Application of CAD Systems in Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview of Systematic Reviews
Abstract
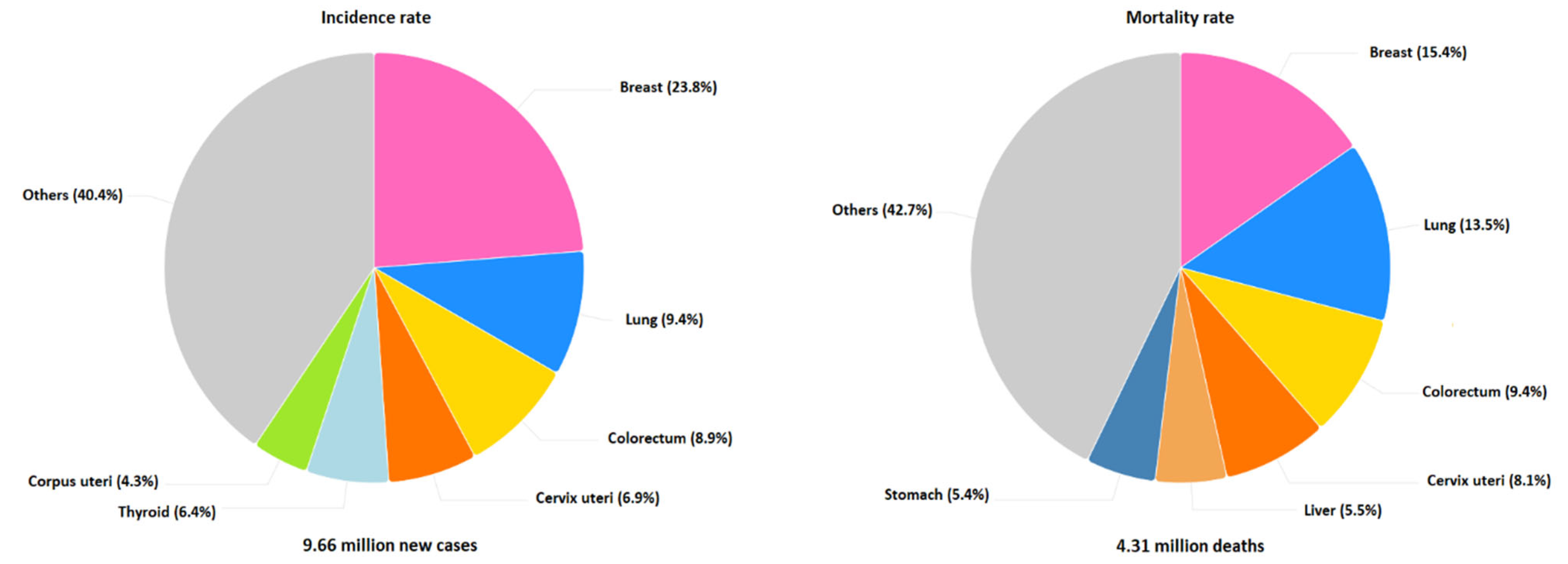
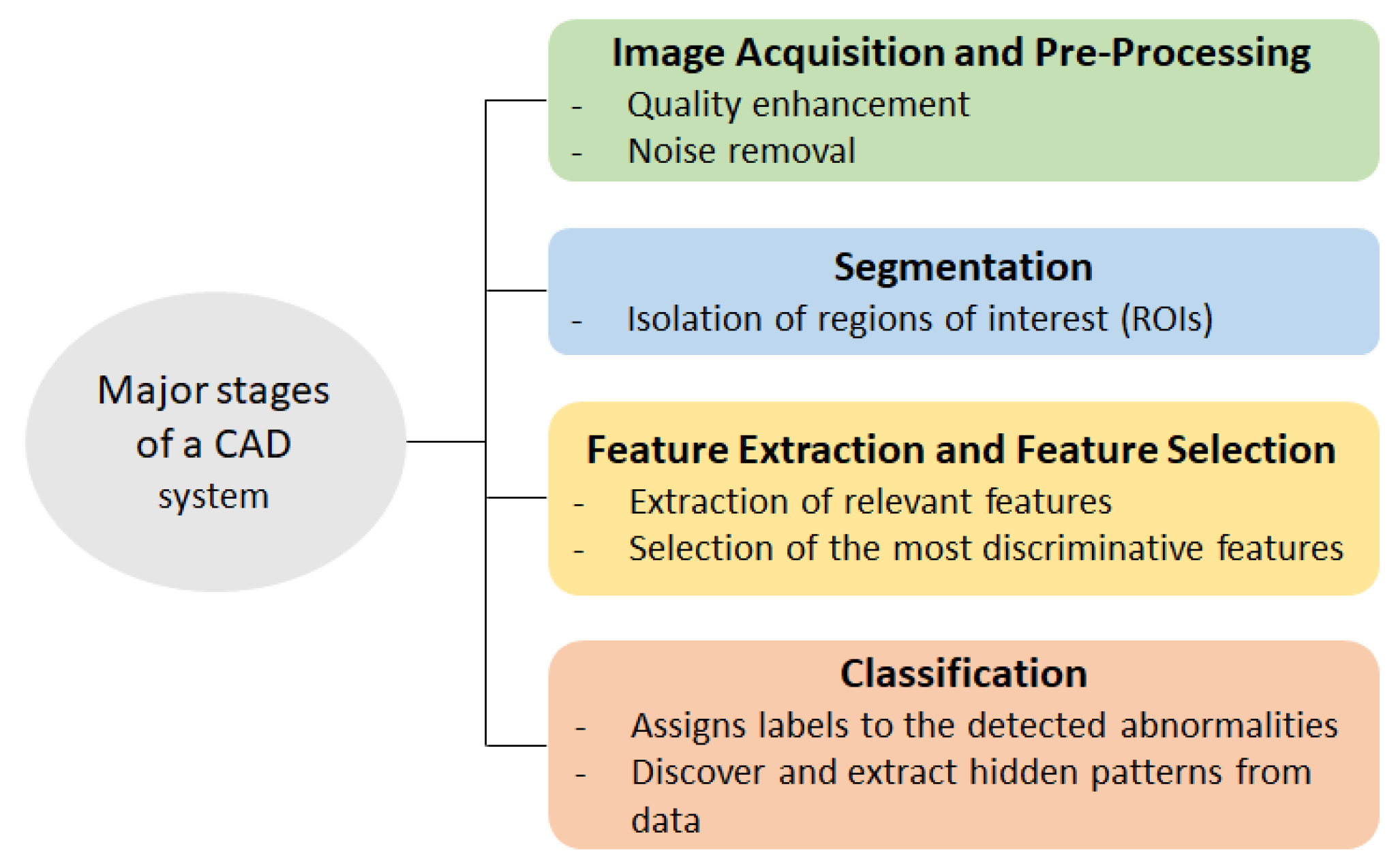
1. Introduction
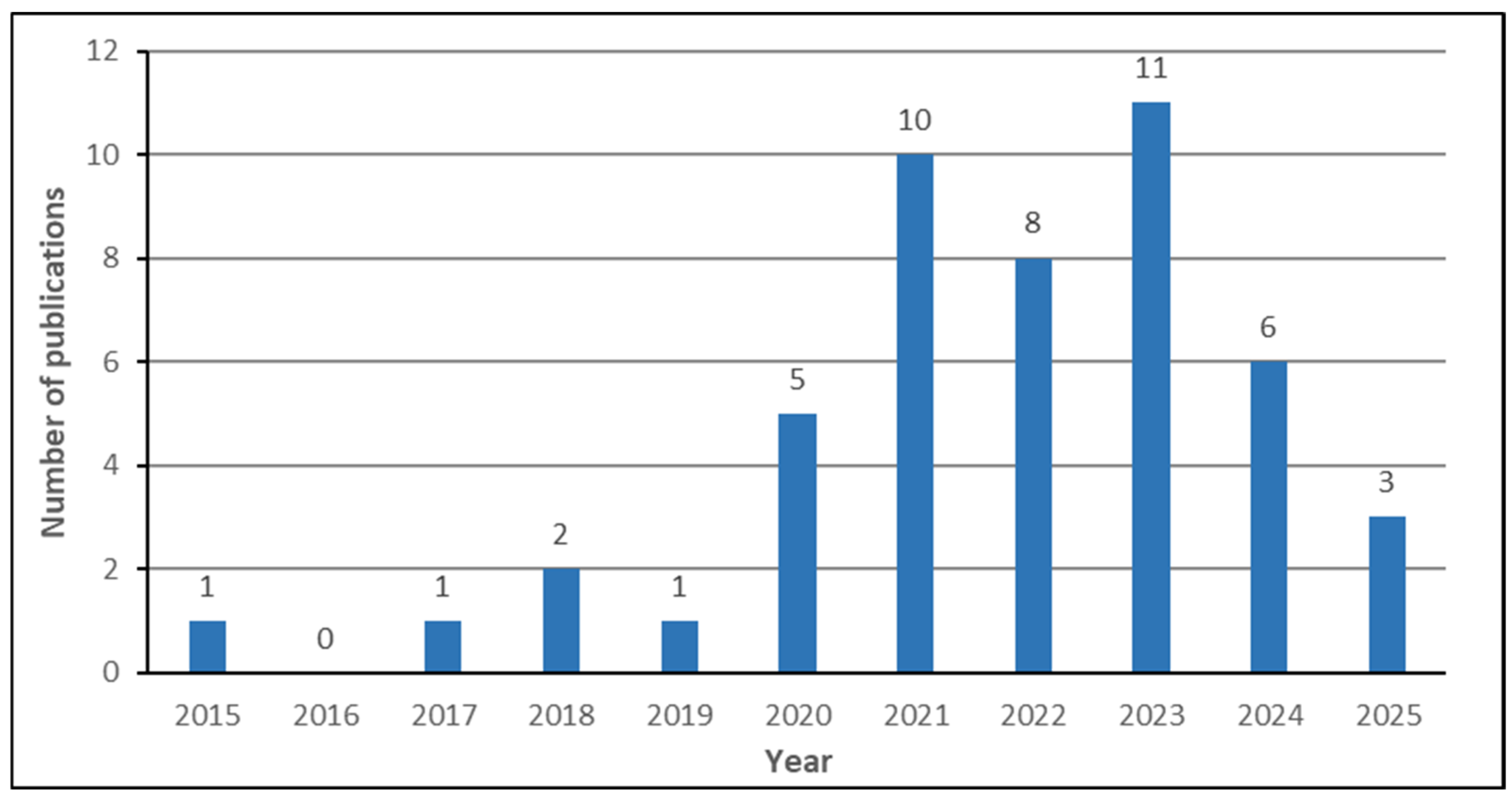
2. Materials and Methods
- What is the chronological growth of published reviews on breast cancer CAD systems?
- Which are the different imaging modalities used for breast cancer diagnosis, and what are their strengths and limitations?
- Which publicly available medical imaging datasets are utilized by the researchers to develop breast cancer CAD systems?
- Which are the most common ML techniques currently applied in breast cancer CAD systems based on medical imaging?
