Bridging Photoacoustic and Protoacoustic Imaging: Material Heterogeneity Effects on Proton Range Verification Using Time-of-Flight Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background
2.2. Three Types of Analysis
2.2.1. Impact of Spatial Temperature Variation in Water Phantom
2.2.2. Effects of Tissue Composition and Property Uniformity
2.2.3. Appropriate Detector Positioning Based on Clinical CT Cases
2.3. Simulation Parameter
2.4. Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Temperature Deviation in Water Phantom
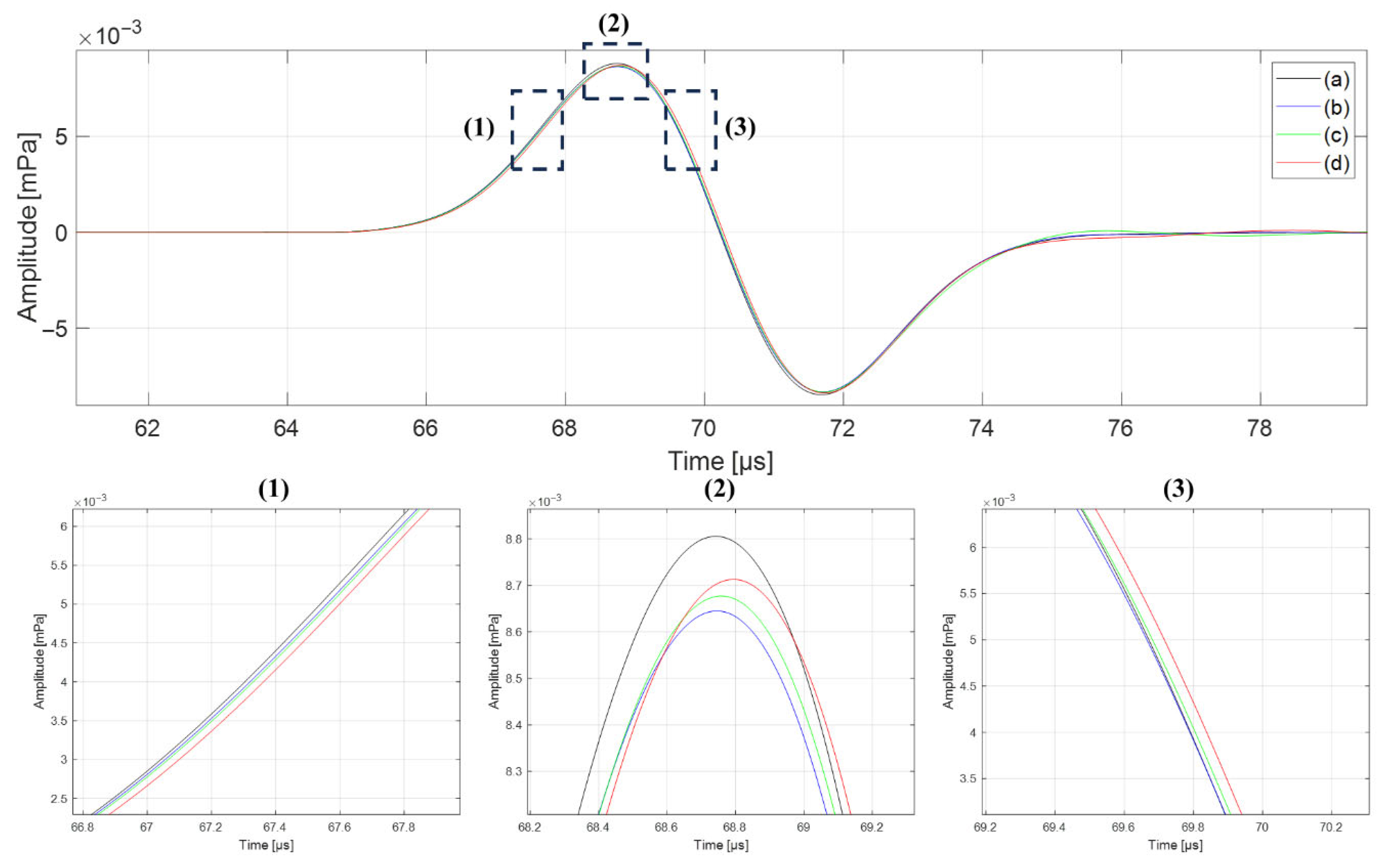
3.2. Effects of Tissue Composition and Property Uniformity
3.3. Appropriate Detector Positioning Based on Clinical CT Cases
4. Discussion
4.1. Validation in Homogeneous Phantom
4.2. Influence of Tissue Heterogeneity on Range Accuracy
4.3. Clinical Feasibility and Detector Placement Optimization
4.4. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeuwissen, J.; Bourne, R.; Kearsley, J. The importance of postoperative radiation therapy in the treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 31, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagawa, N.; Kondo, S.; Morikawa, T.; Okushiba, S.; Katoh, H. Effectiveness of radiation therapy after surgery for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Surg. Today 2005, 35, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, S.R.; Schray, M.F.; Laws, E.R., Jr.; O’Fallon, J.R. Adjuvant radiation therapy after surgical resection of solitary brain metastasis: Association with pattern of failure and survival. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1987, 13, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Bragg, W.H. On the Absorption of Alpha Rays and on the classification of Alpha Rays from Radium. Philos. Mag. 1904, 8, 719–725. [Google Scholar]
- Kooy, H.; Grassberger, C. Intensity modulated proton therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekberg, L.; Holmberg, O.; Wittgren, L.; Bjelkengren, G.; Landberg, T. What margins should be added to the clinical target volume in radiotherapy treatment planning for lung cancer? Radiother. Oncol. 1998, 48, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.S.; Hussey, D.H.; Pennington, E.C.; Stanford, W.; Doornbos, J.F. Analysis of movement of intrathoracic neoplasms using ultrafast computerized tomography. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1990, 18, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unkelbach, J.; Alber, M.; Bangert, M.; Bokrantz, R.; Chan, T.C.; Deasy, J.O.; Fredriksson, A.; Gorissen, B.L.; Van Herk, M.; Liu, W. Robust radiotherapy planning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 22TR02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganetti, H. Range uncertainties in proton therapy and the role of Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-M. A potential method for in vivo range verification in proton therapy treatment. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 1413. [Google Scholar]
