Impact of Fatigue on Spine Dynamic Stability and Gait Patterns in Runners with Moderate Flatfoot Versus Normal Arch
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
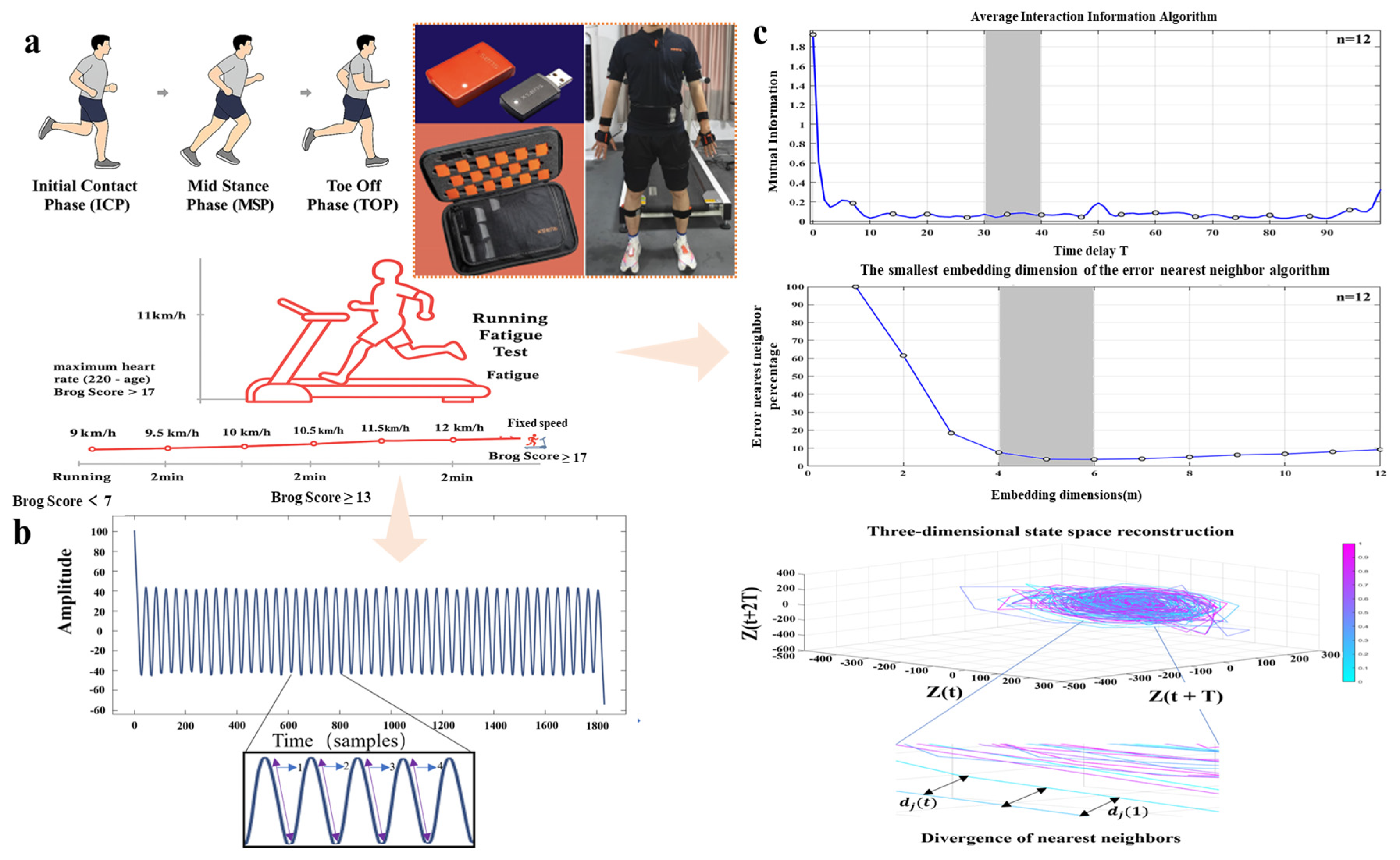
2.3. Data Collection and Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
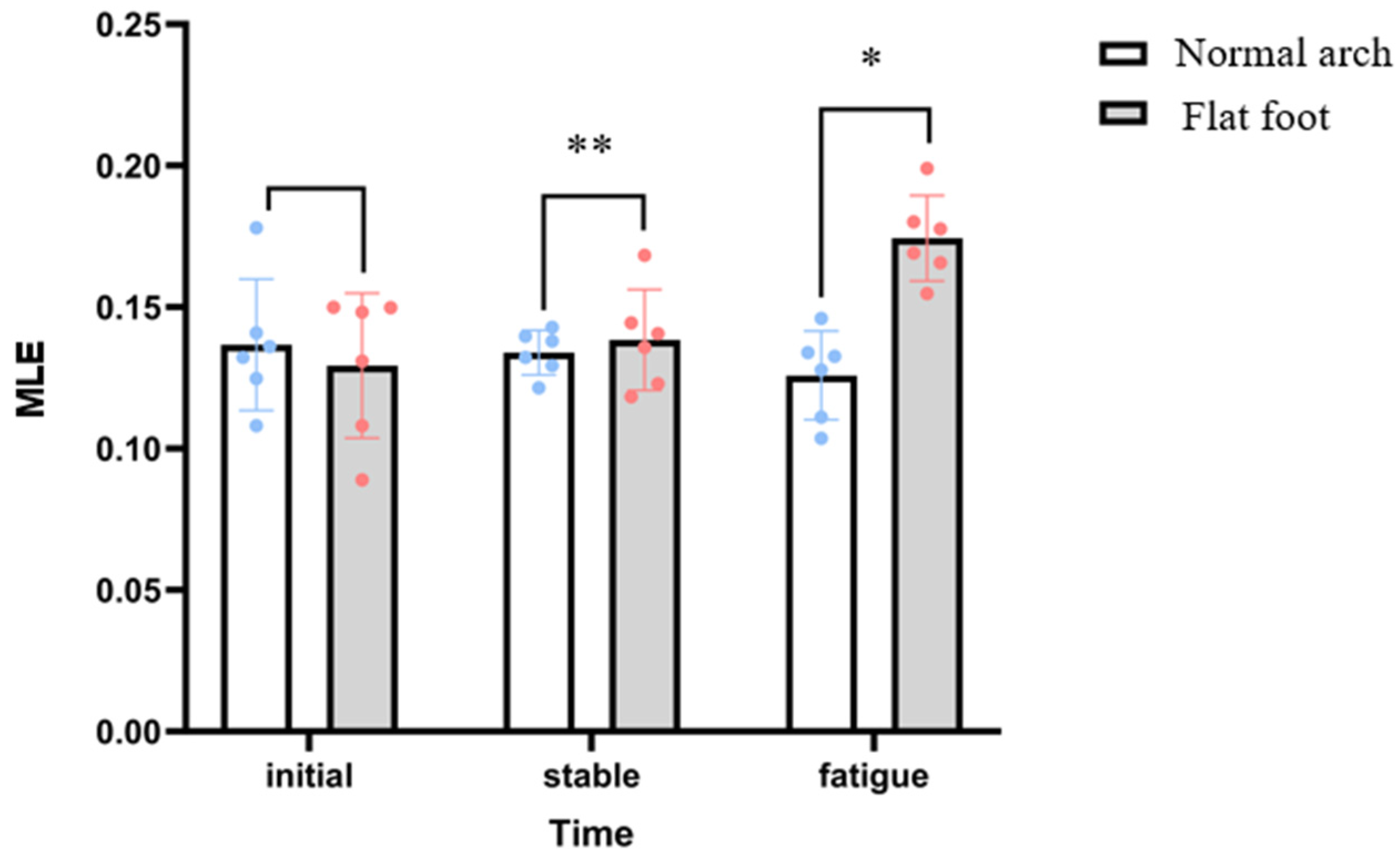
3.1. Lyapunov Exponent
3.2. Center of Pressure (COP) Parameters
3.3. Plantar Mechanics Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MLE | Maximum Lyapunov Exponent |
| IMUs | Inertial measurement units |
| COP | Center of pressure |
| VPSI | Vertical Postural Stability Index |
| DPSI | Dynamic Postural Stability Index |
| LDS | Local Dynamic Stability |
References
- Granata, K.P.; England, S.A. Stability of dynamic trunk movement. Spine 2006, 31, E271–E276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.L.; Powers, C.M. Influence of trunk posture on lower extremity energetics during running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuillerme, N.; Pinsault, N. Re-weighting of somatosensory inputs from the foot and the ankle for controlling posture during quiet standing following trunk extensor muscles fatigue. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 183, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meardon, S.; Klusendorf, A.; Kernozek, T. Influence of injury on dynamic postural control in runners. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2016, 11, 366–377. [Google Scholar]
- Nachbauer, W.; Nigg, B.M. Effects of arch height of the foot on ground reaction forces in running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1992, 24, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.S.; McClay, I.S.; Hamill, J.; Buchanan, T.S. Lower Extremity Kinematic and Kinetic Differences in Runners with High and Low Arches. J. Appl. Biomech. 2001, 17, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataabadi, P.A.; Abbassi, A.; Letafatkar, A.; Vanwanseele, B. The effects of foot orthosis and low-dye tape on lower limb joint angles and moments during running in individuals with pes planus. Gait Posture 2022, 96, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarian, M.; Esmaeili, H. Effects of running-induced fatigue on plantar pressure distribution in novice runners with different foot types. Gait Posture 2016, 48, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boozari, S.; Jamshidi, A.A.; Sanjari, M.A.; Jafari, H. Effect of Functional Fatigue on Vertical Ground-Reaction Force in Individuals With Flat Feet. J. Sport Rehabil. 