Wavelet-Guided Multi-Scale ConvNeXt for Unsupervised Medical Image Registration
Abstract
1. Introduction
- WaveMorph: We propose a frequency-spatial co-optimization framework for unsupervised non-rigid medical image registration by integrating wavelet transforms and ConvNeXt;
- MSWF: We design a novel Multi-Scale Wavelet Feature Fusion downsampling module that leverages Haar wavelet decomposition to preserve spatial information across 8 frequency sub-bands, fused via ConvNeXt-optimized multiscale kernels;
- Dysmaple: We innovatively introduce the lightweight dynamic upsampling module, originally used in image super-resolution, into the medical image registration field. It addresses the issue where traditional upsampling methods often lead to blurring or distortion of key anatomical structures during registration. Extensive experiments in Section 4.4 show that the dynamic upsampling module effectively improves registration accuracy and robustness;
- State-of-the-art results: We extensively validated our model on inter-patient registration and atlas-to-patient brain MRI registration tasks. WaveMorph achieves superior Dice scores (0.779 ± 0.015 for atlas-to-patient MIR; 0.824 ± 0.021 for inter-patient MIR) and real-time inference (0.072 s/image), outperforming all competing methods in accuracy and efficiency.
2. Related Work
2.1. Medical Image Registration
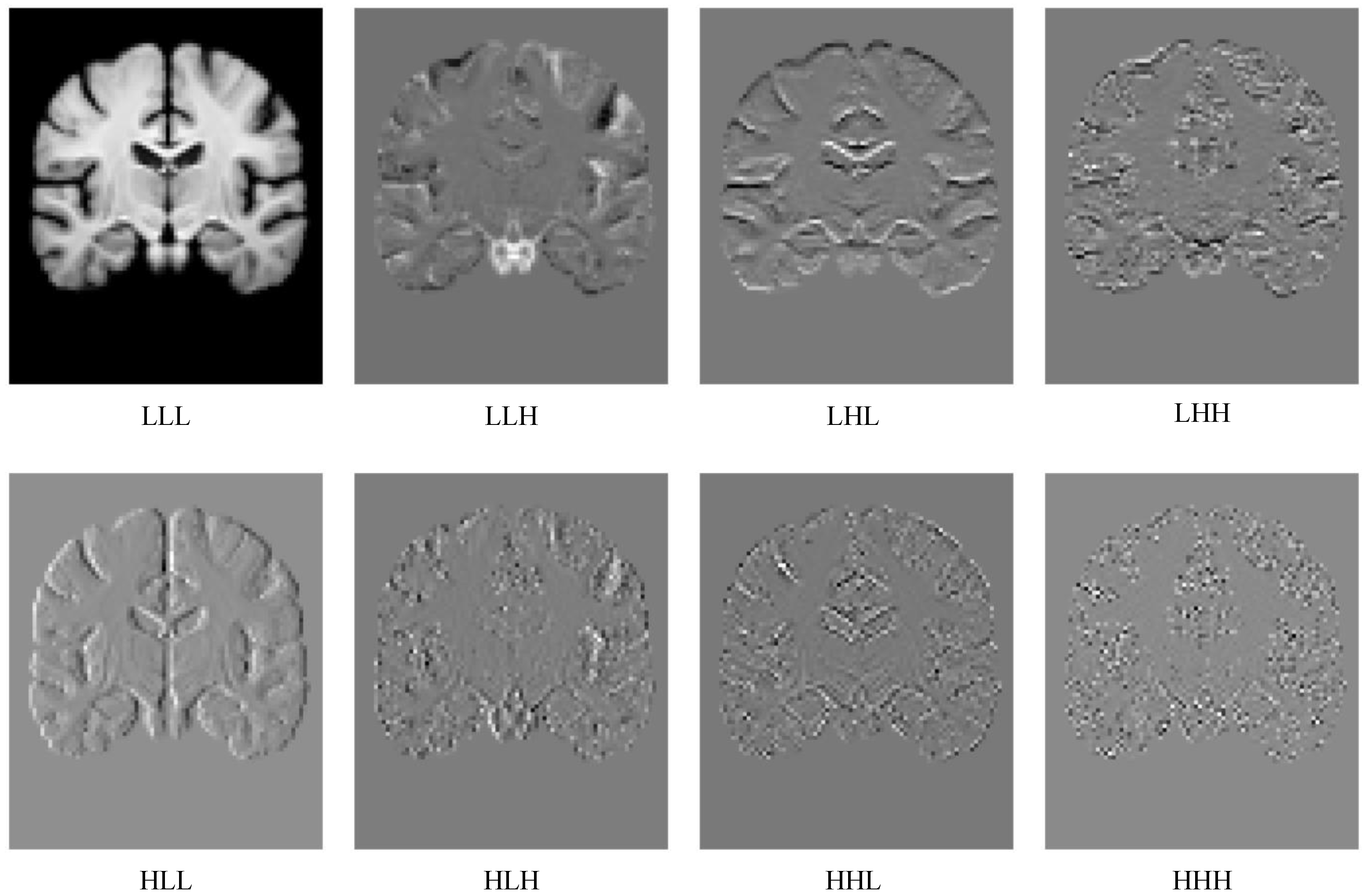
2.2. Wavelet Transform in Deep Learning
3. Methods
3.1. Datasets and Preprocessing
3.2. Implementation Details
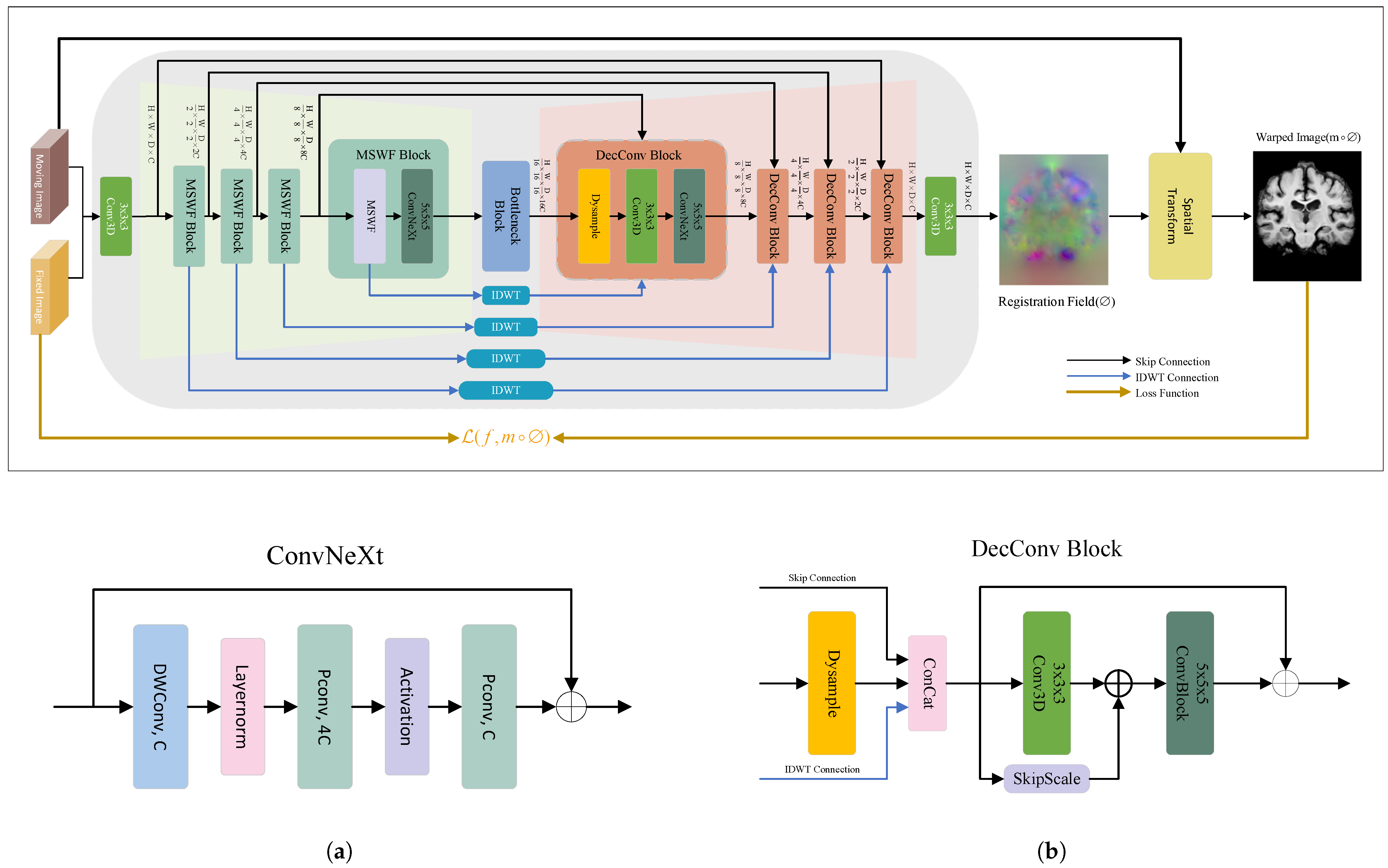
3.3. WaveMorph Architecture for Non-Rigid Registration Network
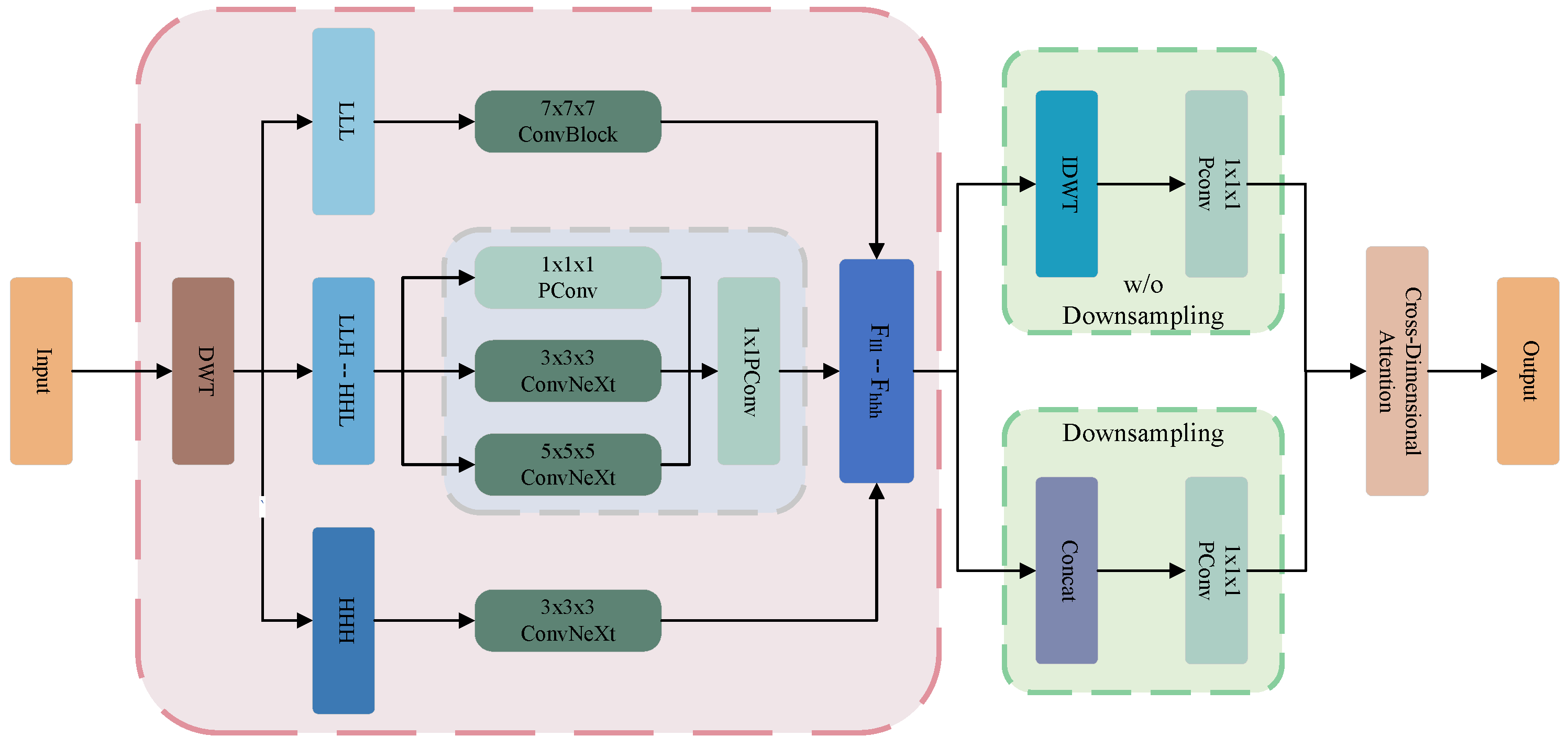
3.4. Multi-Scale Wavelet Feature Fusion Module
3.5. Bottleneck Block
3.6. Lightweight Dynamic Upsampling Module
