Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound-Guided Microwave Ablation for Iatrogenic Hepatic Hemorrhage: A Feasibility Study on Precision Hemostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Instruments and Materials
2.3. Treatment Methods
2.4. Intraoperative Treatment
2.5. Postoperative Management
2.6. Observation Indicators and Evaluation Criteria
3. Results
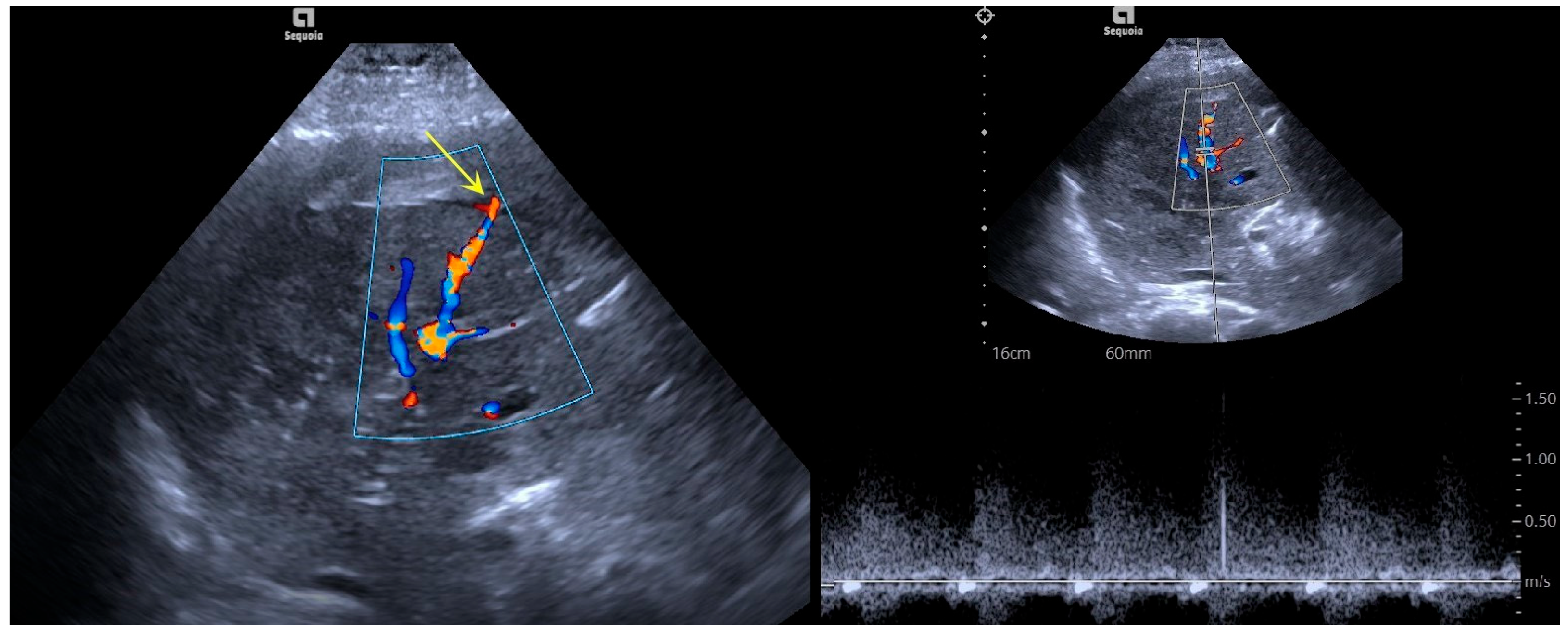
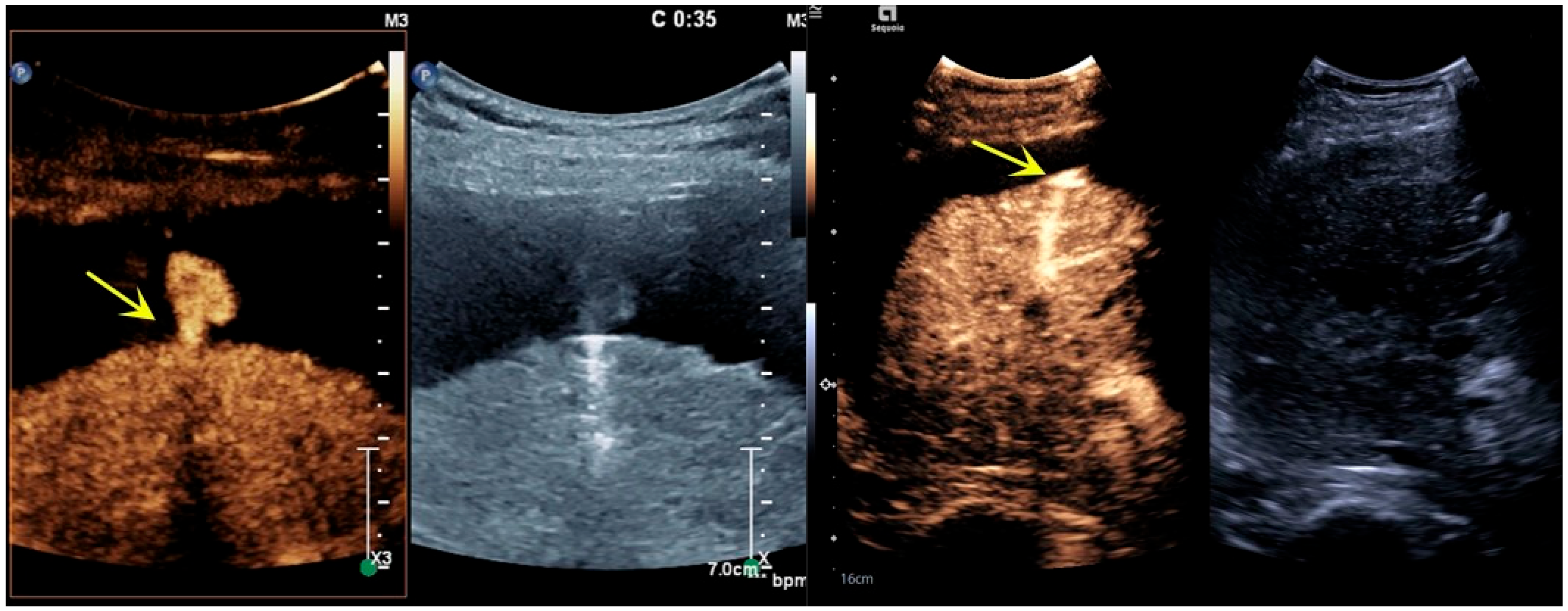
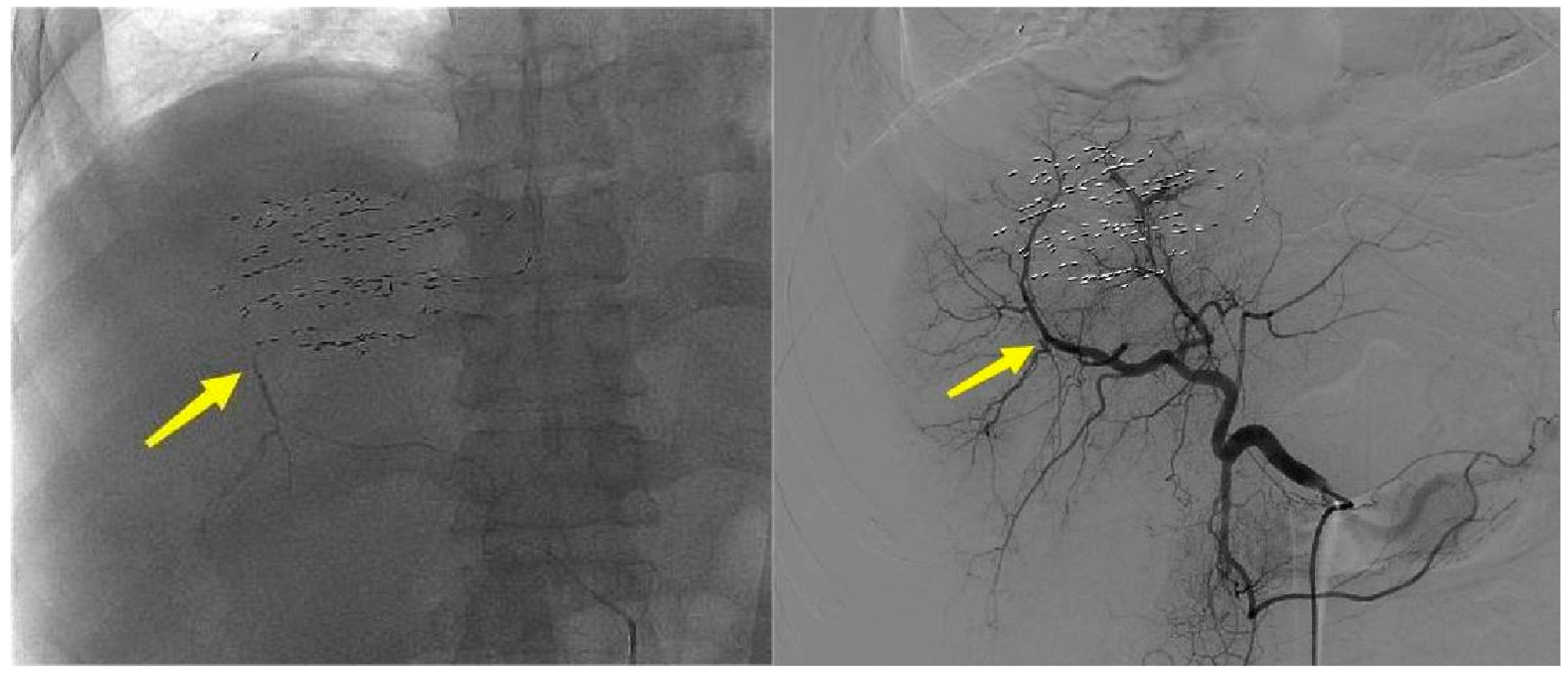
3.1. Imaging Features
3.2. Treatment Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Cao, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Shen, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Shi, L.; et al. Life-threatening event in laparoscopic hepatic surgery: Training curriculum on sudden hepatic artery haemorrhage. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2024, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-H.; Wang, S.-E.; Shyr, B.-S.; Chen, S.-C.; Shyr, Y.-M.; Shyr, B.-U. Impact of hepatic artery variation on surgical and oncological outcomes in robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surg. Endosc. 2024, 38, 3728–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.P.; Yu, M.; Zhang, M.; Han, Z.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhu, T.; Zhou, X.D. Diagnosis of active hemorrhage from the liver with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography after percutaneous transhepatic angioplasty and stent placement for Budd-Chiari syndrome. J. Ultrasound Med. 2009, 28, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Tian, G.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, T. Fast hemostasis: A win-win strategy for ultrasound and microwave ablation. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Yu, J.; Lu, M.D.; Dong, B.W.; Yu, X.L.; Zhou, X.D.; Hu, B.; Xie, M.X.; Cheng, W.; He, W.; et al. Practice guidelines for ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatic malignancy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5430–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Sun, L.; Xu, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, J. Intracystic Hemorrhage and Its Management During Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation for Cystic Thyroid Nodules. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Lin, Y. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2020, 40, 3653–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Go, V.A.; Blanck, J.F.; Singh, B. A Systematic Review of Minimally Invasive Treatments for Uterine Fibroid-Related Bleeding. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 2786–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Itou, H.; Kida, A.; Sunakawa, H.; Kawamura, K. Microwave ablation for the control of bleeding from disintegrated mammary tumours in two dogs. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.P.; Yu, M.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.H.; Su, H.L.; Ren, X.L.; Wei, Z.R.; Luo, W.; He, J.G.; Zhou, X.D. Hemostasis of active bleeding from the liver with percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy under contrast-enhanced ultrasonographic guidance: An experimental study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2008, 27, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, Z.; Gu, F.; He, J.; Yan, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X. The impact of microbubble-enhanced therapeutic ultrasound combined with prothrombin on microwave ablation in the rabbit liver. Med. Ultrason. 2016, 18, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Qian, N.S.; Luo, W.; Han, Z.H.; Yu, M.; Meng, X.; He, J.G.; Zhou, X.D. Percutaneous injection of hemostatic agents for active liver hemorrhage. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2010, 9, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; He, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Luo, W.; Qin, H.; Liu, H.; et al. Ultrasound-Guided Intratumoral Radiofrequency Ablation Coagulation to Facilitate Meningioma Resection: Preliminary Experience. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, F.; Granata, V.; Grassi, R.; Fusco, R.; Palaia, R.; Delrio, P.; Carrafiello, G.; Azoulay, D.; Petrillo, A.; Curley, S.A. Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation in Liver Tumors: An Update. Oncologist 2019, 24, e990–e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Ding, X.M.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, J.; Kong, J.; Sun, W.B. Radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous permanent iodine-125 implantation as salvage therapy for giant recurrent sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma of the chest wall: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2163–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; He, G.