New Gait Representation Maps for Enhanced Recognition in Clinical Gait Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
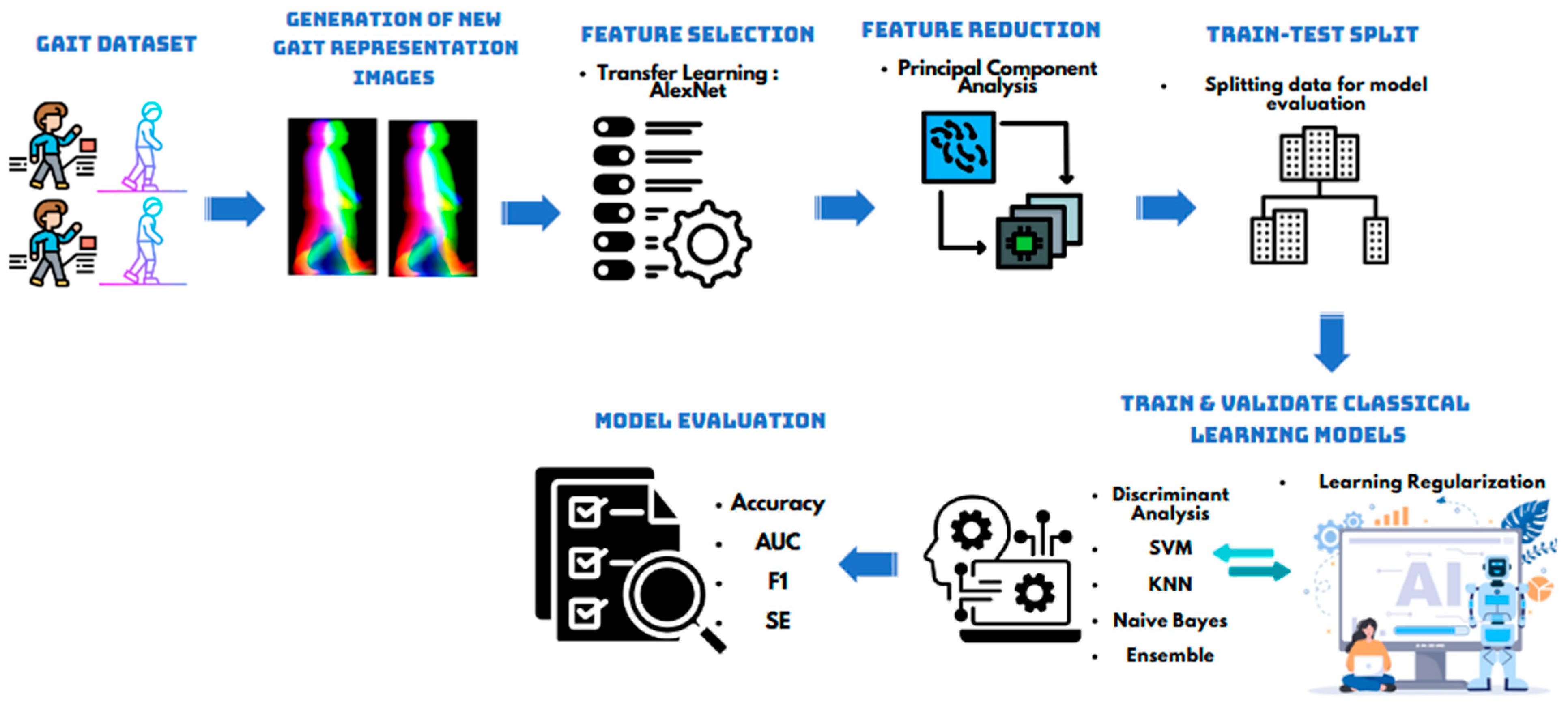
3.2. Proposed Framework
3.2.1. Generation of New Gait Representation Images
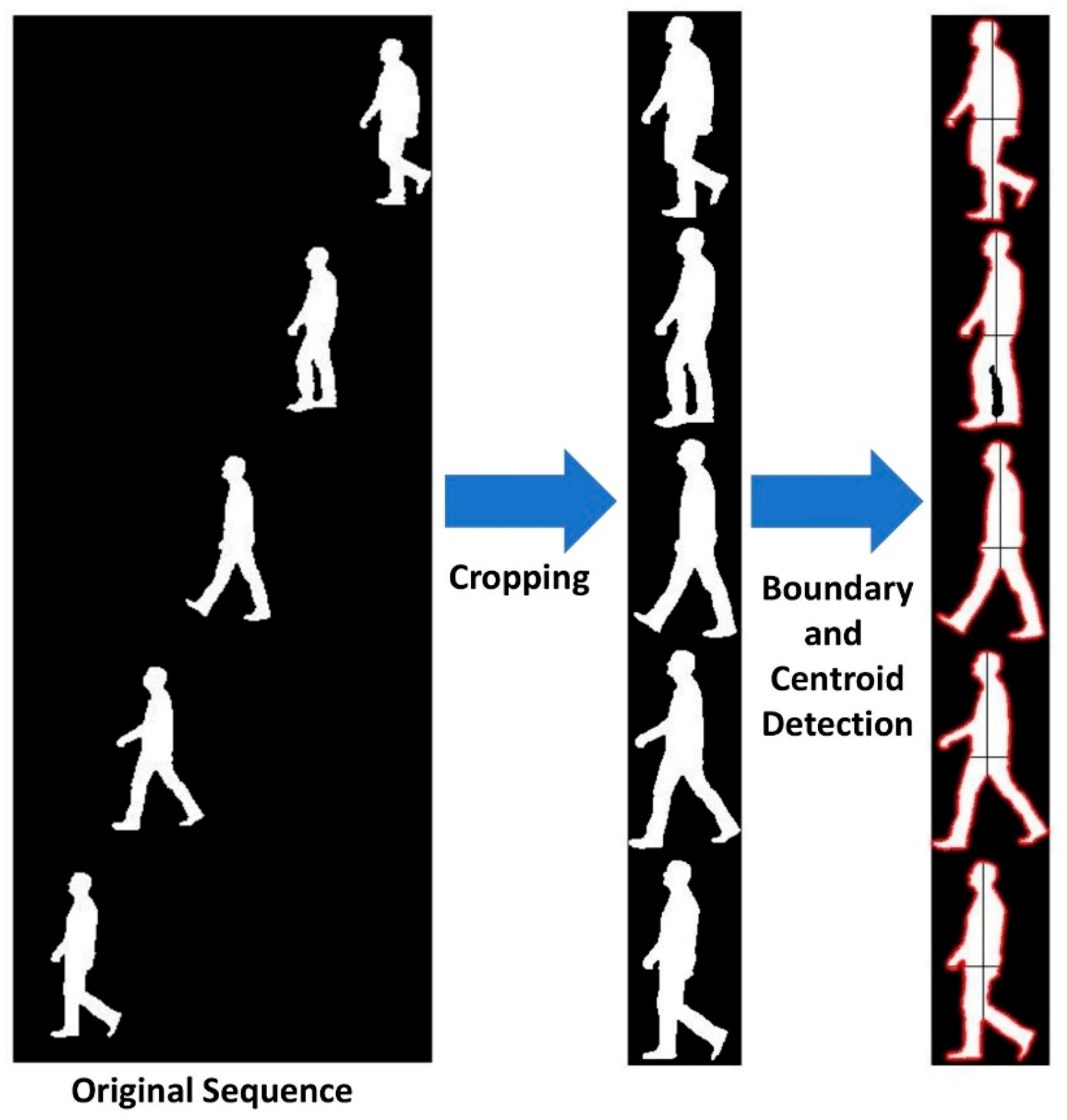
Binary Silhouettes Preprocessing
- A.
