Abstract
Neuroblastoma (NB) is the most common extracranial solid tumor in pediatrics, with rare occurrences of primary and metastatic tumors in the central nervous system (CNS). We previously reported the overexpression of the polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) in embryonal brain tumors. PLK4 has also been found to be overexpressed in a variety of peripheral adult tumors and recently in peripheral NB. Here, we investigated PLK4 expression in NBs of the CNS (CNS-NB) and validated our findings by performing a multi-platform transcriptomic meta-analysis using publicly available data. We evaluated the PLK4 expression by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) on the CNS-NB samples and compared the relative expression levels among other embryonal and non-embryonal brain tumors. The relative PLK4 expression levels of the NB samples were found to be significantly higher than the non-embryonal brain tumors (p-value < 0.0001 in both our samples and in public databases). Here, we expand upon our previous work that detected PLK4 overexpression in pediatric embryonal tumors to include CNS-NB. As we previously reported, inhibiting PLK4 in embryonal tumors led to decreased tumor cell proliferation, survival, invasion and migration in vitro and tumor growth in vivo, and therefore PLK4 may be a potential new therapeutic approach to CNS-NB.
1. Introduction
Embryonal tumors of the central nervous system (CNS) are poorly differentiated tumors resembling the developing embryonic nervous system. Embryonal tumors are biologically aggressive and have a tendency to disseminate along cerebrospinal fluid pathways. In the CNS, this group includes medulloblastoma (MB) [1], atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (ATRT) [2], embryonal tumor with multilayer rosettes (ETMR) [3], a spectrum of tumors called “CNS primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs)” and CNS neuroblastoma (CNS-NB) [4].
Neuroblastoma (NB) is the most common extracranial pediatric solid tumor [5]. Current therapies have led to a 90% survival rate, but relapse and metastases have proven to be challenging to treat with survival rates of less than 40% [6].
Previously, we performed a partial functional screening of the kinome on a well-established embryonal tumor cell line (MON—a rhabdoid tumor cell line provided by Dr. Delattre, Institut Curie, Paris France) [7,8,9] using lentiviral-CRISPR to target 160 individual kinase encoding genes representing the major branches of the human kinome and key isoforms within each branch. With this approach we identified the polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) as a putative genetic hit. The genetic loss-of-function was validated by next-generation sequencing analysis, genomic cleavage detection (GCD) assay, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and western blot [7]. We established that PLK4 is overexpressed in embryonal brain tumors such as ATRT and MB [10,11]. We also demonstrated that inhibiting PLK4 with the small-molecule inhibitor CFI-400945 (CAS#1338800-06-8) [12,13,14] resulted in impairment of proliferation, survival, migration and invasion in ATRT and MB cell lines. Further, we demonstrated that PLK4 inhibition induced apoptosis, senescence and polyploidy in these cells. Moreover, we established that polyploidy induced by PLK4 inhibition increased tumor cell susceptibility to DNA-damaging agents while sparing non-tumor cells [7,10].
PLK4 is a cell cycle regulated protein specifically recruited at the centrosome to promote the duplication of centrioles in dividing cells [15,16,17]. Complete loss of PLK4 is lethal and its overexpression triggers centrosomal amplification, which is associated with genetic instability and consequently, carcinogenesis [18,19]. Active PLK4 protein levels have previously been described to be “mirrored by PLK4 mRNA levels” meaning that mRNA expression varies proportionally to protein expression [15]. Although PLK4 has been found to be overexpressed in a number of adult peripheral tumors like colorectal [20], breast [21], lung [22], melanoma [23], leukemia [24], and pancreatic cancer [25], we were the first to report PLK4 overexpression in embryonal tumors and in pediatric brain tumors [7,10,11]. Recently, Tian and colleagues reported PLK4 overexpression in peripheral NB tumor samples and primary NB cell lines. They also demonstrated that increased PLK4 expression was correlated with poor clinical outcomes [6]. Here, we hypothesize that, as in other CNS embryonal brain tumors, CNS-NB overexpress PLK4. To test our hypothesis, we examined PLK4 expression in NB samples of the CNS as compared to other embryonal brain tumors (ATRT and MB) and low grade gliomas (LGG), which are the most common form of primary CNS tumors. For this, we performed quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) in our patients’ tumor samples and an extensive multi-platform transcriptomic meta-analysis using publicly available databases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Fresh frozen tumor samples were obtained from the Falk Brain Tumor Bank (Chicago, IL, USA) and the Center for Childhood Cancer, Biopathology Center (Columbus, OH, USA), which is a section of the Cooperative Human Tissue Network of The National Cancer Institute (Bethesda, MD, USA). Written informed parental consents were obtained prior to sample collection. The study was approved by the institutional review board of the Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago (IRB 2005–12,252; 2005–12,692; 2009–13,778; and 2012–14,887). Samples in the study included 2 CNS-NB (primary n = 1 and metastatic n = 1), 6 embryonal brain tumors (ATRT n = 3 and MB n = 3) and 6 non-embryonal brain tumors (low grade gliomas—LGG).
