Towards an Automated Computational Workflow to Assess Primary Stability in Total Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
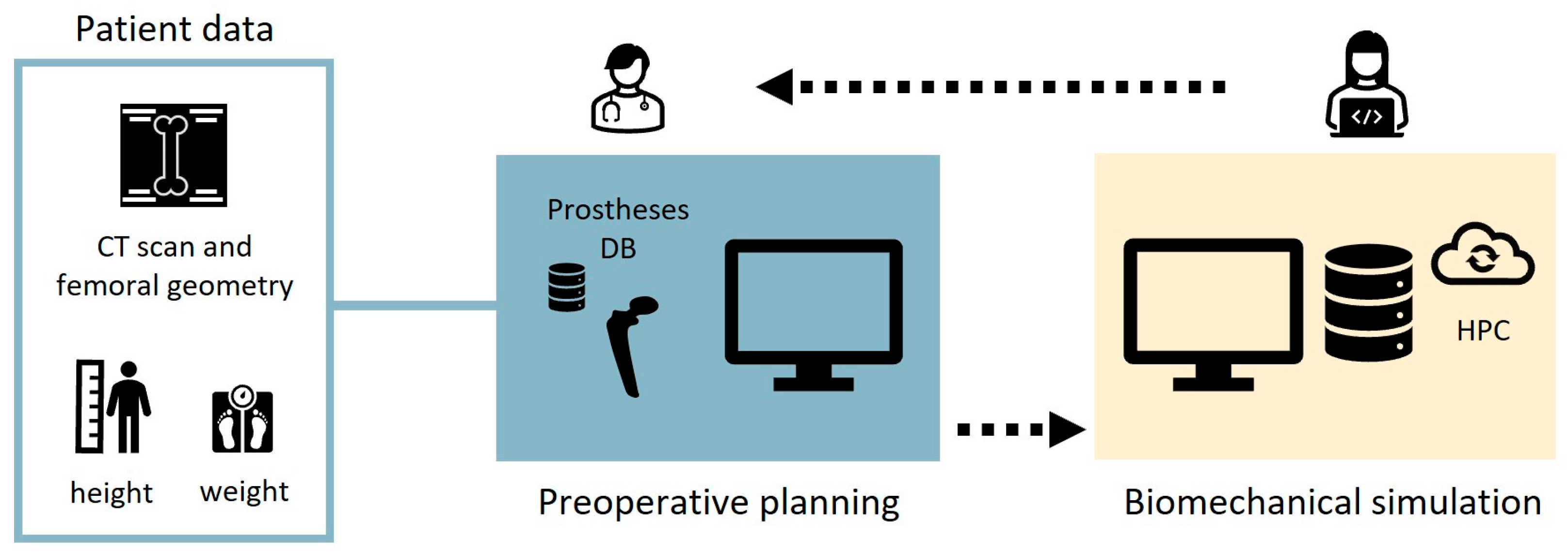
2.1. Description of the Workflow
2.2. Preoperative Planning
2.3. Biomechanical Simulation
2.3.1. Refinement of Femoral Geometry and Local Reference System
2.3.2. Boolean Subtraction
2.3.3. Meshing
2.3.4. Material Property Mapping
2.3.5. FE Simulation
2.4. Case Study
3. Results
3.1. Preoperative Planning
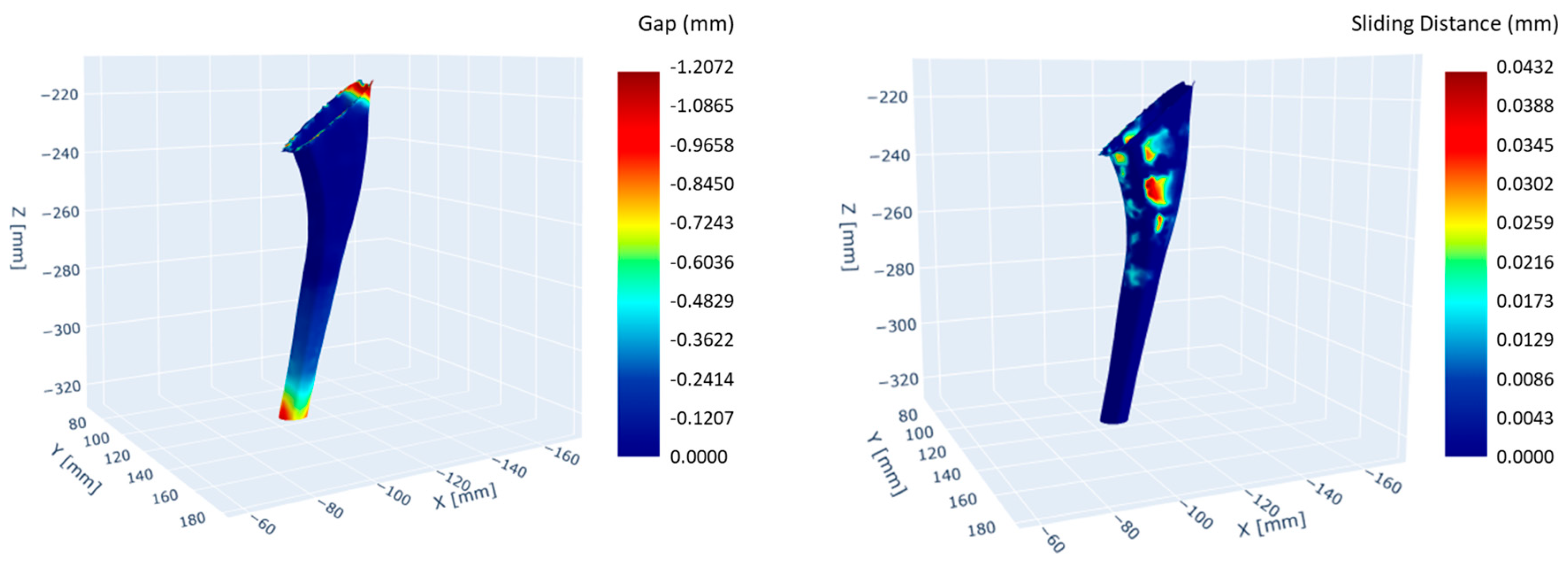
3.2. Biomechanical Simulation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, S.P.; Stambough, J.B.; Huddleston, J.I.; Levine, B.R. Highlights of the 2023 American Joint Replacement Registry Annual Report. Arthroplast. Today 2024, 26, 101325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.; Stambough, J.B.; Levine, B.R.; Springer, B.D. Highlights of the 2022 American Joint Replacement Registry Annual Report. Arthroplast. Today 2023, 21, 101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.M.; Farley, K.X.; Guild, G.N.; Bradbury, T.L. Projections and Epidemiology of Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the United States to 2030. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of Primary and Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. JBJS 2007, 89, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, M.; Young, S.W.; Frampton, C.M.; Hooper, G.J. The lifetime risk of revision following total hip arthroplasty: A New Zealand Joint Registry study. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103-B, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clohisy, J.C.; Calvert, G.; Tull, F.; McDonald, D.; Maloney, W.J. Reasons for Revision Hip Surgery: A Retrospective Review. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 429, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, I.; Nham, F.; Zalikha, A.K.; El-Othmani, M.M. Epidemiology of total hip arthroplasty: Demographics, comorbidities and outcomes. Arthroplasty 2023, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, C.; Dick, S.; Lea, J.; Liu, J.; Ebraheim, N.A. A systematic review of the causes of failure of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Orthop. 2019, 16, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühler, D.W.; Berlemann, U.; Lippuner, K.; Jaeger, P.; Nolte, L.P. Three-dimensional primary stability of cementless femoral stems. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilliar, R.M.; Lee, J.M.; Maniatopoulos, C. Observations on the Effect of Movement on Bone Ingrowth into Porous-Surfaced Implants. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1986, 208, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, N.; Stoddart, J.C.; van Arkel, R.J. The limit of tolerable micromotion for implant osseointegration: A systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søballe, K.; Hansen, E.S.; B.-Rasmussen, H.; Jørgensen, P.H.; Bünger, C. Tissue ingrowth into titanium and hydroxyapatite-coated implants during stable and unstable mechanical conditions. J. Orthop. Res. 1992, 10, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrholm, J.; Borssen, B.; Lowenhielm, G.; Snorrason, F. Does early micromotion of femoral stem prostheses matter? 