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xian, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, D. An Injectable Hydrogel with Ultrahigh Burst Pressure and Innate Antibacterial Activity for Emergency Hemostasis and Wound Repair. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2404811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, A.; Hickman, D.A.; Banerjee, A.; Luc, N.; Ma, Y.; Miyazawa, K.; Sekhon, U.D.S.; Sun, M.; Huang, S.; Sen Gupta, A. Trauma-targeted delivery of tranexamic acid improves hemostasis and survival in rat liver hemorrhage model. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, O.K.; Ng, L.F.; Yu, P.S.; Chan, J.C. Post biopsy Liver Hemorrhage Successfully Controlled by Ultrasound-guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2016, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, K. Post biopsy delayed liver hemorrhage successfully controlled by bedside CEUS-guided microwave ablation: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Li, S.; Gao, N.; Guan, Z.; Song, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q.; He, L.; Guo, J.; An, L. Effect of ultrasonic burst microbubbles on microwave coagulation hemostasis in a pig model of hepatic hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Kelekis, A.; Zhao, Q.; Mazioti, A.; Liu, J.; Kelekis, N.; Tian, G.; Filippiadis, D. Safety and efficacy of percutaneous microwave ablation for post-procedural haemostasis: A bi-central retrospective study focusing on safety and efficacy. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.T. Stabilized sulfur hexafluoride microbubbles. In Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD); National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Facciorusso, A.; Abd El Aziz, M.A.; Tartaglia, N.; Ramai, D.; Mohan, B.P.; Cotsoglou, C.; Pusceddu, S.; Giacomelli, L.; Ambrosi, A.; Sacco, R. Microwave Ablation Versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Cancers 2020, 12, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case | Disease | Bleeding Location | Cause of Bleeding | Bleeding Time | Ablation Power/Time | Successful Hemostasis | Complications and Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CTPV | Right anterior inferior branch | After percutaneous transhepatic portal vein puncture for TIPS Cirrhosis and Platelet deficiency | Immediately | 80 W/120 s | Yes | None |