2013, 22, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, N.A.; Chaudhari, A.M.W. Neuromuscular and trunk control mediate factors associated with injury in fatigued runners. J. Biomech. 2024, 170, 112176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, S.; Sanjari, M.A. Effect of noise and filtering on largest Lyapunov exponent of time series associated with human walking. J. Biomech. 2017, 64, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Wei, M.Y.; Chen, Y.J. Multiple inertial measurement unit combination and location for recognizing general, fatigue, and simulated-fatigue gait. Gait Posture 2022, 96, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutaayamou, M.; Pelzer, D.; Schwartz, C.; Gillain, S.; Garraux, G.; Croisier, J.L.; Verly, J.G.; Brüls, O. Toward Convenient and Accurate IMU-Based Gait Analysis. Sensors 2025, 25, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, H.; Caban, M.; Keller, U.; Courtine, G.; Ijspeert, A.; Vallery, H.; von Zitzewitz, J. Wearable Sensor-Based Real-Time Gait Detection: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, D.J.; Pinto, B.L.; Brown, S.H.M. Differential effects of muscle fatigue on dynamic spine stability: Implications for injury risk. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 43, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Rodgers, M.M. The arch index: A useful measure from footprints. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Yamashita, K.; Sato, M.; Kawasumi, M.; Ata, S. Analysis of skeletal characteristics of flat feet using three-dimensional foot scanner and digital footprint. Biomed. Eng. Online 2022, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Graham, M.; Gu, Y. Biomechanical analysis of the plantar and upper pressure with different sports shoes. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2014, 14, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Sun, D.; Xia, Z.; Shao, E.; Song, Y.; Sárosi, J.; Bíró, I.; Gao, Z.; Gu, Y. Estimating dynamic plantar pressure distribution from wearable inertial sensors using a hybrid CNN-BiLSTM architecture. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2025, 27, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, S.; Santillozzi, F.; Zinno, R.; Barone, G.; Bragonzoni, L. On-Field Biomechanical Assessment of High and Low Dive in Competitive 16-Year-Old Goalkeepers through Wearable Sensors and Principal Component Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walecka, I.; Gąsior, J.S.; Wieniawski, P.; Werner, B. Elite HRV smartphone application using Polar H10 is valid for short-term heart rate variability analysis in pediatric cardiac patients. Kardiol. Pol. 2024, 82, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, J.; Wolfarth, B.; Christle, J.W.; Pressler, A.