Rapid Screening of Anticoagulation Compounds for Biological Target-Associated Adverse Effects Using a Deep-Learning Framework in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Dataset and Materials
2.2. Target Featurisation
2.3. Modelling Approach
2.4. Representation Approach
2.5. Text Normalisation
2.6. Model Evaluation
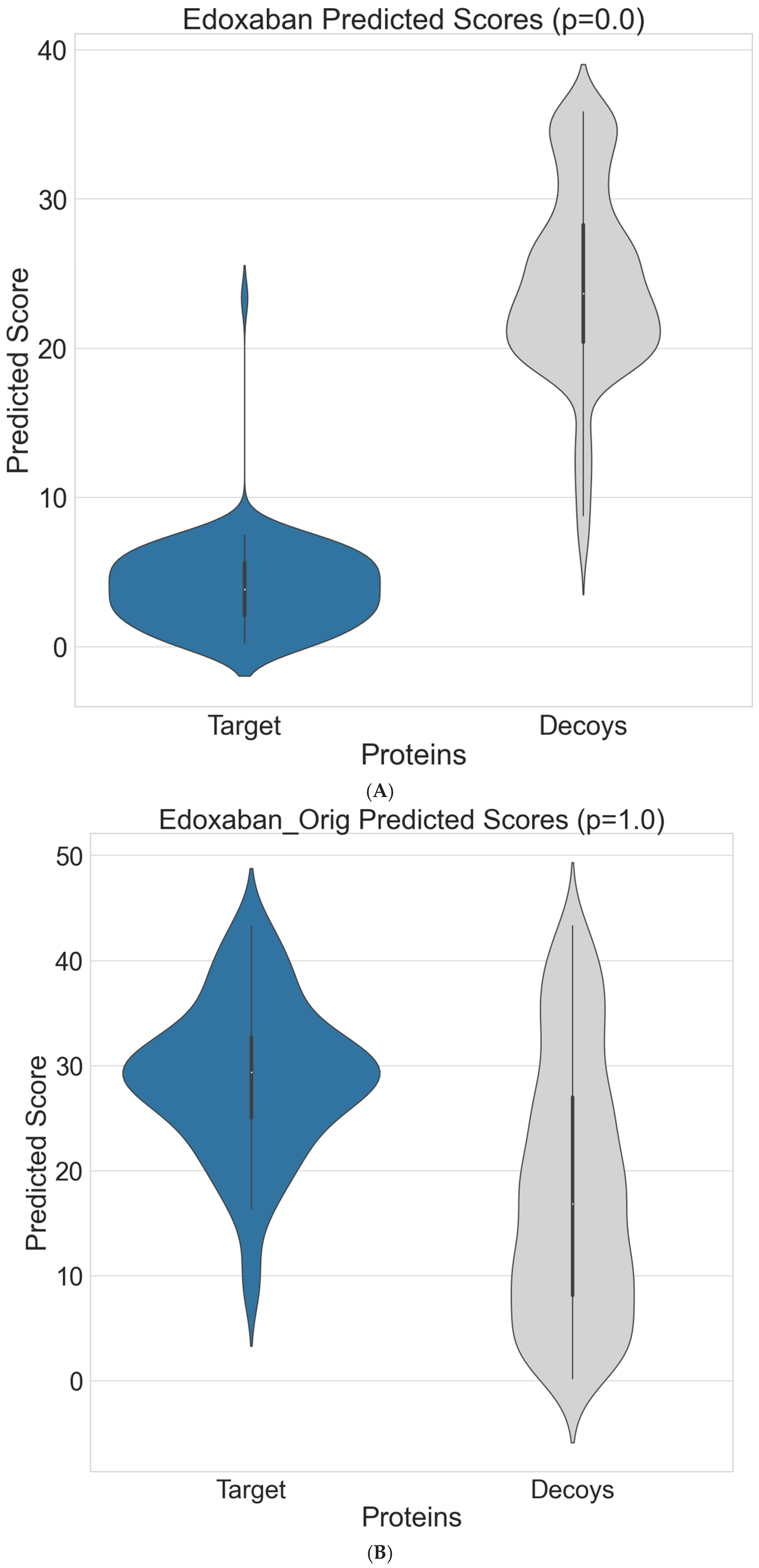
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Future Work and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piccini, J.P.; Caso, V.; Connolly, S.J.; Fox, K.A.A.; Oldgren, J.; Jones, W.S.; Gorog, D.A.; Durdil, V.; Viethen, T.; Neumann, C.; et al. Safety of the Oral Factor XIa Inhibitor Asundexian Compared with Apixaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation (PACIFIC-AF): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, Dose-Finding Phase 2 Study. Lancet 2022, 399, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asundexian Inferior to Apixaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. Available online: https://www.escardio.org/The-ESC/Press-Office/Press-releases/Asundexian-inferior-to-apixaban-for-stroke-prevention-in-atrial-fibrillation (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- García-Abeijon, P.; Costa, C.; Taracido, M.; Herdeiro, M.T.; Torre, C.; Figueiras, A. Factors Associated with Underreporting of Adverse Drug Reactions by Health Care Professionals: A Systematic Review Update. Drug Saf. 2023, 46, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhamme, P.; Yi, B.A.; Segers, A.; Salter, J.; Bloomfield, D.; Büller, H.R.; Raskob, G.E.; Weitz, J.I. Abelacimab for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Sperry, A.; Hartmann, H.; Goldfaden, R.; Ashchi, M.; Kim, R.; Huston, J.; Niman, S.; Choksi, R. Abelacimab. Anti-Factor XI/XIa Monoclonal Antibody, Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation, Treatment of Thrombotic Disorders. Drugs Future 2021, 46, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apixaban 2.5 Mg Film-Coated Tablets-Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)-(Emc) 100159. Available online: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/100159/smpc (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Dong, T.; Llewellyn, R.D.; Hezzell, M.; Angelini, G.D. A Deep Learning Methodology for Screening New Natural Therapeutic Candidates for Pharmacological Cardioversion and Anticoagulation in the Treatment and Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, I.A.; Afzal, A.M.; Allen, C.H.G.; Svensson, F.; Hanser, T.; Bender, A. Systematic Analysis of Protein Targets Associated with Adverse Events of Drugs from Clinical Trials and Postmarketing Reports. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassan, A.; Alves, V.M.; Amberg, A.; Anger, L.T.; Beilke, L.; Bender, A.; Bernal, A.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Hsieh, J.-H.; Johnson, C.; et al. In Silico Approaches in Organ Toxicity Hazard Assessment: Current Status and Future Needs for Predicting Heart, Kidney and Lung Toxicities. Comput. Toxicol. 2021, 20, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiori, M.; Lazzari, L.; Hezzell, M.; Angelini, G.D.; Dong, T. Transcriptomics, Proteomics and Bioinformatics in Atrial Fibrillation: A Descriptive Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, E.; Mofrad, M.R.K. Continuous Distributed Representation of Biological Sequences for Deep Proteomics and Genomics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Sledzieski, S.; Bryson, B.; Cowen, L.; Berger, B. Contrastive Learning in Protein Language Space Predicts Interactions between Drugs and Protein Targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2220778120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Rudin, C.; Browne, E.P. Towards a Comprehensive Evaluation of Dimension Reduction Methods for Transcriptomic Data Visualization. