Evaluation of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System in the Classification of Lesions in Breast Strain Elastography Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
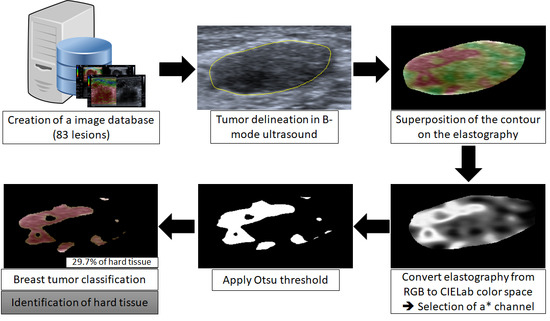
2.1. Image Database
2.2. Delimitation of the Lesion
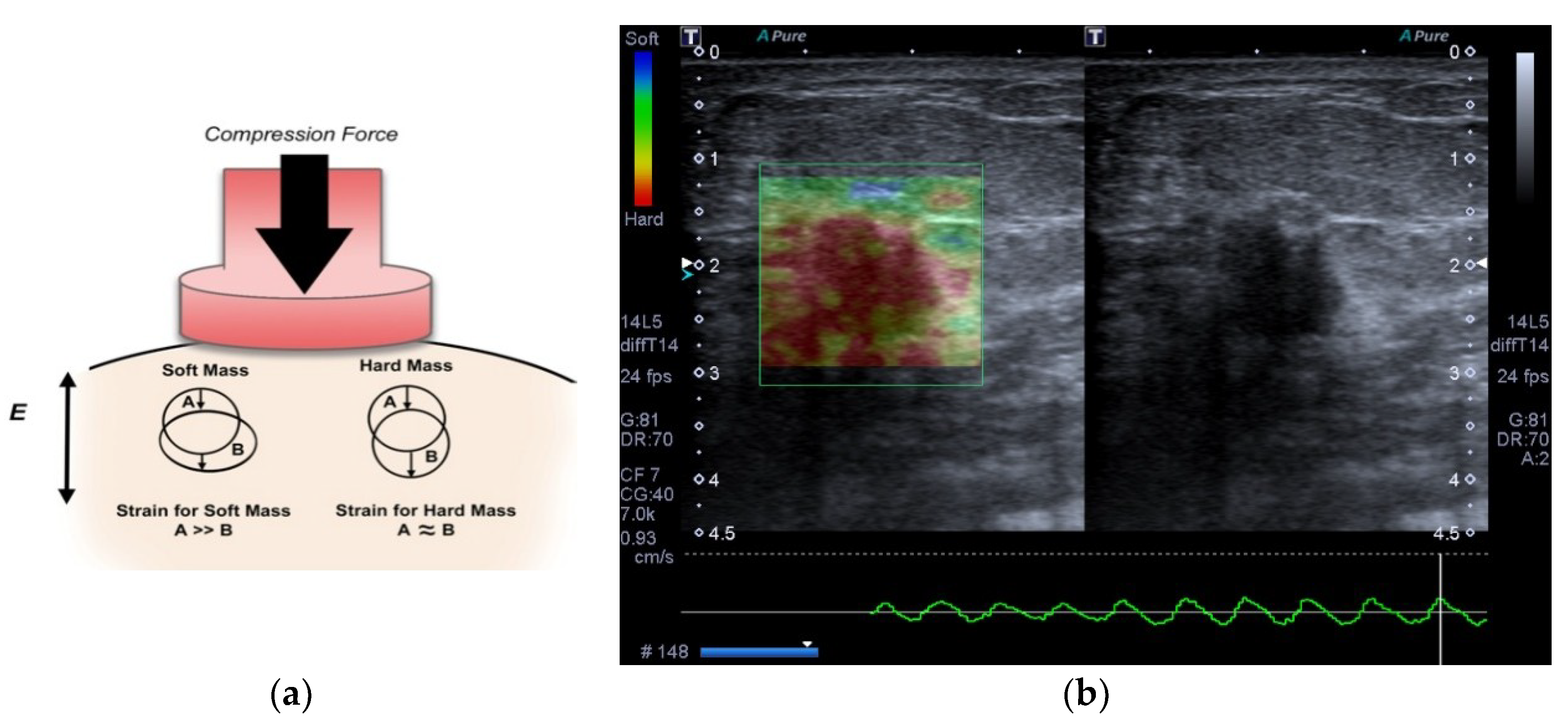
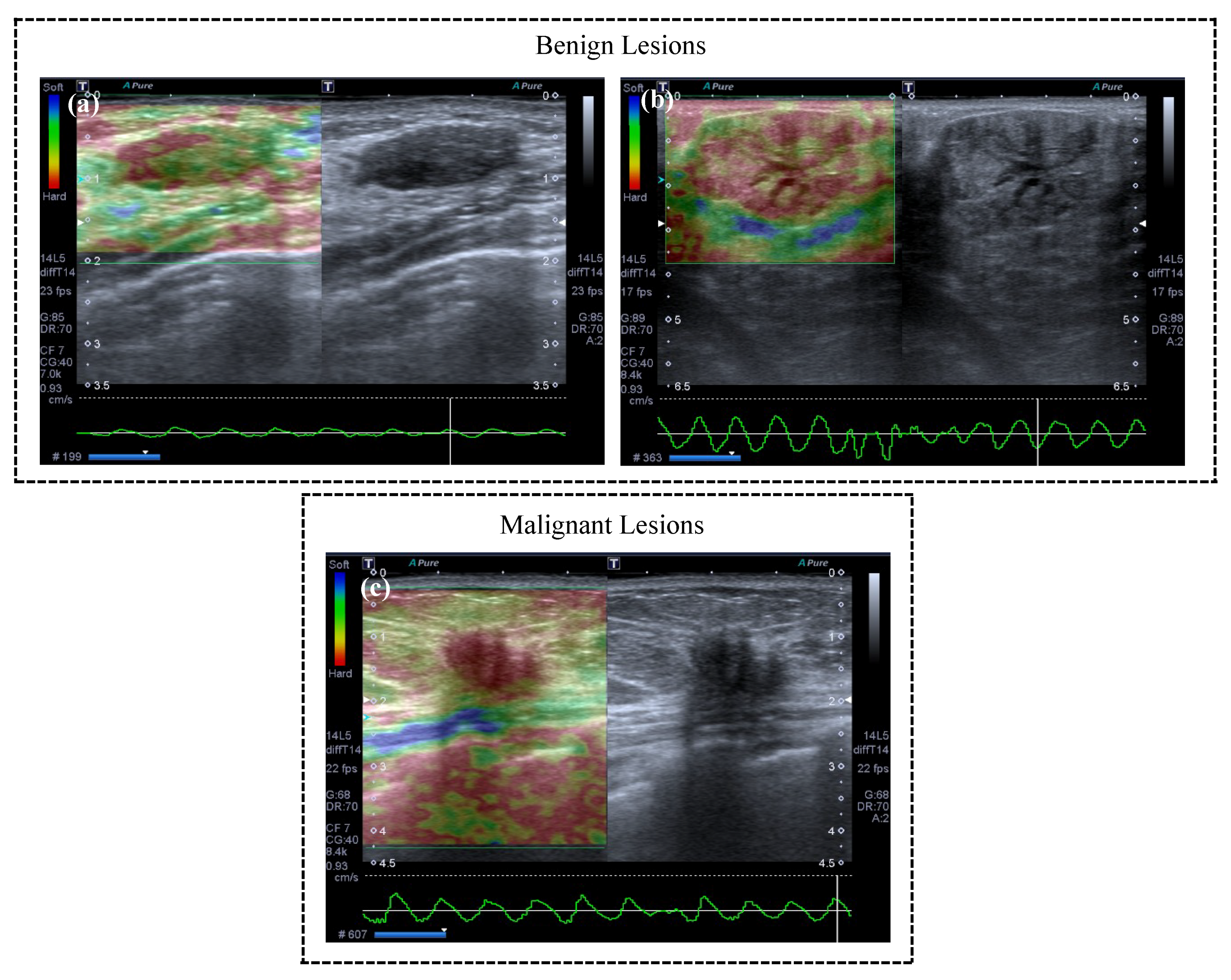
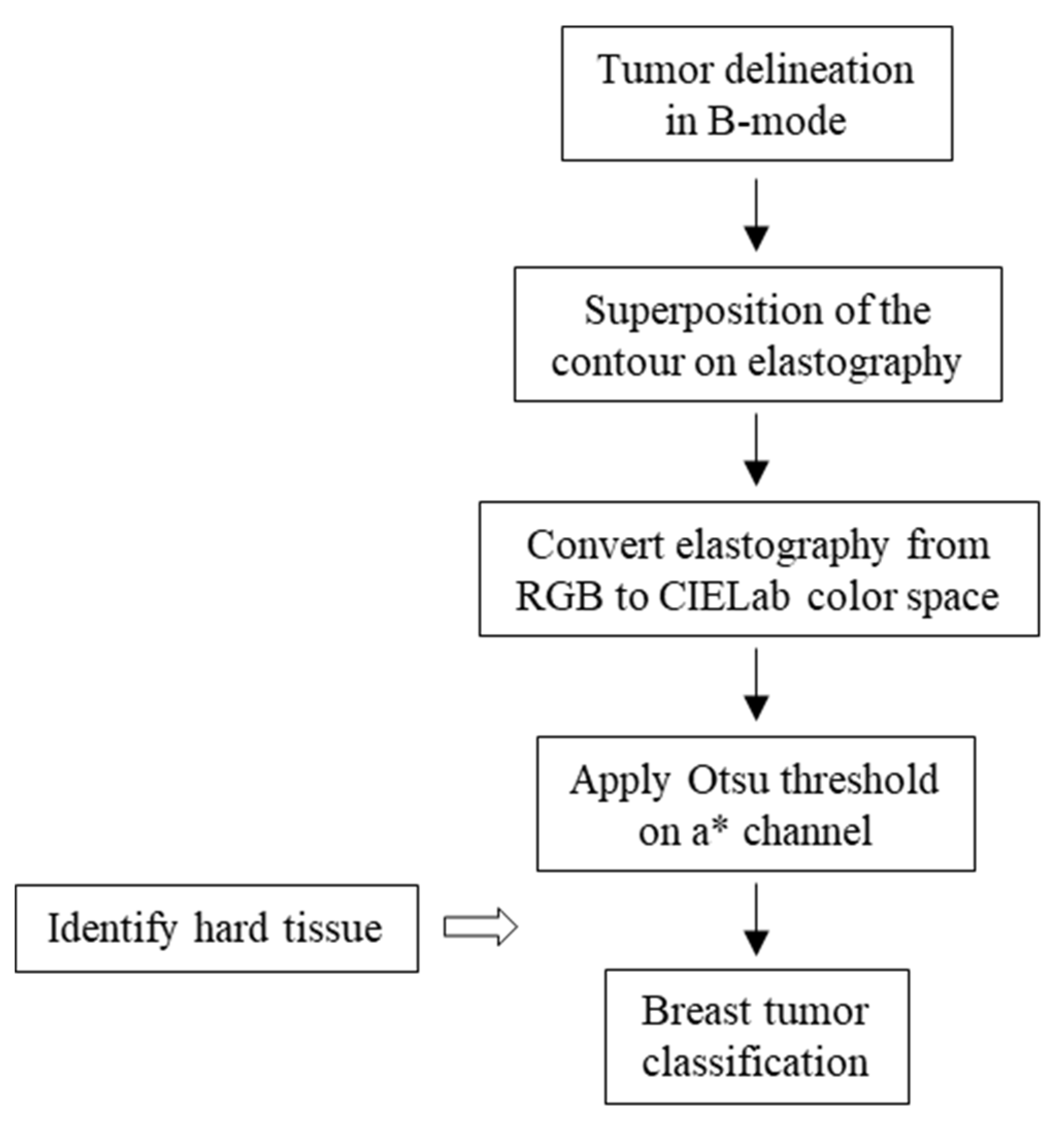
2.3. Classification
2.4. Data Evaluation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Manual Delineation
3.2. Classification Evaluation
3.3. Statistics Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shan, J.; Alam, S.K.; Garra, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ahmed, T. Computer-Aided Diagnosis for Breast Ultrasound Using Computerized BI-RADS Features and Machine Learning Methods. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, P.; Maggini, E.; Mancuso, E.; Lodise, P.; Cantisani, V.; Catalano, C. Clinical application of breast elastography: State of the art. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q. Breast ultrasound image segmentation: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekeh, A.P.; Alleyne, R.S.; Duncan, A.O. Role of mammography in diagnosis of breast cancer in an inner-city hospital. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2000, 92, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stavros, A.T.; Thickman, D.; Rapp, C.L.; Dennis, M.A.; Parker, S.H.; Sisney, G.A. Solid breast nodules: Use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions. Radiology 1995, 196, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, M.; Shi, D. Ultrasound elastography in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant cervical lesions. