Disrupted Corticomuscular Coherence and Force Steadiness During Acute Low Back Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participant
2.3. Electromyography (EMG) Signals
2.4. Electroencephalography (EEG) Signals
2.5. Experimental Setup and Protocol
2.5.1. Force Test
Equipment Setup
Familiarization
Testing Procedure
2.5.2. Experimentally Induced Acute Low Back Pain
2.5.3. Subjective Pain-Intensity Reporting
2.6. Data Analysis
- Preprocessing Force Signal
- Preprocessing Electromyography Signal
- Variance (VAR, µV2) and Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD, µV) are statistical measures that assess data dispersion relative to the mean. Their calculations followed the following equation:
- b.
- MAD was calculated by the following equation:
- c.
- EMG entropy was computed using the sample entropy (SampEn) algorithm, as defined by the following equation [34]:
- d.
- Full-wave rectification was applied to the EMG data, transforming all negative values into positive equivalents to generate a unidirectional representation of signal intensity.
- e.
- The Integral of EMG (Int), quantifying the accumulated EMG signal, was computed using the trapezoidal rule, which approximates the area under the curve, providing a measure of the signal’s overall magnitude [4]:
- f.
- Peak EMG was considered the maximum value of the filtered and rectified amplitude measured for the sample.
- Coherence Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
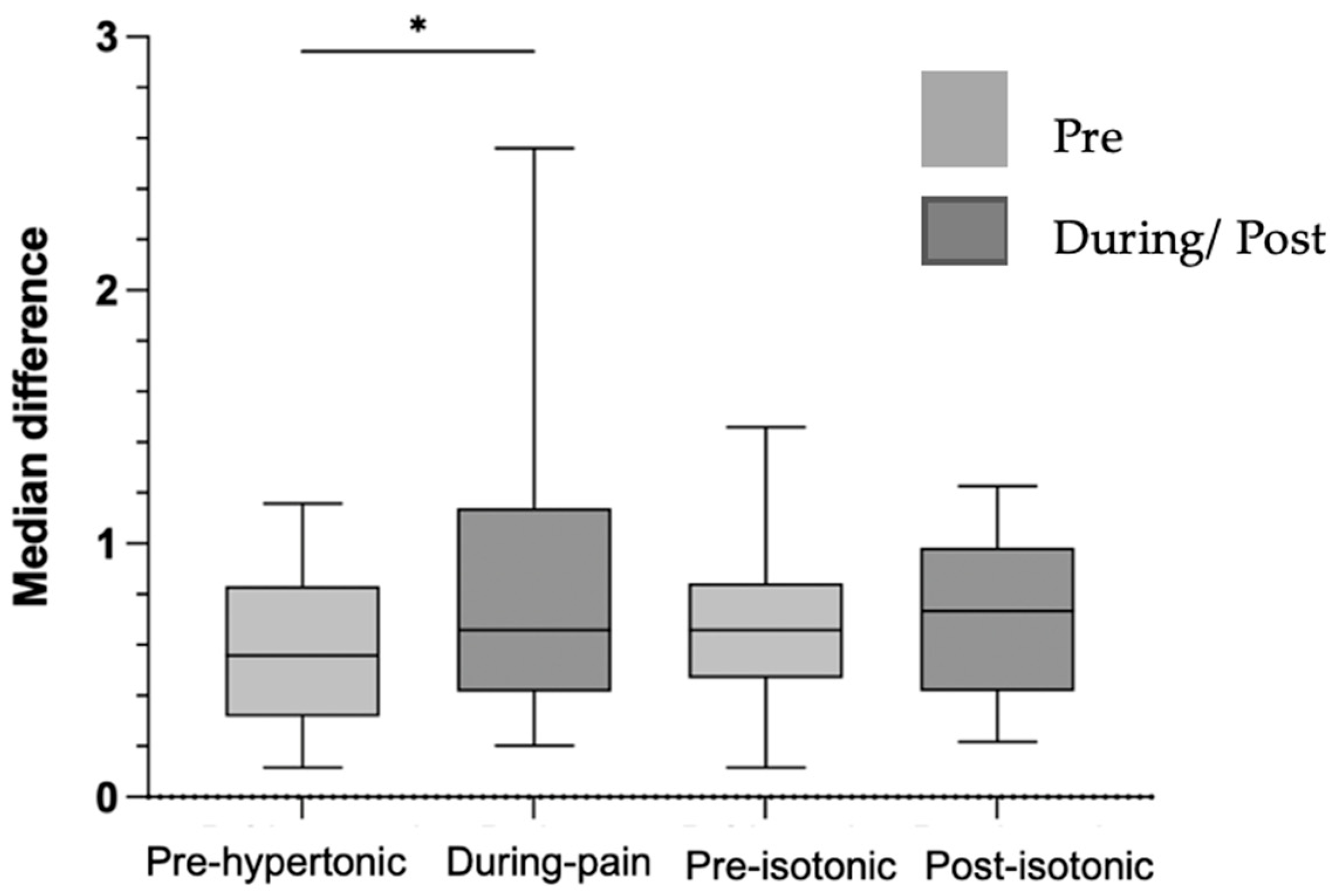
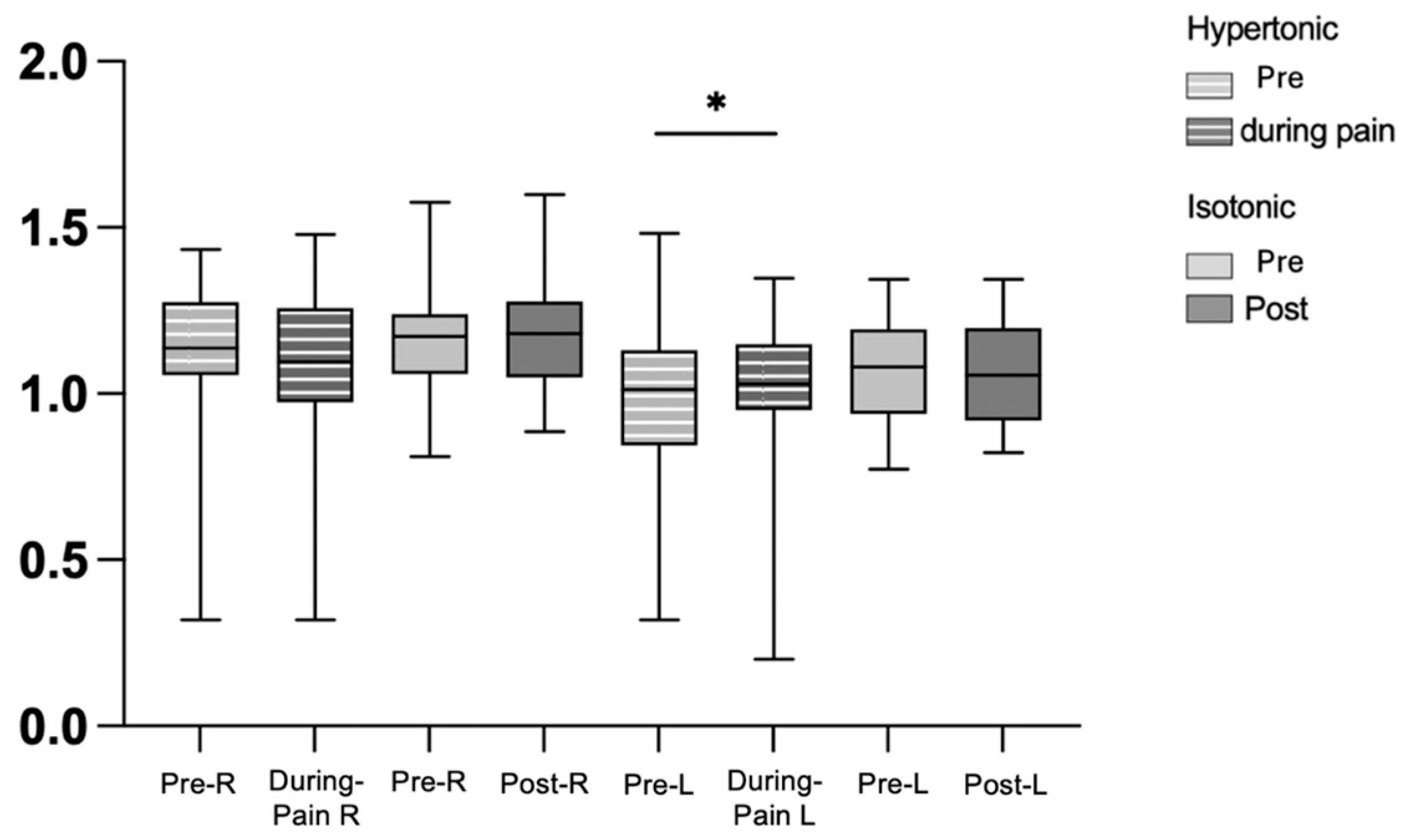
3.1. Electromyography
3.2. Cortical–Cortical Coherence
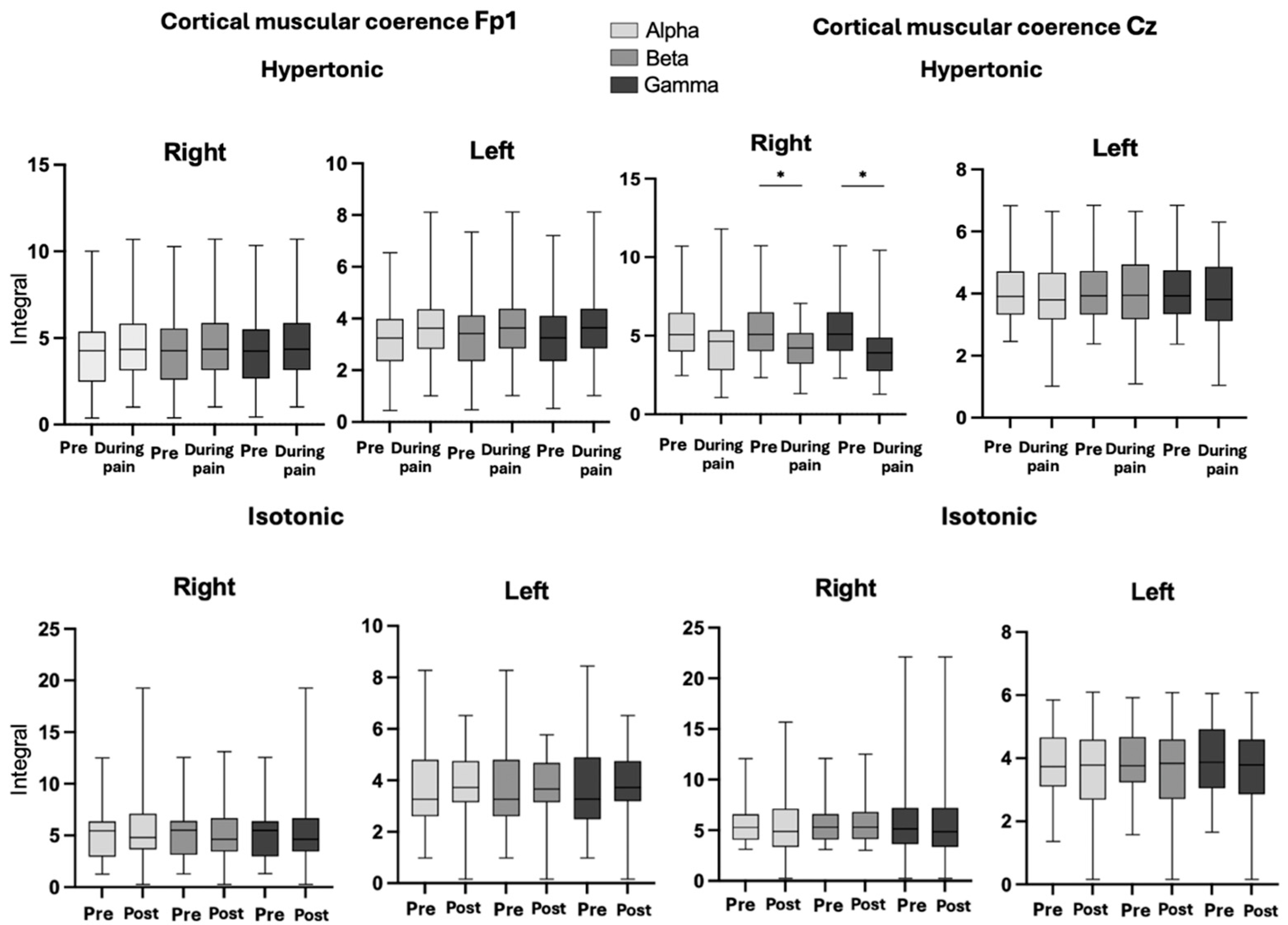
3.3. Corticomuscular Coherence
3.4. Eeg Power Spectra
4. Discussion
4.1. EMG Entropy
4.2. Modulation of CMC in Steadiness During Low Back Pain
4.3. Comparison of CCC Pain and Placebo
4.4. Low Back Pain Adaptations in EEG
4.5. Limitations
4.6. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parolini, F.; Goethel, M.; Becker, K.; Fernandes, C.; Fernandes, R.J.; Ervilha, U.F.; Santos, R.; Vilas-Boas, J.P. Breaking Barriers: Artificial Intelligence Interpreting the Interplay between Mental Illness and Pain as Defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieën, J.; Reeves, N.; Kawchuk, G.; Kawchuk, G.; Dillen, L.; Hodges, P. Motor Control Changes in Low Back Pain: Divergence in Presentations and Mechanisms. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 49, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, L.C.; Chang, W.J.; Buscemi, V.; Liston, M.; Skippen, P.; Cashin, A.G.; McAuley, J.H.; Schabrun, S.M. Low Somatosensory Cortex Excitability in the Acute Stage of Low Back Pain Causes Chronic Pain. J. Pain. 2022, 23, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, S.; Tinazzi, M.; Le Pera, D.; Valeriani, M. Pain-related modulation of the human motor cortex. Neurol. Res. 2003, 25, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graven-Nielsen, T. Fundamentals of muscle pain, referred pain, and deep tissue hyperalgesia. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 35, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, M.; Lorenz, J.; Engel, A.K. Attention to painful stimulation enhances gamma-band activity and synchronization in human sensorimotor cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9270–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristeva-Feige, R.; Fritsch, C.; Timmer, J.; Lücking, C.H. Effects of attention and precision of exerted force on beta range EEG-EMG synchronization during a maintained motor contraction task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitidis, M.; Falla, D.; Sanderson, A.; Martinez-Valdes, E. Does pain influence control of muscle force? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pain. 2025, 29, e4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohel, A.; Desmons, M.; Léonard, G.; Desgagnés, A.; Da Silva, R.; Simoneau, M.; Mercier, C.; Massé-Alarie, H. The influence of experimental low back pain on neural networks involved in the control of lumbar erector spinae muscles. J. Neurophysiol. 2022, 127, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.; Vrana, A.; Schweinhardt, P. Low Back Pain: The Potential Contribution of Supraspinal Motor Control and Proprioception. Neuroscientist 2018, 25, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Valdes, E.; Negro, F.; Farina, D.; Falla, D. Divergent response of low- versus high-threshold motor units to experimental muscle pain. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 2093–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Goethel, M.; Fonseca, P.; Vilas-Boas, J.P.; Ervilha, U. The Strategy of the Brain to Maintain the Force Production in Painful Contractions-A Motor Units Pool Reorganization. Cells 2022, 11, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.; Hodges, P. Changes in motor unit recruitment strategy during pain alters force direction. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poortvliet, P.C.; Tucker, K.J.; Finnigan, S.; Scott, D.; Sowman, P.; Hodges, P.W. Cortical activity differs between position- and force-control knee extension tasks. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poortvliet, P.C.; Tucker, K.J.; Finnigan, S.; Scott, D.; Hodges, P.W. Experimental Pain Decreases Corticomuscular Coherence in a Force- But Not a Position-Control Task. J. Pain. 2019, 20, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viseux, F.; Simoneau, M.; Billot, M. A Comprehensive Review of Pain Interference on Postural Control: From Experimental to Chronic Pain. Medicina 2022, 58, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Mao, H.; Wang, H.; Hao, Z.; Zu, Y.; Wang, C.-H. Postural Control of Patients with Low Back Pain Under Dual-Task Conditions. J. Pain Res. 2023, 16, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, H.; Galea, M.; Hodges, P. Reorganization of the motor cortex is associated with postural control deficits in recurrent low back pain. Brain 2008, 131, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P. Cortical drives to human muscle: The Piper and related rhythms. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 60, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mima, T.; Hallett, M. Corticomuscular coherence: A review. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 16, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seminowicz, D.A.; Thapa, T.; Schabrun, S.M. Corticomotor Depression is Associated With Higher Pain Severity in the Transition to Sustained Pain: A Longitudinal Exploratory Study of Individual Differences. J. Pain 2019, 20, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrkanoon, S.; Breakspear, M.; Boonstra, T. The