Effects of an Avatar Control on VR Embodiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Sense of Embodiment
2.2. Neural Networks for a Full-Body Avatar
2.3. Backgrounds on Inverse Kinematics for an Avatar
3. Experiments
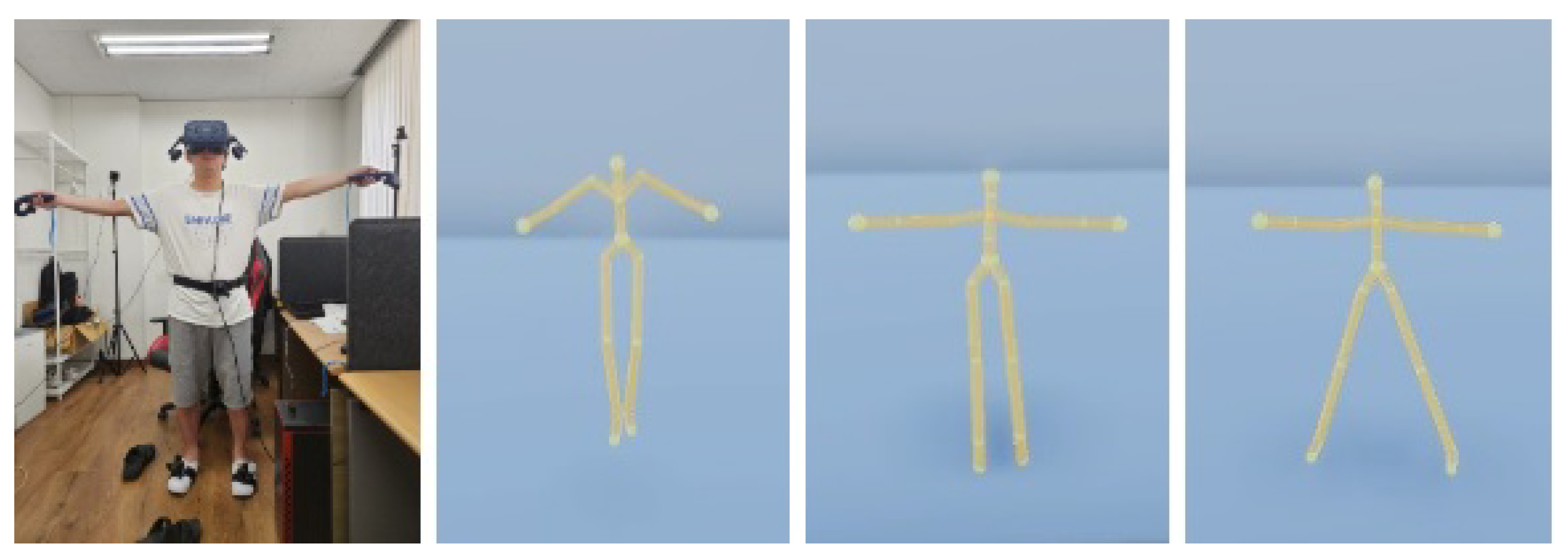
3.1. Avatar Control
3.1.1. Low-Control Avatar
3.1.2. Mid-Control Avatar
3.1.3. High Control Avatar
3.2. Experimental Design
- H1: The low-, mid-, and high-control avatars demonstrate a similar sense of embodiment.
- H2: The mid- and high-control avatars demonstrate a similar sense of embodiment.
- H3: The interaction task using a controlled avatar with another virtual body brings a similar sense of embodiment to a first-person task.
