Dual Functions of Androgen Receptor Overexpression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Complex Prognostic Marker
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Histopathological Analysis
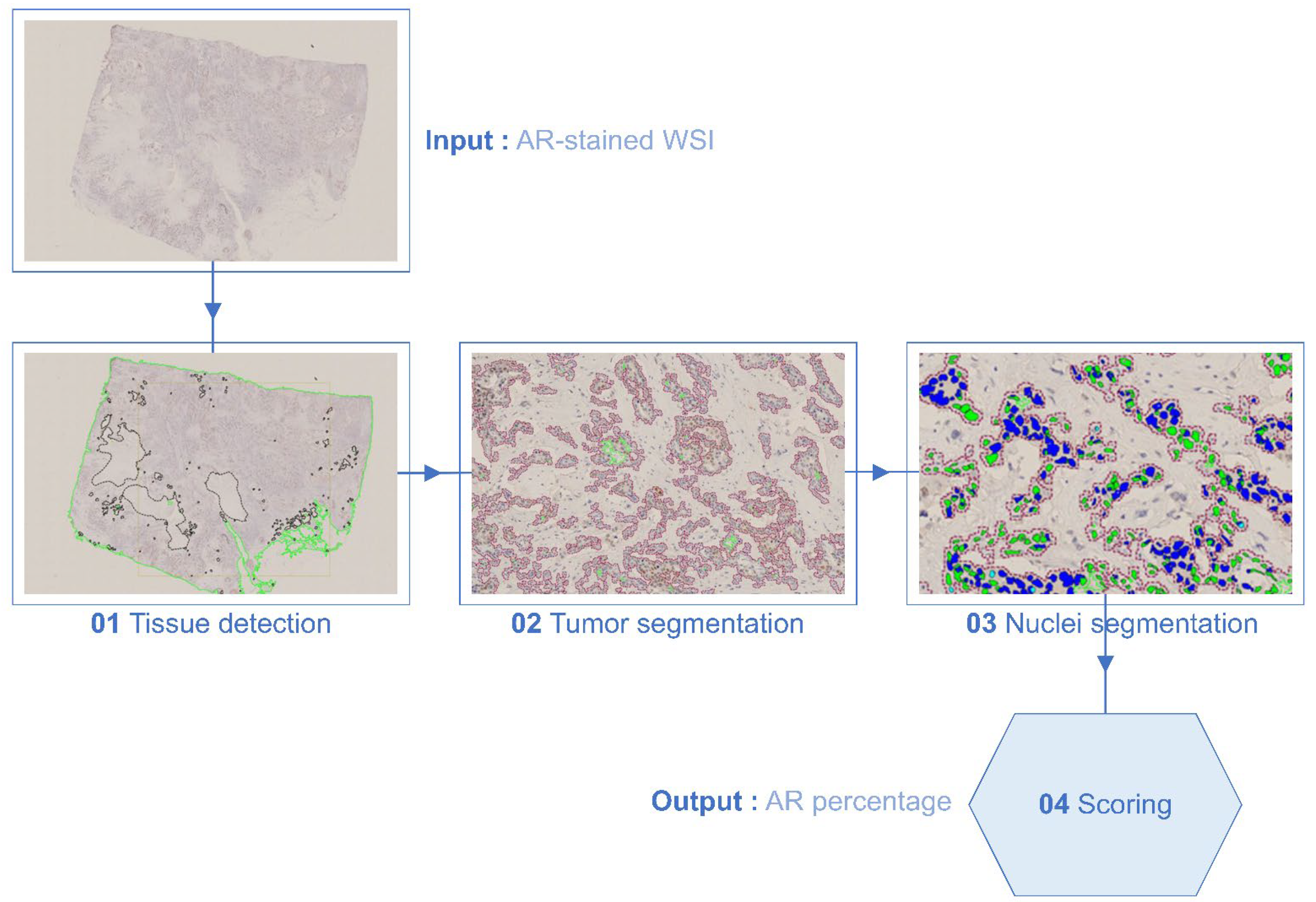
2.2. AR Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
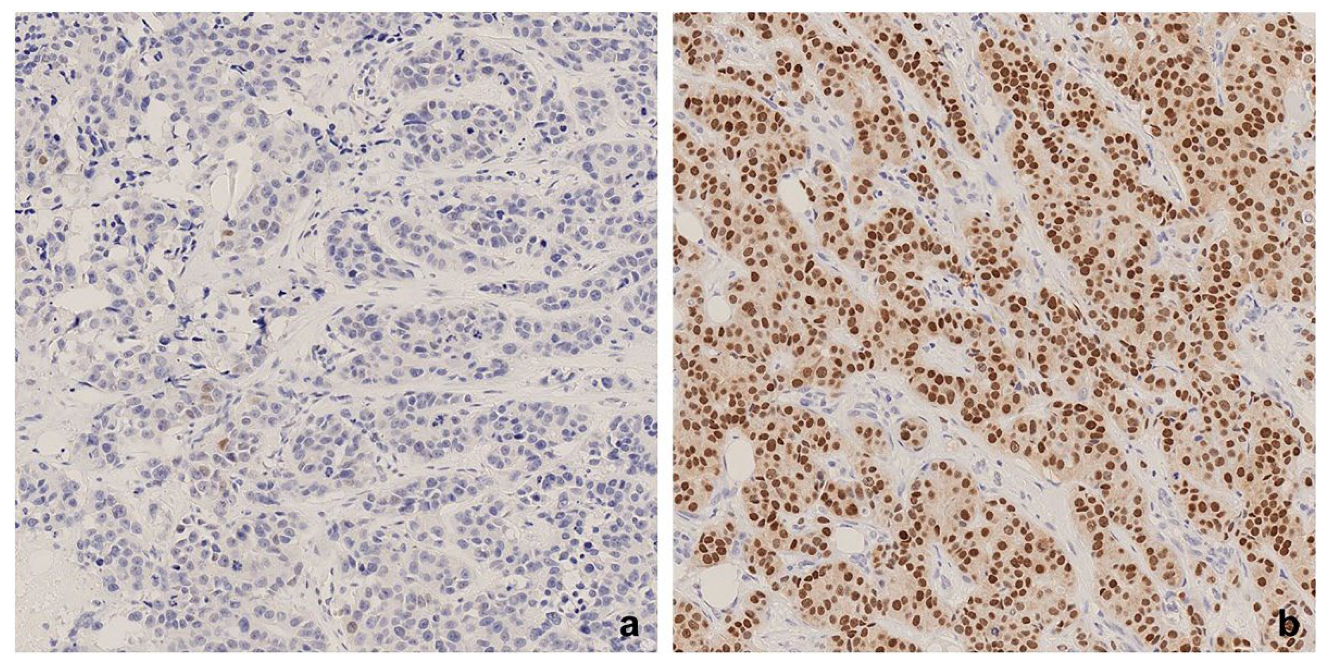
2.3. Assessment of IHC Staining
2.4. Survival Endpoints
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
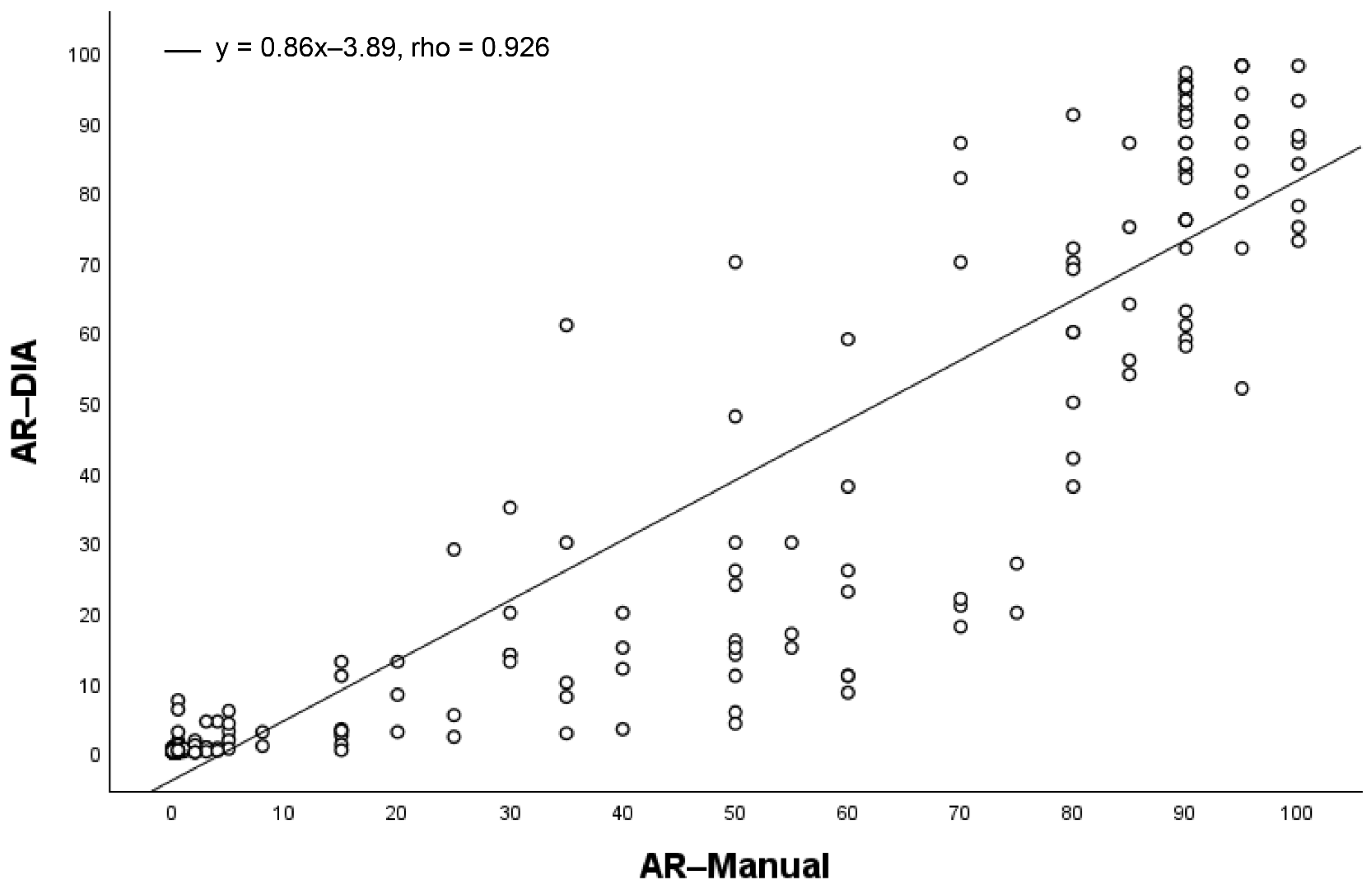
3.1. AR Expression
3.2. AR Expression and Clinicopathological Features
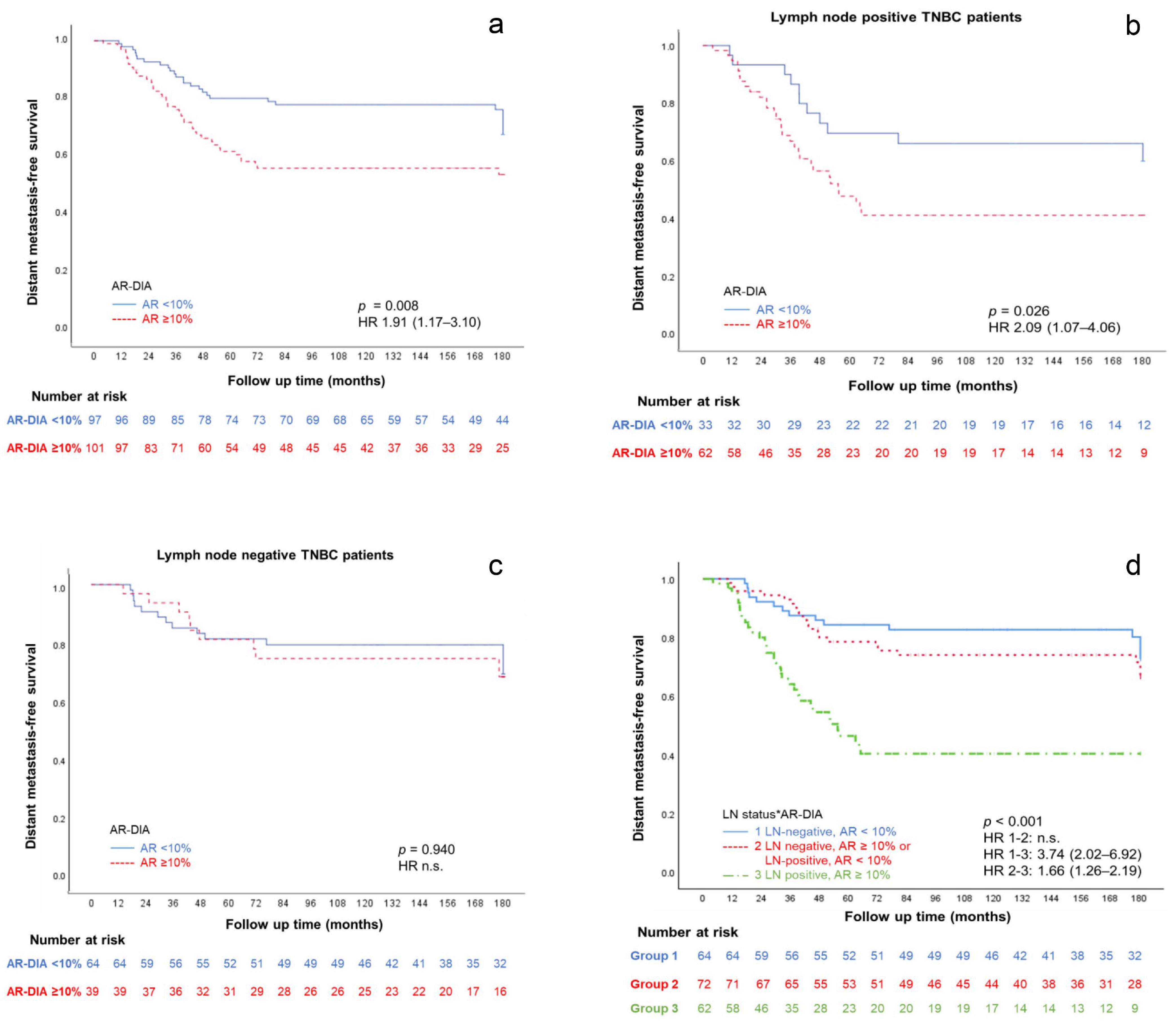
3.3. AR Expression and Prognosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.L.; Li, Z. Incidence trends in triple-negative breast cancer among women in the United States from 2010 to 2019 by race/ethnicity, age and tumor stage. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hercules, S.M.; Alnajar, M.; Chen, C.; Mladjenovic, S.M.; Shipeolu, B.A.; Perkovic, O.; Pond, G.R.; Mbuagbaw, L.; Blenman, K.R.; Daniel, J.M. Triple-negative breast cancer prevalence in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e055735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkert, C.; Liedtke, C.; Tutt, A.; von Minckwitz, G. Molecular alterations in triple-negative breast cancer-the road to new treatment strategies. Lancet 2017, 389, 2430–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P. Triple-negative breast cancer: Epidemiological considerations and recommendations. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23 (Suppl. S6), vi7–vi12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserni, G.; Quinn, C.M.; Foschini, M.P.; Bianchi, S.; Callagy, G.; Chmielik, E.; Decker, T.; Fend, F.; Kovacs, A.; van Diest, P.J.; et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Histological Subtypes with a Favourable Prognosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.C.; Cole, K.S.; Marotti, J.D.; Hu, R.; Schnitt, S.J.; Tamimi, R.M. Androgen receptor expression in breast cancer in relation to molecular phenotype: Results from the Nurses′ Health Study. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Koo, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.I.; Park, B.W.; Lee, K.S. Androgen receptor expression is significantly associated with better outcomes in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozovic-Spasojevic, I.; Zardavas, D.; Brohee, S.; Ameye, L.; Fumagalli, D.; Ades, F.; de Azambuja, E.; Bareche, Y.; Piccart, M.; Paesmans, M.; et al. The Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Clinical and Gene Expression Data. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elebro, K.; Bendahl, P.O.; Jernstrom, H.; Borgquist, S. Androgen receptor expression and breast cancer mortality in a population-based prospective cohort. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 165, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, E.A.; El-Sayed, M.E.; Green, A.R.; Lee, A.H.; Robertson, J.F.; Ellis, I.O. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 2007, 109, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, L.M.; Cao, D.; Sarode, V.; Molberg, K.H.; Torgbe, K.; Haley, B.; Peng, Y. Decreased androgen receptor expression is associated with distant metastases in patients with androgen receptor-expressing triple-negative breast carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W. The expression and clinical significance of the androgen receptor and E-cadherin in triple-negative breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarpour, D.; Pakneshan, S.; Tavassoli, F.A. Androgen receptor (AR) expression in 400 breast carcinomas: Is routine AR assessment justified? Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.E.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Bae, Y.K. Androgen receptor expression predicts decreased survival in early stage triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Chen, W.L.; Ma, H.G.; Jiang, K. Androgen receptor expression identifies patient with favorable outcome in operable triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56364–56374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraby, M.R.; Valla, M.; Opdahl, S.; Haugen, O.A.; Sawicka, J.E.; Engstrom, M.J.; Bofin, A.M. The prognostic value of androgen receptors in breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 172, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.; Klimov, S.; Mittal, K.; Krishnamurti, U.; Li, X.B.; Oprea-Ilies, G.; Wetherilt, C.S.; Riaz, A.; Aleskandarany, M.A.; Green, A.R.; et al. Prognostic Role of Androgen Receptor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Multi-Institutional Study. Cancers 2019, 11, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Peng, R.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Lin, G.; Jiang, X.; Qin, T. Prognostic value of androgen receptor expression in operable triple-negative breast cancer: A retrospective analysis based on a tissue microarray. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieci, M.V.; Tsvetkova, V.; Griguolo, G.; Miglietta, F.; Mantiero, M.; Tasca, G.; Cumerlato, E.; Giorgi, C.A.; Giarratano, T.; Faggioni, G.; et al. Androgen Receptor Expression and Association with Distant Disease-Free Survival in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Analysis of 263 Patients Treated with Standard Therapy for Stage I–III Disease. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Mishra, S.K.; Sharanappa, V.; Krishnani, N.; Kumari, N.; Agarwal, G. Incidence and Prognostic Significance of Androgen Receptors (AR) in Indian Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 15, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, P.; Jiang, J.; Ma, P.; Niu, X.; Ma, S.; Cai, H.; Yang, K. Prognostic Significance of Androgen Receptor Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, e385–e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Pan, B.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, F.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Q. Prognostic value of androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46482–46491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, Y.; Kang, D.W. Digital Validation in Breast Cancer Needle Biopsies: Comparison of Histological Grade and Biomarker Expression Assessment Using Conventional Light Microscopy, Whole Slide Imaging, and Digital Image Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, V.; Soliman, A.T.; Daar, S.; Tzoulis, P.; Fiscina, B.; Kattamis, C. Retrospective observational studies: Lights and shadows for medical writers. Acta. Biomed. 2022, 93, e2022319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Breast tumours. In WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019; Volume 5, pp. 82–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hasebe, T.; Tsuda, H.; Hirohashi, S.; Shimosato, Y.; Iwai, M.; Imoto, S.; Mukai, K. Fibrotic focus in invasive ductal carcinoma: An indicator of high tumor aggressiveness. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1996, 87, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, I.A.; Tan, P.H.; Travis, W.D.; Wesseling, P.; Yagi, Y.; White, V.A.; Lokuhetty, D.; Scolyer, R.A. Counting mitoses: SI (ze) matters! Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Demaria, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Klauschen, F.; Pruneri, G.; Wienert, S.; Van den Eynden, G.; Baehner, F.L.; Penault-Llorca, F.; et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NordiQC. Available online: https://www.nordiqc.org/index.php (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Norwegian Breast Cancer Group (NBCG). Nasjonalt Handlingsprogram Med Retningslinjer for Diagnostikk, Behandling Og Oppfølging Av Pasienter Med Brystkreft. 