reorganization of corticomuscular coherence during a transition between sensorimotor states. NeuroImage 2014, 100, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.A.; Lundbye-Jensen, J.; Nielsen, J.B. Changes in corticospinal drive to spinal motoneurones following visuo-motor skill learning in humans. J. Physiol. 2006, 573, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermens, H.; Freriks, B.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Rau, G. Development of recommendations for SEMG sensors and sensor placement procedures. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2000, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwig, U.; Satrapi, P.; Schönfeldt-Lecuona, C. Using the international 10-20 EEG system for positioning of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Topogr. 2003, 16, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminowicz, D.A.; Moayedi, M. The Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Acute and Chronic Pain. J. Pain 2017, 18, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, F.; Goethel, M.; Robalino, J.; Becker, K.; Sousa, M.; Pulcineli, B.C.; Ervilha, U.F.; Vilas-Boas, J.P.; Santos, R. Precision and Reliability of a Dynamometer for Trunk Extension Strength and Steadiness Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, G.; Maribo, T. Hand-held dynamometry fixated with a tripod is reliable for assessment of back extensor strength in women with osteoporosis. Osteoporos. Int. 2014, 25, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellgren, J.H. Referred Pains from Muscle. Br. Med. J. 1938, 1, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canestri, R.; Franco-Alvarenga, P.E.; Brietzke, C.; Vinícius, Í.; Smith, S.A.; Mauger, A.R.; Goethel, M.F.; Pires, F.O. Effects of experimentally induced muscle pain on endurance performance: A proof-of-concept study assessing neurophysiological and perceptual responses. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagé, M.G.; Katz, J.; Stinson, J.; Isaac, L.; Martin-Pichora, A.L.; Campbell, F. Validation of the numerical rating scale for pain intensity and unpleasantness in pediatric acute postoperative pain: Sensitivity to change over time. J. Pain 2012, 13, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackey, I.G.; Dixon, E.A.; Johnson, K.; Kong, J.T. Dynamic Quantitative Sensory Testing to Characterize Central Pain Processing. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 16, 54452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonsevych, K.; Goethel, M.F.; Mrozowski, J.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Bezuglyi, M. Fingers Movements Control System Based on Artificial Neural Network Model. Radioelectron Commun. Syst. 2019, 62, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, P.J.; Peper, C.E.; Marinus, J.; Beek, P.J.; van Hilten, J.J. Motor consequences of experimentally induced limb pain: A systematic review. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, R.W.; Herman, J.; Purdy, P. Cerebral location of international 10-20 system electrode placement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1987, 66, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, H.; Fürst, G.; Meyer, B.U. Craniocerebral topography within the international 10-20 system. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1989, 72, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, D.M.; Rosenberg, J.R.; Amjad, A.M.; Breeze, P.; Conway, B.A.; Farmer, S.F. A framework for the analysis of mixed time series/point process data--theory and application to the study of physiological tremor, single motor unit discharges and electromyograms. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1995, 64, 237–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.R.; Amjad, A.M.; Breeze, P.; Brillinger, D.R.; Halliday, D.M. The Fourier approach to the identification of functional coupling between neuronal spike trains. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1989, 53, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Tao, L.; Su, R.; Zhu, Y.; Meng, L.; Tuheti, A.; Huang, H.; Shu, F.; Chen, W.; Chen, C. Unsupervised Transfer Learning Approach With Adaptive Reweighting and Resampling Strategy for Inter-Subject EOG-Based Gaze Angle Estimation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, A. Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests [R package rstatix version 0.6.0]. 2020.