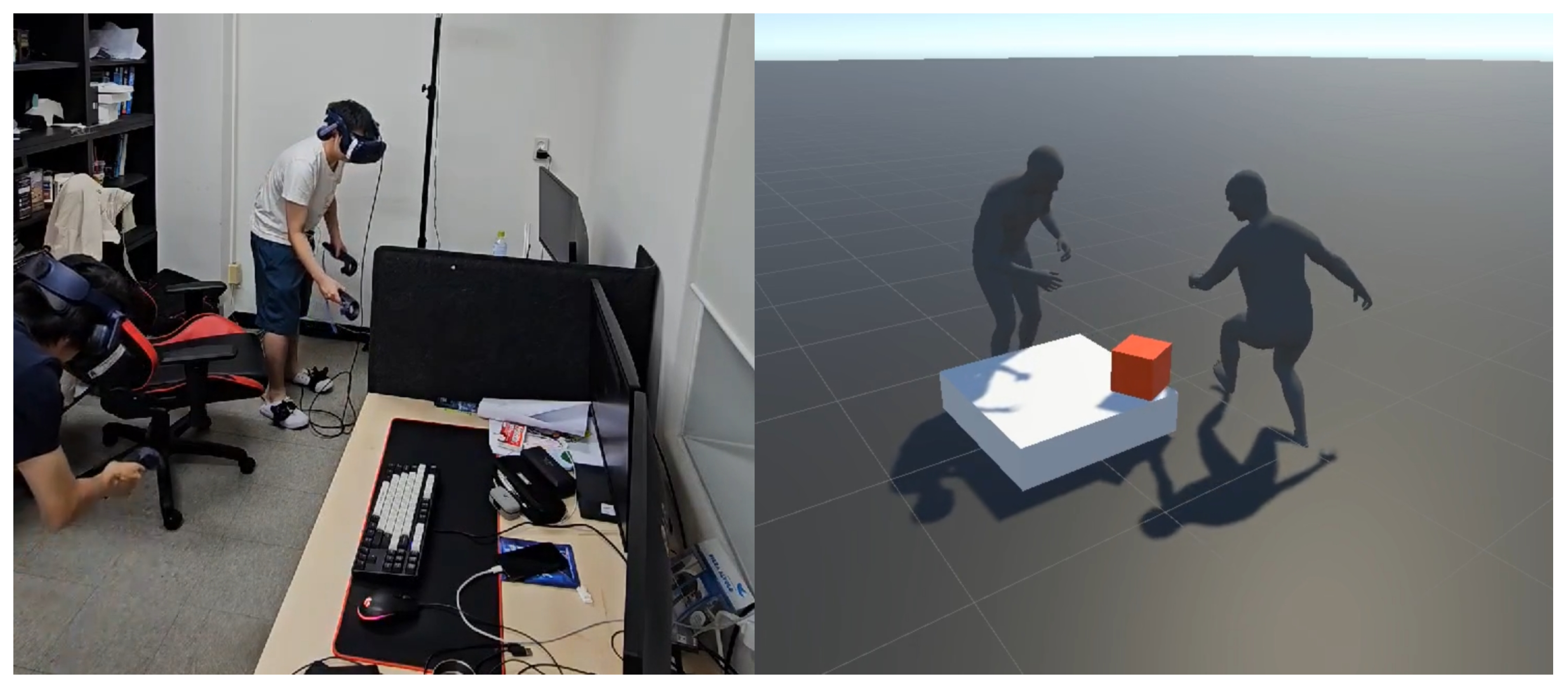
3.2.1. Single-User Experiment
3.2.2. Multi-User Experiment
3.3. Experiment Protocol
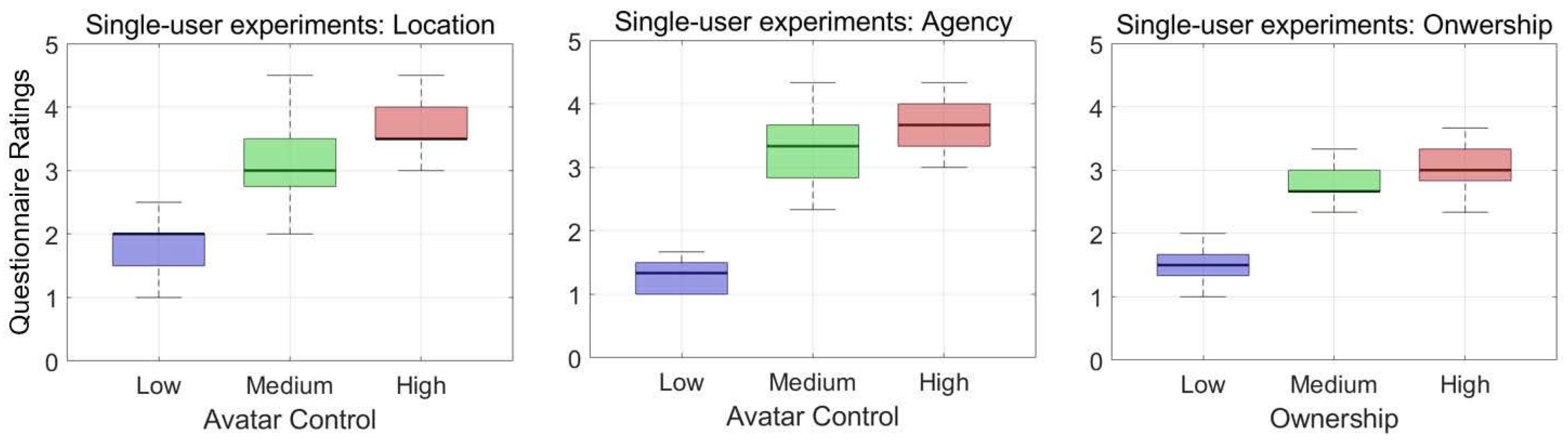
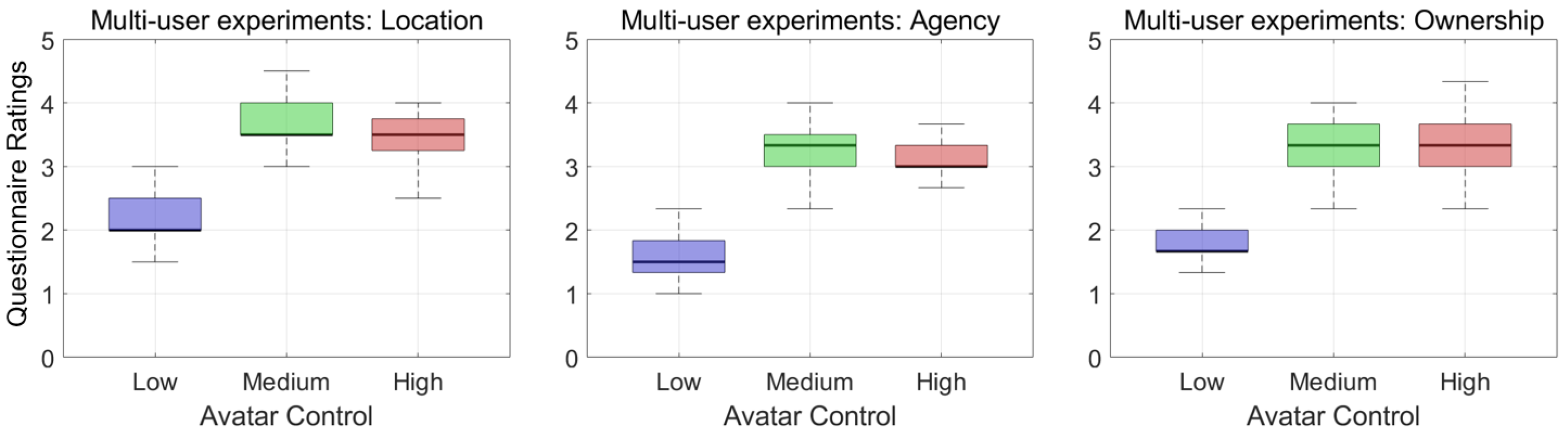
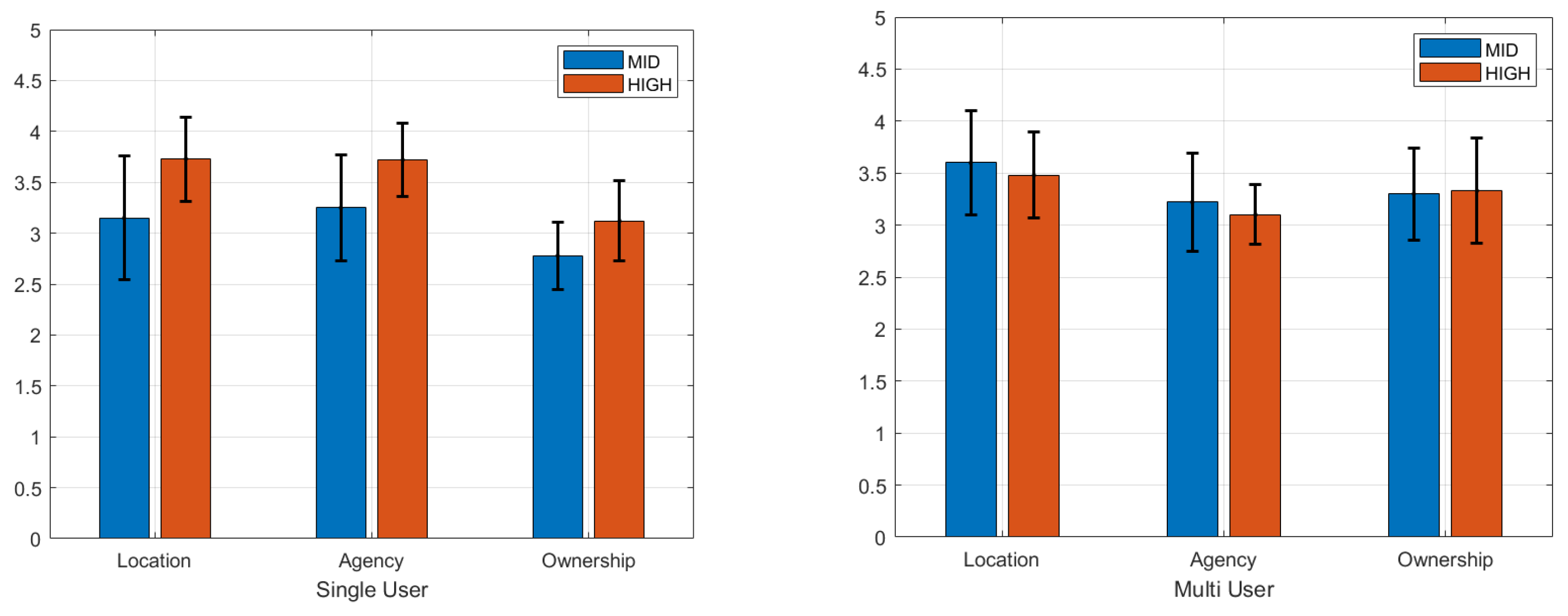
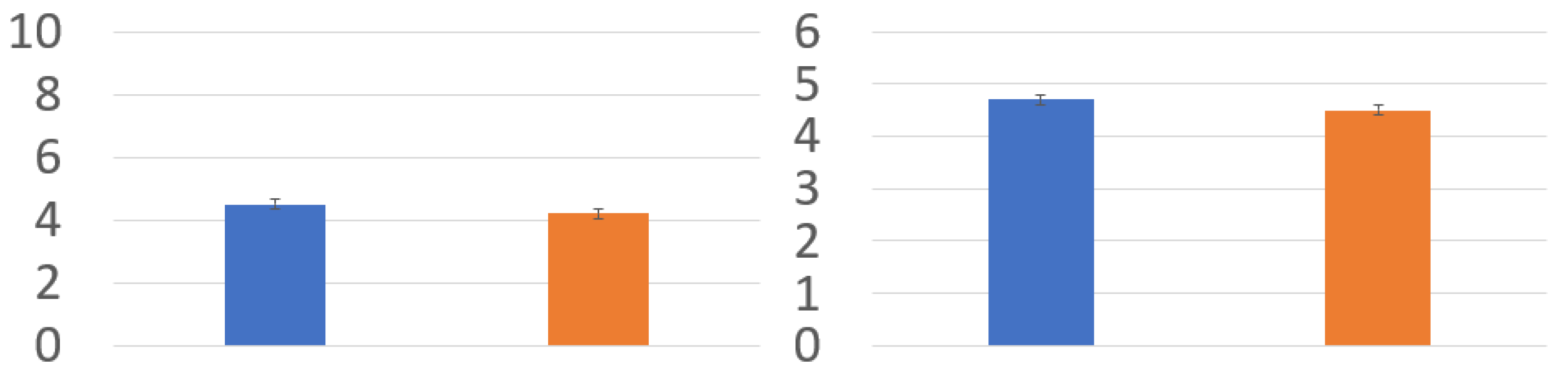
4. Results
4.1. Control Comparison
4.2. Task Comparison
4.3. Post-Questionnaire Results
5. Discussion
5.1. One’s Own Control and Others’ Control
5.2. Influence of the Interaction Task
5.3. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IKs | Inverse Kinematics |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| CCD | Cyclic coordinate descent |
References
- Kilteni, K.; Groten, R.; Slater, M. The sense of embodiment in virtual reality. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Environ. 2012, 21, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerald, J. The VR Book: Human-Centered Design for Virtual Reality; Morgan & Claypool: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Serino, A.; Alsmith, A.; Costantini, M.; Mandrigin, A.; Tajadura-Jimenez, A.; Lopez, C. Bodily ownership and self-location: Components of bodily self-consciousness. Conscious. Cogn. 2013, 22, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Isoyama, N.; Monteiro, D.; Sakata, N.; Kiyokawa, K.; Narumi, T. Head-mounted display with increased downward field of view improves presence and sense of self-location. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2021, 27, 4204–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggard, P. Sense of agency in the human brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiris, M.; Prabhu, G.; Haggard, P. Having a body versus moving your body: How agency structures body-ownership. Conscious. Cogn. 2006, 15, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vignemont, F. Embodiment, ownership and disownership. Conscious. Cogn. 2011, 20, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsmith, A. Mental activity & the sense of ownership. Rev. Philos. Psychol. 2015, 6, 881–896. [Google Scholar]