- What performance evaluation metrics are implemented to assess the performance of the developed breast cancer CAD systems?
- Which medical tasks are most frequently tackled by the breast cancer CAD systems?
- What are the current challenges and opportunities in the field of breast cancer diagnosis using CAD systems?
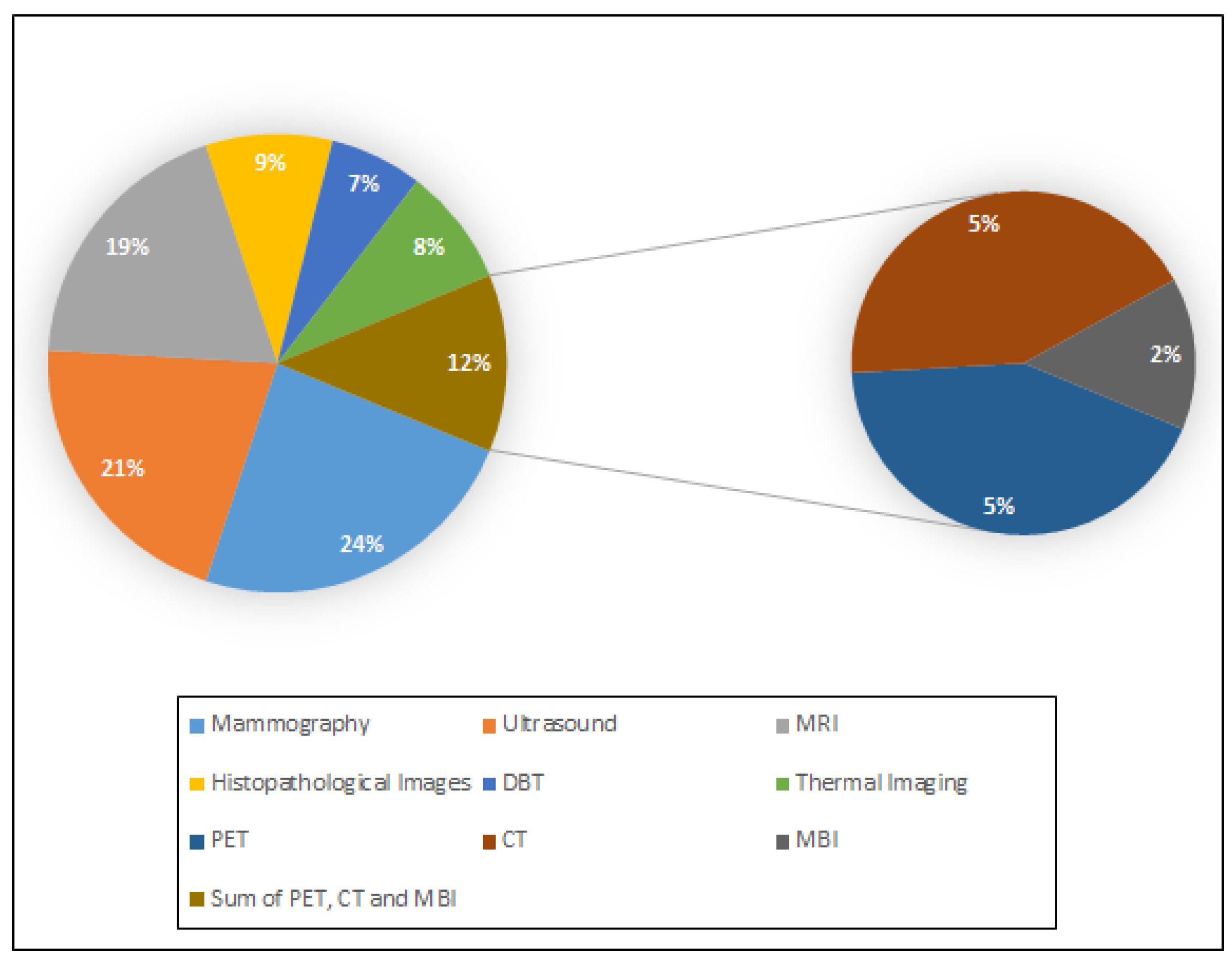
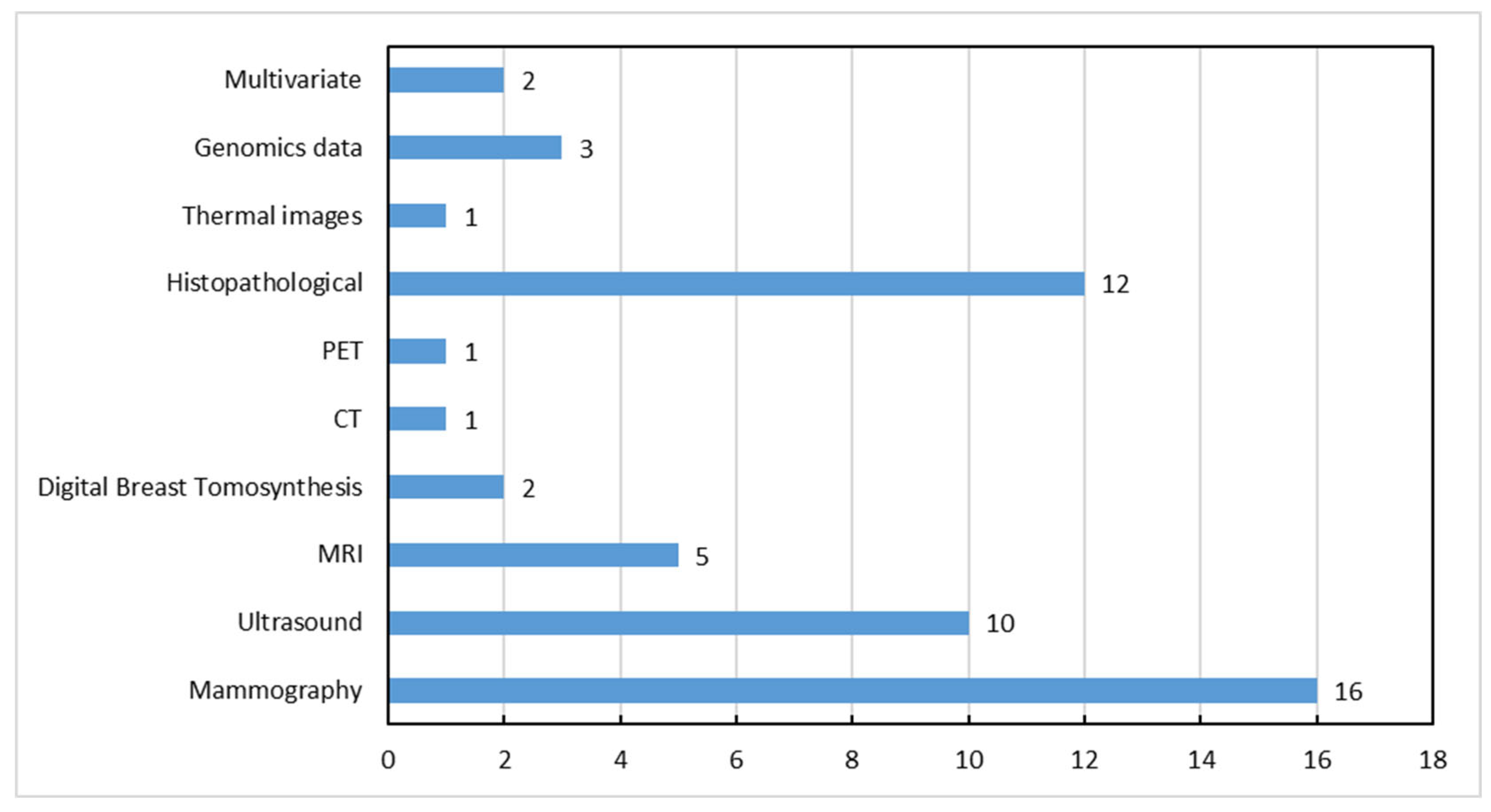
3. Imaging Modalities and Available Datasets for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
3.1. Mammography
3.2. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT)
3.3. Ultrasound
3.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
