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, J.A.; Loftfield, E.; Wedekind, R.; Freedman, N.; Kambanis, C.; Scalbert, A.; Sinha, R. A metabolomic study of the variability of the chemical composition of commonly consumed coffee brews. Metabolites 2019, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Nowak, A.; Wira, D.; Klimowicz, A. The effect of brewing process parameters on antioxidant activity and caffeine content in infusions of roasted and unroasted Arabica coffee beans originated from different countries. Molecules 2021, 26, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdoba, N.; Moreno, F.L.; Osorio, C.; Velásquez, S.; Ruiz, Y. Chemical and sensory evaluation of cold brew coffees using different roasting profiles and brewing methods. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wen, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, J. The influence of ripening stage and region on the chemical compounds in mulberry fruits (Morus atropurpurea Roxb.) based on UPLC-QTOF-MS. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, N.; Gao, L.; Xu, Y.-J.; Huang, C.; Yu, K.; Ling, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, M. Acetylcarnitine is a candidate diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Yang, D. Application of UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS-based metabolomics in the evaluation of metabolites and taste quality of Chinese fish sauce (Yu-lu) during fermentation. Food Chem. 2019, 296, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.E.; Liden, T.; Berger, B.K.; Zanella, D.; Manh, L.H.; Wang, S.; Schug, K.A. Profiling of contemporary beer styles using liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry, multivariate analysis, and machine learning techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1172, 338668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.C.-W.; Wu, H.-Y.; Kan, H.-L.; Lin, Y.-C.; Tsai, P.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Liao, P.-C. Discovery of spoilage markers for chicken eggs using liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry-based untargeted and targeted foodomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4331–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry analysis with accurate-mass database and parallel reaction monitoring for high-throughput screening and quantification of multi-xenobiotics in honey. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1429, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa, L.M.; Pavlovic, R.; Panseri, S.; Arioli, F. Evaluation of parabens and their metabolites in fish and fish products: A comprehensive analytical approach using LC-HRMS. Food Addit. Contam. 2018, 35, 2400–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyuva, H.Z.; Gökmen, V.; Sarikaya, E.A. Future perspectives in Orbitrap™-high-resolution mass spectrometry in food analysis: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2015, 32, 1568–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzulli, F.; Rocchetti, G.; Lambri, M.; Lucini, L. Metabolomics combined with sensory analysis reveals the impact of different extraction methods on coffee beverages from coffea arabica and coffea canephora var. robusta. Foods 2022, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Míguez, R.; Sánchez-López, E.; Plaza, M.; Castro-Puyana, M.; Marina, M.L. A non-targeted metabolomic approach based on reversed-phase liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry to evaluate coffee roasting process. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7859–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, Z.; Pan, X.; Gao, M.; Wu, M.; Wu, J.; Lao, F. Comparative profiling of hot and cold brew coffee flavor using chromatographic and sensory approaches. Foods 2022, 11, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Pan, X.; Lao, F.; Liao, X.; Shi, Y.; Wu, J. Improvement of antioxidant properties of jujube puree by biotransformation of polyphenols via Streptococcus thermophilus fermentation. Food Chem. 2022, 13, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Liao, X.; Hu, X.; Lao, F. Effects of sugar matrices on the release of key aroma compounds in fresh and high hydrostatic pressure processed Tainong mango juices. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Adhikari, K.; Choi, K.S.; Lee, J. Analysis of caffeine, chlorogenic acid, trigonelline, and volatile compounds in cold brew coffee using high-performance liquid chromatography and solid-phase microextraction—Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Foods 2020, 9, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.; Ntai, I.; Tautenhahn, R. Accelerated unknown compound annotation with confidence: From spectra to structure in untargeted metabolomics experiments. Thermo Fish. Sci. Appl. Note 2018, 65362. [Google Scholar]
- Sukor, N.S.M.; Zakri, Z.H.M.; Rasol, N.E.; Salim, F. Annotation and Identification of Phytochemicals from Eleusine indica Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Databases-Driven Approach. Molecules 2023, 28, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapozhnikova, Y. Non-targeted screening of chemicals migrating from paper-based food packaging by GC-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 226, 122120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Good Scents Company Search Page. Available online: http://www.thegoodscentscompany.com/search2.html (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Buffo, R.A.; Cardelli-Freire, C. Coffee flavour: An overview. Flavour Fragr. J. 2004, 19, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, C.; Dinnella, C.; Monteleone, E.; Prescott, J. The impact of individual variations in taste sensitivity on coffee perceptions and preferences. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 138, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, M.; Rao, N.Z. The effect of time, roasting temperature, and grind size on caffeine and chlorogenic acid concentrations in cold brew coffee. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, J.; Tang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, L. Comparison of characterization of cold brew and hot brew coffee prepared at various roasting degrees. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2023, 2023, 3175570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, N.; Zarębska, M.; Biłos, Ł.; Barabosz, K.; Nowakowska-Bogdan, E.; Semeniuk, I.; Błaszkiewicz, J.; Kulesza, R.; Matejuk, R.; Szkutnik, K. Influence of coffee brewing methods on the chromatographic and spectroscopic profiles, antioxidant and sensory properties. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, T.F.F.d.; Meinhart, A.D.; Souza, T.C.L.d.; Cunha, E.C.E.; Moraes, M.R.d.; Lorini, A.; Teixeira Filho, J.; Godoy, H.T. Impact of water temperature of chimarrão on phenolic compounds extraction. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doctor, N.; Parker, G.; Vang, K.; Smith, M.; Kayan, B.; Yang, Y. Stability and extraction of vanillin and coumarin under subcritical water conditions. Molecules 2020, 25, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestdagh, F.; Glabasnia, A.; Giuliano, P. The brew—Extracting for excellence. In The Craft and Science of Coffee; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 355–380. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimowski, D.; Pachura, N.; Oziembłowski, M.; Nawirska-Olszańska, A.; Szumny, A. Coffee roasting and extraction as a factor in cold brew coffee quality. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.A.S.; Wellinger, M.; Gloess, A.N.; Zimmermann, R.; Yeretzian, C. Extraction kinetics of coffee aroma compounds using a semi-automatic machine: On-line analysis by PTR-ToF-MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 401, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
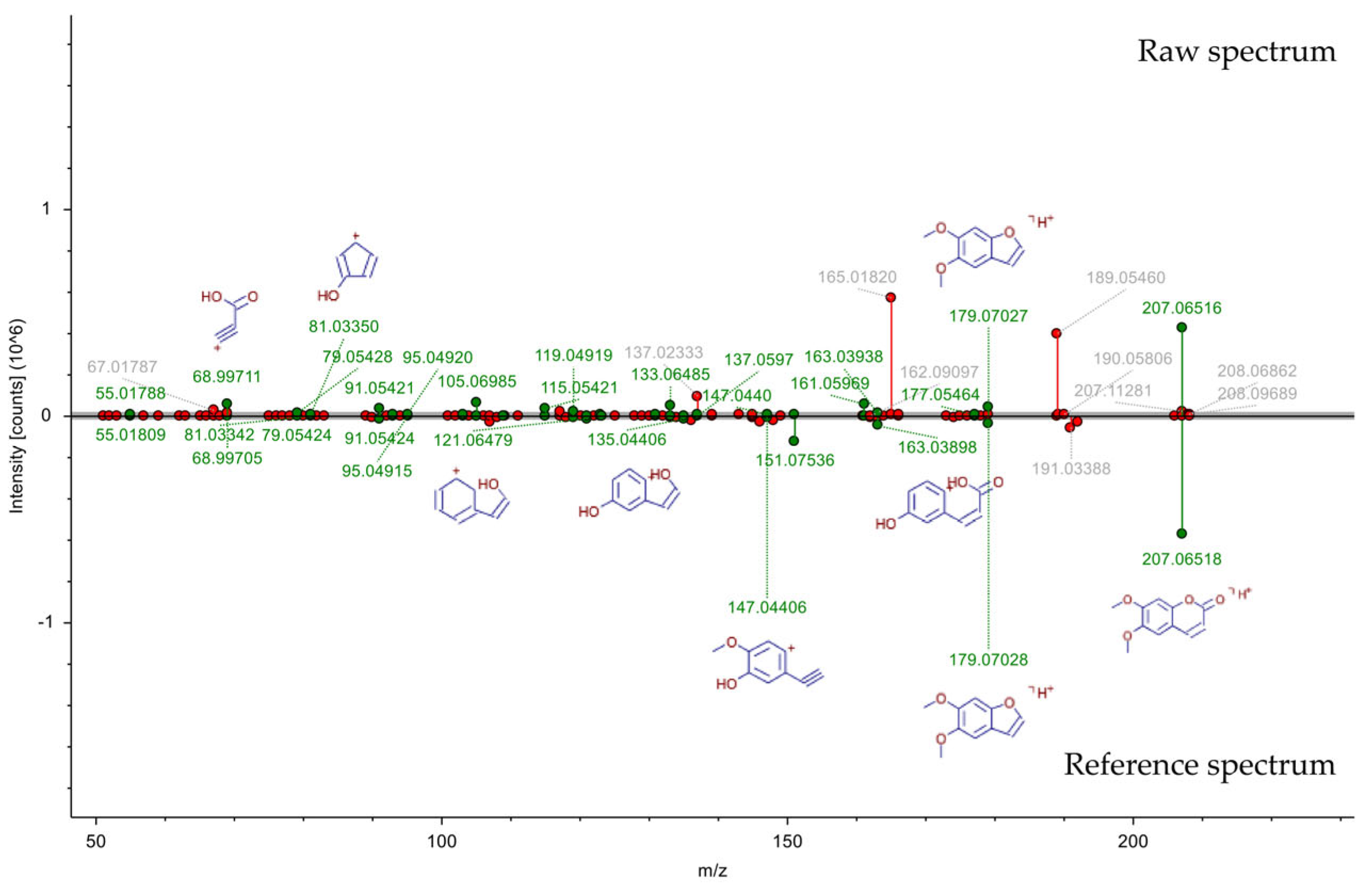

| Compounds | CAS 1 | Formula | Molecule Weight | Reference Ion | Peak Rating |