Total RNA was isolated from each frozen tumor sample using TRIzol Reagent (Thermo Fisher, USA). The expression of PLK4 (Hs00179514_m1) was accessed by TaqMan GE assays (Applied Biosystems, USA). Three housekeeping genes: GAPDH (Hs02758991_g1), HPRT (Hs99999909_m1) and HMBS (Hs00609296_g1) were used as references as previously described [7,10,26,27,28]. Total RNA (2 μg) was used to make cDNA using the Applied Biosystems High Capacity RNA-to-cDNA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Reactions were performed in triplicates with adequate positive and negative controls. The normalized expression levels were calculated by the ΔΔCt method using each housekeeping gene and a pool of all samples as calibrator. The normalized expression levels were also calculated using a normalization factor which was obtained by calculating the geometric mean of relative quantities of all 3 housekeeping genes and dividing the relative quantity of PLK4 with this normalization factor [7,10,26,27,28]. Statistical analysis was performed using a One-Way ANOVA using PRISM (GraphPad 7 Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
2.2. Gene Expression Meta-Analysis
In order to validate the PLK4 expression levels observed in our patients, we performed an extensive meta-analysis compiling publicly available gene expression data. Knowing, from our previous studies that PLK4 is overexpressed in embryonal brain tumors [6,7,11], we selected low grade gliomas (LGG), which are the most common form of primary CNS tumors arising in both children and adults [29,30] to perform this comparison.
To evaluate the PLK4 expression profile in both tumor and normal human tissues, expression levels of PLK4 (ENSG00000142731.6) were compared with expression levels of the neuroendocrine marker used for the diagnosis of neuroblastoma chromogranin A (CHGA, ENSG00000100604.11) [31] and the glioma markers glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP ENSG00000131095.10) and myelin basic protein (MBP, ENSG00000197971.10) [32,33].
Tumors: Open access transcriptomic data (RNAseqV2, FPKM) from NB samples which were deposited in the TARGET (Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments, https://ocg.cancer.gov/programs/target) database and LGG expression data which were deposited in the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas, https://cancergenome.nih.gov/) database, were obtained from the Genomic Data Commons (GDC) (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/).
Normal human tissue: Open access transcriptomic data from 51 tissue types represented in the GTEx (Genotype-Tissue Expression, https://gtexportal.org) portal [34] was analyzed. Each gene of interest was individually searched and gene expression data was manually extracted.
Data analysis: All available NB and LGG samples were downloaded, data were extracted from the Data Transfer Tool using a custom C# script [35] and processed using Microsoft Excel. In order to compare data obtained from multiple databases, we converted FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase Million) to TPM (Transcripts Per Million) using the following equation:
where FPKMg represents the FPKM of the gene of interest and ΣFPKMs represents the sum of all FPKM values from the patient sample [36]. Statistical analysis for the open access RNAseqV2 data was calculated using an unpaired t-test comparing NB samples to LGG.
TPM = (FPKMg/ΣFPKMs) × 106
3. Results
3.1. CNS Neuroblastoma
Among the 3,494 pediatric patients treated for CNS tumors in the Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago (former Children’s Memorial Hospital) from September 1981 to September 2018 (37 years) only 20 cases of CNS-NB were recorded, including 12 children (0.34%) diagnosed with primary CNS-NB (all in the spinal cord) and 8 children (0.23%) diagnosed with NB metastatic to the brain (metastatic CNS-NB). Our study described 2 of our CNS-NB patients which had frozen tissue available for further analyses: (1) a primary CNS-NB that was excised from a 20 month old female patient in 1998 and was diagnosed as a NB according to the 1993 WHO classification [37] (Figure 1) and (2) a NB metastatic from a primary tumor in the adrenal gland, that was removed from a six year old female patient in 2001 and classified according to the 2000 WHO classification of CNS tumors (Figure 2) [38]. Both tumors were located at the supratentorial region of the brain.
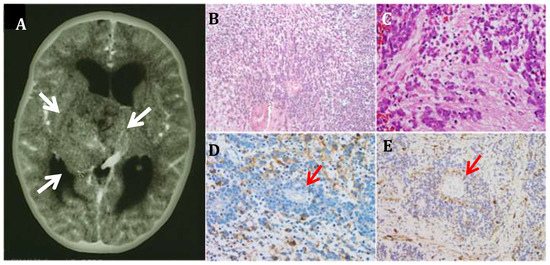
Figure 1.
