A Community Benchmark for the Automated Segmentation of Pediatric Neuroblastoma on Multi-Modal MRI: Design and Results of the SPPIN Challenge at MICCAI 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Challenge Design
- The training phase ran from 14 April 2023 to 1 September 2023, for which data was available after signing a data release form.
- The preliminary test phase ran from 1 May 2023 to 1 September 2023. In the preliminary test phase, teams could test their method to ensure that the method behaved as expected. Teams had 5 attempts to submit their method in the preliminary test phase, and the best scoring method compared to the previous attempts was directly posted on the live leaderboard. This phase allowed teams to test and debug their methods and prevented the tweaking of results for the final leaderboard.
- The final test phase ran from the 14 August 2023 to 1 September 2023. Teams only had one attempt, and the results of this leaderboard were hidden until the SPPIN challenge session during MICCAI on 8 October 2023.
2.2. Datasets
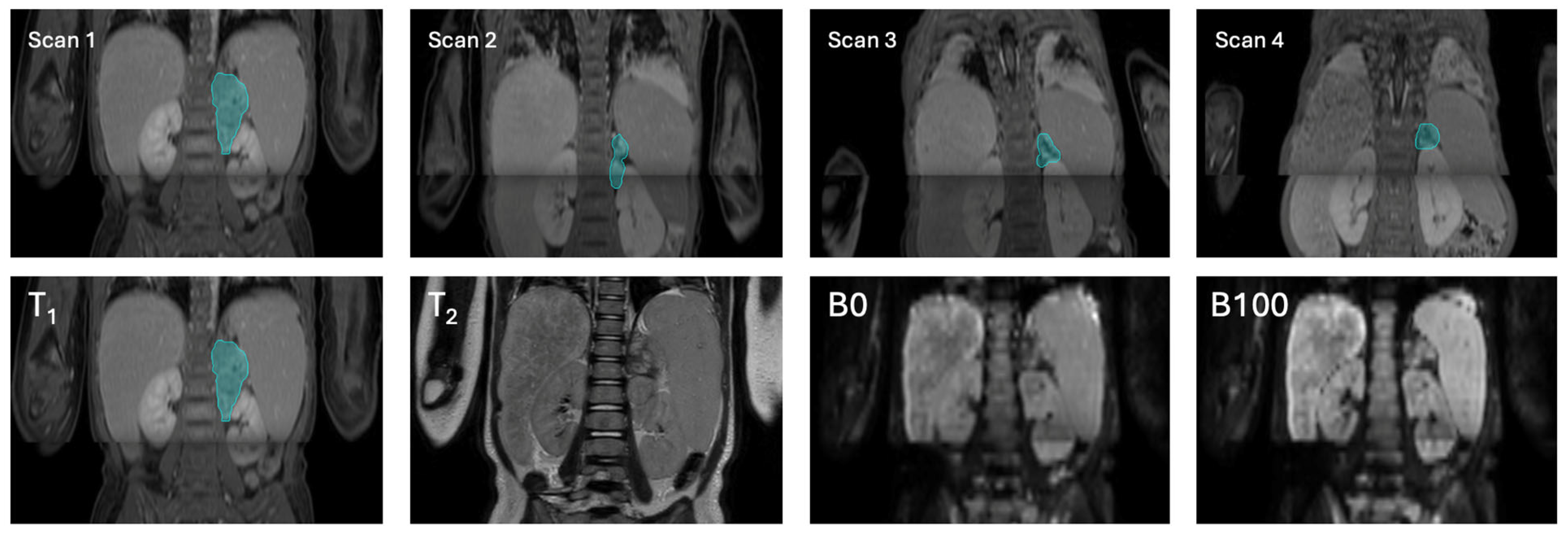
2.2.1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.2.2. Dataset Splits
2.2.3. Manual Annotation
2.3. Challenge Evaluation
2.3.1. Automated Evaluation and Ranking
2.3.2. Confounder Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Challenge Submission and Participating Teams
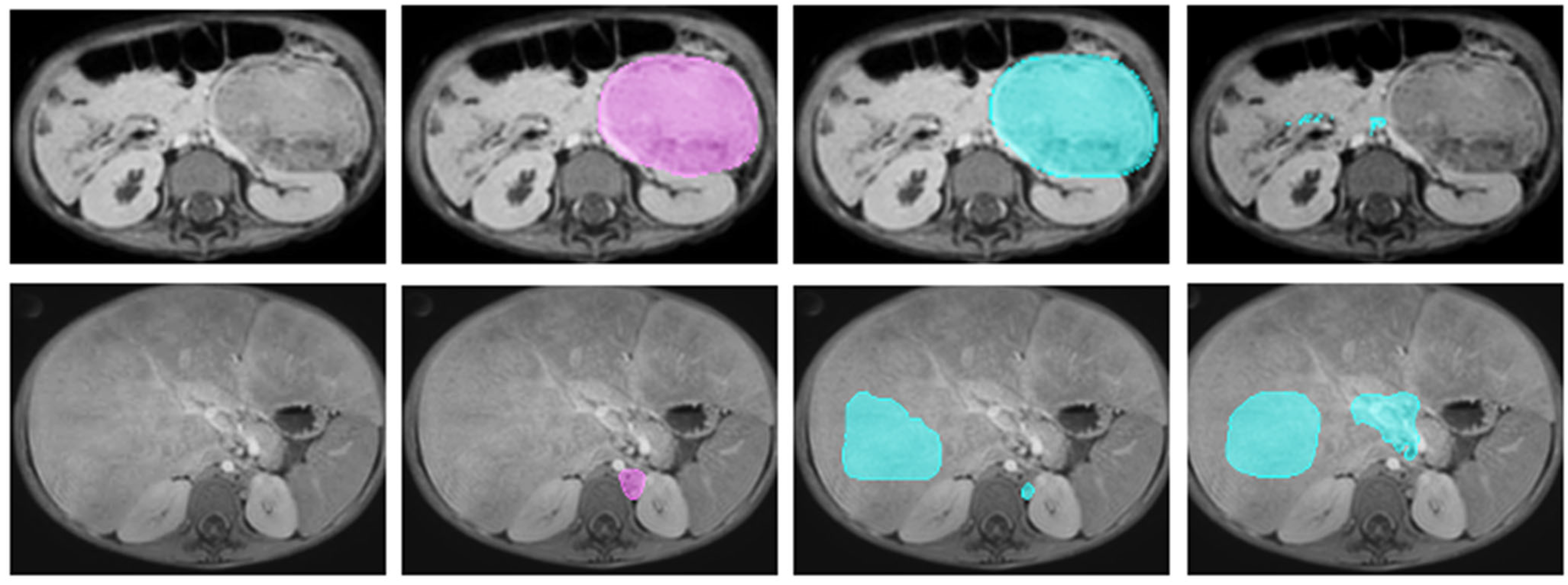
3.2. Metric Values and Ranking
3.3. Confounders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DCOG | Dutch Childhood Oncology Group |
| Dice score | Dice similarity coefficient |
| DL | Deep learning |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| HD95 | 95th percentile Hausdorff distance |
| MICCAI | Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| nnU-Net | No-New-U-Net (self-adapting U-Net segmentation framework) |
| SPPIN | Surgical Planning in PedIatric Neuroblastoma |
| STU-Net | Scalable and Transferable U-Net |
| T1 | T1-weighted MRI sequence |
| T2 | T2-weighted MRI sequence |
| VS | Volumetric similarity |
References
- Park, J.R.; Eggert, A.; Caron, H. Neuroblastoma: Biology, Prognosis, and Treatment. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 55, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Qi, F.; Bian, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Ren, L.; Li, M.; Tang, W. Comparison of Incidence and Outcomes of Neuroblastoma in Children, Adolescents, and Adults in the United States: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program Population Study. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e927218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, M.L.; Reedijk, A.M.J.; Karim-Kos, H.E.; Kremer, L.C.M.; van de Ven, C.P.; Dierselhuis, M.P.; van Eijkelenburg, N.K.A.; van Grotel, M.; Kraal, K.C.J.M.; Peek, A.M.L.; et al. Neuroblastoma between 1990 and 2014 in the Netherlands: Increased incidence and improved survival of high-risk neuroblastoma. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. 