- Liu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, H. Corticomuscular Coherence and Its Applications: A Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.; McNair, N.; Harris, J.; Sharpe, L.; Colagiuri, B. In anticipation of pain: Expectancy modulates corticospinal excitability, autonomic response, and pain perception. Pain 2021, 162, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurcher, U.; Kaufman, M.; Vyhnalek, B.; Sung, P. Entropy measures of back muscles EMG for subjects with and without pain. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mouraux, A.; Plaghki, L. Single-trial detection of human brain responses evoked by laser activation of Adelta-nociceptors using the wavelet transform of EEG epochs. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 361, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Micklewright, D.; Winter, S.L.; Mauger, A.R. Muscle pain from an intramuscular injection of hypertonic saline increases variability in knee extensor torque reproduction. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 130, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.; Tiemann, L.; Schuster, T.; Gross, J.; Ploner, M. Neurophysiological Coding of Traits and States in the Perception of Pain. Cereb. Cortex. 2011, 21, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.; Schnitzler, A.; Timmermann, L.; Ploner, M. Gamma oscillations in human primary somatosensory cortex reflect pain perception. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciotti, R.; Ciancetta, L.; Della Penna, S.; Belardinelli, P.; Pizzella, V.; Romani, G.L. Modulation of alpha oscillations in insular cortex reflects the threat of painful stimuli. NeuroImage 2009, 46, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.S.; Chang, W.J.; Millard, S.K.; Skippen, P.; Bilska, K.; Seminowicz, D.A.; Schabrun, S.M. The Effect of Acute and Sustained Pain on Corticomotor Excitability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Group and Individual Level Data. J. Pain 2022, 23, 1680–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecsy, K.; Brown, C.; Jones, A. Cortical nociceptive processes are reduced by visual alpha-band entrainment in the human brain. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Oswald, M.; Heinl, C.; Romero, O.A.R.; Kaushalya, S.; Monyer, H.; Kuner, R. Gamma oscillations in somatosensory cortex recruit prefrontal and descending serotonergic pathways in aversion and nociception. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.S.; Bi, C.; Furman, A.J.; Chiang, A.K.I.; Skippen, P.; Si, E.; Millard, S.K.; Margerison, S.M.; Spies, D.; Keaser, M.L.; et al. Predicting Individual Pain Sensitivity Using a Novel Cortical Biomarker Signature. JAMA Neurol. 2025, 82, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliki, M.N.; Petre, B.; Torbey, S.; Herrmann, K.M.; Huang, L.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Fields, H.L.; Apkarian, A.V. Corticostriatal functional connectivity predicts transition to chronic back pain. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Women (n = 8) | Men (n = 25) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 29.77 ± 6.20 | 28.79 ± 5.90 |
| Height (cm) | 164.66 ± 6.30 | 175.20 ± 5.50 |
| Body mass (kg) | 65.14 ± 6.20 | 80.00 ± 9.30 |
| VARIABLE | Pre-Hypertonic | During of Pain | Pre-Isotonic | Post-Isotonic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fp1 | ||||
| ALPHA * | 0.04 × 10−3 (IQR-0.09 × 10−3) | 5.87 (IQR-1.0) | 1.71 (IQR-0.08) | 1.87 (IQR-0.11 × 10−6) |
| BETA * | 0.07 × 10−3 (IQR-0.21 × 10−4) | 8.23 (IQR-1.0) | 1.35 (IQR-0.02) | 7.86 × 10−9 (IQR-1.10 × 10−10) |
| GAMMA * | 7.88 × 10−6 (IQR-1.00 × 10−6) | 2.12 × 10−8 (IQR-0.1 × 10−7) | 1.82 × 10−9 (IQR-9.4 × 10−11) | 6.23 × 10−12 (IQR-1.23 × 10−13) |
| Cz | ||||
| ALPHA * | 6.78 × 10−7 (IQR-1.00 × 10−7) | 3.21 × 10−8 (IQR-0.1 × 10−8) | 7.42 × 10−9 (IQR-4.49 × 10−10) | 2.31 × 10−10 (IQR-1.23 × 10−11) |
| BETA * | 1.23 × 10−6 (IQR-4.8 × 10−10) | 2.98 × 10−11 (IQR-6.66 × 10−12) | 1.26 × 10−11 (IQR-6.03 × 10−13) | 9.85 × 10−10 (IQR-1.22 × 10−11) |
| GAMMA ** | 3.01 × 10−9 (IQR-1.01 × 10−12) | 3.34 × 10−9 (IQR-4.69 × 10−10) | 3.80 × 10−11 (IQR-1.47 × 10−11) | 2.04 × 10−12 (IQR-9 × 10−15) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parolini, F.; Becker, K.; Ervilha, U.F.; Santos, R.; Vilas-Boas, J.P.; Goethel, M.F. Disrupted Corticomuscular Coherence and Force Steadiness During Acute Low Back Pain. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111269
Parolini F, Becker K, Ervilha UF, Santos R, Vilas-Boas JP, Goethel MF. Disrupted Corticomuscular Coherence and Force Steadiness During Acute Low Back Pain. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111269
Chicago/Turabian StyleParolini, Franciele, Klaus Becker, Ulysses F. Ervilha, Rubim Santos, João Paulo Vilas-Boas, and Márcio Fagundes Goethel. 2025. "Disrupted Corticomuscular Coherence and Force Steadiness During Acute Low Back Pain" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111269
APA StyleParolini, F., Becker, K., Ervilha, U. F., Santos, R., Vilas-Boas, J. P., & Goethel, M. F. (2025). Disrupted Corticomuscular Coherence and Force Steadiness During Acute Low Back Pain. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111269