Primary CNS-Neuroblastoma. (A) Computerized Tomography image of a primary CNS-NB shows a large heterogeneous well-circumscribed lesion (arrows) measuring 5.7 × 5.2 × 4.8 cm, within the right thalamus (10×). (B,C). Histopathological examination shows islands of densely cellular poorly differentiated tumor cells, interspaced by sparsely cellular areas or finely fibrillary tissue. No mature neurons are identified (10× and 20× respectively). (D) Immunostain for neuron specific enolase (NSE) (20×); (E) Immunostain for synaptophysin (20×). Homer-Wright rosettes are frequent (red arrows).
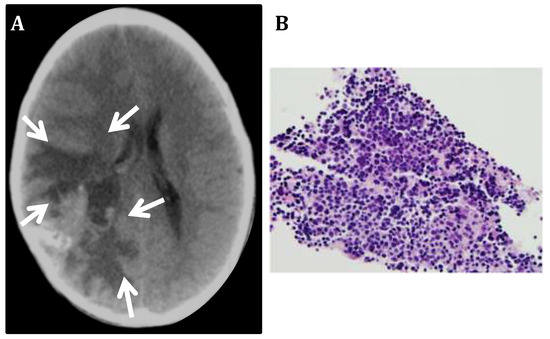
Figure 2.
Neuroblastoma metastatic to the CNS. (A) Computerized Tomography image of a metastatic NB shows a large poorly delimited mass in the right posterior frontoparietal region of the brain (arrows). (B) Biopsy of the metastatic tumor mass shows small poorly differentiated cells with hyperchromatic nucleus and scant cytoplasm.
3.2. PLK4 Expression in CNS-NB Samples Determined by qRT-PCR
Three housekeeping genes (GAPDH, HPRT and HMBS) were used for analysis. In each individual experiment using individual housekeeping genes, CNS-NB samples showed significantly elevated PLK4 expression levels when compared to non-embryonal brain tumors (LGG) (GAPDH p = 0.0016; HPRT1 p < 0.0001; HMBS p = 0.0116) (Figure 3A–C). Accordingly, normalization of expression values using GAPDH, HPRT and HMBS simultaneously [26,27,28] also showed significant overexpression of PLK4 in CNS-NB (FC: 15.05, p < 0.0001) (Figure 3D). Furthermore, in accordance with what we previously described, other embryonal brain tumor samples (ATRT and MB) also overexpressed PLK4 (p < 0.0001) (Figure 3E and Table 1).
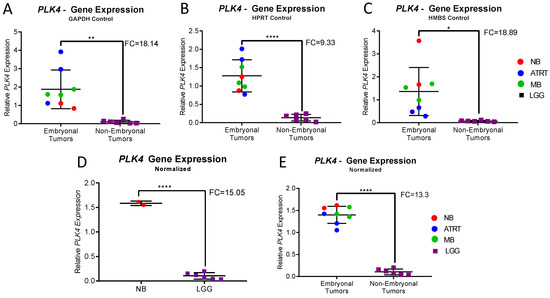
Figure 3.
qRT-PCR Expression Analysis of CNS-NB, ATRT, MB and LGG. (A–C) Relative PLK4 expression in CNS-NB, embryonal and non-embryonal pediatric brain tumors measured by qRT-PCR normalized to the endogenous controls GAPDH, HPRT and HMBS respectively, compared to LGG. (D) Relative PLK4 expression in CNS-NB when normalized to all three endogenous controls compared to LGG. (E) Relative PLK4 expression in embryonal tumors compared to non-embryonal tumors, normalized to all three endogenous controls. Fold changes and p-values were compared to non-embryonal pediatric brain tumors (unpaired t-tests, * p < 0.1, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001).

Table 1.
Relative PLK4 expression in NB, ATRT, MB and LGG. Relative PLK4 expression measured by qRT-PCR, calculated against 3 different endogenous controls individually and normalized together.
3.3. Gene Expression Meta-Analysis
Because CNS-NB is a rare entity [39,40] and due to the limited number of samples available for molecular analysis, we performed an extensive multi-platform transcriptomic meta-analysis compiling publicly available gene expression data to validate the results observed in our patients’ tumors. For this, we compared embryonal CNS tumors to non-embryonal CNS tumors represented by low grade gliomas (LGG), which is the most common form of primary CNS tumor arising in both children and adults [29,30].
The analysis of transcriptomic data from 51 normal tissue types represented in the GTEx Portal database (n = 11,688) and all NB and LGG tumor samples from the TARGET and the TCGA databases (n = 153 and 508 respectively) demonstrated that PLK4 expression was low in almost all tissues, with 75% of them expressing ≤1.3 TPM (transcripts per million). The highest PLK4 expression was observed in testis (23.7 TPM). NB showed significantly high PLK4 expression (14.0 TPM) while LGG showed 2.2 TPM (p < 0.0001, unpaired t-test) (Figure 4, Table 2 and Table 3).
