Intracranial Aneurysm Segmentation with a Dual-Path Fusion Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
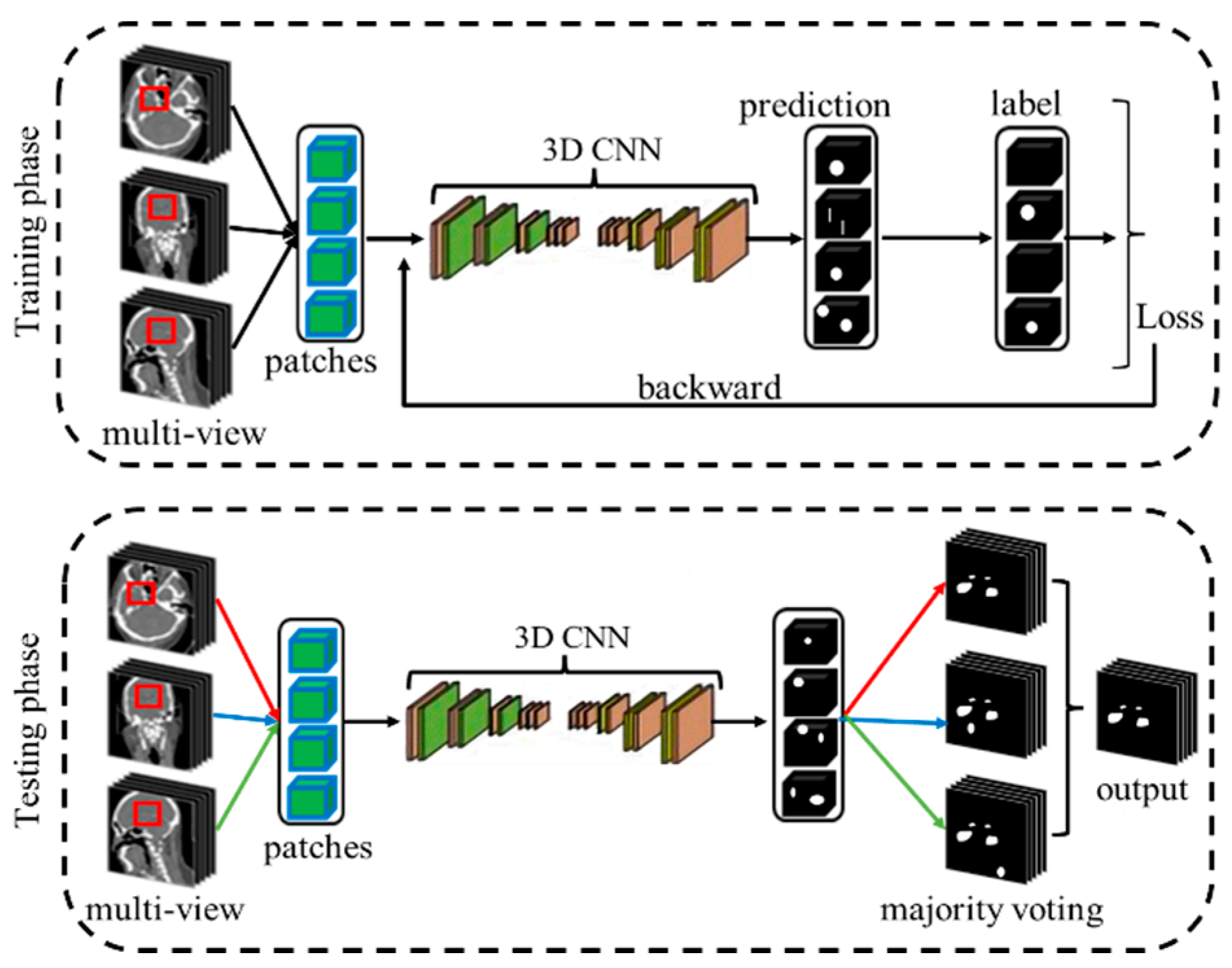
2.1. Overall Framework
2.2. Network Architecture
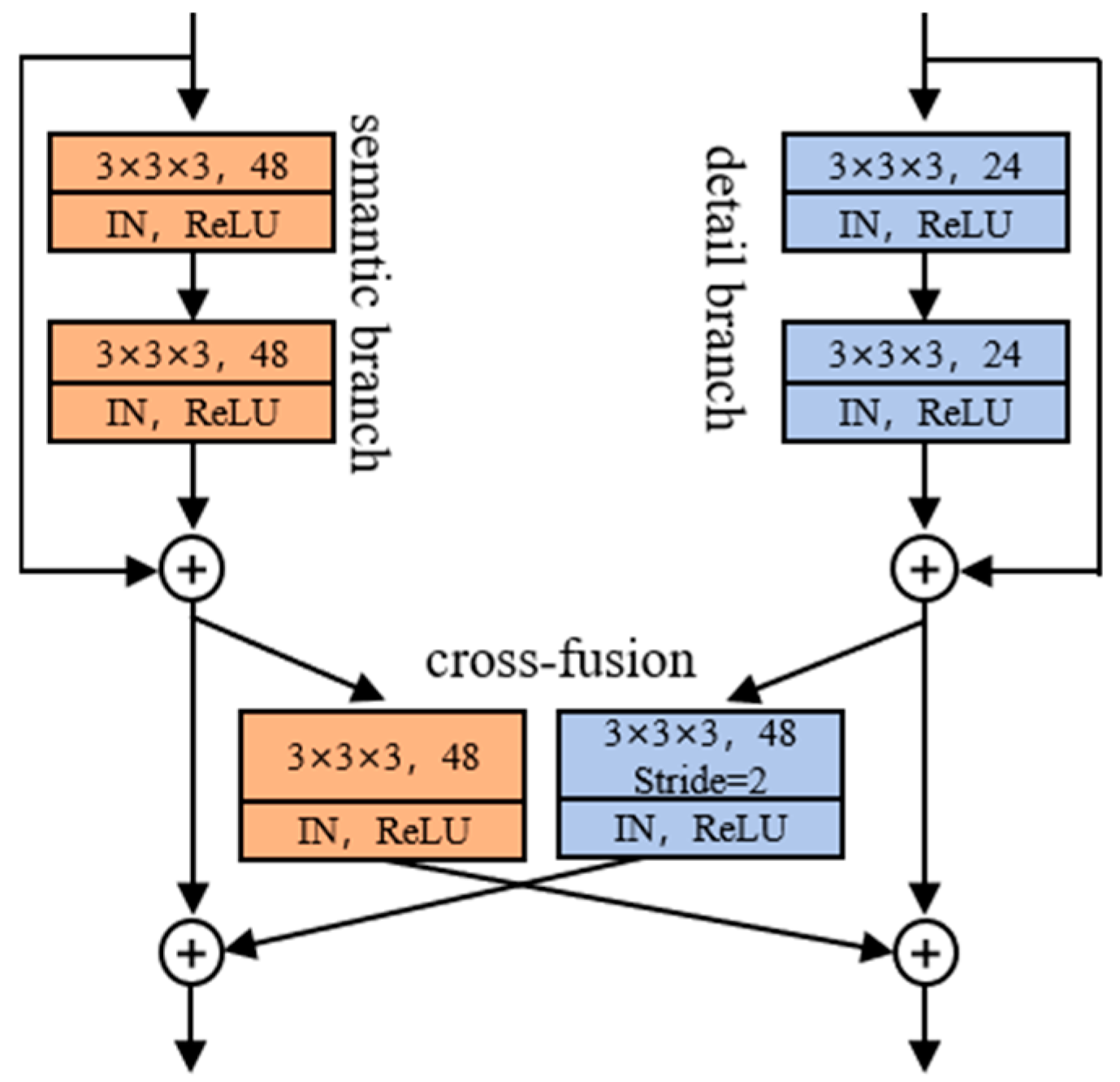
2.2.1. Dual-Path Fusion Network (DPF-Net)
2.2.2. Cross-Fusion Module (CFM)
2.2.3. Detail Aggregation Module (DAM)
2.3. View Fusion for Intracranial Aneurysms (IAs) Segmentation
2.4. Loss Function
2.5. Implementation Details
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Dataset
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Comparison with Other Methods on the CADA Dataset
3.4. Ablation Studies
3.4.1. Comparison with the Model Without Detail Branch
3.4.2. Comparison with the Model Without Detail Aggregation Module
3.4.3. Comparison with the Model Without Cross-Fusion Module
3.5. Impact of Patch Size and Batch Size
3.6. Impact of Deep Supervision
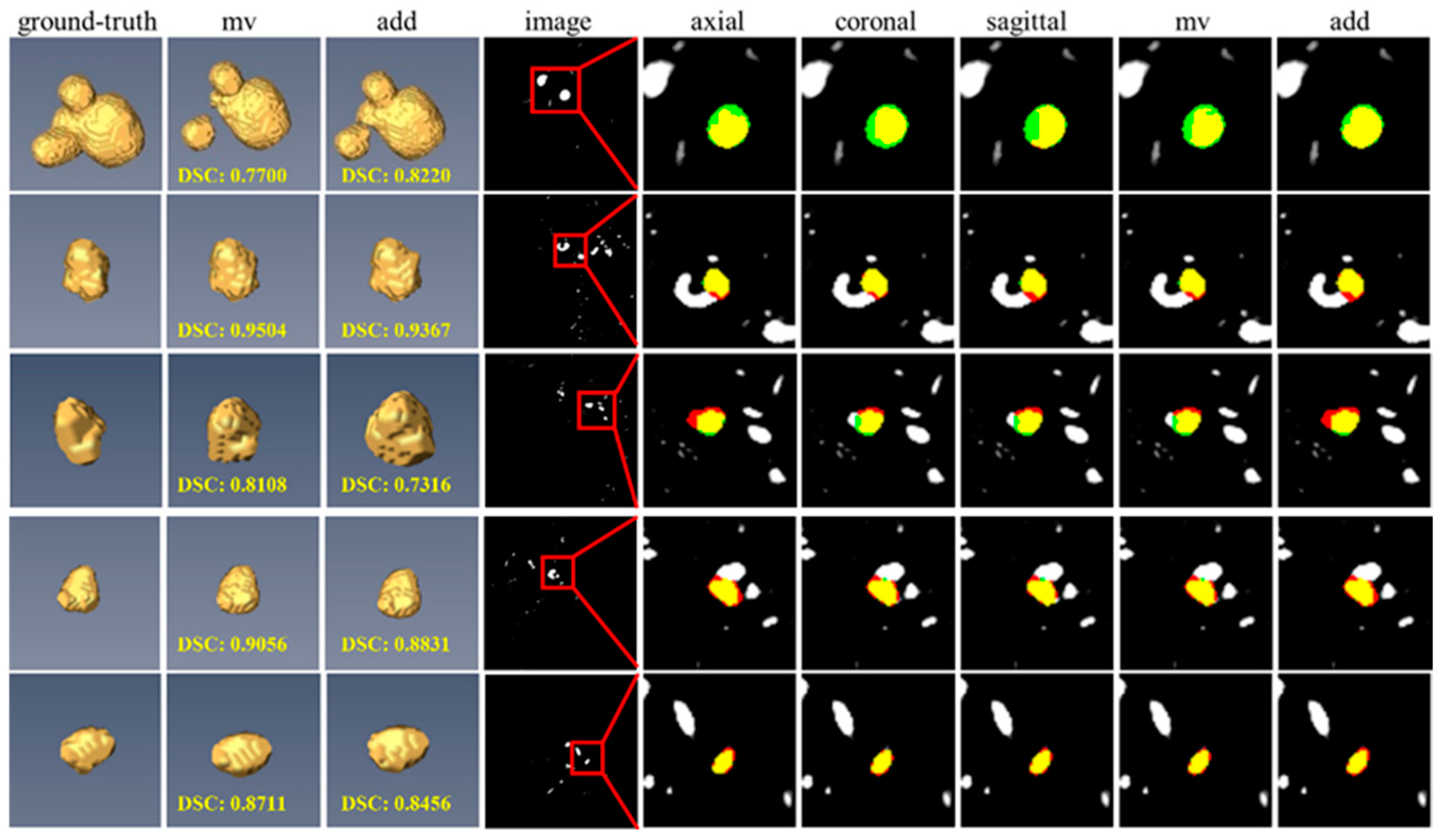
3.7. Impact of Different View Fusion Manners
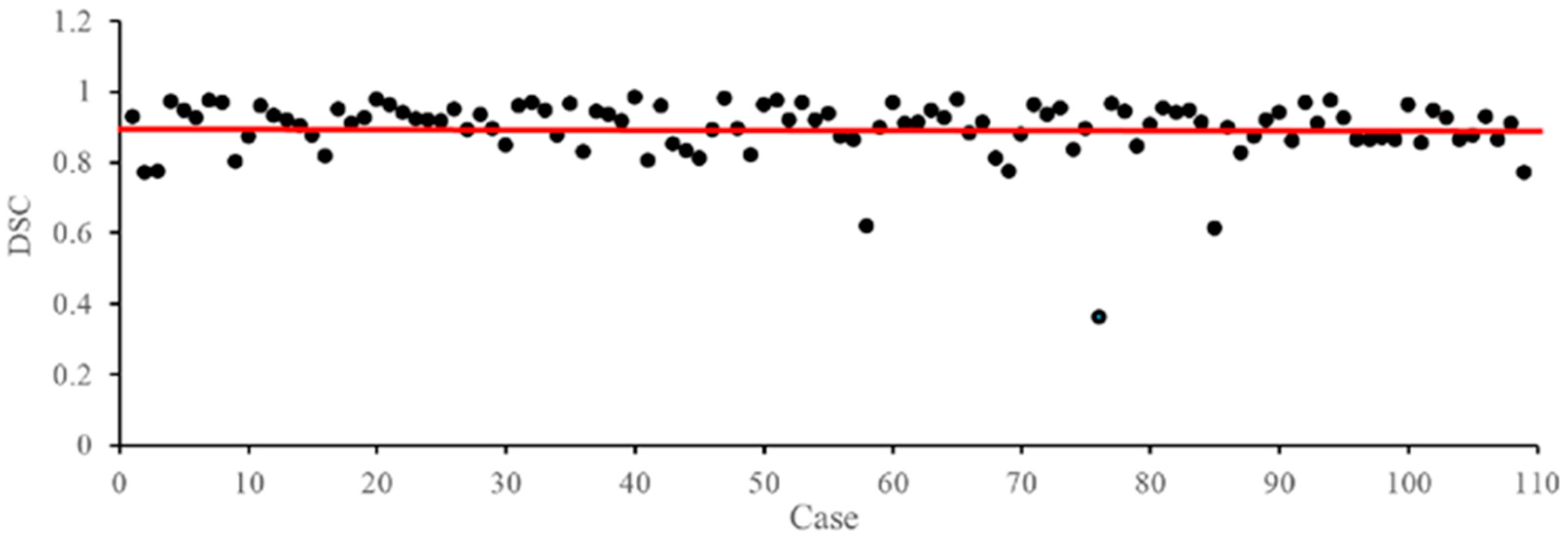
3.8. Failure Case Analysis on the CADA Dataset
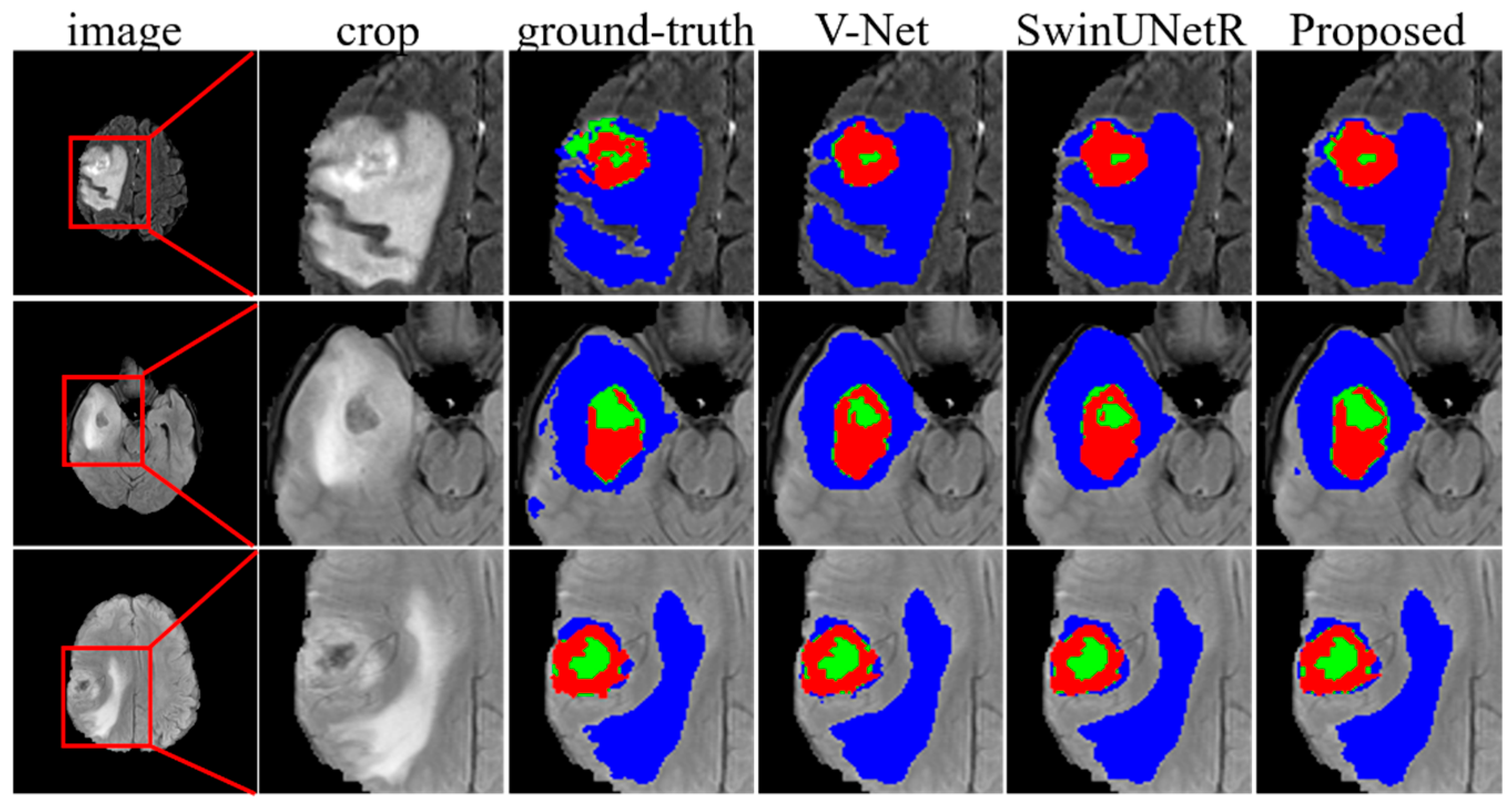
3.9. Evaluation of the Brain Tumor Segmentation Tasks
4. Discussion
4.1. A New Framework for Preserving Detail Features in IAs Segmentation
4.2. Integrity of Spatial Structures Is Important for IAs Segmentation
4.3. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Z.; Miao, C.; Schoepf, U.J.; Savage, R.H.; Dargis, D.M.; Pan, C.; Chai, X.; Li, X.L.; Xia, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. A clinically applicable deep-learning model for detecting intracranial aneurysm in computed tomography angiography images. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Lu, M.; Shi, Z.; Xia, S.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Mao, L.; Li, X.L.; et al. Development and validation of machine learning prediction model based on computed tomography angiography–derived hemodynamics for rupture status of intracranial aneurysms: A Chinese multicenter study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5170–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, N.; Lyu, Z.; Rezaeitaleshmahalleh, M.