Gradual Temperature Rise in Radiofrequency Ablation: Enhancing Lesion Quality and Safety in Porcine Myocardial Tissue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. RFA System and RF Catheter
2.2. In Vitro Experiment
2.3. In Vivo Experiment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Temperature Mode Comparison
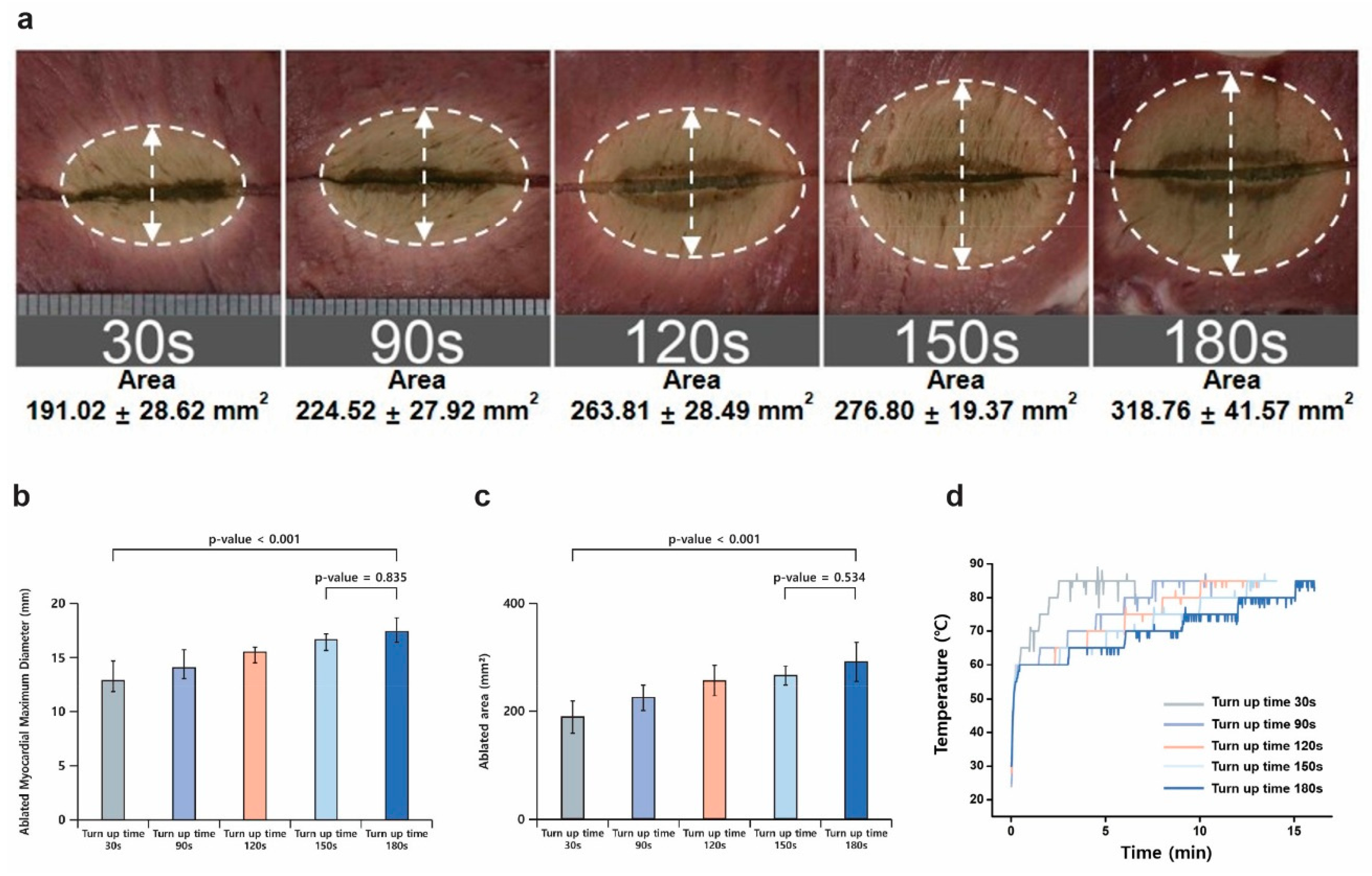
3.2. Turn-Up Time Optimization
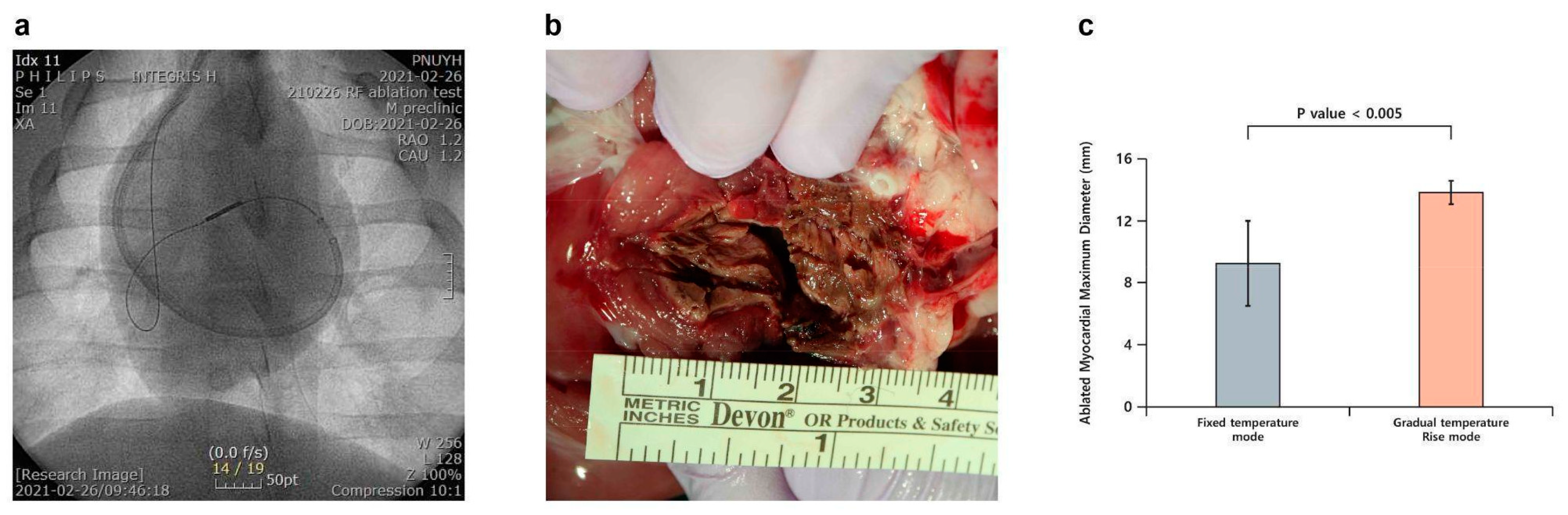
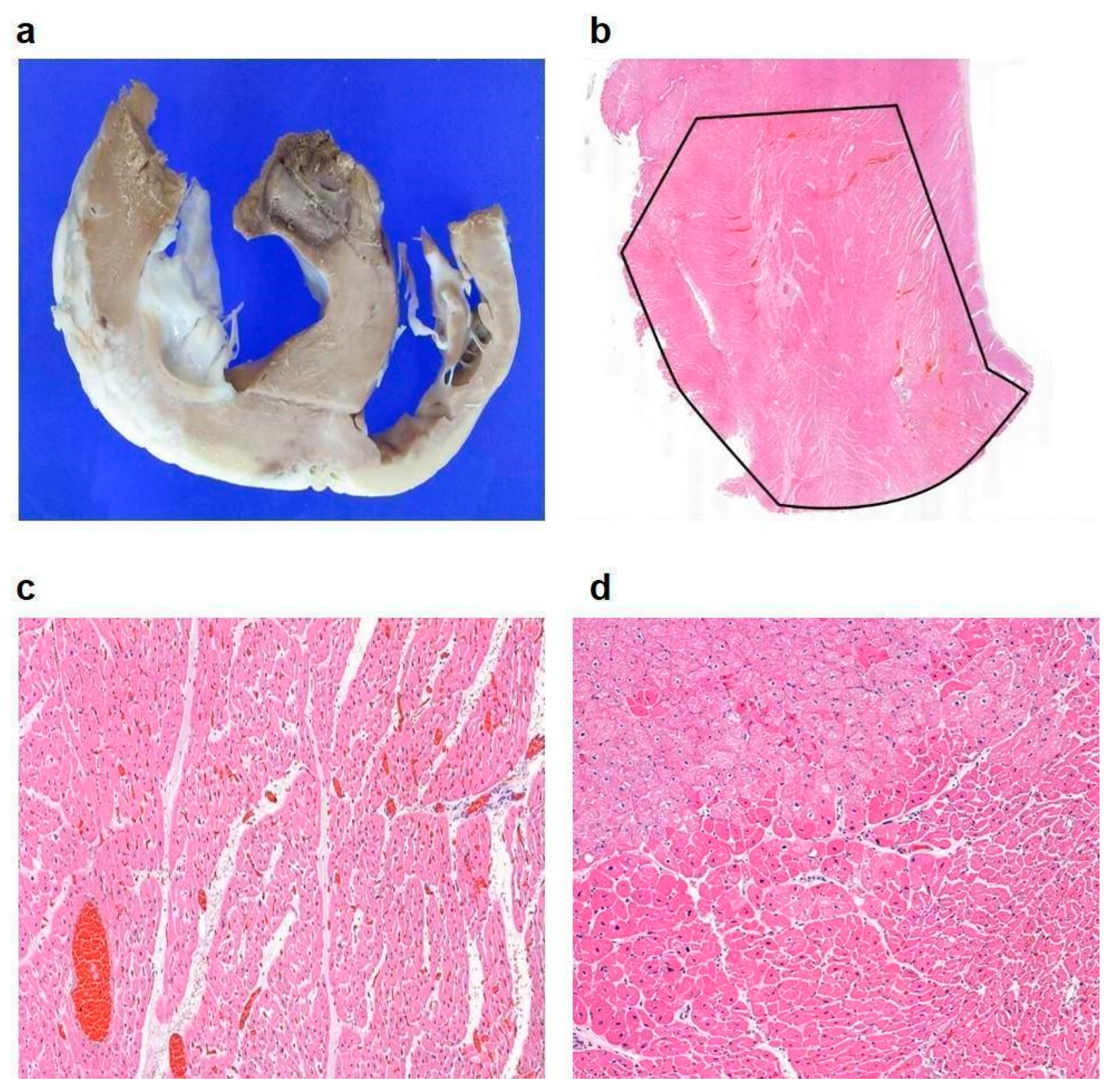
3.3. In Vivo Experimental Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morady, F. Radio-frequency ablation as treatment for cardiac arrhythmias. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, L.M.; Williams, J.A.; Padbury, R.T.; Gotley, D.C.; Stokes, B.; Maddern, G.J. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: A systematic review. Arch. Surg. 2006, 141, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGahan, J.P.; Dodd, G.D., II. Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: Current status. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curley, S.A.; Izzo, F.; Ellis, L.M.; Vauthey, J.N.; Vallone, P. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann. Surg. 2000, 232, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duka, E.; Ierardi, A.M.; Floridi, C.; Terrana, A.; Fontana, F.; Carrafiello, G. The role of interventional oncology in the management of lung cancer. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.N.; Gazelle, G.S.; Mueller, P.R. Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: A unified approach to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging guidance. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 174, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesh, M.D.; Van Hare, G.F.; Epstein, L.M.; Fitzpatrick, A.P.; Scheinman, M.M.; Lee, R.J.; Kwasman, M.A.; Grogin, H.R.; Griffin, J.C. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial arrhythmias. Results Mech. Circ. 1994, 89, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Ta, S.; Hahn, R.T.; Hsi, D.H.; Leon, M.B.; Hu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Percutaneous intramyocardial septal radiofrequency ablation in patients with drug-refractory hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.