- Helmbrecht, S.; Santiago, A.; Enghardt, W.; Kuess, P.; Fiedler, F. On the feasibility of automatic detection of range deviations from in-beam PET data. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.H.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.B. Development of array-type prompt gamma measurement system for in vivo range verification in proton therapy. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freijo, C.; Herraiz, J.L.; Sanchez-Parcerisa, D.; Udias, J.M. Dictionary-based protoacoustic dose map imaging for proton range verification. Photoacoustics 2021, 21, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.C.; Seghal, C.M.; Avery, S. How proton pulse characteristics influence protoacoustic determination of proton-beam range: Simulation studies. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanea, F.; Moskvin, V.; Stantz, K.M. Feasibility of RACT for 3D dose measurement and range verification in a water phantom. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 937–946. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xing, L.; Peng, H. Simulation studies of time reversal-based protoacoustic reconstruction for range and dose verification in proton therapy. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 3649–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.C.; Nie, W.; Chu, J.C.; Turian, J.V.; Kassaee, A.; Sehgal, C.M.; Avery, S. Acoustic-based proton range verification in heterogeneous tissue: Simulation studies. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 025018. [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi, T.; Uesaka, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Unlu, M.B.; Kuriyama, Y.; Uesugi, T.; Ishi, Y.; Kudo, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Umegaki, K. On-line range verification for proton beam therapy using spherical ionoacoustic waves with resonant frequency. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sohn, J.J.; Lei, Y.; Nie, W.; Zhou, J.; Avery, S.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Deep Learning-based Protoacoustic Signal Denoising for Proton Range Verification. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.17500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallicelli, E.A.; Baschirotto, A.; Lehrack, S.; Assmann, W.; Parodi, K.; Viola, S.; Riccobene, G.; De Matteis, M. 22 dB signal-to-noise ratio real-time Proton Sound Detector for experimental beam range verification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 68, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Takayanagi, T.; Uesaka, T.; Unlu, M.B.; Kuriyama, Y.; Ishi, Y.; Uesugi, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kudo, N.; Tanaka, S. Range verification of pulsed proton beams from fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator by means of time-of-flight measurement of ionoacoustic waves. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 5490–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, J.; Gonzalez, G.; Kumar Pandey, P.; Wang, S.; Prather, K.Y.; Ahmad, S.; Xiang, L.; Chen, Y. Single pulse protoacoustic range verification using a clinical synchrocyclotron. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 045011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.; Wieser, H.-P.; Huang, Y.; Ruser, H.; Lascaud, J.; Würl, M.; Chmyrov, A.; Vidal, M.; Herault, J.; Ntziachristos, V. Proton beam range verification by means of ionoacoustic measurements at clinically relevant doses using a correlation-based evaluation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 925542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.; Wieser, H.-P.; Lascaud, J.; Huang, Y.; Vidal, M.; Herault, J.; Ntziachristos, V.; Dollinger, G.; Parodi, K. Range verification of a clinical proton beam in an abdominal phantom by co-registration of ionoacoustics and ultrasound. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gonzalez, G.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Pandey, P.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, S. Real-time tracking of the Bragg peak during proton therapy via 3D protoacoustic Imaging in a clinical scenario. npj Imaging 2024, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasgall, P.A.; Di Gennaro, F.; Baumgartner, C.; Neufeld, E.; Lloyd, B.; Gosselin, M.C.; Payne, D.; Klingenböck, A.; Kuster, N. IT’IS Database for Thermal and Electromagnetic Parameters of Biological Tissues; IT’IS 2018, Version 4.0; IT’IS Foundation: Zurich, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Ruddock, J.M.; Diebold, G.J. Photoacoustic transients generated by laser irradiation of thin films. Photoacoustics 2015, 3, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Treeby, B.E.; Cox, B.T. Modeling power law absorption and dispersion for acoustic propagation using the fractional Laplacian. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, W.; Kellnberger, S.; Reinhardt, S.; Lehrack, S.; Edlich, A.; Thirolf, P.; Moser, M.; Dollinger, G.; Omar, M.; Ntziachristos, V. Ionoacoustic characterization of the proton Bragg peak with submillimeter accuracy. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beard, P. Biomedical photoacoustic imaging. Interface Focus 2011, 1, 602–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treeby, B.E.; Cox, B.T. k-Wave: MATLAB toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave fields. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 021314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, U.; Pedroni, E.; Lomax, A. The calibration of CT Hounsfield units for radiotherapy treatment planning. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarville, A. Visible Human Project CT Datasets Male and Female. Harvard Dataverse. 