- Image Cropping:
- B.
- Centroid and Boundary Calculations:
- C.
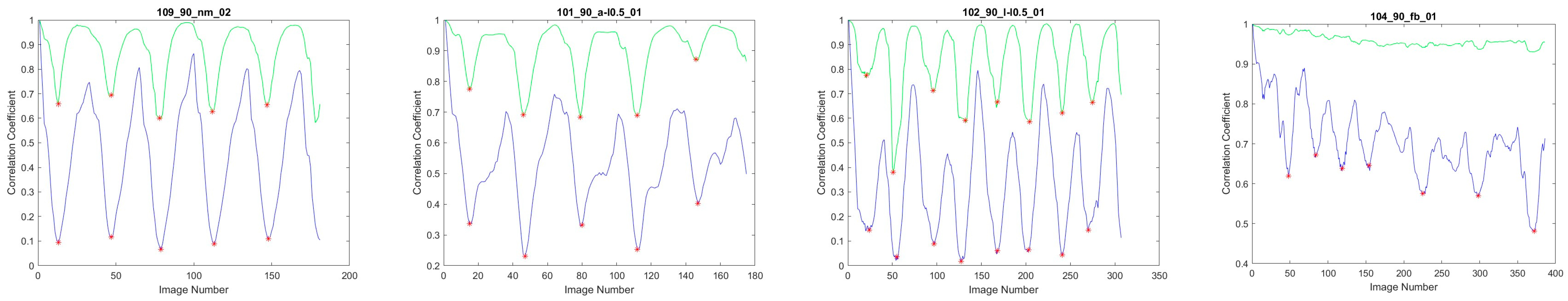
- Gait Cycle Detection:
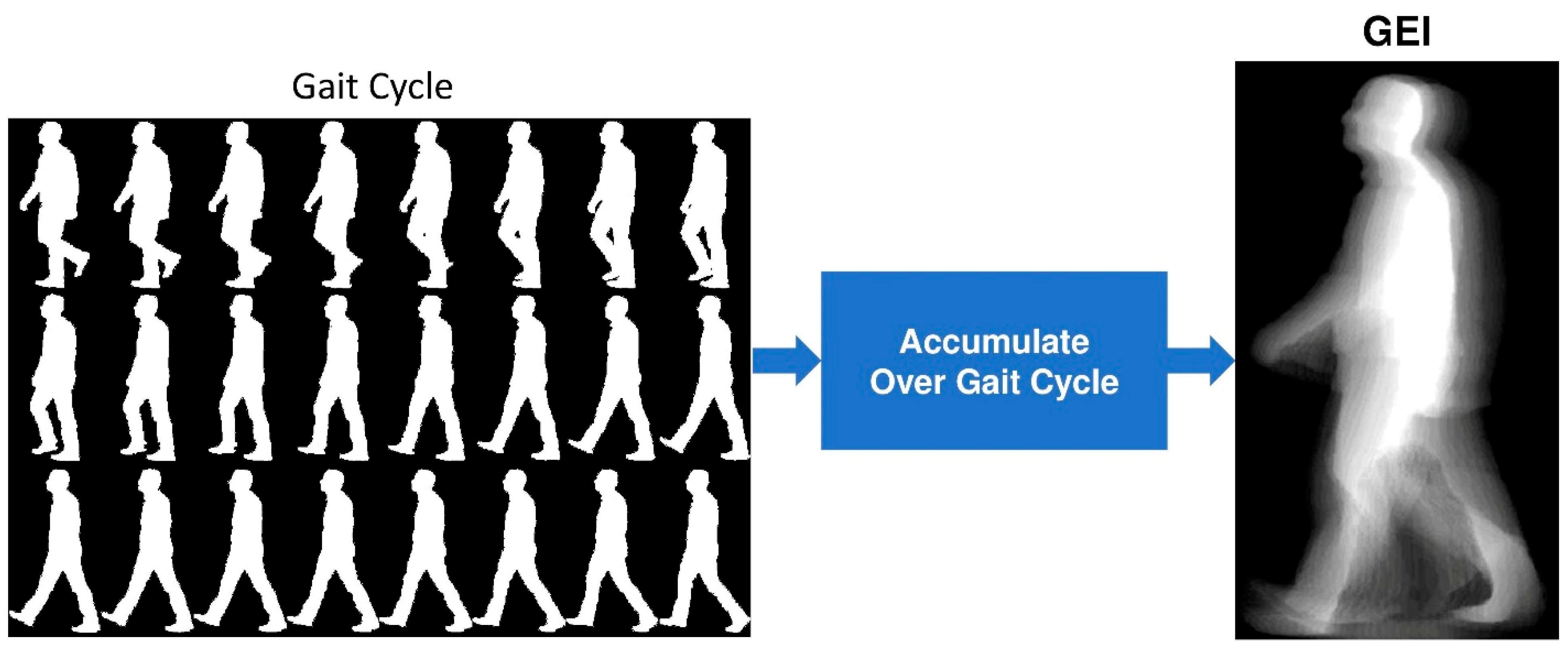
Gait Sequence Image Representations
- A.
- Gait Energy Image (GEI):
- B.