-S.; Chon, M.-K.; Jun, E.J.; Park, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Shin, D.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Cho, M.S.; Lee, S.-W. Septal reduction using transvenous intramyocardial cerclage radiofrequency ablation: Preclinical feasibility. Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 988–998. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, M.K.; Wolf, P.D. Temperature-controlled and constant-power radio-frequency ablation: What affects lesion growth? IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 46, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, M.; Berger, R.D.; Calkins, H. Radiofrequency ablation: Technological trends, challenges, and opportunities. EP Eur. 2021, 23, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Kongsgaard, E.; Steen, T.; Jensen, Ø.; Aass, H.; Amlie, J.P. Temperature guided radiofrequency catheter ablation of myocardium: Comparison of catheter tip and tissue temperatures in vitro. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1997, 20, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eick, O.J. Temperature controlled radiofrequency ablation. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2002, 2, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Haemmerich, D.; Webster, J.G. Automatic control of finite element models for temperature-controlled radiofrequency ablation. Biomed. Eng. Online 2005, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, I.A.; Seol, H.Y.; Cho, Y.; Ji, W.; Seo, J.; Lee, C.; Chon, M.-K.; Shin, D.; Kim, J.H.; Choo, K.-S. Conversion of the bronchial tree into a conforming electrode to ablate the lung nodule in a porcine model. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starek, Z.; Lehar, F.; Jez, J.; Pesl, M.; Neuzil, P.; Sediva, L.; Petru, J.; Dujka, L.; Funasako, M.; Kautzner, J. Efficacy and safety of novel temperature-controlled radiofrequency ablation system during pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: TRAC-AF study. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 64, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Moser, M.A.; Zhang, E.M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W. A review of radiofrequency ablation: Large target tissue necrosis and mathematical modelling. Phys. Medica 2016, 32, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, H.; Prystowsky, E.; Carlson, M.; Klein, L.S.; Saul, J.P.; Gillette, P. Temperature monitoring during radiofrequency catheter ablation procedures using closed loop control. Atakr Multicenter Investigators Group. Circulation 1994, 90, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Peng, Z.; Chen, M.; Peng, H.; Xue, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Efficacy of combining temperature-and power-controlled radiofrequency ablation for malignant liver tumors. Chin. J. Cancer 2010, 29, 408–412. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, J.M.; Sapp, J.L.; Tedrow, U.; Pellegrini, C.P.; Robinson, D.; Epstein, L.M.; Stevenson, W.G. Ablation with an internally irrigated radiofrequency catheter: Learning how to avoid steam pops. Heart Rhythm 2004, 1, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Moser, M.A.; Zhang, E.M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W. A new approach to feedback control of radiofrequency ablation systems for large coagulation zones. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Nan, Q.; Wang, R.; Dong, T.; Tian, Z. Fuzzy proportional integral derivative control of a radiofrequency ablation temperature control system. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), Shanghai, China, 14–16 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Baldinger, S.H.; Kumar, S.; Barbhaiya, C.R.; Mahida, S.; Epstein, L.M.; Michaud, G.F.; John, R.; Tedrow, U.B.; Stevenson, W.G. Epicardial radiofrequency ablation failure during ablation procedures for ventricular arrhythmias: Reasons and implications for outcomes. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2015, 8, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, A.S.; Bahnson, T.D.; Piccini, J.P. Recent advances in lesion formation for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, e003299. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Mulier, S.; Miao, Y.; Michel, L.; Marchal, G. A review of the general aspects of radiofrequency ablation. Abdom. Imaging 2005, 30, 381–400. [Google Scholar]
