A Rapid Head Organ Localization System Based on Clinically Realistic Images: A 3D Two Step Progressive Registration Method with CVH Anatomical Knowledge Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Preparation of CVH
2.2. Methods
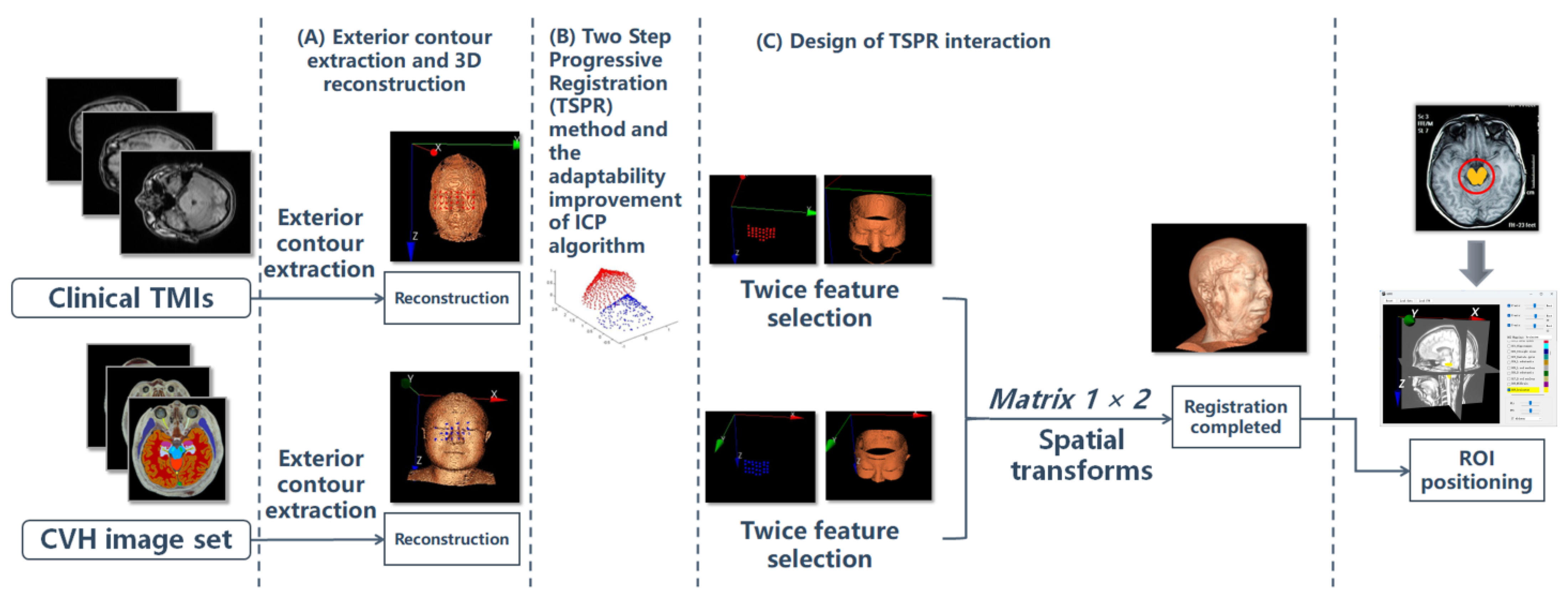
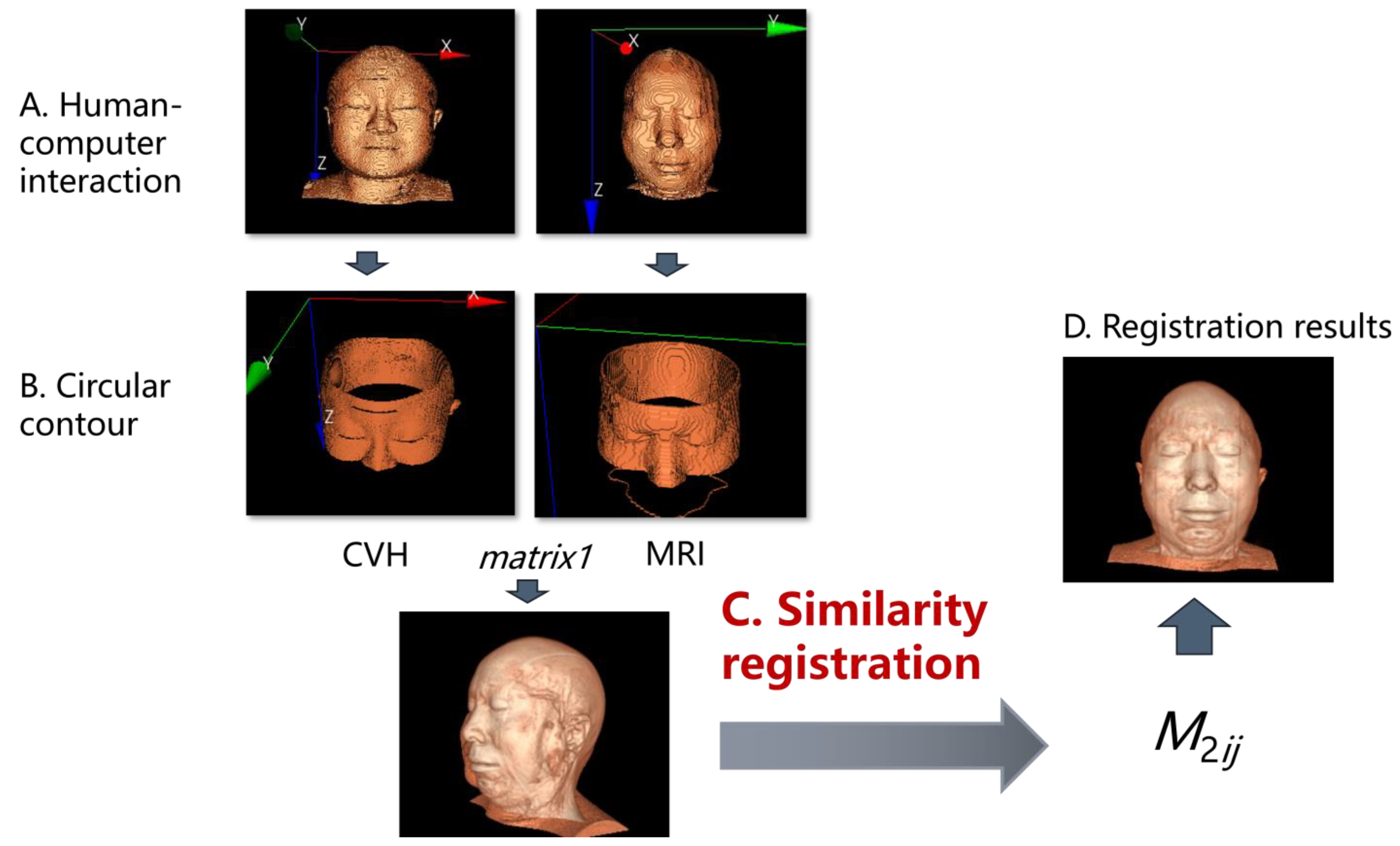
2.2.1. Overall Process
2.2.2. Exterior Contour Extraction and 3D Reconstruction
2.2.3. Introduction to ICP Classic Algorithm
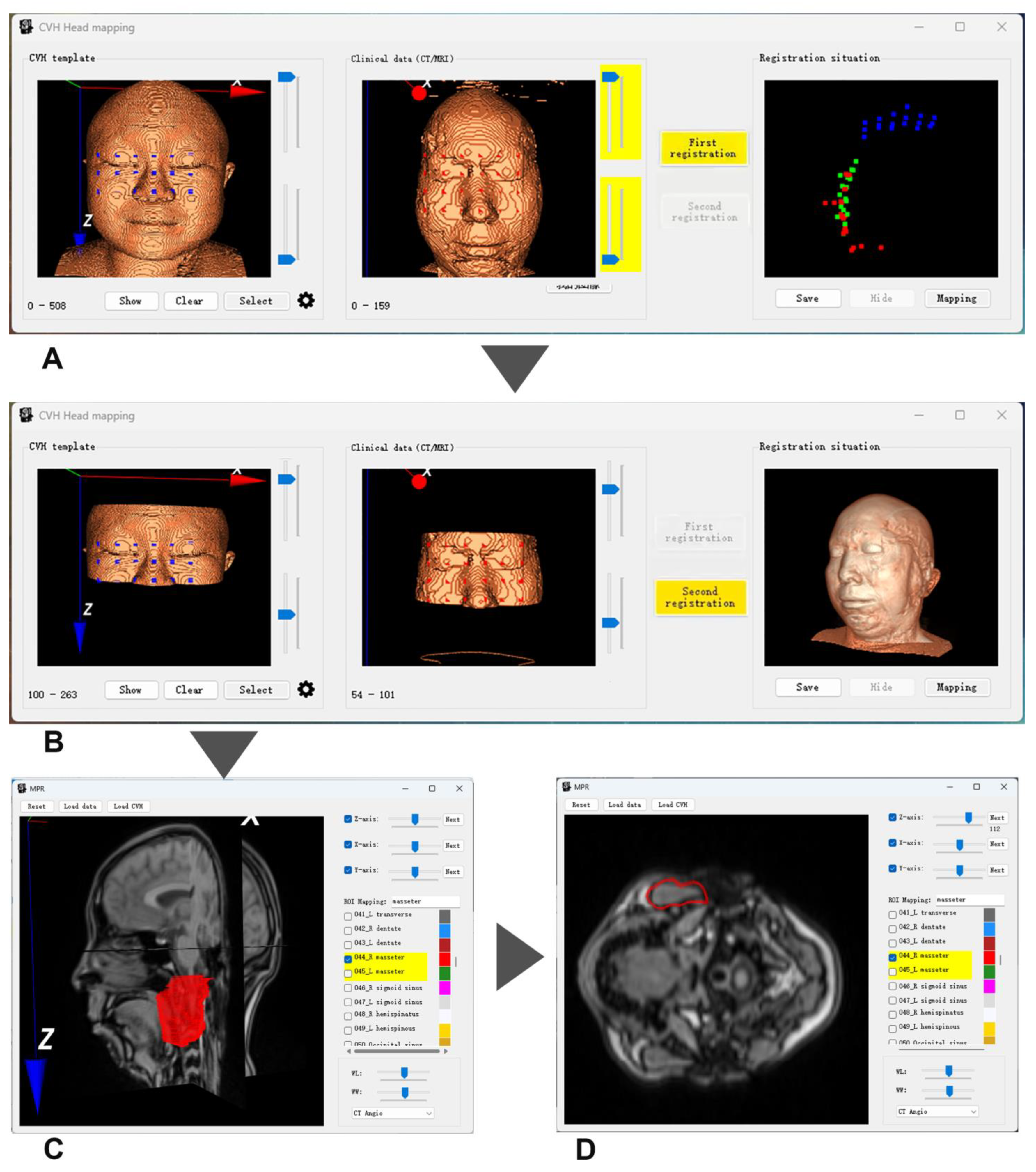
2.2.4. TSPR Method and the Adaptability Improvement of ICP Algorithm
- (i)
- First ICP registration for spatial orientation
- (ii)
- Second ICP registration for spatial scaling