2020, 124, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Mer, J.; Lion, A.; Vik, T.A. Clinical Presentation, Evaluation, and Management of Neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 39, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaveling, S.; Tytgat, G.A.M.; van der Zee, D.C.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A.; Heij, H.A. Is complete surgical resection of stage 4 neuroblastoma a prerequisite for optimal survival or may >95% tumour resection suffice? Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2012, 28, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.C.; Clark, R.A.; Chung, D.H. High-Risk Neuroblastoma: A Surgical Perspective. Children 2023, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitski, M.; Meulstee, J.W.; Littooij, A.S.; Ven, C.P.V.D.; Steeg, A.F.W.V.D.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A. MRI-Based 3-Dimensional Visualization Workflow for the Preoperative Planning of Nephron-Sparing Surgery in Wilms’ Tumor Surgery: A Pilot Study. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8899049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, T.; Meulstee, J.W.; Köllen, M.H.; Van Doormaal, J.A.M.; Van Doormaal, T.P.C.; Hoving, E.W. Comparing the influence of mixed reality, a 3D viewer, and MRI on the spatial understanding of brain tumours. Front. Virtual Real 2023, 4, 12145204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussy, Y.; Vieille, L.; Lacroix, E.; Lenoir, M.; Marie, F.; Corbat, L.; Henriet, J.; Auber, F. 3D reconstruction of Wilms’ tumor and kidneys in children: Variability, usefulness and constraints. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2020, 16, 830.e1–830.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga-Canuto, D.; Cerdà-Alberich, L.; Sangüesa Nebot, C.; Martínez de las Heras, B.; Pötschger, U.; Gabelloni, M.; Carot Sierra, J.M.; Taschner-Mandl, S.; Düster, V.; Cañete, A.; et al. Comparative Multicentric Evaluation of Inter-Observer Variability in Manual and Automatic Segmentation of Neuroblastic Tumors in Magnetic Resonance Images. Cancers 2022, 14, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga-Canuto, D.; Cerdà-Alberich, L.; Jiménez-Pastor, A.; Carot Sierra, J.M.; Gomis-Maya, A.; Sangüesa-Nebot, C.; Fernández-Patón, M.; Martínez de Las Heras, B.; Taschner-Mandl, S.; Düster, V.; et al. Independent Validation of a Deep Learning nnU-Net Tool for Neuroblastoma Detection and Segmentation in MR Images. Cancers 2023, 15, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, I.; Yan, J.; Abbas, Q.; Shaheed, K.; Riaz, A.B.; Wahid, A.; Khan, M.W.J.; Szczuko, P. Medical image segmentation using deep semantic-based methods: A review of techniques, applications and emerging trends. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 316–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya Kayal, E.; Kandasamy, D.; Sharma, R.; Bakhshi, S.; Mehndiratta, A. Segmentation of osteosarcoma tumor using diffusion weighted MRI: A comparative study using nine segmentation algorithms. Signal Image Video Process 2020, 14, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, M.A.D.; van der Steeg, A.F.W.