Breathomics: A Non-Invasive Approach for the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
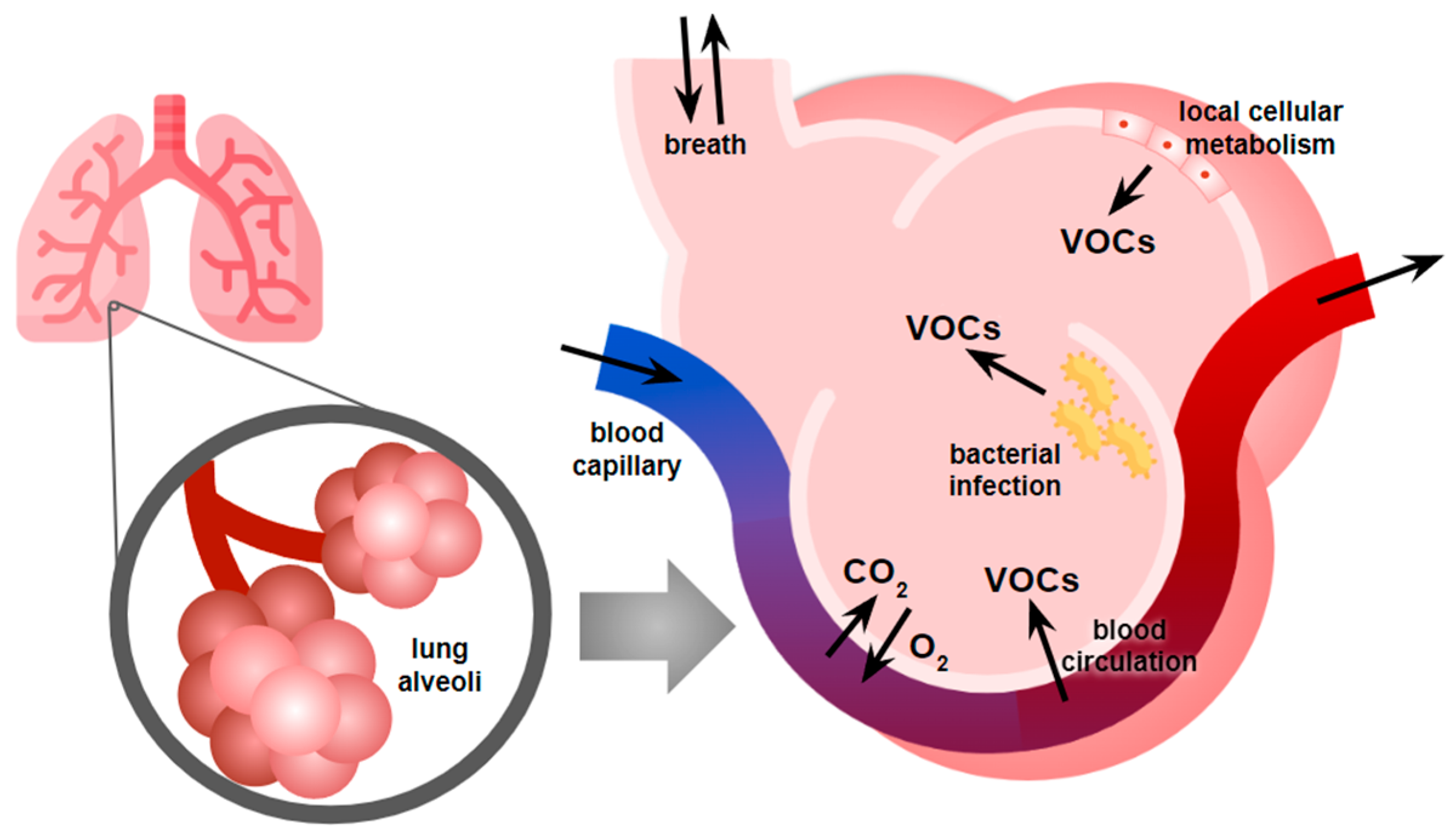
2. Breathomics as a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tool for Breast Cancer Detection
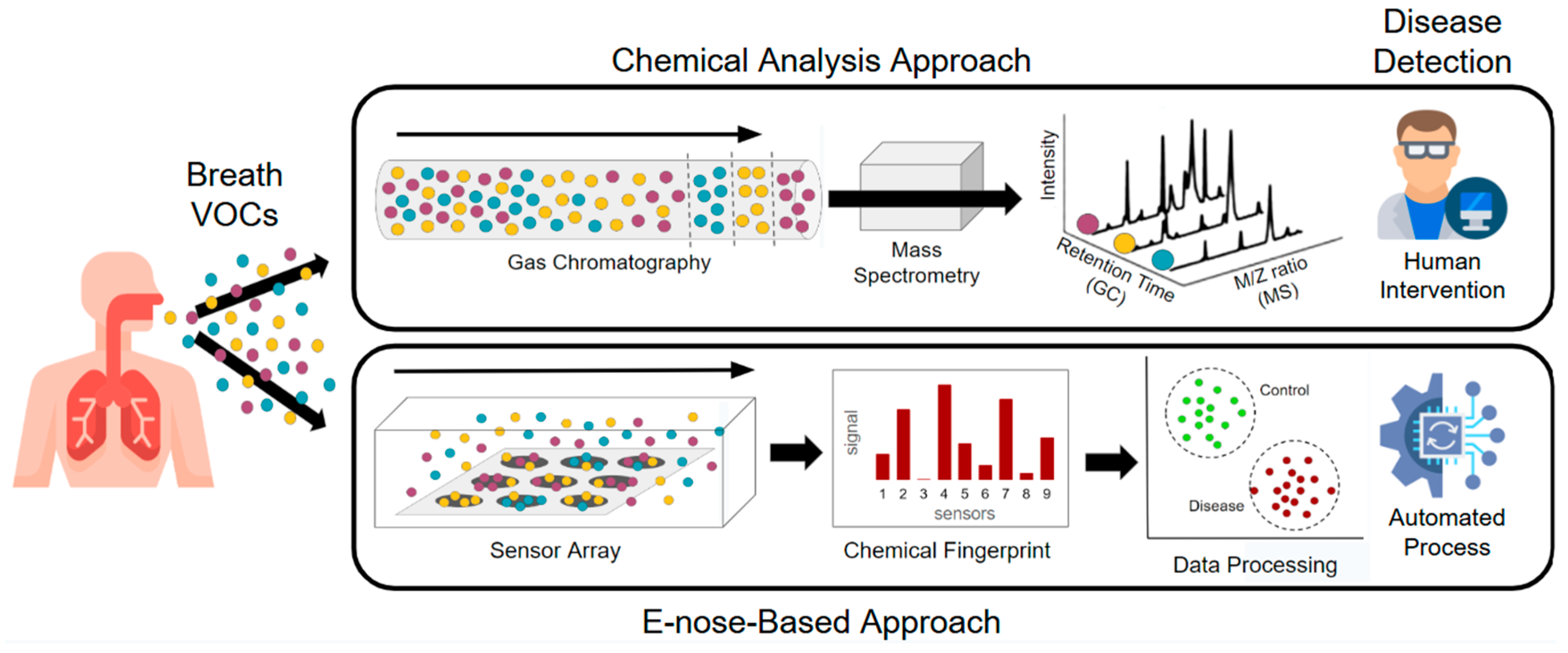
3. Technologies Used in Breathomics Analysis
4. Research Clinical Studies on Breathomics for Breast Cancer
4.1. Patient Selection and Study Design
4.2. Confounding Factors and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Breath Sample Collection and Environment
4.4. Breast Cancer Diagnosis: Sensitivity, Specificity, and Data Processing Methods
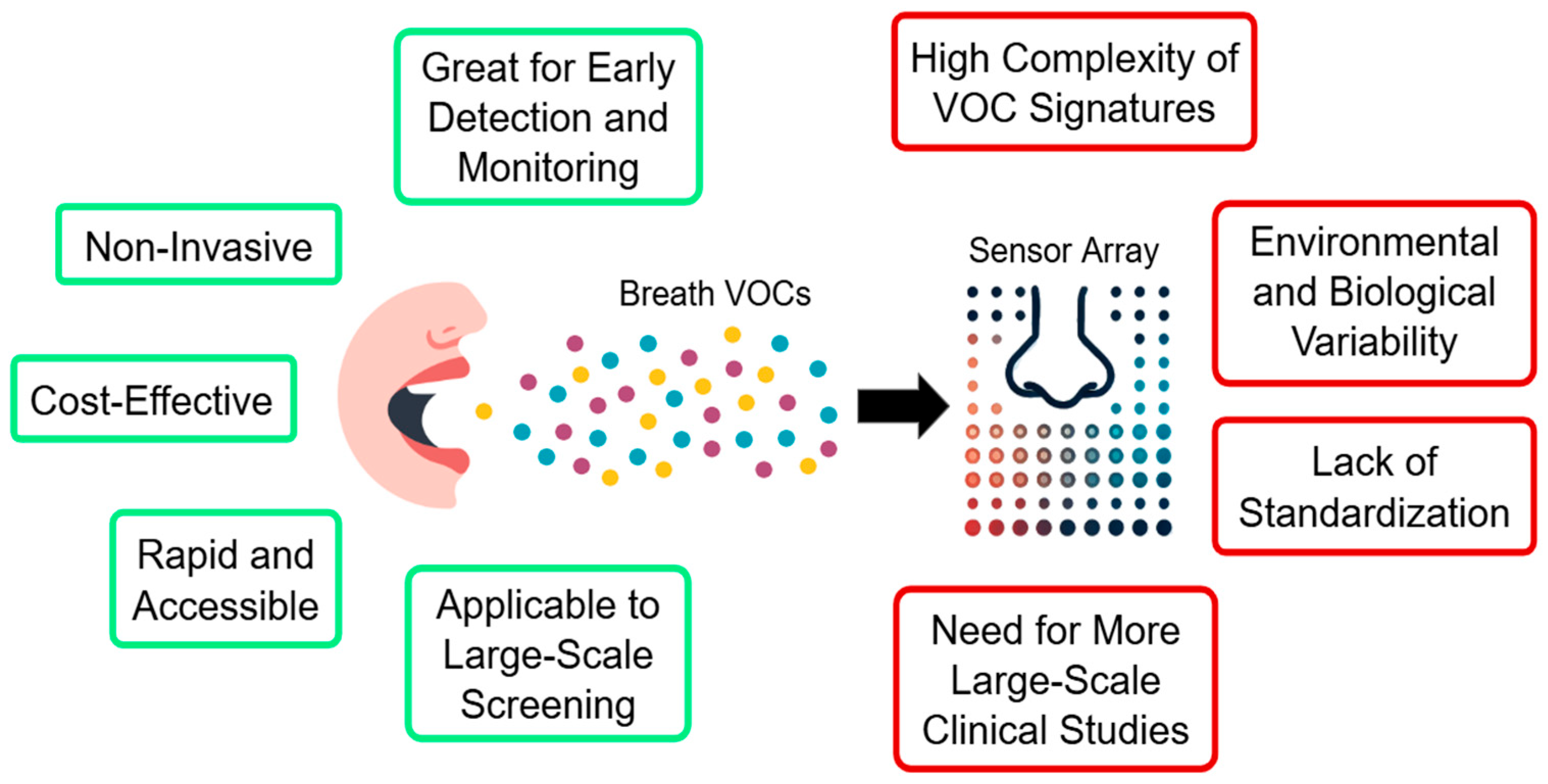
5. Advantages and Limitations of the Approach, Future Prospects, and Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, E.; Lindeman, G.J.; Visvader, J.E. Deciphering Breast Cancer: From Biology to the Clinic. Cell 2023, 186, 1708–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.; Livingstone, V.; Herbison, G.P. Interventions for Relieving the Pain and Discomfort of Screening Mammography. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2008, CD002942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandraki, I.; Mooradian, A.D. Barriers Related to Mammography Use for Breast Cancer Screening among Minority Women. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2010, 102, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerlikowske, K.; Ichikawa, L.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Buist, D.S.M.; Vacek, P.M.; Smith-Bindman, R.; Yankaskas, B.; Carney, P.A.; Ballard-Barbash, R. National Institutes of Health Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium Longitudinal Measurement of Clinical Mammographic Breast Density to Improve Estimation of Breast Cancer Risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, B.L.; Gangnon, R.E.; Burt, V.; Trentham-Dietz, A.; Hampton, J.M.; Wellman, R.D.; Kerlikowske, K.; Miglioretti, D.L. Prevalence of Mammographically Dense Breasts in the United States. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, J.J.; Pitcher, C.K.; Ferrandino, G.; Hobson, A.R.; Pappan, K.L.; Lawson, J.L.D. Breathing New Life into Clinical Testing and Diagnostics: Perspectives on Volatile Biomarkers from Breath. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2022, 59, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Rahimpour, E.; Soleymani, J.; Saei, A.A.; Jouyban, A. Breathomics: Review of Sample Collection and Analysis, Data Modeling and Clinical Applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 1461–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizário, J.E.; Faintuch, J.; Malpartida, M.G. Breath Biopsy and Discovery of Exclusive Volatile Organic Compounds for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 564194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeler, S.E. Quantitative Analysis by Gas Chromatography of Volatile Carbonyl Compounds in Expired Air from Mice and Human. J. Chromatogr. B 1997, 702, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, F.; Lupi, M.; Giraudo, E.; Lanzetti, L. Breast Cancers as Ecosystems: A Metabolic Perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, O.; Zhang, W.; Halpern, J.M.; Hua, Q.