A Lightweight Machine Learning Model for High Precision Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Identification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Description and Details of the Dataset
2.2. Data Augmentation and Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
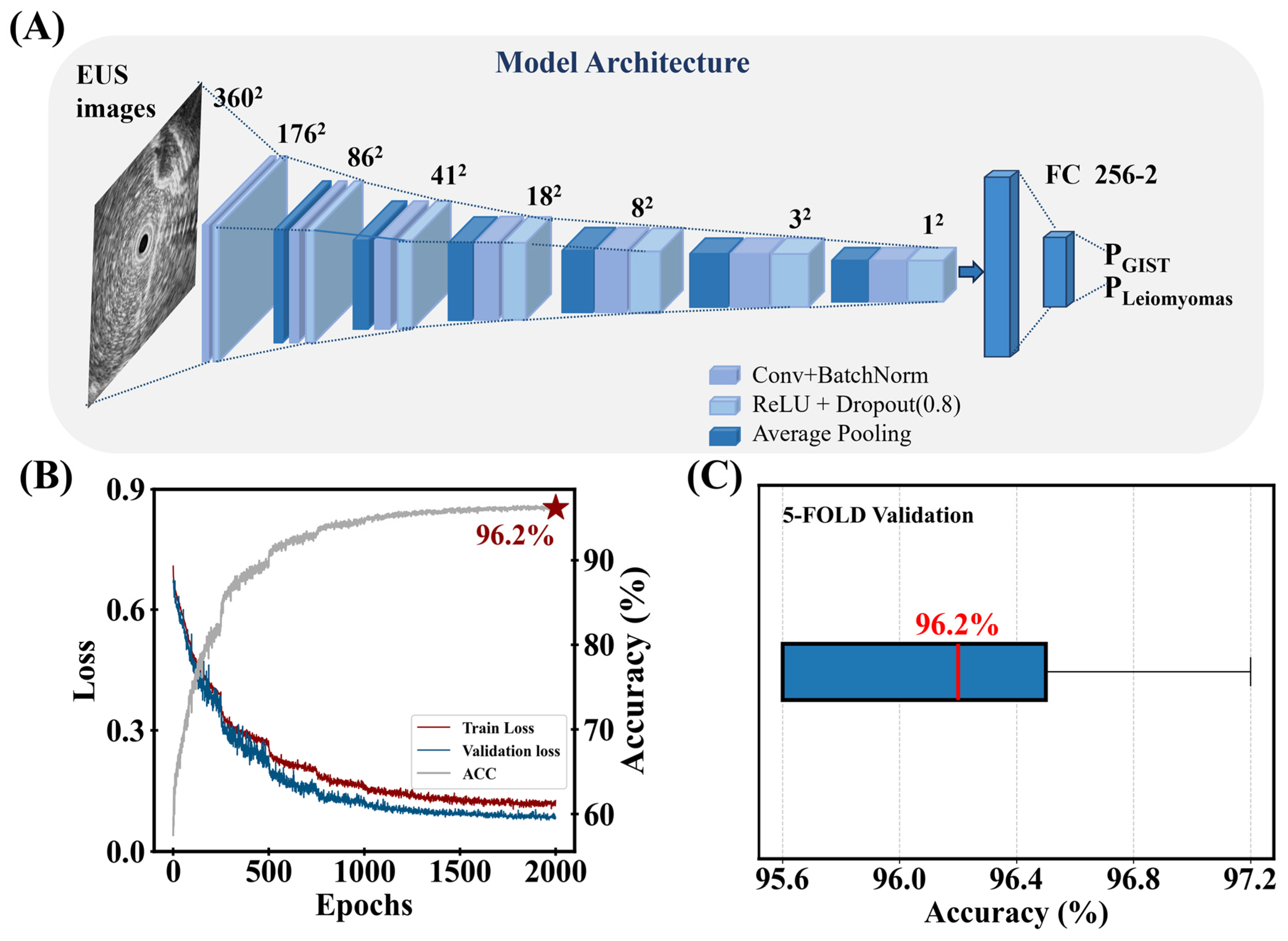
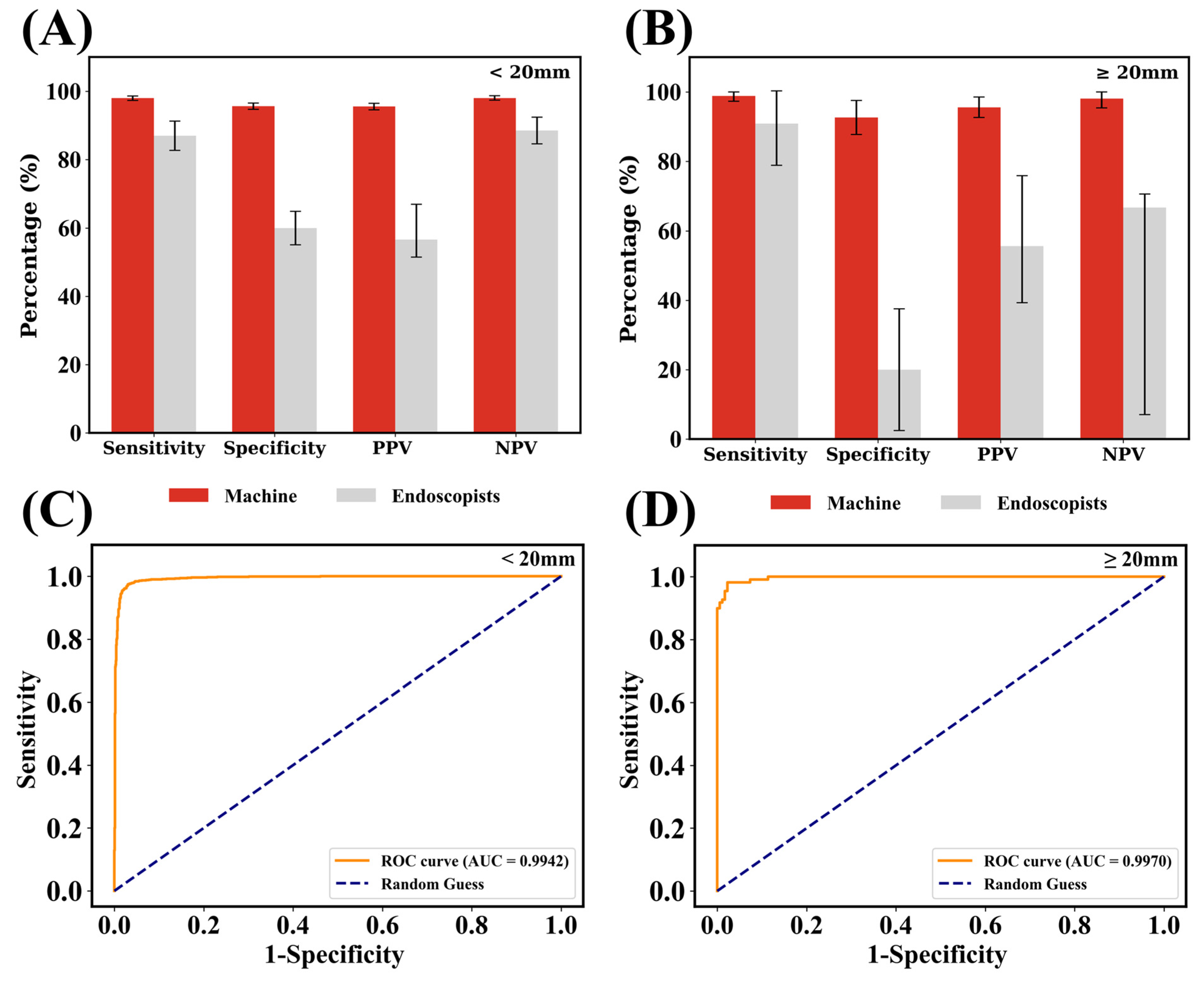
3.1. Performance of the Lightweight Model
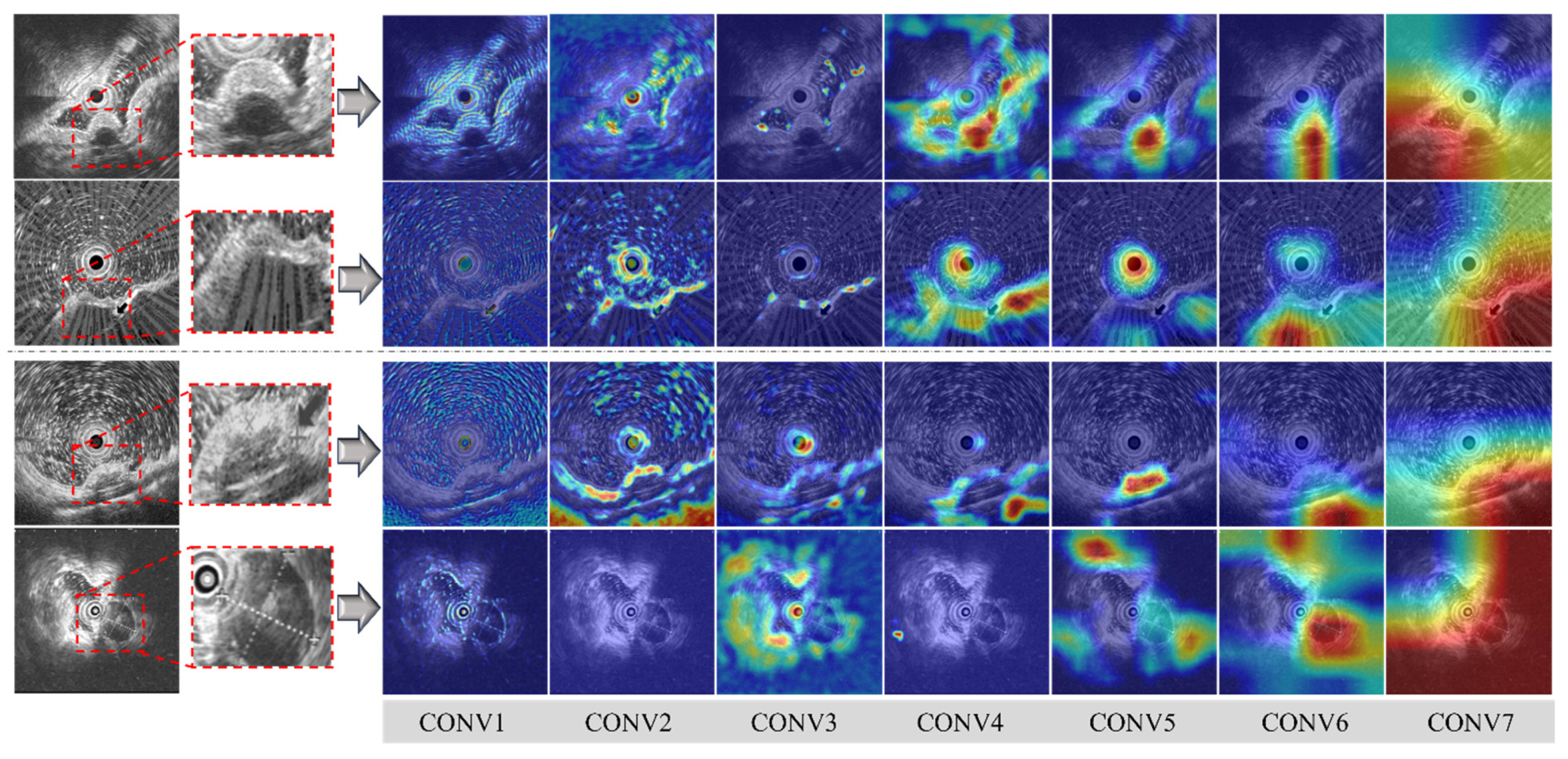
3.2. Visualization of the Lightweight Model
4. Discussion
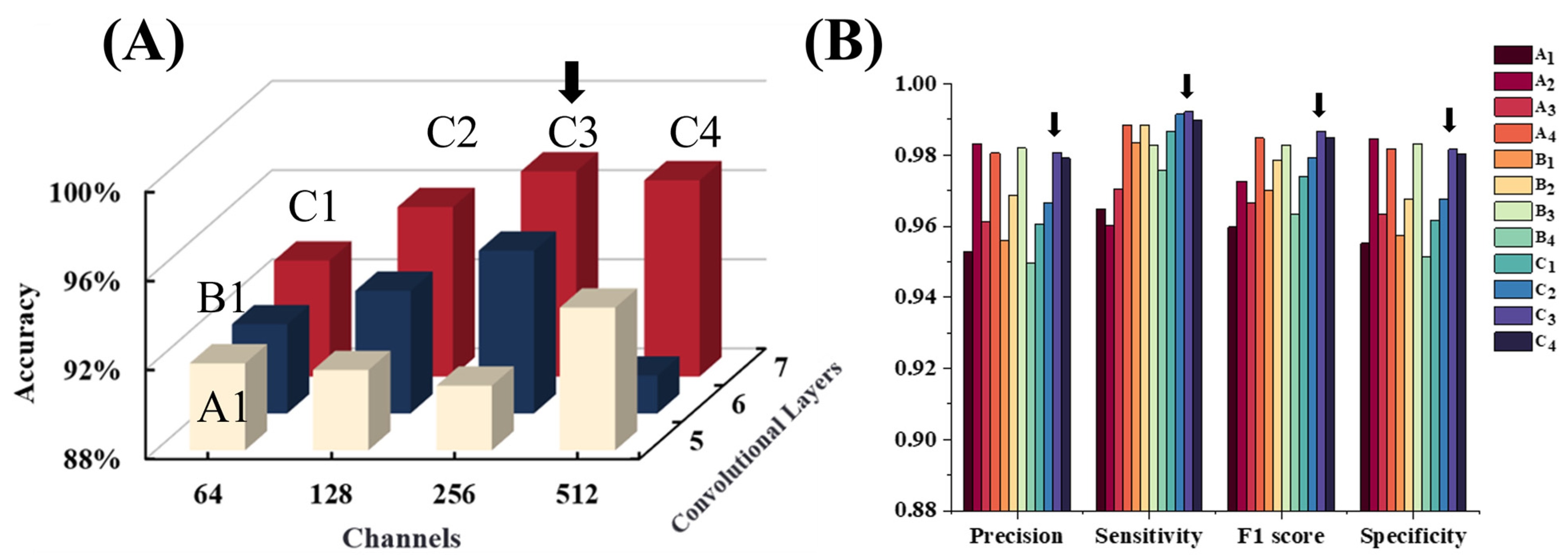
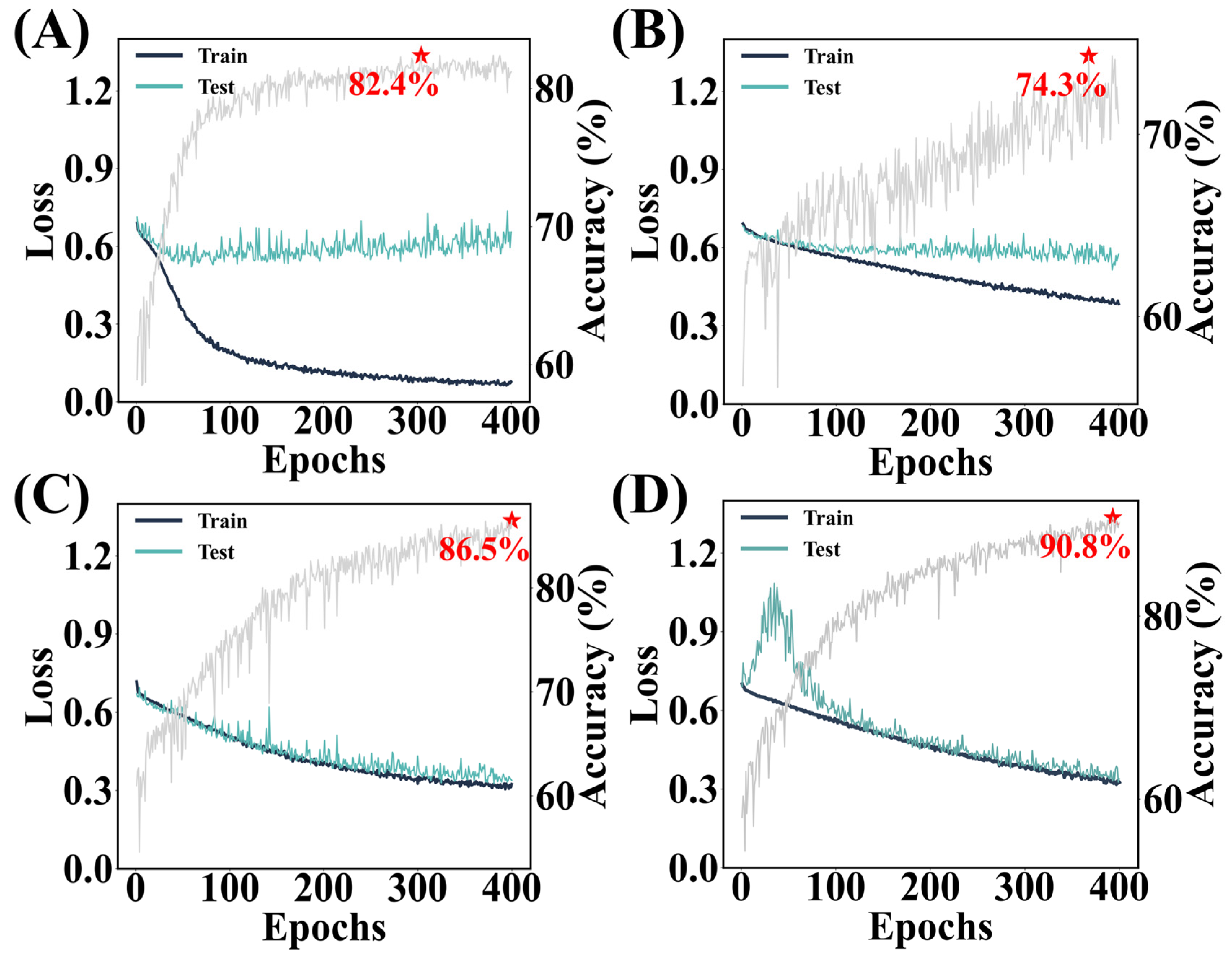
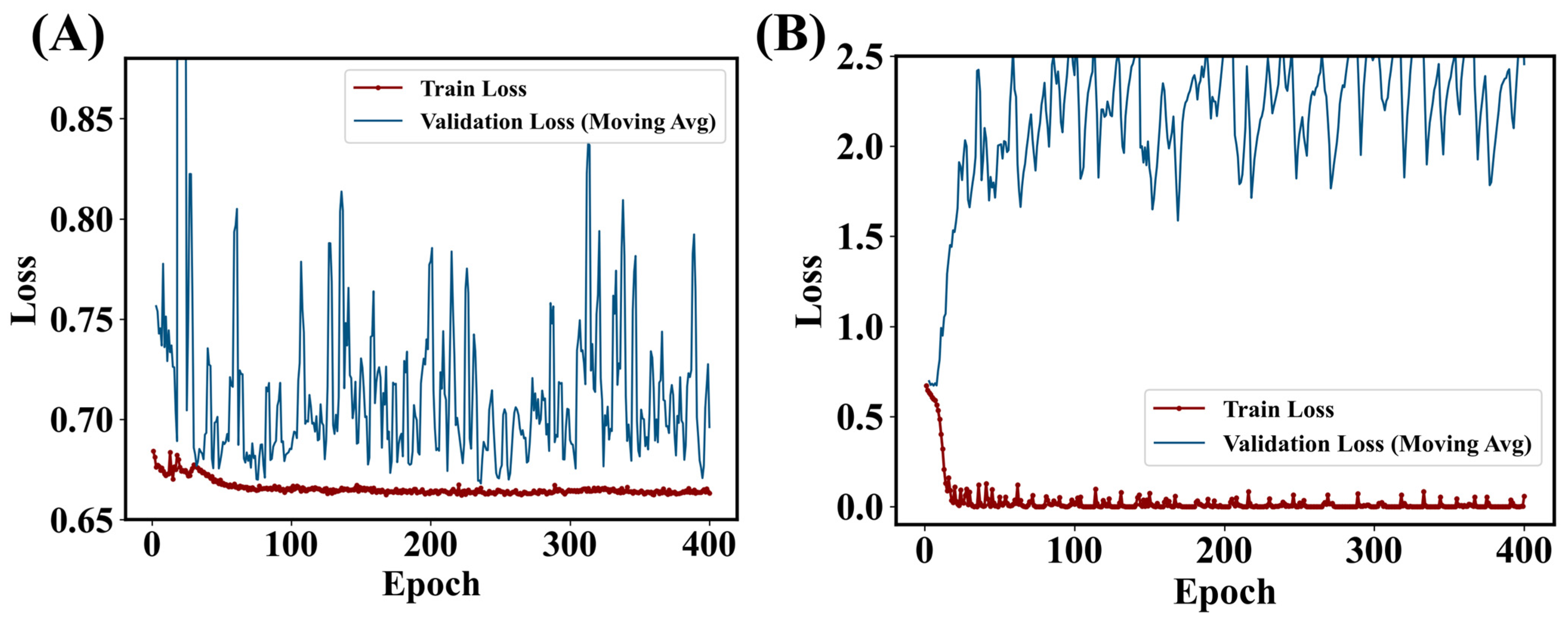
4.1. Explorations in Model Architectures
4.2. Remark: Which Factors Benefit the Lightweight Model?
4.3. Benchmarks and Outlook: A Deep Model or a Lightweight Model?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kindblom, L.G.; Remotti, H.E.; Aldenborg, F.; Meis-Kindblom, J.M. Gastrointestinal Pacemaker Cell Tumor (GIPACT): Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Show Phenotypic Characteristics of the Interstitial Cells of Cajal. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandrasegaran, K.; Rajesh, A.; Rydberg, J.; Rushing, D.A.; Akisik, F.M.; Henley, J.D. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: Clinical, Radiologic, and Pathologic Features. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hidalgo, J.M.; Duran-Martinez, M.; Molero-Payan, R.; Rufian-Peña, S.; Arjona-Sanchez, A.; Casado-Adam, A.; Cosano-Alvarez, A.; Briceño-Delgado, J. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: A Multidisciplinary Challenge. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1925–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M. Smooth Muscle Tumors of Soft Tissue and Non-Uterine Viscera: Biology and Prognosis. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, S17–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-E.; Tzen, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Yeh, C.-N. Clinical Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): From the Molecular Genetic Point of View. Cancers 2019, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charville, G.W.; Longacre, T.A. Surgical Pathology of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: Practical Implications of Morphologic and Molecular Heterogeneity for Precision Medicine. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2017, 24, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekky, M.A.; Yamao, K.; Sawaki, A.; Mizuno, N.; Hara, K.; Nafeh, M.A.; Osman, A.M.; Koshikawa, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Bhatia, V. Diagnostic Utility of EUS-Guided FNA in Patients with Gastric Submucosal Tumors. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.B.; Sahai, A.V.; Aabakken, L.; Penman, I.D.; Van Velse, A.; Webb, J.; Wilson, M.; Hoffman, B.J.; Hawes, R.H. Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy: A Large Single Centre Experience. Gut 1999, 44, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, N.; Goto, H.; Niwa, Y.; Hirooka, Y.; Ohmiya, N.; Nagasaka, T.; Hayakawa, T. The Diagnosis of GI Stromal Tumors with EUS-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration with Immunohistochemical Analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 55, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallio, S.; Crinò, S.F.; Maida, M.; Sinagra, E.; Tripodi, V.F.; Facciorusso, A.; Ofosu, A.; Conti Bellocchi, M.C.; Shahini, E.; Melita, G. Endoscopic Ultrasound Advanced Techniques for Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours. Cancers 2023, 15, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulx, A.L.; Kothari, S.; Acosta, R.D.; Agrawal, D.; Bruining, D.H.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Eloubeidi, M.A.; Fanelli, R.D.; Gurudu, S.R.; Khashab, M.A.; et al. The Role of Endoscopy in Subepithelial Lesions of the GI Tract. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.W.; Choi, C.W.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, S.B.; Kim, S.J. Endoscopic Ultrasound without Tissue Acquisition Has Poor Accuracy for Diagnosing Gastric Subepithelial Tumors. Medicine 2016, 95, e5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.S.; Shim, K.-N.; Lee, J.H. Comparison of the Diagnostic Ability of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and Abdominopelvic Computed Tomography in the Diagnosis of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors. Clin. Endosc. 2019, 52, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Qiao, M.; Jiang, F.; Guo, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. TN-USMA Net: Triple Normalization-based Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Classification on Multicenter EUS Images with Ultrasound-specific Pretraining and Meta Attention. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 7199–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, F.; Li, P.; Zhu, J. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: A Meta-Analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoda, Y.; Ihara, E.; Komori, K.; Ogino, H.; Otsuka, Y.; Chinen, T.; Tsuda, Y.; Ando, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Ogawa, Y. Efficacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound with Artificial Intelligence for the Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.H.; Zhao, L.L.; Wang, L. Diagnostic Accuracy of Endoscopic Ultrasound with Artificial Intelligence for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: A Meta-Analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2022, 23, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Qian, Q.; Xue, E.; Chen, Z. Deep Learning-Based Segmentation and Risk Stratification for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors in Transabdominal Ultrasound Imaging. J. Ultrasound Med. 2024, 43, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, G.; Su, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Luo, J.; Cao, F.; Zhen, P.; Huang, B.; et al. A Deep Learning–Based System Trained for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Screening Can Identify Multiple Types of Soft Tissue Tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Karanian, M.; Perret, R.; Camara, A.; Le Loarer, F.; Jean-Denis, M.; Hostein, I.; Michot, A.; Ducimetiere, F.; Giraud, A.; et al. Deep Learning Predicts Patients Outcome and Mutations from Digitized Histology Slides in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. npj Precis. Onc. 2023, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, G.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Liu, G.; He, Q.; Zhou, J.; et al. Development and Interpretation of a Multimodal Predictive Model for Prognosis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. npj Precis. Onc. 2024, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, B.E.; Baek, D.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.C. Application of A Convolutional Neural Network in The Diagnosis of Gastric Mesenchymal Tumors on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoda, Y.; Ihara, E.; Fujimori, N.; Nagatomo, S.; Esaki, M.; Hata, Y.; Bai, X.; Tanaka, Y.; Ogino, H.; Chinen, T.; et al. Efficacy of Ultrasound Endoscopy with Artificial Intelligence for the Differential Diagnosis of Non-Gastric Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, D.C.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, B.E.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, K.B. Artificial Intelligence-Based Diagnosis of Gastric Mesenchymal Tumors Using Digital Endosonography Image Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Kamata, K.; Ishihara, R.; Handa, H.; Otsuka, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Yoshikawa, T.; Ishikawa, R.; Okamoto, A.; Yamazaki, T.; et al. Value of Artificial Intelligence with Novel Tumor Tracking Technology in the Diagnosis of Gastric Submucosal Tumors by Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic Endoscopic Ultrasonography. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, K.; Kuwahara, T.; Furukawa, K.; Kakushima, N.; Furune, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Marukawa, T.; Asai, H.; Matsui, K.; Sasaki, Y.