3.7. Spatial Transformation Function
3.8. Loss Functions
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
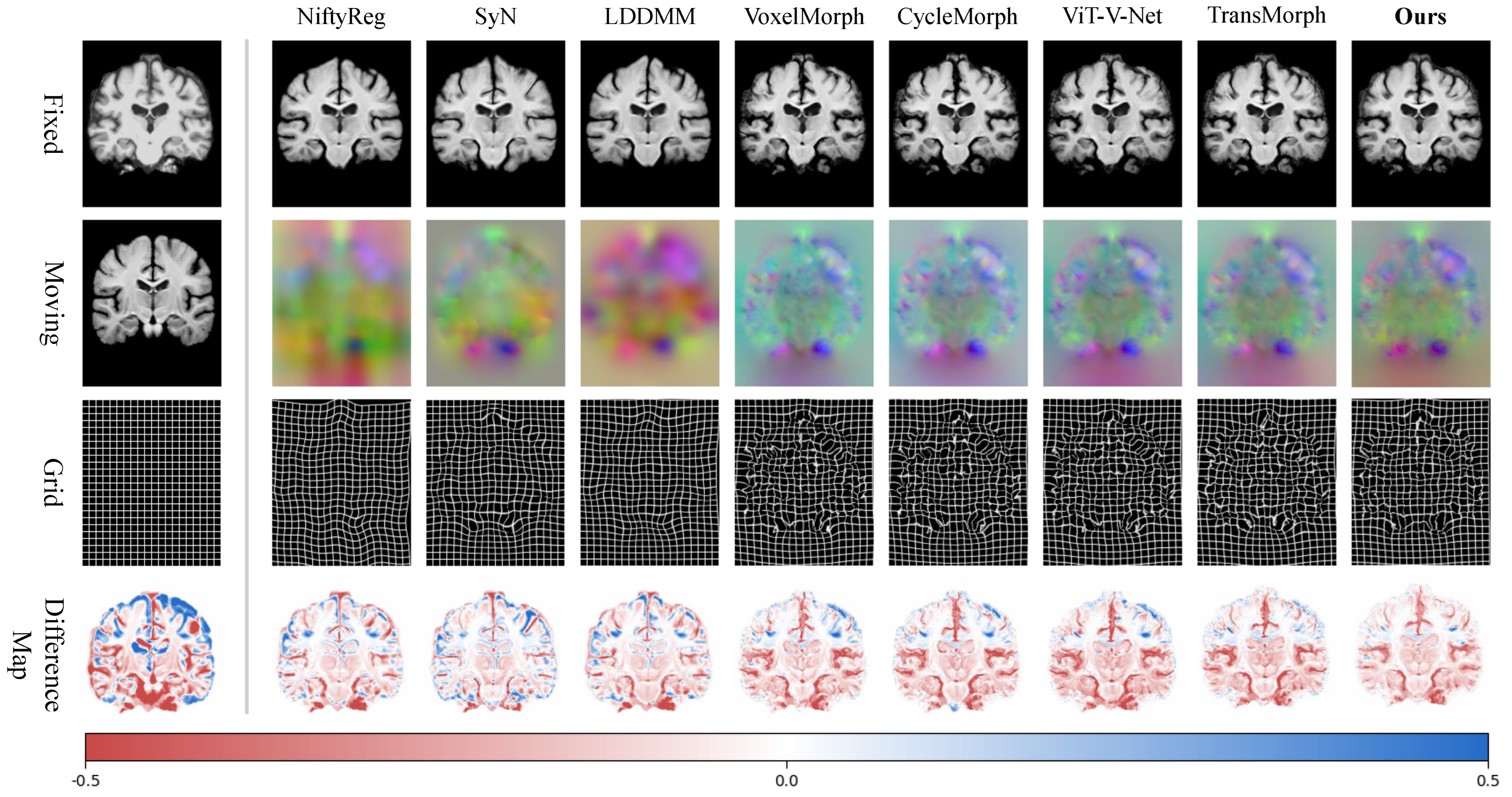
4.2. Registration Results
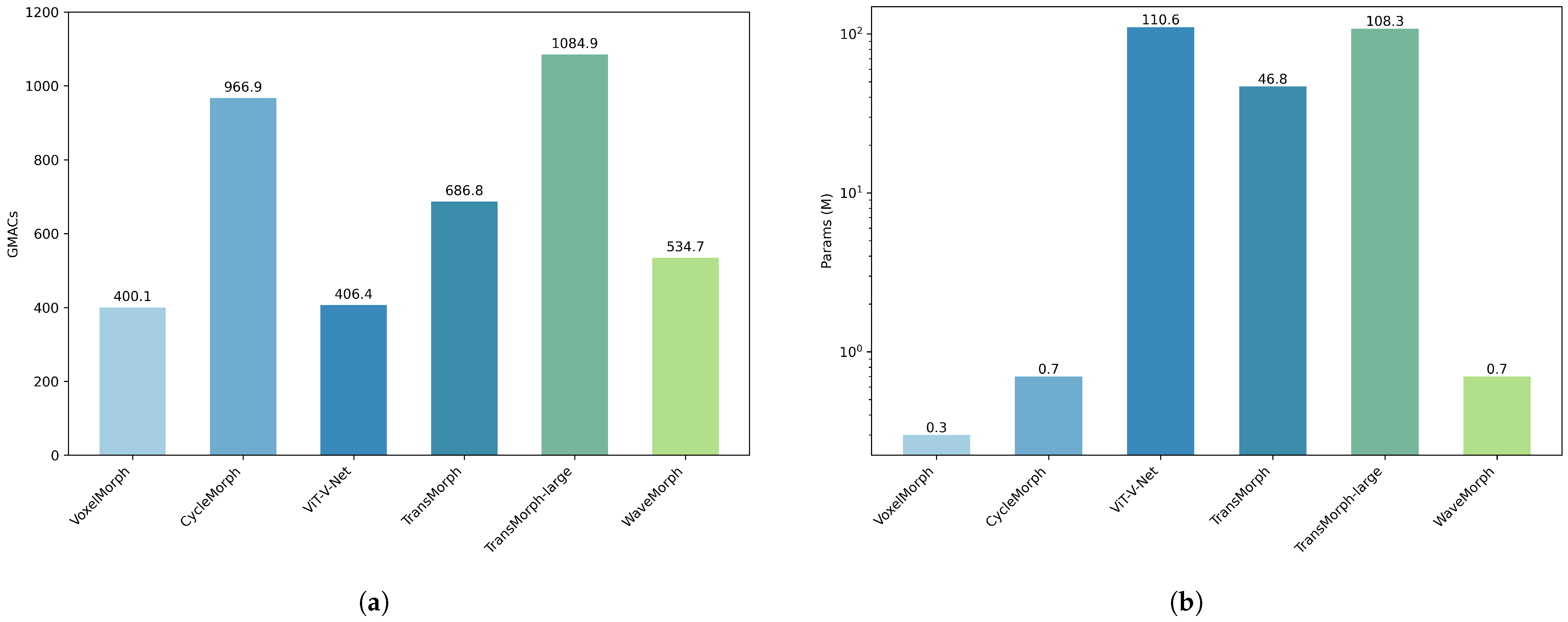
4.3. Computational and Model Complexity
4.4. Ablation Studies
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Information Importance
5.2. Convergence and Speed
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Diaz-Pinto, A.; Ravikumar, N.; Frangi, A.F. Deep learning in medical image registration. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 3, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanam, M.S.T.; Iyer, K.; Joshi, S.; Elhabian, S. MORPH-LER: Log-Euclidean Regularization for Population-Aware Image Registration. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.02029. [Google Scholar]
- Sotiras, A.; Davatzikos, C.; Paragios, N. Deformable medical image registration: A survey. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 1153–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Zhao, A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Guttag, J.; Dalca, A.V. Voxelmorph: A learning framework for deformable medical image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.G.; Ye, J.C. CycleMorph: Cycle consistent unsupervised deformable image registration. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 71, 102036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, M.; Bi, L.; Feng, D.; Kim, J. Non-iterative coarse-to-fine registration based on single-pass deep cumulative learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Bian, Z.; Subramanian, S.; Carass, A.; Prince, J.L.; Du, Y. A survey on deep learning in medical image registration: New technologies, uncertainty, evaluation metrics, and beyond. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 100, 103385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J.; Song, T.; Li, L.; Tian, L. Coarse-to-fine hybrid network for robust medical image registration in the presence of large deformations. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 106926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharir, G.; Noy, A.; Zelnik-Manor, L. An image is worth 16 × 16 words, what is a video worth? arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.13915. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.A.A.; Awais, M.; Kittler, J. Sit: Self-supervised vision transformer. CoRR abs/2104.03602 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16000–16009. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; proceedings, part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, A.; Aamir, M.; Mohd Nawi, N.; Arshad, A.; Riaz, S.; Alruban, A.; Dutta, A.K.; Almotairi, S. A comparison of pooling methods for convolutional neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Fadnavis, S. Image interpolation techniques in digital image processing: An overview. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2014, 4, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Dumoulin, V.; Visin, F. A guide to convolution arithmetic for deep learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.07285. [Google Scholar]
- Finder, S.E.; Amoyal, R.; Treister, E.; Freifeld, O. Wavelet convolutions for large receptive fields. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Lin, L.; Zuo, W. Multi-level wavelet-CNN for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 773–782. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; He, J.; Feng, M.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Mian, A. High frequency matters: Uncertainty guided image compression with wavelet diffusion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.12538. [Google Scholar]
- Avants, B.B.; Epstein, C.L.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J.C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modat, M.; McClelland, J.; Ourselin, S. Lung registration using the NiftyReg package. Med. Image Anal. Clin.-A Grand Chall. 2010, 2010, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, M.; Billot, B.; Iglesias, J.E.; Fischl, B.; Dalca, A.V. Learning mri contrast-agnostic registration. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 899–903. [Google Scholar]
- Amor, B.B.; Arguillère, S.; Shao, L. ResNet-LDDMM: Advancing the LDDMM framework using deep residual networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 3707–3720. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Nie, D.; Kim, M.; Wang, Q.; Shen, D. Deformable image registration based on similarity-steered CNN regression. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2017: 20th International Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; Proceedings, Part I 20. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Rohé, M.M.; Datar, M.; Heimann, T.; Sermesant, M.; Pennec, X. SVF-Net: Learning deformable image registration using shape matching. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention- MICCAI 2017: 20th International Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; Proceedings, Part I 20. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Sokooti, H.; De Vos, B.; Berendsen, F.; Lelieveldt, B.P.; Išgum, I.; Staring, M. Nonrigid image registration using multi-scale 3D convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention- MICCAI 2017: 20th International Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; Proceedings, Part I 20. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Kwitt, R.; Styner, M.; Niethammer, M. Quicksilver: Fast predictive image registration—A deep learning approach. NeuroImage 2017, 158, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, B.D.; Berendsen, F.F.; Viergever, M.A.; Staring, M.; Išgum, I. End-to-end unsupervised deformable image registration with a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: Third International Workshop, DLMIA 2017, and 7th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Québec City, QC, Canada, 14 September 2017; Proceedings 3. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, B.D.; Berendsen, F.F.; Viergever, M.A.; Sokooti, H.; Staring, M.; Išgum, I. A deep learning framework for unsupervised affine and deformable image registration. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 52, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Zhao, A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Guttag, J.; Dalca, A.V. An unsupervised learning model for deformable medical image registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 9252–9260. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Frey, E.C.; He, Y.; Segars, W.P.; Li, Y.; Du, Y. Transmorph: Transformer for unsupervised medical image registration. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 82, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppenhof, K.A.; Lafarge, M.W.; Veta, M.; Pluim, J.P. Progressively trained convolutional neural networks for deformable image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.C.; Chung, A.C. Large deformation diffeomorphic image registration with laplacian pyramid networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Proceedings, Part III 23. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Liao, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; He, X.; Wu, X. Haar wavelet downsampling: A simple but effective downsampling module for semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 143, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, S.; Takayama, K.; Hachisuka, T. Wavelet convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.08620. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Li, Y.; Lin, K.; Chen, G.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, J.; Yoo, Y.F.; Polley, M.O. Wavelet synthesis net for disparity estimation to synthesize dslr calibre bokeh effect on smartphones. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2407–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, D.S.; Wang, T.H.; Parker, J.; Csernansky, J.G.; Morris, J.C.; Buckner, R.L. Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS): Cross-sectional MRI data in young, middle aged, nondemented, and demented older adults. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, B.; Yan, Z.; Kalantidis, Y.; Rohrbach, M.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. Drop an octave: Reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3435–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.; Fu, H.; Cao, Z. Learning to upsample by learning to sample. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 6027–6037. [Google Scholar]
- Im, D.J.; Tao, M.; Branson, K. An Empirical Analysis of Deep Network Loss. 2016. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=rkuDV6iex (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Sutskever, I.; Martens, J.; Dahl, G.; Hinton, G. On the importance of momentum and initialization in deep learning. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; pp. 404–439. [Google Scholar]