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, F.M. Role of supersonic shear wave imaging quantitative elastography (SSI) in differentiating benign and malignant solid breast masses. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2013, 44, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, E.-K.; Moon, H.J.; Kwak, J.Y.; Kim, M.J. Interobserver Variability of Ultrasound Elastography: How It Affects the Diagnosis of Breast Lesions. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R.G. Breast Elastography; Thieme Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Balleyguier, C.; Canale, S.; Hassen, W.B.; Vielh, P.; Bayou, E.H.; Mathieu, M.C.; Uzan, C.; Bourgier, C.; Dromain, C. Breast elasticity: Principles, technique, results: An update and overview of commercially available software. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zippel, D.; Shalmon, A.; Rundstein, A.; Novikov, I.; Yosepovich, A.; Zbar, A.; Goitein, D.; Sklair-Levy, M. Freehand Elastography for Determination of Breast Cancer Size: Comparison With B-Mode Sonography and Histopathologic Measurement. J. Ultrasound Med. 2014, 33, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ophir, J. Elastography: A quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason. Imaging 1991, 13, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T. In vivo real-time freehand palpation imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.J.; Castellanos, N.P.; Pineda, C.; Hernandez, C.; Ventura, L.; Gutierrez, J. Algorithm to estimate the level of elasticity of biological tissue with ultrasound elastography images. In Proceedings of the 2015 Pan American Health Care Exchanges (PAHCE), Vina del Mar, Chile, 23–28 March 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Wen, Y.L.; Ou, B.; Luo, B.M.; Liang, B.L. Semi-quantitating Stiffness of Breast Solid Lesions in Ultrasonic Elastography. Acad. Radiol. 