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J. An attention residual u-net with differential preprocessing and geometric postprocessing: Learning how to segment vasculature including intracranial aneurysms. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 84, 102697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Qian, Y.; Chong, W.; Hou, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Si, W.; Duan, C.Z. A deep learning–based automatic system for intracranial aneurysms diagnosis on three-dimensional digital subtraction angiographic images. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 7038–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivantsits, M.; Goubergrits, L.; Kuhnigk, J.; Huellebrand, M.; Bruening, J.; Kossen, T.; Pfahringer, B.; Schaller, J.; Spuler, A.; Kuehne, T.; et al. Detection and analysis of cerebral aneurysms based on X-ray rotational angiography—The CADA 2020 challenge. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 77, 102333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, B.; Ahn, S.S.; Yoon, P.H.; Bae, S.; Sohn, B.; Lee, Y.E.; Bae, J.H.; Park, M.S.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, S. A deep learning algorithm may automate intracranial aneurysm detection on MR angiography with high diagnostic performance. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5785–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanders, A.E. Machine Learning Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms-Will It Play in Peoria? Radiology 2019, 290, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faron, A.; Sichtermann, T.; Teichert, N.; Luetkens, J.A.; Keulers, A.; Nikoubashman, O.; Freiherr, J.; Mpotsaris, A.; Wiesmann, M. Performance of a Deep-Learning Neural Network to Detect Intracranial Aneurysms from 3D TOF-MRA Compared to Human Readers. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2020, 30, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafees Ahmed, S.; Prakasam, P. A systematic review on intracranial aneurysm and hemorrhage detection using machine learning and deep learning techniques. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2023, 183, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, N.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, J.; Guo, S. Automatic Diagnosis Based on Spatial Information Fusion Feature for Intracranial Aneurysm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 1448–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Diao, Z.; Shi, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, W.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S.; Tong, G.; Yao, Y. A review of deep learning-based multiple-lesion recognition from medical images: Classification, detection and segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 157, 106726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.F.; Hossain, M.M.; Nahiduzzaman, M.; Islam, M.R.; Islam, M.R.; Ahsan, M.; Haider, J. A review on brain tumor segmentation based on deep learning methods with federated learning techniques. Comput. Med. Imaging Grap. 2023, 110, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q. Transformers in medical image segmentation: A review. Biomed. Signal Process. 2023, 84, 104791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, T.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, G. A deep residual attention-based U-Net with a biplane joint method for liver segmentation from CT scans. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fu, R.; Pan, L.; Zheng, S.; Huang, L.; Zheng, B.; He, B. Coarse-to-fine airway segmentation using multi information fusion network and CNN-based region growing. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, T.; Wang, X.; Fang, C.; Mao, L.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Qu, J.; Li, X.; Xue, H.; Yu, Y.; et al. M3Net: A multi-scale multi-view framework for multi-phase pancreas segmentation based on cross-phase non-local attention. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 75, 102232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkels, M.; Cohen, T.S. Pulmonary nodule detection in CT scans with equivariant CNNs. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 55, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y. Pulmonary nodule detection based on model fusion and adaptive false positive reduction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, F.; Uçan, O.; Karaçam, S.; Tunçman, D. Fully Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Image Using an AIM-Unet. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Li, D.; Xue, J. Temperature guided network for 3D joint segmentation of the pancreas and tumors. Neural Netw. 2023, 157, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, I.; Javed, A.; Malik, K.M.; Malik, G. DeepInfusion: A dynamic infusion based-neuro-symbolic AI model for segmentation of intracranial aneurysms. Neurocomputing 2023, 551, 126510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Lu, X.; Liu, X. 3D Intracranial Aneurysm Classification and Segmentation via Unsupervised Dual-Branch Learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2023, 27, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stember, J.N.; Chang, P.; Stember, D.M.; Liu, M.; Grinband, J.; Filippi, C.G.; Meyers, P.; Jambawalikar, S. Convolutional Neural Networks for the Detection and Measurement of Cerebral Aneurysms on Magnetic Resonance Angiography. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmins, K.M.; Schaaf, I.C.V.D.; Vos, I.N.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Velthuis, B.K.; Kuijf, H.J. Geometric Deep Learning Using Vascular Surface Meshes for Modality-Independent Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm Detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 