3.5. Histopathology
3.6. Thermography
3.7. Computed Tomography (CT)
3.8. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
3.9. Microwave Breast Imaging (MBI)
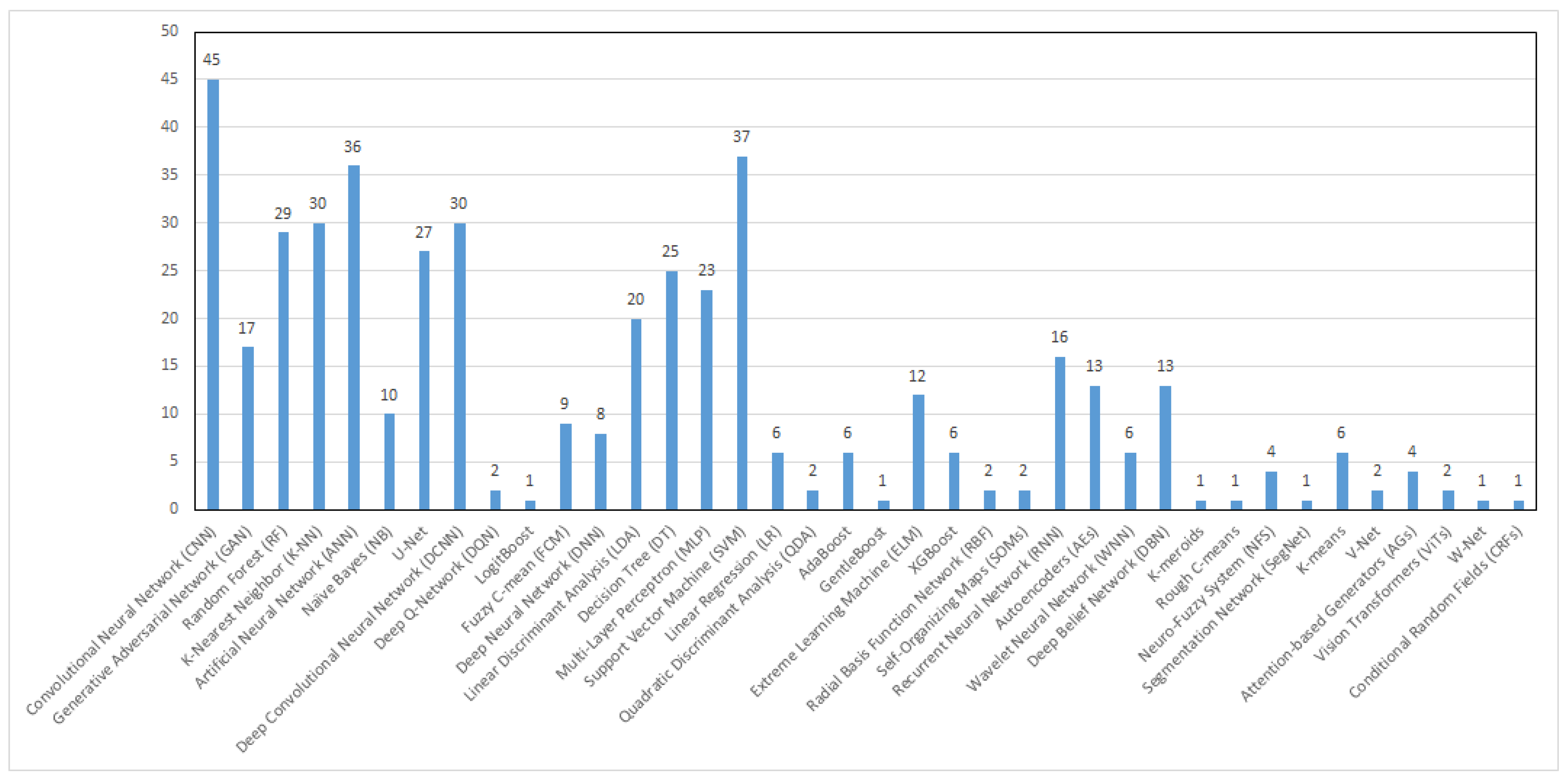
4. Machine Learning Techniques Applied in Breast Cancer CAD Systems
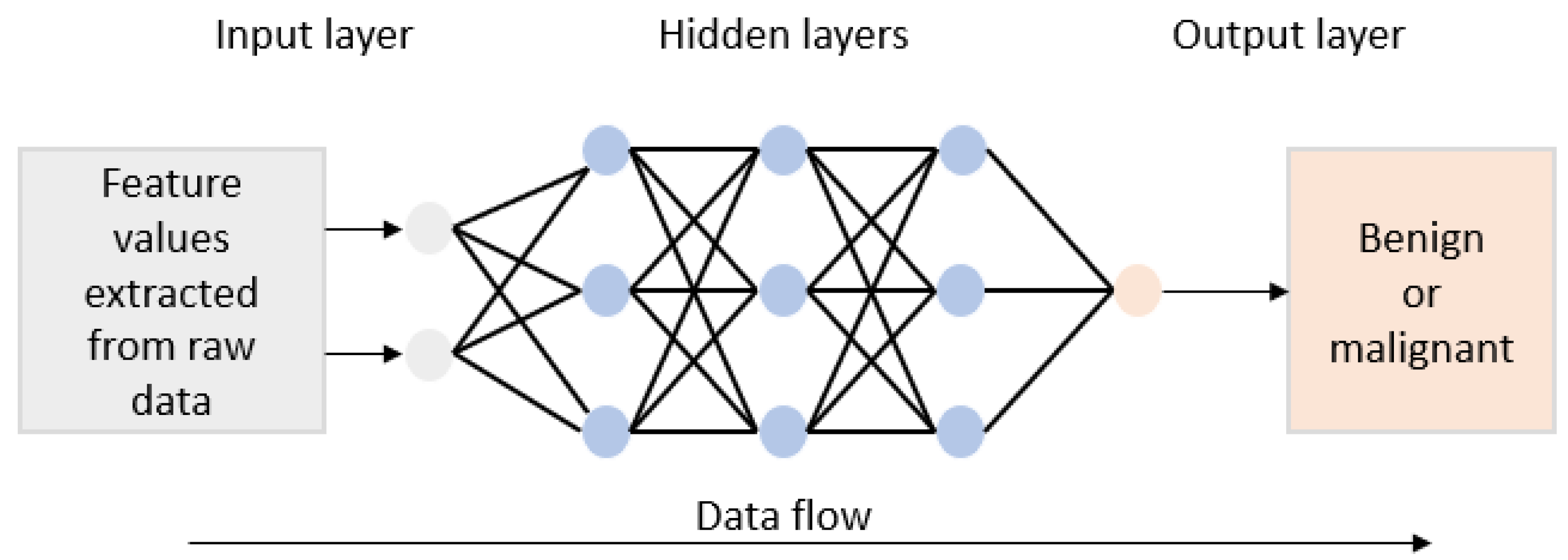
4.1. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
4.2. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
4.3. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
4.4. K-Nearest Neighbor (K-NN)
4.5. Decision Tree (DT) and Random Forest (FR)
4.6. Discriminant Analysis (DA)
4.7. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