- Künzli, B.M.; Abitabile, P.; Maurer, C.A. Radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: Actual limitations and potential solutions in the future. World J. Hepatol. 2011, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Melnik, R. Thermal ablation of biological tissues in disease treatment: A review of computational models and future directions. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2020, 39, 49–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Lu, J.; Lin, J.; Feng, T.; Suo, N.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, G.; Fan, X.; Zhang, S. Efficiency, safety, and efficacy of high-power short-duration radiofrequency ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 8821467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuyun, M.F.; Stafford, P.J.; Sandilands, A.J.; Samani, N.J.; Ng, G.A. The impact of power output during percutaneous catheter radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation on efficacy and safety outcomes: A systematic review. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Voglreiter, P.; Mariappan, P.; Pollari, M.; Flanagan, R.; Sequeiros, R.B.; Portugaller, R.H.; Fütterer, J.; Schmalstieg, D.; Kolesnik, M.; Moche, M. RFA guardian: Comprehensive simulation of radiofrequency ablation treatment of liver tumors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Ahmed, F.; Goyal, V.; Patel, M.; Orelaru, F.; Haines, D.E.; Wong, W.S. High-power, low-flow, short-ablation duration—the key to avoid collateral injury? J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2019, 55, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- El Baba, M.; Sabayon, D.; Refaat, M.M. Radiofrequency catheter ablation: How to manage and prevent collateral damage? J. Innov. Card. Rhythm. Manag. 2020, 11, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Group | Average Impedance (Ω) | Total Energy (J) | Ablated Myocardial Maximum Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 75 °C; 10 min | 69.41 ± 8.28 | 1986.17 ± 334.24 | 7.67 ± 0.37 |