3451–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Gu, D.; Qi, P.; Cao, X.; Wu, D.; Chen, L.; Qu, G.; Wang, J.; Pan, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Evaluation of an automated intracranial aneurysm detection and rupture analysis approach using cascade detection and classification networks. Comput. Med. Imaging Grap. 2022, 102, 102126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. FSTIF-UNet: A Deep Learning-Based Method Towards Automatic Segmentation of Intracranial Aneurysms in Un-Reconstructed 3D-RA. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2023, 27, 4028–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wei, X.; Lei, H.; Liqin, Y.; Yuxin, L.; Yakang, D.; Daoying, G. Automated computer—Assisted detection system for cerebral aneurysms in time—Of—Flight magnetic resonance angiography using fully convolutional network. Biomed. Eng. Online 2020, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.; Chute, C.; Rajpurkar, P.; Lou, J.; Ball, R.L.; Shpanskaya, K.; Jabarkheel, R.; Kim, L.H.; Mckenna, E.; Tseng, J.; et al. Deep Learning-Assisted Diagnosis of Cerebral Aneurysms Using the HeadXNet Model. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e195600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Nie, Z. Exploring Large Context for Cerebral Aneurysm Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep Dual-resolution Networks for Real-time and Accurate Semantic Segmentation of Road Scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 2023, 24, 3448–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y. View adaptive learning for pancreas segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. 2021, 66, 102347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.06650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Le Folgoc, L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; Mcdonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S. V-Net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.04797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Nath, V.; Tang, Y.; Yang, D.; Roth, H.; Xu, D. Swin UNETR: Swin Transformers for Semantic Segmentation of Brain Tumors in MRI Images. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.01266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menze, B.H.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.; Burren, Y.; Porz, N.; Slotboom, J.; Wiest, R.; et al. The Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, H.; Goel, V.; Sethuraman, R.; Sheet, D. Distill DSM: Computationally efficient method for segmentation of medical imaging volumes. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 143, 473–483. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, G.; Huang, H.; Yang, W.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lai, X. ME-Net: Multi-encoder net framework for brain tumor segmentation. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Sheng, N.; He, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. SGEResU-Net for brain tumor segmentation. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 5576–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkovits, S.; Lefkovits, L.; Szilágyi, L. HGG and LGG Brain Tumor Segmentation in Multi-Modal MRI Using Pretrained Convolutional Neural Networks of Amazon Sagemaker. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, W.; Xu, X.; Jiang, W.; Lai, X. Nonlocal convolutional block attention module VNet for gliomas automatic segmentation. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2022, 32, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Methods | DSC | Recall | Precision | IoU | p-Value | IS | Param. MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [32] | 0.8038 ± 0.0358 | 0.8503 ± 0.0528 | 0.7921 ± 0.0547 | 0.6978 ± 0.0413 | - | - | |
| Attention U-Net [33] | 0.8207 ± 0.0341 | 0.8224 ± 0.0447 | 0.8439 ± 0.0147 | 0.7197 ± 0.0379 | - | - | |
| Trans U-Net [34] | 0.8311 ± 0.0250 | 0.8339 ± 0.0446 | 0.8518 ± 0.0280 | 0.7344 ± 0.0299 | - | - | |
| Ou et al. [4] | 0.8368 ± 0.0242 | 0.8587 ± 0.0357 | 0.8397 ± 0.0327 | 0.7381 ± 0.0293 | - | - | |