2023. Available online: https://nbcgblog.files.wordpress.com/2023/02/11.01.2023-nasjonalt-handlingsprogram-for-brystkreft-19.-utgave-publisert-11.01.23.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Kumar, V.; Yu, J.; Phan, V.; Tudor, I.C.; Peterson, A.; Uppal, H. Androgen Receptor Immunohistochemistry as a Companion Diagnostic Approach to Predict Clinical Response to Enzalutamide in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.Y.; Chehade, R.; Qazi, M.; Moravan, V.; Nofech-Mozes, S.; Jerzak, K.J. Androgen Receptor Is Expressed in the Majority of Breast Cancer Brain Metastases and Is Subtype-Dependent. Cancers 2023, 15, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilenic, P.; Herman, A.; Langerholc, E.; Gazic, B.; Seruga, B. Association of androgen receptor and tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes with bone recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Bone Oncol. 2024, 44, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrava, A.L.; Kyaw, P.S.P.; Newman, J.; Pringle, J.; Westhuyzen, J.; La Hera Fuentes, G.; Shakespeare, T.P.; Sakalkale, R.; Aherne, N.J. Androgen Receptor Status in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Does It Correlate with Clinicopathological Characteristics? Breast Cancer 2023, 15, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.A.; Buchanan, G.; Ricciardelli, C.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Centenera, M.M.; Harris, J.M.; Jindal, S.; Segara, D.; Jia, L.; Moore, N.L.; et al. Androgen receptor inhibits estrogen receptor-alpha activity and is prognostic in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6131–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaland, I.; Nordhus, M.; Gudlaugsson, E.; Klos, J.; Kjellevold, K.H.; Janssen, E.A.; Baak, J.P. Evaluation of 5 different labeled polymer immunohistochemical detection systems. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2010, 18, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soiland, H.; Skaland, I.; van Diermen, B.; Janssen, E.A.; Korner, H.; Varhaug, J.E.; Soreide, J.A.; Baak, J.P. Androgen receptor determination in breast cancer: A comparison of the dextran-coated charcoal method and quantitative immunohistochemical analysis. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2008, 16, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewcastle, E.; Skaland, I.; Gudlaugsson, E.; Fykse, S.K.; Baak, J.P.A.; Janssen, E.A.M. The Ki67 Dilemma: Investigating Prognostic Cut-Offs and Inter-Platform Reproducibility for Automated Ki67 Scoring in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 207, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Templeton, A.J.; de Gouveia, P.; Diaz-Padilla, I.; Bedard, P.L.; Al-Mubarak, M.; Seruga, B.; Tannock, I.F.; Ocana, A.; Amir, E. Androgen receptor expression and outcomes in early breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, T.E.; Robinson, J.L.; Carroll, J.S.; Tilley, W.D. Minireview: The androgen receptor in breast tissues: Growth inhibitor, tumor suppressor, oncogene? Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1252–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, M.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Poage, G.M.; Covington, K.R.; Contreras, A.; Fuqua, S.A.; Savage, M.I.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Chang, J.C.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies novel subtypes and targets of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucalp, A.; Traina, T.A. The Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer: Biology and Treatment Considerations. Curr. Breast Cancer Rep. 2011, 4, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soiland, H.; Korner, H.; Skaland, I.; Janssen, E.A.; Gudlaugsson, E.; Varhaug, J.E.; Baak, J.P.; Soreide, J.A. Prognostic relevance of androgen receptor detection in operable breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 98, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, S.; Drubay, D.; Adams, S.; Pruneri, G.; Francis, P.A.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Joensuu, H.; Dieci, M.V.; Badve, S.; Demaria, S.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Prognosis: A Pooled Individual Patient Analysis of Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bairi, K.; Haynes, H.R.; Blackley, E.; Fineberg, S.; Shear, J.; Turner, S.; de Freitas, J.R.; Sur, D.; Amendola, L.C.; Gharib, M.; et al. The tale of TILs in breast cancer: A report from The International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvir, K.; Giordano, S.; Leone, J.P. Immunotherapy in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S. Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, A.H.; Sadar, M.D. Treatments Targeting the Androgen Receptor and Its Splice Variants in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Qiu, F. Androgen Receptor in Breast Cancer: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowsett, T.; Verghese, E.; Pollock, S.; Pollard, J.; Heads, J.; Hanby, A.; Speirs, V. The value of archival tissue blocks in understanding breast cancer biology. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AR-Manual | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| AR-DIA | <10% | ≥10% | Total |