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A.; Fitski, M.; van Tinteren, H.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Littooij, A.S.; van der Velden, B.H.M. Radiologic versus Segmentation Measurements to Quantify Wilms Tumor Volume on MRI in Pediatric Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Farag, I.; Weickert, J.; Braun, Y.; Lollert, A.; Dobberstein, J.; Hötker, A.; Graf, N. Benchmarking Wilms’ tumor in multisequence MRI data: Why does current clinical practice fail? Which popular segmentation algorithms perform well? J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strijbis, V.I.J.; de Bloeme, C.M.; Jansen, R.W.; Kebiri, H.; Nguyen, H.-G.; de Jong, M.C.; Moll, A.C.; Bach-Cuadra, M.; de Graaf, P.; Steenwijk, M.D. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for automated ocular structure and tumor segmentation in retinoblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, R.; Lamki, N.; Fan, S.; Singleton, E.B.; Eftekhari, F.; Shirkhoda, A.; Kumar, R.; Madewell, J.E. The many faces of neuroblastoma. Radiogr. Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc. 1989, 9, 859–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, M.A.D.; Steeg, A.F.W.v.d.; Simons, D.C.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A.; Littooij, A.S.; ter Brugge, A.H.; Vos, I.N.; Velden, B.H.M. van der Surgical Planning in Pediatric Neuroblastoma. April 2023. Available online: https://sppin.grand-challenge.org/sppin/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- GitHub—Myrthebuser/SPPIN2023. Available online: https://github.com/myrthebuser/SPPIN2023 (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Dutch Childhood Oncology Group (DCOG) NBL 2009 Treatment Protocol 2009. Available online: https://www.skion.nl/richtlijn/dcog-nbl-2009/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Ritter, F.; Boskamp, T.; Homeyer, A.; Laue, H.; Schwier, M.; Link, F.; Peitgen, H.-O. Medical Image Analysis. IEEE Pulse 2011, 2, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.A.; Hanbury, A. Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: Analysis, selection, and tool. BMC Med. Imaging 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Deng, Z.; Ye, J.; Su, Y.; Sun, H.; He, J.; Gu, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhang, S.; et al. STU-Net: Scalable and Transferable Medical Image Segmentation Models Empowered by Large-Scale Supervised Pre-training 2023. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.06716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method fordeep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserthal, J.; Breit, H.-C.; Meyer, M.T.; Pradella, M.; Hinck, D.; Sauter, A.W.; Heye, T.; Boll, D.; Cyriac, J.; Yang, S.; et al. TotalSegmentator: Robust segmentation of 104 anatomical structures in CT images. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, e230024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Lin, F.; Chen, W.; Xu, M. Pre-training in Medical Data: A Survey. Mach. Intell. Res. 2023, 20, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, D.C.; Buser, M.A.D.; Fitski, M.; van de Ven, C.P.; Ten Haken, B.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A.; Tan, C.O.; van der Steeg, A.F.W. Multi-modal 3-Dimensional Visualization of Pediatric Neuroblastoma: Aiding Surgical Planning Beyond Anatomical Information. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2024, 59, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, S.; Singleton, K.W.; Curtin, L.; Paulson, L.; Clark-Swanson, K.; Hawkins-Daarud, A.; Mitchell, J.R.; Jackson, P.R.; Swanson, A.K.R. Towards Longitudinal Glioma Segmentation: Evaluating combined pre- and post-treatment MRI training data for automated tumor segmentation using nnU-Net. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Guan, Q.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Xia, Y. Advances in attention mechanisms for medical image segmentation. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2025, 56, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Hafiz, M.S.; Jim, J.R.; Kabir, M.M.; Mridha, M.F. A systematic review of deep learning data augmentation in medical imaging: Recent advances and future research directions. Healthc. Anal. 2024, 5, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhade, P.; Shirke, P. Federated Learning for Healthcare: A Comprehensive Review. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Han, M.; Wright, J.; Kuwabara, M.; Mevorach, J.; Fu, G.; Choudhury, O.; Ratan, U.; Zhang, M.; Wagner, M.W. An international study presenting a federated learning AI platform for pediatric brain tumors. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, F.; Corbat, L.; Chaussy, Y.; Delavelle, T.; Henriet, J.; Lapayre, J.-C. Segmentation of deformed kidneys and nephroblastoma using Case-Based Reasoning and Convolutional Neural Network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 127, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazerooni, A.F.; Khalili, N.; Liu, X.; Haldar, D.; Jiang, Z.; Anwar, S.M.; Albrecht, J.; Adewole, M.; Anazodo, U.; Anderson, H.; et al. The Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) Challenge 2023: Focus on Pediatrics (CBTN-CONNECT-DIPGR-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS-PEDs). arXiv 2024, arXiv:2305.17033v7. [Google Scholar]



| Sequence | T1-Weighted Gradient Echo | T2-Weighted Spin Echo | Diffusion-Weighted Imaging |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repetition time (ms) | 6.1 | 458 | 2537 |
| Echo time (ms) | 2.9 | 90 | 76.4 |
| Voxel size (mm3) | 0.71 × 0.71 × 3 | 0.833 × 0.833 × 1.15 | 1.39 × 1.39 × 5 |
| Dimensions (voxels) | 560 × 560 × Z | 480 × 480 × Z | 288 × 288 × Z |
| b-values (s/mm2) | N/A | N/A | 0, 100 |
| Contrast | Gadovist, 0.1 mmol/kg body weight | - | - |