- Argelaguet, F.; Hoyet, L.; Trico, M.; Lécuyer, A. The role of interaction in virtual embodiment: Effects of the virtual hand representation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Virtual Reality (VR), Greenville, SC, USA, 19–23 March 2016; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lougiakis, C.; Katifori, A.; Roussou, M.; Ioannidis, I.P. Effects of virtual hand representation on interaction and embodiment in HMD-based virtual environments using controllers. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–26 March 2020; pp. 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Parger, M.; Mueller, J.H.; Schmalstieg, D.; Steinberger, M. Proceedings of the Human Upper-Body Inverse Kinematics for Increased Embodiment in Consumer-Grade Virtual Reality, Tokyo Japan, 28 November 2018–1 December 2018; VRST ’18; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.; Pan, X. Visual fidelity effects on expressive self-avatar in virtual reality: First impressions matter. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Christchurch, New Zealand, 12–16 March 2022; pp. 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, D.; Lugrin, J.L.; Büser, J.; Bente, G.; Fuhrmann, A.; Latoschik, M.E. A simplified inverse kinematic approach for embodied VR applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Virtual Reality (VR), Greenville, SC, USA, 19–23 March 2016; pp. 275–276. [Google Scholar]
- Makled, E.; Weidner, F.; Broll, W. Investigating User Embodiment of Inverse-Kinematic Avatars in Smartphone Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Singapore, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 666–675. [Google Scholar]