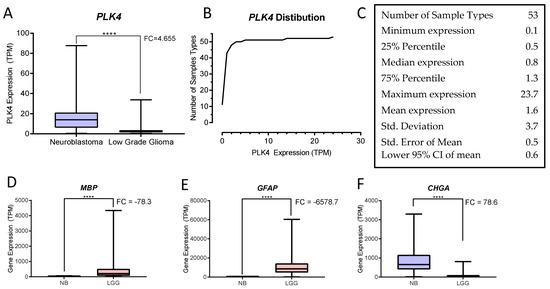
Figure 4.
GDC Expression Analysis of NB and LGG. (A) PLK4 expression in NB and LGG shows significant overexpression in neuroblastoma (NB) when compared with low grade gliomas (LGG) (**** p < 0.0001, unpaired t-test). (B) Relative frequency distribution of PLK4 expression among samples described in Table 2: NB (TARGET n = 153), LGG (TCGA n = 508) and 51 normal human tissue sample types (GTEx Portal). (C) Descriptive statistics of PLK4 expression in the cohort of tissue sample types (GraphPad). (D,E) The glioma markers MBP and GFAP respectively, show significant overexpression in LGG compared to NB (**** p < 0.0001, unpaired t-test). (F) The NB maker CHGA, shows overexpression in NB compared to LGG (**** p < 0.0001, unpaired t-test). All graphs were generated and statistics calculated using PRISM (GraphPad Software, Inc.).

Table 2.
GDC and GTEx Portal Gene Expression Data. RNAseqV2 data extracted from the GDC database (Neuroblastoma and Low Grade Glioma) and GTEx Portal (51 normal human tissue samples). Genes displayed are: PLK4 (Polo-like kinase 4), CHGA (Chromogranin A), MBP (Myelin basic protein) and GFAP (Glial fibrillary acidic protein). Expression is represented as median TPM (Transcripts per million) values.

Table 3.
Expression of PLK4, CHGA, MBP and GFAP obtained from the GDC. Genes displayed are: PLK4 (polo-like kinase 4), CHGA (chromogranin A), MBP (myelin basic protein) and GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein). Expression is represented as average TPM (Transcripts per million) values. Statistics were calculated in PRISM (unpaired t-test; p < 0.0001).
4. Discussion and Literature Review
Primary CNS-NB is a rare malignant embryonal tumor that can arise intracerebrally, intraorbitally or intraspinally [41]. Although it can be found in adults, it most often occurs within the first 5 years of life [39]. CNS-NB is a controversial entity which diagnostic classification has undergone a number of changes since the first publication of the WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System in 1979 where primary NB of the CNS was classified as a “poorly differentiated neuronal tumor” [42]. In the second edition, published in 1993, CNS-NB was classified for the first time as an “embryonal tumor”, which is the designation that persists today [37]. In 2000, CNS-NB was subclassified as an embryonal tumor of the “supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumor” (sPNET) subgroup [38]. The WHO’s fourth edition classification in 2007 changed the terminology of sPNET to CNS-PNET and primary NB of the CNS was then classified as “CNS-NB” [43]. In the WHO’s most recent classification published in 2016, the categorization of embryonal tumors underwent extensive changes. The term primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) was eliminated from the diagnostic terminology and a category of CNS embryonal tumor “not otherwise specified”, that includes tumors previously designated as CNS-PNET was created. Currently, CNS-NB is again classified as a singular entity under the umbrella of embryonal tumors [44]. Recently, extensive CNS-NB molecular data has been published. In a large study, 323 tumor samples diagnosed as CNS-PNET were subjected to histological examination, DNA methylation profiling, Affymetrix GeneChip Array and next-generation DNA and RNA sequencing analyses. Within the CNS-PNET samples, 44 CNS-NB samples were found to overexpress FOXR2 and thus categorized as “CNS NB-FOXR2” [45]. Interestingly, FOXR1 has been previously found to be overexpressed in peripheral neuroblastoma [45] and PHOX2B mutations have been recently described in NB as a potential target for therapy [46,47].
Metastases of NB to the CNS are very rare, comprising less than 10% of all cases of metastatic NB [15]. These are often osseous involving the calvarium, orbit or skull base, while primary CNS-NB commonly originate intraparenchymally spreading to the leptomeninges and subarachnoid space [48]. NB metastatic to the CNS is most commonly found within the first 18 months of age after the initial diagnosis and increased MYCN amplification has been reported in these recurrent tumors [41,49]. A recent meta-analysis combining profiles of NB from 761 patients with MYCN amplification, identified enrichment of the members of the P13K family of kinases as biomarkers of MYCN amplification and suggested that P13K inhibitors may represent a new therapeutic opportunity for MYCN-amplified NB [50].