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Belousov, M.; Friedrichs, J.; Hakala, K.; Kiritchenko, S.; Mehryary, F.; Han, S.; Tran, T.; Rios, A.; Kavuluru, R.; et al. Data and Systems for Medication-Related Text Classification and Concept Normalization from Twitter: Insights from the Social Media Mining for Health (SMM4H)-2017 Shared Task. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Nejat, P.; Saha, A.; Campbell, C.J.V.; Norgan, A.P.; Lokker, C. Performance of Externally Validated Machine Learning Models Based on Histopathology Images for the Diagnosis, Classification, Prognosis, or Treatment Outcome Prediction in Female Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Pathol. Inform. 2023, 15, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoughery, E.P.; Shatzel, J.J. A Comparative Analysis of the Safety Profile of Direct Oral Anticoagulants Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Eur. J. Haematol. 2019, 103, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos, C.F.; Segovia, G.F.; Nuñez-Navarro, N.; Faúndez, M.A.; Zacconi, F.C. Novel FXa Inhibitor Identification through Integration of Ligand- and Structure-Based Approaches. Molecules 2017, 22, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, N.; Colombo, E.; Tenconi, M.; Baldessin, L.; Corsini, A. Drug-Drug Interactions of Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs): From Pharmacological to Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.Y.; Yeh, C.H.; Dale, B.J.; Leslie, B.A.; Stafford, A.R.; Fredenburgh, J.C.; Hirsh, J.; Weitz, J.I. Mechanistic Basis for the Differential Effects of Rivaroxaban and Apixaban on Global Tests of Coagulation. Open 2018, 2, e190–e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, S.; Zaidi, S.T.R.; Merchant, H.A.; Babar, Z.-U.-D.; Hasan, S.S. Prescribing Trends of Oral Anticoagulants in England over the Last Decade: A Focus on New and Old Drugs and Adverse Events Reporting. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Peng, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, R.; Miao, J. Predictors of Hemorrhagic Complications after Intravenous Thrombolysis in Acute Cerebral Infarction Patients: A Single-Center Study of 391 Cases. Medicine 2021, 100, e27053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Deng, H.; Shantsila, A.; Lip, G.Y.H. Rivaroxaban Versus Dabigatran or Warfarin in Real-World Studies of Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 2017, 48, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, T.; Fujita, S.; Kawai, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kimura, T.; Fukuzawa, M.; Abe, K.; Tachibana, S. Efficacy and Safety of Edoxaban versus Enoxaparin for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism Following Total Hip Arthroplasty: STARS J-V. Thromb. J. 2015, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiv, R.; Beradid, S.; Suissa, S.; Renoux, C. Effectiveness and Safety of Edoxaban Compared with Apixaban in Elderly Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Real-World Population-Based Cohort Study. Stroke 2024, 55, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, X.L.; Wang, R.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Zimmermann, L.; Ye, X.; Gao, X.; Brüggenjürgen, B.; Unverdorben, M. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Edoxaban versus Apixaban, Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, and Vitamin K Antagonists in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Germany: A Real-World Cohort Study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 346, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenburgh, J.C.; Weitz, J.I. News at XI: Moving beyond Factor Xa Inhibitors. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipworth, K; Factor XI/XIa Inhibitors: What We Now Know. EMJ Cardiol. 2024, 12, 2–13.
