Opportunities for Artificial Intelligence in Operational Medicine: Lessons from the United States Military
Abstract
1. Background
2. Early AI
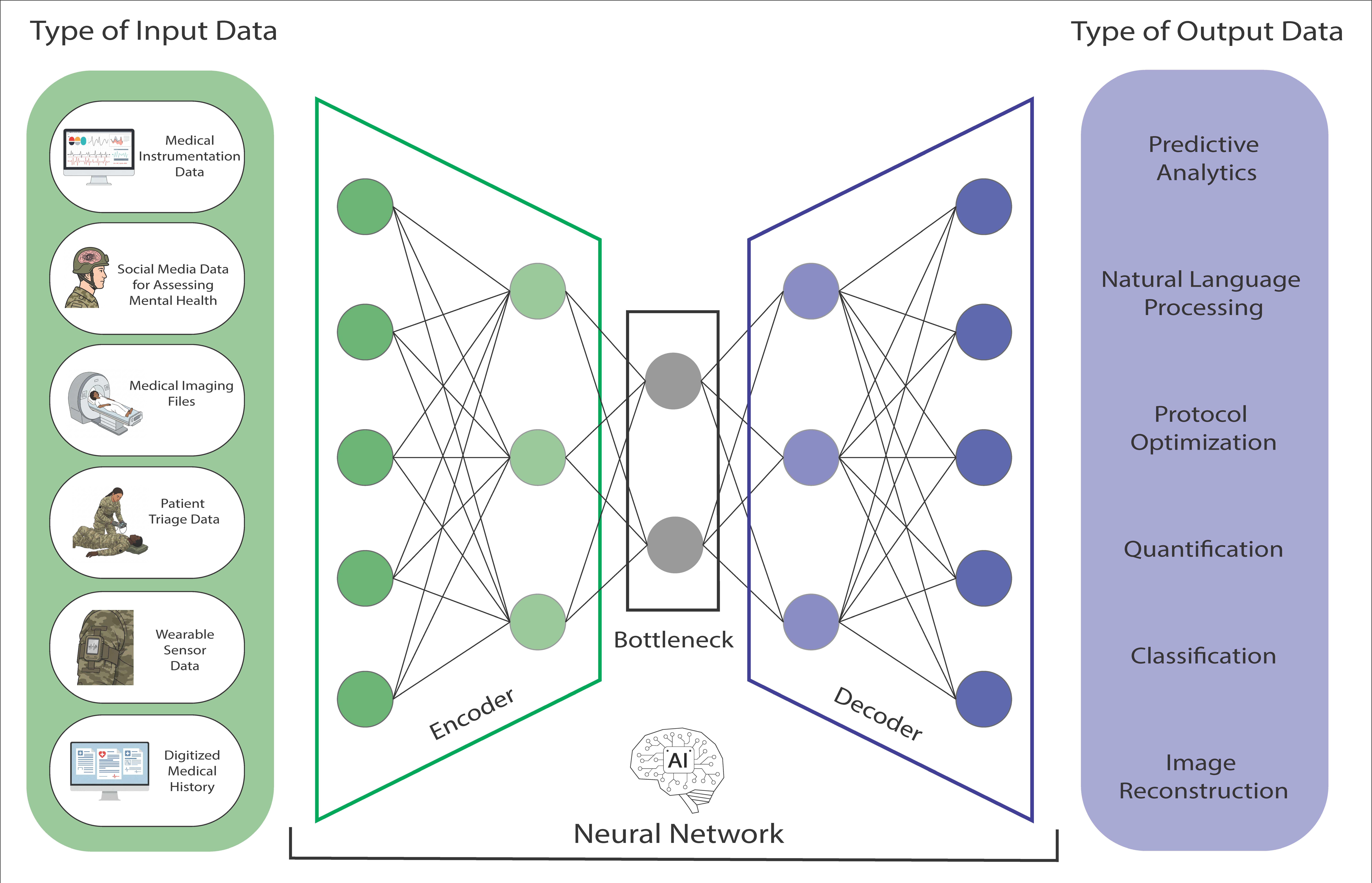
3. AI Health Applications in Austere Locations: Lessons from the US Military
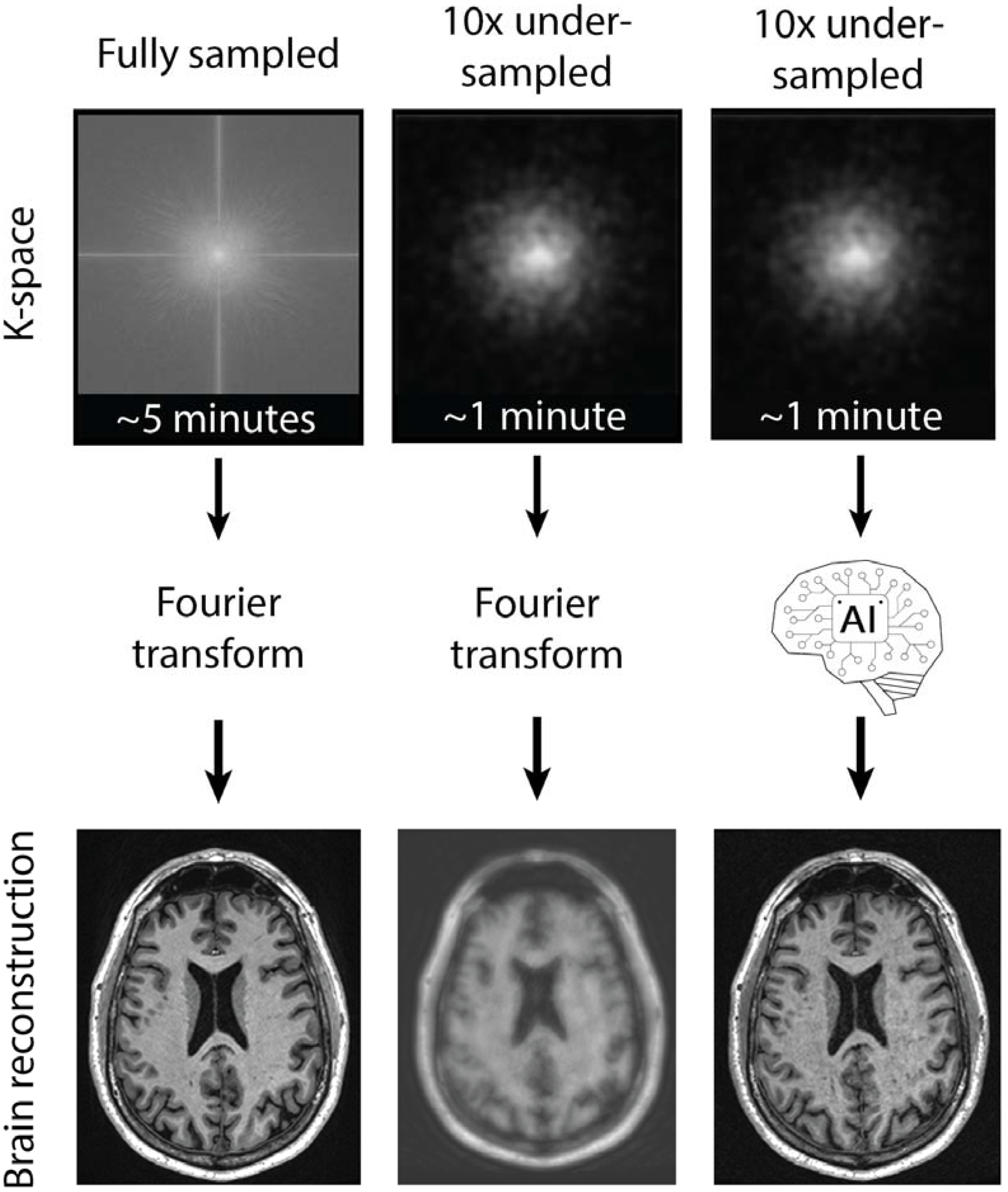
4. AI for Military Medical Imaging
5. AI for Mental Health
6. Limitations of AI
7. Future of AI
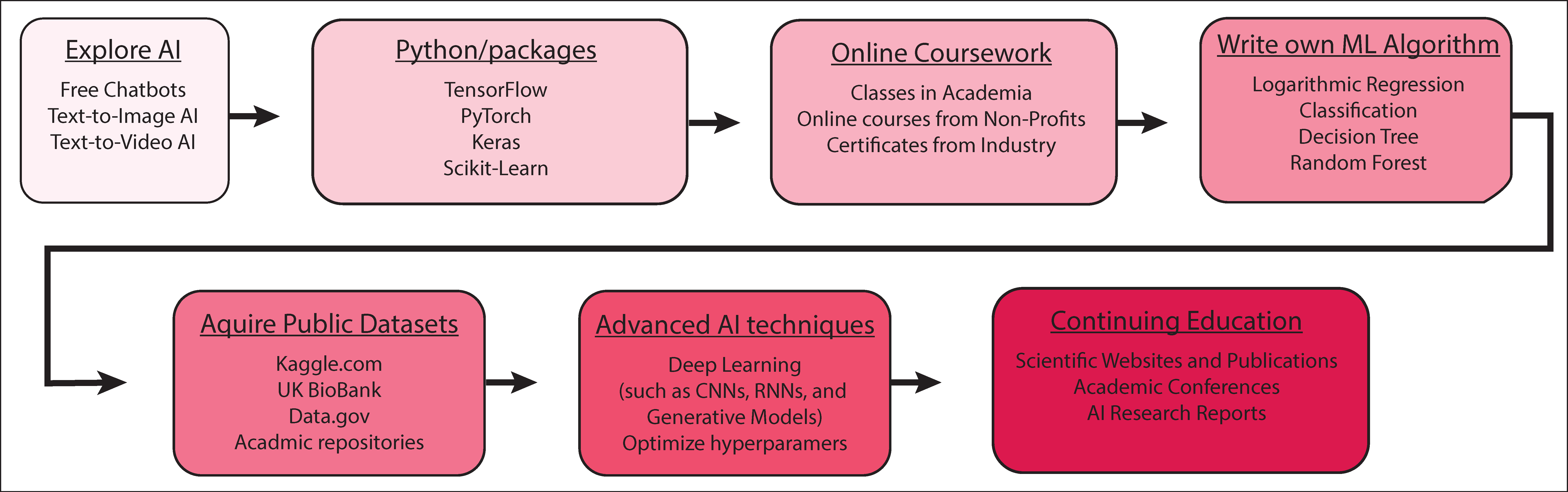
8. How to Get Started in the World of AI
9. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGI | Artificial general intelligence |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DARPA | Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency |
| DES | Disability Evaluation System |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| DoD | Department of Defense |
| DoDTR | DoD Trauma Registry |
| GPT | Generative Pre-Trained Network |
| GPU | Graphics processing unit |
| ITM | In The Moment |
| JAIC | Joint Artificial Intelligence Center |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| MedCOP | Medical Common Operating Picture |
| MEDEVAC | Medical evacuation |
| MERIT | Medical Evaluation Readiness Information Toolset |
| MHS | Military Health System |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| PTSD | Post-traumatic stress disorder |
| REACH-VET | Recovery Engagement and Coordination for Health—Veterans Enhanced Treatment |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| RoBERTa | Robustly optimized BERT approach |