-L.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Kayal, H.; Khoury, K.; Liu, H.; Davies, M.P.A.; Haick, H. Differentiation between Genetic Mutations of Breast Cancer by Breath Volatolomics. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44864–44876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Jin, Y.; Tang, Z.; Duan, Y. Investigation of Potential Breath Biomarkers for the Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 436, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Ditkoff, B.A.; Fisher, P.; Greenberg, J.; Gunawardena, R.; Kwon, C.S.; Tietje, O.; Wong, C. Prediction of Breast Cancer Using Volatile Biomarkers in the Breath. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 99, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Qiu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, E. Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer from Exhaled Breath by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) Analysis: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sun, B.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Ke, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Luo, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Volatile Organic Metabolites Identify Patients with Breast Cancer, Cyclomastopathy and Mammary Gland Fibroma. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavra, L.; Catini, A.; Ulivieri, A.; Capuano, R.; Baghernajad Salehi, L.; Sciacchitano, S.; Bartolazzi, A.; Nardis, S.; Paolesse, R.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Investigation of VOCs Associated with Different Characteristics of Breast Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Detection of Lung, Breast, Colorectal, and Prostate Cancers from Exhaled Breath Using a Single Array of Nanosensors. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, P.; Wilde, M.; Ahmed, W.; Wang, R.; van der Schee, M.; Abuhelal, S.; Schaber, C.; Cunoosamy, D.; Clarke, G.W.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.-H.; et al. Fulfilling the Promise of Breathomics: Considerations for the Discovery and Validation of Exhaled Volatile Biomarkers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallos, I.K.; Tryfonopoulos, D.; Shani, G.; Amditis, A.; Haick, H.; Dionysiou, D.D. Advancing Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis with AI-Powered Breathomics: Navigating Challenges and Future Directions. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Cummin, A.R.C.; Gagliardi, A.J.; Gleeson, K.; Greenberg, J.; Maxfield, R.A.; Rom, W.N. Detection of Lung Cancer with Volatile Markers in the Breath. Chest 2003, 123, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Condos, R.; Ring Erickson, G.A.; Greenberg, J.; La Bombardi, V.; Munawar, M.I.; Tietje, O. Volatile Biomarkers of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in the Breath. Tuberculosis 2007, 87, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Greenberg, J.; Gunawardena, R.; Naidu, A.; Rahbari-Oskoui, F. Effect of Age on the Breath Methylated Alkane Contour, a Display of Apparent New Markers of Oxidative Stress. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2000, 136, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabehi, A.; Helal, H.; Zappa, D.; Comini, E. Advancements and Prospects of Electronic Nose in Various Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Meng, Q.-H.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Qi, P.-F. Development of Compact Electronic Noses: A Review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 062002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Electronic Nose: Current Status and Future Trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Joshi, R.; Anil Vishnu, G.K.; Bhalerao, S.; Pandya, H.J. Electronic Nose: A Non-Invasive Technology for Breath Analysis of Diabetes and Lung Cancer Patients. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, R.J.; Farajikhah, S.; Oveissi, F.; Dehghani, F.; Naficy, S. Chemiresistive Sensor Arrays for Gas/volatile Organic Compounds Monitoring: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 25, 2200830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. The Optoelectronic Nose: Colorimetric and Fluorometric Sensor Arrays. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 231–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, R.L.; Ayala, C.; Park, J.-Y.; Choi, J.-W.; Warner, I. Coating-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Detection Methods of Environmentally Relevant Volatile Organic Compounds. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Länge, K. Bulk and Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor Arrays for Multi-Analyte Detection: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abideen, Z.U.; Arifeen, W.U.; Bandara, Y.N.D. Emerging Trends in Metal Oxide-Based Electronic Noses for Healthcare Applications: A Review. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 9259–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysoev, V.V.; Strelcov, E.; Kolmakov, A. Multisensor Micro-Arrays Based on Metal Oxide Nanowires for Electronic Nose Applications. In Metal Oxide Nanomaterials for Chemical Sensors; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 465–502. ISBN 9781461453949. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, U.; Roznyatovskaya, N.V.; Mirsky, V.M. Conducting Polymers in Chemical Sensors and Arrays. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 614, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Savagatrup, S.; He, M.; Lin, S.; Swager, T.M. Carbon Nanotube Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 599–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, D.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; He, G.; Li, X.; Hu, N.; Yin, G.; He, D.; Zhang, L. A Review on Graphene-Based Gas/vapor Sensors with Unique Properties and Potential Applications. Nanomicro Lett. 2016, 8, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Arrays of Chemisensitive Monolayer-Capped Metallic Nanoparticles for Diagnostic Breath Testing. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2010, 26, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, B.C.; Steinthal, G.; Sunshine, S. Conductive Polymer-carbon Black Composites-based Sensor Arrays for Use in an Electronic Nose. Sens. Rev. 1999, 19, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A. An Electronic Nose Based on Carbon Nanotube -Titanium Dioxide Hybrid Nanostructures for Detection and Discrimination of Volatile Organic Compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 357, 131418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, O.; Haick, H. Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds as Noninvasive Markers in Breast Cancer. In Omics Approaches in Breast Cancer; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 461–481. ISBN 9788132208426. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing Lung Cancer in Exhaled Breath Using Gold Nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisch, U.; Schlesinger, I.; Ionescu, R.; Nassar, M.; Axelrod, N.; Robertman, D.; Tessler, Y.; Azar, F.; Marmur, A.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; et al. Detection of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease from Exhaled Breath Using Nanomaterial-Based Sensors. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Ditkoff, B.A.; Fisher, P.; Greenberg, J.; Gunawardena, R.; Kwon, C.S.; Rahbari-Oskoui, F.; Wong, C. Volatile Markers of Breast Cancer in the Breath. Breast J. 2003, 9, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, M.; Jezierski, T.; Broffman, M.; Hubbard, A.; Turner, K.; Janecki, T. Diagnostic Accuracy of Canine Scent Detection in Early- and Late-Stage Lung and Breast Cancers. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Abouelnasr, M.F.; Bayer, C.W.; Gabram, S.G.; Mizaikoff, B.; Rogatko, A.; Vidakovic, B. Mining Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds for Breast Cancer Detection. Adv. Appl. Stat. Sci. 2009, 1, 327–342. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Saunders, C.; Hope, P.; Schmitt, P.; Wai, J. Volatile Biomarkers in the Breath of Women with Breast Cancer. J. Breath Res. 2010, 4, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, S.G.; Bayer, C.W.; Hendry, R.J.; Sellers, N.; Lee, K.S.; Vidakovic, B.; Mizaikoff, B.; Gabram-Mendola, S.G.A. Breath Analysis by Mass Spectrometry: A New Tool for Breast Cancer Detection? Am. Surg. 2011, 77, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, G.; Gallimidi, Z.; Reiss, A.H.; Dovgolevsky, E.