| 85 °C; 10 min | 73.09 ± 11.88 | 2290.33 ± 355.60 | 8.05 ± 0.36 |
| Gradual; 10 min | 72.47 ± 4.48 | 2823.23 ± 489.17 | 10.48 ± 0.56 |
| Turn-Up Time (s) | Average Impedance (Ω) | Total Energy (J) | Cumulative Time (s) | Ablated Maximum Diameter (mm2) | Ablated Area (mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 180 | 57.17 | 10,688.67 | 993.17 ± 44.14 | 17.42 ± 1.27 | 318.76 ± 41.57 |
| 150 | 55.6 | 8509.33 | 837.5 ± 36.36 | 16.65 ± 0.54 | 276.80 ± 19.37 |
| 120 | 61.97 | 7939.5 | 769.5 ± 103.12 | 15.52 ± 0.43 | 263.81 ± 28.49 |
| 90 | 62.72 | 5825.33 | 645.67 ± 148.09 | 14.07 ± 1.66 | 224.52 ± 27.92 |
| 30 | 64.07 | 4034.33 | 326 ± 115.89 | 12.87 ± 1.83 | 191.02 ± 28.62 |
| Group | Cumulative Time (min) | Total Energy (J) | Average Impedance (Ω) | Maximum Diameter (mm) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-temperature mode (n = 4) | 13.25 | 7624.75 | 47.5 | 9.25 ± 2.75 | 0.004 |
| Gradual-temperature-rise mode (n = 6) | 14.17 | 9933.67 | 50 | 13.83 ± 0.75 | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-M.; Seo, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-C.; Chon, M.-K. Gradual Temperature Rise in Radiofrequency Ablation: Enhancing Lesion Quality and Safety in Porcine Myocardial Tissue. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040360
Lee C-M, Seo J-Y, Kim J-C, Chon M-K. Gradual Temperature Rise in Radiofrequency Ablation: Enhancing Lesion Quality and Safety in Porcine Myocardial Tissue. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040360
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Cheol-Min, Jae-Young Seo, Jin-Chang Kim, and Min-Ku Chon. 2025. "Gradual Temperature Rise in Radiofrequency Ablation: Enhancing Lesion Quality and Safety in Porcine Myocardial Tissue" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040360
APA StyleLee, C.-M., Seo, J.-Y., Kim, J.-C., & Chon, M.-K. (2025). Gradual Temperature Rise in Radiofrequency Ablation: Enhancing Lesion Quality and Safety in Porcine Myocardial Tissue. Bioengineering, 12(4), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040360