To date, there is no established protocol for treating primary CNS-NB, references [4,51] with treatment approaches varying from palliative care to aggressive multimodality therapies. Surgery, craniospinal radiotherapy and chemotherapy have led to increased median survival, however, NB metastatic to CNS are almost universally lethal [52]. The heterogeneous nature of NB leads to diverse clinical presentations [53]. Depending on the location of the primary tumor and metastases, as well as histology and genomic data, treatment regimens range from observation of low-risk patients, to multimodal approaches in high risk patients [5]. Due to the lack of adequate drugs with sufficient brain-blood-barrier penetrance, the CNS is considered a “safe haven” for many cancer types, making both primary and metastatic CNS-NB difficult to treat and therefore, classified as high risk [52,54]. Treatments for both metastatic and primary CNS-NB begin with surgical resection, as much as possible. After surgery, a combination of chemotherapeutic agents is used, followed by craniospinal radiation and additional chemotherapy [52]. More recently GD2-targeted immunotherapy has been found to improve progression-free survival in NB metastatic to the CNS [54,55]. Stem cell implantation has been used with immunotherapy, but has not led to significantly increased survival [55].
We previously demonstrated PLK4 overexpression in pediatric embryonal brain tumors and suggested its potential as a therapeutic target for these tumors. Furthermore, it has been recently demonstrated that PLK4 is upregulated and negatively correlated with clinical outcome in peripheral NB [6]. While promising treatments for NB [54] have led to an increase in survival rates, both primary and metastatic CNS-NB have proven more difficult to treat than peripheral NB, leading to significantly decreased survival rates [4,56]. Here, we show that PLK4 was overexpressed in CNS-NB both primary and metastatic to the CNS and validate these findings by performing a multi-platform transcriptomic meta-analysis of PLK4 in normal and tumor tissue.
The Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) is a member of the polo-like family of serine/threonine protein kinases that shares little homology with the other members. While PLK1-3 have two structural polo-box domains, PLK4’s second domain has been replaced with a crypto polo-box domain [15]. PLK4 is involved in cell cycle regulation and is localized to the centrosome during cell division, where it plays a major role in centriole duplication. PLK4 overexpression results in centrosome amplification, which has been found to cause genetic instability and spontaneous tumorigenesis [18,57]. PLK4 expression levels are tightly regulated by an auto-regulatory feedback loop in which PLK4 autophosphorylates its own phosphodegron, marking it for proteasomally mediated degredation [58]. This tight control maintains its expression low [59] and therefore preventing centriole over-duplication [60]. In recent years, PLK4 is becoming a subject of interest for the treatment of multiple types of adult peripheral tumors.
Although we were the first to identify PLK4 as a potential therapeutic target for pediatric embryonal tumors [7,10], PLK4 overexpression has also been described in adult peripheral tumors such as colorectal [20], breast [21], lung [22], melanoma [23], pancreatic cancer [25] and leukemia [24]. In fact, PLK4 inhibition using the small molecule CFI-400945 (CAS#1338800-06-8) [12,13,61] is currently in clinical trial for advanced solid tumors in adults (NCT01954316).
PLK4 substrates are mainly involved in cell cycle progression. PLK4 mediated phosphorylation of the centriolar assembly protein STIL, recruits STIL to site of the pre-procentriole and facilitates its interaction with Sas6 [62], which together, form the centriolar cartwheel, a complex essential to proper centriole duplication [63]. PLK4 is also involved in the regulation of centriole assembly through its direct phosphorylation of CP110, a coiled-coil protein controlling centriole length [64]. PLK4 has been found to be implicated in the localization and stabilization of the cleavage furrow through its interactions with Ect2, a Rho GEF, which activates RhoA [16]. Other notable cell cycle related PLK4 substrates include CDC25c [65], FBXW5 [66] and AURKA [67].
5. Conclusions
Our previous findings together with the findings of the present study highlight the prevalence of PLK4 overexpression in embryonal tumors and suggest the potential of PLK4 as a new target for therapeutic intervention. Although we recognize that the number of cases in this study is small, the rarity of CNS-NB, the consistency of the results corroborated by extensive meta-analysis, the novelty and the translational potential of PLK4 as a biomarker and/or a therapeutic target is suitable for further investigation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.T.S., A.W.B., A.S. and T.T.; Study design, experiments and analyses: S.T.S., A.W.B., A.S., S.L.R. and S.G.; Pathology and image: S.T.S., P.M.C. and T.P.; Manuscript writing: S.T.S., A.W.B. and A.S.; Manuscript review and approval: S.T.S., A.W.B., A.S., P.M.C., T.P., S.L.R., S.G., and T.T.