| Training Set (n = 34) | Preliminary Test Set (n = 3) | Final Test Set (n = 9) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of included scans | 84 | 7 | 18 |
| Age in years at diagnosis (median, min–max) | 2.5 (0–11) | 2 (0–3) | 2 (0–12) |
| Sex | Male = 17 | Male = 2 | Male = 6 |
| Female = 17 | Female = 1 | Female = 3 | |
| Tumor volume in mL (median, min–max) | 53.48 (2.03–1249.7) | 7.7 (4.28–304.7) | 51.1 (4.9–745.4) |
| Team | Network | Input | Pre-Training | Preprocessing | Patch Size | Data Augmentation | Loss | Post-Processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blackbean | Scalable and Transferable U-Net | T1 | TotalSegmentor dataset | nnU-Net default | Yes, size not specified | Yes | Dice loss | N.R. |
| jishenyu | nnU-Net | T1, T2, DWI_b0, DWI_b100 | Pre-trained nnU-Net weights | Registration of input to T1 | N.R. | Yes | Dice + cross entropy loss | N.R. |
| Ouradiology | nnU-Net | T1 | N.R. | nnU-Net default | 64 × 288 × 288 | N.R. | nnU-Net default | nnU-Net default |
| Drehimpuls | nnU-Net | T1, T2, DWI_b0, DWI_b100 | N.R. | Resampling input to T1 space, z-score normalization | 128 × 128 × 128 | N.R. | Fbeta + cross entropy loss | Fallback network |
| SK | 2.5D U-Net, with EfficientNet as encoder | T1, T2 | N.R. | Resampling input to T1 space | N.R. | - | Dice + cross entropy loss | N.R. |
| AGHSSO | ResUNet | T1, T2, DWI_b0, DWI_b100 | N.R. | Resampling input to [2243], normalization | Whole image | Yes | Soft + focal loss | Delete connected components < 20 voxels |
| UNMC | DynUNet | T1, T2, DWI_b0, DWI_b100 | N.R. | Registration of input T1, foreground cropping, z-score intensity normalization, linear resampling [192 × 192 × 192] | N.R. | Yes | Dice loss | Selection of largest component |
| SPPIN_SCNU | UNETR | T1 | N.R. | N.R. | N.R. | Yes | N.R. | N.R. |
| GIBI230 | nnU-Net | T2 | N.R. | Resampling to [0.695 × 0.695 × 8] mm voxel size, z-score normalization | N.R. | N.R. | Dice loss | N.R. |
| Team Name | Median Dice [Min–Max] | Ranking Dice | Median HD95 (mm) | Ranking HD95 | Median VS | Ranking VS | Final Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blackbean | 0.82 [0.00–0.93] | 1 | 7.69 [2.82–127.35] | 1 | 0.91 [0.16–0.99] | 1 | 1 |
| Jishenyu | 0.79 [0.00–0.93] | 3 | 13.19 [2.83–146.91] | 2 | 0.86 [0.01–1.00] | 2 | 2 |
| Ouradiology | 0.80 [0.00– 0.94] | 2 | 15.91 [2.83–127.82] | 3 | 0.85 [0.04–0.99] | 4 | 3 |
| Drehimpuls | 0.77 [0.00–0.91] | 4 | 20.71 [3.16–129.65] | 4 | 0.85 [0.02–1.00] | 3 | 4 |
| SK | 0.57 [0.00–0.83] | 5 | 32.32 [5.48–128.51] | 6 | 0.77 [0.09–0.98] | 5 | 5 |
| AGHSSO | 0.48 [0.00–0.87] | 6 | 24.11 [6.08–132.51] | 5 | 0.64 [0.03–0.99] | 7 | 6 |
| UNMC | 0.40 [0.00–0.76] | 7 | 36.26 [11.58–116.97] | 7 | 0.69 [0.07–0.91] | 6 | 7 |
| SPPIN_SCNU | 0.24 [0.00–0.61] | 8 | 93.54 [27.20–274.0] | 9 | 0.58 [0.03–0.99] | 8 | 8 |
| GIBI230 | 0.21 [0.00–0.89] | 9 | 63.41 [5.48–170.38] | 8 | 0.31 [0.00–0.96] | 9 | 9 |