- Gagnon, A.L.; Scansen, B.A.; Olver, C.; Shropshire, S.; Hess, A.; Orton, E.C. Phase I Clinical Trial of an Antithrombotic Drug Protocol Combining Apixaban and Clopidogrel in Dogs. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2021, 36, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcome to the NOAH Compendium. Available online: https://www.noahcompendium.co.uk/home (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Myers, J.A.; Wittenburg, L.A.; Olver, C.S.; Martinez, C.M.; Bright, J.M. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of the Factor Xa Inhibitor Apixaban after Oral and Intravenous Administration to Cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 76, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiodarone Hydrochloride Drugs BNF Content Published by NICE. Available online: https://bnf.nice.org.uk/drugs/amiodarone-hydrochloride/ (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Um, K.J.; McIntyre, W.F.; Healey, J.S.; Mendoza, P.A.; Koziarz, A.; Amit, G.; Chu, V.A.; Whitlock, R.P.; Belley-Côté, E.P. Pre- and Post-Treatment with Amiodarone for Elective Electrical Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. EP Europace 2019, 21, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.; Mares, A.C.; Porres-Aguilar, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Barnes, G.D. Factor XI/XIa Inhibitors for the Prevention and Treatment of Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism: A Narrative Review. Vasc. Med. 2023, 29, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Chen, Q. The Future of Pharmaceuticals: Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery and Development. J. Pharm. Anal. 2025, 15, 101248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Gao, T.; Lyu, W.; Qiang, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z. Deep-Learning-Driven