| <10% | 81 (100%) | 16 (14%) | 97 (49%) |
| ≥10% | 0 (0%) | 101 (86%) | 101 (51%) |
| Total | 81 (41%) | 117 (59%) | 198 |
| Characteristics | Total | AR-Manual | AR-DIA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <10% | ≥10% | <10% | ≥10% | ||
| Age (Years) | |||||
| <50 | 75 | 32 (42.7) | 43 (57.3) | 39 (52.0) | 36 (48.0) |
| ≥50 | 123 | 49 (39.8) | 74 (60.2) | 58 (47.2) | 65 (52.8) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.694 n.s. | 0.559 n.s. | |||
| Tumor Size (cm) | |||||
| <1 | 11 | 6 (54.5) | 5 (45.5) | 6 (54.5) | 5 (45.5) |
| 1–1.9 | 67 | 34 (50.7) | 33 (49.3) | 41 (61.2) | 26 (38.8) |
| 2–2.9 | 54 | 16 (29.6) | 38 (70.4) | 20 (37.0) | 34 (63.0) |
| ≥3 | 64 | 23 (35.9) | 41 (64.1) | 28 (43.8) | 36 (56.3) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.071 n.s. | 0.047 0.76, 0.21–2.74 2.04, 0.55–7.55 1.54, 0.42–5.58 | |||
| Nottingham Grade | |||||
| Grade 1 | 11 | 2 (18.2) | 9 (81.8) | 3 (27.3) | 8 (72.7) |
| Grade 2 | 37 | 11 (29.7) | 26 (70.3) | 13 (35.1) | 24 (64.9) |
| Grade 3 | 150 | 68 (45.3) | 82 (54.7) | 81 (54.0) | 69 (46.0) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.065 n.s. | 0.038 0.69, 0.15–3.06 0.31, 0.82–1.25 | |||
| Nottingham Grade | |||||
| Grade 1 + 2 | 48 | 13 (27.1) | 35 (72.9) | 16 (33.3) | 32 (66.7) |
| Grade 3 | 150 | 68 (45.3) | 82 (54.7) | 81 (54.0) | 69 (46.0) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.029 0.44, 0.22–0.91 | 0.014 0.42, 0.21–0.84 | |||
| Histologic Type | |||||
| NST | 169 | 68 (40.2) | 101 (59.8) | 84 (49.7) | 85 (50.3) |
| Others | 29 | 13 (44.8) | 16 (55.2) | 13 (44.8) | 16 (55.2) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.642 n.s. | 0.627 n.s. | |||
| MAI5 | |||||
| <5 | 25 | 4 (16.0) | 25 (84.0) | 5 (20.0) | 20 (80.0) |
| ≥5 | 173 | 77 (44.5) | 96 (55.5) | 92 (53.2) | 81 (46.8) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.007 0.23, 0.78–0.72 | 0.004 0.22, 0.07–0.61 | |||
| MAI10 | |||||
| <10 | 59 | 12 (20.3) | 47 (79.7) | 15 (25.4) | 44 (74.6) |
| ≥10 | 139 | 69 (49.6) | 70 (50.4) | 82 (59.0) | 57 (41.0) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | <0.001 0.25, 0.12–0.53 | <0.001 0.23, 0.12–0.45 | |||
| sTILs (%) | |||||
| <40 | 145 | 58 (40.0) | 87 (60.0) | 65 (44.8) | 80 (55.2) |
| ≥40 | 53 | 23 (43.4) | 30 (56.6) | 32 (60.4) | 21 (39.6) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.745 n.s. | 0.056 n.s. | |||
| Fibrotic Focus | |||||
| Absent | 108 | 43 (39.8) | 65 (60.2) | 50 (46.3) | 58 (53.7) |
| Present | 90 | 38 (42.2) | 52 (57.8) | 47 (52.2) | 43 (47.8) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.773 n.s. | 0.476 n.s. | |||
