Topical Allopurinol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Novel Approach for Wound Healing Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
2.3. Animals
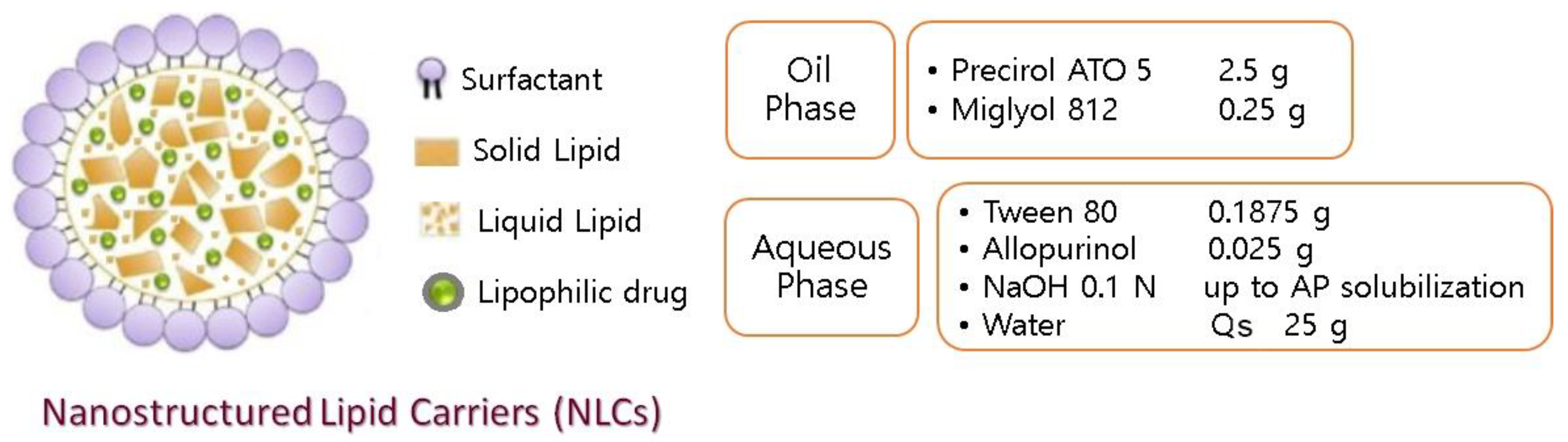
2.4. AP-NLC Preparation
2.5. Size and Zeta Potential
2.6. Quantification of Allopurinol
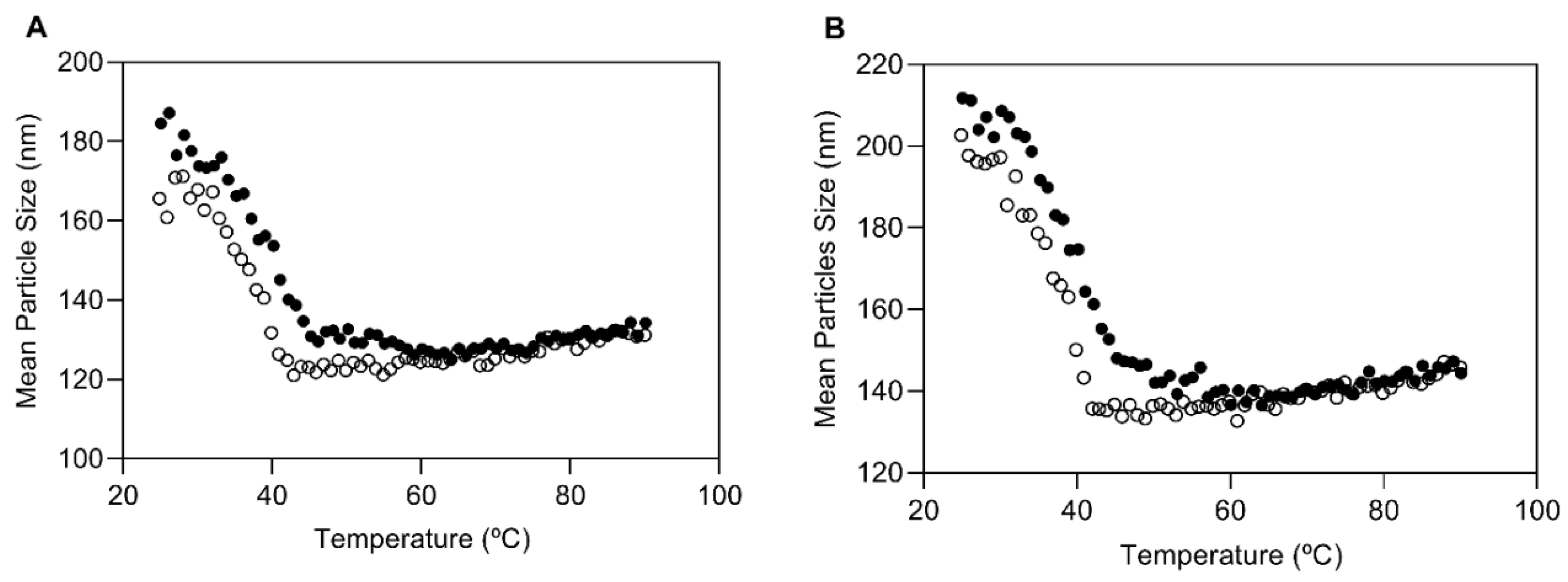
2.7. AP-NLC Thermal Analysis
2.8. Skin Delivery Studies
2.9. Rheology Studies
2.10. Cell-Based Assays
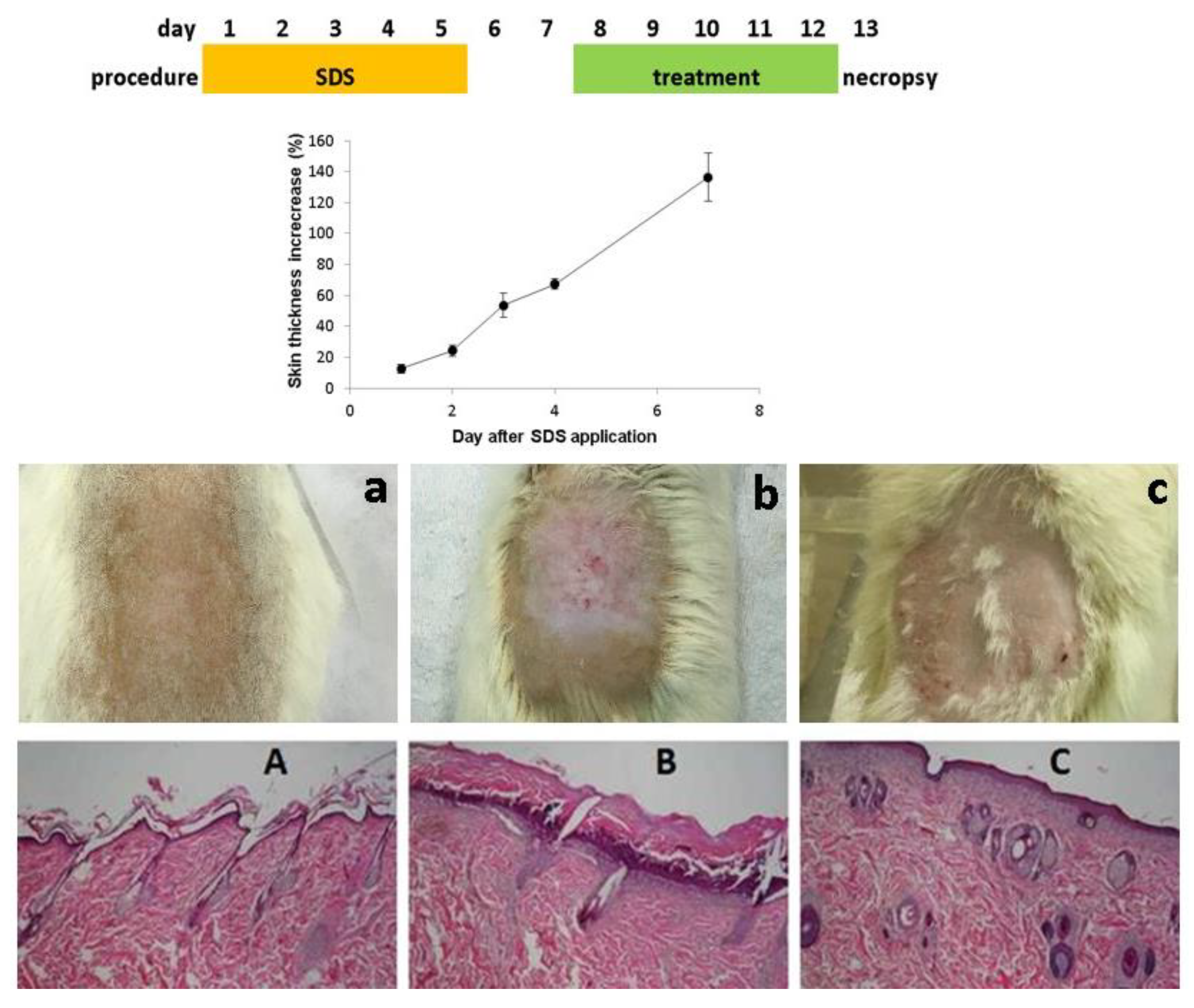
2.11. In Vivo Assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AP-NLC Formulation
3.2. Skin Delivery Study
3.3. Assessment of Cellular Cytotoxicity against HaCaT Cells
3.4. In Vivo Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quitério, M.; Simões, S.; Ascenso, A.; Carvalheiro, M.; Leandro, A.P.; Correia, I.; Viana, A.S.; Faísca, P.; Ascensão, L.; Molpeceres, J.; et al. Development of a Topical Insulin Polymeric Nanoformulation for Skin Burn Regeneration: An Experimental Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frykberg, R.G.; Banks, J. Challenges in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 560–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.; Simões, S.; Ascenso, A.; Reis, C.P. Therapeutic advances in wound healing. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.L.; Upton, Z.; Shooter, G.K. Uric acid and xanthine oxidoreductase in wound healing. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.L.; Upton, Z.; Edwards, H.; Finlayson, K.; Shooter, G.K. Elevated uric acid correlates with wound severity. Int. Wound J. 2012, 9, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.L.; Stupar, D.; Croll, T.; Leavesley, D.; Upton, Z. Xanthine Oxidoreductase: A Novel Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Chronic Wounds? Adv. Wound Care 2018, 7, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacher, P.; Nivorozhkin, A.; Szabó, C. Therapeutic Effects of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors: Renaissance Half a Century after the Discovery of Allopurinol. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.C.; McEnaney, R.M.; Shukla, A.J.; Hong, G.; Kelley, E.E.; Tarpey, M.M.; Gladwin, M.; Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Tzeng, E. Xanthine Oxidoreductase Function Contributes to Normal Wound Healing. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. Effectiveness Allopurinol Topical Agent Prevention Capecitabine-induced Hand-foot Syndrome. 2014. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01609166 (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Rodemer, Y.; Nobera Pharma SL. Use of Allopurinol for the Treatment of Palmar Plantar Erythrodysesthesia. U.S. Patent US8557829B2, 15 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sekundo, W.; Augustin, A.J.; Strempel, I. Topical Allopurinol or Corticosteroids and Acetylcysteine in the Early Treatment of Experimental Corneal Alkali Burns: A Pilot Study. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 12, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Triviño, F.J. Tattoo skin reaction treatment with topical allopurinol: A good alternative. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, e250–e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.S.; Cheruvu, H.S.; Mangion, S.E.; Alinaghi, A.; Benson, H.A.E.; Mohammed, Y.; Holmes, A.; van der Hoek, J.; Pastore, M.; Grice, J.E. Topical drug delivery: History, percutaneous absorption, and product development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 177, 113929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascenso, A.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Cabral Marques, H.; Simões, S. Topical Delivery of Antioxidants. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 640–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitorino, C.; Sousa, J.; Pais, A. Overcoming the Skin Permeation Barrier: Challenges and Opportunities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2698–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, S.; Carvalheiro, M.; Gaspar, M.M. Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Cutaneous Leishmaniais and Buruli Ulcer Management. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 6577–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, A.; Mestre, H.; Ascenso, A.; Simões, S.; Reis, C. Nanomaterials in wound healing: From material sciences to wound healing applications. Nano Sel. 2020, 1, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, G.; Figueroa, C.; Merino, I.; Osuna, A. Allopurinol encapsulated in polycyanoacrylate nanoparticles as potential lysosomatropic carrier: Preparation and trypanocidal activity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 49, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandav, G.; Bhatt, D.C.; Jindal, D.K.; Singh, S.K. Formulation, Optimization, and Evaluation of Allopurinol-Loaded Bovine Serum Albumin Nanoparticles for Targeting Kidney in Management of Hyperuricemic