Comparative Study on Three Different Designs of Locking Mechanisms in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
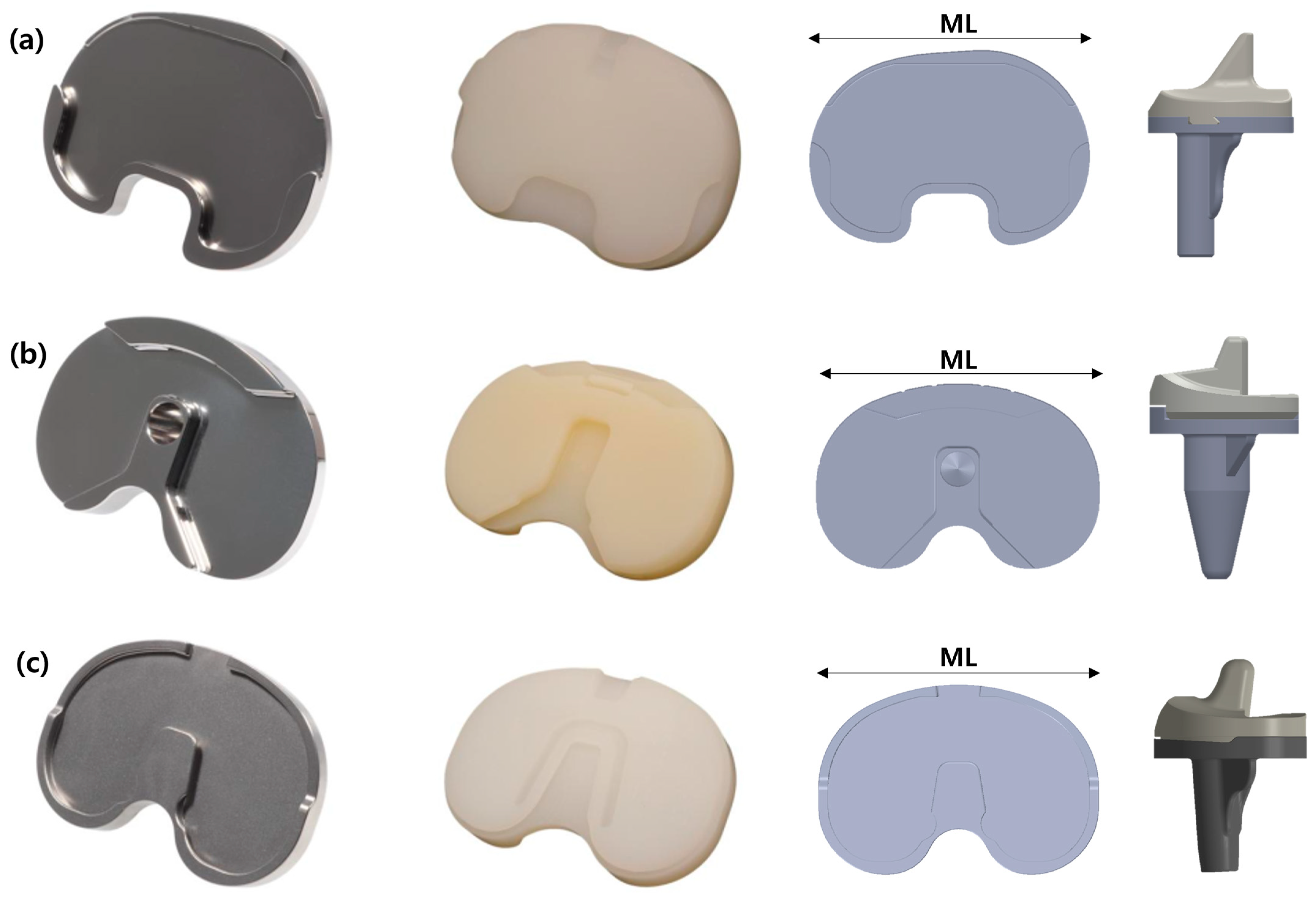
2.1. Total Knee Arthroplasty Implant Models
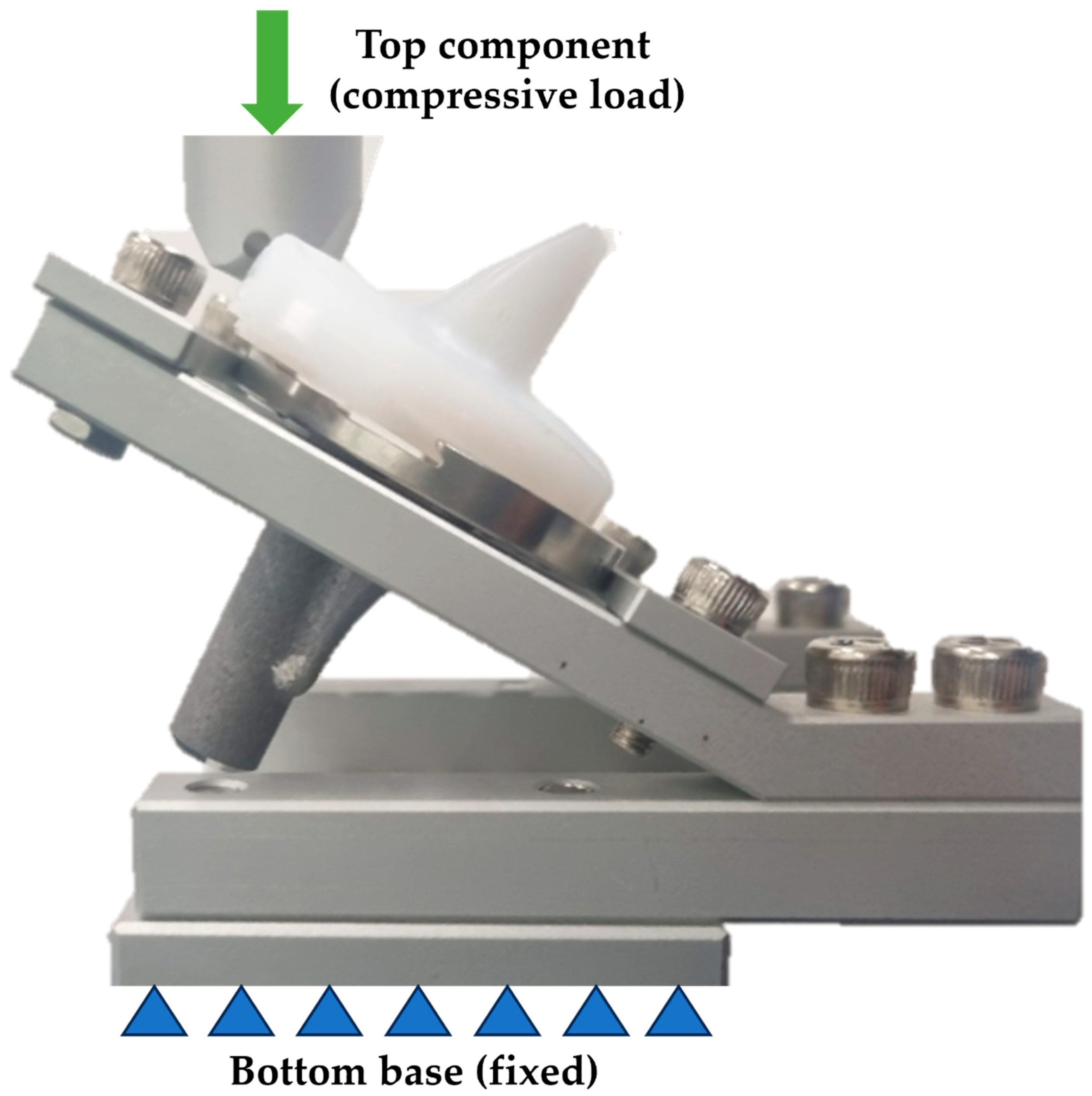
2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.3. Specimen Preparation
2.4. Equipment Setup for Disassembly Test
2.5. Disassembly Test Procedure
2.6. Assembly Test Procedure
3. Results
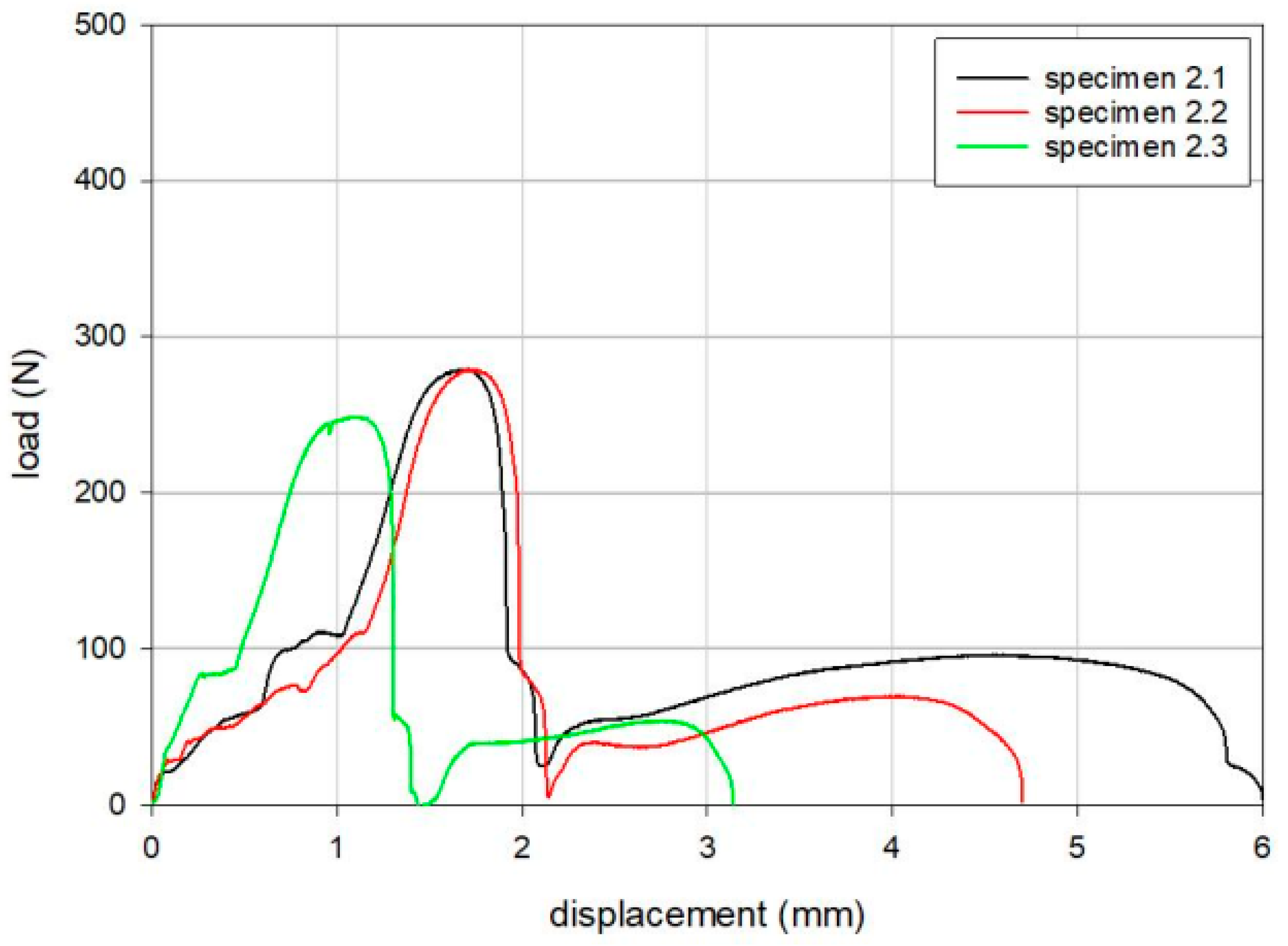
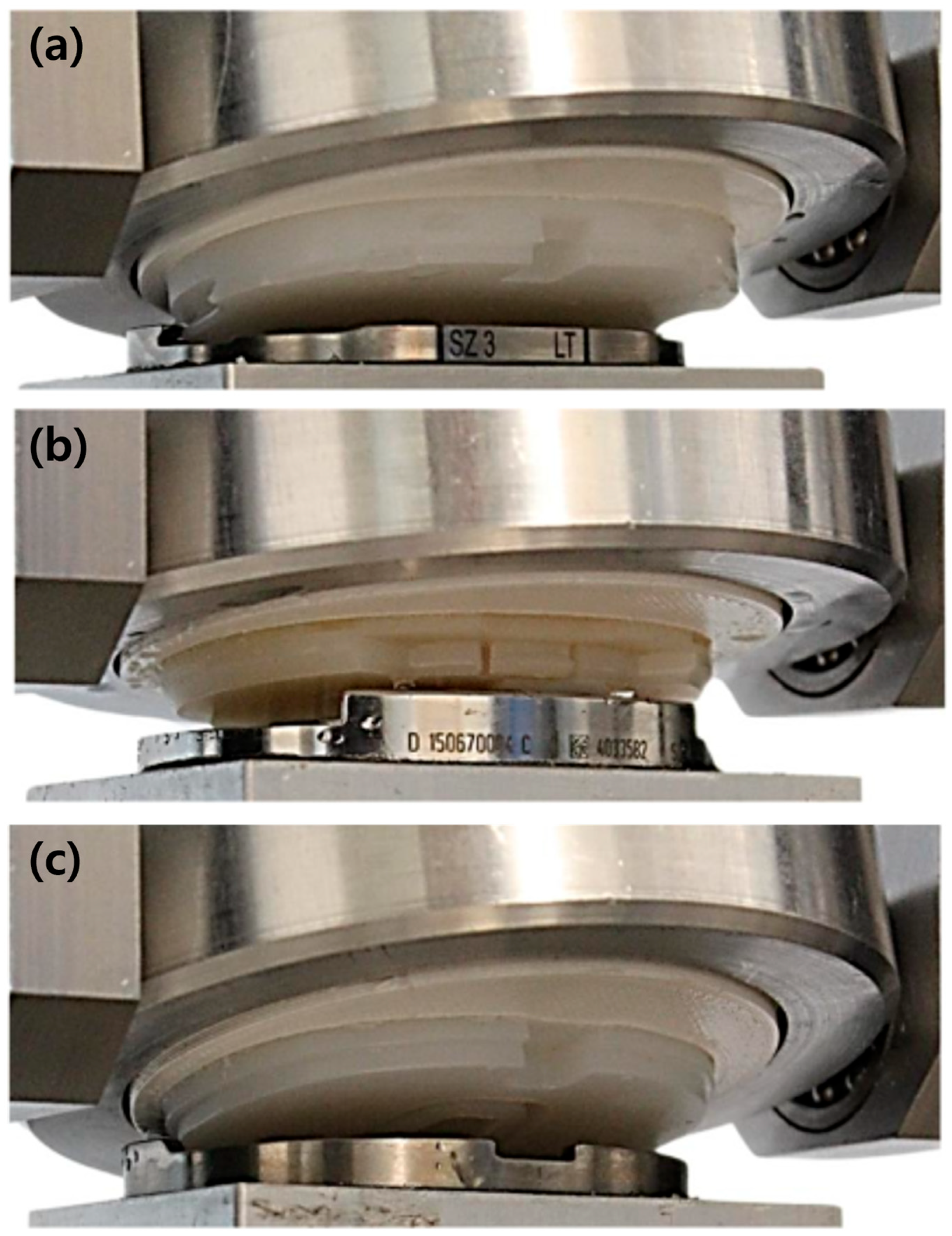
3.1. Disassembly Test of the Tibial Inserts
3.2. Assembly Test of the Tibial Inserts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FB | Fixed-bearing |
| TKA | Total knee arthroplasty |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| UTM | Universal testing machine |
References
- Capella, M.; Dolfin, M.; Saccia, F. Mobile bearing and fixed bearing total knee arthroplasty. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engh, G.A.; Lounici, S.; Rao, A.R.; Collier, M.B. In vivo deterioration of tibial baseplate locking mechanisms in contemporary modular total knee components. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2001, 83, 1660–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, O.J.; Doran, E.; Beverland, D.E. Spinout/dislocation in mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: A report of 26 cases. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, R.A.; Lewicki, K.A.; Currier, J.H.; Mayor, M.B.; Van Citters, D.W. Contribution of micro-motion to backside wear in a fixed bearing total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Res. 2016, 34, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łapaj, Ł.; Mróz, A.; Kokoszka, P.; Markuszewski, J.; Wendland, J.; Helak-Łapaj, C.; Kruczyński, J. Peripheral snap-fit locking mechanisms and smooth surface finish of tibial trays reduce backside wear in fixed-bearing total knee arthroplasty: A retrieval analysis of 102 inlays. Acta Orthop. 2017, 88, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisko, Z.W.; Teeter, M.G.; Lanting, B.A.; Howard, J.L.; McCalden, R.W.; Naudie, D.D.; MacDonald, S.J.; Vasarhelyi, E.M. Current total knee designs: Does baseplate roughness or locking mechanism design affect polyethylene backside wear? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 2970–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, J.; Goodman, S.B.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Wimmer, M.A.; Holinka, M. Osteolysis around total knee arthroplasty: A review of pathogenetic mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8046–8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, M.D. Dissociation of an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene insert from the tibial baseplate after total knee arthroplasty: A case report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2004, 86, 1522–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, S.; Janssen, R. Spontaneous late dislocation of the high flexion tibial insert after Genesis II total knee arthroplasty. A case report. Knee 2009, 16, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-E.; Juhn, R.-J.; Ko, J.