Discovery of SN3–1, a Potent NLRP3 Inhibitor with Therapeutic Potential for Inflammatory Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 17833–17854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, L.; Zhang, C.; Kovalchuk, O.; Boklan, J.; Trippett, T.; Narendran, A. Dual Functionality of the Antimicrobial Agent Taurolidine Which Demonstrates Effective Anti-Tumor Properties in Pediatric Neuroblastoma. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozerov, I.V.; Lezhnina, K.V.; Izumchenko, E.; Artemov, A.V.; Medintsev, S.; Vanhaelen, Q.; Aliper, A.; Vijg, J.; Osipov, A.N.; Labat, I.; et al. In Silico Pathway Activation Network Decomposition Analysis (iPANDA) as a Method for Biomarker Development. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
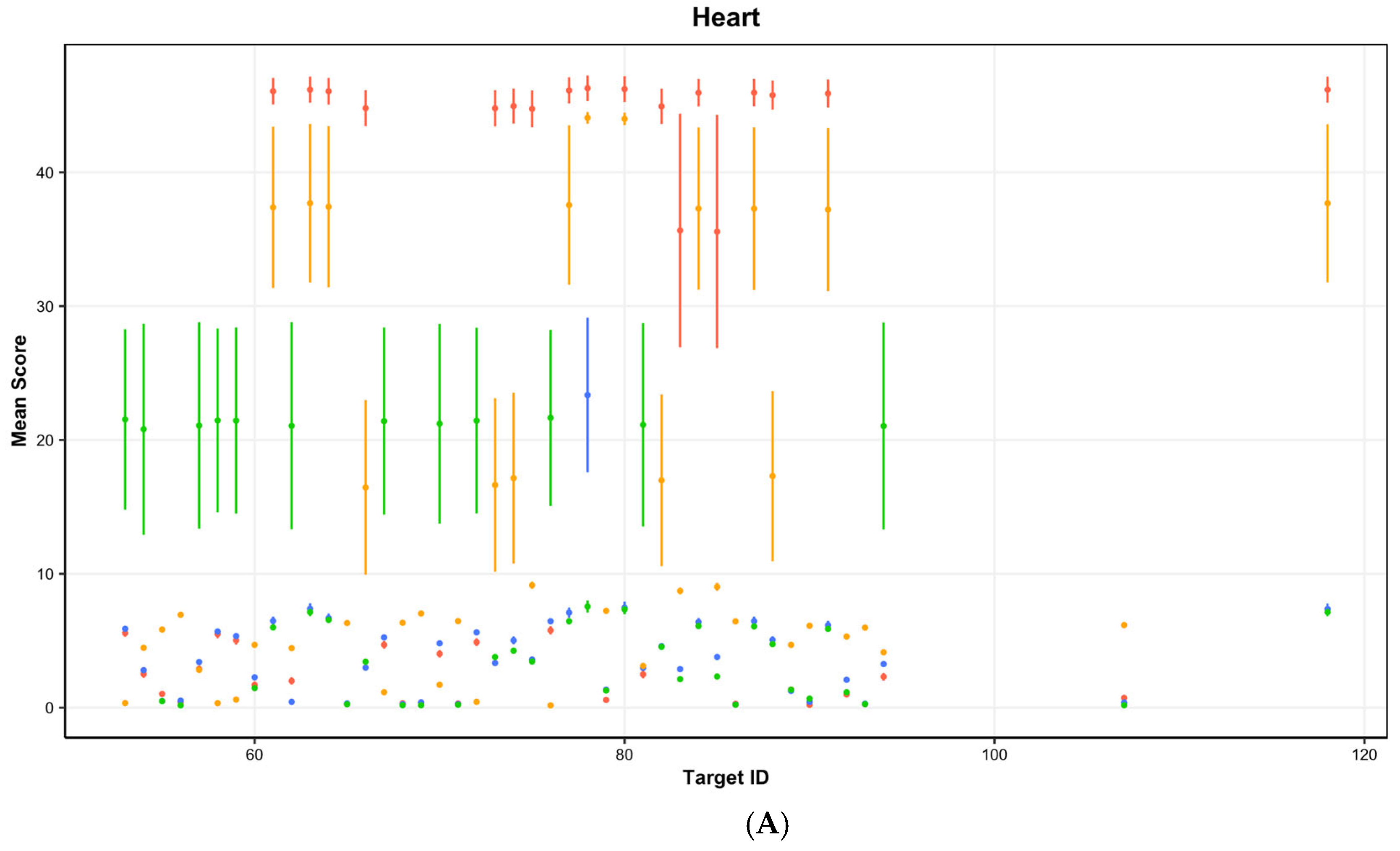
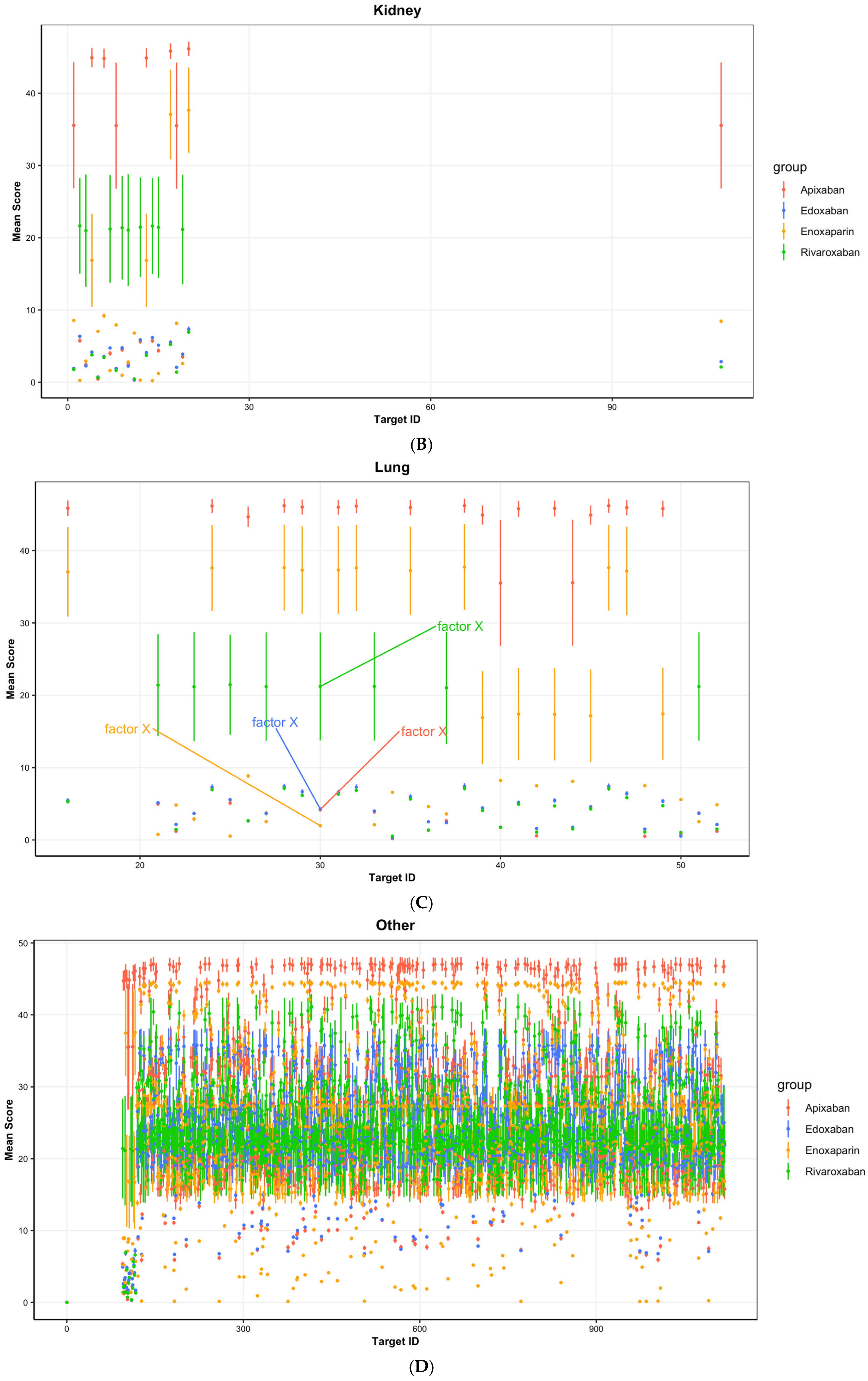
| (A) | ||||
| Dataset | Drugs | Targets | Training | Validation |
| BIOSNAP | 4510 | 2181 | 19,238 (9670/9568) | 2748 (1396/1352) |
| DUD-E | 852,292 | 57 | 415,204 (8996/406,208) | — |
| (B) | ||||
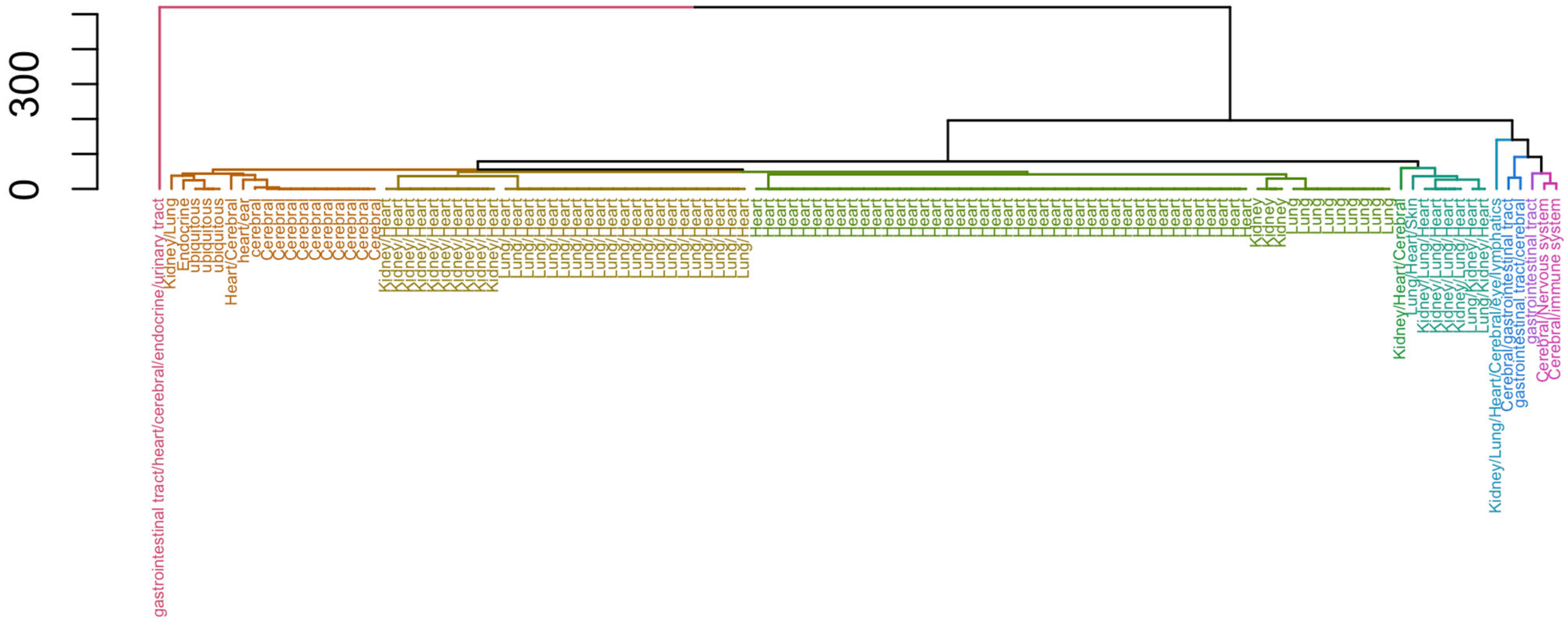
| Organ | Smit et al. 2020 [8] | Bassan et al. 2021 [9] | Representative Terms | |
| Cerebral | 11 | 0 | drug abuse/dependence; drug abuse/dependence; heart rate increased; neurotoxicity; pain; acne; depression; dyskinesia; dystonia; parkinsonism | |
| Cerebral/Nervous system | 1 | 0 | dizziness; drug abuse/dependence; constipation; emesis; abdominal distension; apnoea; constipation; hard stool; hyperglycaemia; ischemic colitis | |
| Cerebral/gastrointestinal tract | 1 | 0 | inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretions; anxiogenic; causes vasoconstriction (venous); inhibits acid secretion; inhibits gastric emptying; inhibits gut motility; ↓ eating; ↓/↑ inflammation | |
