Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Dermatologic Screening: Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Seborrheic Keratosis and Actinic Keratosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Features
2.1. Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma (nBCC)
2.2. Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma (sBCC)
2.3. Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma (MorBCC)
2.4. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
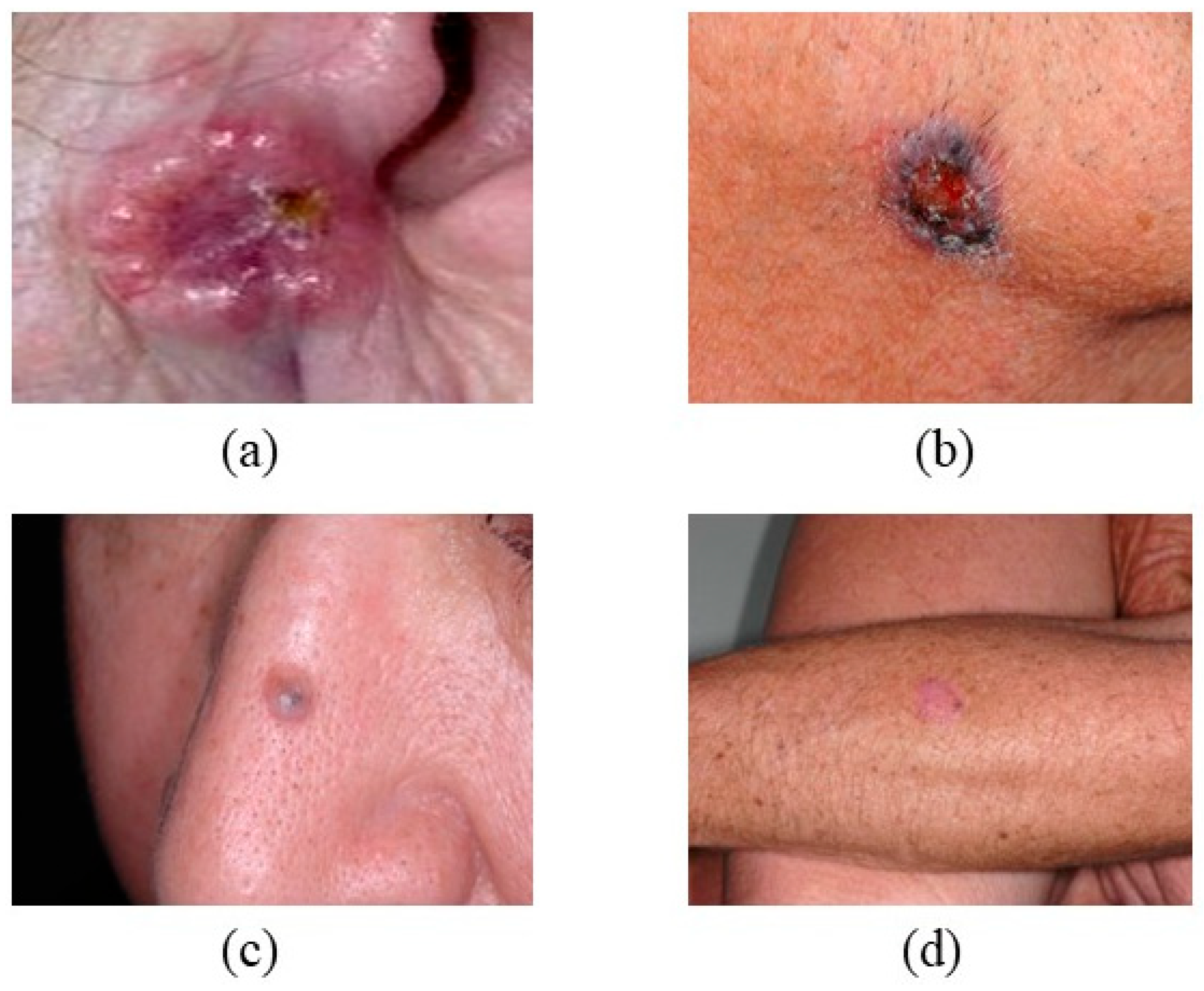
2.5. Seborrheic Keratosis (SK)
2.6. Actinic Keratosis (AK)
3. Screening and Diagnosis of BCC, SCC, SK, and AK
3.1. Screening and Diagnosis of BCC
3.2. Screening and Diagnosis of SCC
3.3. Screening and Diagnosis of SK
3.4. Screening and Diagnosis of AK
4. Machine Learning Applications in Skin Cancer Detection
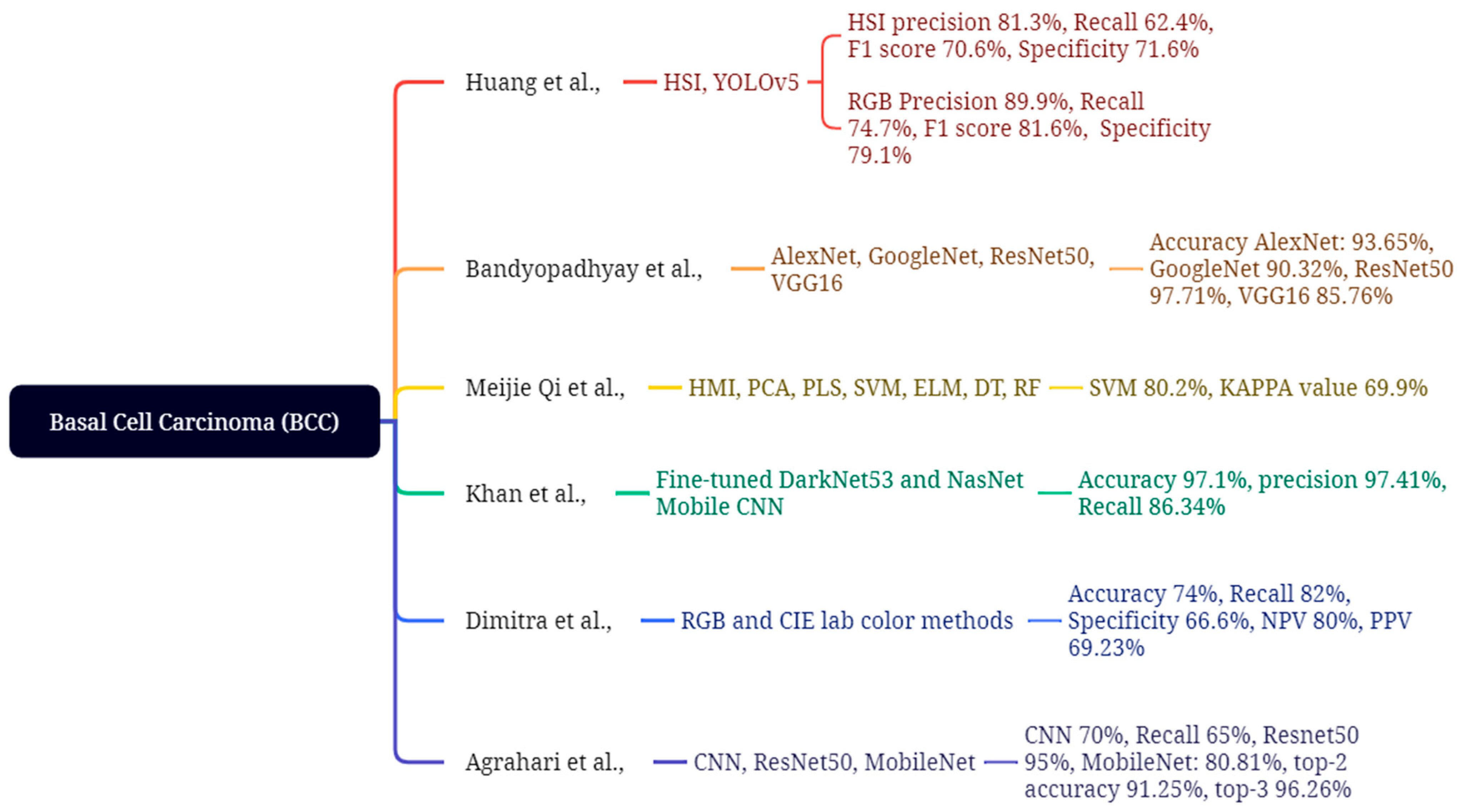
4.1. Basal Cell Carcinoma
4.2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
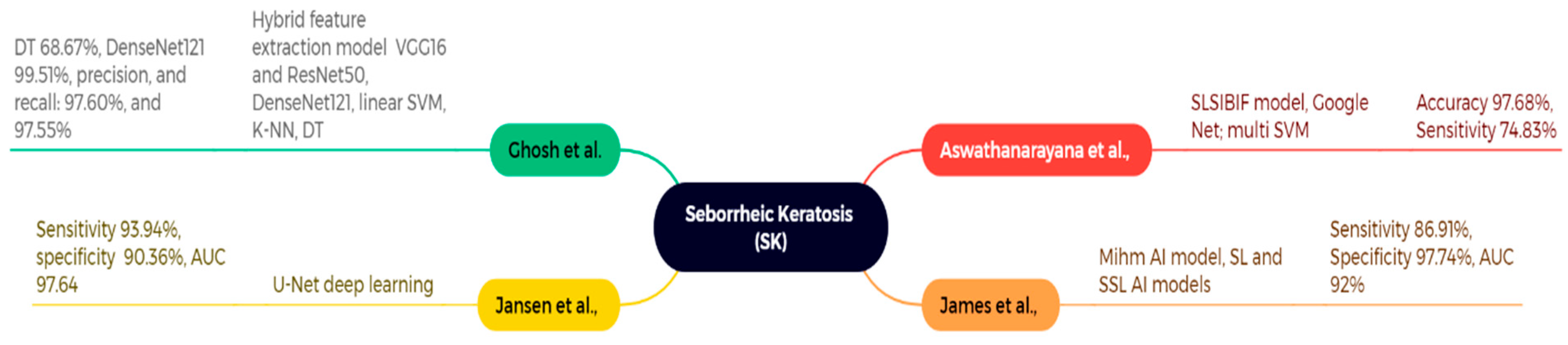
4.3. Seborrheic Keratosis (SK)
4.4. Actinic Keratosis (AK)
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panthakkan, A.; Anzar, S.M.; Jamal, S.; Mansoor, W. Concatenated Xception-ResNet50—A novel hybrid approach for accurate skin cancer prediction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, A.; Ghalib, M.R. Automatic detection and classification of skin cancer. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2017, 10, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Riffat, F. Epidemiology and aetiology of non-melanoma skin cancer. In Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer of the Head and Neck; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Roky, A.H.; Islam, M.M.; Ahasan, A.M.F.; Mostaq, S.; Mahmud, Z.; Amin, M.N.; Mahmud, A. Overview of skin cancer types and prevalence rates across continents. Cancer Pathog. Ther. 2024, 2, E01–E36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciążyńska, M.; Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Lange, D.; Lewandowski, B.; Reich, A.; Sławińska, M.; Pabianek, M.; Szczepaniak, K.; Hankiewicz, A.; Ułańska, M.; et al. The incidence and clinical analysis of non-melanoma skin cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrocini, G.; Triassi, M.; Mauriello, M.C.; Torre, G.; Annunziata, M.C.; De Vita, V.; Pastore, F.; D’arco, V.; Monfrecola, G. Epidemiology of skin cancer: Role of some environmental factors. Cancers 2010, 2, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinarayan, M.; Krishnamurthy, S.P. Clinicopathological evaluation of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Indian J. Dermatol. 2011, 56, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauvar, A.N.; Cronin, T., Jr.; Roenigk, R.; Hruza, G.; Bennett, R. Consensus for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment: Basal cell carcinoma, including a cost analysis of treatment methods. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41, 550–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, R.I.; Brgoch, M.; Gastman, B.R. Treatment of squamous and basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Cutan. Malig. A Surg. Perspect. 2018, 2018, 43–85. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M.S.; Jamil, M.A.; Shehzad, A.; Mazhar, S.; Hameed, F. Basal Cell Carcinoma. In Skin Cancer—Past, Present and Future; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fania, L.; Didona, D.; Morese, R.; Campana, I.; Coco, V.; Di Pietro, F.R.; Ricci, F.; Pallotta, S.; Candi, E.; Abeni, D.; et al. Basal cell carcinoma: From pathophysiology to novel therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, J.K.; Brant, J.M.; Conde, F.; Saria, M. (Eds.) Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers. Characteristics of BCC. In Core Curriculum for Oncology Nursing-E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Zak-Prelich, M.; Narbutt, J.; Sysa-Jedrzejowska, A. Environmental risk factors predisposing to the development of basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Pyne, J.H.; Myint, E.; Barr, E.M.; Clark, S.P.; David, M.; Na, R.; Hou, R. Superficial basal cell carcinoma: A comparison of superficial only subtype with superficial combined with other subtypes by age, sex and anatomic site in 3150 cases. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2017, 44, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, S.; Ghezelbash, S.; Nallanathan, B.; Lefrançois, P. Clinical and Molecular Features of Morpheaform Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 9906–9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchado-Cobos, R.; García-Sancha, N.; González-Sarmiento, R.; Pérez-Losada, J.; Cañueto, J. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: From biology to therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallini, J.R.; Hamed, N.; Khachemoune, A. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Epidemiology, classification, management, and novel trends. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immerman, S.C.; Scanlon, E.F.; Christ, M.; Knox, K.L. Recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Cancer 1983, 51, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratigos, A.J.; Garbe, C.; Dessinioti, C.; Lebbe, C.; Bataille, V.; Bastholt, L.; Dreno, B.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Forsea, A.M.; Frenard, C.; et al. European interdisciplinary guideline on invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: Part 1. epidemiology, diagnostics and prevention. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 128, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollina, U. Recent advances in managing and understanding seborrheic keratosis. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, E.L. Skin Tumors. In Family Medicine: Principles and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1681–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, C.; Binder, S. Comparison of Seborrheic Keratoses, Inflamed Seborrheic Keratoses, and Inverted Follicular Keratoses Using P53, BCL-1, and BCL-2. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2005, 32, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Wollina, U. Seborrheic keratoses—The most common benign skin tumor of humans. Clinical presentation and an update on pathogenesis and treatment options. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscarella, E.; Brancaccio, G.; Briatico, G.; Ronchi, A.; Piana, S.; Argenziano, G. Differential Diagnosis and Management on Seborrheic Keratosis in Elderly Patients. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, D.P.; Nair, A.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, P. Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis: Clinical update. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 12, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.-L.; Popa, A.C.; Tanase, C.; Gheorghisan-Galateanu, A.-A. Acanthosis nigricans: To be or not to be afraid. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4133–4138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortes, H.R.; von Ranke, F.M.; Escuissato, D.L.; Neto, C.A.A.; Zanetti, G.; Hochhegger, B.; Souza, C.A.; Marchiori, E. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A state-of-the-art review. Respir. Med. 2017, 126, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianzani, C.; Conforti, C.; Giuffrida, R.; Corneli, P.; Di Meo, N.; Farinazzo, E.; Moret, A.; Rizzi, G.M.; Zalaudek, I. Current therapies for actinic keratosis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, B.; Cockerell, C.J. Pathobiology of actinic keratosis: Ultraviolet-dependent keratinocyte proliferation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, S10–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris, K.; Micantonio, T.; Piccolo, D.; Concetta, M. Dermoscopic features of actinic keratosis. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2007, 5, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, E.C.; da Motta, V.R.; Pantoja, P.C.; Ilha, C.S.D.O.; Magalhaes, R.F.; Galadari, H.; Leonardi, G.R. Actinic keratosis—Review for clinical practice. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockfleth, E.; Peris, K.; Guillen, C.; Cerio, R.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Foley, P.; Sanches, J.; Culshaw, A.; Erntoft, S.; Lebwohl, M. Physician perceptions and experience of current treatment in actinic keratosis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, K.A.; Parker, E.R.; Drolet, B.C. Sunscreen Coverage as Preventive Care Under the Affordable Care Act: A Low-Cost Way to Reduce the Prevalence of the Most Common Cancer. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2025, 18, 56. [Google Scholar]