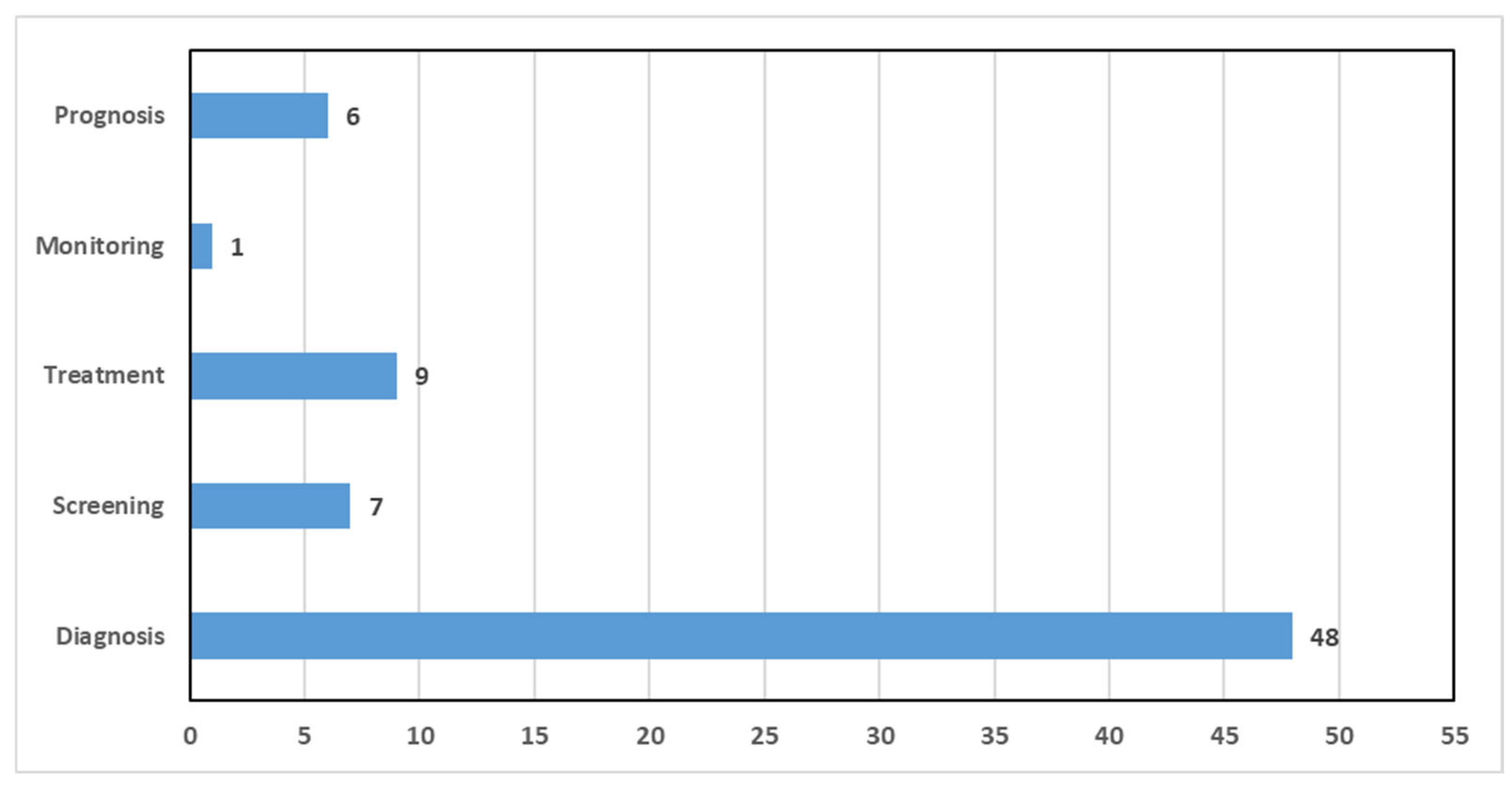
5. Medical Tasks Tackled by Breast Cancer CAD Systems
6. Evaluation Metrics
- True positive (TP), i.e., the number of patients for whom the system predicts that they are suffering from cancer, and they actually do.
- True negative (TN), i.e., the number of patients for whom the system predicts that they are not suffering from cancer, and they actually do not.
- False positive (FP), i.e., the number of patients who are predicted to be suffering from cancer but are not, in fact, suffering from cancer.
- False negative (FN), i.e., the number of patients predicted as healthy patients but in fact, they are suffering from cancer.