- Waltemate, T.; Senna, I.; Hülsmann, F.; Rohde, M.; Kopp, S.; Ernst, M.; Botsch, M. The impact of latency on perceptual judgments and motor performance in closed-loop interaction in virtual reality. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Munich Germany, 2–4 November 2016; VRST ’16. ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; McMillan, L. Human Motion Estimation from a Reduced Marker Set. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Sketches, Redwood City, CA, USA, 14–17 March 2006; SIGGRAPH ’06. ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 9-es. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wei, X.; Chai, J.; Ha, I.; Rhee, T. Realtime Human Motion Control with a Small Number of Inertial Sensors. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–20 February 2011; I3D ’11. ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- von Marcard, T.; Rosenhahn, B.; Black, M.J.; Pons-Moll, G. Sparse Inertial Poser: Automatic 3D Human Pose Estimation from Sparse IMUs. Comput. Graph. Forum 2017, 36, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kaufmann, M.; Aksan, E.; Black, M.J.; Hilliges, O.; Pons-Moll, G. Deep Inertial Poser: Learning to Reconstruct Human Pose from Sparse Inertial Measurements in Real Time. ACM Trans. Graph. 2018, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, F. TransPose: Real-Time 3D Human Translation and Pose Estimation with Six Inertial Sensors. ACM Trans. Graph. 2021, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Habermann, M.; Shimada, S.; Golyanik, V.; Theobalt, C.; Xu, F. Physical Inertial Poser (PIP): Physics-aware Real-time Human Motion Tracking from Sparse Inertial Sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, M.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, C.; Tao, L.; Twigg, C.; Song, J.; Wang, R.; Hilliges, O. EM-POSE: 3D Human Pose Estimation from Sparse Electromagnetic Trackers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wouda, F.J.; Giuberti, M.; Rudigkeit, N.; van Beijnum, B.J.F.; Poel, M.; Veltink, P.H. Time