| TRACIR | Trauma Care In a Rucksack |
| USC ICT | University of Southern California Institute for Creative Technologies |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Marshall, C. Here’s What’s in ‘Stargate’, the $500-Billion Trump-Endorsed Plan to Power U.S. AI. Scientific American, 22 January 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H. Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Overview on Techniques, Taxonomy, Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Living in a brave new AI era. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2023, 7, 1799. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makridakis, S. The forthcoming Artificial Intelligence (AI) revolution: Its impact on society and firms. Futures 2017, 90, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S. Advancements in Neural Machine Translation: Techniques and Applications. Acad. Pinnacle 2024, 7, 5767–5772. [Google Scholar]
- Ilicki, J. Challenges in evaluating the accuracy of AI-containing digital triage systems: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, E.; Wang, Z.; She, Q.; Ward, T. Generative Adversarial Networks in Time Series: A Systematic Literature Review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengesi, S.; El-Sayed, H.; Sarker, K.; Houkpati, Y.; Irungu, J.; Oladunni, T. Advancements in Generative AI: A Comprehensive Review of GANs, GPT, Autoencoders, Diffusion Model, and Transformers. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 69812–69837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Choi, D.; Chung, J.; Kushman, N.; Schrittwieser, J.; Leblond, R.; Eccles, T.; Keeling, J.; Gimeno, F.; Dal Lago, A.; et al. Competition-level code generation with AlphaCode. Science 2022, 378, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civit, M.; Civit-Masot, J.; Cuadrado, F.; Escalona, M.J. A systematic review of artificial intelligence-based music generation: Scope, applications, and future trends. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, U.; Polyak, A.; Hayes, T.; Yin, X.; An, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Q.; Yang, H.; Ashual, O.; Gafni, O.; et al. Make-A-video: Text-to-video generation without textvideo data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.14792. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Kamel Boulos, M.N. Generative AI in Medicine and Healthcare: Promises, Opportunities and Challenges. Future Internet 2023, 15, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, M.A. AI: Its Nature and Future; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Widrow, B.; Hoff, M.E. Adaptive switching circuits; 1960 IRE WESCON Convention Record. In Proceedings of the 1960 IRE WESCON, Convention Record; IRE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 96–104.
