Design of a Janus Composite Patch with Anti-Adhesive and Growth-Promoting Functions for Abdominal Wall Defect Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Biomaterial Inks
2.3. Manufacturing of Patch
2.4. Micromorphology Characterization
2.5. Pore Size and Porosity Test
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.7. Wettability Analysis
2.8. Mechanical Property Evaluation
2.9. In Vitro Cell Experiments
2.9.1. Cell Culture
2.9.2. Adhesion Analysis
2.9.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.9.4. Cell Morphology Assay
2.10. In Vivo Animal Experiment
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
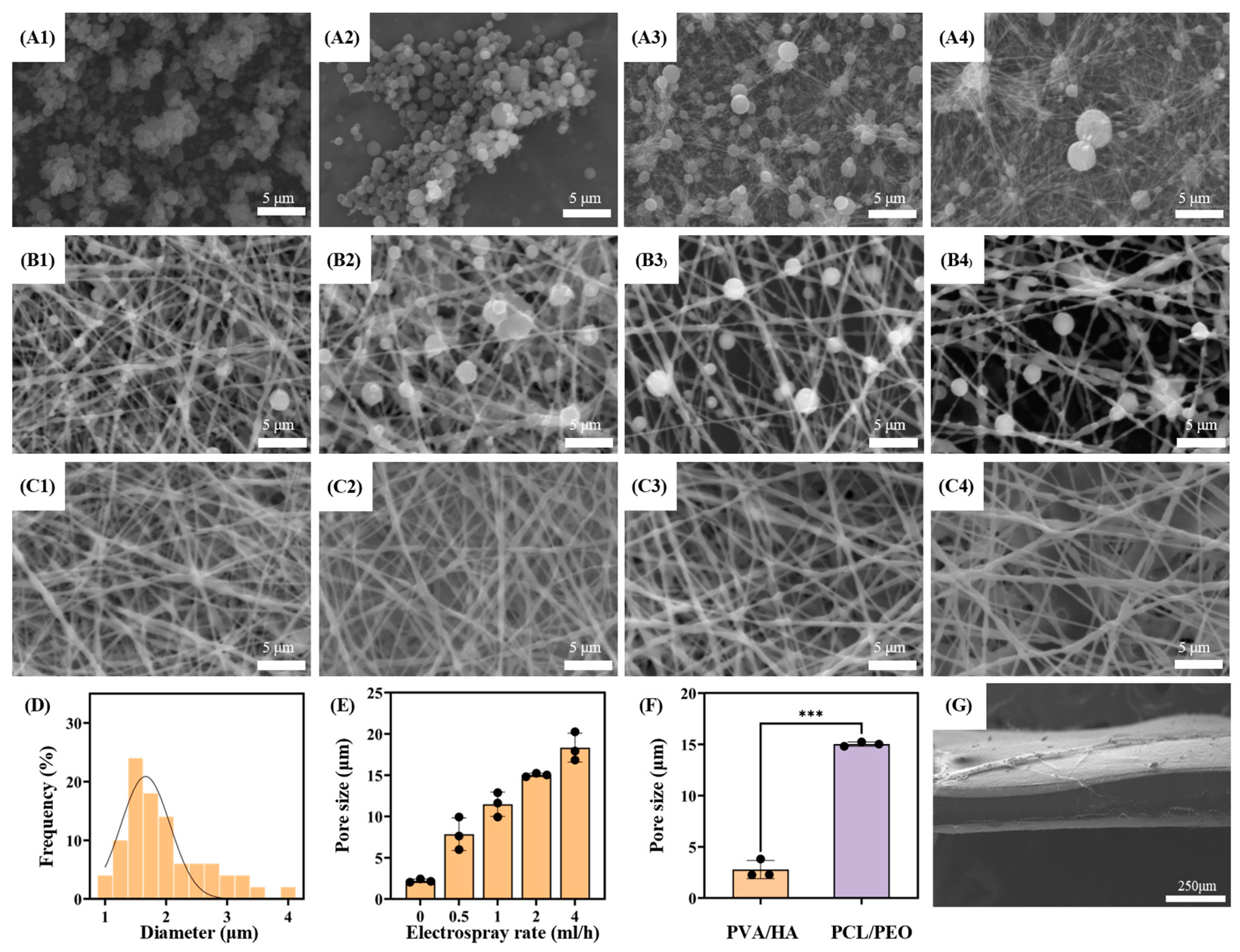
3.1. Micromorphology Characterization and Pore Size and Porosity Test
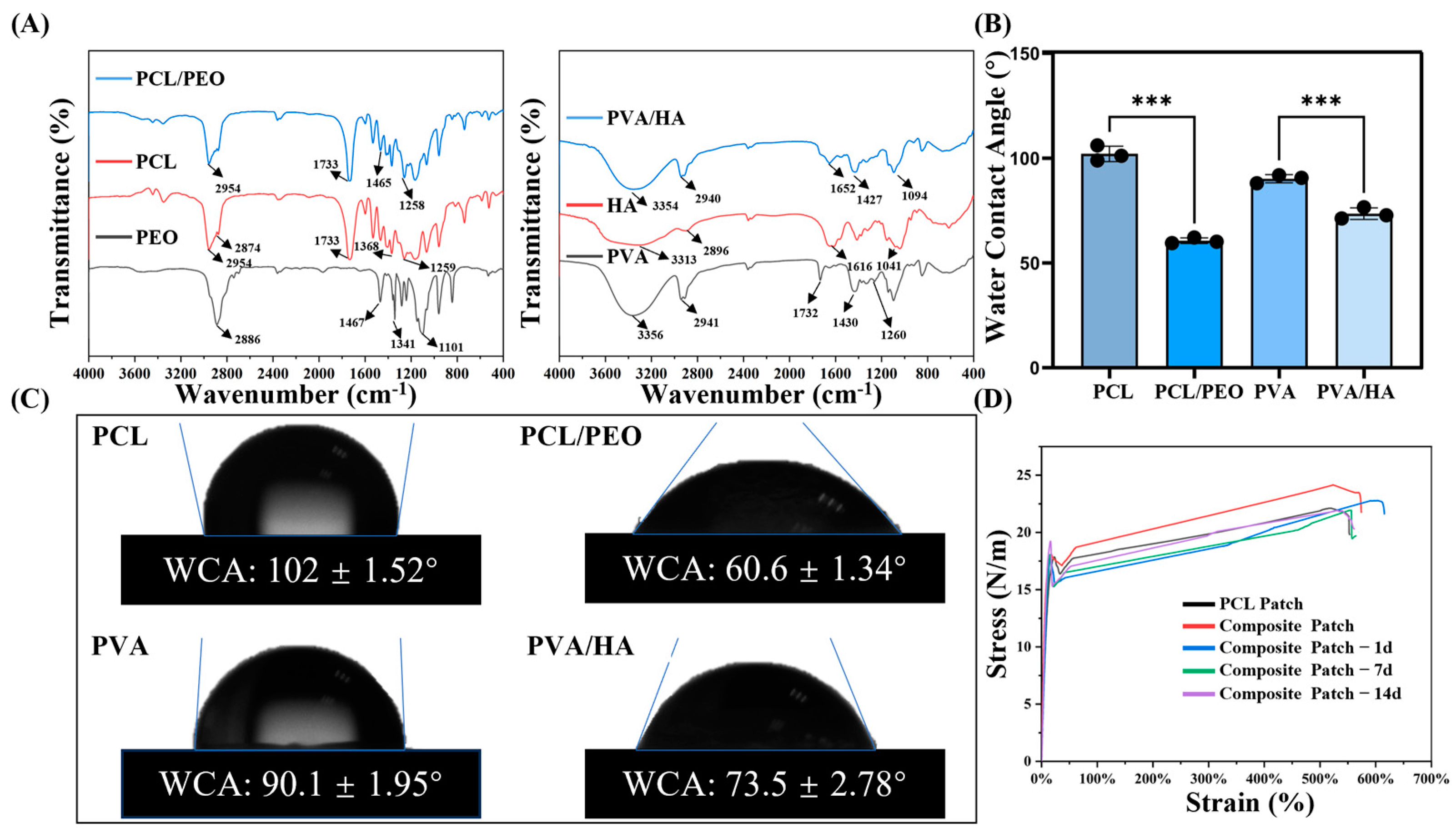
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. Wettability Analysis
3.4. Mechanical Property Evaluation
3.5. In Vitro Cell Experiments
3.5.1. Adhesion Analysis
3.5.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.5.3. Cell Morphology Assay
3.6. In Vivo Animal Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PP | polypropylene |
| PET | poly(ethylene terephthalate) |
| PTFE | polytetrafluoroethylene |
| SIS | small intestinal submucosa |
| PVA | polyvinyl alcohol) |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| PLGA | poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PCL | polycaprolactone |
| PEO | Poly(ethylene oxide) |
| HA | sodium hyaluronate |
| SP | soy peptide |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| AA | acetic acid |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| WCA | water contact angle |
| HUVECs | human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| ANOVA | one-way analysis of variance |
| OD | optical density |
References
- Kalaba, S.; Gerhard, E.; Winder, J.S.; Pauli, E.M.; Haluck, R.S.; Yang, J. Design strategies and applications of biomaterials and devices for hernia repair. Bioact. Mater. 2016, 1, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringman, S.; Conze, J.; Cuccurullo, D.; Deprest, J.; Junge, K.; Klosterhalfen, B.; Parra-Davila, E.; Ramshaw, B.; Schumpelick, V. Hernia repair: The search for ideal meshes. Hernia 2010, 14, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J. Chapter 7: Possible Gains of Optimizing Surgical Techniques in Preventing Incisional Hernia. In Incisional Hernia Etiology, Prevention, Treatment; Erasmus University Rotterdam: Rotterdam, The Netherlands; pp. 81–92.
- Kaufmann, R.; Halm, J.A.; Eker, H.H.; Klitsie, P.J.; Nieuwenhuizen, J.; van Geldere, D.; Simons, M.P.; van der Harst, E.; van’t Riet, M.; van der Holt, B. Mesh versus suture repair of umbilical hernia in adults: A randomised, double-blind, controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Adamo, S.; Gossetti, F.; D’Amore, L.; Ceci, F.; Negro, P.; Bruzzone, P. Biological scaffolds for abdominal wall repair: Future in clinical application? Materials 2019, 12, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Y. 3D printing/electrospinning of a bilayered composite patch with antibacterial and antiadhesive properties for repairing abdominal wall defects. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 10054–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todros, S.; Pavan, P.; Natali, A. Synthetic surgical meshes used in abdominal wall surgery: Part I—Materials and structural conformation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Macdougall, K.; Olabisi, O.; McGuire, N. In vivo response to polypropylene following implantation in animal models: A review of biocompatibility. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2017, 28, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Hao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Mei, L.; Sui, K.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, J. Bio-multifunctional hydrogel patches for repairing full-thickness abdominal wall defects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Halm, J.; Wijsmuller, A.; Raa, S.T.; Jeekel, J. Evaluation of new prosthetic meshes for ventral hernia repair. Surg. Endosc. 2006, 20, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; He, W.; Huang, R.; Tang, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, B.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, D. Peritoneum-inspired Janus porous hydrogel with anti-deformation, anti-adhesion, and pro-healing characteristics for abdominal wall defect treatment. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Zou, M.; Ju, R.; Feng, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, T. Study on repair of abdominal wall defect rats with hernia mesh coated with chitosan-based photosensitive hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scimone, M.L.; Cote, L.E.; Reddien, P.W. Orthogonal muscle fibres have different instructive roles in planarian regeneration. Nature 2017, 551, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, R.; Song, L.; Luan, S. Endogenous stimulation-driven Janus mesh with antibacterial, anti-adhesive and prohealing performances for hernia repair. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 152764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhosseininia, M.; Bazgir, S.; Joupari, M.D. Fabrication and investigation of silica nanofibers via electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, A.P.; Hatton, P.V. Biopolymer Methods in Tissue Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 238. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Guidoin, R.; Brochu, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, L. Facile fabrication of phospholipid-functionalized nanofiber-based barriers with enhanced anti-adhesion efficiency. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Mchugh, K.; Chew, S.Y.; Anderson, J.M. The topographical effect of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds on the in vivo and in vitro foreign body reaction. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalony, C.; Aguilar, L.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Development of electrospun core–shell polymeric mat using poly (ethyl-2) cyanoacrylate/polyurethane to attenuate biological adhesion on polymeric mesh implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 122, 111930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, P.