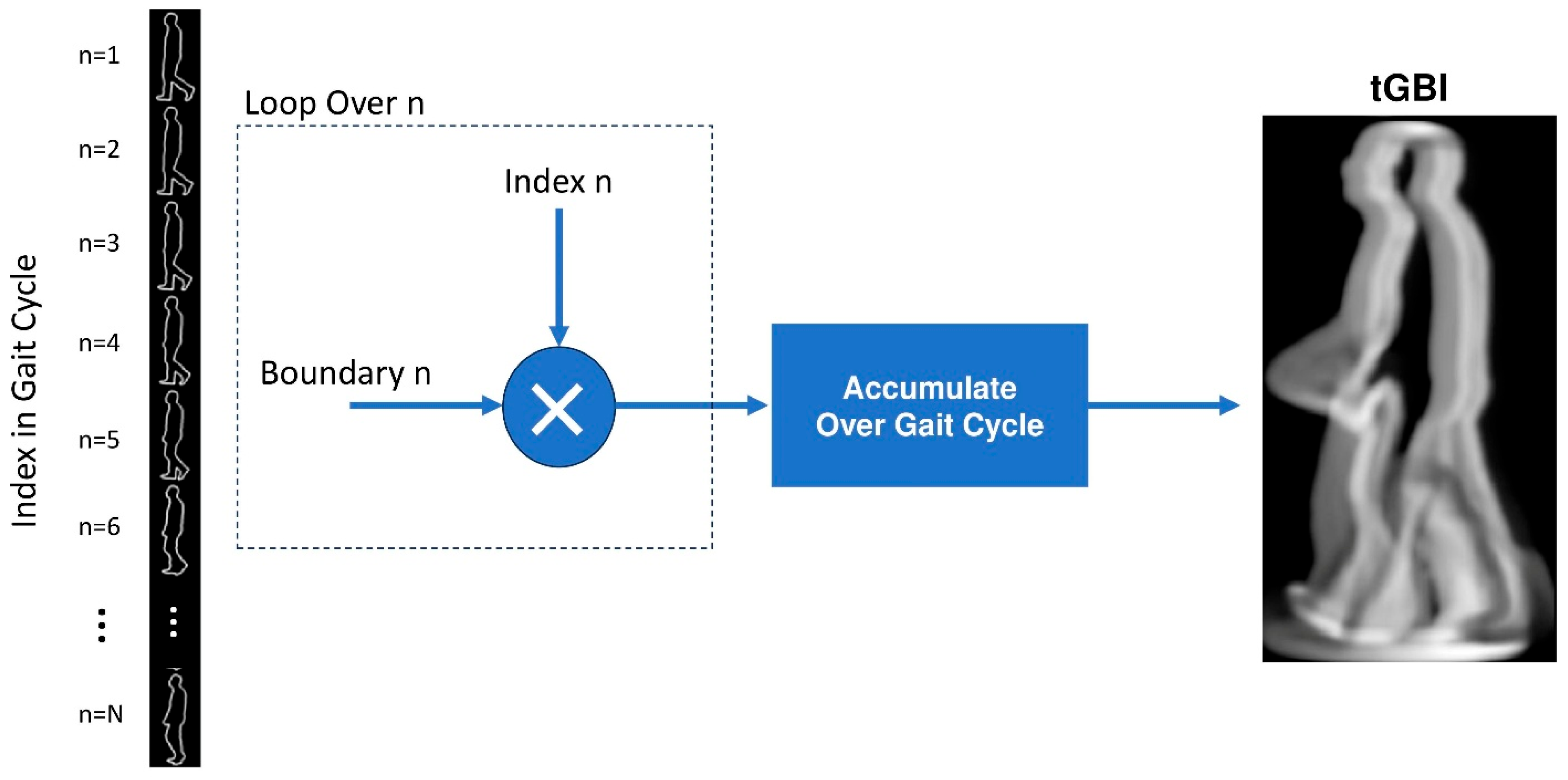
- Time-Coded Gait Boundary Image (tGBI):
- C.
- Color-Coded Gait Energy Image (cGEI):
- D.
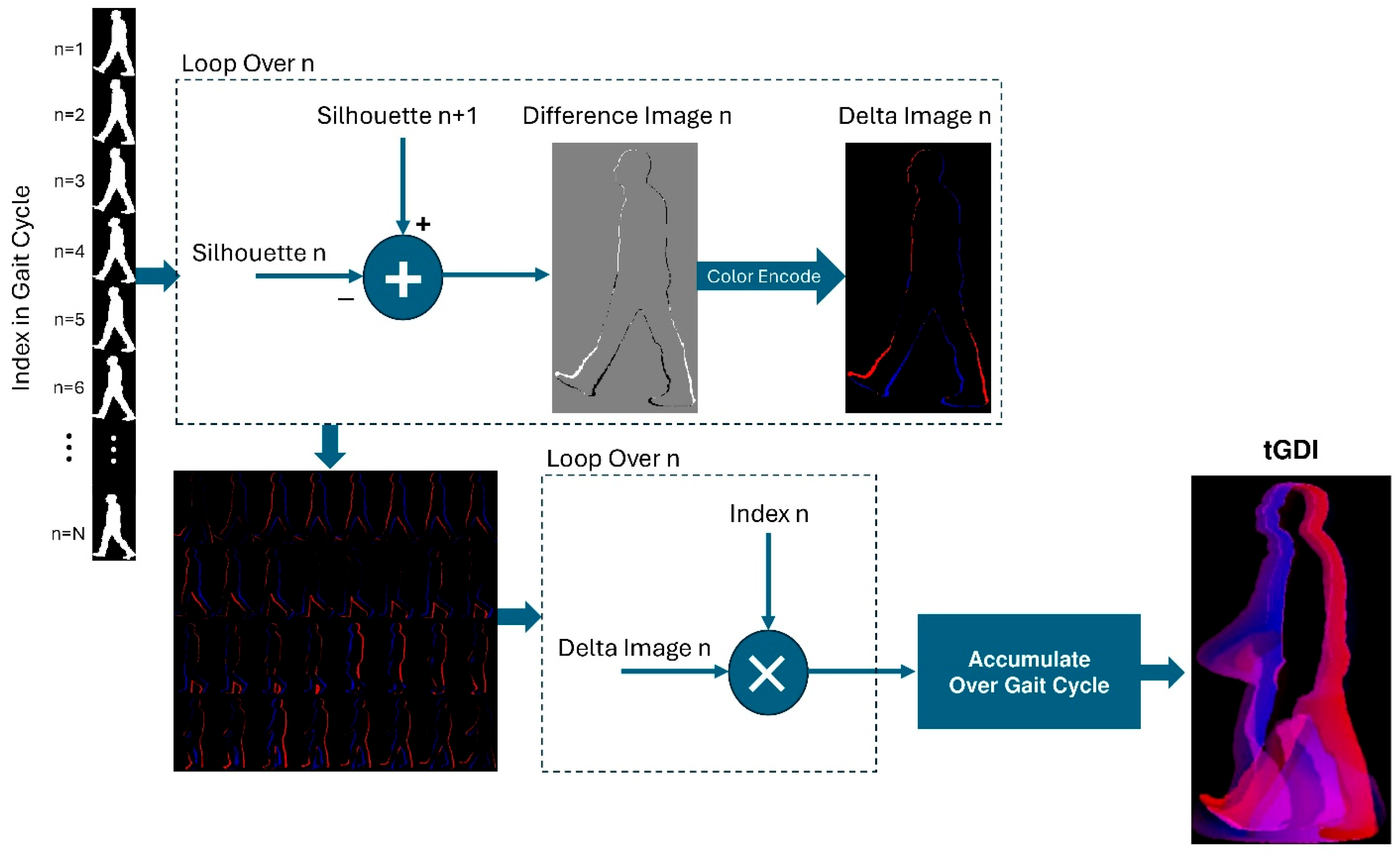
- Time-Coded Gait Delta Image (tGDI):
- E.