- Kohonen, T. The self-organizing map. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 1464–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.; McClelland, J.; Feldman, J.A. Parallel Distributed Processing Volume 1: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition: Foundations; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Competition 2012 (ILSVRC2012). Available online: https://image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/2012/results.html (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810:04805. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.P. ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, S.; Wang, P.; Bi, X.; et al. DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.12948. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M.; McDougall, I.; Anandaraj, S.; Machchhar, D.; Jain, R.; Sankaralingam, K. A Journey of a 1,000 Kernels Begins with a Single Step: A Retrospective of Deep Learning on GPUs. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, La Jolla, CA, USA, 27 April–1 May 2024; Volume 2, pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Duenas, T.; Ruiz, D. The Path to Superintelligence: A Critical Analysis of OpenAI’s Five Levels of AI Progression.pdf. ResearchGate 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogel, G.T. The role of the Department of Defense in PACS and telemedicine research and development. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2003, 27, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, J.; Serving Over 9.5 Million Service Members, Retirees, and their Families. Web Video. Available online: https://www.dvidshub.net/video/943224/dha-sizzle-2024 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Army Futures Command. Army Futures Command Concept for Medical 2028; Army Futures Command: Austin, TX, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Poropatich, R.K.; Pinsky, M.R. Robotics Enabled Autonomous and Closed Loop Trauma Care in a Rucksack. Healthc. Transform. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Developing Trustworthy AI to Inform Decision When Every Moment Counts. Available online: https://www.darpa.mil/news/2023/trustworthy-ai (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Molineaux, M.; Weber, R.O.; Floyd, M.W.; Menager, D.; Larue, O.; UAddison, U.; Kulhanek, R.; Reifsnyder, N.; Rauch, C.; Mainali, M.; et al. Aligning to Human Decision-Makers in Military Medical Triage. In Proceedings of ICCBR 2024, Mérida, Mexico, 1 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, C.; Amos-Binks, A.; Burris, C.; Keeney, N.; Pinevich, Y.; Pickering, B.W.; Rule, G.; Laufersweiler, D.; Herasevich, V.; Sun, M.G. Decision Support for Tactical Combat Casualty Care Using Machine Learning to Detect Shock. Mil. Med. 2021, 186, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, A.; Mark, N.; Kohlberg, G.D.; Gerasi, R.; Avraham, L.W.; Fan-Marko, R.; Eisenkraft, A.; Nachman, D. Hemopneumothorax detection through the process of artificial evolution—A feasibility study. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Frock, A.; Nagaraja, S.; Wallqvist, A.; Reifman, J. AI algorithm for personalized resource allocation and treatment of hemorrhage casualties. Front. Physiol 2024, 15, 1327948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, E.; Neuschwander, A.; Fave, G.; Abback, P.S.; Esnault, P.; Geeraerts, T.; Harrois, A.; Hanouz, J.L.; Kipnis, E.; Leone, M.; et al. Clinical decision support for severe trauma patients: Machine learning based definition of a bundle of care for hemorrhagic shock and traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2022, 92, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallings, J.D.; Laxminarayan, S.; Yu, C.; Kapela, A.; Frock, A.; Cap, A.P.; Reisner, A.T.; Reifman, J. Appraise-Hri: An Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for Triage of Hemorrhage Casualties. Shock 2023, 60, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, D. MERIT Delivers on Its Name with AI to Improve Military Medical Readiness. Available online: https://www.mitre.org/news-insights/impact-story/merit-delivers-on-its-name-ai-improves-military-medical-readiness (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- McCarthy, J.F.; Cooper, S.A.; Dent, K.R.; Eagan, A.E.; Matarazzo, B.B.; Hannemann, C.M.; Reger, M.A.; Landes, S.J.; Trafton, J.A.; Schoenbaum, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Recovery Engagement and Coordination for Health-Veterans Enhanced Treatment Suicide Risk Modeling Clinical Program in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2129900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fact Sheet: Medical Common Operation Picture (MedCOP); Joint Operational Medicine Information Systems Program Office: Arlington, VA, USA, 2023.