-Y. Dissociation of polyethylene insert from the tibial baseplate following revision total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2011, 26, 339.e11–339.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, Y.; Sur, Y.-J.; Won, H.-Y.; Moon, Y.-S. Recurrent dissociation of the tibial insert after mini-subvastus posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty: A case report. Knee 2011, 18, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-H.; Lee, T.G.; Park, S.-J.; Han, S.-B. Spontaneous late dissociation of the tibial insert after high-flex posterior-stabilized Genesis II total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 374.e13–374.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voskuijl, T.; Nijenhuis, T.A.; Van Hellemondt, G.G.; Goosen, J. Insert dissociation after fixed bearing PS constrained Genesis II total knee arthroplasty. A case series of nine patients. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2015, 81, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, S.; Vijayvargiya, M. Traumatic dissociation of the tibial insert with patellar tendon rupture after high-flex posterior-stabilized Genesis II total knee arthroplasty. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2018, 53, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.G.; Rajan, D.S.; Chiranjeevi, T.; Karthik, C.; Kiran, E.K. Failure of polyethelene insert locking mechanism after a posterior stabilised total knee arthroplasty-a case report. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Bhimji, S.; Wang, A.; Schmalzried, T. Tibial insert micromotion of various total knee arthroplasty devices. J. Knee Surg. 2010, 23, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM F1814-22; Standard Guide for Evaluating Modular Hip and Knee Joint Components. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Triathlon® Total Knee System Design Rationale. STRYKER. TRIATH-BRO-12_Rev-1_25139. Available online: https://www.stryker.com/content/dam/stryker/no-index/training-and-education/jr45/june/resources/Triathlon%20Design%20Rationale.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Value Brief: Attune Knee System; 0612-39-513 0113; DePuy Orthopaedics: Warsaw, IN, USA, 2013.