| Team | Mean Dice Diagnostic | Mean Dice Post-Chemo | p-Value | Mean HD Diagnostic | Mean HD Post-Chemo | p-Value | Mean VS Diagnostic | Mean VS Post-Chemo | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blackbean | 0.89 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 6.40 | 30.17 | 0.69 | 0.94 | 0.75 | 0.05 |
| Jishenyu | 0.89 | 0.57 | 0.00 | 5.24 | 42.32 | 0.11 | 0.93 | 0.66 | 0.02 |
| Ouradiology | 0.80 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 11.51 | 39.31 | 0.20 | 0.83 | 0.61 | 0.11 |
| Drehimpuls | 0.76 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 12.55 | 48.04 | 0.40 | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.24 |
| SK | 0.65 | 0.40 | 0.12 | 19.26 | 50.87 | 0.46 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.55 |
| AGHSSO | 0.66 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 31.50 | 54.11 | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.53 | 0.08 |
| UNMC | 0.57 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 31.15 | 54.82 | 0.08 | 0.68 | 0.57 | 0.73 |
| SPPIN_SCNU | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 53.43 | 118.93 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.55 | 1.00 |
| GIBI230 | 0.66 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 31.31 | 83.64 | NaN | 0.75 | 0.33 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buser, M.A.D.; Simons, D.C.; Fitski, M.; Wijnen, M.H.W.A.; Littooij, A.S.; Brugge, A.H.t.; Vos, I.N.; Janse, M.H.A.; de Boer, M.; ter Maat, R.; et al. A Community Benchmark for the Automated Segmentation of Pediatric Neuroblastoma on Multi-Modal MRI: Design and Results of the SPPIN Challenge at MICCAI 2023. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111157
Buser MAD, Simons DC, Fitski M, Wijnen MHWA, Littooij AS, Brugge AHt, Vos IN, Janse MHA, de Boer M, ter Maat R, et al. A Community Benchmark for the Automated Segmentation of Pediatric Neuroblastoma on Multi-Modal MRI: Design and Results of the SPPIN Challenge at MICCAI 2023. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111157
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuser, Myrthe A. D., Dominique C. Simons, Matthijs Fitski, Marc H. W. A. Wijnen, Annemieke S. Littooij, Annemiek H. ter Brugge, Iris N. Vos, Markus H. A. Janse, Mathijs de Boer, Rens ter Maat, and et al. 2025. "A Community Benchmark for the Automated Segmentation of Pediatric Neuroblastoma on Multi-Modal MRI: Design and Results of the SPPIN Challenge at MICCAI 2023" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111157
APA StyleBuser, M. A. D., Simons, D. C., Fitski, M., Wijnen, M. H. W. A., Littooij, A. S., Brugge, A. H. t., Vos, I. N., Janse, M. H. A., de Boer, M., ter Maat, R., Sato, J., Kido, S., Kondo, S., Kasai, S., Wodzinski, M., Müller, H., Ye, J., He, J., Kirchhoff, Y., ... van der Steeg, A. F. W. (2025). A Community Benchmark for the Automated Segmentation of Pediatric Neuroblastoma on Multi-Modal MRI: Design and Results of the SPPIN Challenge at MICCAI 2023. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111157