| Cerebral/immune system | 1 | 0 | inflammation; lupus-like syndrome; sarcoidosis; ↑ pain; ↓ BP | |
| Endocrine | 1 | 0 | anaemia; ↓ attention; ↑ body weight; bone pain; depression; ↑ in hostility; hot flashes; impotence; ↓ memory; oedema | |
| Heart | 1 | 41 | angina, unspecified; angina, unstable; heart failure, abortion, alopecia, androgenic; alopecia, unspecified; heart failure; cardiomyopathy, ischaemic; cardiac hypertrophy; dermatological disease, unspecified; | |
| Heart/Cerebral | 0 | 1 | bipolar disorder; depression, major depressive, psychosis, unspecified; schizophrenia, disorder; headache, cluster; migraine; | |
| Kidney | 0 | 3 | arrhythmia; heart failure; death, cerebral complications, convulsions; ↑ urine excretion; death; oligoamnios; renal failure; hypocalvaria; limb defects; intrauterine growth retardation; persistent patent ductus arteriosus; respiratory distress syndrome; ↑ pain; ↑ urine excretion; ↑ urinary sodium excretion; haemolysis chronic dosing: neurodegeneration, ↑ urinary sodium excretion; heart: ↓ pain; ↓ HR; ↓ BP; AV block; cardiac | |
| Kidney/Heart | 0 | 10 | myocardial hypertrophy; perturbations of blood pressure, ↑ HR; ↑ thrombosis; hypertension, pulmonary; infarction, myocardial; nephropathy, diabetic; heart failure; ↓/↑ locomotor activity; drowsiness; ↓ urinary | |
| Kidney/Heart/Cerebral | 0 | 1 | fibrotic valvular heart, abuse/dependence; convulsions; ↑ arousal; psychosis; ↑/↓ locomotor activity; dyskinesia; perturbations of blood pressure; dizziness; ↑ urine excretion; neurodegeneration; headache; | |
| Kidney/Lung | 0 | 1 | renal dysfunction; gastric and pulmonary bleeding | |