Funding
Voices Against Brain Cancer, Musella Foundation for Cancer Research and Information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ramaswamy, V.; Taylor, M.D. Medulloblastoma: From myth to molecular. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sredni, S.T.; Tomita, T. Rhabdoid tumor predisposition syndrome. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2015, 18, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, M.U.; Ahmad, Z.; Minhas, M.K.; Memon, A.; Mushtaq, N.; Hawkins, C. Embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes, c19mc-altered: Report of an extremely rare malignant pediatric central nervous system neoplasm. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 2050313X17745208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, F.; Tamburrini, G.; Gessi, M.; Frassanito, P.; Massimi, L.; Caldarelli, M. Central nervous system (cns) neuroblastoma. A case-based update. Child. Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, J.M.; Hogarty, M.D.; Bagatell, R.; Cohn, S.L. Neuroblastoma. Lancet (London, England) 2007, 369, 2106–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhou, D.; Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhong, B.; Cao, Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Polo-like kinase 4 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in neuroblastoma via pi3k/akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sredni, S.T.; Suzuki, M.; Yang, J.P.; Topczewski, J.; Bailey, A.W.; Gokirmak, T.; Gross, J.N.; de Andrade, A.; Kondo, A.; Piper, D.R.; et al. A functional screening of the kinome identifies the polo-like kinase 4 as a potential therapeutic target for malignant rhabdoid tumors, and possibly, other embryonal tumors of the brain. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Davies, K.P.; Allen, J.; Zhu, L.; Pestell, R.G.; Zagzag, D.; Kalpana, G.V. Cell cycle arrest and repression of cyclin d1 transcription by ini1/hsnf5. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5975–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, P.; Belin, M.F.; Delattre, O. The tumour suppressor hsnf5/ini1 controls the differentiation potential of malignant rhabdoid cells. Eur. J. Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990) 2006, 42, 2326–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sredni, S.T.; Bailey, A.W.; Suri, A.; Hashizume, R.; He, X.; Louis, N.; Gokirmak, T.; Piper, D.R.; Watterson, D.M.; Tomita, T. Inhibition of polo-like kinase 4 (plk4): A new therapeutic option for rhabdoid tumors and pediatric medulloblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 111190–111212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sredni, S.T.; Tomita, T. The polo-like kinase 4 gene (plk4) is overexpressed in pediatric medulloblastoma. Child. Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, P.B.; Liu, Y.; Forrest, B.; Cumming, G.; Li, S.W.; Patel, N.K.; Edwards, L.; Laufer, R.; Feher, M.; Ban, F.; et al. The discovery of polo-like kinase 4 inhibitors: Identification of (1r,2s).2-(3-((e).4-(((cis).2,6-dimethylmorpholino)methyl)styryl). 1h.Indazol-6-yl)-5’-methoxyspiro[cyclopropane-1,3’-indolin]-2’-one (cfi-400945) as a potent, orally active antitumor agent. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, J.M.; Lin, D.C.; Wei, X.; Che, Y.; Yao, Y.; Kiarash, R.; Cescon, D.W.; Fletcher, G.C.; Awrey, D.E.; Bray, M.R.; et al. Functional characterization of cfi-400945, a polo-like kinase 4 inhibitor, as a potential anticancer agent. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Yu, Z.; Qi, P.P.; Yu, D.Q.; Liu, H.M. Discovery of orally active anticancer candidate cfi-400945 derived from biologically promising spirooxindoles: Success and challenges. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 95, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillibourne, J.E.; Bornens, M. Polo-like kinase 4: The odd one out of the family. Cell Division 2010, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, C.O.; Kazazian, K.; Zih, F.S.; Brashavitskaya, O.; Haffani, Y.; Xu, R.S.; George, A.; Dennis, J.W.; Swallow, C.J. A novel role for plk4 in regulating cell spreading and motility. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3441–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettencourt-Dias, M.; Rodrigues-Martins, A.; Carpenter, L.; Riparbelli, M.; Lehmann, L.; Gatt, M.K.; Carmo, N.; Balloux, F.; Callaini, G.; Glover, D.M. Sak/plk4 is required for centriole duplication and flagella development. Curr. Biol. CB 2005, 15, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.S.; Bakker, B.; Boeckx, B.; Moyett, J.; Lu, J.; Vitre, B.; Spierings, D.C.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Cleveland, D.W.; Lambrechts, D.; et al. Centrosome amplification is sufficient to promote spontaneous tumorigenesis in mammals. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinmura, K.; Kurabe, N.; Goto, M.; Yamada, H.; Natsume, H.; Konno, H.; Sugimura, H. Plk4 overexpression and its effect on centrosome regulation and chromosome stability in human gastric cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 6635–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macmillan, J.C.; Hudson, J.W.; Bull, S.; Dennis, J.W.; Swallow, C.J. Comparative expression of the mitotic regulators sak and plk in colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marina, M.; Saavedra, H.I. Nek2 and plk4: Prognostic markers, drivers of breast tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Edition) 2014, 19, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Mustachio, L.M.