2008, 15, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Qiu, W.; Qian, M.; Wang, C.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, H. Computer-assisted assessment of ultrasound real-time elastography: Initial experience in 145 breast lesions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, E.F.C. The importance of breast elastography added to the BI-RADS(R) (5th edition) lexicon classification. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2015, 61, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, W.C.; Cheng, P.W.; Wang, C.T.; Liao, L.J. Real-time ultrasound elastography: An assessment of enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 2351–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Baek, J.H. Ultrasound elastography for evaluation of cervical lymph nodes. Ultrasonography 2015, 34, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, W.K.; Chang, S.C.; Chang, J.M.; Cho, N.; Huang, C.S.; Kuo, J.W.; Chang, R.F. Classification of Breast Tumors Using Elastographic and B-mode Features: Comparison of Automatic Selection of Representative Slice and Physician-Selected Slice of Images. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Qian, M.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, H. Quantitative analysis of peri-tumor tissue elasticity based on shear-wave elastography for breast tumor classification. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 518055, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.M.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, Y.W.; Huang, C.S.; Chang, R.F. Quantitative breast mass classification based on the integration of B-mode features and strain features in elastography. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 64, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, W.K.; Huang, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.-W.; Chang, S.-C.; Lo, C.-M.; Yang, M.-C.; Bae, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Chang, J.M.; Huang, C.-S.; et al. Computer-aided tumor diagnosis using shear wave breast elastography. Ultrasonics 2017, 78, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvan, S.; Shenbagadevi, S.; Suresh, S. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Breast Elastography and B-Mode Ultrasound. In Artificial Intelligence and Evolutionary Algorithms in Engineering Systems; Suresh, L.P., Dash, S.S., Panigrahi, B., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.M.; Chen, Y.P.; Chang, Y.C.; Lo, C.; Huang, C.S.; Chang, R.F. Computer-Aided Strain Evaluation for Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging of Breast Masses. Ultrason. Imaging 2014, 36, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, W.K.; Huang, C.S.; Shen, W.C.; Takada, E.; Chang, R.F.; Joe, J.; Nakajima, M.; Kobayashi, M. Analysis of Elastographic and B-mode Features at Sonoelastography for Breast Tumor Classification. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osher, S.; Sethian, J.A. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1988, 79, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.-F.; Shen, W.-C.; Yang, M.-C.; Moon, W.K.; Takada, E.; Ho, Y.