| 2 | Primary Liver Cancer | Right anterior inferior branch | Percutaneous puncture particle implantation | Immediately | 80 W/120 s | Yes | None |
| 3 | CTPV | Right posterior inferior branch | After percutaneous transhepatic portal vein puncture for TIPS Cirrhosis and Platelet deficiency | Immediately | 80 W/120 s | Yes | None |
| 4 | CTPV | Right posterior inferior branch | After percutaneous transhepatic portal vein puncture for TIPS Cirrhosis and Platelet deficiency | Immediately | 80 W/120 s | Yes | None |
| 5 | CTPV | Right posterior inferior branch | After percutaneous transhepatic portal vein puncture for TIPS Cirrhosis and Platelet deficiency | 4 h | 80 W/180 s | Yes | Mild abdominal pain |
| 6 | Primary Liver Cancer | Right anterior inferior branch | Percutaneous puncture particle implantation | Immediately | 80 W/120 s | Yes | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yan, L. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound-Guided Microwave Ablation for Iatrogenic Hepatic Hemorrhage: A Feasibility Study on Precision Hemostasis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060584
Li Q, Liu Y, Han Z, Zhou X, Wang J, Zhou X, Yan L. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound-Guided Microwave Ablation for Iatrogenic Hepatic Hemorrhage: A Feasibility Study on Precision Hemostasis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060584
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qing, Yi Liu, Zenghui Han, Xuan Zhou, Jianwei Wang, Xiaodong Zhou, and Li Yan. 2025. "Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound-Guided Microwave Ablation for Iatrogenic Hepatic Hemorrhage: A Feasibility Study on Precision Hemostasis" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060584
APA StyleLi, Q., Liu, Y., Han, Z., Zhou, X., Wang, J., Zhou, X., & Yan, L. (2025). Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound-Guided Microwave Ablation for Iatrogenic Hepatic Hemorrhage: A Feasibility Study on Precision Hemostasis. Bioengineering, 12(6), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060584