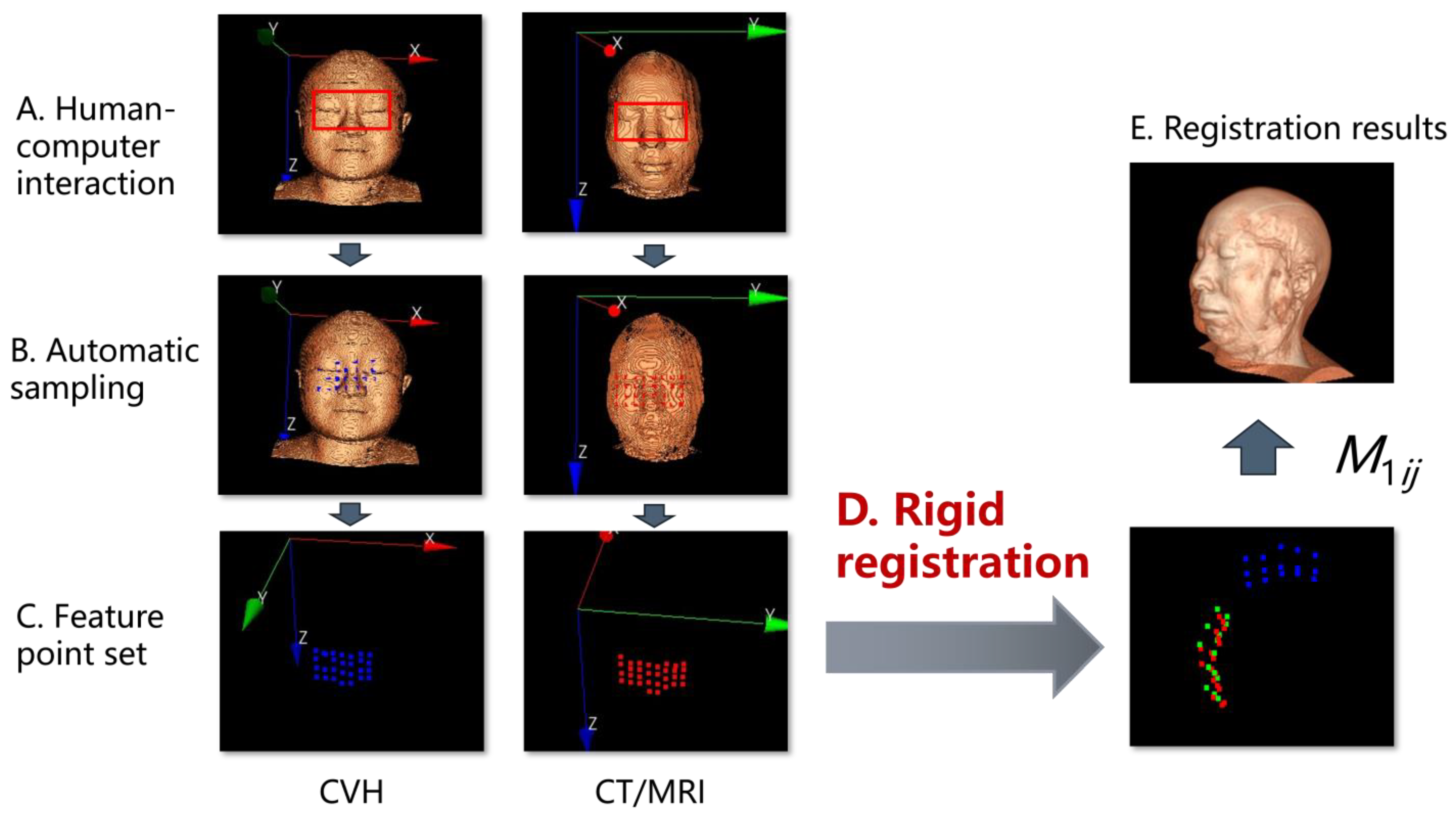
2.2.5. Design of TSPR Interaction
3. Results
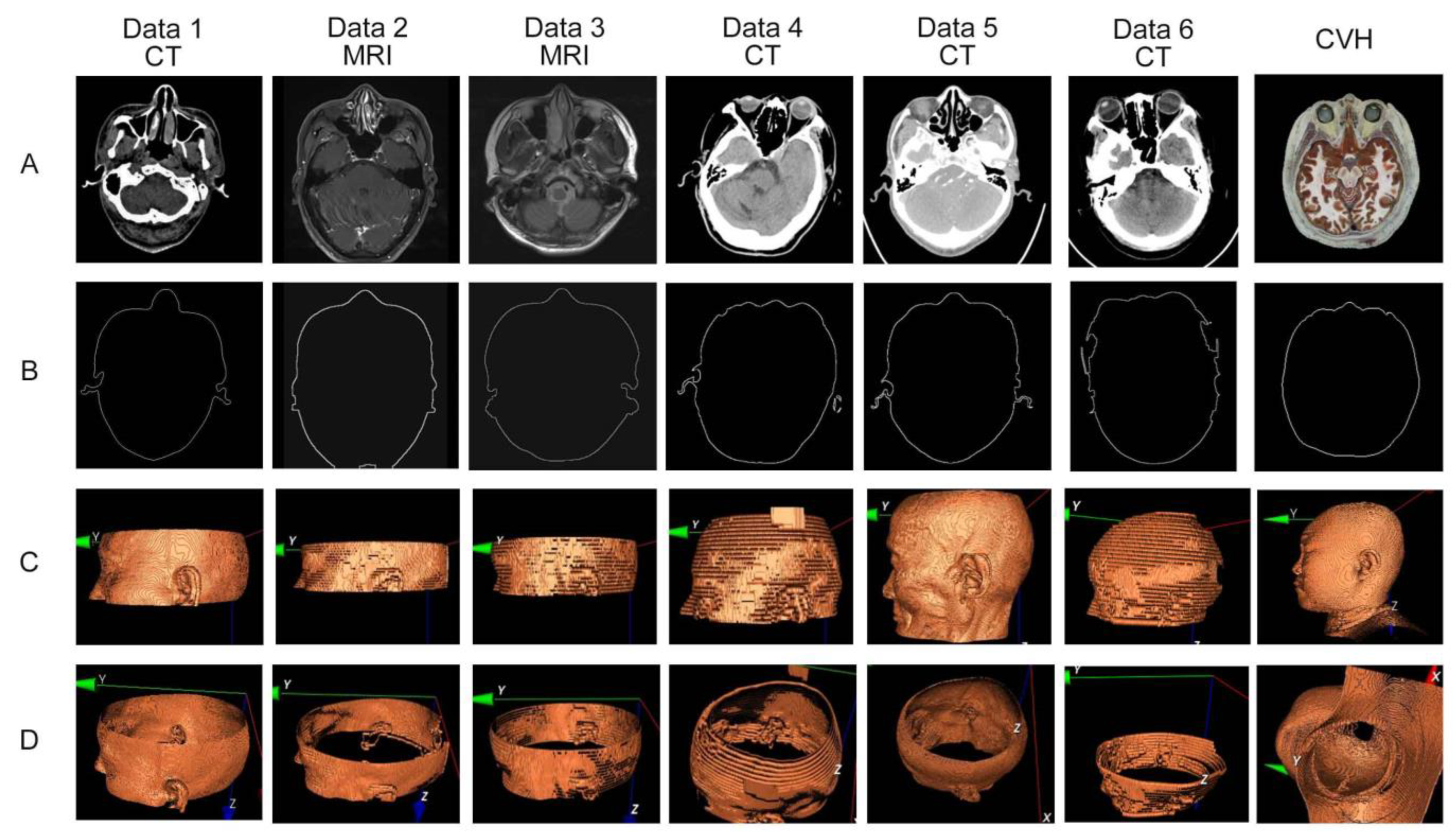
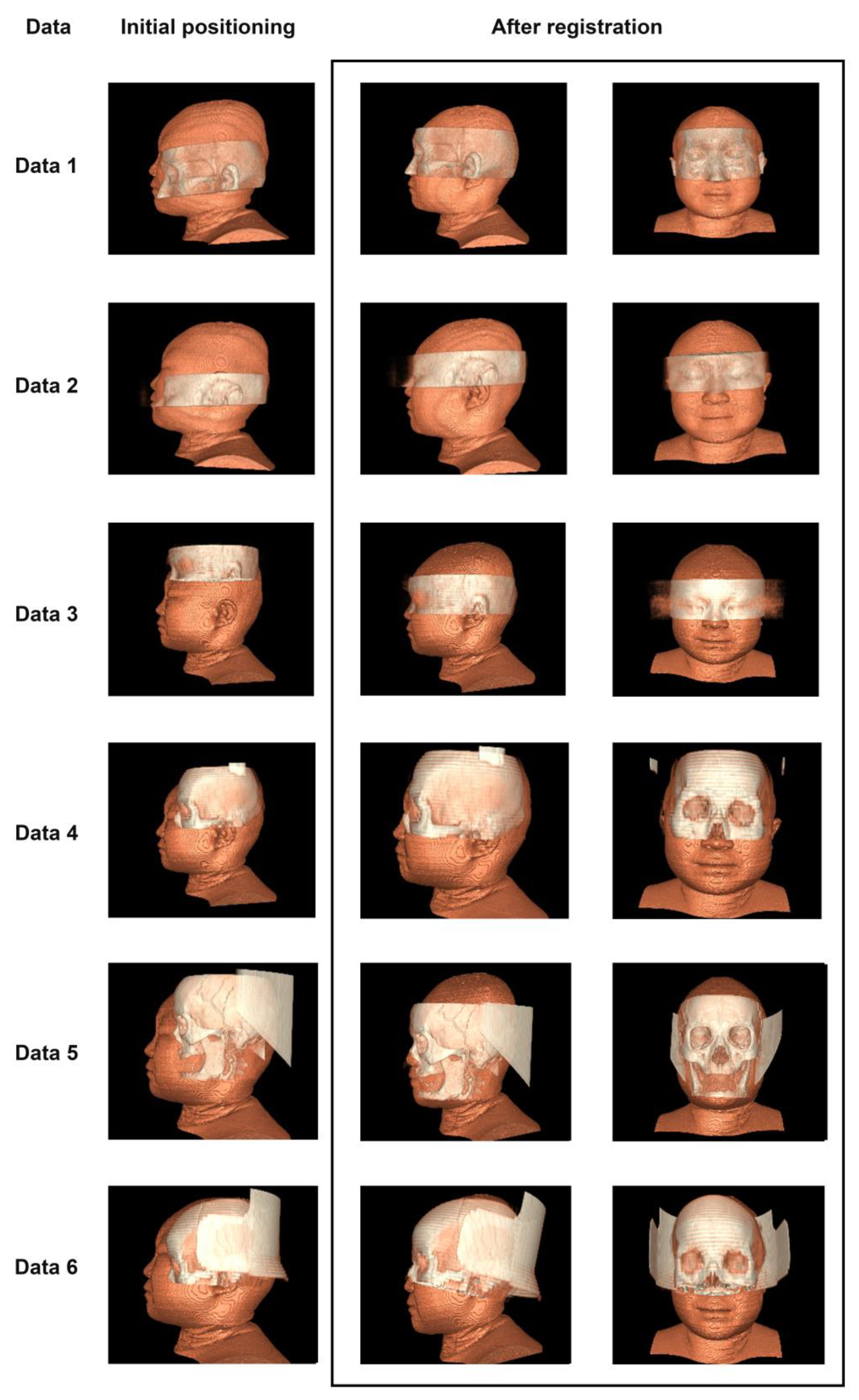
3.1. Selection of Test Data
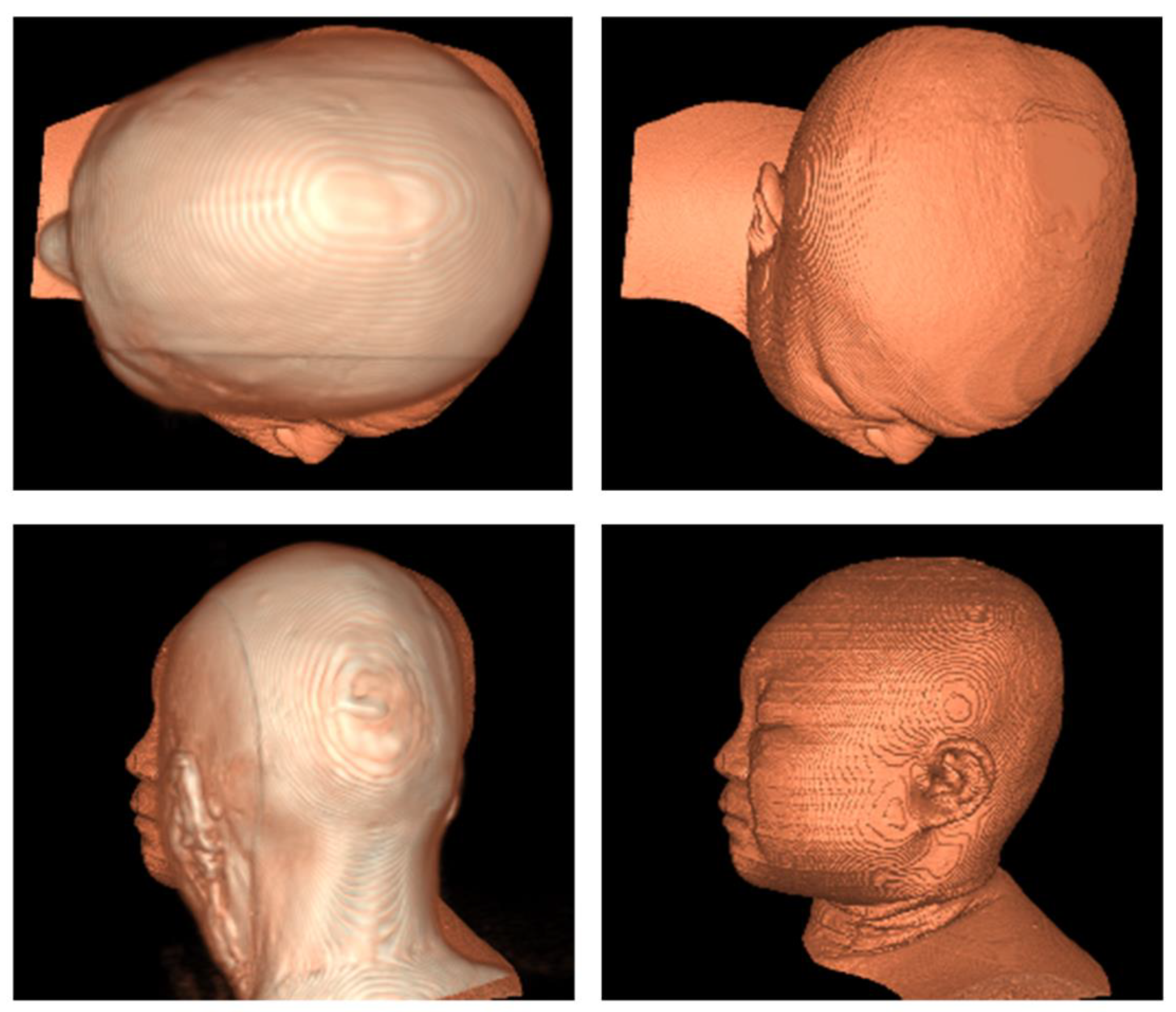
3.2. Registration Effect of Clinical Data and CVH
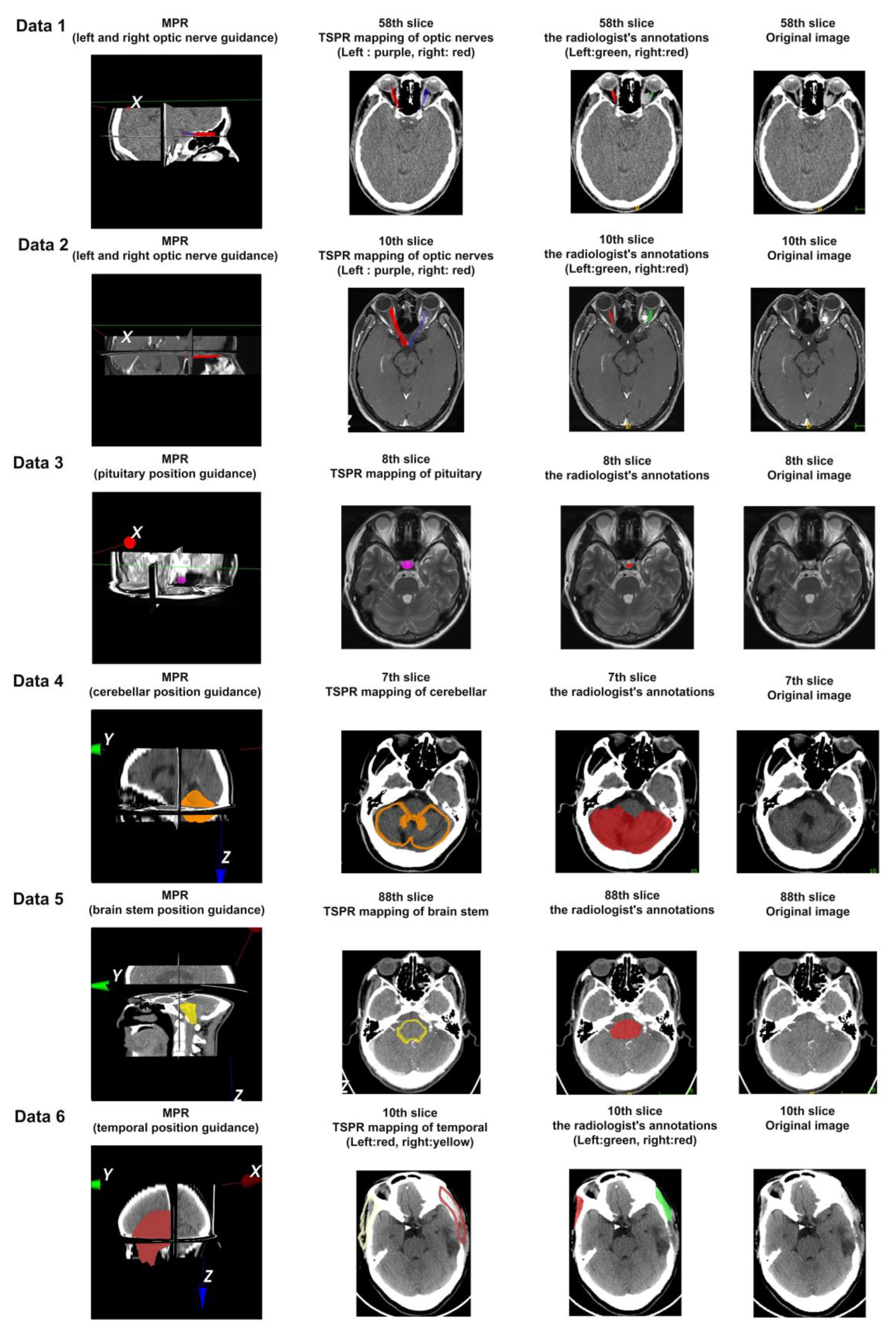
3.3. Five-Point Scale Method Based on the Mapping Effect of Typical Anatomical Structures
3.4. The Quantitative Analysis Method Based on ROI Area Coverage, the Mapping Effect of Typical Anatomical Structures
4. Discussion
4.1. Adaptability Requirements for Test Data
