Stable Gene Regulatory Network Modeling From Steady-State Data †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
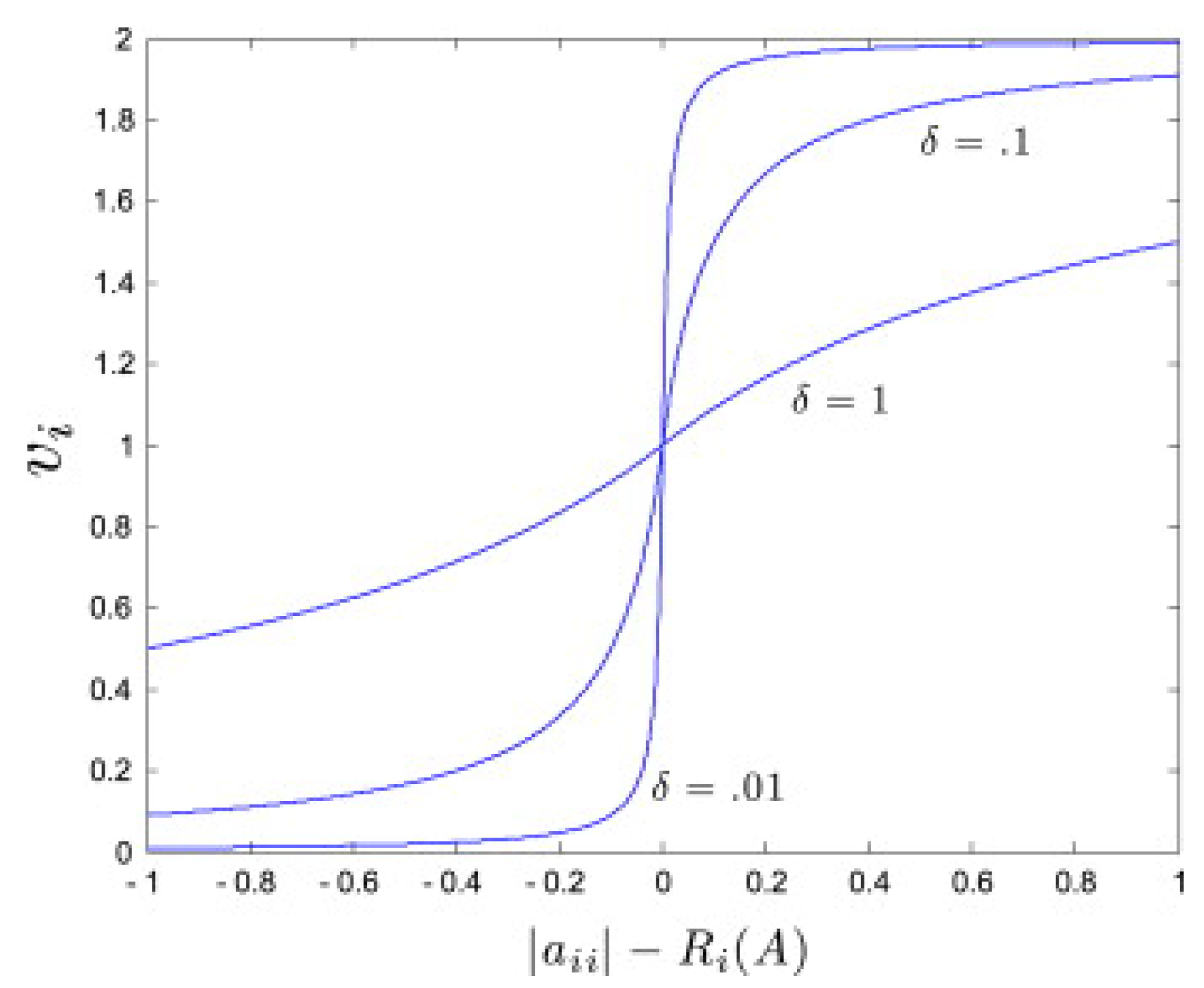
2.1. Network Identification Approach