- Hedlundh, U.; Andersson, M.; Enskog, L.; Gedin, P. Traumatic late dissociation of the polyethylene articulating surface in a total knee arthroplasty—A case report. Acta Orthop. Scand. 2000, 71, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.A.; MacDessi, S.J.; Della Valle, A.G. Spontaneous, recurrent dislodgment of the polyethylene tibial insert after total knee arthroplasty: A case report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.F.; Bocell, J.R., Jr.; Tullos, H.S. Dissociation of the tibial component in total knee replacements. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991, 272, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, S.; Bajwa, S.; Vijayvargiya, M. Intra-operative fractures in primary total knee arthroplasty. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 10, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidman, A.; Green, A.; McCall, D.; Finch, J.; Smith, L.C. Intraoperative tibia fractures during primary total knee arthroplasty. Cureus 2021, 13, e17017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klahn, C.; Singer, D.; Meboldt, M. Design guidelines for additive manufactured snap-fit joints. Procedia CIRP 2016, 50, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conditt, M.A.; Thompson, M.T.; Usrey, M.M.; Ismaily, S.K.; Noble, P.C. Backside wear of polyethylene tibial inserts: Mechanism and magnitude of material loss. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2005, 87, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
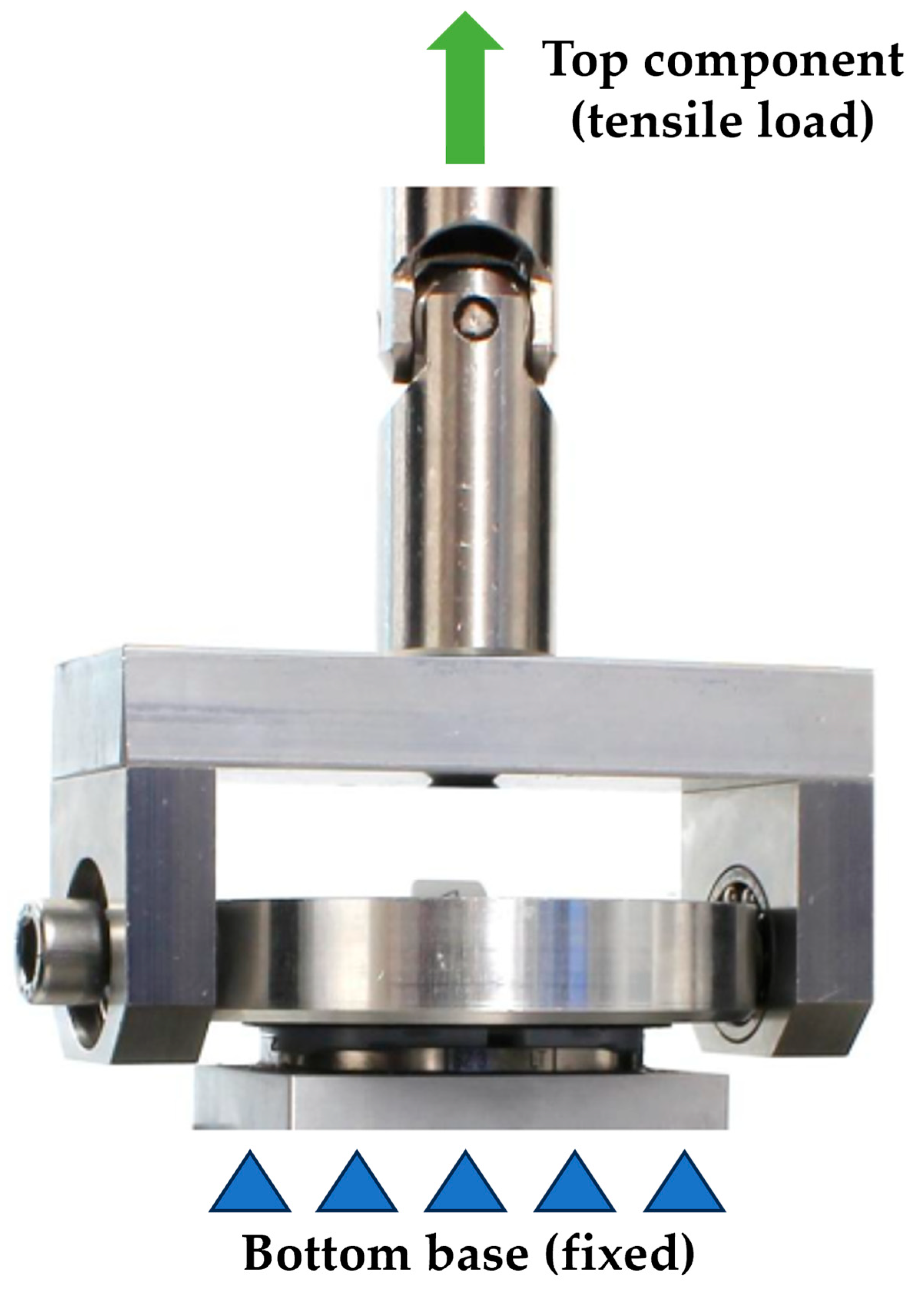



| Parameter | ASTM F1814 [17] |
|---|---|
| Tensile loading rate | 5 mm/min |
| Load application | Double cardan joint |
| Load transfer | Glued negative matching the articulating surface |
| Test environment | Bounding surface moistened with deionized water at room temperature |