| Lymph Node Status | |||||
| Negative | 103 | 54 (52.4) | 49 (47.6) | 64 (62.1) | 39 (37.9) |
| Positive | 95 | 27 (28.4) | 68 (71.6) | 33 (34.7) | 62 (65.3) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.001 2.77, 1.53–5.00 | <0.001 3.08, 1.72–5.50 | |||
| Distant Metastasis (DM) | |||||
| Non-DM | 129 | 57 (44.2) | 72 (55.8) | 70 (54.3) | 59 (45.7) |
| DM | 69 | 24 (34.8) | 45 (65.2) | 27 (39.1) | 42 (60.9) |
| p-Value OR, CI 95% | 0.227 n.s. | 0.052 1.84, 1.01–3.34 | |||
| Characteristics | Events/At Risk (DMFS %) | Log Rank p-Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | <50 | 25/75 (67) | 0.266 | n.s. | n.s. |
| ≥50 | 44/123 (64) | ||||
| Tumor Size (cm) | <1 | 1/11 (91) | 0.180 | n.s. | n.s. |
| 1–1.9 | 24/67 (64) | ||||
| 2–2.9 | 17/54 (68) | ||||
| ≥3 | 27/64 (58) | ||||
| Nottingham Grade | Grade 1 | 3/11 (73) | 0.089 | n.s. | n.s. |
| Grade 2 | 8/37 (78) | ||||
| Grade 3 | 58/150 (61) | ||||
| Nottingham Grade | Grade 1 + 2 | 11/48 (77) | 0.029 | 2.02 | 1.06–3.85 |
| Grade 3 | 58/150 (61) | ||||
| Histologic Type | NST | 61/169 (64) | 0.287 | n.s. | n.s. |
| Others | 8/29 (72) | ||||
| MAI5 | <5 | 3/25 (88) | 0.015 | 3.81 | 1.19–12.12 |
| ≥5 | 66/173 (62) | ||||
| MAI10 | <10 | 17/59 (71) | 0.263 | n.s. | n.s. |
| ≥10 | 52/139 (63) | ||||
| sTILs (%) | <40 | 58/145 (60) | 0.012 | 0.44 | 0.23–0.85 |
| ≥40 | 11/53 (79) | ||||
| Fibrotic Focus (FF) | Absent | 27/108 (75) | 0.001 | 2.21 | 1.36–3.59 |
| Present | 42/90 (53) | ||||
| AR-Manual (%) | <10 | 24/81 (70) | 0.065 | n.s. | n.s. |
| ≥10 | 45/117 (61) | ||||
| AR-DIA (%) | <10 | 27/97 (72) | 0.008 | 1.91 | 1.17–3.10 |
| ≥10 | 42/101 (58) | ||||
| Lymph Node Status | Negative | 24/103 (77) | <0.001 | 2.82 | 1.71–4.65 |
| Positive | 45/95 (53) | ||||
| Treatment | No Chemotherapy | 22/62 (64) | 0.978 | n.s. | n.s. |
| Chemotherapy | 42/113 (63) | ||||
| Features | Beta | Standard Error Beta | Wald | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN and AR-DIA interaction | 0.49 | 0.099 | 24.6 | <0.001 | 1.63 | 1.34–1.98 |
| FF | 0.65 | 0.251 | 6.8 | 0.009 | 1.93 | 1.18–3.16 |
| MAI5 | 1.41 | 0.598 | 5.5 | 0.018 | 4.10 | 1.27–13.23 |
| sTILs40 | −0.67 | 0.331 | 4.1 | 0.041 | 0.50 | 0.26–0.97 |
| Characteristics of Subgroup | AR-DIA (%) | Events/At Risk (DMFS %) | Log Rank p-Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN Pos | <10 | 12/33 (64) | 0.026 | 2.09 | 1.07–4.06 |
| ≥10 | 33/62 (47) | ||||
| MAI ≥ 5 | <10 | 26/92 (72) | <0.001 | 2.38 | 1.45–3.91 |
| ≥10 | 40/81 (51) | ||||
| FF-Present | <10 | 17/47 (64) | 0.007 | 2.30 | 1.23–4.29 |