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Engel, A.; Shiban, A.; Tisch, U.; et al. Classification of Breast Cancer Precursors through Exhaled Breath. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 126, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangler, M.; Freitag, C.; Lanowska, M.; Staeck, O.; Schneider, A.; Speiser, D. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Exhaled Breath of Patients with Breast Cancer in a Clinical Setting. Ginekol. Pol. 2012, 83, 730–736. [Google Scholar]
- Herman-Saffar, O.; Boger, Z.; Libson, S.; Lieberman, D.; Gonen, R.; Zeiri, Y. Early Non-Invasive Detection of Breast Cancer Using Exhaled Breath and Urine Analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 96, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Cruz-Ramos, J.A.; Huston, J.; Ornelas, O.; Pappas, N.; Pathak, S. Prediction of Breast Cancer Risk with Volatile Biomarkers in Breath. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz de León-Martínez, L.; Rodríguez-Aguilar, M.; Gorocica-Rosete, P.; Domínguez-Reyes, C.A.; Martínez-Bustos, V.; Tenorio-Torres, J.A.; Ornelas-Rebolledo, O.; Cruz-Ramos, J.A.; Balderas-Segura, B.; Flores-Ramírez, R. Identification of Profiles of Volatile Organic Compounds in Exhaled Breath by Means of an Electronic Nose as a Proposal for a Screening Method for Breast Cancer: A Case-Control Study. J. Breath Res. 2020, 14, 046009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Peng, H.-Y.; Huang, C.-H. Breath Biopsy of Breast Cancer Using Sensor Array Signals and Machine Learning Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Hanada, M.; Koda, H.; Sugimoto, M.; Takada, M.; Toi, M. Breast Cancer Detection Using Volatile Compound Profiles in Exhaled Breath via Selected Ion-Flow Tube Mass Spectrometry. J. Breath Res. 2022, 17, 016006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, F.; Groom, A.G.; Mohiuddin, M.D.; Sengupta, A.; Daigle-Maloney, T.; Burnell, M.J.; Michael, J.C.R.; Graham, S.; Beydaghyan, G.; Scheme, E.; et al. Using Infrared Spectroscopy to Analyze Breath of Patients Diagnosed with Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, e13579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Jia, Z.; Zou, J.; Liu, G.; et al. A Novel Non-Invasive Exhaled Breath Biopsy for the Diagnosis and Screening of Breast Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Gong, X.; Jiao, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z. Identification Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosis, and Progress of Breast Cancer by Using High-Pressure Photon Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1320, 342883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, J.; Davis, C.; Pleil, J. Breathborne Biomarkers and the Human Volatilome; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, T.