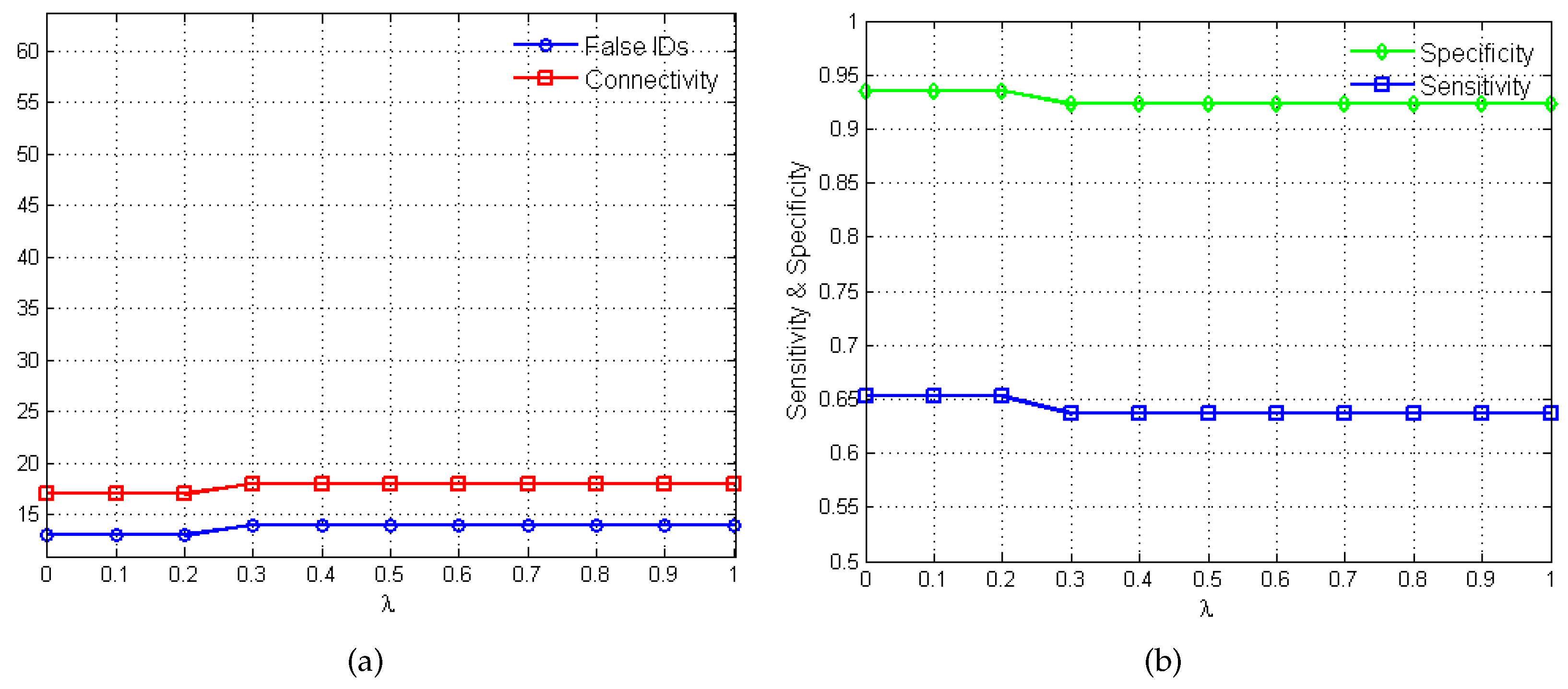
2.2. Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
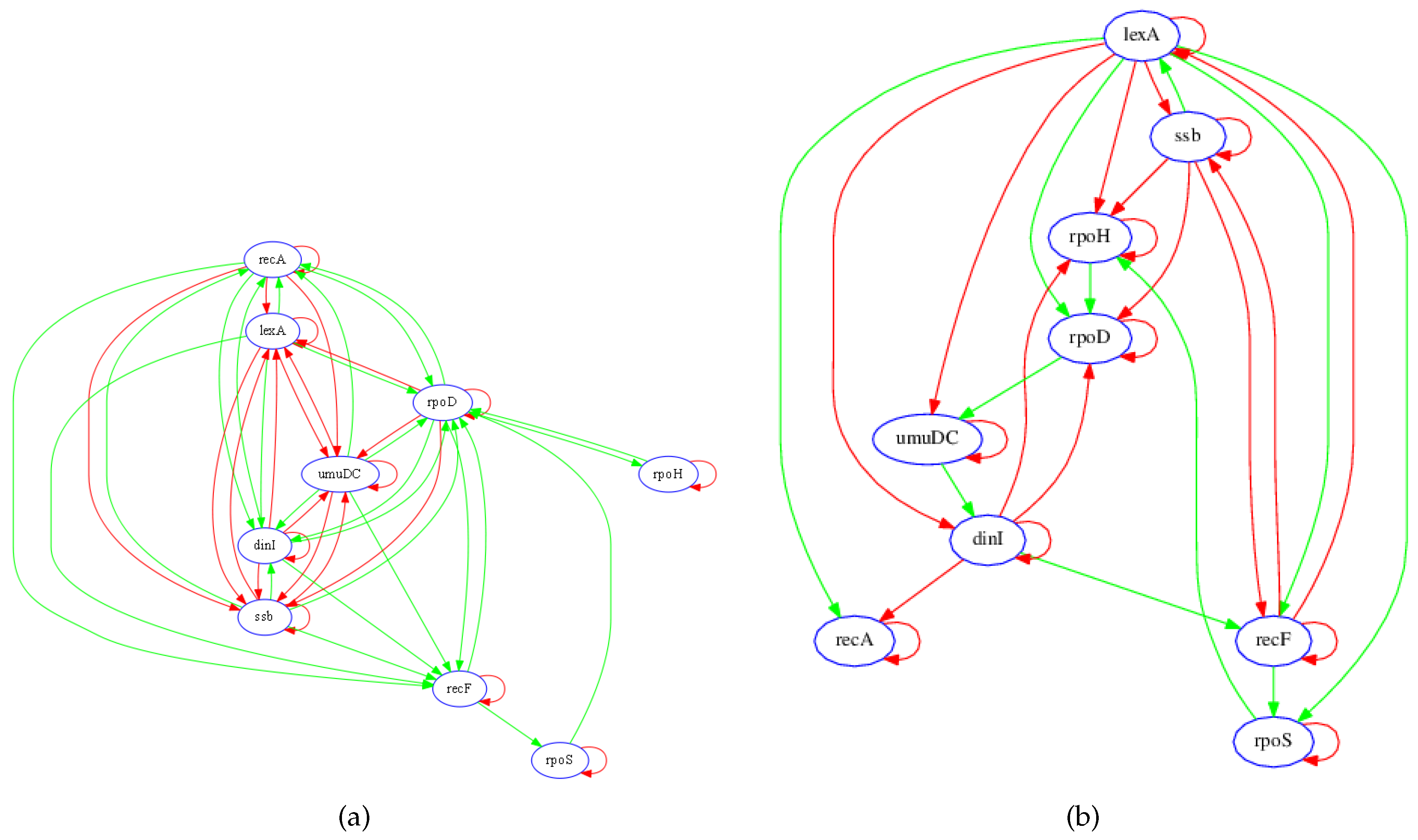
3.1. SOS Pathway in Escherichia coli
3.1.1. Network Recovery
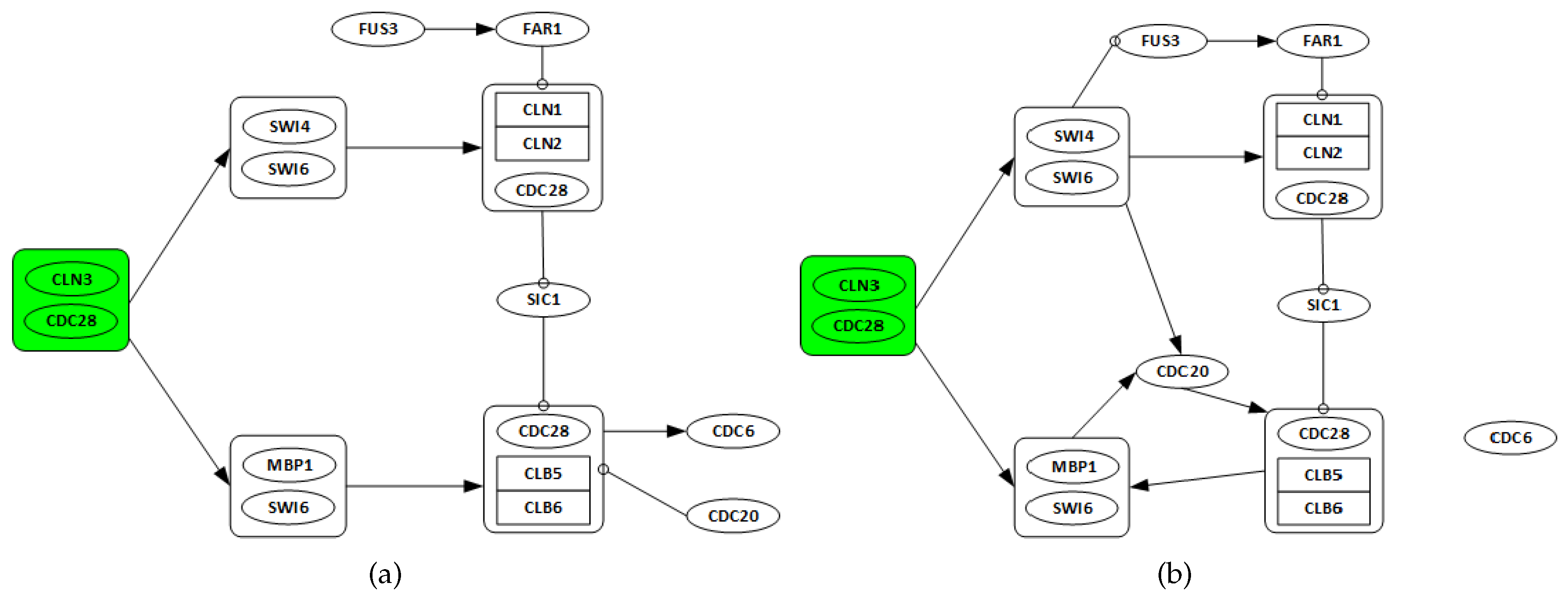
3.2. Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Cell Cycle
3.2.1. Network Recovery
- Genes CLN3 and CDC28 are only considered as possible regulators, as they are starters of the cell cycle network.
- All discovered links from any gene in one complex to any other genes in a different complex are considered as a single regulation.
- All regulations among genes in the same complex are ignored.