7. Discussion
8. Challenges and Future Work
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Apparent Diffusion Coefficient |
| AEs | Autoencoders |
| AGs | Attention-based Generators |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| AUC | Area Under Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| BDT | Boosted Decision Tree |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Diagnosis |
| CC | Craniocaudal View |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CRF | Conditional Random Field |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DBN | Deep Belief Network |
| DBT | Digital Breast Tomosynthesis |
| DCE-MRI | Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DM | Digital Mammogram |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network |
| DSC | Dice Similarity Coefficient |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| DTF | Decision Tree Forest |
| DWI-MRI | Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machine |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| EUSOBI | European Society of Breast Imaging |
| FCM | Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| GLCM | Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix |
| GLRM | Gray-Level Run-Length Matrix |
| GMM | Gaussian Mixture Model |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IRT | Infrared Thermography |
| K-NN | K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| LR | Linear Regression |
| MBI | Microwave Breast Imaging |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLO | Mediolateral Oblique View |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NAC | Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy |
| NB | Naïve Bayes Classifier |
| NFS | Neuro-Fuzzy System |
| OPF | Optimum-Path Forest |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication Systems |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| QDA | Quadratic Discriminant Analysis |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function Network |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit Function |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| SDT | Single Decision Tree |
| SegNet | Segmentation Network |
| SFM | Screen Film Mammogram |
| SOM | Self-Organizing Map |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TN | True Negative |
| TP | True Positive |
| UF-MRI | Ultrafast Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| US | Ultrasound |
| ViTs | Vision Transformers |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WNNs | Wavelet Neural Networks |
| WSI | Whole-Slide Image |
| XAI | Explainable AI |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast cancer-epidemiology, risk factors, classification, prognostic markers, and current treatment strategies-an updated review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörmann, B. Breast cancer: Basics, screening, diagnostics and treatment. Med. Monatsschr Pharm. 2017, 40, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, B.W.; Wild, C.P. World Cancer Report 2014. IARC Publications Website. 2014. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/Non-Series-Publications/World-Cancer-Reports/World-Cancer-Report-2014 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Miller, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Newman, L.A.; Minihan, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, L. Delay in breast cancer: Implications for stage at diagnosis and survival. Front. Public. Health 2014, 2, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Q. Multi-region radiomics for artificially intelligent diagnosis of breast cancer using multimodal ultrasound. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichter, I.; Lederman, R.; Buchbinder, S.; Bamberger, P.; Novak, B.; Fields, S. Optimizing parameters for computer-aided diagnosis of microcalcifications at mammography. Acad. Radiol. 2005, 7, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Rangayyan, R.M.; Xu, J.; El Naqa, I.; Yang, Y. Computer-aided detection and diagnosis of breast cancer with mammography: Recent advances. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Samala, R.K. Computer-aided diagnosis in the era of deep learning. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, e218–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalian, A.; Mashohor, S.; Mahmud, R.; Karasfi, B.; Saripan, M.I.B.; Ramli, A.R.B. Foundation and methodologies in computer-aided diagnosis systems for breast cancer detection. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, A. Using machine learning for healthcare challenges and opportunities. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 30, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, N.; Babavalian, M.R.; Moghadam, A.M.E.; Tabar, V.K. Knowledge discovery in medicine: Current issue and future trend. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4434–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbarzadeh, R.; Dorosti, S.; Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S.; Caputo, A.; Tirkolaee, E.B.; Ali, S.S.; Arshadi, Z.; Bendechache, M. Breast tumor localization and segmentation using machine learning techniques: Overview of datasets, findings, and methods. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssein, E.H.; Emam, M.M.; Ali, A.A.; Suganthan, P.N. Deep and machine learning techniques for medical imaging-based breast cancer: A comprehensive review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwimana, A.; Gnecco, G.; Riccaboni, M. Artificial intelligence for breast cancer detection and its health technology assessment: A scoping review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 184, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, M.; Behzadi, M.M.; Nabavi, S. The Role of Deep Learning in Advancing Breast Cancer Detection Using Different Imaging Modalities: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 4, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, N.I.R.; Omran, S.; El Houby, E.M.F.; Allam, H. Machine learning techniques for breast cancer computer aided diagnosis using different image modalities: A systematic review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 156, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriero, A.; Groenhoff, L.; Vologina, E.; Basile, P.; Albera, M. Deep Learning in Breast Cancer Imaging: State of the Art and Recent Advancements in Early 2024. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswathi, D.; Srinivasan, E. Computer-aided mammogram diagnosis system using deep learning convolutional fully complex-valued relaxation neural network classifier. IET Comput. Vision. 2017, 11, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadi, I.; Rae, W.; Clarke, J.; McEntee, M.; Ekpo, E. Diagnostic Performance of Adjunctive Imaging Modalities Compared to Mammography Alone in Women with Non-Dense and Dense Breasts: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Wei, J.; Sahiner, B.; Rafferty, E.A.; Wu, T.; Roubidoux, M.A.; Moore, R.H.; Kopans, D.B.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Helvie, M.A. Computer-aided Detection System for Breast Masses on Digital Tomosynthesis Mammograms: Preliminary Experience. Radiology 2005, 237, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinzi, F.; Orlando, A.; Gaglio, S.; Vitabile, S. Interpretable Radiomic Signature for Breast Microcalcification Detection and Classification. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 37, 1038–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Margolies, L.R.; Rothstein, J.H.; Fluder, E.; McBride, R.; Sieh, W. Deep Learning to Improve Breast Cancer Detection on Screening Mammography. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooley, R.J.; Durand, M.A.; Philpotts, L.E. Advances in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplack, S.P.; Tosteson, T.D.; Kogel, C.A.; Nagy, H.M. Digital breast tomosynthesis: Initial experience in 98 women with abnormal digital screening mammography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, H.S.; Kim, H.H.; Shin, H.J.; Cha, J.H.; Ruppel, P.L.; Oh, H.Y.; Chae, E.Y. Assessment of extent of breast cancer: Comparison between digital breast tomosynthesis and full-field digital mammography. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, J.O.P.; Holland, K.; Veldhuis, W.B.; Mann, R.M.; Pijnappel, R.M.; Peeters, P.H.M.; Van Gils, C.H.; Karssemeijer, N. Volumetric breast density affects performance of digital screening mammography. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 162, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.F.; Guo, H.; Martin, L.J.; Sun, L.; Stone, J.; Fishell, E.; Jong, R.A.; Hislop, G.; Chiarelli, A.; Minkin, S.; et al. Mammographic density and the risk and detection of breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, M.S.; Han, W.; Koo, H.R.; Cho, N.; Chang, J.M.; Yi, A.; Park, I.A.; Noh, D.Y.; Choi, W.S.; Moon, W.K. Characteristics of breast cancers detected by ultrasound screening in women with negative mammograms. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1862–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Arao, R.F.; Sprague, B.L.; Kerlikowske, K.; Lehman, C.D.; Smith, R.A.; Henderson, L.M.; Rauscher, G.H.; Miglioretti, D.L. Performance of Screening Ultrasonography as an Adjunct to Screening Mammography in Women Across the Spectrum of Breast Cancer Risk. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruchtman Brot, H.; Mango, V.L. Artificial intelligence in breast ultrasound: Application in clinical practice. Ultrasonography 2024, 43, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.A.; Liberman, L. Breast MRI: Diagnosis and Intervention, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, R.M.; Athanasiou, A.; Baltzer, P.A.T.; Camps-Herrero, J.; Clauser, P.; Fallenberg, E.M.; Forrai, G.; Fuchsjäger, M.H.; Helbich, T.H.; Killburn-Toppin, F.; et al. Breast cancer screening in women with extremely dense breasts recommendations of the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI). Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 4036–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Strobel, K.; Bieling, H.; Leutner, C.; Schild, H.H.; Schrading, S.; Supplemental Breast, M.R. Imaging Screening of Women with Average Risk of Breast Cancer. Radiology 2017, 283, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssami, N.; Hayes, D.F. Review of preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in breast cancer: Should MRI be performed on all women with newly diagnosed, early stage breast cancer? CA Cancer J. Clin. 2009, 59, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Yu, X.; Sahoo, D.; Mazurowski, M.A. Effects of MRI scanner parameters on breast cancer radiomics. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 87, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mridha, M.F.; Hamid, M.A.; Monowar, M.M.; Keya, A.J.; Ohi, A.Q.; Islam, M.R.; Kim, J.M. A Comprehensive Survey on Deep-Learning-Based Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Iqbal, S.; Ayesha, H.; Abbas, I.; Ahmad, K.T.; Niazi, M.F.K. Medical image based breast cancer diagnosis: State of the art and future directions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, M.A.; Jagannath, M. Detection of breast cancer on digital histopathology images: Present status and future possibilities. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2017, 8, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhisheka, B.; Biswas, S.K.; Purkayastha, B. A Comprehensive Review on Breast Cancer Detection, Classification and Segmentation Using Deep Learning. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 5023–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, X.Y.; Hameed, N.; Clos, J. A Review of Computer-Aided Expert Systems for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, F.; Ren, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, S. A Selective Review of Multi-Level Omics Data Integration Using Variable Selection. High Throughput 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantanowitz, L.; Valenstein, P.N.; Evans, A.J.; Kaplan, K.J.; Pfeifer, J.D.; Wilbur, D.C.; Collins, L.C.; Colgan, T.J. Review of the current state of whole slide imaging in pathology. J. Pathol. Inform. 2011, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, F.A.; Da Costa, C.A.; Roehe, A.V.; Righi, R.D.R. Marques NMC Breast cancer intelligent analysis of histopathological data: A systematic review. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 113, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossam, A.; Harb, H.M.; Abd El Kader, H.M. Automatic image segmentation method for breast cancer analysis using thermography. J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 46, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashekova, A.; Zhao, Y.; Ng, E.Y.K.; Zarikas, V.; Fok, S.C.; Mukhmetov, O. Early detection of the breast cancer using infrared technology—A comprehensive review. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 27, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchartt, T.B.; Conci, A.; Lima, R.C.F.; Resmini, R.; Sanchez, A. Breast thermography from an image processing viewpoint: A survey. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 2785–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, A.K. Role of image thermography in early breast cancer detection- Past, present and future. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 183, 105074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desperito, E.; Schwartz, L.; Capaccione, K.M.; Collins, B.T.; Jamabawalikar, S.; Peng, B.; Patrizio, R.; Salvatore, M.M.; Chest, C.T. for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Life 2022, 12, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, B.M.; FitzGerald, P.F.; Edic, P.M.; Lambert, J.W.; Colborn, R.E.; Marino, M.E.; Evans, P.M.; Roberts, J.C.; Wang, Z.J.; Wong, M.J.; et al. Opportunities for new CT contrast agents to maximize the diagnostic potential of emerging spectral CT technologies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 113, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhu, J.; Hong, C.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X. Diagnostic accuracy of cone-beam breast computed tomography and head-to-head comparison of digital mammography, magnetic resonance imaging and cone-beam breast computed tomography for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gland. Surg. 2023, 12, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, F.L.; Dehdashti, F.; Siegel, B.A. PET in breast cancer. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1998, 28, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercher-Conejero, J.L.; Pelegrí-Martinez, L.; Lopez-Aznar, D.; Cozar-Santiago, M.D.P. Positron Emission Tomography in Breast Cancer. Diagnostics 2015, 5, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Wu, N.; Qian, T.; Li, X.; Wan, D.Q.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Progress and Future Trends in PET/CT and PET/MRI Molecular Imaging Approaches for Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.M.; Strigel, R.M. Clinical advances in PET-MRI for breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, e32–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, M.G.; Naghavi-Behzad, M.; Vogsen, M. A role of FDG-PET/CT for response evaluation in metastatic breast cancer? Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSawaftah, N.; El-Abed, S.; Dhou, S.; Zakaria, A. Microwave Imaging for Early Breast Cancer Detection: Current State, Challenges, and Future Directions. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.; Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Q.Q.; Shi, W. Machine learning and new insights for breast cancer diagnosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2024, 52, 03000605241237867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basurto-Hurtado, J.A.; Cruz-Albarran, I.A.; Toledano-Ayala, M.; Ibarra-Manzano, M.A.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A. Diagnostic Strategies for Breast Cancer Detection: From Image Generation to Classification Strategies Using Artificial Intelligence Algorithms. Cancers 2022, 14, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Choi, J.Y. Impact of 18F-FDG PET, PET/CT, and PET/MRI on Staging and Management as an Initial Staging Modality in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.X.; Yin, L.; Hadjiloucas, S. Pattern classification approaches for breast cancer identification via MRI: State-of-the-art and vision for the future. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; N Qureshi, A.; Li, J.; Mahmood, T. On the Analyses of Medical Images Using Traditional Machine Learning Techniques and Convolutional Neural Networks. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3173–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalloul, R.; Chethan, H.K.; Alkhatib, R. A Review of Machine Learning Techniques for the Classification and Detection of Breast Cancer from Medical Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Mammography with deep learning for breast cancer detection. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1281922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulusu, G.; Vidyasagar, K.E.C.; Mudigonda, M.; Saikia, M.J. Cancer Detection Using Artificial Intelligence: A Paradigm in Early Diagnosis. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2025, 32, 2365–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Kumar, S.; Sasikala, S. Review on Deep Learning-Based CAD Systems for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231177977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loizidou, K.; Skouroumouni, G.; Nikolaou, C.; Pitris, C. A Review of Computer-Aided Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Sequential Mammograms. Tomography 2022, 8, 2874–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.; Kim, W.H. Artificial intelligence in breast ultrasonography. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.P.; Purwar, R.K. Computer-Aided Detection and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: A Review. ADCAIJ Adv. Distrib. Comput. Artif. Intell. J. 2024, 13, e31412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizidou, K.; Elia, R.; Pitris, C. Computer-aided breast cancer detection and classification in mammography: A comprehensive review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 153, 106554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkenende, L.; Teuwen, J.; Mann, R.M. Application of Deep Learning in Breast Cancer Imaging. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xie, J.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Li, B.; Yao, Y. A review of the current state of the computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems for breast cancer diagnosis. Open Life Sci. 2022, 17, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemade, V.; Pathak, S.; Dubey, A.K.; Deepti Barhate, D. A Review and Computational Analysis of Breast Cancer Using Different Machine Learning Techniques. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2022, 12, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Jiao, W.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Q. Deep Learning on Ultrasound Imaging for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment: Current Applications and Future Perspectives. Adv. Ultrasound Diagn. Ther. 2023, 7, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Samala, R.K.; Hadjiiski, L.M. CAD and AI for breast cancer-recent development and challenges. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, M.B.; Ayachi, F.L.; De Paiva, A.C.; Ksantini, R.; Mahjoubi, H. Harnessing Deep Learning for Early Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Review of Datasets, Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions. Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst. 2024, 16, 1643–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Gaona, Y.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, M.J.