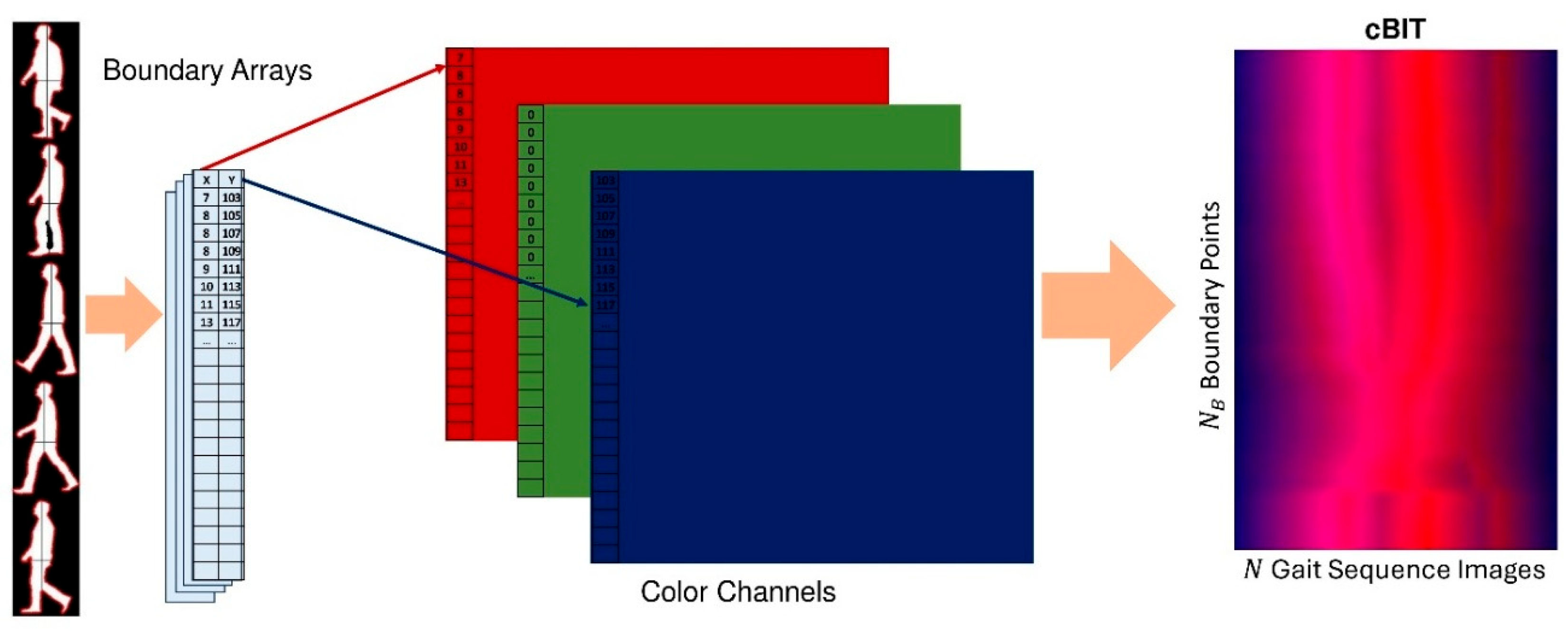
- Color-Coded Boundary-to-Image Transform (cBIT):
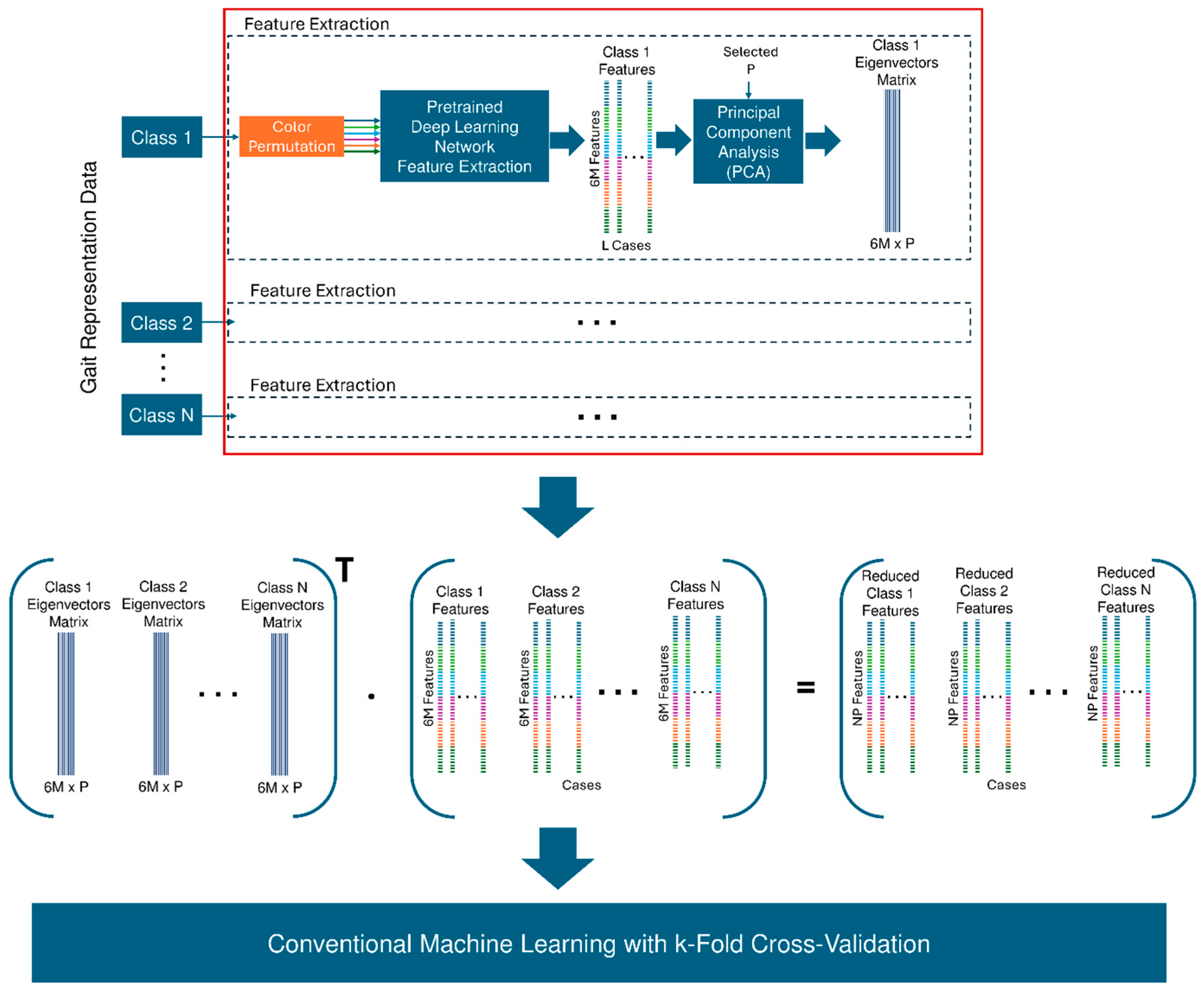
3.2.2. Gait Classification
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsushita, Y.; Tran, D.T.; Yamazoe, H.; Lee, J.-H. Recent use of deep learning techniques in clinical applications based on gait: A survey. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2021, 8, 1499–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlekar, T.T.; Soares, L.D.; Correia, P.L. Automatic classification of gait impairments using a markerless 2D video-based system. Sensors 2018, 18, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Feng, D.; Chen, S.; Ban, N.; Pan, J. Portable vision-based gait assessment for post-stroke rehabilitation using an attention-based lightweight CNN. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Ahmedt-Aristizabal, D.; Armin, M.A.; Kim, J. Computer Vision for Clinical Gait Analysis: A Gait Abnormality Video Dataset. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.04190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, M.W. Gait Analysis: An introduction; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Hou, S.; Huang, Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Shan, C. Gait Attribute Recognition: A New Benchmark for Learning Richer Attributes from Human Gait Patterns. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.C.; Kuo, C.; Loza, J.; Kurt, M.; Laksari, K.; Yanez, L.Z.; Senif, D.; Anderson, S.C.; Miller, L.E.; Urban, J.E. Detection of American football head impacts using biomechanical features and support vector machine classification. Sci. Rep. 2017, 8, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ziaat, H.; El-Bendary, N.; Moawad, R. Using Multi-Feature Fusion for Detecting Freezing of Gait Episodes in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Innovative Trends in Communication and Computer Engineering (ITCE), Aswan, Egypt, 8–9 February 2020; pp. 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-W.; Wen, T.-C.; Setiawan, F. Evaluation of vertical ground reaction forces pattern visualization in neurodegenerative diseases identification using deep learning and recurrence plot image feature extraction. Sensors 2020, 20, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, J.; Correia, P.L. Using a skeleton gait energy image for pathological gait classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2020), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Li, J.; Yu, M.; Zhu, M.; Clifford, R. A novel computer vision based gait analysis technique for normal and Parkinson’s gaits classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, Intl Conf on Cloud and Big Data Computing, Intl Conf on Cyber Science and Technology Congress (DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/CyberSciTech), Calgary, AB, Canada, 17–22 August 2020; pp. 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Bhanu, B. Individual recognition using gait energy image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 28, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, P. Exploiting pose dynamics for human recognition from their gait signatures. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 35903–35921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, M.; Bajwa, K.B.; Gillani, S.; Maqsood, M.; Durrani, M.Y.; Mehmood, I.; Ugail, H.; Rho, S. An efficient gait recognition method for known and unknown covariate conditions. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 6465–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenac, K.; Sušanj, D.; Ramakić, A.; Pinčić, D. Extending appearance based gait recognition with depth data. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Makihara, Y.; Li, X.; Yagi, Y.; Lu, J. Speed-invariant gait recognition using single-support gait energy image. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 26509–26536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Kusakunniran, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Yang, W. Robust gait recognition using hybrid descriptors based on skeleton gait energy image. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 150, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlrichs, C.; Samà, A.; Lawo, M.; Cabestany, J.; Rodríguez-Martín, D.; Pérez-López, C.; Sweeney, D.; Quinlan, L.R.; Laighin, G.Ò.; Counihan, T. Detecting freezing of gait with a tri-axial accelerometer in Parkinson’s disease patients. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2016, 54, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Zaarour, I.; Guerin, F.; Bejjani, P.; Ayache, M.; Lefebvre, D. Detection of freezing of gait for Parkinson’s disease patients with multi-sensor device and Gaussian neural networks. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2017, 8, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linda, G.M.; Themozhi, G.; Bandi, S.R. Color-mapped contour gait image for cross-view gait recognition using deep convolutional neural network. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolution Inf. Process. 2020, 18, 1941012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.; Bansal, S. Gait Recogniton System for Human Identification Using BPNN Classifier. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2013, 3, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.; Fu, H. Siamese neural network based gait recognition for human identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 2832–2836. [Google Scholar]
- Gaba, I.; Ahuja, S.P. Gait analysis for identification by using BPNN with LDA and MDA techniques. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on MOOC, Innovation and Technology in Education (MITE), Patiala, India, 19–20 December 2014; pp. 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, F.M.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Guil, N.; Perez De La Blanca, N. Automatic learning of gait signatures for people identification. In Proceedings of the International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks; Cadiz, Spain, 14–16 June 2017, Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hawas, A.R.; El-Khobby, H.A.; Abd-Elnaby, M.; Abd El-Samie, F.E. Gait identification by convolutional neural networks and optical flow. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 25873–25888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.; Mahmood, A. Improved gait recognition based on specialized deep convolutional neural network. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 164, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, S.; Narsingani, S.; Patel, Y. Cross View and Cross Walking Gait Recognition Using a Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing, Jammu, India, 3–5 November 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 112–123. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Masni, M.A.; Marzban, E.N.; Al-Shamiri, A.K.; Al-Antari, M.A.; Alabdulhafith, M.I.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Abdel Samee, N.; Kadah, Y.M. Gait Impairment Analysis Using Silhouette Sinogram Signals and Assisted Knowledge Learning. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, S.; Malik, M.I.; Khan, G.M.; Shafait, F. Multi-view gait recognition system using spatio-temporal features and deep learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 179, 115057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogan, J.N.; Lee, C.P.; Lim, K.M.; Ali, M.; Alqahtani, A. Gait-CNN-ViT: Multi-model gait recognition with convolutional neural networks and vision transformer. Sensors 2023, 23, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunardi, R.T.; Sardjono, T.A.; Mardiyanto, R. Skeleton-Based Gait Recognition Using Modified Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Long Short-Term Memory for Person Recognition. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 121131–121143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R. A Faster R-CNN and recurrent neural network based approach of gait recognition with and without carried objects. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 205, 117730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.I.; Prakash, A.J.; Ari, S. Human gait recognition using joint spatiotemporal modulation in deep convolutional neural networks. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 105, 104322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, S.; Narsingani, S.; Patel, Y. A Unified Convolutional Neural Network for Gait Recognition. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, Kitakyushu, Japan, 5–8 November 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 230–242. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jia, N.; Wang, L. Gaitnet: An end-to-end network for gait based human identification. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 96, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C. Digital Image Processing; Pearson Education: Chennai, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Elkholy, A.; Makihara, Y.; Gomaa, W.; Ahad, M.A.R.; Yagi, Y. Unsupervised GEI-based gait disorders detection from different views. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 5423–5426. [Google Scholar]
- Whytock, T.; Belyaev, A.; Robertson, N.M. Dynamic distance-based shape features for gait recognition. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2014, 50, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, H.; Okumura, M.; Makihara, Y.; Yagi, Y. The OU-ISIR gait database comprising the large population dataset and performance evaluation of gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Hidalgo, M.; García-Chamizo, J.M. Classification of pathologies using a vision based feature extraction. In Proceedings of the Ubiquitous Computing and Ambient Intelligence: 11th International Conference, UCAmI 2017, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–10 November 2017; pp. 265–274. [Google Scholar]

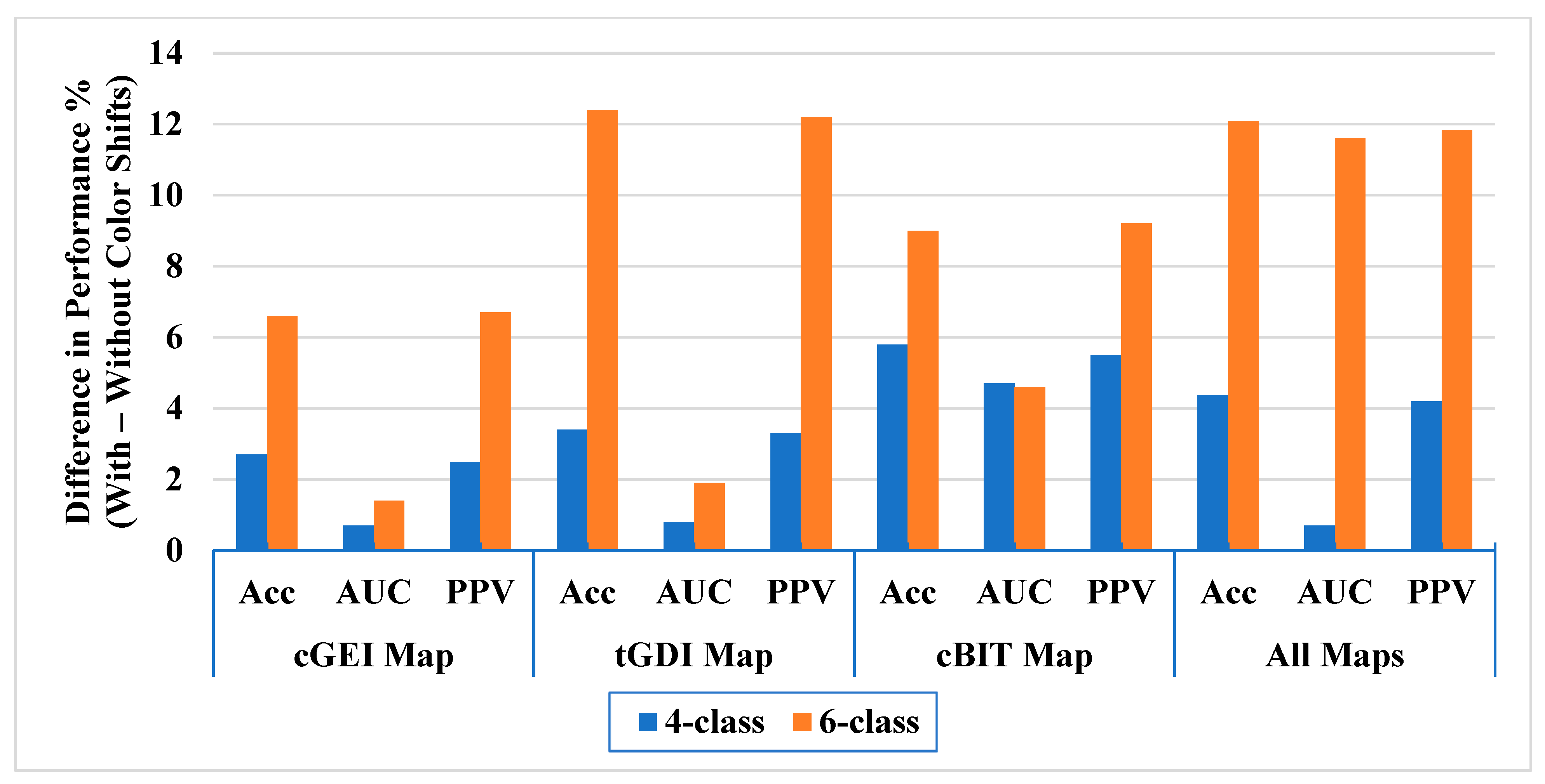
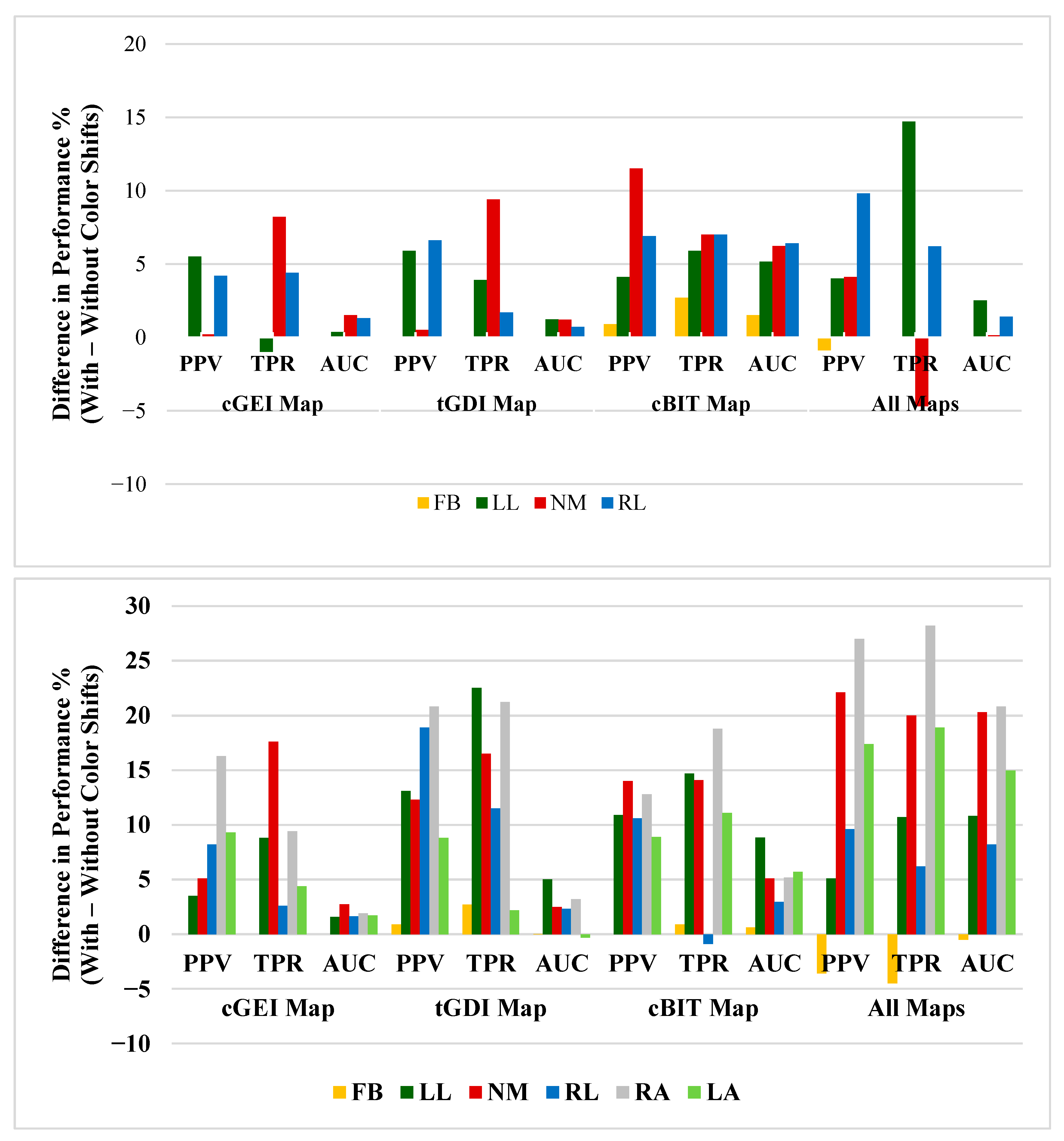
| Map | 4-Class Problem | 6-Class Problem | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Color Shift | with Color Shift | Without Color Shift | with Color Shift | |
| GEI | Discriminant Analysis | Not Applicable | KNN | Not Applicable |
| Acc: 95.4% | Acc: 83.5% | |||
| AUC: 99.4% | AUC: 98.0% | |||
| SE: 95.38% | SE: 83.48% | |||
| F1-score: 95.47% | F1-score: 83.98% | |||
| tGBI | Discriminant Analysis | Not Applicable | KNN | Not Applicable |
| Acc: 91.5% | Acc: 83.0% | |||
| AUC: 98.8% | AUC: 98.0% | |||
| SE: 91.53% | SE: 82.97% | |||
| F1-score: 91.64% | F1-score: 83.25% | |||
| cGEI | Discriminant Analysis | KNN | KNN | KNN |
| Acc: 94.4% | Acc: 97.1% | Acc: 87.6% | Acc: 94.2% | |
| AUC: 99.1% | AUC: 99.8% | AUC: 98.3% | AUC: 99.7% | |
| SE: 94.42% | SE: 97.08% | SE: 87.58% | SE: 94.19% | |
| F1-score: 94.49% | F1-score: 97.1% | F1-score: 87.58% | F1-score: 94.24% | |
| tGDI | Discriminant Analysis | KNN | KNN | KNN |
| Acc: 94.9% | Acc: 98.3% | Acc: 82.8% | Acc: 95.2% | |
| AUC: 99.1% | AUC: 99.9% | AUC: 97.1% | AUC: 99.0% | |
| SE: 94.92% | SE: 98.29% | SE: 82.8% | SE: 95.24% | |
| F1-score: 94.94% | F1-score: 98.31% | F1-score: 82.95% | F1-score: 95.29% | |
| cBIT | KNN | KNN | KNN | KNN |
| Acc: 91.5% | Acc: 97.3% | Acc: 83.0% | Acc: 92.0% | |
| AUC: 94.5% | AUC: 99.2% | AUC: 94.8% | AUC: 99.4% | |