4.2. Discussion on the Generalization Performance of Diversified Images with Significant Pathological Changes
4.3. Advantages of the Method Proposed in This Study
- (i)
- Two-step strategy for image registration
- (ii)
- Selection of feature points
- (iii)
- Comparison of Registration Methods
4.4. Clinical Application Prospects of the Software
- (i)
- Applicability and Data Processing Capability:
- (ii)
- Adaptability:
- (iii)
- Usability and operational efficiency:
- (iv)
- Potential educational value and interdisciplinary applications:
- (v)
- Potential of Digital Public Health and Medical Education:
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.X.; Heng, P.A.; Liu, Z.J. Chinese visible human project. Clin. Anat. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Clin. Anat. Br. Assoc. Clin. Anat. 2006, 19, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.J. Anatomy and Visualisation of Digital Three-Dimensional Sections of the Head and Neck Region. Bachelor’s Thesis, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Establishment of Digital Human Whole Body Segmentation Dataset and Digitisation of Human Thoracic and Pelvic Cavities. Bachelor’s Thesis, Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, D.F.; Ma, Z.B. Double modality fusion between CT and MRI for human head based on surface anatomic characters. ACTA Anat. Sin. 2019, 50, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, J.M.; Goatman, K.A.; Siebert, J.P. Learning Rigid Image Registration-Utilizing Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Image Registration; SCITEPRESS-Science and Technology Publications: Setúbal, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Meng, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Lian, W.; Deng, K.; Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B.; Long, X. 3D facial analysis in acromegaly: Gender-specific features and clinical correlations. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, D.D.P.; Stucki, S.; Gkantidis, N. Assessment of methods used for 3-dimensional superimposition of craniofacial skeletal structures: A systematic review. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.; Brandt, J.; Lin, Z.; Bourdev, L.; Huang, T.S. Interactive facial feature localization. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; Proceedings, Part III 12. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.G. Research on Techniques Related to Digital Geometry Processing in Orthopaedic Navigation Surgery and Their Applications. (Bachelor’s thesis) Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2009.
- Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Miao, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Qu, L. Progressive 3D biomedical image registration network based on deep self-calibration. Front. Neuroinf. 2022, 16, 932879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzia, S.; Capellini, K.; Gasparotti, E.; Pizzuto, D.; Spinelli, G.; Berti, S.; Positano, V.; Celi, S. Three-Dimensional Multi-Modality Registration for Orthopaedics and Cardiovascular Settings: State-of-the-Art and Clinical Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Z.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Ren, H.; Meng, M.Q. 3D Rigid Point Set Registration for Computer-Assisted Orthopedic Surgery (CAOS): A Review from the Algorithmic Perspective. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2023, 5, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.F.; Zu, D.L.; Wang, W.D.; Deng, Y.M.; You, J.S.; Bao, S.L. SVD-ICP registration method for multimodal medical images. CT Theor. Appl. Res. 2000, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Iterative closest point (ICP). In Computer Vision: A Reference Guide; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 718–720. [Google Scholar]
- Kurobe, A.; Sekikawa, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Saito, H. Corsnet: 3d point cloud registration by deep neural network. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3960–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viergever, M.A.; Maintz, J.A.; Klein, S.; Murphy, K.; Staring, M.; Pluim, J.P. A survey of medical image registration–under review. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 33, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Qiu, T.; Fen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Brain PET/CT image atlas registration and brain region segmentation based on anatomical landmark constraints. J. Dalian Univ. Technol./Dalian Ligong Daxue Xuebao 2021, 61, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; Hou, M.; Fan, J.; Luo, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.Q. Study on influencing factors of registration accuracy between cone-beam CT reconstructed dentition and laser-scanned dental model in digital orthognathic surgery. Chin. J. Plast. Surg. 2022, 38, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Hu, X.H.; Yang, K.; Zhao, Y. Analysis and Improvement of Head Motion Correction Registration Method for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Images Based on SPM. Chin. J. Med. Imaging 2015, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindseth, F.; Langø, T.; Selbekk, T.; Hansen, R.; Reinertsen, I.; Askeland, C.; Solheim, O.; Unsgård, G.; Mårvik, R.; Hernes, T.A.N. Ultrasound-based guidance and therapy. In Advancements and Breakthroughs in Ultrasound Imaging; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.X.; He, S.R.; He, B.C.; He, Q.Y.; He, J.L. 3D/3D registration of CT and MRI images based on facial regions. China Med. Equip. 2023, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilna, K.T.; Anitha, J.; Hemanth, D.J. A novel framework for segmentation of uterus fibroids in ultrasound images using machine learning models. Int. J. Model. Identif. Control. 2022, 41, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.R.; Mala, G.A.; Sarika, C.; Shruthi, S.; Sripradha, S. Segmentation of pancreatic cysts and roi extraction from pancreatic ct images using machine learning. Eur. J. Mol. Clin. Med. 2020, 7, 116444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.X.; Qi, M.K.; Song, T.; Lu, G.W. A study of head and neck pseudo-CT generation based on segmented B-spline deformation registration method. Chin. J. Med. Phys. 2022, 39, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Tavakoli, M.; Boveiri, H.R.; Shirazi, M.A.M.; Khayami, R.; Khorasani, H.; Javidan, R.; Mehdizadeh, A. Medical image registration using unsupervised deep neural network: A scoping literature review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 73, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, M.; Nunes, J.C.; Chourak, H.; Largent, A.; Tahri, S.; Acosta, O.; De Crevoisier, R.; Lafond, C.; Barateau, A. Deep learning methods to generate synthetic CT from MRI in radiotherapy: A literature review. Phys. Medica 2021, 89, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. Deep learning in medical image registration: A review. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 20TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, G.; Kruger, U.; Yan, P. Deep learning in medical image registration: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2020, 31, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Huang, S.; Yang, X. A multi-view assisted registration network for MRI registration pre-and post-therapy. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2023, 14, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Rahman, S.U.; Ullah, S.; Gulati, K. Medical image registration in image guided surgery: Issues, challenges and research opportunities. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengjun, Z.; Lirong, Q.; Zhenhua, D. Using Mimics Software to Measure Compressed Lung Suffered from Pneumothorax; Forensic Science and Technology: Austin, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mandolini, M.; Brunzini, A.; Facco, G.; Mazzoli, A.; Forcellese, A.; Gigante, A. Comparison of three 3D segmentation software tools for hip surgical planning. Sensors 2022, 22, 5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Cavichini, M.; Bartsch, D.U.G.; Freeman, W.R.; Nguyen, T.Q.; An, C. Two-Step Registration on Multi-Modal Retinal Images via Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, F. Application of Opening and Closing Morphology in Deep Learning-Based Brain Image Registration. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. Engl. Ed. 2023, 32, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Bi, X. A Medical Image Registration Model Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Transformer Parallel. Comput. Appl. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Modality | Parameter | MPR of Scan Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data 1 | CT | Slice Spatial Resolution: 512 × 512 Slice Quantity: 121 Pixel Spacing: 0.4336 mm\0.4336 mm Thickness: 1.0 mm ROI from radiological description: An oval-shaped nodular shadow can be seen on the inner side of the left optic nerve behind the orbital ball, suspected to be a hemangioma | 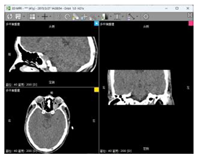 |