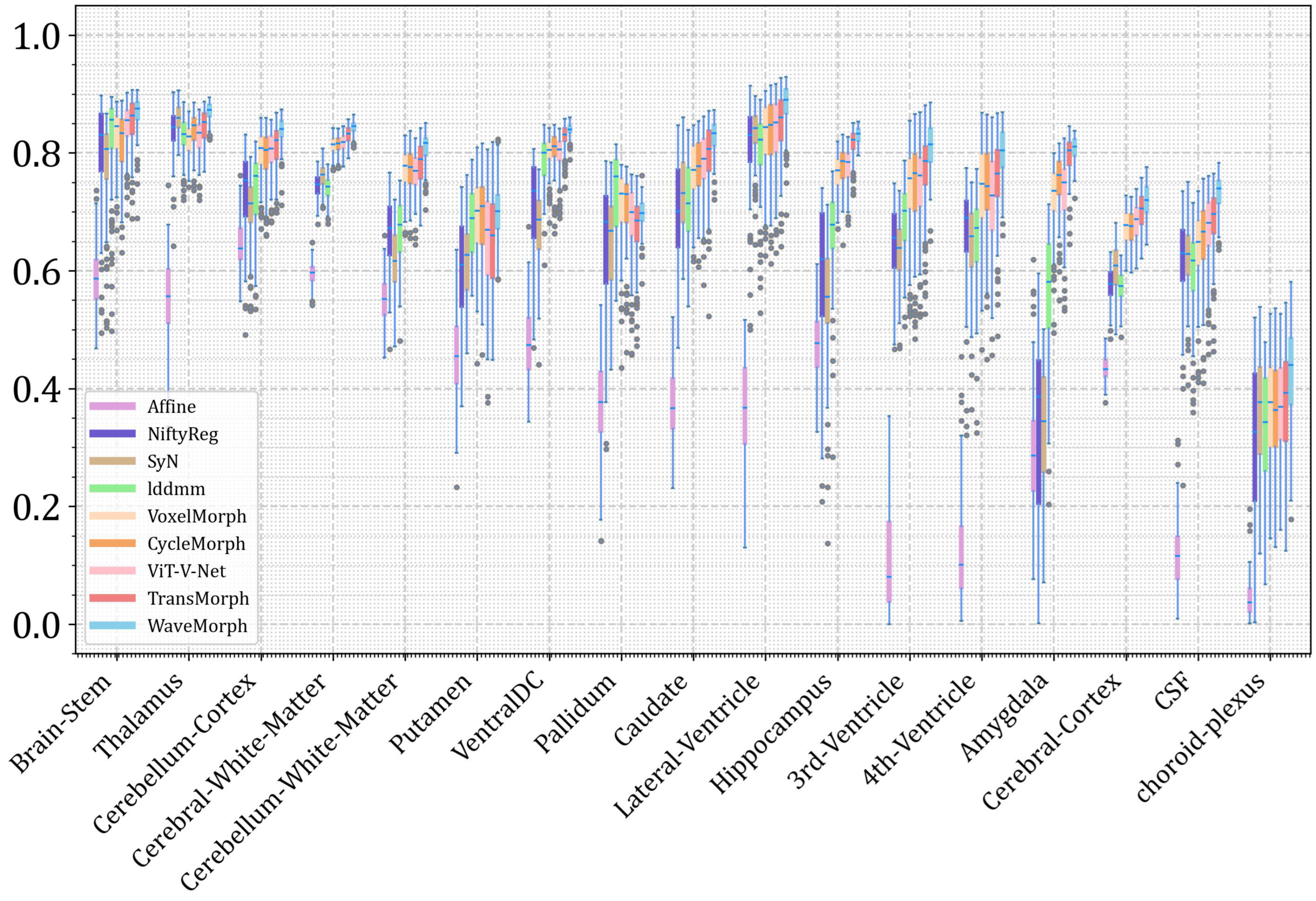
| Atlas-to-Patient MRI | Inter-Patient MRI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | DSC | FR | DSC | FR |
| Affine | 0.406 ± 0.035 | - | 0.571 ± 0.053 | - |
| SyN | 0.645 ± 0.152 | <0.0001 | 0.769 ± 0.028 | <0.0001 |
| NiftyReg | 0.645 ± 0.167 | 0.020 ± 0.046 | 0.762 ± 0.034 | 0.020 ± 0.046 |
| LDDMM | 0.733 ± 0.126 | <0.0001 | 0.733 ± 0.126 | <0.0001 |
| VoxelMorph | 0.729 ± 0.129 | 1.590 ± 0.339 | 0.787 ± 0.026 | 1.290 ± 0.319 |
| CycleMorph | 0.737 ± 0.029 | 1.719 ± 0.382 | 0.793 ± 0.025 | 1.219 ± 0.362 |
| ViT-V-Net | 0.732 ± 0.030 | 1.554 ± 0.270 | 0.808 ± 0.023 | 1.224 ± 0.348 |
| TransMorph | 0.752 ± 0.029 | 1.440 ± 0.303 | 0.809 ± 0.022 | 0.390 ± 0.328 |
| Ours | 0.779 ± 0.015 | 1.310 ± 0.313 | 0.824 ± 0.021 | 0.204 ± 0.047 |
| Model | Training (min/epoch) | Inference (s/image) |
|---|---|---|
| SyN | - | 192.140 |
| NiftyReg | - | 30.723 |
| LDDMM | - | 66.829 |
| VoxelMorph | 4.93 | 0.430 |
| CycleMorph | 21.99 | 0.281 |
| ViT-V-Net | 4.83 | 0.197 |
| TransMorph | 7.56 | 0.329 |
| Ours | 3.88 | 0.072 |
| Up | Nearest | Trilinear | Dysample | Atlas-to-Patient MRI | Inter-Patient MRI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Down | DSC | FR | DSC | FR | |||
| maxpooling | ✓ | × | × | 0.747 ± 0.030 | 1.581 ± 0.329 | 0.809 ± 0.017 | 0.167 ± 0.056 |
| × | ✓ | × | 0.748 ± 0.029 | 1.578 ± 0.348 | 0.811 ± 0.019 | 0.174 ± 0.055 | |
| × | × | ✓ | 0.756 ± 0.028 | 1.591 ± 0.355 | 0.815 ± 0.018 | 0.222 ± 0.062 | |
| patchmerging | ✓ | × | × | 0.748 ± 0.030 | 1.511 ± 0.321 | 0.811 ± 0.017 | 0.171 ± 0.055 |
| × | ✓ | × | 0.748 ± 0.030 | 1.540 ± 0.346 | 0.812 ± 0.017 | 0.174 ± 0.058 | |