Coherent Full-Body Poses Estimated Using Only Five Inertial Sensors: Deep versus Shallow Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.H. LoBSTr: Real-time Lower-body Pose Prediction from Sparse Upper-body Tracking Signals. Comput. Graph. Forum 2021, 40, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, K.; Ofek, E.; Gonzalez-Franco, M.; Holz, C.; Wilson, A.D. CoolMoves: User Motion Accentuation in Virtual Reality. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2021, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittadi, A.; Dziadzio, S.; Cosker, D.; Lundell, B.; Cashman, T.J.; Shotton, J. Full-body motion from a single head-mounted device: Generating SMPL poses from partial observations. In Proceedings of theIEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11687–11697. [Google Scholar]
- Aliakbarian, S.; Cameron, P.; Bogo, F.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Cashman, T.J. Flag: Flow-based 3d avatar generation from sparse observations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 13253–13262. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Streli, P.; Qiu, H.; Fender, A.; Laich, L.; Snape, P.; Holz, C. AvatarPoser: Articulated Full-Body Pose Tracking from Sparse Motion Sensing. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, L.; Hu, L.; Xia, S. Neural3Points: Learning to Generate Physically Realistic Full-body Motion for Virtual Reality Users. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.05753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Won, J.; Ye, Y. QuestSim: Human Motion Tracking from Sparse Sensors with Simulated Avatars. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia 2022 Conference Papers, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 6–9 December 2022; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Aristidou, A.; Lasenby, J.; Chrysanthou, Y.; Shamir, A. Inverse Kinematics Techniques in Computer Graphics: A Survey. Comput. Graph. Forum 2018, 37, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RootMotion. Available online: http://root-motion.com (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Yang, S.; Quan, Z.; Nie, M.; Yang, W. Transpose: Keypoint localization via transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11802–11812. [Google Scholar]




| Test | N | Chi-Square | DF | p | sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| single-user | 20 | 37.696 | 2 | <0.001 | yes |
| multi-user | 20 | 31.579 | 2 | <0.001 | yes |
| Single-User | Multi-User | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group1 | Group2 | Stats | p | sig | Group1 | Group2 | Stats | p | sig |
| Low | Mid | −3.399 | 0.002 | yes | Low | Mid | −4.743 | 0.000 | yes |
| Low | High | −6.087 | 0.000 | yes | Low | High | −4.743 | 0.000 | yes |
| Mid | High | −2.688 | 0.022 | yes | Mid | High | 0.000 | 1.000 | no |
| Embodiment | Location | Agency | Ownership | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p (sig) | p (sig) | p (sig) | p (sig) | |
| low | <0.001 (yes) | 0.056 (no) | 0.043 (yes) | 0.004 (yes) |
| mid | 0.002 (yes) | 0.017 (yes) | 0.904 (no) | <0.001 (yes) |
| high | 0.012 (yes) | 0.114 (no) | <0.001 (yes) | 0.192 (no) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Yeo, H.; Park, K. Effects of an Avatar Control on VR Embodiment. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010032
Kim D, Yeo H, Park K. Effects of an Avatar Control on VR Embodiment. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, DoHyung, Halim Yeo, and Kyoungju Park. 2025. "Effects of an Avatar Control on VR Embodiment" Bioengineering 12, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010032
APA StyleKim, D., Yeo, H., & Park, K. (2025). Effects of an Avatar Control on VR Embodiment. Bioengineering, 12(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12010032