- ReflexAI Introduces HomeTeam to Revolutionize Veteran Mental Health Support. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2023/11/08/2776353/0/en/ReflexAI-Introduces-HomeTeam-to-Revolutionize-Veteran-Mental-Health-Support.html (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Rizzo, A.A.; Scherer, S.; DeVault, D.; Gratch, J.; Artstein, R.; Hartholt, A.; Lucas, G.; Marsella, S.; Morbini, F.; Nazarian, A.; et al. Detection and Computational Analysis of Psychological Signals Using a Virtual Human Interviewing Agent. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Disability, Virtual Reality & Associated Technologies, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2–4 September 2014; Volume 2–4, pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Doubleday, J. DOD wants $75 million to establish Joint AI Center, forecasts $1.7B over six years. Inside Defense 2018, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Noack, D. USMEPCOM Invests in AI to Aide Prescreen Process. Available online: https://www.mepcom.army.mil/Media/News-and-Press-Releases/Article-View/Article/3547681/usmepcom-invests-in-ai-to-aide-prescreen-process/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Zuromski, K.L.; Low, D.M.; Jones, N.C.; Kuzma, R.; Kessler, D.; Zhou, L.; Kastman, E.K.; Epstein, J.; Madden, C.; Ghosh, S.S.; et al. Detecting suicide risk among U.S. servicemembers and veterans: A deep learning approach using social media data. Psychol. Med. 2024, 54, 3379–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.T. Defense Innovation Unit Teaching Artificial Intelligence to Detect Cancer. DOD News, 24 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, C.B.; Vreeman, D.J.; Sothmann, M.S.; Wilson, S.L.; Oldridge, N.B. A review of the long-term health outcomes associated with ware-related amputation. Mil. Med. 2009, 174, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siavash, B.; Thompson, D.; Siskind, S.; Bilge, K.D.; Patel, V.M.; Mussa, F.F. Cleaning Up the MESS: Can Machine Learning Be Used to Predict Lower Extremity Amputation after Trauma-Associated Arterial Injury? J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2020, 232, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, Z.B.; Yet, B.; Sharrock, A.; Rickard, R.; Marsh, W.; Rasmussen, T.E.; Tai, N.R.M. Predicting the Outcome of Limb Revascularization in Patients With Lower-extremity Arterial Trauma. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Turan, H.; Elsawah, S.; Richmond, M.; Cao, T. The future of military medical evacuation: Literature analysis focused on the potential adoption of emerging technologies and advanced decision-analysis techniques. J. Def. Model. Simul. 2023, 2023, 15485129231207660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, R.S.; Howard, J.T.; Orman, J.A.; Tarpey, B.W.; Bailey, J.A.; Champion, H.R.; Mabry, R.L.; Holcomb, J.B.; Gross, K.R. The Effect of a Golden Hour Policy on the Morbidity and Mortality of Combat Casualties. JAMA Surg. 2016, 151, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihorac, A.; Ozrazgat-Baslanti, T.; Ebadi, A.; Motaei, A.; Madkour, M.; Pardalos, P.M.; Lipori, G.; Hogan, W.R.; Efron, P.A.; Moore, F.; et al. MySurgeryRisk: Development and Validation of a Machine-learning Risk Algorithm for Major Complications and Death After Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Four, Q. The Future of Warfare: AI-Powered Biometric Wearables Revolutionizing Soldier Performance. Available online: https://quadrantfour.com/perspective/the-future-of-warfare-ai-powered-biometric-wearables-revolutionizing-soldier-performance (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Oliveto, R.; Lazich, A.; Torricelli, L.; Picariello, F.; Ceccarelli, R.; Torchitti, P.; Boldi, F.; De Vito, L.; Tudosa, I.; Picariello, F.; et al. MIPHAS: Military Performances and Health Analysis System. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Valletta, Malta, 24–26 February 2020; pp. 198–207. [Google Scholar]
- Chioma, V.A.; Nweke, H.F.; Ikegwu, A.C.; Egwuonwu, C.A.; Onu, F.U.; Alo, U.R.; Teh, Y.W. Mobile and wearable sensors for data-driven health monitoring system: State-of-the-art and future prospect. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yin, J.; Xu, J.; Tat, T.; Chen, J. Advances in Machine Learning for Wearable Sensors. ACS Nano 2024, 2024, 22734–22751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X.; Shang, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Deep learning reconstruction CT for liver metastases: Low-dose dual-energy vs standard-dose single-energy. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.; De Santis, D.; Tremamunno, G.; Santangeli, C.; Polidori, T.; Bona, G.G.; Zerunian, M.; Del Gaudio, A.; Pugliese, L.; Laghi, A. Deep learning reconstruction algorithm and high-concentration contrast medium: Feasibility of a double-low protocol in coronary computed tomography angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 35, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissaux, B.; Le Floch, P.Y.; Robin, P.; Bourhis, D.; Couturaud, F.; Salaun, P.Y.; Nonent, M.; Le Roux, P.Y. Pulmonary perfusion by iodine subtraction maps CT angiography in acute pulmonary embolism: Comparison with pulmonary perfusion SPECT (PASEP trial). Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4857–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeram, E. Computed Tomography Image Reconstruction. Radiol. Technol. 2020, 92, 155CT–169CT. [Google Scholar]
- Next Generation CT Scanner Launched for Military Use. Available online: https://www.defenseadvancement.com/news/next-generation-ct-scanner-launched-for-military-use/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Philips Optimizes CT Workflows with In-House AI, Launches CT 5300 in North America at #RSNA2024. Available online: https://www.usa.philips.com/a-w/about/news/archive/standard/news/press/2024/philips-optimizes-ct-workflows-with-in-house-ai-launches-ct-5300-in-north-america-at-rsna2024.html (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Kirsh, D. FDA Clears Hyperfine’s AI Software for Improved Image Quality on Portable MRI System. Available online: https://www.massdevice.com/fda-clears-hyperfines-ai-software-for-improved-image-quality-on-portable-mri-system/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Mertz, L. Ultra-High to Ultra-Low: MRI Goes to Extremes. Available online: https://www.embs.org/pulse/articles/ultra-high-to-ultra-low-mri-goes-to-extremes/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Donnay, C.; Okar, S.V.; Tsagkas, C.; Gaitan, M.I.; Poorman, M.; Reich, D.S.; Nair, G. Super resolution using sparse sampling at portable ultra-low field MR. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1330203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, E.; Morley, C.; Newman, J.; Qian, M.; Abu-Amara, D.; Marmar, C.; Lui, Y.W. Prevalence of Cerebral Microhemorrhage following Chronic Blast-Related Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Military Service Members Using Susceptibility-Weighted MRI. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, T.C.; Tu, D.; Okar, S.V.; Nair, G.; By, S.; Kawatra, K.D.; Robert-Fitzgerald, T.E.; Desiderio, L.M.; Schindler, M.K.; Shinohara, R.T.; et al. Sensitivity of portable low-field magnetic resonance imaging for multiple sclerosis lesions. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 35, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, H.; Herrmann, J.; Gassenmaier, S.; Lingg, A.; Nickel, M.D.; Kannengiesser, S.; Arberet, S.; Othman, A.E.; Afat, S. Combined Deep Learning-based Super-Resolution and Partial Fourier Reconstruction for Gradient Echo Sequences in Abdominal MRI at 3 Tesla: Shortening Breath-Hold Time and Improving Image Sharpness and Lesion Conspicuity. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, J.C. Artificial intelligence in medical imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 68, A1–A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlotz, C.P. The Future of AI and Informatics in Radiology: 10 Predictions. Radiology 2023, 309, e231114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.A.; Manning, W.J.; Nezafat, R. Present and Future Innovations in AI and Cardiac MRI. Radiology 2024, 310, e231269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.M.; Chandarana, H. AI-powered Diagnostics: Transforming Prostate Cancer Diagnosis with MRI. Radiology 2024, 312, e241009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, C.J.; Griffith, J.E.; Pace, B.T.; Hinkson, K.; Bryan, A.O.; Clemans, T.A.; Imel, Z.E. Combat Exposure and Risk for Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors Among Military Personnel and Veterans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Suicide Life-Threat. Behav. 2015, 45, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichter, B.; Stein, M.B.; Norman, S.B.; Hill, M.L.; Straus, E.; Haller, M.; Pietrzak, R.H. Prevalence, correlates, and treatment of suicidal behavior in US military veterans: Results from the 2019–2020 National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2021, 82, 20m13714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C.; Hwang, I.; Hoffmire, C.A.; McCarthy, J.F.; Petukhova, M.V.; Rosellini, A.J.; Sampson, N.A.; Schneider, A.L.; Bradley, P.A.; Katz, I.R.; et al. Developing a practical suicide risk prediction model for targeting high-risk patients in the Veterans health Administration. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 26, e1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, J.T.; Stewart, I.J.; Amuan, M.E.; Janak, J.C.; Howard, K.J.; Pugh, M.J. Trends in Suicide Rates Among Post-9_11 US Military Veterans With and Without Traumatic Brain Injury From 2006-2020.pdf. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmar, C.R.; Brown, A.D.; Qian, M.; Laska, E.; Siegel, C.; Li, M.; Abu-Amara, D.; Tsiartas, A.; Richey, C.; Smith, J.; et al. Speech-based markers for posttraumatic stress disorder in US veterans. Depress. Anxiety 2019, 36, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, G.; Diaz, M.J.; Batchu, S.; Lucke-Wold, B. Racial underrepresentation in dermatological datasets leads to biased machine learning models and inequitable healthcare. J. Biomed. Res. 2022, 3, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kocon, R.; Cichecki, I.; Kaszyca, O.; MKochanek, M.; Szydlo, D.; Baran, J.; Bielaniewicz, J.; Gruza, M.; Janz, A.; Kanclerz, K.; et al. ChatGPT: Jack of all trades, master of none. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohnam, B.P. Data Desert: Military Medicine’s Artificial Intelligence Implementation Barriers. Available online: https://military-medicine.com/article/4256-data-desert-military-medicine-s-artificial-intelligence-implementation-barriers.html (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Joint Trauma System—Registries. Available online: https://jts.health.mil/index.cfm/data/registries (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, D.T.; Khairat, S.S. Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) for indexing and retrieving open-source healthcare data. In Integrating Information Technology and Management for Quality of Care; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Volume 202.
- Bertin-Mahieux, T.; Ellis, D.P.W.; Whitman, B.; Lamere, P. The Million Song Dataset. In Proceedings of 12th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference, Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Talib, M.A.; Majzoub, S.; Nasir, Q.; Jamal, D. A systematic literature review on hardware implementation of artificial intelligence algorithms. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 1897–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baen, M. Army Tests Commercial Satellite Internet in Pilot Program. Available online: https://www.army.mil/article/254316/army_tests_commercial_satellite_internet_in_pilot_program (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Gunning, D.; Stefik, M.; Choi, J.; Miller, T.; Tumpf, S.; Yang, G.Z. XAI—Explainable artificial intelligence. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DOD Adopts Ethical Principles for Artificial Intelligence. Available online: https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/2091996/dod-adopts-ethical-principles-for-artificial-intelligence/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Summary of the NATO Artificial Intelligence Strategy. Available online: https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/official_texts_187617.htm (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Baker, A.; Perov, Y.; Middleton, K.; Baxter, J.; Mullarkey, D.; Sangar, D.; Butt, M.; DoRosario, A.; Johri, S. A Comparison of Artificial Intelligence and Human Doctors for the Purpose of Triage and Diagnosis. Front. Artif. Intell. 2020, 3, 543405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Agarwal, S.; Coombs, L.; Wald, C.; Dreyer, K. 2020 ACR Data Science Institute Artificial Intelligence Survey. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirnak, J.R.; Antani, S. The Need for Artificial Intelligence Curriculum in Military Medical Education. Mil. Med. 2024, 189, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Densen, P. Challenges and opportunities facing medical education. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2011, 122, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Under, C.D. The AI Search Revolution: Perplexity AI vs. Google Gemini vs. ChatGPT. Available online: https://medium.com/@cognidownunder/the-ai-search-revolution-perplexity-ai-vs-google-gemini-vs-chatgpt-e435caa726e3 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Hachman, M. The Best AI Art Generators: Bring your Wildest Dreams to Life; PC World: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Gao, C.; Chen, R.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; Gao, J.; et al. Sora: A Review on Background, Technology, Limitations, and opportunities of Large Vision Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.17177. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford Machine Learning Specialization. Available online: https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning-introduction (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Machine Learning: Fundamentals and Algorithms. Available online: https://execonline.cs.cmu.edu/machine-learning (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Professional Certificate in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence. Available online: https://em-executive.berkeley.edu/professional-certificate-machine-learning-artificial-intelligence (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Applied Machine Learning. Available online: https://online-exec.cvn.columbia.edu/applied-machine-learning (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Machine Learninig Cornell Certificate Program. Available online: https://ecornell.cornell.edu/certificates/technology/machine-learning/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- AI & Machine Learning Bootcamp. Available online: https://pg-p.ctme.caltech.edu/ai-machine-learning-bootcamp-online-certification-course (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Certificate in Machine Learning. Available online: https://www.pce.uw.edu/certificates/machine-learning (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Google Machine Learning Education. Available online: https://developers.google.com/machine-learning (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Intro to Machine Learning. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/learn/intro-to-machine-learning (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Artificial Intelligence for Beginners. Available online: https://microsoft.github.io/AI-For-Beginners/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Machine Learning with Python. Available online: https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning-with-python (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Rodriguez, C.O. MOOCs and the AI-Stanford Like Courses: Two Successful and Distinct Course Formats for Massive Open Online Courses. Eur. J. Open Distance E-Learn. 2012, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
| Developer | Project Name | Features | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| MITRE | MERIT [38] | Predictive modeling to identify service members at risk for disability | Implemented |
| Department of Veterans Affairs | REACH-VET [39] | Identification of veterans at risk for suicide achieved by analyzing health records | Implemented |
| Joint Health Services | MedCOP [40] | Data synchronization and real-time sharing of information from wearable sensors | Implemented |
| ReflexAI | HomeTeam [41] | Chatbot that provides emergency counseling, available 24 h per day | Implemented |
| USC Institute for Creative Technologies (DARPA-funded) | Ellie [42] | AI virtual therapist that assists in the diagnosis of mental illness and provides summaries for the provider | Implemented |
| DoD | JAIC [43] | Central hub of AI technologies to accelerate adoption and integration of AI in military medicine | Implemented |
| USMEPCOM | MHS GENESIS [44] | Uses AI to prescreen personnel for medical treatment | Implemented |
| Harvard University | RoBERTa [45] | Screening of social media posts to identify potential suicide ideation | Implemented |
| DARPA | ITM [31,32] | AI-integrated decision-making programs for battlefield triage | In Development |
| DoD Defense Innovation Unit | Predictive Health [46] | Uses AI to screen for cancers and other medical irregularities | In Development |
| University of Pittsburgh (DoD-sponsored) | TRACIR [30] | Provides autonomous trauma care and predictive analytics in remote locations | In Development |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakhilin, N.; Morris, H.D.; Pham, D.L.; Hood, M.N.; Ho, V.B. Opportunities for Artificial Intelligence in Operational Medicine: Lessons from the United States Military. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050519
Rakhilin N, Morris HD, Pham DL, Hood MN, Ho VB. Opportunities for Artificial Intelligence in Operational Medicine: Lessons from the United States Military. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(5):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050519
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakhilin, Nikolai, H. Douglas Morris, Dzung L. Pham, Maureen N. Hood, and Vincent B. Ho. 2025. "Opportunities for Artificial Intelligence in Operational Medicine: Lessons from the United States Military" Bioengineering 12, no. 5: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050519
APA StyleRakhilin, N., Morris, H. D., Pham, D. L., Hood, M. N., & Ho, V. B. (2025). Opportunities for Artificial Intelligence in Operational Medicine: Lessons from the United States Military. Bioengineering, 12(5), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12050519