4. Conclusion and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quackenbush, J. Computational analysis of microarray data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidis, G.; d’Alché Buc, F. Autoregressive models for gene regulatory network inference: Sparsity, stability and causality issues. Math. Biosci. 2013, 246, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasty, J.; McMillen, D.; Isaacs, F.; Collins, J.J. Computational studies of gene regulatory networks: In numero molecular biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolin, A.A.; Nemenman, I.; Basso, K.; Wiggins, C.; Stolovitzky, G.; Favera, R.D.; Califano, A. ARACNE: an algorithm for the reconstruction of gene regulatory networks in a mammalian cellular context. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Reguly, T.; Boucher, L.; Breitkreutz, A.; Tyers, M. BioGRID: A general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D535–D539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegnér, J.; Yeung, M.K.S.; Hasty, J.; Collins, J.J. Reverse engineering gene networks: Integrating genetic perturbations with dynamical modeling. PNAS 2003, 100, 5944–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, T.S.; Di Bernardo, D.; Lorenz, D.; Collins, J.J. Inferring genetic networks and identifying compound mode of action via expression profiling. Science 2003, 301, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.E.; Loh, S.K.; Low, S.T.; Mohamad, M.S.; Deris, S.; Zakaria, Z. A review on the computational approaches for gene regulatory network construction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 48, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, F.M.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Cesar, R.M. Inference of gene regulatory networks from time series by Tsallis entropy. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.R.; Huang, H. Review on statistical methods for gene network reconstruction using expression data. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 362, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polynikis, A.; Hogan, S.J.; di Bernardo, M. Comparing different ODE modelling approaches for gene regulatory networks. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 261, 511–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, H. Modeling and simulation of genetic regulatory systems: a literature review. J. Comput. Biol. 2002, 9, 67–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, M.; Lambeck, S.; Toepfer, S.; van Someren, E.; Guthke, R. Gene regulatory network inference: Data integration in dynamic models—A review. Biosystems 2009, 96, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, J.; Bourdon, J.; Eveillard, D.; Fromentin, J.; Roux, O.; Sinoquet, C. Temporal constraints of a gene regulatory network: Refining a qualitative simulation. Biosystems 2009, 98, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Someren, E.V.; Wessels, L.; Backer, E.; Reinders, M. Genetic network modeling. Pharmacogenomics 2002, 3, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartemink, A.J. Reverse engineering gene regulatory networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 554–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.S.; Tegnér, J.; Collins, J.J. Reverse engineering gene networks using singular value decomposition and robust regression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6163–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Joshi, T.; Zhang, X.S.; Xu, D.; Chen, L. Inferring gene regulatory networks from multiple microarray datasets. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlebach, G.; Shamir, R. Modelling and analysis of gene regulatory networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordmahalleh, M.M.; Sefidmazgi, M.G.; Homaifar, A.; Karimoddini, A.; Guiseppi-Elie, A.; Graves, J.L. Delayed and Hidden Variables Interactions in Gene Regulatory Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Boca Raton, FL, USA, 10–12 November 2014; pp. 23–29.
- D’haeseleer, P.; Liang, S.; Somogyi, R. Genetic network inference: From co-expression clustering to reverse engineering. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 707–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, S. Metabolic stability and epigenesis in randomly constructed genetic nets. J. Theor. Biol. 1969, 22, 437–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornholdt, S. Less is more in modeling large genetic networks. Science 2005, 310, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.; Linial, M.; Nachman, I.; Pe’er, D. Using Bayesian networks to analyze expression data. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavlanos, M.M.; Julius, A.A.; Boyd, S.P.; Pappas, G.J. Inferring stable genetic networks from steady-state data. Automatica 2011, 47, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, W.; Matteson, D.; Bien, J. Structured Regularization for Large Vector Autoregression; Technical report; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Larvie, J.E.; Gorji, M.S.; Homaifar, A. Inferring stable gene regulatory networks from steady-state data. In Proceedings of the 2015 41st Annual Northeast Biomedical Engineering Conference (NEBEC), Troy, NY, USA, 17–19 April 2015; pp. 1–2.
- Fujita, A.; Sato, J.R.; Garay-Malpartida, H.M.; Yamaguchi, R.; Miyano, S.; Sogayar, M.C.; Ferreira, C.E. Modeling gene expression regulatory networks with the sparse vector autoregressive model. BMC Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lütkepohl, H. New Introduction to Multiple Time Series Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; Chatterjee, S. Causality and pathway search in microarray time series experiment. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating Causal Relations by Econometric Models and Cross-Spectral Methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.J.; Hung, H.L.; Chang, Y.M. Subset selection for vector autoregressive processes using Lasso. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 3645–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Sufficient conditions on stability of interval matrices: connections and new results. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1992, 37, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, J.C.; Mundra, P.A. Stability of building gene regulatory networks with sparse autoregressive models. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CVX Research Inc. CVX: Matlab Software for Disciplined Convex Programming, Version 2.0, 2012. Available online: http://cvxr.com/cvx (accessed on 15 October 2015).