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Based Diagnosis of Upper Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Lesions on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images. Gastric. Cancer 2022, 25, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Dong, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Yan, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, C.; Li, X. An Artificial Intelligence System for Distinguishing between Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors and Leiomyomas Using Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.K.; Kim, T.; Cho, Y.K.; Cheung, D.Y.; Lee, B.-I.; Cho, Y.-S.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, M.-G.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, S. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Object Detection Model to Identify Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors in Endoscopic Ultrasound Images. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 3387–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seven, G.; Silahtaroglu, G.; Seven, O.O.; Senturk, H. Differentiating Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors from Leiomyomas Using a Neural Network Trained on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Images. Dig. Dis. 2021, 40, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Training and Validation Dataset (2014–2020) | Test Dataset (2022–2024) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic information | Age (years, mean ± SD) | 56.26 ± 9.89 | 57.59 ± 10.74 |
| Male | 249 (36.6%) | 10 (45.5%) | |
| Female | 432 (63.4%) | 12 (54.5%) | |
| Lesion size | Total (mean ± SD) | 9.3 ± 5.7 mm | 18.7 ± 10.7 mm |
| size < 20 mm | 636 (93.4%) | 14 (63.64%) | |
| size ≥ 20 mm | 45 (6.6%) | 8 (36.36%) | |
| Location | Esophagus | 226 (33.2%) | 4 (18.2%) |