| 6-Methyl-2-pyridinemethanol | 1122-71-0 | C7H9NO | 123.0683 | [M + H] + 1 | 9.2 |
| 2-Methylbenzoic acid | 118-90-1 | C8H8O2 | 136.0524 | [M − H] − 1 | 9.2 |
| Tyrosol | 501-94-0 | C8H10O2 | 138.0681 | [M − H] − 1 | 9 |
| 3-(3-pyridinyl)propanoic acid 2 | 3724-19-4 | C8H9NO2 | 151.0632 | [M + H] + 1 | 8.3 |
| 6-Methoxyquinoline | 5263-87-6 | C10H9NO | 159.0683 | [M + H] + 1 | 8.8 |
| 4-Coumaric acid | 7400-08-0 | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 | [M − H] − 1 | 8.7 |
| Norharman | 244-63-3 | C11H8N2 | 168.0687 | [M + H] + 1 | 9.6 |
| 3-Dehydroshikimate | 2922-42-1 | C7H8O5 | 172.0371 | [M − H] − 1 | 9.2 |
| Indole-3-acetic acid | 87-51-4 | C10H9NO2 | 175.0633 | [M − H] − 1 | 8.8 |
| 1-(4-Methylphenyl)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione | − | C11H11NO2 | 189.0790 | [M + H] + 1 | 8.7 |
| Scoparone | 120-08-1 | C11H10O4 | 206.0579 | [M + H] + 1 | 8.5 |
| Euparin | 532-48-9 | C13H12O3 | 216.0787 | [M − H] − 1 | 9 |
| Resveratrol | 510-36-0 | C14H12O3 | 228.0786 | [M − H] − 1 | 10 |
| Naringenin | 480-41-1 | C15H12O5 | 272.0686 | [M − H] − 1 | 8.6 |
| N-Caffeoyltryptophan | 109163-69-1 | C20H18N2O5 | 366.1215 | [M − H] − 1 | 9.2 |
| Mascaroside II | − | C26H34O9 | 490.2206 | [M + H] + 1 | 10 |
| Mascaroside I | − | C26H36O10 | 508.2311 | [M + H] + 1 | 9.4 |
| 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 57378-72-0 | C25H24O12 | 516.1268 | [M − H] − 1 | 9.6 |
| C25H24O12 | 516.1272 | [M + H] + 1 | 8.8 |
| Up-Regulation | Compounds | Molecule Weight | CAS 1 | Odor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold brew | Cedrenol | 220.1827 | 28231-03-0 | Woody, sweet [32] |
| 7,9-Di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro(4,5)deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione | 276.1725 | 82304-66-3 | ||
| Dicyclohexyl adipate | 310.2144 | 849-99-0 | ||
| Hot brew | Catechol | 110.0368 | 120-80-9 | |
| Indole | 117.0578 | 120-72-9 | Animal, floral, moth ball [25] | |
| 3-Methylindole | 131.0735 | 83-34-1 | Animal [32] | |
| 1,3-Benzenediol, 4-ethyl- | 138.0681 | 2896-60-8 | ||
| 3-Methoxy-1,2-benzenediol | 140.0473 | 934-00-9 | ||
| 2-Naphthalenol | 144.0575 | 135-19-3 | Slight phenolic odor [32] | |
| 2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol | 150.0681 | 7786-61-0 | Smoky, woody, powdery [32] | |
| 2-Amino-5-methoxybenzaldehyde | 151.0633 | 26831-52-7 | ||
| 1-(2,3-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethanone | 152.0473 | − | ||
| 4-Vinylphenol | 162.0681 | 2628-16-2 | Sweet, vanilla [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Han, E.; Kang, J.; Kwon, S.; Sung, M.; Kim, M.; Cho, H.; Lee, G. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis Using High-Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for the Comparison of Volatile and Non-Volatile Compounds in Hot and Cold Brew Coffee. Beverages 2025, 11, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11010010
Lee S, Han E, Kang J, Kwon S, Sung M, Kim M, Cho H, Lee G. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis Using High-Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for the Comparison of Volatile and Non-Volatile Compounds in Hot and Cold Brew Coffee. Beverages. 2025; 11(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seongeung, Eunmee Han, Jisun Kang, Seohee Kwon, Minkyung Sung, Minkyoung Kim, Hyeokjun Cho, and Gyeonghweon Lee. 2025. "Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis Using High-Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for the Comparison of Volatile and Non-Volatile Compounds in Hot and Cold Brew Coffee" Beverages 11, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11010010
APA StyleLee, S., Han, E., Kang, J., Kwon, S., Sung, M., Kim, M., Cho, H., & Lee, G. (2025). Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis Using High-Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for the Comparison of Volatile and Non-Volatile Compounds in Hot and Cold Brew Coffee. Beverages, 11(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11010010