| Kidney/Lung/Heart | 0 | 4 | alopecia, androgenic; cardiomyopathy, ischaemic; cognitive disorder, dermatological disease, unspecified; hypertension, unspecified; infarction, hyperuricemic, toxicity: ↑ risk spontaneous abortion; diabetic complication | |
| Kidney/Lung/Heart/Cerebral/eye/lymphatics | 1 | 0 | ↑/↓ inflammation, ↓ uterine motility | |
| Lung | 0 | 9 | asthma; rhinitis; bipolar disorder; chronic obstructive pulmonary, bronchoconstriction, cardiac hypertrophy; Crohn’s disease; depression, unspecified; epileptic encephalopathy, foetal akinesia deformation, gastritis; incontinence, urinary; inflammation, hyperekplexia, hereditary | |
| Lung/Heart | 0 | 21 | acute coronary syndrome; angina, unstable; acidosis; irritability; ↓ pupil diameter; exhaustion; ptosis; muscle cramps; centrilobular liver, ↑ body temperature; sweating; atherosclerosis; infarction, cerebral; blood/clotting disease; cough; Buerger’s syndrome; hypertension, pulmonary; | |
| Lung/Heart/Skin | 0 | 1 | conjunctivitis, allergic; depression, major; eczema; eczema, atopic; insomnia; keratoconjunctivitis; ocular disorder; bipolar disorder; schizophrenia; skin disorder; urticaria; ↑ sleep; allergic, seasonal; depressive disorder; cardiac arrhythmia; ↓ GI transit; | |
| Lung/Kidney/Heart | 0 | 2 | ↓ cardiac contractility; ↓ BP; bronchoconstriction; ↑ airway, excretion, hypertension; left ventricular, hypertrophy; bronchoconstriction; inflammation; pain; tubulointerstitial structural injury; ↓ HR; ↓ urine excretion; ↓ urinary sodium | |
| gastrointestinal tract | 1 | 0 | abdominal pain hypersensitivity; anxiety; bloating; cholelithiasis; cholestasis; fatigue; gas; nausea; pancreatic enzyme secretion; ↑ BP | |
| gastrointestinal tract/cerebral | 1 | 0 | inflammation; immunosuppression; ↑ GI transit; ↓ GI transit | |