| Cardia | 33 (4.8%) | 1 (4.5%) | |
| Fundus | 337 (49.5%) | 11 (50%) | |
| Body | 85 (12.5%) | 6 (27.3%) | |
| Gastric wall layers | Mucosa | 91 (13.4%) | 2 (9.1%) |
| Submucosa | 18 (2.6%) | 1 (4.5%) | |
| Muscularis propria | 572 (84%) | 19 (86.4%) | |
| Layer Name | Kernel Size (Stride, Padding) | Channels | Output Size | Pooling Layers | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv1 | 9 × 9 (1,0) | 1→32 | 352 × 352 × 32 | AvgPool (2 × 2,2) | 2624 |
| Conv2 | 5 × 5 (1,0) | 32→32 | 172 × 172 × 32 | AvgPool (2 × 2,2) | 25,632 |
| Conv3 | 5 × 5 (1,0) | 32→64 | 82 × 82 × 64 | AvgPool (2 × 2,2) | 51,264 |
| Conv4 | 5 × 5 (1,0) | 64→128 | 37 × 37 × 128 | AvgPool (2 × 2,2) | 204,928 |
| Conv5 | 3 × 3 (1,0) | 128→256 | 16 × 16 × 256 | AvgPool (2 × 2,2) | 295,168 |
| Conv6 | 3 × 3 (1,0) | 256→256 | 6 × 6 × 256 | AvgPool (2 × 2,2) | 590,080 |
| Conv7 | 2 × 2 (1,0) | 256→256 | 2 × 2 × 256 | AvgPool (2 × 2,2) | 262,400 |
| FC1 | - | 256→2 | 2 | - | 514 |
| Sensitivity % | Specificity % | Accuracy % | PPV % | NPV % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance (validation set) | 97.7 | 94.7 | 96.2 | 94.6 | 97.7 |
| Performance * (test set) | 93.9 | 95.4 | 94.5 | 96.9 | 91.1 ** |
| Endoscopists | 55.6 | 79.6 | 67.6 | 73.2 | 64.2 |
| Approaches | Authors | Goals | Dataset | Accuracy % | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | Joo et al. | GIST vs. Non-GIST | 464 patients | 89.6 | [24] |
| Xception | Minoda et al. | GIST vs. Non-GIST | 273 patients | SELs ≥ 20 mm: 90.0, SELs < 20 mm: 86.3 | [16] |
| ResNet-50 | Tanaka et al. | GIST vs. Leiomyoma | 53 patients | 90.6 | [25] |
| EfficientNetV2-L | Hirai et al. | GIST vs. Non-GIST | 664 patients | 89.3 | [26] |