Nephrolithiasis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandav, G.; Bhatt, D.; Jindal, D.K. Formulation and evaluation of allopurinol loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gibaly, I.; Abdel-Ghaffar, S.K. Effect of hexacosanol on the characteristics of novel sustained-release allopurinol solid lipospheres (SLS): Factorial design application and product evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 294, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Tiwari, G.; Singh, R. Allopurinol loaded transferosomes for the alleviation of symptomatic after-effects of Gout: An Account of Pharmaceutical implications. Curr. Drug Ther. 2020, 15, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Baldim, I.; Oliveira, W.P.; Rao, R.; Yadav, N.; Gama, F.M.; Mahant, S. SLN and NLC for topical, dermal, and transdermal drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, K.A.D.; Krawczyk-Santos, A.P.; Andrade, L.M.; Souza, L.C.; Marreto, R.N.; Gratieri, T.; Taveira, S.F. Voriconazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for drug delivery in deeper regions of the nail plate. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, C.; Basri, M.; Ismail, R.; Lau, H.; Tejo, B.; Kanthimathi, M.; Hassan, H.; Choo, Y. Effect of compositions in nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) on skin hydration and occlusion. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pivetta, T.P.; Simões, S.; Araújo, M.M.; Carvalho, T.; Arruda, C.; Marcato, P.D. Development of nanoparticles from natural lipids for topical delivery of thymol: Investigation of its anti-inflammatory properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 164, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloqui, A.; Coco, R.; Alhouayek, M.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Muccioli, G.G.; Préat, V. Budesonide-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers reduce inflammation in murine DSS-induced colitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. OECD Guideline 428 for the Testing of Chemicals: Skin Absorption: In Vitro method; OECD: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Marto, J.; Vitor, C.; Guerreiro, A.; Severino, C.; Eleutério, C.; Ascenso, A.; Simões, S. Ethosomes for enhanced skin delivery of griseofulvin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Guedes, L.; Martinez, R.M.; Bou-Chacra, N.A.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Rosado, C.; Baby, A.R. An Overview on Topical Administration of Carotenoids and Coenzyme Q10 Loaded in Lipid Nanoparticles. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changdeo, J.S.; Vinod, M.; Shankar, K.B.; Rajaram, C.A. Physicochemical characterization and solubility enhancement studies of allopurinol solid dispersions. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 47, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, R.H.; Hespeler, D.; Jin, N.; Pyo, S.M. smartPearls—Novel physically stable amorphous delivery system for poorly soluble dermal actives. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 555, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranda, L.; Gonzalez-Amaro, R.; Torres-Alvarez, B.; Alvarez, C.; Ramirez, V. Correlation between pH and irritant effect of cleansers marketed for dry skin. Int. J. Dermatol. 2002, 41, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, J.R.; Harris, K.L.; Jubin, K.; Bainbridge, N.J.; Jordan, N.R. The effect of pH in modulating skin cell behaviour. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firooz, A.; Nafisi, S.; Maibach, H.I. Novel drug delivery strategies for improving econazole antifungal action. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatipamula, R.; Palem, C.; Gannu, R.; Mudragada, S.; Yamsani, M. Formulation and in vitro characterization of domperidone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers. Daru 2011, 19, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.O.; Aditya, N.P.; Ko, S. Effect of aqueous pH and electrolyte concentration on structure, stability and flow behavior of non-ionic surfactant based solid lipid nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcês, A.; Amaral, M.H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Formulations based on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for cutaneous use: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Potential of Nanoparticles as Permeation Enhancers and Targeted Delivery Options for Skin: Advantages and Disadvantages. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3271–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, G.; Gonçalves, L.M.D.; Marto, J.; Carvalho, F.A.; Simões, S.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Almeida, A.J. Increased Therapeutic Efficacy of SLN Containing Etofenamate and Ibuprofen in Topical Treatment of Inflammation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, D.P.; Faria, V.; Gonçalves, L.M.D.; Taboada, P.; Remuñán-López, C.; Almeida, A.J. Rifabutin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for inhaled antitubercular therapy: Physicochemical and in vitro studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 497, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praça, F.S.G.; Medina, W.S.G.; Eloy, J.O.; Petrilli, R.; Campos, P.M.; Ascenso, A.; Bentley, M.V.L.B. Evaluation of critical parameters for in vitro skin permeation and penetration studies using animal skin models. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Mirza, R.; Kwon, Y.; DiPietro, L.A.; Koh, T.J. The murine excisional wound model: Contraction revisited. Wound Repair Regen. 2015, 23, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gainza, G.; Bonafonte, D.C.; Moreno, B.; Aguirre, J.J.; Gutierrez, F.B.; Villullas, S.; Hernandez, R.M. The topical administration of rhEGF-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (rhEGF-NLC) improves healing in a porcine full-thickness excisional wound model. J. Control. Release 2015, 197, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, A.S.; Davis, F.M.; denDekker, A.; Joshi, A.D.; Schaller, M.A.; Bermick, J.; Xing, X.; Burant, C.F.; Obi, A.T.; Nysz, D.; et al. The Histone Methyltransferase Setdb2 Modulates Macrophage Phenotype and Uric Acid Production in Diabetic Wound Repair. Immunity 2019, 51, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varrica, C.; Carvalheiro, M.; Faria-Silva, C.; Eleutério, C.; Sandri, G.; Simões, S. Topical Allopurinol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Novel Approach for Wound Healing Management. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8120192
Varrica C, Carvalheiro M, Faria-Silva C, Eleutério C, Sandri G, Simões S. Topical Allopurinol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Novel Approach for Wound Healing Management. Bioengineering. 2021; 8(12):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8120192
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarrica, Carla, Manuela Carvalheiro, Catarina Faria-Silva, Carla Eleutério, Giuseppina Sandri, and Sandra Simões. 2021. "Topical Allopurinol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Novel Approach for Wound Healing Management" Bioengineering 8, no. 12: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8120192
APA StyleVarrica, C., Carvalheiro, M., Faria-Silva, C., Eleutério, C., Sandri, G., & Simões, S. (2021). Topical Allopurinol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Novel Approach for Wound Healing Management. Bioengineering, 8(12), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8120192