-C.; Tan, C.-E.; Wang, S.-Y.; Lin, O.A.; Su, B.-H.; Hsu, M.-T.; Lin, J.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Chen, C.-S.; Yang, Y.-C.; et al. Human Breathomics Database. Database 2020, 2020, baz139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.-H.; Jhong, Y.-C.; Kuo, T.-C.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Kuo, C.-H.; Tseng, Y.J. A Clinical Breathomics Dataset. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Velde, S.; Nevens, F.; Van Hee, P.; van Steenberghe, D.; Quirynen, M. GC-MS Analysis of Breath Odor Compounds in Liver Patients. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 875, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, T.; Zaim, O.; Moufid, M.; El Bari, N.; Ionescu, R.; Bouchikhi, B. Exhaled Breath Analysis Using Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–mass Spectrometry for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease, Diabetes Mellitus and Healthy Subjects. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibola, O.A.; Smith, D.; Spaněl, P.; Ferns, G.A.A. Effects of Dietary Nutrients on Volatile Breath Metabolites. J. Nutr. Sci. 2013, 2, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Ulanowska, A.; Ligor, T.; Denderz, N.; Amann, A. Analysis of Exhaled Breath from Smokers, Passive Smokers and Non-Smokers by Solid-Phase Microextraction Gas Chromatography/mass Spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, C.; Turner, C. Breath Analysis in Disease Diagnosis: Methodological Considerations and Applications. Metabolites 2014, 4, 465–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gilio, A.; Palmisani, J.; Ventrella, G.; Facchini, L.; Catino, A.; Varesano, N.; Pizzutilo, P.; Galetta, D.; Borelli, M.; Barbieri, P.; et al. Breath Analysis: Comparison among Methodological Approaches for Breath Sampling. Molecules 2020, 25, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C.M.; Fadel, M.G.; Jamel, S.H.; Hanna, G.B. Breath Testing in the Surgical Setting: Applications, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Eur. Surg. Res. 2023, 64, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haick, H.; Broza, Y.Y.; Mochalski, P.; Ruzsanyi, V.; Amann, A. Assessment, Origin, and Implementation of Breath Volatile Cancer Markers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1423–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglioretti, D.L.; Abraham, L.; Sprague, B.L.; Lee, C.I.; Bissell, M.C.S.; Ho, T.-Q.H.; Bowles, E.J.A.; Henderson, L.M.; Hubbard, R.A.; Tosteson, A.N.A.; et al. Association between False-Positive Results and Return to Screening Mammography in the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium Cohort. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Du, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, X. Recent Advances in Signal Processing Algorithms for Electronic Noses. Talanta 2025, 283, 127140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Recent Progress in Smart Electronic Nose Technologies Enabled with Machine Learning Methods. Sensors 2021, 21, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Schubert, J.K.; Trefz, P.; Miekisch, W. Natural Menstrual Rhythm and Oral Contraception Diversely Affect Exhaled Breath Compositions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Grzegorzewski, S.; Broderius, C.; Trefz, P.; Mittlmeier, T.; Fischer, D.-C.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.K. Physiological and Metabolic Effects of Healthy Female Aging on Exhaled Breath Biomarkers. iScience 2022, 25, 103739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krilaviciute, A.; Leja, M.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Barash, O.; Khatib, S.; Amal, H.; Broza, Y.Y.; Polaka, I.; Parshutin, S.; Rudule, A.; et al. Associations of Diet and Lifestyle Factors with Common Volatile Organic Compounds in Exhaled Breath of Average-Risk Individuals. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 026006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Luo, G.; Qin, K.; Wang, N.; Niu, W. Online Sensor Drift Compensation for E-Nose Systems Using Domain Adaptation and Extreme Learning Machine. Sensors 2018, 18, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Xu, S.; Zhou, X.; Lü, H. Electronic Nose Humidity Compensation System Based on Rapid Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Murillas, I.; Cutts, R.; Abbott, C.; Boyle, S.M.; Pugh, J.; Chen, R.; Dunne, K.; Bunce, C.; Johnston, S.R.D.; Ring, A.E.; et al. Ultra-Sensitive ctDNA Mutation Tracking to Identify Molecular Residual Disease and Predict Relapse in Patients with Early Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-W.; Ryu, J.K.; An, J.K.; Choi, N.; Park, Y.M.; Ko, K.H.; Han, K. Artificial Intelligence for Breast Cancer Screening in Mammography (AI-STREAM): Preliminary Analysis of a Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Top Author, Year, Ref. | Study Population | Equipment and Data Processing Methods | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ebeler, 1997, [10] | 3 BC patients/3 healthy controls | GC-FPD | ||
| Phillips, 2003, [43] | 51 BC patients/50 women with abnormal mammogram but no cancer/42 healthy controls | TD-GC-MS with FSDA (SPSS software version 8.0) | Model 1: 88.2% Model 2: 60.8% | Model 1: 73.8% Model 2: 82.0% |
| Phillips, 2006, [14] | 51 BC patients/42 healthy controls | TD-GC-MS with Fuzzy Logic | 93.80% | 84.60% |
| McCulloch, 2006, [44] | 31 BC patients/55 lung cancer patients/83 healthy controls | trained dog | 88% | 98% |
| Lee, 2009, [45] | 17 BC patients/24 healthy controls | TD-GC-MS with Laplacian Eignemaps and LDA, QDA, SVM | 75% | 75% |
| Peng, 2020, [18] | 18 BC patients/30 lung cancer patients/26 colon cancer patients/18 prostate cancer/82 healthy controls | NaNose e-nose and GC-MS with PCA | 90% | 85% |