| Ma et al. [29] | 0.8861 | 0.9036 | 0.8934 | - | - | - | |
| V-Net [35] | 0.8137 ± 0.1779 | 0.8469 ± 0.1974 | 0.8039 ± 0.1537 | 0.7027 ± 0.1785 | <0.001 a | 47 | 3.75 |
| SwinUNetR [36] | 0.8498 ± 0.1485 | 0.8638 ± 0.1458 | 0.8375 ± 0.1397 | 0.7845 ± 0.1473 | <0.001 a | 52 | 16.83 |
| Proposed | 0.8967 ± 0.0837 | 0.8972 ± 0.1199 | 0.9033 ± 0.1084 | 0.8214 ± 0.1164 | - | 43 | 1.45 |
| Methods | Small (N = 15) | Medium (N = 88) | Large (N = 6) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-Net [35] | 0.5704 ± 0.2327 | 0.8478 ± 0.1539 | 0.9217 ± 0.0872 | <0.001 a |
| SwinNetR [36] | 0.6184 ± 0.1869 | 0.8539 ± 0.1275 | 0.9317 ± 0.0735 | <0.001 a |
| Proposed | 0.8616 ± 0.0816 | 0.9005 ± 0.0840 | 0.9281 ± 0.0686 |
| Methods | DSC | Recall | Precision | IoU | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| network 1 | 0.9007 ± 0.0615 | 0.9072 ± 0.1009 | 0.9072 ± 0.0855 | 0.8245 ± 0.1000 | - |
| network 2 | 0.8576 ± 0.1140 | 0.8807 ± 0.1544 | 0.8740 ± 0.1448 | 0.7655 ± 0.1574 | <0.005 a |
| network 3 | 0.8657 ± 0.1551 | 0.8724 ± 0.2049 | 0.9056 ± 0.0828 | 0.7863 ± 0.1813 | <0.005 b |
| network 4 | 0.8913 ± 0.0590 | 0.9220 ± 0.0906 | 0.8748 ± 0.0922 | 0.8087 ± 0.0950 | <0.005 c |
| Patch Size | Batch Size | DSC | Recall | Precision | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 × 48 × 48 | 2 | 0.8664 ± 0.0961 | 0.9317 ± 0.0939 | 0.8237 ± 0.1294 | 0.7754 ± 0.1403 |
| 4 | 0.8625 ± 0.1407 | 0.8957 ± 0.1281 | 0.8466 ± 0.1704 | 0.7780 ± 0.1710 | |
| 6 | 0.8678 ± 0.1335 | 0.8899 ± 0.1402 | 0.8565 ± 0.1535 | 0.7847 ± 0.1652 | |
| 8 | 0.8760 ± 0.1203 | 0.8665 ± 0.1284 | 0.8666 ± 0.1284 | 0.7956 ± 0.1625 | |
| 64 × 64 × 64 | 2 | 0.8572 ± 0.1237 | 0.8825 ± 0.1252 | 0.8581 ± 0.1690 | 0.7676 ± 0.1715 |
| 4 | 0.9007 ± 0.0615 | 0.9072 ± 0.1009 | 0.9072 ± 0.0855 | 0.8245 ± 0.1000 | |
| 6 | 0.8722 ± 0.0990 | 0.8903 ± 0.1297 | 0.8670 ± 0.1153 | 0.7852 ± 0.1436 | |
| 96 × 96 × 96 | 2 | 0.7710 ± 0.3100 | 0.7991 ± 0.3219 | 0.8643 ± 0.1547 | 0.6980 ± 0.3001 |