2023. Available online: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/3JDZCT (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Jones, K.C.; Vander Stappen, F.; Sehgal, C.M.; Avery, S. Acoustic time-of-flight for proton range verification in water. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 5213–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallicelli, E.A.; Baschirotto, A.; Stevenazzi, L.; Tambaro, M.; De Matteis, M. Proton Range Measurement Precision in Ionoacoustic Experiments with Wavelet-Based Denoising Algorithm. Sensors 2025, 25, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Xiang, L.; Yousefi, S.; Xing, L. Theoretical detection threshold of the proton-acoustic range verification technique. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 5735–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.C.; Vander Stappen, F.; Bawiec, C.R.; Janssens, G.; Lewin, P.A.; Prieels, D.; Solberg, T.D.; Sehgal, C.M.; Avery, S. Experimental observation of acoustic emissions generated by a pulsed proton beam from a hospital-based clinical cyclotron. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 7090–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, W.; Jones, K.C.; Petro, S.; Kassaee, A.; Sehgal, C.M.; Avery, S. Proton range verification in homogeneous materials through acoustic measurements. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 025036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, N.; Mandelis, A. The effect of acoustic impedance on subsurface absorber geometry reconstruction using 1D frequency-domain photoacoustics. Photoacoustics 2015, 3, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Haiat, G.; Laporte, C.; Belanger, P. Effect of the acoustic impedance mismatch at the bone-soft tissue interface as a function of frequency in transcranial ultrasound: A simulation and in vitro experimental study. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2020, 68, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirberger, R.M. Imaging artifacts in diagnostic ultrasound—A review. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 1995, 36, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lindström, K.; Mauritzson, L.; Benoni, G.; Svedman, P.; Willner, S. Application of air-borne ultrasound to biomedical measurements. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1982, 20, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arjomandy, B.; Taylor, P.; Ainsley, C.; Safai, S.; Sahoo, N.; Pankuch, M.; Farr, J.B.; Yong Park, S.; Klein, E.; Flanz, J. AAPM task group 224: Comprehensive proton therapy machine quality assurance. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e678–e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
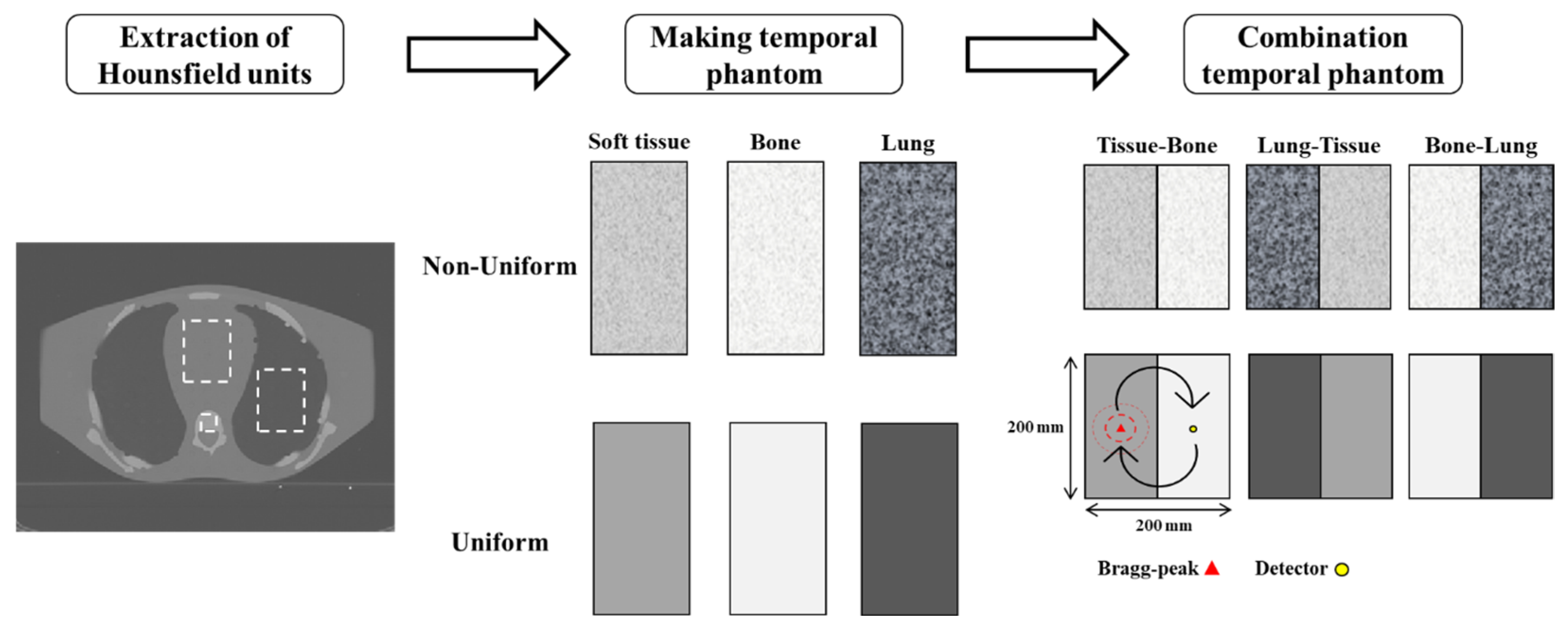



| Hounsfield Units | [kg/m3] | [m/s] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | |
| Soft-tissue | 1042.5 | 62.5 | 1050.4 | 32.8 | 1567.1 | 36.8 |
| Bone | 1850.0 | 50.0 | 1574.4 | 19.3 | 2153.9 | 21.6 |