| ResNet-50 | Yang et al. | GIST vs. Leiomyoma | 752 patients | Internal: 96.2, External: 66.0 | [27] |
| EfficientNet | Oh et al. | GIST vs. Leiomyoma | 168 patients | 92.3 | [28] |
| ResNet-50 | Seven et al. | GIST vs. Leiomyoma | 145 patients | 86.98 | [29] |
| CNN | Kim et al. | GIST vs. Non-GIST | 248 patients | 79.2 | [22] |
| CNN | This model | GIST vs. Leiomyoma | 703 patients | Validation: 96.2 Test: 94.5 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Mo, X.; Shi, J.; Zhou, X.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, X.-D.; Li, M.; Li, Y. A Lightweight Machine Learning Model for High Precision Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Identification. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040381
Sun X, Mo X, Shi J, Zhou X, Niu Y, Zhang X-D, Li M, Li Y. A Lightweight Machine Learning Model for High Precision Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Identification. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040381
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xin, Xiwen Mo, Jing Shi, Xinran Zhou, Yanqing Niu, Xiao-Dong Zhang, Man Li, and Yonghui Li. 2025. "A Lightweight Machine Learning Model for High Precision Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Identification" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040381
APA StyleSun, X., Mo, X., Shi, J., Zhou, X., Niu, Y., Zhang, X.-D., Li, M., & Li, Y. (2025). A Lightweight Machine Learning Model for High Precision Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Identification. Bioengineering, 12(4), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040381