| Methods | DSC | Recall | Precision | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/DS | 0.9007 ± 0.0615 | 0.9072 ± 0.1009 | 0.9072 ± 0.0855 | 0.8245 ± 0.1000 |
| w/o DS | 0.8849 ± 0.0848 | 0.9015 ± 0.1421 | 0.8910 ± 0.0885 | 0.8026 ± 0.1263 |
| Methods | DSC | Recall | Precision | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| add | 0.8927 ± 0.0662 | 0.9417 ± 0.0774 | 0.8608 ± 0.1098 | 0.8121 ± 10.46 |
| mv | 0.9007 ± 0.0615 | 0.9072 ± 0.1009 | 0.9072 ± 0.0855 | 0.8245 ± 0.1000 |
| Methods | WT | TC | ET | Mean | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maheshwari et al. [39] | 0.8730 | 0.7420 | 0.7530 | 0.7893 | - |
| Zhang et al. [40] | 0.8940 | 0.8250 | 0.7340 | 0.8177 | - |
| Liu et al. [41] | 0.9048 | 0.8522 | 0.7940 | 0.8503 | - |
| Lefkovits et al. [42] | 0.9000 | 0.8400 | 0.7800 | 0.8400 | - |
| Fang et al. [43] | 0.9050 | 0.8850 | 0.7480 | 0.8460 | - |
| V-Net [35] | 0.8914 ± 0.0635 | 0.8297 ± 0.1638 | 0.7693 ± 0.1933 | 0.8301 ± 0.1583 | <0.05 a |
| SwinUNetR [36] | 0.9038 ± 0.0593 | 0.8538 ± 0.1579 | 0.7717 ± 0.1889 | 0.8431 ± 0.1468 | <0.05 b |
| Proposed | 0.9058 ± 0.0547 | 0.8528 ± 0.1400 | 0.8002 ± 0.1763 | 0.8535 ± 0.1385 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, B. Intracranial Aneurysm Segmentation with a Dual-Path Fusion Network. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020185
Wang K, Zhang Y, Fang B. Intracranial Aneurysm Segmentation with a Dual-Path Fusion Network. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(2):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020185
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ke, Yong Zhang, and Bin Fang. 2025. "Intracranial Aneurysm Segmentation with a Dual-Path Fusion Network" Bioengineering 12, no. 2: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020185
APA StyleWang, K., Zhang, Y., & Fang, B. (2025). Intracranial Aneurysm Segmentation with a Dual-Path Fusion Network. Bioengineering, 12(2), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020185