-C.; Nakajima, M.; Kobayashi, M. Computer-aided diagnosis of breast color elastography. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2008: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Houston, TX, USA, 10–15 February 2018; Giger, M.L., Karssemeijer, N., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008; p. 691501. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Niu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, T.; Wang, C.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, H. Computer-aided diagnosis based on quantitative elastographic features with supersonic shear wave imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvan, S.; Kavitha, M.; Shenbagadevi, S.; Suresh, S. Feature Extraction for Characterization of Breast Lesions in Ultrasound Echography and Elastography. J. Comput. Sci. 2010, 6, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, E.F.C.; Fleury, J.C.V.; Piato, S.; Junior, D.R. New elastographic classification of breast lesions during and after compression. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 15, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, P.; Rajini, V.; Rajkumar, R.I. Segmentation and edge detection of color images using CIELAB Color Space and Edge detectors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Robotics and Communication Technologies, INTERACT-2010, Chennai, India, 3–5 December 2010; pp. 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldevbhai, P.J.; Anand, R.S. Color Image Segmentation for Medical Images using L*a*b* Color Space. J. Electron. Commun. Eng. 2012, 1, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcomini, K.D.; Fleury, E.F.C.; Schiabel, H.; Nishikawa, R.M. Proposal of semi-automatic classification of breast lesions for strain sonoelastography using a dedicated CAD system. In Breast Imaging, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop, IWDM 2016, Malmö, Sweden, 19–22 June 2016; Springer: New York, NY, USA; pp. 454–460. [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. Distribution comparée de la flore alpine dans quelques régions des Alpes occidentales et orientales. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1901, 37, 241–272. (In Franch) [Google Scholar]
- Pei, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, S. Segmentation of the Breast Region in Mammograms using Marker-controlled Watershed Transform. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 4–6 December 2010; pp. 2371–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orsi, C.; Sickles, E.; Mendelson, E.; Morris, E. Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System: ACR BI-RADS—Breast Imaging Atlas, 5th ed.; American College of Radology: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
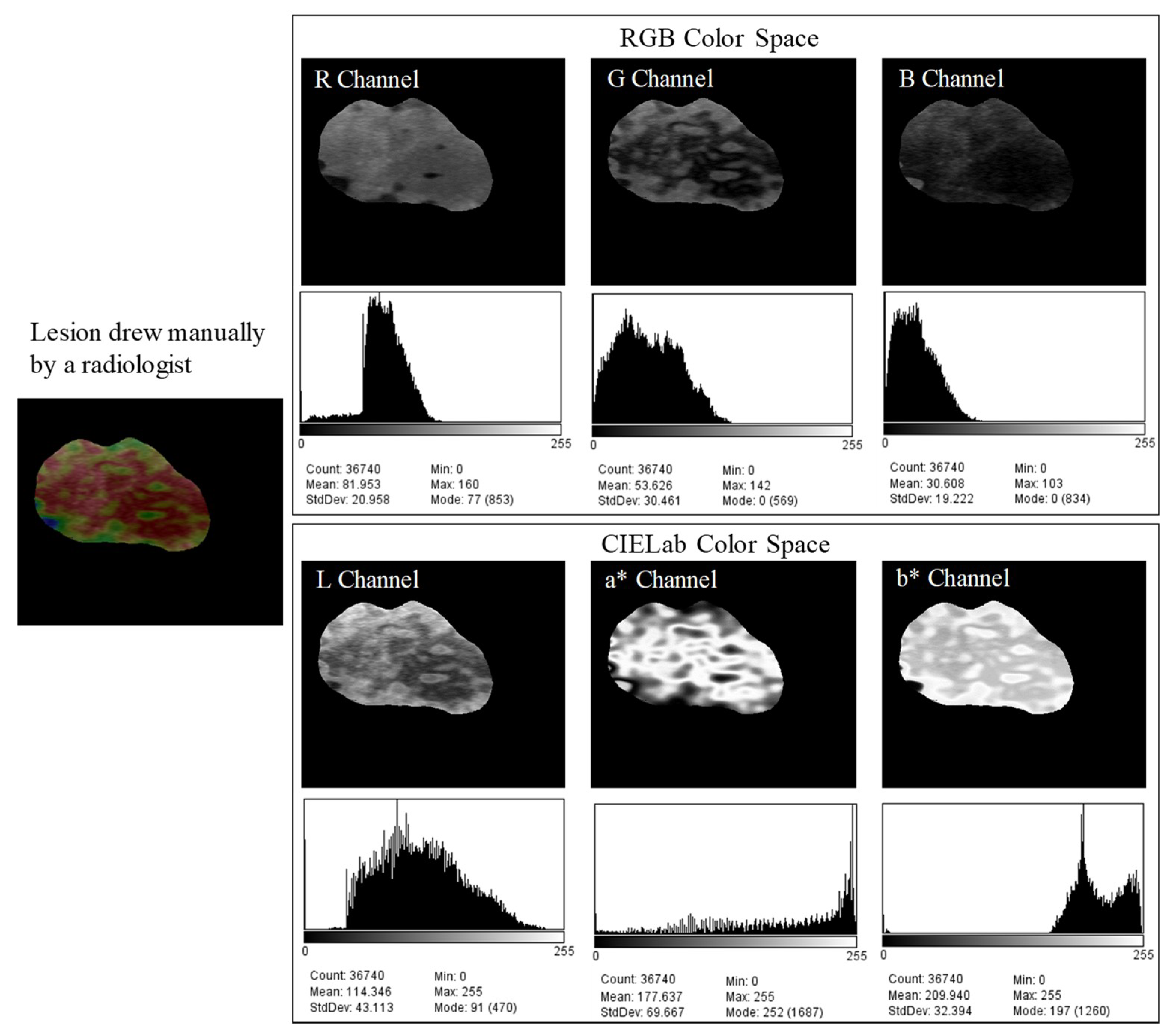
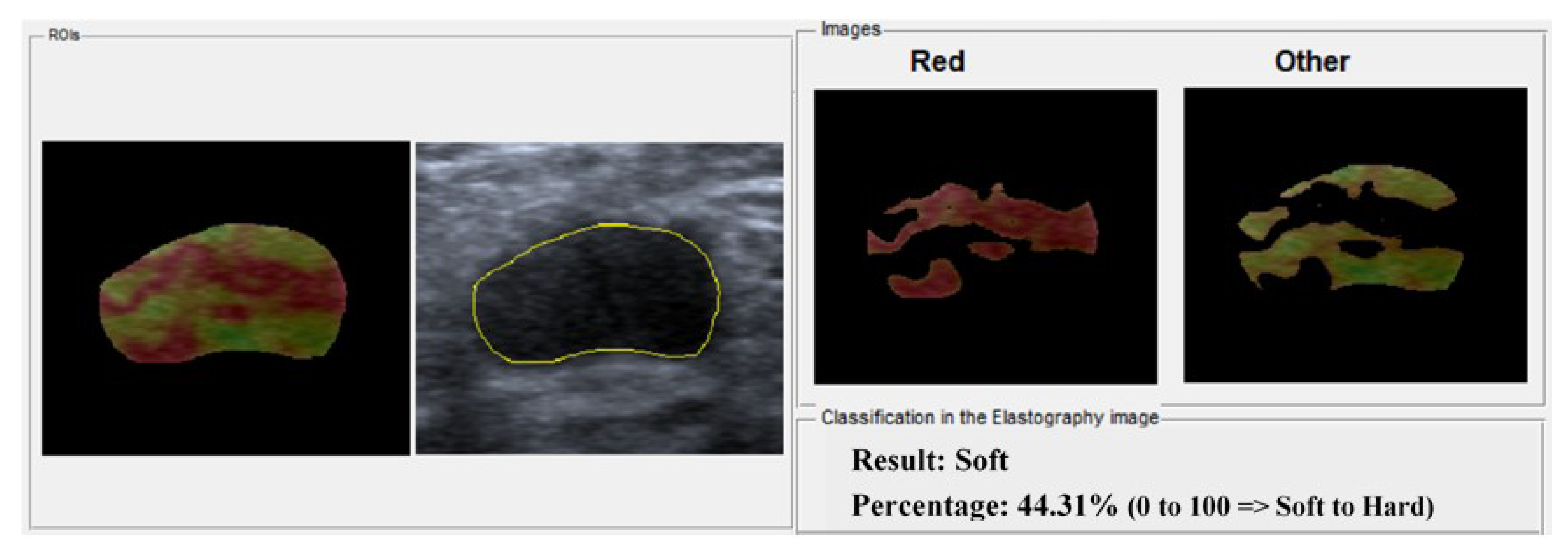
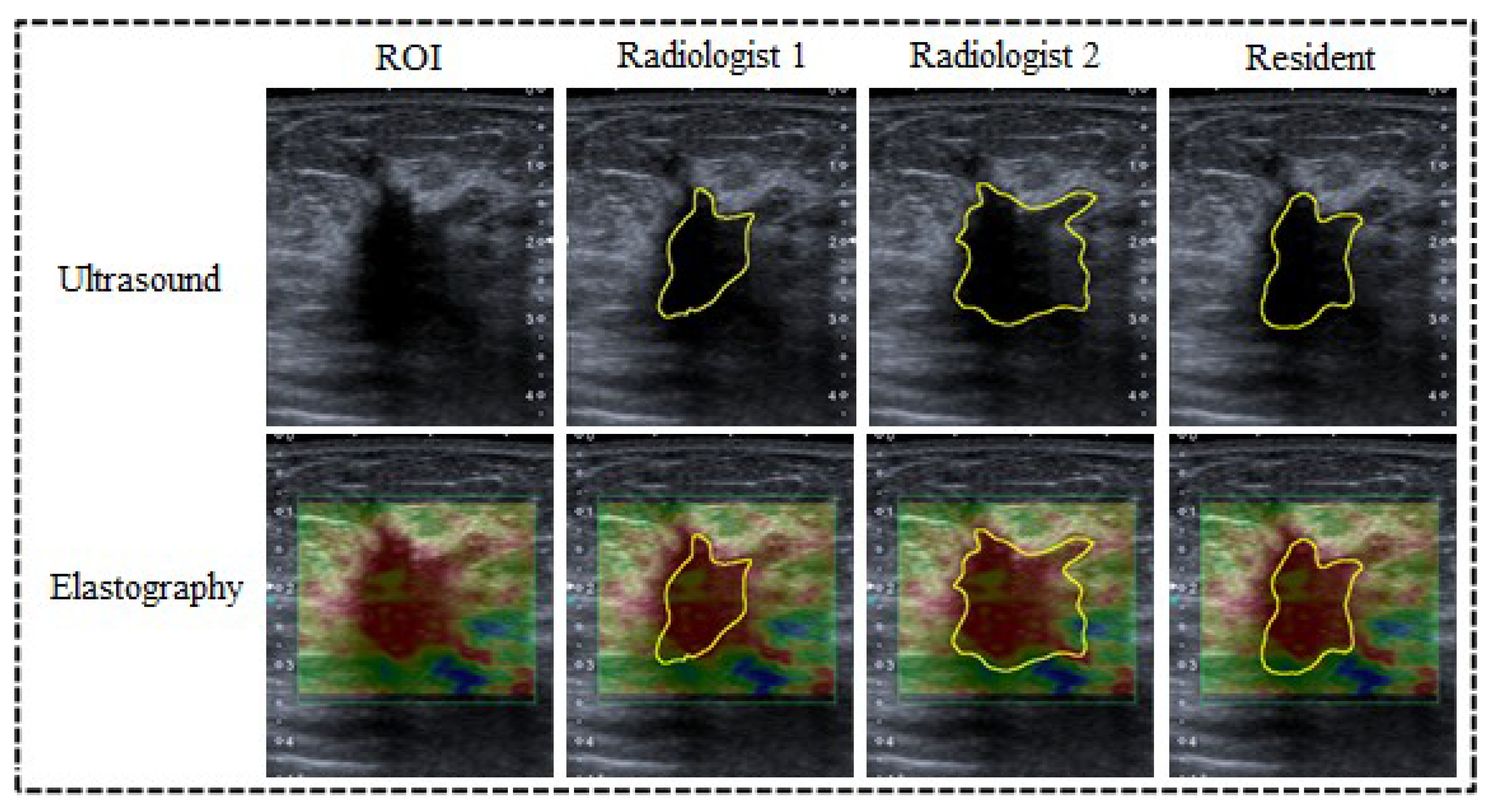
| Observers | AUC—70% of Hard Tissue | AUC—75% of Hard Tissue | AUC—80% of Hard Tissue | AUC—90% of Hard Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiologist 1 | 0.841 | 0.853 | 0.802 | 0.790 |
| Radiologist 2 | 0.813 | 0.806 | 0.815 | 0.707 |
| Resident | 0.802 | 0.814 | 0.789 | 0.723 |
| Visual Analysis—Radiologist 1 | 0.829 | |||
| Observers | Jaccard | Undersegmentation | Oversegmentation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiologist 1 and Radiologist 2 | Average | 0.565 | 0.147 | 0.355 |