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Mino, B.; Kurie, J.M.; Roszik, J.; Villalobos, P.A.; Thu, K.L.; et al. Polo-like kinase 4 inhibition produces polyploidy and apoptotic death of lung cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denu, R.A.; Shabbir, M.; Nihal, M.; Singh, C.K.; Longley, B.J.; Burkard, M.E.; Ahmad, N. Centriole overduplication is the predominant mechanism leading to centrosome amplification in melanoma. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2018, 16, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goroshchuk, O.; Kolosenko, I.; Vidarsdottir, L.; Azimi, A.; Palm-Apergi, C. Polo-like kinases and acute leukemia. Oncogene 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, I.; Mason, J.; Cao, P.M.; Pintilie, M.; Bray, M.; Hedley, D.W. Activity of the novel polo-like kinase 4 inhibitor cfi-400945 in pancreatic cancer patient-derived xenografts. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3064–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative rt-pcr data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, Research0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, F.; Kulle, B.; Schwager, S.; Gunawan, B.; von Heydebreck, A.; Sultmann, H.; Fuzesi, L. Equivalence test in quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction: Confirmation of reference genes suitable for normalization. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 335, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, V.; Teixeira, S.A.; Neder, L.; Okamoto, O.K.; Oba-Shinjo, S.M.; Marie, S.K.; Scrideli, C.A.; Paco-Larson, M.L.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr. Selection of suitable housekeeping genes for expression analysis in glioblastoma using quantitative rt-pcr. Ann. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodenberger, M.L.; Jenkins, R.B. Genetics of adult glioma. Cancer Genet. 2012, 205, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, R.J.; Pfister, S.; Bouffet, E.; Avery, R.; Bandopadhayay, P.; Bornhorst, M.; Bowers, D.C.; Ellison, D.; Fangusaro, J.; Foreman, N.; et al. Pediatric low-grade gliomas: Implications of the biologic era. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 19, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgantzi, K.; Sköldenberg, E.G.; Stridsberg, M.; Kogner, P.; Jakobson, Å.; Janson, E.T.; Christofferson, R.H.B. Chromogranin a and neuron-specific enolase in neuroblastoma: Correlation to stage and prognostic factors. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 35, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popko, B.; Pearl, D.K.; Walker, D.M.; Comas, T.C.; Baerwald, K.D.; Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Yates, A.J. Molecular markers that identify human astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hol, E.M.; Pekny, M. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (gfap) and the astrocyte intermediate filament system in diseases of the central nervous system. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, G.T.; Aguet, F.; Brown, A.A.; Castel, S.E.; Davis, J.R.; He, Y.; Jo, B.; Mohammadi, P.; Park, Y.; Parsana, P.; et al. Genetic effects on gene expression across human tissues. Nature 2017, 550, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, S.; White, M.W.; Schroeder, A.M.; DeLuca, N.V.; Leszczynski, A.L.; Raimondi, S.L. Aberrant dnmt3b7 expression correlates to tissue type, stage, and survival across cancers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loir, P. Models for transcript quantification for rna-seq. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1104.3889. [Google Scholar]
- Kleihues, P.; Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W. The new who classification of brain tumours. Brain Pathol. (Zurich, Switzerland) 1993, 3, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleihues, P.; Louis, D.N.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Rorke, L.B.; Reifenberger, G.; Burger, P.C.; Cavenee, W.K. The who classification of tumors of the nervous system. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horten, B.C.; Rubinstein, L.J. Primary cerebral neuroblastoma. A clinicopathological study of 35 cases. Brain A J. Neurol. 1976, 99, 735–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etus, V.; Kurtkaya, O.; Sav, A.; Ilbay, K.; Ceylan, S. Primary cerebral neuroblastoma: A case report and review. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2002, 197, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latchaw, R.E.; L’Heureux, P.R.; Young, G.; Priest, J.R. Neuroblastoma presenting as central nervous system disease. AJNR. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1982, 3, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zulch, K.J. Principles of the new world health organization (who) classification of brain tumors. Neuroradiology 1980, 19, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 who classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 world health organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, D.; Orr, B.A.; Toprak, U.H.; Hovestadt, V.; Jones, D.T.W.; Capper, D.; Sill, M.; Buchhalter, I.; Northcott, P.A.; Leis, I.; et al. New brain tumor entities emerge from molecular classification of cns-pnets. Cell 2016, 164, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrescu, S.; Paulson, V.; Dubuc, A.; Ligon, A.; Lidov, H.G. Phox2b is a reliable immunomarker in distinguishing peripheral neuroblastic tumours from cns embryonal tumours. Histopathology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardani, S.; Di Lascio, S.; Belperio, D.; Di Biase, E.; Ceccherini, I.; Benfante, R.; Fornasari, D. Desogestrel down-regulates phox2b and its target genes in progesterone responsive neuroblastoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, R.A.; Bilaniuk, L.T. Ct of primary and secondary craniocerebral neuroblastoma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1980, 135, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, K.K.; Brisse, H.; Couanet, D.; Couturier, J.; Benard, J.; Mosseri, V.; Edeline, V.; Lumbroso, J.