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. An anti-inflammatory chondroitin sulfate-poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) composite electrospinning membrane for postoperative abdominal adhesion prevention. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 6573–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.; Andric, T.; Freeman, J. Utilizing NaCl to increase the porosity of electrospun materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wong, Y.S.; Wen, F.; Ng, K.W.; Ng, G.K.L.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Tan, L.P. Human mesenchymal stem-cell behaviour on direct laser micropatterned electrospun scaffolds with hierarchical structures. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhu, J.; Luo, J.; Xiong, J. Investigation of microporous composite scaffolds fabricated by embedding sacrificial polyethylene glycol microspheres in nanofibrous membrane. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 91, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yao, G. Electrospinning/3D printing drug-loaded antibacterial polycaprolactone nanofiber/sodium alginate-gelatin hydrogel bilayer scaffold for skin wound repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 129705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Yao, G.; Zhang, H. Electrospinning drug-loaded polycaprolactone/polycaprolactone-gelatin multi-functional bilayer nanofibers composite scaffold for postoperative wound healing of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 8, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, P.; Narmadha, R.; Selvakumar, R. Synthesis and characterization of anti-adhesion tricomposite electrospun nanofiber barrier membrane for use in post-surgical adhesion conditions. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 129038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, X.; He, C.; Wang, H. Intermolecular interactions in electrospun collagen–chitosan complex nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, N.; Zhang, X. Hyaluronic acid and oxidized regenerated cellulose prevent adhesion reformation after adhesiolysis in rat models. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3501–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo-Javé, E.E.; Mendoza-Barrera, G.E.; García-Pineda, M.A.; Jaime Limón, Á.R.; Montalvo-Arenas, C.; Castell Rodríguez, A.E.; Jurado, J.T. Histological analysis of intra-abdominal adhesions treated with sodium hyaluronate and carboxymethylcellulose gel. J. Investig. Surg. 2016, 29, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbez, B.; Libouban, H. Biomaterials preparation by electrospinning of gelatin and sodium hyaluronate/gelatin nanofibers with non-toxic solvents. Morphologie 2020, 104, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutschmidt, D.; Hazra, R.S.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Sabzi, M.; Jiang, L. Electrospun, sepiolite-loaded poly (vinyl alcohol)/soy protein isolate nanofibers: Preparation, characterization, and their drug release behavior. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 594, 120172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftoonazad, N.; Shahamirian, M.; John, D.; Ramaswamy, H. Development and evaluation of antibacterial electrospun pea protein isolate-polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite mats incorporated with cinnamaldehyde. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, W.; Gu, Y.; Liu, S. Designing Double-Layer Multimaterial Composite Patch Scaffold with Adhesion Resistance for Hernia Repair. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejazi, F.; Mousavi, S.M. Electrospun nanofibrous composite membranes of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol-polyacrylonitrile: Preparation, characterization, and performance. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, S.J.; Sampson, W.W. Statistical geometry of pores and statistics of porous nanofibrous assemblies. J. R. Soc. Interface 2005, 2, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Hu, X.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H. 3D printed biomimetic composite scaffolds with sequential releasing of copper ions and dexamethasone for cascade regulation of angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, J.; Dagher, H. 3D hybrid ballistic fabric testing using a 3d digital image correlation system. Exp. Tech. 2011, 35, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortillés, Á.; Pascual, G.; Peña, E.; Rodríguez, M.; Pérez-Köhler, B.; Mesa-Ciller, C.; Calvo, B.; Bellón, J. Biomechanical and histologic evaluation of two application forms of surgical glue for mesh fixation to the abdominal wall. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 75, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskitoros-Togay, Ş.M.; Bulbul, Y.E.; Tort, S.; Korkmaz, F.D.; Acartürk, F.; Dilsiz, N. Fabrication of doxycycline-loaded electrospun PCL/PEO membranes for a potential drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avsar, G.; Agirbasli, D.; Agirbasli, M.A.; Gunduz, O.; Oner, E.T. Levan based fibrous scaffolds electrospun via co-axial and single-needle techniques for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Y.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Kamoun, E.A.; Loutfy, S.A.; Amin, R.; Taha, T.H.; Salim, S.A.; Amer, M. Electrospun PVA/hyaluronic acid/L-arginine nanofibers for wound healing applications: Nanofibers optimization and in vitro bioevaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Z.K.; Fang, M.Y.; Wu, T.Y.; Yang, T.; Tseng, H.W.; Chen, C.C.; Cheng, C.M. Hydrophilic films: How hydrophilicity affects blood compatibility and cellular compatibility. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Xiao, W.; Sun, J.; Zhong, M.; Guo, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X.J. A biocompatible hydrogel with improved stiffness and hydrophilicity for modular tissue engineering assembly. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2753–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonov, D.V.; Islamova, A.G.; Strizhak, P.A. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces: Features of interaction with liquid drops. Materials 2023, 16, 5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Ma, P.; Jiang, G.; Wan, A. Mechanical properties of polypropylene warp-knitted hernia repair mesh with different pull densities. Polymers 2018, 10, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeken, C.R.; Lake, S.P. Mechanical properties of the abdominal wall and biomaterials utilized for hernia repair. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 74, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurth, J.J.; Blumenthal, N.R.; Shastri, V.P. Hydrophilization of poly (caprolactone) copolymers through introduction of oligo (ethylene glycol) moieties. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zhong, C.; Xu, R.; Zou, T.; Wang, F.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z. Novel large-pore lightweight polypropylene mesh has better biocompatibility for rat model of hernia. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanprasert, P.; Tepmalai, K.; Chakrabandhu, B.; Yodkeeree, S.; Piyamongkol, W.; Yamada, S.L. Collagen deposition and inflammatory response associated with macroporous mesh shrinkage in incisional hernia repair: A rat model. J. Investig. Surg. 2022, 35, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikfarjam, S.; Aldubaisi, Y.; Swami, V.; Swami, V.; Xu, G.; Vaughan, M.B.; Wolf, R.F.; Khandaker, M. Polycaprolactone electrospun nanofiber membrane with skin graft containing collagen and bandage containing MgO nanoparticles for wound healing applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, M.; Cakir, M.; Avsar, F.M.; Tekin, A.; Kucukkartallar, T.; Akoz, M. The effects of anti-adhesion materials in preventing postoperative adhesion in abdominal cavity (anti-adhesion materials for postoperative adhesions). Inflammation 2007, 30, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvashnina, A.; Melnychenko, M.; Rybalchenko, V. Clinical effectiveness of sodium hyaluronate gel usage for prevention of postoperative adhesion in children. Mod. Pediatr. Ukr. 2022, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Q.; Hou, X.; Shi, H.; Song, Y.; Zhou, B.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Y. Design of a Janus Composite Patch with Anti-Adhesive and Growth-Promoting Functions for Abdominal Wall Defect Repair. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050522
Hu Q, Hou X, Shi H, Song Y, Zhou B, Hu X, Zhang H, Gu Y. Design of a Janus Composite Patch with Anti-Adhesive and Growth-Promoting Functions for Abdominal Wall Defect Repair. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050522
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Qingxi, Xiaoyang Hou, Hekai Shi, Yongteng Song, Bing Zhou, Xinli Hu, Haiguang Zhang, and Yan Gu. 2025. "Design of a Janus Composite Patch with Anti-Adhesive and Growth-Promoting Functions for Abdominal Wall Defect Repair" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050522
APA StyleHu, Q., Hou, X., Shi, H., Song, Y., Zhou, B., Hu, X., Zhang, H., & Gu, Y. (2025). Design of a Janus Composite Patch with Anti-Adhesive and Growth-Promoting Functions for Abdominal Wall Defect Repair. Bioengineering, 12(5), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050522