| SE: 91.74% | SE: 97.3% | SE: 82.98% | SE: 92% | |
| F1-score: 91.78% | F1-score: 97.32% | F1-score: 82.96% | F1-score: 92.06% | |
| All Maps | SVM | KNN | KNN | KNN |
| Acc: 92% | Acc: 96.36% | Acc: 77.17% | Acc: 89.26% | |
| AUC: 99.0% | AUC: 99.7% | AUC: 86.47% | AUC: 98.08% | |
| SE: 91.99% | SE: 96.36% | SE: 77.18% | SE: 89.25% | |
| F1-score: 92.03% | F1-score: 96.35% | F1-score: 77.4% | F1-score: 89.35% | |
| Maps | Class | PPV (%) | TPR/SE (%) | AUC (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Color Shift | With Color Shifts | Without Color Shift | With Color Shifts | Without Color Shift | With Color Shifts | ||
| GEI | FB | 100.00 | Not Applicable | 100.00 | Not Applicable | 100.0 | Not Applicable |
| LL | 92.40 | 95.10 | 99.2 | ||||
| NM | 98.60 | 85.90 | 98.9 | ||||
| RL | 91.70 | 98.20 | 99.4 | ||||
| Average | 95.55 | 95.38 | 99.4 | ||||
| tGBI | FB | 100.00 | Not Applicable | 99.10 | Not Applicable | 99.4 | Not Applicable |
| LL | 89.00 | 87.30 | 98.4 | ||||
| NM | 93.20 | 81.20 | 98.1 | ||||
| RL | 85.00 | 95.60 | 99.2 | ||||
| Average | 91.76 | 91.53 | 98.8 | ||||
| cGEI | FB | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| LL | 91.40 | 96.90 | 94.10 | 93.10 | 99.4 | 99.7 | |
| NM | 97.40 | 97.60 | 87.10 | 95.30 | 98.2 | 99.7 | |
| RL | 89.90 | 94.10 | 94.70 | 99.10 | 98.5 | 99.8 | |
| Average | 94.56 | 97.12 | 94.42 | 97.08 | 99.1 | 99.8 | |
| tGDI | FB | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| LL | 93.10 | 99.00 | 92.20 | 96.10 | 98.6 | 99.9 | |
| NM | 95.00 | 95.50 | 89.40 | 98.80 | 98.5 | 99.7 | |
| RL | 91.60 | 98.20 | 96.50 | 98.20 | 99.1 | 99.8 | |
| Average | 94.96 | 98.33 | 94.92 | 98.29 | 99.1 | 99.8 | |
| cBIT | FB | 99.10 | 100.00 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 98.5 | 100.0 |
| LL | 90.90 | 95.00 | 88.20 | 94.10 | 92.7 | 97.8 | |
| NM | 88.50 | 100.00 | 90.60 | 97.60 | 93.8 | 100.0 | |
| RL | 87.90 | 94.80 | 90.30 | 97.30 | 92.8 | 99.2 | |
| Average | 91.81 | 97.34 | 91.75 | 97.30 | 94.5 | 99.2 | |
| All Maps | FB | 100.00 | 99.10 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| LL | 91.10 | 95.10 | 80.40 | 95.10 | 97.3 | 99.9 | |
| NM | 92.30 | 96.40 | 98.80 | 94.10 | 99.6 | 99.7 | |
| RL | 84.90 | 94.70 | 89.40 | 95.60 | 97.9 | 99.3 | |
| Average | 92.07 | 96.35 | 91.99 | 96.36 | 98.7 | 99.7 | |
| Maps | Class | PPV (%) | TPR/SE (%) | AUC (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Color Shift | With Color Shifts | Without Color Shift | With Color Shifts | Without Color Shift | With Color Shifts | ||
| GEI | FB | 100.00 | Not Applicable | 100.00 | Not Applicable | 100.0 | Not Applicable |
| LA | 76.70 | 76.70 | 96.1 | ||||
| LL | 95.50 | 83.30 | 98.7 | ||||
| NM | 74.30 | 64.70 | 95.4 | ||||
| RA | 61.50 | 78.80 | 95.7 | ||||
| RL | 90.30 | 90.30 | 98.5 | ||||
| Average | 84.48 | 83.48 | 97.6 | ||||
| tGBI | FB | 100.00 | Not Applicable | 100.00 | Not Applicable | 100.0 | Not Applicable |
| LA | 73.20 | 78.90 | 96.8 | ||||
| LL | 94.00 | 77.50 | 97.5 | ||||
| NM | 77.30 | 68.20 | 95.7 | ||||
| RA | 72.00 | 78.80 | 96.7 | ||||
| RL | 79.40 | 88.50 | 98.3 | ||||
| Average | 83.54 | 82.97 | 97.6 | ||||
| cGEI | FB | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| LA | 85.10 | 94.40 | 88.90 | 93.30 | 97.8 | 99.5 | |
| LL | 90.70 | 94.20 | 86.30 | 95.10 | 98.2 | 99.8 | |
| NM | 80.30 | 85.40 | 71.80 | 89.40 | 96.3 | 99.1 | |
| RA | 78.90 | 95.20 | 83.50 | 92.90 | 97.9 | 99.8 | |
| RL | 86.40 | 94.60 | 90.30 | 92.90 | 97.9 | 99.6 | |
| Average | 87.57 | 94.29 | 87.58 | 94.19 | 98.1 | 99.6 | |
| tGDI | FB | 99.10 | 100.00 | 97.30 | 100.00 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| LA | 82.10 | 90.90 | 86.70 | 88.90 | 97.6 | 97.3 | |
| LL | 85.90 | 99.00 | 71.60 | 94.10 | 94.2 | 99.2 | |
| NM | 77.60 | 89.90 | 77.60 | 94.10 | 96.8 | 99.3 | |