| × | × | ✓ | 0.752 ± 0.028 | 1.536 ± 0.361 | 0.818 ± 0.018 | 0.213 ± 0.054 | |
| wavesample | ✓ | × | × | 0.749 ± 0.022 | 1.531 ± 0.325 | 0.812 ± 0.018 | 0.170 ± 0.057 |
| × | ✓ | × | 0.751 ± 0.030 | 1.542 ± 0.337 | 0.814 ± 0.017 | 0.175 ± 0.054 | |
| × | × | ✓ | 0.754 ± 0.028 | 1.539 ± 0.341 | 0.819 ± 0.018 | 0.211 ± 0.055 | |
| MSWF | ✓ | × | × | 0.758 ± 0.018 | 1.386 ± 0.337 | 0.815 ± 0.019 | 0.178 ± 0.050 |
| × | ✓ | × | 0.764 ± 0.020 | 1.411 ± 0.324 | 0.819 ± 0.018 | 0.184 ± 0.055 | |
| × | × | ✓ | 0.779 ± 0.015 | 1.310 ± 0.313 | 0.824 ± 0.021 | 0.204 ± 0.047 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Xu, A.; Ouyang, G.; Xu, Z.; Shen, S.; Chen, W.; Liang, M.; Zhang, G.; Wei, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. Wavelet-Guided Multi-Scale ConvNeXt for Unsupervised Medical Image Registration. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040406
Zhang X, Xu A, Ouyang G, Xu Z, Shen S, Chen W, Liang M, Zhang G, Wei J, Zhou X, et al. Wavelet-Guided Multi-Scale ConvNeXt for Unsupervised Medical Image Registration. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040406
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuejun, Aobo Xu, Ganxin Ouyang, Zhengrong Xu, Shaofei Shen, Wenkang Chen, Mingxian Liang, Guiqi Zhang, Jiashun Wei, Xiangrong Zhou, and et al. 2025. "Wavelet-Guided Multi-Scale ConvNeXt for Unsupervised Medical Image Registration" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040406
APA StyleZhang, X., Xu, A., Ouyang, G., Xu, Z., Shen, S., Chen, W., Liang, M., Zhang, G., Wei, J., Zhou, X., & Wu, D. (2025). Wavelet-Guided Multi-Scale ConvNeXt for Unsupervised Medical Image Registration. Bioengineering, 12(4), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040406