- US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Skin Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2023, 329, 1290–1295. [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Tabuchi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Hara, A. Basal cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J. Ski. Cancer 2011, 2011, 496910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Yap, F.B. Clinical characteristics of basal cell carcinoma in a tertiary hospital in Sarawak, Malaysia. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourmishev, L.A.; Rusinova, D.; Botev, I. Clinical variants, stages, and management of basal cell carcinoma. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2013, 4, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șerbănescu, M.-S.; Bungărdean, R.M.; Georgiu, C.; Crișan, M. Nodular and Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes Are Different Tumors Based on Their Morphological Architecture and Their Interaction with the Surrounding Stroma. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vantuchova, Y.; Curik, R. Histological types of basal cell carcinoma. Scr. Medica 2006, 79, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Betti, R.; Menni, S.; Radaelli, G.; Bombonato, C.; Crosti, C. Micronodular basal cell carcinoma: A distinct subtype? Relationship with nodular and infiltrative basal cell carcinomas. J. Dermatol. 2010, 37, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diepgen, T.; Fartasch, M.; Drexler, H.; Schmitt, J. Occupational skin cancer induced by ultraviolet radiation and its prevention. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167 (Suppl. S2), 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, K.; Sambrano, B.; Fox, P.; Bassett, R.; Chon, S.; Prieto, V. Thickness of superficial basal cell carcinoma (sBCC) predicts imiquimod efficacy: A proposal for a thickness-based definition of sBCC. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, M.S. Treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma with ingenol mebutate gel, 0.05%. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 9, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Raasch, B. Management of superficial basal cell carcinoma: Focus on imiquimod. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 2, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnlide, I.; Zalaudek, I.; Nilsson, F.; Bjellerup, M.; Nielsen, K. Preoperative prediction of histopathological outcome in basal cell carcinoma: Flat surface and multiple small erosions predict superficial basal cell carcinoma in lighter skin types1111. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Garbe, C.; Kaufmann, R.; Bastholt, L.; Seguin, N.B.; Bataille, V.; Marmol, V.D.; Dummer, R.; Harwood, C.A.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma: European consensus-based interdisciplinary guidelines. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 118, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccialanza, M.; Piccinno, R.; Çuka, E.; Violetti, S.A.; Rozza, M. Radiotherapy of morphea-type basal cell carcinoma: Results in 127 cases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camela, E.; Anca, P.I.; Lallas, K.; Papageorgiou, C.; Manoli, S.-M.; Gkentsidi, T.; Eftychidou, P.; Liopyris, K.; Sgouros, D.; Apalla, Z.; et al. Dermoscopic Clues of Histopathologically Aggressive Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes. Medicina 2023, 59, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadiminti, U.; Rakkhit, T.; Washington, C. Morpheaform basal cell carcinoma in African Americans. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naik, P.P.; Desai, M.B. Basal cell carcinoma: A narrative review on contemporary diagnosis and management. Oncol. Ther. 2022, 10, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumagic-Halilovic, E.; Hasic, M.; Ovcina-Kurtovic, N. A clinical study of basal cell carcinoma. Med. Arch. 2019, 73, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthouli-Anagnostopoulou, F.; Hatziolou, E. Recurrent morphean basal cell carcinoma of the skin. A clinico-histopathological study of 97 cases. Adv. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 6, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.L.; Asgari, M. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC): Clinical features and diagnosis. UpToDate. Retrieved Febr. 2020, 10, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniappan, V.; Karthikeyan, K. Bowen’s disease. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2022, 13, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Hu, L.; Rao, Y.; Ren, R.; Tong, X.; Guo, A.; Huang, J.; Tang, Z. Application of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy in the diagnosis of Bowen’s disease. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2024, 87, 2842–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omry, A.; El Ayoun, R.Z.; Behi, H.; Changuel, A.; Tlili, K.; Khalifa, M.B. Surgical perspective on perianal Bowen’s disease: A rare case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 117, 109459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, H.; Safi, Y.; Baharvand, M.; Rahmani, S.; Jafari, S. Peripheral exophytic oral lesions: A clinical decision tree. Int. J. Dent. 2017, 2017, 9193831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, D.; Beddy, D.; Dozois, E.J. Neoplasms of anal canal and perianal skin. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2011, 24, 054–063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bharadwaj, M.; Mehrotra, R. Skin cancer concerns in people of color: Risk factors and prevention. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2016, 17, 5257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lahbacha, B.; Nechi, S.; Chaabane, A.; Bani, A.; Kchaou, M.; Chtourou, F.; Mfarrej, M.K.; Douggaz, A.; Chelbi, E. Seborrheic Keratosis: Report of a Rare Presentation and Reminder of the Current Knowledge of the Problem. Clin. Pathol. 2024, 17, 2632010X241255874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzeo, M.; Manfreda, V.; Diluvio, L.; Dattola, A.; Bianchi, L.; Campione, E. Dermoscopic analysis of 72 “atypical” seborrheic keratoses. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas 2019, 110, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.D.; Halpern, A.C. Advances in the etiology, detection, and clinical management of seborrheic keratoses. Dermatology 2022, 238, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Lu, H. Overexpression of Amyloid Precursor Protein Promotes the Onset of Seborrhoeic Keratosis and is Related to Skin Ageing. Acta Dermato-Venereol. 2018, 98, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simandi, C. Alteration in skin function and integrity. In Pathophysiology, Concepts of Altered Health States, 3rd ed; Porth, C.M., Ed.; JB Lippincott Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 108–140. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, K.d.A.P.; Martinez, D.C.S.; Nobre, A.B.; Campos-do-Carmo, G. Collision tumor: Pigmented Bowen’s disease and seborrheic keratosis. An. Bras. De Dermatol. 2018, 93, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmann, S.; Butsch, F.; Lang, B.M.; Stege, H.; Großmann, B.; Schepler, H.; Grabbe, S. Seborrheic keratosis. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2023, 21, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luba, M.C.; A Bangs, S.; Mohler, A.M.; Stulberg, D.L. Common benign skin tumors. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 67, 729–738. [Google Scholar]
- Chetty, P.; Choi, F.; Mitchell, T. Primary care review of actinic keratosis and its therapeutic options: A global perspective. Dermatol. Ther. 2015, 5, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cham, B.E. Holistic Approach in the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis: Benefits and Disadvantages of 5-Fluorouracil, Imiquimod, Diclofenac and Curaderm. Int. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 14, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.V.; Miot, H.A. Actinic keratosis: A clinical and epidemiological revision. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2012, 87, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, M.; Nürnberg, B.; Forman, J.; Thomsen, J.; Thrane, L.; Jemec, G. In vivo thickness measurement of basal cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis with optical coherence tomography and 20-MHz ultrasound. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, A.; Chia, A.; Shumack, S. Actinic keratosis: Rationale and management. Dermatol. Ther. 2014, 4, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras Nart, I.; Cerio, R.; Dirschka, T.; Dréno, B.; Lear, J.; Pellacani, G.; Peris, K.; de Casas, A.R.; On Behalf of Progressing Evidence in AK (PEAK) Working Group. Defining the actinic keratosis field: A literature review and discussion. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themstrup, L.; Pellacani, G.; Welzel, J.; Holmes, J.; Jemec, G.; Ulrich, M. In vivo microvascular imaging of cutaneous actinic keratosis, Bowen’s disease and squamous cell carcinoma using dynamic optical coherence tomography. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firnhaber, J.M. Diagnosis and treatment of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Am. Fam. Physician 2012, 86, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Krakowski, A.C.; Hafeez, F.; Westheim, A.; Pan, E.Y.; Wilson, M. Advanced basal cell carcinoma: What dermatologists need to know about diagnosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, S1–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molho-Pessach, V.; Lotem, M. Ultraviolet radiation and cutaneous carcinogenesis. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2007, 35, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Altamura, D.; Menzies, S.W.; Argenziano, G.; Zalaudek, I.; Soyer, H.P.; Sera, F.; Avramidis, M.; DeAmbrosis, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Peris, K. Dermatoscopy of basal cell carcinoma: Morphologic variability of global and local features and accuracy of diagnosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijušković, Ž.P. Etiology and pathogenesis of basal cell carcinoma. Serbian J. Dermatol. Venerol. 2013, 5, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, P.R.; Ramachandran, S.; Strange, R.C. Environment, phenotype and genetics: Risk factors associated with BCC of the skin. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2002, 2, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Han, J.; Laden, F.; Qureshi, A.A. Long-term ultraviolet flux, other potential risk factors, and skin cancer risk: A cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Xu, D.; Tao, X.; Fan, Y. Ultraviolet radiation and basal cell carcinoma: An environmental perspective. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 666528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichakjian, C.; Armstrong, A.; Baum, C.; Bordeaux, J.S.; Brown, M.; Busam, K.J.; Eisen, D.B.; Iyengar, V.; Lober, C.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of basal cell carcinoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 540–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letada, P.R.; Uebelhoer, N.S.; Masters, R. 16 Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer. In Year Book of Dermatology and Dermatological Surgery; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 2012, p. 363. [Google Scholar]
- Quazi, S.J.; Aslam, N.; Saleem, H.; Rahman, J.; Khan, S. Surgical margin of excision in basal cell carcinoma: A systematic review of literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.; Walton, S. Treatment of facial basal cell carcinoma: A review. J. Ski. Cancer 2011, 2011, 380371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, C.; Gyulai, R.; Lengyel, Z. Topical Fluorouracil Therapy for Basal Cell Carcinoma. In Skin Cancer—Past, Present and Future; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Y.; Zuo, L.; Shang, L.; Bazan, J.G. Radiotherapy treatment for nonmelanoma skin cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2015, 15, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, C.F.; MacAulay, C.E.; Laronde, D.M.; Williams, P.M.; Zhang, L.; Rosin, M.P. Squamous cell carcinoma and precursor lesions: Diagnosis and screening in a technical era. Periodontology 2000 2011, 57, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombino, M.; Palmieri, G.; Rodio, M.; Tettamanzi, M.; Rampazzo, S.; Margani, R.; Trignano, E.; Cossu, A.; Fedeli, M.A.; Fadda, G.M.; et al. Mutational Profiles of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas with Different Patterns of Clinical Aggression from Head and Neck Regions. Cancers 2024, 16, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Armstrong, A.; Baum, C.; Bordeaux, J.S.; Brown, M.; Busam, K.J.; Eisen, D.B.; Iyengar, V.; Lober, C.; Margolis, D.J.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Valentino, J.; Manna, S.; Tripathi, P.K.; Bhattacharya-Chatterjee, M.; Foon, K.A.; O’MAlley, B.W.; Chatterjee, S.K. Gene therapy for head and neck cancer using vaccinia virus expressing IL-2 in a murine model, with evidence of immune suppression. Mol. Ther. 2001, 4, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karia, P.S. Epidemiology and outcomes of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. In High-Risk Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- de Gruijl, F.R.; van Kranen, H.J.; Mullenders, L.H. UV-induced DNA damage, repair, mutations and oncogenic pathways in skin cancer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2001, 63, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.; Bajdik, C.; Willemze, R.; Bavinck, J.B. Chemical exposures other than arsenic are probably not important risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma and malignant melanoma of the skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Otley, C.C. Skin cancer in organ transplant recipients: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.M.; Smith, N.R. Mohs surgery versus standard local excision for basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma skin cancer. Facial Plast. Surg. 2020, 36, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zaorsky, N.G.; Lee, C.T.; Zhang, E.; Galloway, T.J. Skin CanceR Brachytherapy vs External beam radiation therapy (SCRiBE) meta-analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffray, J.D.; Gospodarowicz, M.K. Radiation therapy for cancer. PMC 2015, 3, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Chargari, C.; Deutsch, E.; Blanchard, P.; Gouy, S.; Martelli, H.; Guérin, F.; Dumas, I.; Bossi, A.; Morice, P.; Viswanathan, A.N.; et al. Brachytherapy: An overview for clinicians. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronek, J. Current status of brachytherapy in cancer treatment-short overview. J. Contemp. Brachytherapy 2017, 9, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, S.; Kamberoglu, I. Cryotherapy for common premalignant and malignant skin disorders. Dermatol. Surg. Proced. 2018, 15, 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Likhacheva, A.; Awan, M.; Barker, C.A.; Bhatnagar, A.; Bradfield, L.; Brady, M.S.; Buzurovic, I.; Geiger, J.L.; Parvathaneni, U.; Zaky, S.; et al. Definitive and Postoperative Radiation Therapy for Basal and Squamous Cell Cancers of the Skin: Executive Summary of an American Society for Radiation Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 10, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, I.; McGrath, E.; Harwood, C.; Botting, J.; Buckley, P.; Budny, P.; Fairbrother, P.; Fife, K.; Gupta, G.; Hashme, M.; et al. British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of adults with basal cell carcinoma 2021. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.M.; Baker, D.R.; Coldiron, B.M.; Fazio, M.J.; Storrs, P.A.; Vidimos, A.T.; Zalla, M.J.; Brewer, J.D.; Begolka, W.S.; Berger, T.G.; et al. AAD/ACMS/ASDSA/ASMS 2012 appropriate use criteria for Mohs micrographic surgery: A report of the American Academy of Dermatology, American College of Mohs Surgery, American Society for Dermatologic Surgery Association, and the American Society for Mohs Surgery. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 531–550. [Google Scholar]
- Hafner, C.; Hartmann, A.; van Oers, J.M.M.; Stoehr, R.; Zwarthoff, E.C.; Hofstaedter, F.; Landthaler, M.; Vogt, T. FGFR3 mutations in seborrheic keratoses are already present in flat lesions and associated with age and localization. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, S.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, S.S.M.; Khan, H.D.; Raza, M.A.; Etaee, F.; Cockerell, C.J.; Apalla, Z.; Goldust, M. Update of pathophysiology and treatment options of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, S. The Clinical Research of Dermoscopy in the Diagnosis of Solar Lentigines, Seborrheic Keratosis, and Actinic Keratosis. Int. Core J. Eng. 2022, 8, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, N.K.; Hahn, H.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Choe, Y.B.; Ahn, K.J. Clinical and histopathological investigation of seborrheic keratosis. Annals of dermatology. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Hwang, E.J.; Bae, J.H.; Park, H.E.; Lee, J.C.; Youn, J.I.; Chung, J.H. Seborrheic keratosis in the Korean males: Causative role of sunlight. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2003, 19, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raulin, C.; Kimmig, W. Laser therapy in dermatology and aesthetic medicine: Side effects, complications, and treatment errors. In Energy for the Skin; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Wu, S.; Ding, Y.; Yao, G.; Chen, J. Advancements in elucidating the pathogenesis of actinic keratosis: Present state and future prospects. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1330491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcere, A.; Konrāde-Jilmaza, L.; Pauliņa, L.A.; Čēma, I.; Krūmiņa, A. Clinical characteristics of actinic keratosis associated with the risk of progression to invasive squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez Figueras, M.T. From actinic keratosis to squamous cell carcinoma: Pathophysiology revisited. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, T.; Lebwohl, M.G. Prevalence and awareness of actinic keratosis: Barriers and opportunities. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C. Conventional treatment of actinic keratosis: An overview. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2015, 46, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, B.; Amini, S. Pharmacotherapy of actinic keratosis: An update. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2012, 13, 1847–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Kittler, H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, B.; Kendrick, C.; Brodzicki, A.; Jaworek-Korjakowska, J.; Yap, M.H. Analysis of the ISIC image datasets: Usage, benchmarks and recommendations. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 75, 102305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-P.; Mukundan, A.; Tsao, Y.-M.; Chang, W.-Y.; Wang, H.-C. Classification of skin cancer using novel hyperspectral imaging engineering via YOLOv5. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Bose, P.; Bhaumik, A.; Poddar, S. Machine learning and deep learning integration for skin diseases prediction. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2022, 70, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z. Classification of skin cancer based on hyperspectral microscopic imaging and machine learning. In Proceedings of the SPIE-CLP Conference on Advanced Photonics 2022, Online, 21–23 November 2023; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Akram, T.; Sharif, M.; Kadry, S.; Nam, Y. Computer Decision Support System for Skin Cancer Localization and Classification. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 1041–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumaki, D.; Manios, G.; Papadakis, M.; Doxastaki, A.; Zacharopoulos, G.V.; Katoulis, A.; Manios, A. Color Analysis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Comparative Study with Cherry Angiomas, Hemangiomas, Basal Cell Carcinomas, and Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrahari, P.; Agrawal, A.; Subhashini, N. Skin cancer detection using deep learning. In Futuristic Communication and Network Technologies: Select Proceedings of VICFCNT 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Qi, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, J. Staging of skin cancer based on hyperspectral microscopic imaging and machine learning. Biosensors 2022, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Sierra, E.; Cheng, S.; Cuenca, R.; Ahmed, B.; Ji, J.; Yakovlev, V.V.; Martinez, M.; Al-Khalil, M.; Al-Enazi, H.; Cheng, Y.-S.L.; et al. Machine-learning assisted discrimination of precancerous and cancerous from healthy oral tissue based on multispectral autofluorescence lifetime imaging endoscopy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, M.; Al Mamun, M.; Uddin, M.S. A machine learning approach for skin disease detection and classification using image segmentation. Health Anal. 2022, 2, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Moon, I.J.; Lim, W.; Suh, I.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Na, J.-I.; Kim, S.H.; Chang, S.E. Keratinocytic skin cancer detection on the face using region-based convolutional neural network. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathanarayana, S.H.; Kanipakapatnam, S.K. An effective semantic mathematical model for skin cancer classification using a saliency-based level set with improved boundary indicator function. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2023, 16, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requa, J.; Godard, T.; Mandal, R.; Balzer, B.; Whittemore, D.; George, E.; Barcelona, F.; Lambert, C.; Lee, J.; Lambert, A.; et al. High-fidelity detection, subtyping, and localization of five skin neoplasms using supervised and semi-supervised learning. J. Pathol. Inform. 2023, 14, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, P.; Godard, T.; Mandal, R.; Balzer, B.; Whittemore, D.; George, E.; Barcelona, F.; Lambert, C.; Lee, J.; Lambert, A.; et al. Evaluation of a deep learning approach to differentiate Bowen’s disease and seborrheic keratosis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, H.; Rahat, I.S.; Mohanty, S.N.; Ravindra, J.V.R.; Sobur, A. A Study on the Application of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for Skin Cancer Detection. Int. J. Comput. Syst. Eng. 2024, 18, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, K.; Majeed, F.; Siddique, A.; Meraj, T.; Rauf, H.T.; El-Meligy, M.A.; Sharaf, M.; Elgawad, A.E.E.A. A lightweight approach for skin lesion detection through optimal features fusion. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, C.; Tavares, J.M.R.; Mendes, J.; Vardasca, R. Comparison of machine learning strategies for infrared thermography of skin cancer. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2021, 69, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridonos, P.; Gaitanis, G.; Likas, A.; Bassukas, I.D. A convolutional neural network based system for detection of actinic keratosis in clinical images of cutaneous field cancerization. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2023, 79, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Singhania, U.; Tripathy, B.; Nasr, E.A.; Aboudaif, M.K.; Kamrani, A.K. Deep learning-based transfer learning for classification of skin cancer. Sensors 2021, 21, 8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junayed, M.S.; Anjum, N.; Noman, A.; Islam, B. A deep CNN model for skin cancer detection and classification. Comput. Sci. Res. Notes 2021, 3101, 71–80. [Google Scholar]