| Specimen | Maximum Load (N) | Displacement at Maximum Load (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | 428 | 0.6 |
| 1.2 | 360 | 0.7 |
| 1.3 | 351 | 0.7 |
| Mean | 379 | 0.7 |
| SD | 42 | 0.0 |
| Specimen | Maximum Load (N) | Displacement at Maximum Load (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | 279 | 1.7 |
| 2.2 | 279 | 1.7 |
| 2.3 | 249 | 1.1 |
| Mean | 269 | 1.5 |
| SD | 18 | 0.3 |
| Specimen | Maximum Load (N) | Displacement at Maximum Load (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.1 | 379 | 1.0 |
| 3.2 | 371 | 0.9 |
| 3.3 | 276 | 1.2 |
| Mean | 342 | 1.0 |
| SD | 58 | 0.2 |
| Specimen | Maximum Load (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | |
| #1 | 71 | 50 | 51 |
| #2 | 74 | 48 | 43 |
| #3 | 68 | 51 | 51 |
| Mean | 71 | 49.7 | 48.7 |
| SD | 3 | 1.5 | 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, B.W.; Hong, H.-T.; Koh, Y.-G.; Park, K.K.; Kang, K.-T. Comparative Study on Three Different Designs of Locking Mechanisms in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020169
Cho BW, Hong H-T, Koh Y-G, Park KK, Kang K-T. Comparative Study on Three Different Designs of Locking Mechanisms in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Byung Woo, Hyoung-Taek Hong, Yong-Gon Koh, Kwan Kyu Park, and Kyoung-Tak Kang. 2025. "Comparative Study on Three Different Designs of Locking Mechanisms in Total Knee Arthroplasty" Bioengineering 12, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020169
APA StyleCho, B. W., Hong, H.-T., Koh, Y.-G., Park, K. K., & Kang, K.-T. (2025). Comparative Study on Three Different Designs of Locking Mechanisms in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Bioengineering, 12(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020169





