Spatial Regulation of Endocytosis and Adhesion Formation Governs Breast Cancer Cell Migration Under Confinement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
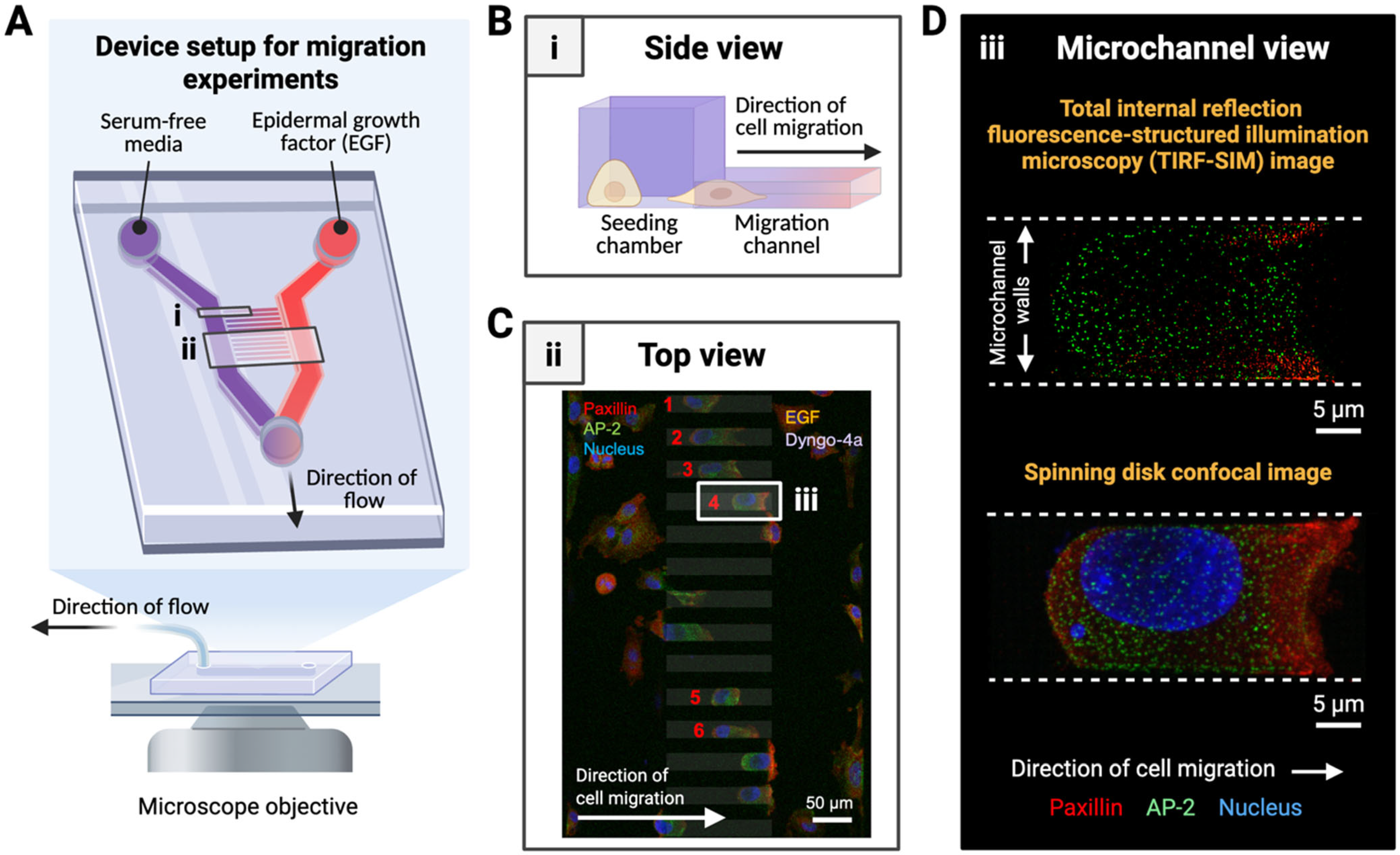
2.2. Fabrication of Microfluidic Migration Devices
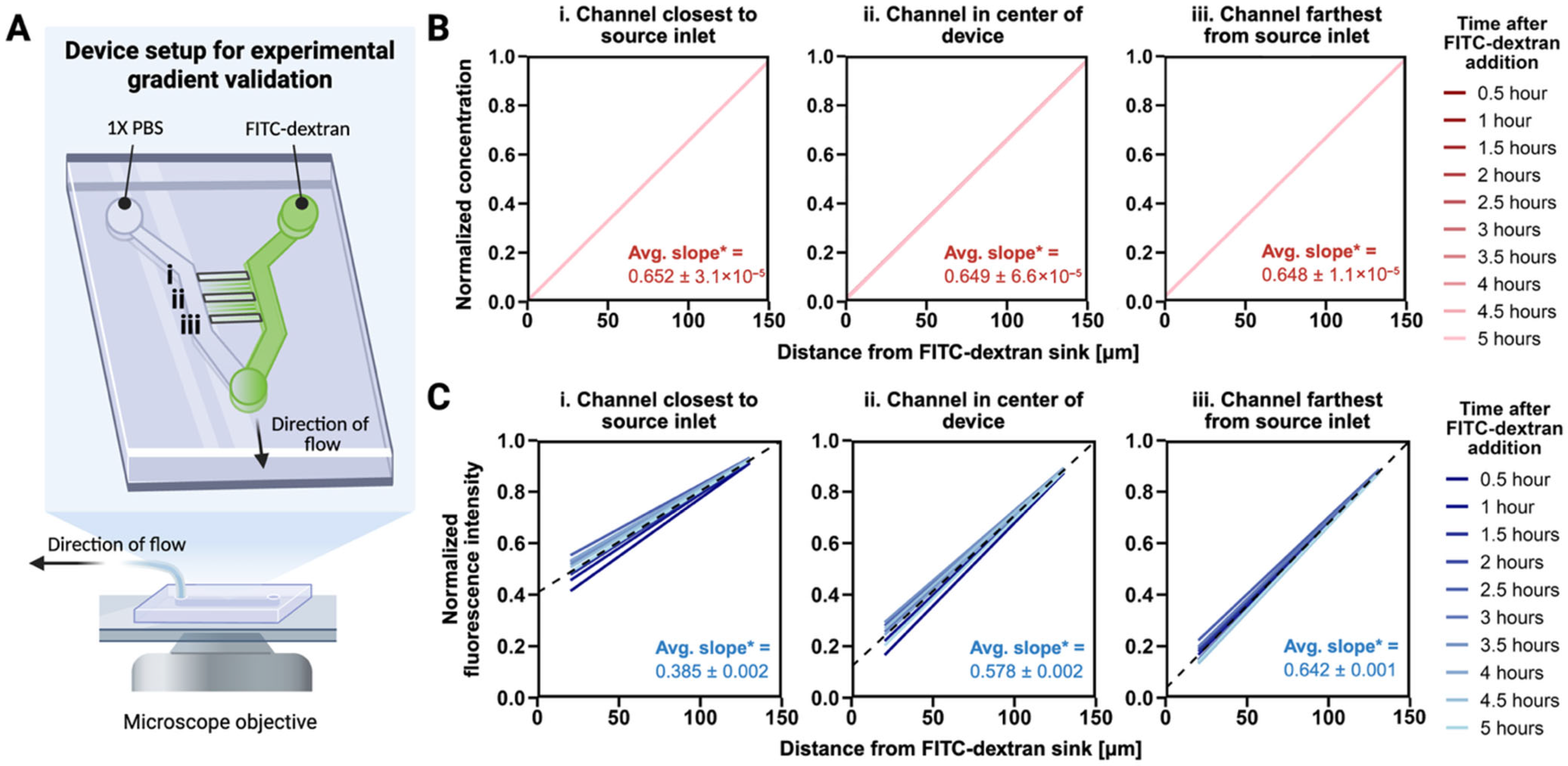
2.3. Gradient Characterization in Migration Devices
2.4. Cell Loading into Migration Device
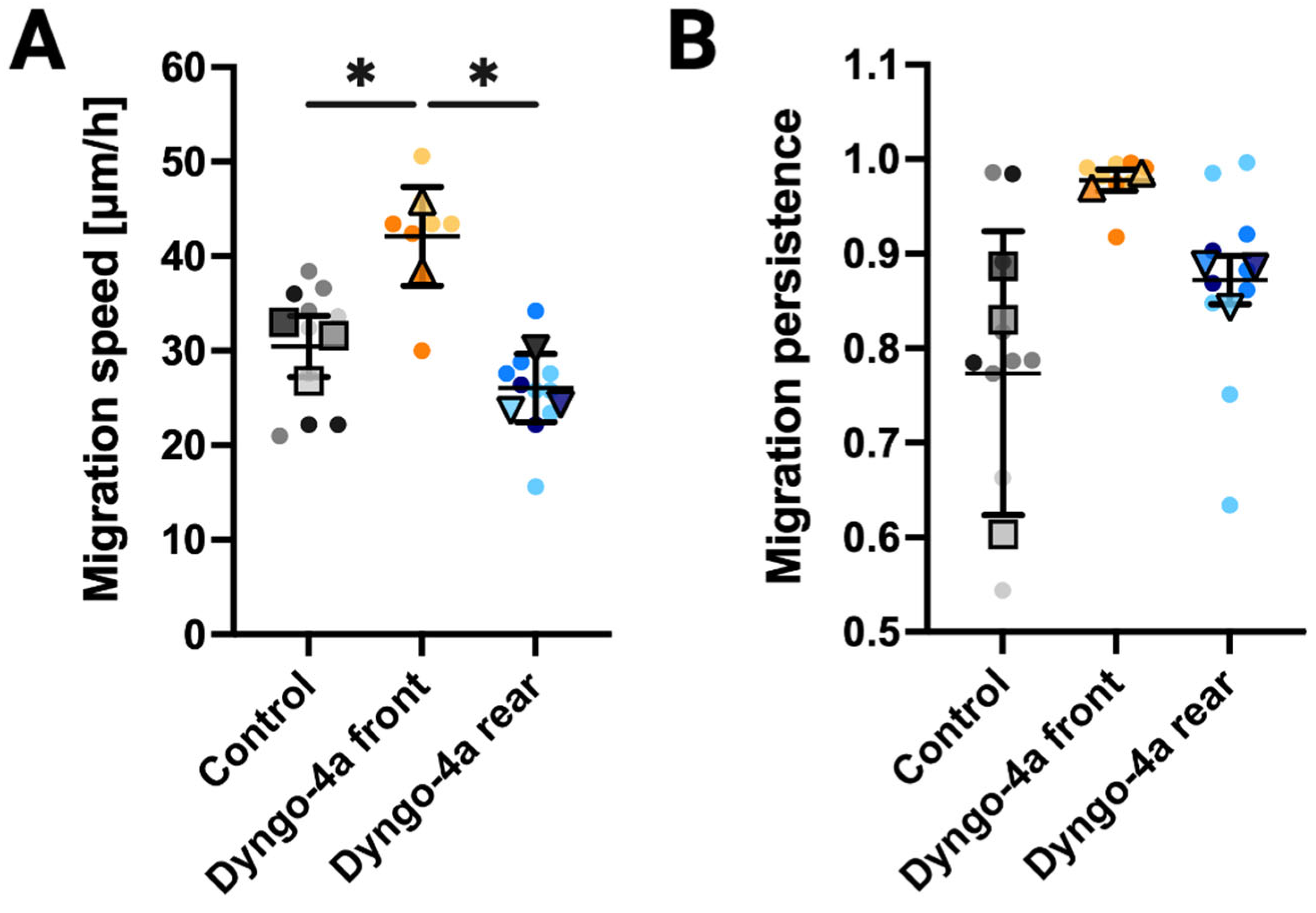
2.5. Acquisition of Cell Migration Speeds and Persistence
2.6. Analysis of Cell Migration Speeds and Persistence
2.7. Immunofluorescence Imaging of Migrated Cells
2.8. Spinning Disk Confocal Image Acquisition
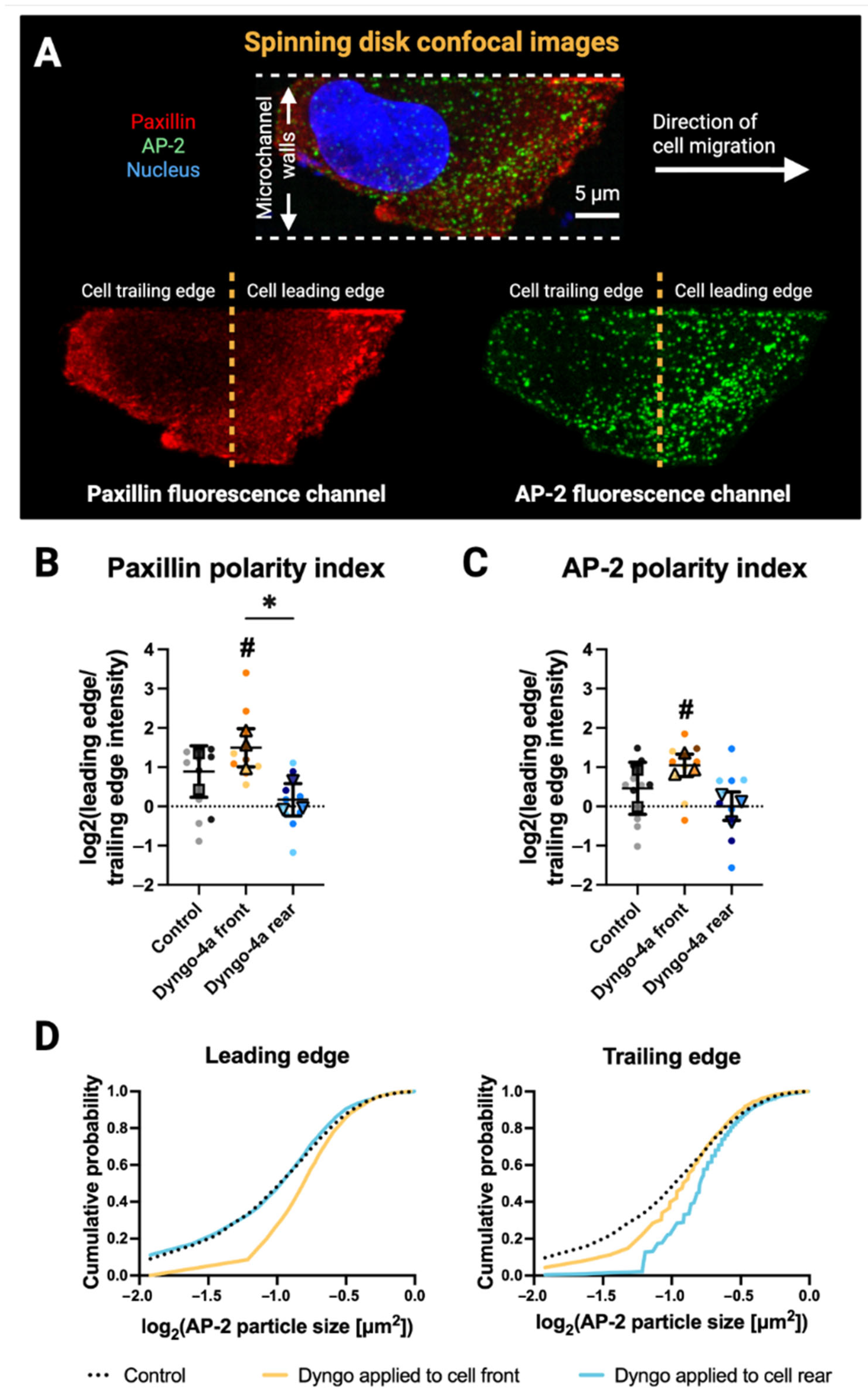
2.9. Analysis of Focal Adhesions and Clathrin Pits
2.10. Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Structured Illumination Microscope (TIRF-SIM) Image Acquisition
2.11. Statistics and Reproducibility
3. Results
3.1. A Stable EGF Gradient Exists Across All Microchannels
3.2. Microdevice Design Supports High-Resolution Imaging of Subcellular Structures During Directed Cell Migration
3.3. Front–Rear Endocytic Inhibition Reveals Spatial Control of Paxillin and AP-2 Distribution
3.4. Endocytic Inhibition Differentially Impacts Migration Speed and Persistence Depending on the Site of Application
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohme, M.; Riethdorf, S.; Pantel, K. Circulating and disseminated tumour cells—Mechanisms of immune surveillance and escape. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, M.; Di Russo, J.; Probst, D.; Schwarz, U.S.; Das, T.; Spatz, J.P. Mechanical interactions among followers determine the emergence of leaders in migrating epithelial cell collectives. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, G.; Pulgar, E.; Concha, M.L. Cell migration: From tissue culture to embryos. Development 2014, 141, 1999–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.D.; Mistriotis, P.; Konstantopoulos, K. Cancer cell motility: Lessons from migration in confined spaces. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charras, G.; Sahai, E. Physical influences of the extracellular environment on cell migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RPetrie, J.; Koo, H.; Yamada, K.M. Generation of Compartmentalized Pressure by a Nuclear Piston Governs Cell Motility in 3D Matrix. Science 2014, 345, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A.D.; Yamada, K.M. Mechanosensing via cell-matrix adhesions in 3D microenvironments. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 343, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettlen, M.; Chen, P.-H.; Srinivasan, S.; Danuser, G.; Schmid, S.L. Regulation of Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 871–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezratty, E.J.; Bertaux, C.; Marcantonio, E.E.; Gundersen, G.G. Clathrin mediates integrin endocytosis for focal adhesion disassembly in migrating cells. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.V.; Lamaze, C.; Schmid, S.L. Control of EGF Receptor Signaling by Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. Science 1996, 274, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kural, C.; Akatay, A.A.; Gaudin, R.; Chen, B.-C.; Legant, W.R.; Betzig, E.; Kirchhausen, T. Asymmetric formation of coated pits on dorsal and ventral surfaces at the leading edges of motile cells and on protrusions of immobile cells. MBoC 2015, 26, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willy, N.M.; Ferguson, J.P.; Huber, S.D.; Heidotting, S.P.; Aygün, E.; Wurm, S.A.; Johnston-Halperin, E.; Poirier, M.G.; Kural, C. Membrane mechanics govern spatiotemporal heterogeneity of endocytic clathrin coat dynamics. MBoC 2017, 28, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamidessi, A.; Frittoli, E.; Garré, M.; Faretta, M.; Mione, M.; Testa, I.; Diaspro, A.; Lanzetti, L.; Scita, G.; Di