| Data 2 | MRI | Slice Spatial Resolution: 288 × 384 Slice Quantity: 18 Pixel Spacing: 0.625 mm\0.625 mm Thickness: 3.0 mm ROI from radiological description: An oval-shaped nodular shadow can be seen on the inner side of the left optic nerve behind the orbital ball, suspected to be a hemangioma | 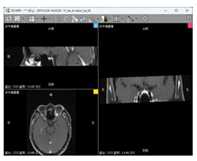 |
| Data 3 | MRI | Slice Spatial Resolution: 512 × 512 Slice Quantity: 15 Pixel Spacing: 0.4296875 mm\0.4296875 mm Thickness: 3.5 mm ROI from radiological description: Nodular shadow on the left side of the saddle area, considering the possibility of pituitary adenoma | 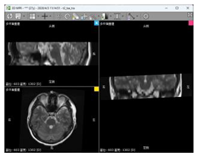 |
| Data 4 | CT | Slice Spatial Resolution: 512 × 512 Slice Quantity: 25 Pixel Spacing: 0.430 mm\0.430 mm Thickness: 5 mm ROI from radiological description: postoperative cerebellar changes, abnormal structural disturbances in the cerebellar region, occipital bone showing postoperative changes | 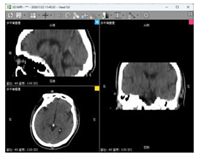 |
| Data 5 | CT | Slice Spatial Resolution: 512 × 512 Slice Quantity: 177 Pixel Spacing: 0.401 mm\0.401 mm Thickness: 1 mm ROI from radiological description: cerebral softening foci in the left part of the brainstem, demyelinating changes in the cerebral white matter | 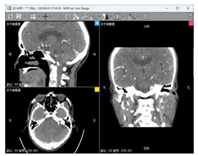 |
| Data 6 | CT | Slice Spatial Resolution: 512 × 512 Slice Quantity: 30 Pixel Spacing: 0.46289 mm\0.46289 mm Thickness: 5 mm ROI from radiological description: large area of bone defect in the left temporoparietal bone adjacent to the left temporalis muscle, edema in the left temporoparietal lobe of the brain, formation of softening lesions, and slight swelling of the temporalis muscle. | 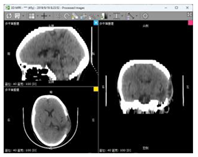 |
| Theme | Five-Point Scale Design | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| Accuracy of TSPR interaction behavior (A smooth operation, one-time success, B relatively smooth operation, some steps need to be repeated, C achieve mapping objectives, D not very useful, E ineffective) | 15 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Efficiency of TSPR interaction behavior (A can be completed in 1 min, B can be completed in 2 min, C can be completed in 3 min, D is cumbersome, E cannot complete the operation) | 17 | 1 | |||
| Degree of match between the mapped region of the ROI of the CVH and datasets (A perfect match, B mostly match, C half match, D less than half, E not valid at all) | 15 | 3 | |||
| Data 1 | Layer | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| Recall | 0.8894 | 0.8366 | 0.8277 | 0.8601 | 0.8302 | 0.8637 | 0.8949 | 0.9350 | 0.9384 | |
| Data 2 | Layer | 10 | ||||||||
| Recall | 0.8838 | |||||||||
| Data 3 | Layer | 8 | ||||||||
| Recall | 1.0 | |||||||||
| Data 4 | Layer | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Recall | 0.7320 | 0.8894 | 0.9369 | 0.9533 | 0.9640 | 0.9115 | 0.8795 | 0.9447 | 0.9503 | |
| Layer | 11 | 12 | ||||||||
| Recall | 0.9711 | 0.4417 | ||||||||
| Data 5 | Layer | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| Recall | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9965 | 0.9203 | 0.9937 | 0.9976 | |
| Layer | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | |
| Recall | 0.9879 | 0.8713 | 0.8813 | 0.9934 | 0.9882 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9784 | |
| Layer | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | |
| Recall | 0.9876 | 0.9485 | 0.9229 | 0.9497 | 0.8786 | 0.8096 | 0.7717 | 0.5987 | 0.6247 | |
| Layer | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 | 101 | 102 | |
| Recall | 0.6731 | 0.5881 | 0.5374 | 0.6125 | 0.6908 | 0.7283 | 0.6901 | 0.6126 | 0.6586 | |
| Layer | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 | 109 | 110 | 111 | |
| Recall | 0.6325 | 0.6547 | 0.5833 | 0.5724 | 0.6558 | 0.7003 | 0.7737 | 0.7672 | 0.7104 | |
| Layer | 112 | 113 | 114 | 115 | 116 | 117 | 118 | |||
| Recall | 0.6720 | 0.7466 | 0.7578 | 0.7619 | 0.7796 | 0.8255 | 0.6970 | |||
| Data 6 | Layer | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Recall | 0.8026 | 0.7408 | 0.6842 | 0.6884 | 0.7196 | 0.7558 | 0.7716 | 0.8242 | 0.8353 | |
| Layer | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | ||
| Recall | 0.8367 | 0.7917 | 0.7782 | 0.7313 | 0.7641 | 0.7797 | 0.7882 | 0.8368 |
| Maximum Recall Rate | Minimum Recall Rate | Median Recall Rate | Average Recall Rate | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data 1 | 93.84% | 82.77% | 86.37% | 87.46% | [84.716%, 90.204%] |
| Data 2 | 88.38% | 88.38% | 88.38% | 88.38% | |
| Data 3 | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| Data 4 | 97.11% | 44.17% | 93.69% | 87.04% | [78.392%, 95.688%] |
| Data 5 | 100% | 53.74% | 90.08% | 82.79% | [75.234%, 90.346%] |
| Data 6 | 83.68% | 68.42% | 77.97% | 78.88% | [75.418%, 78.942%] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Tong, F.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Ou, M.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, M.; Wu, W.; Gong, Y.; Luo, Z.; et al. A Rapid Head Organ Localization System Based on Clinically Realistic Images: A 3D Two Step Progressive Registration Method with CVH Anatomical Knowledge Mapping. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090891
Sun C, Tong F, Luo J, Wang Y, Ou M, Wu Y, Qiu M, Wu W, Gong Y, Luo Z, et al. A Rapid Head Organ Localization System Based on Clinically Realistic Images: A 3D Two Step Progressive Registration Method with CVH Anatomical Knowledge Mapping. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(9):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090891
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Changjin, Fei Tong, Junjie Luo, Yuting Wang, Mingwen Ou, Yi Wu, Mingguo Qiu, Wenjing Wu, Yan Gong, Zhongwen Luo, and et al. 2024. "A Rapid Head Organ Localization System Based on Clinically Realistic Images: A 3D Two Step Progressive Registration Method with CVH Anatomical Knowledge Mapping" Bioengineering 11, no. 9: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090891
APA StyleSun, C., Tong, F., Luo, J., Wang, Y., Ou, M., Wu, Y., Qiu, M., Wu, W., Gong, Y., Luo, Z., & Qiao, L. (2024). A Rapid Head Organ Localization System Based on Clinically Realistic Images: A 3D Two Step Progressive Registration Method with CVH Anatomical Knowledge Mapping. Bioengineering, 11(9), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090891