| Phillips, 2010, [46] | 54 BC patients/204 healthy controls | TD-GC-MS with Weighted Digital Analysis | 75.3% | 84.8% |
| Patterson, 2011, [47] | 20 BC patients/20 healthy controls | TD-GC-MS with Laplacian Eignemaps and LDA, QDA, SVM | 72% | 64% |
| Shuster, 2011, [48] | 13 BC patients/16 patients with benign breast tumor/7 healthy controls | NaNose e-nose with PCA and SVM | 94% | 80% |
| Mangler, 2012, [49] | 10 BC patients/10 healthy controls | TD-GC-MS with SPSS version 15.0 analysis | 80 to 100% | 40 to 70% |
| Wang, 2014, [16] | 85 BC patients/45 healthy controls | SPME-GC-MS with PCA and PLSDA, OPLSDA | ||
| Li, 2014, [13] | 22 BC patients/17 breast benign tumors/24 healthy controls | GC-MS with Fisher Discriminant Analysis using SPSS | 72.7% | 91.7% |
| Barash, 2015, [12] | 169 malignant BC patients/25 DCIS/52 benign breast conditions/30 controls | GC-MS and NaNose e-nose with DFA | 70 to 88% | 71 to 87% |
| Herman-Saffar, 2018, [50] | 48 BC patients/45 healthy controls | MK4 and Cyranose e-noses with ANN | MK4: 89 to 93% Cyranose: 88 to 92% | MK4: 95 to 100% Cyranose: 78 to 85% |
| Phillips, 2018, [51] | 54 BC patients/124 healthy controls | GC-MS and GC-SAW with Weighted Digital Analysis | 85% | 85% |
| Díaz de León-Martínez, 2020, [52] | 262 BC patients/181 healthy controls | Cyranose 320 e-nose with CDA and RBF-SVM | 100% | 100% |
| Zhang, 2020, [15] | 71 BC patients/54 gastric cancer patients/78 healthy controls | HS-GC-MS with PCA and PLSDA | 93.59% | 71.62% |
| Yang, 2021, [53] | 351 malignant BC/88 healthy controls/222 benign breast tumors | Cyranose 320 e-nose with different ML models | 86% | 97% |
| Nakayama, 2022, [54] | 45 BC patients/51 healthy controls | SIFT-MS with PCA and MLR | 86.3% | 55.6% |
| Naz, 2022, [55] | 71 BC patients/40 healthy controls | TD-IR-CRDS with SVM | 86.8% | 75.0% |
| Liu, 2023, [56] | 465 BC patients/4504 healthy controls | HPPI-TOFMS with RF | 89.16% | 87.70% |
| Zhang, 2024, [57] | 937 BC patients/1044 healthy controls | HPPI-TOFMS with RF | 85.9% | 90.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yockell-Lelièvre, H.; Philip, R.; Kaushik, P.; Masilamani, A.P.; Meterissian, S.H. Breathomics: A Non-Invasive Approach for the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040411
Yockell-Lelièvre H, Philip R, Kaushik P, Masilamani AP, Meterissian SH. Breathomics: A Non-Invasive Approach for the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040411
Chicago/Turabian StyleYockell-Lelièvre, Hélène, Romy Philip, Palash Kaushik, Ashok Prabhu Masilamani, and Sarkis H. Meterissian. 2025. "Breathomics: A Non-Invasive Approach for the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040411
APA StyleYockell-Lelièvre, H., Philip, R., Kaushik, P., Masilamani, A. P., & Meterissian, S. H. (2025). Breathomics: A Non-Invasive Approach for the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Bioengineering, 12(4), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040411