Fiore, P.P. Endocytic Trafficking of Rac Is Required for the Spatial Restriction of Signaling in Cell Migration. Cell 2008, 134, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.R.; Castillo-Badillo, J.A.; Meshik, X.; Kalyanaraman, V.; Melgarejo, K.; Gautam, N. Membrane Flow Drives an Adhesion-Independent Amoeboid Cell Migration Mode. Dev. Cell 2018, 46, 9–22.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoun, L.; Farutin, A.; Garcia-Seyda, N.; Nègre, P.; Rizvi, M.S.; Tlili, S.; Song, S.; Luo, X.; Biarnes-Pelicot, M.; Galland, R.; et al. Amoeboid Swimming Is Propelled by Molecular Paddling in Lymphocytes. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 1157–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, W.; Rhee, S.W.; Lin, F.; Vahidi, B.; Chung, B.G.; Jeon, N.L. Generation of stable concentration gradients in 2D and 3D environments using a microfluidic ladder chamber. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 9, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Wu, J.; Wilkins, J.A.; Lin, F. T Cells Chemotaxis Migration Studies with a Multi-Channel Microfluidic Device. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCluskey, A.; Daniel, J.A.; Hadzic, G.; Chau, N.; Clayton, E.L.; Mariana, A.; Whiting, A.; Gorgani, N.N.; Lloyd, J.; Quan, A.; et al. Building a Better Dynasore: The Dyngo Compounds Potently Inhibit Dynamin and Endocytosis. Traffic 2013, 14, 1272–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Beek, C.; Alriksson, L.; Palle, J.; Gustafson, A.-M.; Grujic, M.; Melo, F.R.; Sellin, M.E.; Pejler, G. Dynamin inhibition causes context-dependent cell death of leukemia and lymphoma cells. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft lithography for micro- and nanoscale patterning. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijering, E.; Dzyubachyk, O.; Smal, I. Methods for cell and particle tracking. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 504, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akatay, A.A.; Wu, T.; Djakbarova, U.; Thompson, C.; Cocucci, E.; Zandi, R.; Rudnick, J.; Kural, C. Endocytosis at extremes: Formation and internalization of giant clathrin-coated pits under elevated membrane tension. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 959737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, G.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Liang, Y.; Jin, X.; Xing, Y.; Jiu, Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. High-fidelity structured illumination microscopy by point-spread-function engineering. Light. Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, S.J.; Velle, K.B.; Mullins, R.D.; Fritz-Laylin, L.K. SuperPlots: Communicating reproducibility and variability in cell biology. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e202001064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Li, S.; Li, P.; Xia, Q.; Yang, R.; Li, T.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Shear stress stimulates integrin β1 trafficking and increases directional migration of cancer cells via promoting deacetylation of microtubules. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, S.; Damke, H.; Schmid, S.L. Dynamin:Gtp Controls the Formation of Constricted Coated Pits, the Rate Limiting Step in Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kural, M.H.; Djakbarova, U.; Cakir, B.; Tanaka, Y.; Chan, E.T.; Muniz, V.I.A.; Madraki, Y.; Qian, H.; Park, J.; Sewanan, L.R.; et al. Mechano-inhibition of endocytosis sensitizes cancer cells to Fas-induced Apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preta, G.; Cronin, J.G.; Sheldon, I.M. Dynasore—Not just a dynamin inhibitor. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritzen, T.; Schachtner, H.; Legler, D.F. On the move: Endocytic trafficking in cell migration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2119–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Scita, G. The ‘endocytic matrix reloaded’ and its impact on the plasticity of migratory strategies. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2018, 54, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretscher, M.S.; Aguado-Velasco, C. EGF induces recycling membrane to form ruffles. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disanza, A.; Frittoli, E.; Palamidessi, A.; Scita, G. Endocytosis and spatial restriction of cell signaling. Mol. Oncol. 2009, 3, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalukula, Y.; Luciano, M.; Simanov, G.; Charras, G.; Brückner, D.B.; Gabriele, S. The actin cortex acts as a mechanical memory of morphology in confined migrating cells. Nat. Phys. 2025, 21, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Yaddanapudi, S.; Weins, A.; Osborn, T.; Reiser, J.; Pollak, M.; Hartwig, J.; Sever, S. Direct dynamin–actin interactions regulate the actin cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3593–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djakbarova, U.; Madraki, Y.; Chan, E.T.; Wu, T.; Atreaga-Muniz, V.; Akatay, A.A.; Kural, C. Tension-induced adhesion mode switching: The interplay between focal adhesions and clathrin-containing adhesion complexes. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klabukov, I.; Smirnova, A.; Yakimova, A.; Kabakov, A.E.; Atiakshin, D.; Petrenko, D.; Shestakova, V.A.; Sulina, Y.; Yatsenko, E.; Stepanenko, V.N.; et al. Oncomatrix: Molecular Composition and Biomechanical Properties of the Extracellular Matrix in Human Tumors. J. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 5, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, H.T.; Munn, L.L.; Jain, R.K. Physical traits of cancer. Science 2020, 370, eaaz0868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, D.