| Lung | 234.5 | 71.5 | 234.0 | 42.7 | 652.8 | 47.8 |
| Bragg-Peak | Detector | Type | [μs] | [mm] | Difference [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | Lung | Uniform | 101.05 | 141.81 | +3.62 |
| Non-uniform | 103.63 | 145.43 | |||
| Lung | Bone | Uniform | 102.14 | 143.34 | +3.72 |
| Non-uniform | 104.79 | 147.06 | |||
| Bone | Tissue | Uniform | 56.07 | 104.32 | +0.15 |
| Non-uniform | 56.15 | 104.47 | |||
| Tissue | Bone | Uniform | 56.25 | 104.65 | +0.17 |
| Non-uniform | 56.34 | 104.82 | |||
| Lung | Tissue | Uniform | 111.65 | 123.92 | +2.95 |
| Non-uniform | 114.31 | 126.87 | |||
| Tissue | Lung | Uniform | 110.74 | 122.91 | +2.87 |
| Non-uniform | 113.33 | 125.78 |
| Treatment Case | Detector Position | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) | ||
| Brain | [mm] | 94.7 | 111.14 | 141.03 | 116.5 | 74.65 |
| [mm] | 93.97 | 112.97 | 249.15 | 171.678 | 91.19 | |
| [mm] | 0.73 | 1.83 | 108.12 | 55.18 | 16.54 | |
| [%] | 0.77 | 1.65 | 76.66 | 47.36 | 22.16 | |
| Head & Neck | [mm] | 104.66 | 99.02 | 93.01 | 100.22 | 72.8 |
| [mm] | 189.52 | 112.76 | 130.86 | 115.15 | 103.34 | |
| [mm] | 84.86 | 13.74 | 37.85 | 14.93 | 30.54 | |
| [%] | 81.08 | 13.88 | 40.69 | 14.90 | 41.95 | |
| Liver | [mm] | 130.6 | 134.62 | 215.18 | 265.19 | 282.18 |
| [mm] | 143.14 | 107.94 | 296.83 | 282.79 | 331.46 | |
| [mm] | 12.54 | 26.68 | 81.65 | 17.60 | 49.28 | |
| [%] | 9.60 | 19.82 | 37.94 | 6.64 | 17.46 | |
| Prostate | [mm] | 163.03 | 121.02 | 127.26 | 132.97 | 130.38 |
| [mm] | 202.09 | 117.63 | 90.35 | 121.63 | 172.1 | |
| [mm] | 39.06 | 3.39 | 36.91 | 11.34 | 41.72 | |
| [%] | 23.96 | 2.80 | 29.00 | 8.53 | 32.00 | |
| Lung | [mm] | 130 | 143.69 | 241.05 | 252.56 | 182.22 |
| [mm] | 95.71 | 175.28 | 322.37 | 444.95 | 245.62 | |
| [mm] | 34.29 | 31.59 | 81.32 | 192.39 | 63.40 | |
| [%] | 26.38 | 21.98 | 33.74 | 76.18 | 34.79 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.; Cheon, W.; Han, Y.; Cho, S. Bridging Photoacoustic and Protoacoustic Imaging: Material Heterogeneity Effects on Proton Range Verification Using Time-of-Flight Analysis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101123
Jeong S, Cheon W, Han Y, Cho S. Bridging Photoacoustic and Protoacoustic Imaging: Material Heterogeneity Effects on Proton Range Verification Using Time-of-Flight Analysis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101123
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Sangwoon, Wonjoong Cheon, Youngyih Han, and Sungkoo Cho. 2025. "Bridging Photoacoustic and Protoacoustic Imaging: Material Heterogeneity Effects on Proton Range Verification Using Time-of-Flight Analysis" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101123
APA StyleJeong, S., Cheon, W., Han, Y., & Cho, S. (2025). Bridging Photoacoustic and Protoacoustic Imaging: Material Heterogeneity Effects on Proton Range Verification Using Time-of-Flight Analysis. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101123