| SD | 0.178 | 0.144 | 0.213 | |
| Radiologist 1 and Resident | Average | 0.654 | 0.227 | 0.169 |
| SD | 0.122 | 0.148 | 0.135 | |
| Radiologist 2 and Resident | Average | 0.537 | 0.402 | 0.144 |
| SD | 0.193 | 0.212 | 0.174 | |
| Mean Value Desired | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Observers | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiologist 1 | 70.97 | 88.46 | 0.853 |
| Radiologist 2 | 67.74 | 84.62 | 0.806 |
| Resident | 58.06 | 90.38 | 0.814 |
| Visual Analysis—Radiologist 1 | 61.29 | 88.46 | 0.829 |
| Type | n | Radiologist 1 | Radiologist 2 | Resident | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Mean | Median | Mean | Median | Mean | |||
| Benign (n = 48) | Fibrocystic changes | 30 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| Fibroadenoma | 18 | 2.0 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 1.6 | |
| Malignant (n = 31) | Invasive ductal carcinoma | 23 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 2 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | |
| Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) | 4 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | |
| Others | 2 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | |
| Indeterminate (n = 4) | Indeterminate lesions | 4 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Total | 83 | - | ||||||
| Observers | Kappa |
|---|---|
| Radiologist 1 and Radiologist 2 | 0.796 |
| Radiologist 1 and Resident | 0.758 |
| Radiologist 2 and Resident | 0.682 |
| Observers | Difference in AUC | 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Analysis—Radiologist 1 | 0.024 | −0.048–0.096 | 0.517 |
| Visual Analysis—Radiologist 2 | 0.023 | −0.050–0.096 | 0.538 |