| gastrointestinal tract/heart/cerebral/endocrine/urinary tract | 1 | 0 | facilitates gastrointestinal transit; diarrhoea; fainting; mechanical intestinal allodynia; ↑ GI transit; ↑ HR; ↑ QTc interval; ↓ BP; ↓ GI transit; ↓ blood volume | |
| heart/ear | 1 | 0 | atrial fibrillation; long QT syndrome; deafness; potential hearing impairment | |
| ubiquitous | 3 | 0 | insulin resistance; osteoporosis; convulsions; facilitates bronchial constriction; facilitates uterine constriction; facilitates vascular constriction; hypoglycaemia; immunosuppression; allergic inflammation; oedema | |
| Total | 24 | 94 | ||
| N Adverse Effects (SIDER) | |
|---|---|
| Dabigatran | 67 |
| Apixaban | 102 |
| Rivaroxaban | 89 |
| Warfarin | 56 |
| Nadverse effects (FAERS) | |
| Edoxaban | 612 |
| Enoxaparin | 1161 |
| New Model | ConPlex | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | Precision | Recall | |
| Dabigatran | 0.314 | 0.702 a | 0 | 0 |
| Apixaban | 0.325 | 0.673 | 0 | 0 |
| Rivaroxaban | 0.366 | 0.746 a | 0 | 0 |
| Warfarin | 0.275 | 0.683 | 0 | 0 |
| Edoxaban | 0.770 a | 0.703 a | 0 | 0 |
| Enoxaparin | 0.879 b | 0.537 | 0 | 0 |
| Dabigatran | Apixaban | Rivaroxaban | Warfarin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Euclidean Distance | Ranking | Euclidean Distance | Ranking | Euclidean Distance | Ranking | Euclidean Distance | Ranking | |
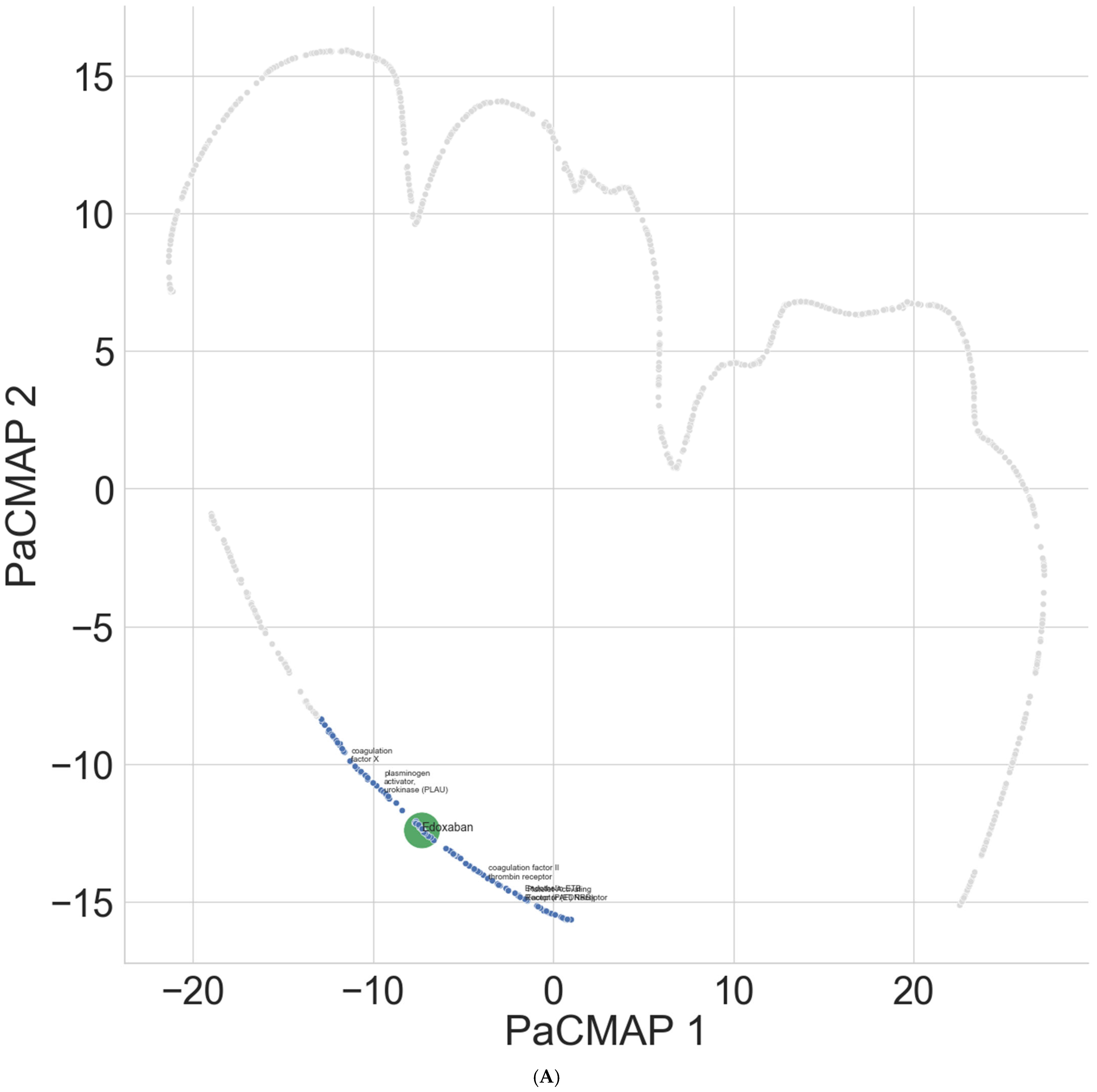
| Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor | 4.98 | 55 | 45.84 | 984 | 5.28 | 62 | 4.34 | 51 |
| Plasminogen activator urokinase (PLAU) | 9.13 | 90 | 2.63 | 37 | 21.04 | 199 | 25.19 | 564 |
| Endothelin ETB receptor (EDNRB) | 4.71 | 51 | 45.78 | 979 | 4.73 | 57 | 4.20 | 50 |
| Coagulation factor X | 9.69 | 101 | 4.20 | 47 * | 21.22 | 215 | 25.95 | 631 |
| Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor | 3.54 | 40 | 44.74 | 944 | 3.45 | 45 | 2.37 | 33 |