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Deep-learning-based computer-aided systems for breast cancer imaging: A critical review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebari, D.A.; Ibrahim, D.A.; Zeebaree, D.Q.; Haron, H.; Salih, M.S.; Damaševičius, R.; Mohammed, M.A. Systematic Review of Computing Approaches for Breast Cancer Detection Based Computer Aided Diagnosis Using Mammogram Images. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 2157–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, B.; Heacock, L.; Geras, K.J.; Moy, L. Machine learning in breast MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 998–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Das, P.K.; Meher, S. Recent advancements in machine learning and deep learning-based breast cancer detection using mammograms. Phys. Med. 2023, 114, 103138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoro, E.; Akhloufi, M.A. Applying Deep Learning for Breast Cancer Detection in Radiology. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 8767–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.; Khan, R.A.; Arif, S.; Sajid, U. Artificial intelligence for breast cancer analysis: Trends & directions. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 142, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Base, A.; Morra, L.; Tahmassebi, A.; Lobbes, M.; Meyer-Base, U.; Pinker, K. AI-Enhanced Diagnosis of Challenging Lesions in Breast MRI: A Methodology and Application Primer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Jalal, A.S.; Rai, R. Breast Cancer Image Classification: A Review. Curr. Med. Imaging 2021, 17, 720–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, W.M. The utilization of artificial intelligence applications to improve breast cancer detection and prognosis. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Sheng, D.L.; Chen, J.G.; You, C.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.X.; Chang, C. Artificial intelligence in breast imaging: Potentials and challenges. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 23TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.M.; Yin, M.; Yu, M.H.; Yu, J.; Zeng, S.E.; Lv, W.Z.; Li, J.; Ye, H.R.; Cui, X.W.; Dietrich, C.F. Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging of the Breast. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 600557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, H.; Larson, N.B.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Deep Learning in Different Ultrasound Methods for Breast Cancer, from Diagnosis to Prognosis: Current Trends, Challenges, and an Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, E.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Kulwa, F.; Li, J. Breast Cancer Segmentation Methods: Current Status and Future Potentials. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9962109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Karawi, D.; Al-Zaidi, S.; Helael, K.A.; Obeidat, N.; Mouhsen, A.M.; Ajam, T.; Alshalabi, B.A.; Salman, M.; Ahmed, M.H. A Review of Artificial Intelligence in Breast Imaging. Tomography 2024, 10, 705–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, N.; Calabrese, M.; Martinoli, C.; Tagliafico, A.S. Artificial Intelligence in Breast Ultrasound: From Diagnosis to Prognosis-A Rapid Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengec Tasdemir, S.B.; Tasdemir, K.; Aydin, Z. A review of mammographic region of interest classification. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 10, e1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosni, M.; Abnane, I.; Idri, A.; Carrillo de Gea, J.M.; Fernández Alemán, J.L. Reviewing ensemble classification methods in breast cancer. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 177, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, J.R.; Torosdagli, N.; Khosravan, N.; RaviPrakash, H.; Mortazi, A.; Tissavirasingham, F.; Hussein, S.; Bagci, U. Deep learning beyond cats and dogs: Recent advances in diagnosing breast cancer with deep neural networks. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithya, R.; Santhi, B. Computer aided diagnosis system for mammogram analysis: A survey. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2015, 5, 653–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelee, T.G.; Schwenker, F.; Ibenthal, A.; Yohannes, D. Survey of deep learning in breast cancer image analysis. Evol. Syst. 2020, 11, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, J.L.L.; He, G.S.; Ngiam, K.Y.; Hartman, M.; Ng, Q.X.; Goh, S.S.N. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence to Enhance Global Breast Cancer Care: A Scoping Review of Applications, Outcomes, and Challenges. Cancers 2025, 17, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannatdoust, P.; Valizadeh, P.; Saeedi, N.; Valizadeh, G.; Salari, H.M.; Saligheh Rad, H.; Gity, M. Computer-Aided Detection (CADe) and Segmentation Methods for Breast Cancer Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2025, 61, 2376–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Galelli, S.; Razavi, S.; Castelletti, A.; Rizzoli, A.; Athanasiadis, I.N.; Sànchez-Marrè, M.; Acutis, M.; Wu, W.; Humphrey, G.B. Exploding the myths: An introduction to artificial neural networks for prediction and forecasting. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 167, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Sohail, A.; Zahoora, U.; Qureshi, A.S. A survey of the recent architectures of deep convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5455–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Oerlemans, A.; Lao, S.; Wu, S.; Lew, M.S. Deep learning for visual understanding: A review. Neurocomputing 2016, 187, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, H.; Wu, D.; Vapnik, V.N. Support vector machines for spam categorization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejani, Y.; Selvi, S.T. Early detection of breast cancer using SVM classifier technique. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2009, 1, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayarajeswari, R.; Parthasarathy, P.; Vivekanandan, S.; Basha, A.A. Classification of mammogram for early detection of breast cancer using SVM classifier and Hough transform. Measurement 2019, 146, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiani, N.; Shawe-Taylor, J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-Based Learning Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chorowski, J.; Wang, J.; Zurada, J.M. Review and performance comparison of SVM- and ELM-based classifiers. Neurocomputing 2014, 128, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, B.; Yoon, S.W.; Ko, H.S. A support vector machine-based ensemble algorithm for breast cancer diagnosis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 267, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, A.; Hassanien, A.E.; Elnaghi, B.E. A BA-based algorithm for parameter optimization of Support Vector Machine. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 93, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Khanna, P. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Malignant Mammograms using Zernike Moments and SVM. J. Digit. Imaging 2015, 28, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H.; Bentley, J.L.; Finkel, R.A. An Algorithm for Finding Best Matches in Logarithmic Expected Time. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1977, 3, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaguru, H.; Sannasi Chakravarthy, S.R. Analysis of Decision Tree and K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm in the Classification of Breast Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 3777–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgel, P.; Sertbas, A.; Ucan, O.N. A comparative study of breast mass classification based on spherical wavelet transform using ANN and KNN classifiers. Int. J. Electron. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2012, 2, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Cherif, W. Optimization of K-NN algorithm by clustering and reliability coefficients: Application to breast-cancer diagnosis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 127, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.; Leong, T.Y. Application of K-nearest neighbors algorithm on breast cancer diagnosis problem. Proc. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. Annu. Symp. 2000, 759–763. [Google Scholar]
- Roshanpoor, A.; Ghazisaeidi, M.; Niakan Kalhor, S.R.; Maghooli, K.; Safdari, R. The Performance of K-Nearest Neighbors on Malignant and Benign Classes: Sensitivity, Specificity, and Accuracy Analysis for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 180, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, U.; Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Gudigar, A.; Tan, J.H.; Chokkadi, S. Application of gabor wavelet and locality sensitive discriminant analysis for automated identification of breast cancer using digitized mammogram images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 46, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Shuib, L.; Mujtaba, G.; Raza, G. Breast Cancer Multi-Classification through Deep Neural Network and Hierarchical Classification Approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 15481–15511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Larose, D.T. Discovering Knowledge in Data: An Introduction to Data Mining; Wiley Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sumbaly, R.; Vishnusri, N.; Jeyalatha, S. Diagnosis of breast cancer using decision tree data mining technique. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 98, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsagayathri, P.; Sampath, P. Performance analysis of breast cancer classification using decision tree classifiers. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2017, 9, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y. An improved random forest-based rule extraction method for breast cancer diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 86, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, A.; Cutler, D.R.; Stevens, J.R. Random Forests. In Ensemble Machine Learning; Zhang, C., Ma, Y., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 157–175. [Google Scholar]