- De Muth, J. Basic Statistics and Pharmaceutical Statistical Applications, 2nd ed.; Pharmacy Education Series, Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, P.T.; Sherlock, G.; Zhang, M.Q.; Iyer, V.R.; Anders, K.; Eisen, M.B.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D.; Futcher, B. Comprehensive Identification of Cell Cycle-regulated Genes of the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Microarray Hybridization. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 3273–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Yeast Cell Cycle Analysis Database. Available online: http://genome-www.stanford.edu/cellcycle/data/rawdata/combined.txt (accessed on 15 November 2015).
- Lodish, H. Molecular Cell Biology, 5th ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- KEGG PATHWAY: map04111. Available online: http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/wwwbget?map04111 (accessed on 27 April 2015).
- Kim, S.Y.; Imoto, S.; Miyano, S. Inferring gene networks from time series microarray data using dynamic Bayesian networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2003, 4, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatz, M.; Langmead, B. The DNA data deluge. IEEE Spectr. 2013, 50, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Barrett, T. Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ (accessed on 15 October 2015).
- Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene Ontology Consortium: going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1049–D1056. [Google Scholar]
- Fehrmann, R.S.N.; Karjalainen, J.M.; Krajewska, M.; Westra, H.J.; Maloney, D.; Simeonov, A.; Pers, T.H.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Jansen, R.C.; Schultes, E.A.; et al. Gene expression analysis identifies global gene dosage sensitivity in cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Yi, B.; Wozniak, M.; Wong, L. IntPath–an integrated pathway gene relationship database for model organisms and important pathogens. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6 (Suppl. 2), S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, B. After 30 Years of Study, the Bacterial SOS Response Still Surprises Us. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberghina, L.; Mavelli, G.; Drovandi, G.; Palumbo, P.; Pessina, S.; Tripodi, F.; Coccetti, P.; Vanoni, M. Cell growth and cell cycle in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Basic regulatory design and protein-protein interaction network. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Dreher, K.; Karp, P.D. The challenge of constructing, classifying, and representing metabolic pathways. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 345, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, D.; Mundo, A.F.; Haw, R.; Milacic, M.; Weiser, J.; Wu, G.; Caudy, M.; Garapati, P.; Gillespie, M.; Kamdar, M.R.; et al. The Reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D472–D477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgat, A.; Coissac, E.; Coudert, E.; Axelsen, K.B.; Keller, G.; Bairoch, A.; Bridge, A.; Bougueleret, L.; Xenarios, I.; Viari, A. UniPathway: a resource for the exploration and annotation of metabolic pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D761–D769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, P.D. Pathway databases: a case study in computational symbolic theories. Science 2001, 293, 2040–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| True Network | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inferred Network | True Positive | False Postive | P’ |
| False Negative | True Negative | N’ | |
| Total | P | N | |
| TP | FP | TN | FN | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LASSO-VAR | 39 | 11 | 5 | 26 | 60% | 31% | 78% |
| ZAVLANOS [26] | 40 | 10 | 15 | 16 | 71% | 60% | 80% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larvie, J.E.; Sefidmazgi, M.G.; Homaifar, A.; Harrison, S.H.; Karimoddini, A.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Stable Gene Regulatory Network Modeling From Steady-State Data. Bioengineering 2016, 3, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering3020012
Larvie JE, Sefidmazgi MG, Homaifar A, Harrison SH, Karimoddini A, Guiseppi-Elie A. Stable Gene Regulatory Network Modeling From Steady-State Data. Bioengineering. 2016; 3(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering3020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarvie, Joy Edward, Mohammad Gorji Sefidmazgi, Abdollah Homaifar, Scott H. Harrison, Ali Karimoddini, and Anthony Guiseppi-Elie. 2016. "Stable Gene Regulatory Network Modeling From Steady-State Data" Bioengineering 3, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering3020012
APA StyleLarvie, J. E., Sefidmazgi, M. G., Homaifar, A., Harrison, S. H., Karimoddini, A., & Guiseppi-Elie, A. (2016). Stable Gene Regulatory Network Modeling From Steady-State Data. Bioengineering, 3(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering3020012