4–7-year stereoradiographic follow-up of 84 cemented prostheses. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1994, 76-B, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dirini, R.M.A.; Huff, D.; Zhang, J.; Besier, T.; Clement, J.G.; Taylor, M. Influence of collars on the primary stability of cementless femoral stems: A finite element study using a diverse patient cohort. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dirini, R.M.A.; Martelli, S.; Huff, D.; Zhang, J.; Clement, J.G.; Besier, T.; Taylor, M. Evaluating the primary stability of standard vs lateralised cementless femoral stems—A finite element study using a diverse patient cohort. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 59, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bah, M.T.; Shi, J.; Heller, M.O.; Suchier, Y.; Lefebvre, F.; Young, P.; King, L.; Dunlop, D.G.; Boettcher, M.; Draper, E.; et al. Inter-subject variability effects on the primary stability of a short cementless femoral stem. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dirini, R.M.A.; Martelli, S.; Taylor, M. Computational efficient method for assessing the influence of surgical variability on primary stability of a contemporary femoral stem in a cohort of subjects. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2020, 19, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dirini, R.M.A.; Martelli, S.; O’ROurke, D.; Huff, D.; Zhang, J.; Clement, J.G.; Besier, T.; Taylor, M. Virtual trial to evaluate the robustness of cementless femoral stems to patient and surgical variation. J. Biomech. 2019, 82, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancanti, A.; Bernakiewicz, M.; Viceconti, M. The primary stability of a cementless stem varies between subjects as much as between activities. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viceconti, M.; Testi, D.; Simeoni, M.; Zannoni, C. An automated method to position prosthetic components within multiple anatomical spaces. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2003, 70, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moralidou, M.; Laura, A.D.; Henckel, J.; Hothi, H.; Hart, A.J. Three-dimensional pre-operative planning of primary hip arthroplasty: A systematic literature review. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knafo, Y.; Houfani, F.; Zaharia, B.; Egrise, F.; Clerc-Urmès, I.; Mainard, D. Value of 3D Preoperative Planning for Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Based on Biplanar Weightbearing Radiographs. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1932191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, S.; Kabata, T.; Maeda, T.; Kajino, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Kuroda, K.; Fujita, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Tsuchiya, H. Three-dimensional kinetic simulation before and after rotational acetabular osteotomy. J. Orthop. Sci. 2014, 19, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, J.; Chênes, C.; Chagué, S.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Christofilopoulos, P.; Bernardoni, M.; Charbonnier, C. MyHip: Supporting planning and surgical guidance for a better total hip arthroplasty. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2015, 10, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viceconti, M.; Zannoni, C.; Testi, D.; Petrone, M.; Perticoni, S.; Quadrani, P.; Taddei, F.; Imboden, S.; Clapworthy, G. The multimod application framework: A rapid application development tool for computer aided medicine. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2007, 85, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, D.; Kabata, T.; Maeda, T.; Kajino, Y.; Fujita, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Takagi, T.; Ohmori, T.; Tsuchiya, H. Usefullness of three-dimensional templating software to quantify the contact state between implant and femur in total hip arthroplasty. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. Orthop. Traumatol. 2015, 25, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, R.; Viceconti, M.; Zannoni, C.; Quadrani, P.; Toni, A. Hip-Op: An innovative software to plan total hip replacement surgery. Med. Inform. Internet Med. 2002, 27, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testi, D.; Quadrani, P.; Petrone, M.; Zannoni, C.; Fontana, F.; Viceconti, M. JIDE: A new software for computer-aided design of hip prosthesis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2004, 75, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, B.; Cristofolini, L.; Varini, E.; Viceconti, M. Predicting the subject-specific primary stability of cementless implants during pre-operative planning: Preliminary validation of subject-specific finite-element models. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldieri, A.; La Mattina, A.A.; Szyszko, J.A.; Baruffaldi, F.; Viceconti, M. HFValid Collection: Hip-Fracture Validation Collection; Alma Mater Studiorum—Università di Bologna: Bologna, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viceconti, M.; Lattanzi, R.; Zannoni, C.; Cappello, A. Effect of display modality on spatial accuracy of orthopaedic surgery pre-operative planning applications. Med. Inform. Internet Med. 2002, 27, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Nakano, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Kamenaga, T.; Tsubosaka, M.; Tachibana, S.; Kuroda, R. The assessment of canal flare index and proximal femoral bone density can improve stem selection for peri-prosthetic bone maintenance after total hip arthroplasty. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2024, 144, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, F.; Merlo, M.; Liang, Y.; Kupcha, P.; Jamison, J.; Harcke, H.T. Femoral version and neck shaft angle. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1993, 13, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayiannis, P.N.; Cassidy, R.S.; Hill, J.C.; Dorr, L.D.; Beverland, D.E. The Relationship Between Canal Diameter and the Dorr Classification. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 3204–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.D. Mastering GUI Programming with Python: Develop Impressive Cross-Platform GUI Applications with PyQt; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, W.; Martin, K.; Lorensen, B. The Visualization Toolkit, 4th ed.; Kitware Inc.: Clifton Park, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, M.M.; Liu, X.; Ibanez, L.; Jomier, J.; Marion, C. ITK: Enabling reproducible research and open science. Front. Neuroinformatics 2014, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldieri, A.; Biondi, R.; La Mattina, A.A.; Szyszko, J.A.; Polizzi, S.; Dall’oLio, D.; Curti, N.; Castellani, G.; Viceconti, M. Development and validation of a semi-automated and unsupervised method for femur segmentation from CT. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, G.; Deuretzbacher, G.; Heller, M.; Graichen, F.; Rohlmann, A.; Strauss, J.; Duda, G. Hip contact forces and gait patterns from routine activities. J. Biomech. 2001, 34, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, F.; Schileo, E.; Helgason, B.; Cristofolini, L.; Viceconti, M. The material mapping strategy influences the accuracy of CT-based finite element models of bones: An evaluation against experimental measurements. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldieri, A.; Curreli, C.; Szyszko, J.A.; La Mattina, A.A.; Viceconti, M. Credibility assessment of computational models according to ASME V&V40: Application to the Bologna Biomechanical Computed Tomography solution. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 240, 107727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, M.; La Mattina, A.A.; Curreli, C.; Tassinari, E.; Viceconti, M. A finite element model to simulate intraoperative fractures in cementless hip stem designs. Med. Eng. Phys. 2025, 135, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigart, K.C.; Nahhas, C.R.; Ruzich, G.P.; Culvern, C.N.; Salzano, M.B.; Della Valle, C.J.; Nam, D. Does Femoral Morphology Predict the Risk of Periprosthetic Fracture After Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty? J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S359–S363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Efficacy and safety of modular versus monoblock stems in revision total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2023, 24, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercuri, M.; Toccaceli, E.; Sun, X.; Marongiu, G.; Viceconti, M.; La Mattina, A.A.; Curreli, C. Towards an Automated Computational Workflow to Assess Primary Stability in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070723
Mercuri M, Toccaceli E, Sun X, Marongiu G, Viceconti M, La Mattina AA, Curreli C. Towards an Automated Computational Workflow to Assess Primary Stability in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070723
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercuri, Massimiliano, Enrico Toccaceli, Xiaoshu Sun, Giuseppe Marongiu, Marco Viceconti, Antonino Amedeo La Mattina, and Cristina Curreli. 2025. "Towards an Automated Computational Workflow to Assess Primary Stability in Total Hip Arthroplasty" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070723
APA StyleMercuri, M., Toccaceli, E., Sun, X., Marongiu, G., Viceconti, M., La Mattina, A. A., & Curreli, C. (2025). Towards an Automated Computational Workflow to Assess Primary Stability in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Bioengineering, 12(7), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070723