| Visual Analysis—Resident | 0.033 | −0.047–0.113 | 0.420 |
| Radiologist 1 and Radiologist 2 | 0.047 | −0.024–0.118 | 0.196 |
| Radiologist 1 and Resident | 0.057 | −0.015–0.128 | 0.120 |
| Radiologist 2 and Resident | 0.010 | −0.081–0.101 | 0.830 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcomini, K.D.; Fleury, E.F.C.; Oliveira, V.M.; Carneiro, A.A.O.; Schiabel, H.; Nishikawa, R.M. Evaluation of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System in the Classification of Lesions in Breast Strain Elastography Imaging. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5030062
Marcomini KD, Fleury EFC, Oliveira VM, Carneiro AAO, Schiabel H, Nishikawa RM. Evaluation of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System in the Classification of Lesions in Breast Strain Elastography Imaging. Bioengineering. 2018; 5(3):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5030062
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcomini, Karem D., Eduardo F. C. Fleury, Vilmar M. Oliveira, Antonio A. O. Carneiro, Homero Schiabel, and Robert M. Nishikawa. 2018. "Evaluation of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System in the Classification of Lesions in Breast Strain Elastography Imaging" Bioengineering 5, no. 3: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5030062
APA StyleMarcomini, K. D., Fleury, E. F. C., Oliveira, V. M., Carneiro, A. A. O., Schiabel, H., & Nishikawa, R. M. (2018). Evaluation of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System in the Classification of Lesions in Breast Strain Elastography Imaging. Bioengineering, 5(3), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering5030062