| ≥10 | 25/43 (42) | ||||
| sTILs < 40 | <10 | 22/65 (66) | 0.047 | 2.21 | 0.67–7.26 |
| ≥10 | 36/80 (55) | ||||
| LN Pos, MAI ≥ 5 | <10 | 11/31 (65) | 0.009 | 2.43 | 1.21–4.86 |
| ≥10 | 31/53 (42) | ||||
| LN Pos, FF-Present | <10 | 6/18 (67) | 0.004 | 3.62 | 1.42–9.19 |
| ≥10 | 19/28 (32) | ||||
| LN Pos, sTILs < 40 | <10 | 8/21 (62) | 0.034 | 2.29 | 1.04–5.03 |
| ≥10 | 29/50 (42) | ||||
| LN Pos, MAI ≥ 5, FF-Present | <10 | 6/18 (67) | 0.003 | 3.87 | 1.51–9.90 |
| ≥10 | 18/25 (28) | ||||
| LN Pos, MAI ≥ 5, sTILs < 40 | <10 | 7/20 (65) | 0.010 | 2.86 | 1.23–6.60 |
| ≥10 | 27/42 (36) | ||||
| LN Pos, MAI ≥ 5, FF-Present, sTILs < 40 | <10 | 4/12 (67) | 0.004 | 4.58 | 1.49–14.05 |
| ≥10 | 15/20 (25) | ||||
| LN Pos, FF-Present, sTILs < 40 | <10 | 4/12 (67) | 0.006 | 4.17 | 1.37–12.66 |
| ≥10 | 16/23 (30) | ||||
| MAI ≥ 5, FF-Present | <10 | 17/47 (64) | 0.002 | 2.60 | 1.38–4.88 |
| ≥10 | 24/38 (37) | ||||
| MAI ≥ 5, sTILs < 40 | <10 | 21/61 (66) | 0.005 | 2.15 | 1.24–3.71 |
| ≥10 | 34/63 (46) | ||||
| MAI ≥ 5, FF-Present, sTILs < 40 | <10 | 15/37 (60) | 0.006 | 2.58 | 1.29–5.16 |
| ≥10 | 19/29 (35) | ||||
| FF-Present, sTILs < 40 | <10 | 15/37 (60) | 0.021 | 2.17 | 1.10–4.27 |
| ≥10 | 20/34 (41) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiraz, U.; Rewcastle, E.; Fykse, S.K.; Lundal, I.; Gudlaugsson, E.G.; Skaland, I.; Søiland, H.; Baak, J.P.A.; Janssen, E.A.M. Dual Functions of Androgen Receptor Overexpression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Complex Prognostic Marker. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010054
Kiraz U, Rewcastle E, Fykse SK, Lundal I, Gudlaugsson EG, Skaland I, Søiland H, Baak JPA, Janssen EAM. Dual Functions of Androgen Receptor Overexpression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Complex Prognostic Marker. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiraz, Umay, Emma Rewcastle, Silja K. Fykse, Ingrid Lundal, Einar G. Gudlaugsson, Ivar Skaland, Håvard Søiland, Jan P. A. Baak, and Emiel A. M. Janssen. 2025. "Dual Functions of Androgen Receptor Overexpression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Complex Prognostic Marker" Bioengineering 12, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010054
APA StyleKiraz, U., Rewcastle, E., Fykse, S. K., Lundal, I., Gudlaugsson, E. G., Skaland, I., Søiland, H., Baak, J. P. A., & Janssen, E. A. M. (2025). Dual Functions of Androgen Receptor Overexpression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Complex Prognostic Marker. Bioengineering, 12(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010054