| Study (Year) | Dataset/Sample Size | Methodology/Model | Lesion Types | Key Findings | Reported Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huang et al., 2023 [120] | HSI & RGB images; 654 train + 168 val (non-ISIC) | YOLOv5 (HSI vs. RGB) | BCC | RGB: P 89.9%, R 74.7%, F1 81.6%, Spec 79.1; HSI: P 81.3%, R 62.4%, F1 70.6%, Spec 71.6 | Limited spectral window; lower HSI metrics vs. RGB; modest sample size |
| Bandyopadhyay et al., 2022 [121] | Dataset not specified in manuscript text (general DL/ML ensemble summary) | DL backbones (AlexNet/GoogLeNet/ResNet50/VGG16) + SVM/AdaBoost/DT | BCC, SCC | Accuracies up to 93.65% (AlexNet + SVM), with model-wise results as reported | Computational complexity; no real-time clinical validation noted |
| Qi et al., 2023 [122] | Hyperspectral microscopic imaging (synthetic RGB); classical ML | PCA/PLS + GLCM/LBP → ELM/SVM/DT/RF | BCC | SVM best: Accuracy 80.2%, κ = 0.699 (others lower) | Small dataset; synthetic-to-real domain gap |
| Khan et al., 2021 [123] | ISIC2018/ISIC2019/HAM10000 (multi-dataset) | Fine-tuned DarkNet53 & NasNet; fusion + SoftMax | BCC, SCC, SK, AK (+others) | Accuracy 97.1%, Sensitivity 86.34%, Precision 97.41% | Class imbalance; high compute; multi-dataset harmonization |
| Duran-Sierra et al., 2021 [127] | maFLIM endoscopic imaging (23 pts) | QDA/LDA/SVM/LOGREG on spectral & time-resolved features; ensemble (SVM + QDA) | SCC (oral dysplastic/malignant vs. healthy) | Time-resolved QDA: F1 83%, Sens 91%; Ensemble: F1 85%, Sens 94%, Spec 74% (best overall) | Small, single-center; external validation lacking |
| Ahammed et al., 2022 [128] | ISIC2019/HAM10000 | SVM/KNN/DT on GLCM features | SCC | SVM: Accuracy 95%, Precision 95.13%, F1 94.88% | Hand-crafted features; limited external validation |
| Aswathanarayana et al., 2023 [130] | ISIC 2017 (n = 2750) | GoogleNet features + SLSIBIF-MSVM | SK (with other ISIC’17 classes) | Accuracy 97.68%, Sensitivity 74.83% | Moderate recall for some classes; per-class counts limited |
| Jansen et al., 2022 [132] (replaces unverified “James/Mihm AI” row) | Multi-center WSIs (center 0: 3213 slides; centers 1 & 2 also used) | U-Net-based DL segmentation/classification | SK vs. Bowen’s disease (BD) | AUC 97.64, Sensitivity 93.94%, Specificity 90.36% | Scanner/stain variability; domain shift possible |
| Manzoor et al., 2022 [134] | ISIC + Mendeley (>5000 images) | AlexNet features + SVM; segmentation + ABCD + GLCM | AK (+other classes) | AK accuracy 100%; overall 95.4% | Possible overfitting; AK subset size considerations |
| Spyridonos et al., 2023 [136] | Cross-polarized clinical images; patch-level datasets (AK/SK/healthy) | VGG16 feature layers (pool3/pool5/FC7) + multi-class SVM; AKCNN system | AK, SK, Healthy | Macro F1 = 78%, Region-based F1 = 81% (note: F1, not AUC) | Class imbalance; limited external validation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, T.-L.; Lee, K.-H.; Karmakar, R.; Mukundan, A.; Sundarraj, J.; Lu, C.-T.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Wang, H.-C. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Dermatologic Screening: Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Seborrheic Keratosis and Actinic Keratosis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111258
Lin T-L, Lee K-H, Karmakar R, Mukundan A, Sundarraj J, Lu C-T, Hsieh S-C, Wang H-C. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Dermatologic Screening: Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Seborrheic Keratosis and Actinic Keratosis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Teng-Li, Kun-Hua Lee, Riya Karmakar, Arvind Mukundan, Jeevitha Sundarraj, Chun-Te Lu, Shang-Chin Hsieh, and Hsiang-Chen Wang. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Dermatologic Screening: Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Seborrheic Keratosis and Actinic Keratosis" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111258
APA StyleLin, T.-L., Lee, K.-H., Karmakar, R., Mukundan, A., Sundarraj, J., Lu, C.-T., Hsieh, S.-C., & Wang, H.-C. (2025). Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Dermatologic Screening: Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Seborrheic Keratosis and Actinic Keratosis. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111258