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Halle, M. Associations between Borg’s rating of perceived exertion and physiological measures of exercise intensity. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimunová, M.; Bozděch, M.; Bernaciková, M.; Fernandes, R.; Kumstát, M.; Paludo, A. The relationship between low energy availability, injuries, and bone health in recreational female athletes. PeerJ. 2024, 12, e17533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Fekete, G.; Baker, J.S.; Liang, M.; Xuan, R.; Gu, Y. Effects of running fatigue on lower extremity symmetry among amateur runners: From a biomechanical perspective. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 899818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bötzel, K.; Marti, F.M.; Rodríguez, M.; Plate, A.; Vicente, A.O. Gait recording with inertial sensors--How to determine initial and terminal contact. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennerley, A.S.; Dunn, M.; Middleton, K.; Webster, K.E.; Wheat, J. The effect of run duration, gait variable and Lyapunov exponent algorithm on the inter-session reliability of local dynamic stability in healthy young people. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2025, 99, 103325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Song, Y.; Sun, D.; Cen, X.; Wang, M.; Lu, Z.; Gu, Y. Impact of Becker muscular dystrophy on gait patterns: Insights from biomechanical analysis. Gait Posture 2025, 121, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini Panebianco, G.; Bisi, M.C.; Stagni, R.; Fantozzi, S. Analysis of the performance of 17 algorithms from a systematic review: Influence of sensor position, analysed variable and computational approach in gait timing estimation from IMU measurements. Gait Posture 2018, 66, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Gu, Y.; Wang, A.; Mei, Q.; Yu, P.; Shim, V.; Fernandez, J. Effect of foot pronation during distance running on the lower limb impact acceleration and dynamic stability. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2022, 24, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, A.M.; Swinney, H.L. Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information. Phys. Rev. A Gen. Phys. 1986, 33, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennel, M.B.; Brown, R.; Abarbanel, H.D. Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Phys. Rev. A. 1992, 45, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffalt, P.C.; Kent, J.A.; Wurdeman, S.R.; Stergiou, N. Selection Procedures for the Largest Lyapunov Exponent in Gait Biomechanics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdizadeh, S. The largest Lyapunov exponent of gait in young and elderly individuals: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2018, 60, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauchly, J.W. Significance Test for Sphericity of a Normal n-Variate Distribution. Ann. Math. Stat. 1940, 11, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H. The greenhouse-geisser correction. Encycl. Res. Des. 2010, 1, 544–548. [Google Scholar]
- Paillard, T. Effects of general and local fatigue on postural control: A review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercovitz, T.; Herman, A.; Solomonow-Avnon, D.; Wolf, A.; Kodesh, E. Plantar pressure modifications in experienced runners following an exhaustive run. Sports Biomech. 2022, 21, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.-Y.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, M.-M. The Comparison of the Difference in Foot Pressure, Ground Reaction Force, and Balance Ability According to the Foot Arch Height in Young Adults. Original Article. Ann. Appl. Sport Sci. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstein, M.T.; Collins, J.J.; De Luca, C.J. A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1993, 65, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldt, A.K.; Murley, G.S.; Butterworth, P.; Levinger, P.; Menz, H.B.; Landorf, K.B. The relationship between foot posture and lower limb kinematics during walking: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Kwon, Y.H.; Kim, C.S.; Ahn, S.H.; Park, S.H. Differences of ground reaction forces and kinematics of lower extremity according to landing height between flat and normal feet. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2012, 25, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ugbolue, U.C. Biomechanical Analysis of Lower Limbs Based on Unstable Condition Sports Footwear: A Systematic Review. Phys. Act. Health 2024, 8, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.W.; Ho, M.Y.M.; Loh, R.; Iskandar, M.N.S. Foot morphology and running gait pattern between the left and right limbs in recreational runners. Phys. Act. Health 2023, 7, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cen, X.; Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; Tan, Q.; Sun, D.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. A systematic review of finite element analysis in running footwear biomechanics: Insights for running-related musculoskeletal injuries. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2025, 24, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J.; Plisky, P. Using the Star Excursion Balance Test to assess dynamic postural-control deficits and outcomes in lower extremity injury: A literature and systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Indicator | Flat Feet Group (Forefatigue) | Flat Feet (Afterfatigue) | Normal Group (Forefatigue) | Normal Group (Afterfatigue) | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLE (s−1) | 0.129 ± 0.01 | 0.174 ± 0.006 | 0.134 ± 0.008 | 0.126 ± 0.006 | 8.365 | 0.020 |
| Maximum pressure (N/cm2) | 16.5 ± 2.05 | 16.9 ± 2.2 | 12.4 ± 0.9 | 11.8 ± 0.9 | 14.848 | 0.003 |
| Maximum force (N) | 400 ± 29.8 | 394.7 ± 47.8 | 396.5 ± 31.2 | 384.5 ± 29.2 | 8.881 | 0.014 |
| Contact time (%) of stance time (Midfoot) | 61.9 ± 3.1 | 63.5 ± 2.9 | 60.2 ± 2.2 | 61.4 ± 2.8 | 6.120 | 0.033 |
| Stance phase (%) | 38.75 ± 4.99 | 37.12 ± 4.08 | 37.92 ± 3.41 | 34.5 ± 1.03 | 4.92 | 0.048 |
| Swing phase (%) | 61.23 ± 4.97 | 62.88 ± 4.08 | 62.08 ± 3.43 | 65.5 ± 1.03 | 5.03 | 0.046 |
| Length of gait line (mm) | 244.6 ± 12.9 | 230.6 ± 13.5 | 259.9 ± 5.6 | 252.3 ± 7.8 | 4.996 | 0.049 |
| Max gait line velocity (cm/sec) | 744.6 ± 162.5 | 932.3 ± 161.2 | 424.6 ± 95.7 | 710.7 ± 207.1 | 18.723 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Xiang, L.; Song, Y.; Sun, D.; Radak, Z.; Cen, X. Impact of Fatigue on Spine Dynamic Stability and Gait Patterns in Runners with Moderate Flatfoot Versus Normal Arch. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111256
Xu Z, Gao Z, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Pan J, Xiang L, Song Y, Sun D, Radak Z, Cen X. Impact of Fatigue on Spine Dynamic Stability and Gait Patterns in Runners with Moderate Flatfoot Versus Normal Arch. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111256
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zihang, Zixiang Gao, Zhanyi Zhou, Yucheng Wang, Jianqi Pan, Liangliang Xiang, Yang Song, Dong Sun, Zsolt Radak, and Xuanzhen Cen. 2025. "Impact of Fatigue on Spine Dynamic Stability and Gait Patterns in Runners with Moderate Flatfoot Versus Normal Arch" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111256
APA StyleXu, Z., Gao, Z., Zhou, Z., Wang, Y., Pan, J., Xiang, L., Song, Y., Sun, D., Radak, Z., & Cen, X. (2025). Impact of Fatigue on Spine Dynamic Stability and Gait Patterns in Runners with Moderate Flatfoot Versus Normal Arch. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111256