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Searson, P.C. The physics of cancer: The role of physical interactions and mechanical forces in metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Medina, M.; Bushman, A.R.; Beshay, P.E.; Adorno, J.J.; Menyhert, M.M.; Hildebrand, R.M.; Agarwal, S.S.; Avendano, A.; Friedman, A.K.; Song, J.W. Chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, and hyaluronic acid differentially modify the biophysical properties of collagen-based hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2024, 174, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshay, P.E.; Cortes-Medina, M.G.; Menyhert, M.M.; Song, J.W. The Biophysics of Cancer: Emerging Insights from Micro- and Nanoscale Tools. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2022, 2, 2100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, E.T.; Jones, T.H.; Thompson, C.M.; Kannan, H.; D’Souza, M.W.; Ali, M.M.; Kural, C.; Song, J.W. Spatial Regulation of Endocytosis and Adhesion Formation Governs Breast Cancer Cell Migration Under Confinement. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111148
Chan ET, Jones TH, Thompson CM, Kannan H, D’Souza MW, Ali MM, Kural C, Song JW. Spatial Regulation of Endocytosis and Adhesion Formation Governs Breast Cancer Cell Migration Under Confinement. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111148
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Emily T., Travis H. Jones, Cristopher M. Thompson, Hariharan Kannan, Malcolm W. D’Souza, Mushtaq M. Ali, Cömert Kural, and Jonathan W. Song. 2025. "Spatial Regulation of Endocytosis and Adhesion Formation Governs Breast Cancer Cell Migration Under Confinement" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111148
APA StyleChan, E. T., Jones, T. H., Thompson, C. M., Kannan, H., D’Souza, M. W., Ali, M. M., Kural, C., & Song, J. W. (2025). Spatial Regulation of Endocytosis and Adhesion Formation Governs Breast Cancer Cell Migration Under Confinement. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111148