| Edoxaban | Enoxaparin | Sequoiaflavone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Euclidean Distance | Ranking | Euclidean Distance | Ranking | Euclidean Distance | Ranking | |
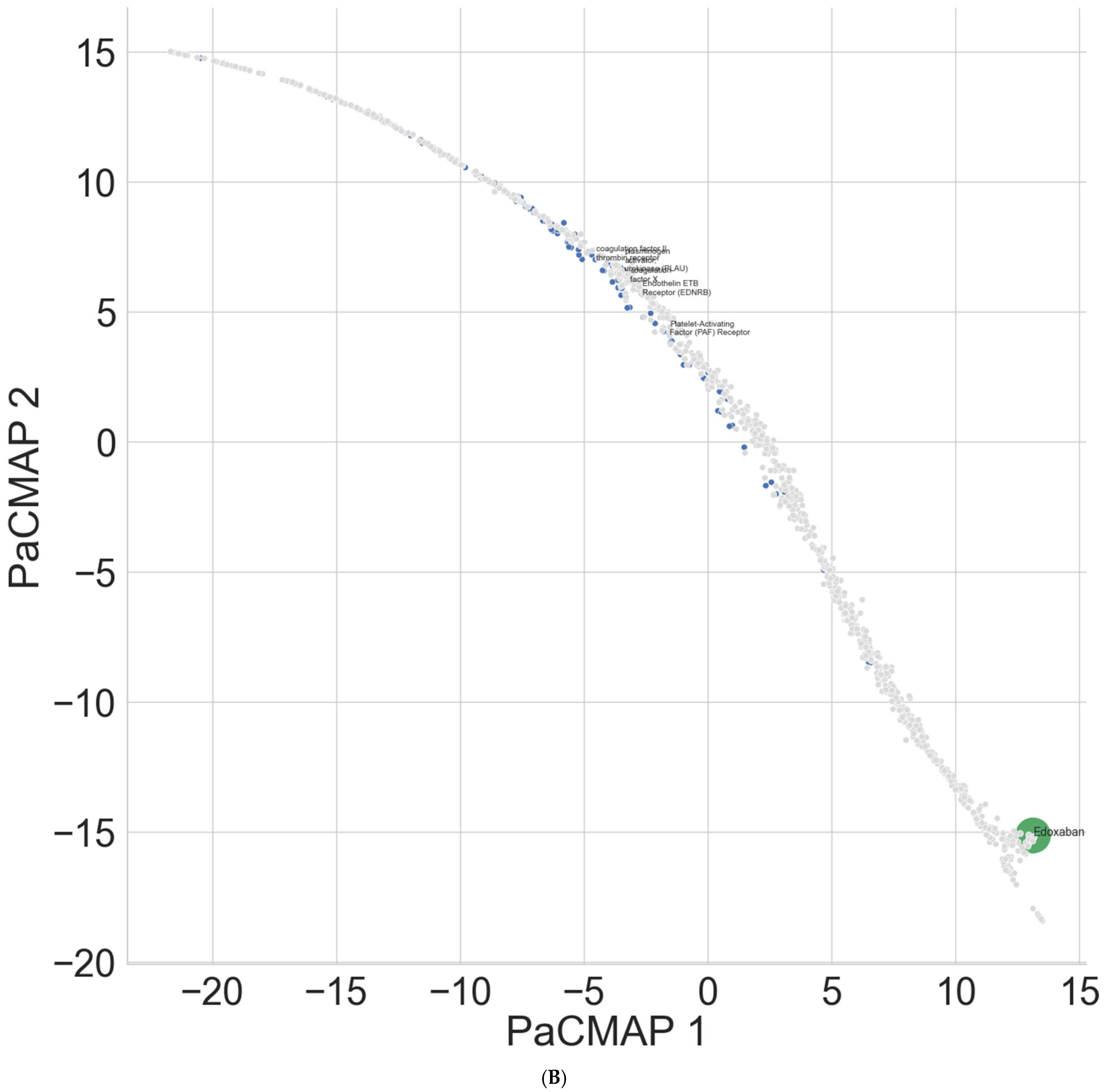
| Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor | 5.44 | 85 | 37.07 | 895 | 4.13 | 55 |
| Plasminogen activator urokinase (PLAU) | 2.40 | 37 | 3.60 | 57 | 18.26 | 166 |
| Endothelin ETB receptor (EDNRB) | 5.37 | 84 | 17.44 | 336 | 3.73 | 52 |
| Coagulation factor X | 4.28 | 66 | 1.98 | 34 * | 19.37 | 186 |
| coagulation factor II thrombin receptor | 3.59 | 55 | 9.15 | 143 | 1.63 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, T.; Llewellyn, R.; Hezzell, M.; Angelini, G.D. Rapid Screening of Anticoagulation Compounds for Biological Target-Associated Adverse Effects Using a Deep-Learning Framework in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090972
Dong T, Llewellyn R, Hezzell M, Angelini GD. Rapid Screening of Anticoagulation Compounds for Biological Target-Associated Adverse Effects Using a Deep-Learning Framework in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090972
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Tim, Rhys Llewellyn, Melanie Hezzell, and Gianni D. Angelini. 2025. "Rapid Screening of Anticoagulation Compounds for Biological Target-Associated Adverse Effects Using a Deep-Learning Framework in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090972
APA StyleDong, T., Llewellyn, R., Hezzell, M., & Angelini, G. D. (2025). Rapid Screening of Anticoagulation Compounds for Biological Target-Associated Adverse Effects Using a Deep-Learning Framework in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Bioengineering, 12(9), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090972