| RA | 70.30 | 91.10 | 75.30 | 96.50 | 95.0 | 98.2 | |
| RL | 79.30 | 98.20 | 85.00 | 96.50 | 97.0 | 99.4 | |
| Average | 83.11 | 95.33 | 82.80 | 95.24 | 96.9 | 99.0 | |
| cBIT | FB | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.10 | 100.00 | 99.4 | 100.0 |
| LA | 80.60 | 89.50 | 83.30 | 94.40 | 93.9 | 99.6 | |
| LL | 82.10 | 93.00 | 76.50 | 91.20 | 90.4 | 99.3 | |
| NM | 77.20 | 91.20 | 71.80 | 85.90 | 93.5 | 98.6 | |
| RA | 69.80 | 82.60 | 70.60 | 89.40 | 93.4 | 98.6 | |
| RL | 82.90 | 93.50 | 90.30 | 89.40 | 96.5 | 99.5 | |
| Average | 82.95 | 92.13 | 82.98 | 92.0 | 94.7 | 99.3 | |
| All Maps | FB | 100.00 | 96.40 | 100.00 | 95.50 | 100.0 | 99.5 |
| LA | 66.30 | 83.70 | 72.20 | 91.10 | 82.8 | 97.8 | |
| LL | 84.90 | 90.00 | 77.50 | 88.20 | 87.3 | 98.1 | |
| NM | 63.60 | 85.70 | 57.60 | 77.60 | 76.0 | 96.3 | |
| RA | 55.80 | 82.80 | 62.40 | 90.60 | 77.0 | 97.8 | |
| RL | 84.80 | 94.40 | 84.10 | 90.30 | 90.2 | 98.4 | |
| Average | 77.61 | 89.44 | 77.18 | 89.25 | 86.5 | 98.1 | |
| Reference | Map/Feature Extraction Approach | Classifier | Dataset(s) | Classes | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verlekar et al., 2018 [2] | GEI and silhouette features using image processing. | SVM | INIT | FB, LL, RL, and NM | Acc.: 98.8% |
| Elkholy et al., 2019 [37] | GEI and applying convolutional autoencoder | Isolation forests | OU-ISIR (train) [39] and INIT (test) | Normal and abnormal | AUC: 0.94 |
| Gong et al., 2020 [11] | GEI and applying R-CNN on video clips | OC-SVM | Their own dataset and Youtube videos | Normal and Parkinsonian | Acc. 97.33% |
| Loureiro et al., 2020 [10] | GEI and SEI (VGG-19) | VGG-19 | GAIT-IST | Normal, diplegic, hemiplegic, neuropathic, and Parkinsonian | Acc.: 98.5% |
| GEI and SEI (VGG-19 + PCA) | LDA / SVM | GAIT-IST | Acc.: 96.4% | ||
| GEI (VGG-19 + PCA) | LDA | GAIT-IST (train) and DAI 2 (test) [40] | Acc.: 76.7% | ||
| Zhou et al. 2024 [3] | GEI (lightweight CNN) | CNN | GAIT-IST [10] | Normal, diplegic, hemiplegic, neuropathic and Parkinsonian | Acc.: 98.1% |
| GEI (lightweight CNN) | CNN | GAIT-IST | Normal + 3 levels hemiplegia | Acc.: 96.92% | |
| Al-masni et al., 2024 [28] | GEI (2D CNN) | CNN | INIT | FB, LL, RL, LA, RA, and NM | Acc. 70.94% |
| GEI (ResNet50) | ResNet50 | FB, LL, RL, and NM | Acc.: 86.25% | ||
| Proposed Method | New maps (AlexNet features) | KNN | INIT | FB, LL, RL, and NM | Acc.: 98.3% |
| F1 score: 98.31% | |||||
| AUC: 0.999 | |||||
| FB, LL, RL, LA, RA, and NM | Acc.: 95.2% | ||||
| F1 score: 95.29% | |||||
| AUC: 0.990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samee, N.A.; Al-masni, M.A.; Marzban, E.N.; Al-Shamiri, A.K.; Al-antari, M.A.; Alabdulhafith, M.I.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Kadah, Y.M. New Gait Representation Maps for Enhanced Recognition in Clinical Gait Analysis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101130
Samee NA, Al-masni MA, Marzban EN, Al-Shamiri AK, Al-antari MA, Alabdulhafith MI, Mahmoud NF, Kadah YM. New Gait Representation Maps for Enhanced Recognition in Clinical Gait Analysis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101130
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamee, Nagwan Abdel, Mohammed A. Al-masni, Eman N. Marzban, Abobakr Khalil Al-Shamiri, Mugahed A. Al-antari, Maali Ibrahim Alabdulhafith, Noha F. Mahmoud, and Yasser M. Kadah. 2025. "New Gait Representation Maps for Enhanced Recognition in Clinical Gait Analysis" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101130
APA StyleSamee, N. A., Al-masni, M. A., Marzban, E. N., Al-Shamiri, A. K., Al-antari, M. A., Alabdulhafith, M. I., Mahmoud, N. F., & Kadah, Y. M. (2025). New Gait Representation Maps for Enhanced Recognition in Clinical Gait Analysis. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101130