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Michon, J. Central nervous system metastases in neuroblastoma: Radiologic, clinical, and biologic features in 23 patients. Cancer 2003, 98, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, I.; Suntsova, M.; Ilnitskaya, E.; Roumiantsev, S.; Sorokin, M.; Garazha, A.; Spirin, P.; Lebedev, T.; Gaifullin, N.; Larin, S.; et al. Gene expression and molecular pathway activation signatures of mycn-amplified neuroblastomas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83768–83780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Beniwal, M.; Nandeesh, B.N.; Srinivas, D.; Somanna, S. Primary pediatric intracranial neuroblastoma: A report of two cases. J Pediatr. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kramer, K.; Kushner, B.; Heller, G.; Cheung, N.K. Neuroblastoma metastatic to the central nervous system. The memorial sloan-kettering cancer center experience and a literature review. Cancer 2001, 91, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodenko, I.V.; Kalinovsky, D.V.; Doronin, I.I.; Deyev, S.M.; Kholodenko, R.V. Neuroblastoma origin and therapeutic targets for immunotherapy. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 7394268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, K.K.; Maris, J.M.; Schleiermacher, G.; Nakagawara, A.; Mackall, C.L.; Diller, L.; Weiss, W.A. Neuroblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, B.H.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Cheung, I.Y.; Kuk, D.; Kramer, K.; Modak, S.; Yataghene, K.; Cheung, N.-K.V. Prolonged progression-free survival after consolidating second or later remissions of neuroblastoma with anti-gd2 immunotherapy and isotretinoin: A prospective phase ii study. OncoImmunology 2015, 4, e1016704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, K.; Kushner, B.H.; Modak, S.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Smith-Jones, P.; Zanzonico, P.; Humm, J.L.; Xu, H.; Wolden, S.L.; Souweidane, M.M.; et al. Compartmental intrathecal radioimmunotherapy: Results for treatment for metastatic cns neuroblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2010, 97, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, M.A.; Rosario, C.O.; Hudson, J.W.; Kulkarni, S.; Pollett, A.; Dennis, J.W.; Swallow, C.J. Plk4 haploinsufficiency causes mitotic infidelity and carcinogenesis. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, A.J.; Lan, W.; Niessen, S.; Hoover, H.; Cleveland, D.W. Polo-like kinase 4 kinase activity limits centrosome overduplication by autoregulating its own stability. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fode, C.; Binkert, C.; Dennis, J.W. Constitutive expression of murine sak-a suppresses cell growth and induces multinucleation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 4665–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillibourne, J.E.; Tack, F.; Vloemans, N.; Boeckx, A.; Thambirajah, S.; Bonnet, P.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Bornens, M.; Grand-Perret, T. Autophosphorylation of polo-like kinase 4 and its role in centriole duplication. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, P.B.; Liu, Y.; Patel, N.K.; Feher, M.; Forrest, B.; Li, S.W.; Edwards, L.; Laufer, R.; Lang, Y.; Ban, F.; et al. The discovery of polo-like kinase 4 inhibitors: Design and optimization of spiro[cyclopropane-1,3’[3h]indol]-2’(1’h).Ones as orally bioavailable antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzhindzhev, N.S.; Tzolovsky, G.; Lipinszki, Z.; Abdelaziz, M.; Debski, J.; Dadlez, M.; Glover, D.M. Two-step phosphorylation of ana2 by plk4 is required for the sequential loading of ana2 and sas6 to initiate procentriole formation. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; O’Rourke, B.P.; Soni, R.K.; Jallepalli, P.V.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Tsou, M.B. Promotion and suppression of centriole duplication are catalytically coupled through plk4 to ensure centriole homeostasis. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Seo, M.Y.; Chang, J.; Hwang, D.S.; Rhee, K. Plk4 phosphorylation of cp110 is required for efficient centriole assembly. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonni, S.; Ganuelas, M.L.; Petrinac, S.; Hudson, J.W. Human plk4 phosphorylates cdc25c. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puklowski, A.; Homsi, Y.; Keller, D.; May, M.; Chauhan, S.; Kossatz, U.; Grunwald, V.; Kubicka, S.; Pich, A.; Manns, M.P.; et al. The scf-fbxw5 e3-ubiquitin ligase is regulated by plk4 and targets hssas-6 to control centrosome duplication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bury, L.; Coelho, P.A.; Simeone, A.; Ferries, S.; Eyers, C.E.; Eyers, P.A.; Zernicka-Goetz, M.; Glover, D.M. Plk4 and aurora a cooperate in the initiation of acentriolar spindle assembly in mammalian oocytes. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3571–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).