- Azar, A.T.; El-Metwally, S.M. Decision tree classifiers for automated medical diagnosis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 23, 2387–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Senapati, M.R.; Beberta, S.; Lenka, S.K. Texture-based features for classification of mammograms using decision tree. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 23, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asri, H.; Mousannif, H.; Al Moatassime, H.; Noel, T. Using Machine Learning Algorithms for Breast Cancer Risk Prediction and Diagnosis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 83, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.B.; Passos, L.A.; Da Silva, L.A.; Da Costa, K.A.P.; Papa, J.P.; Romero, R.A.F. Unsupervised Breast Masses Classification through Optimum-Path Forest. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, Sao Carlos, Brazil, 27 July 2015; pp. 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghongade, R.D.; Wakde, D.G. Computer-aided diagnosis system for breast cancer using RF classifier. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, India, 22–24 March 2017; pp. 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubern-Merida, A.; Marti, R.; Melendez, J.; Hauth, J.L.; Mann, R.M.; Karssemeijer, N.; Platel, B. Automated localization of breast cancer in DCE-MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2015, 20, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; He, B.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, G. Preliminary Study on Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2018, 42, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularized linear discriminant analysis and its application in microarrays. Biostatistics 2007, 8, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.B. Mammographic Image Based Breast Tissue Classification with Kernel Self-optimized Fisher Discriminant for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 36, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esener, İ.I.; Ergin, S.; Yüksel, T. A new ensemble of features for breast cancer diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2015 38th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 25–29 May 2015; pp. 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhol, F.A.; Oliveira, L.S.; Petitjean, C.; Heutte, L. A Dataset for Breast Cancer Histopathological Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebaili, A.; Lapuyade-Lahorgue, J.; Ruan, S. Deep Learning Approaches for Data Augmentation in Medical Imaging: A Review. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Walia, E.; Babyn, P. Generative adversarial network in medical imaging: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hou, X.; Pan, M.; Zhang, H. Attention-based generative adversarial network in medical imaging: A narrative review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Loew, M. Breast cancer detection using synthetic mammograms from generative adversarial networks in convolutional neural networks. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 031411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Liu, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Zeng, T.; Gao, X.; Li, L. Generative adversarial network-based super-resolution of diffusion-weighted imaging: Application to tumour radiomics in breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2020, 33, e4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiecicki, A.; Konz, N.; Buda, M.; Mazurowski, M.A. A generative adversarial network-based abnormality detection using only normal images for model training with application to digital breast tomosynthesis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Rashwan, H.A.; Romani, S.; Akram, F.; Pandey, N.; Sarker, M.M.K.; Saleh, A.; Arenas, M.; Arquez, M.; Puig, D.; et al. Breast tumor segmentation and shape classification in mammograms using generative adversarial and convolutional neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 139, 112855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Catchpoole, D. A review of the machine learning datasets in mammography, their adherence to the FAIR principles and the outlook for the future. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
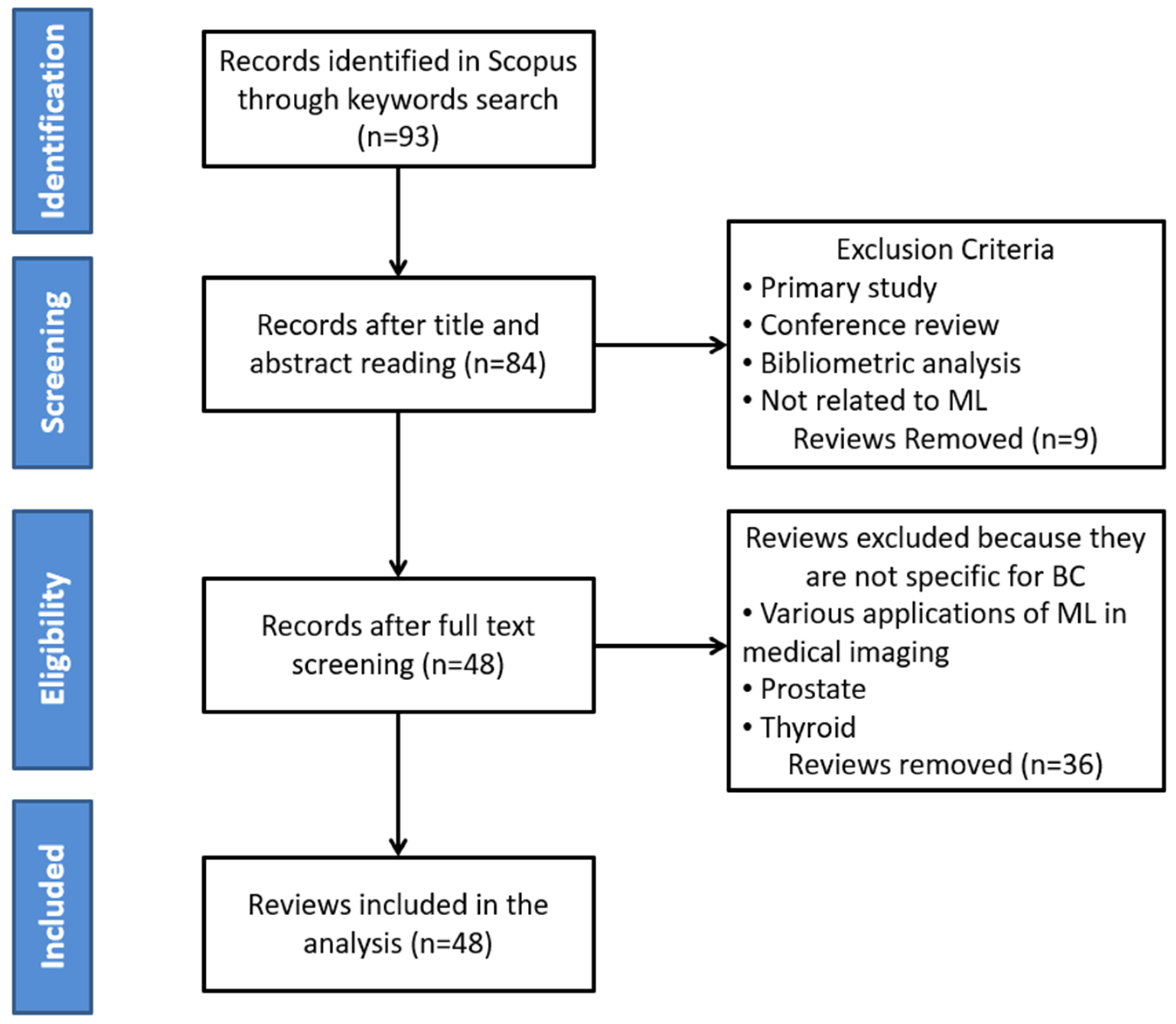

| Group A: Machine Learning-related keywords | Machine Learning AND Computer-Aided Diagnosis System |
| Group B: Medical-related keywords | Breast lesion AND Breast Tumor AND Breast cancer |
| Group C: Screening modalities related keywords | MRI OR Ultrasound OR Mammography OR Histopathological OR Thermography OR Digital Breast Tomosynthesis |
| Query | (Group A) AND (Group B) AND (Group C) |
| Cancers (6) | Ultrasonography (1) |
| Computers in Biology and Medicine (4) | Applied Artificial Intelligence (1) |
| Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (3) | Seminars in Nuclear Medicine (1) |
| Diagnostics (3) | Open Life Sciences (1) |
| British Journal of Radiology (2) | Physica Medica (1) |
| Expert Systems with Applications (2) | Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics (1) |
| Frontiers in Oncology (2) | BioMed Research International (1) |
| Tomography (2) | Current Oncology (1) |
| Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine (2) | Evolving Systems (1) |
| Saudi Medical Journal (1) | Current Medical Imaging (1) |
| Journal of International Medical Research (1) | Advanced Ultrasound in Diagnosis and Therapy (1) |
| Applied Sciences (Switzerland) (1) | EXCLI Journal (1) |
| Physics in Medicine and Biology (1) | Technology in Cancer Research and Treatment (1) |
| Advances in Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence Journal (1) | International Journal of Computing and Digital Systems (1) |
| International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering (1) | Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery (1) |
| Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering (1) |
| Imaging Modality | Principle | Radiation Exposure | Invasiveness | Suitable for | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammography | 2D imaging using low-intensity X-rays | Yes | Non-invasive | Routine breast cancer screening | - Widely available - Effective for detecting micro-calcifications - Cost-effective | - Low sensitivity in dense breasts - High false positive rate - Patient discomfort |
| DBT | 3D imaging using multiple low-intensity X-ray projections | Yes | Non-invasive | Breast cancer detection in dense breasts | - Reduces tissue overlap - Able to detect small tumors - Good for dense breasts | - Higher radiation exposure and additional reading time compared to mammography - Expensive |
| Ultrasound | Image generation using high-frequency sound waves | No | Non-invasive | Detecting and characterizing cystic vs. solid masses | - Widely available - Cost effective - No radiation - Good for dense breasts - Fast acquisition | - Operator dependent - Low specificity |
| MRI | Generation of high-quality 3D images using strong magnetic fields | No | Non-invasive | - Breast cancer detection in high-risk patients or patients with dense breasts - Staging evaluation - Assist in treatment planning | - High sensitivity - No radiation - Good for dense breasts | - Expensive - Low specificity - Time consuming - Limited availability |
| Histopathology | Breast tissue biopsy analyzed under a microscope | No | Invasive (Biopsy required) | Definitive cancer diagnosis | - Gold standard for diagnosing malignancy - Provides tumor molecular insights | - Invasive (requires sample collection) - Time consuming |
| Thermography | Detects heat patterns associated with higher metabolic activity | No | Non-invasive | Early detection based on metabolic activity | - No radiation - Painless - Cost effective - Suitable for frequent monitoring | - Low specificity - Affected by external factors (room temperature) |
| Computed Tomography | Generation of high-resolution cross-sectional images using X-ray beams | Yes | Minimally invasive (requires contrast agent injection) | - Staging and metastasis evaluation - Assist in treatment planning | - Able to detect distant metastases - Less costly than MRI | - Radiation exposure - Low contrast - Not ideal for routine screening |
| PET | Visualize and identify changes in metabolic processes of breast tissue using radiotracers | Yes | Minimally invasive (requires radiotracer injection) | - Detect advanced breast cancer - Staging evaluation - Assessing cancer metastases and disease recurrence | - Functional imaging - Detects metastases effectively | - Radiation exposure - Expensive |
| Microwave Breast Imaging | Use low-power microwave signals to differentiate breast tissue based on dielectric properties | No | Non-invasive | Potential alternative for early cancer detection | - No radiation - Painless - Cost effective | - Lower resolution - Still under research |
| Class | Number of Layers | Use Case | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow CNNs | 2–10 | Simple tasks, such as binary tumor classification (benign vs. malignant) on small datasets | LeNet-5, AlexNet |
| Moderately Deep CNNs | 10–50 |
| VGG-16, VGG-19, GoogLeNet |
| Deep CNNs | 50+ |
| ResNet, DenseNet, EfficientNet, DarkNet, ConvNeXt |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andreadis, T.; Gasteratos, A.; Seimenis, I.; Koulouriotis, D. Application of CAD Systems in Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111160
Andreadis T, Gasteratos A, Seimenis I, Koulouriotis D. Application of CAD Systems in Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111160
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndreadis, Theofilos, Antonios Gasteratos, Ioannis Seimenis, and Dimitrios Koulouriotis. 2025. "Application of CAD Systems in Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview of Systematic Reviews" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111160
APA StyleAndreadis, T., Gasteratos, A., Seimenis, I., & Koulouriotis, D. (2025). Application of CAD Systems in Breast Cancer Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111160








