Effects of Exercise on the Inter-Session Accuracy of sEMG-Based Hand Gesture Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.3.1. Filtering
2.3.2. Bad Channel Repairing
2.3.3. Feature Extraction
2.4. Methods of Analysis
2.4.1. Data Augmentation
2.4.2. Linear Discriminant Analysis
2.5. Validation Protocols
2.5.1. Intra-Session Validation
2.5.2. Inter-Session Validation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Two-Dimensional Heat Map of Muscle Activation
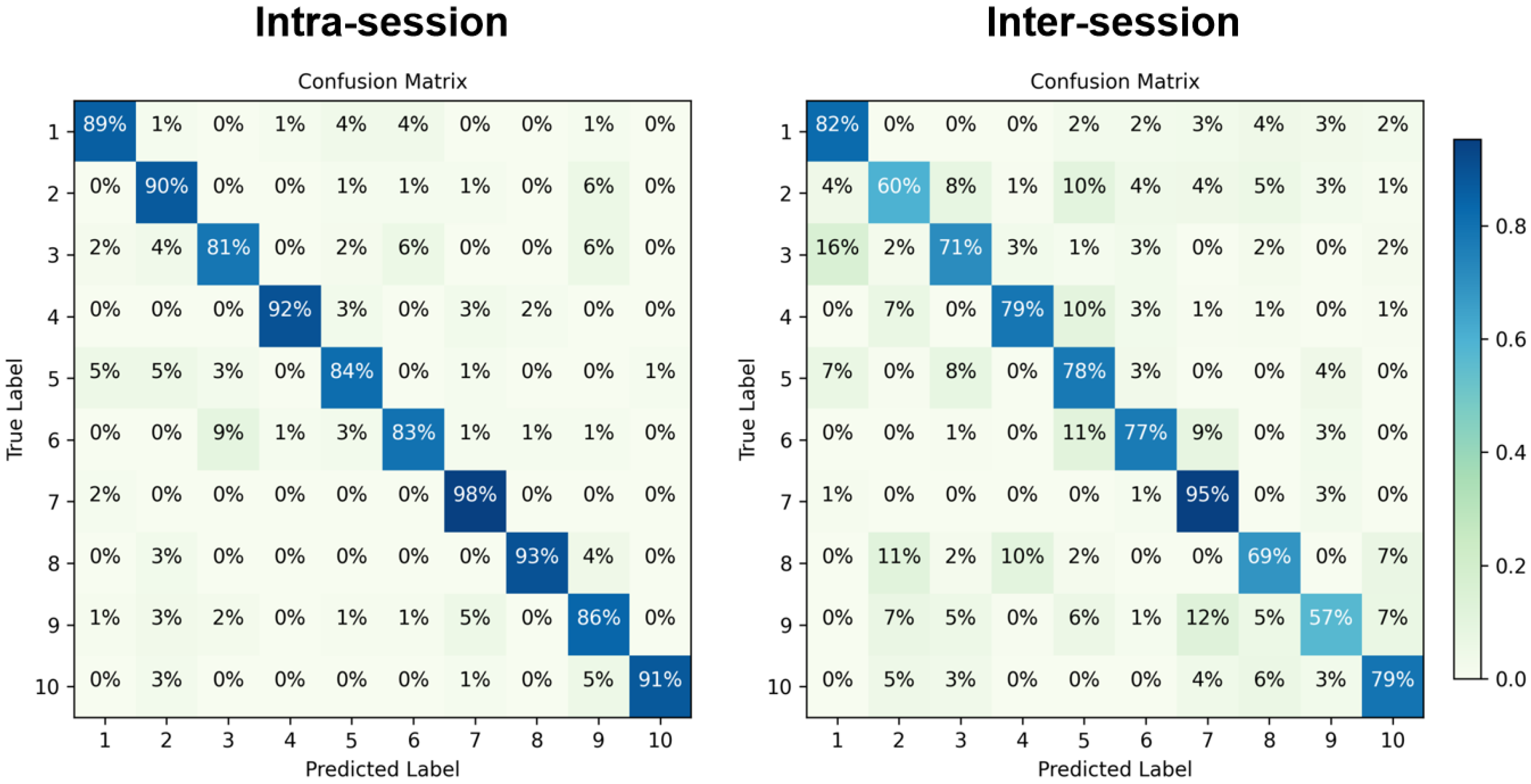
3.2. Intra-Session Recognition Accuracy of Exercise and Non-Exercise Groups
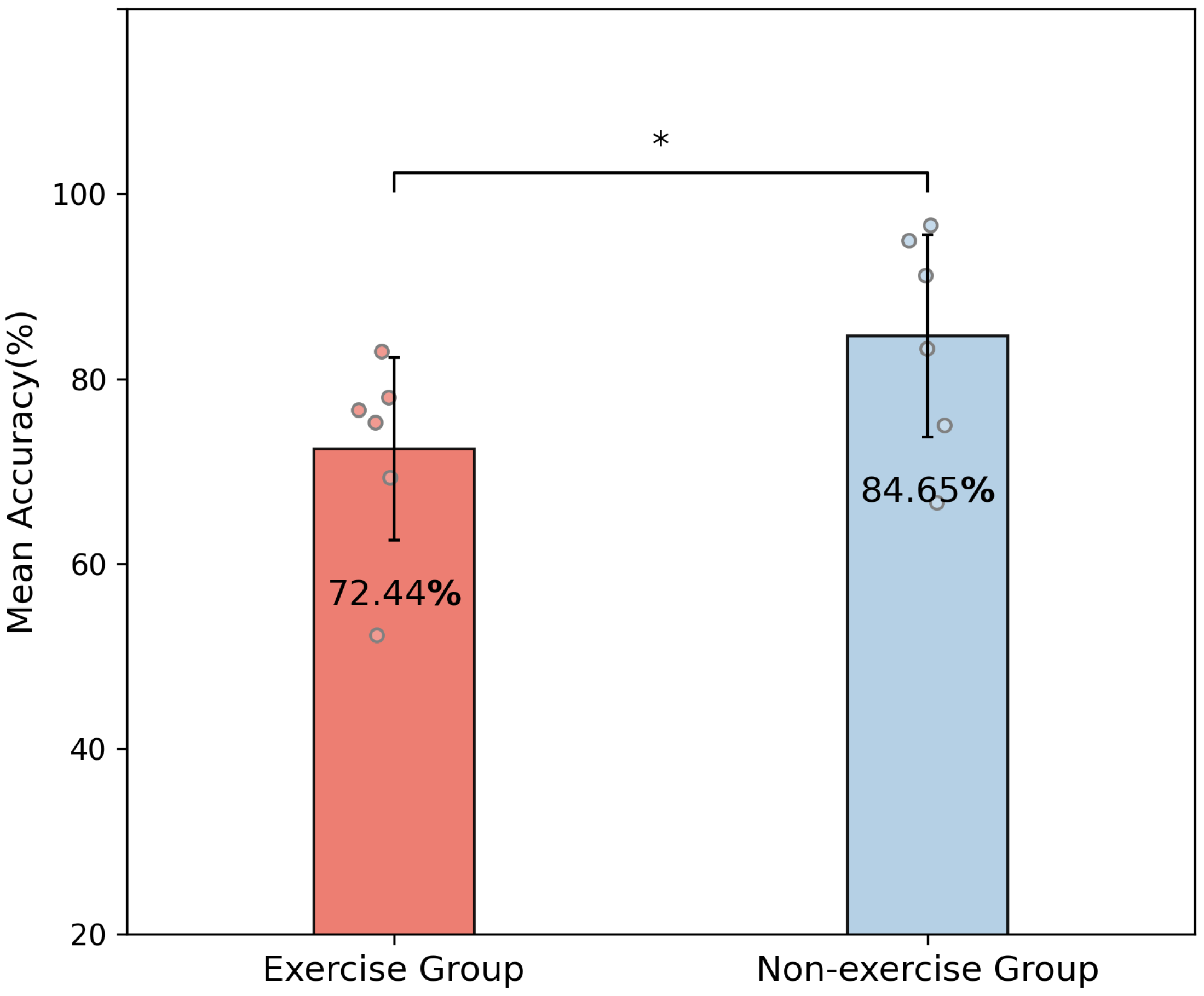
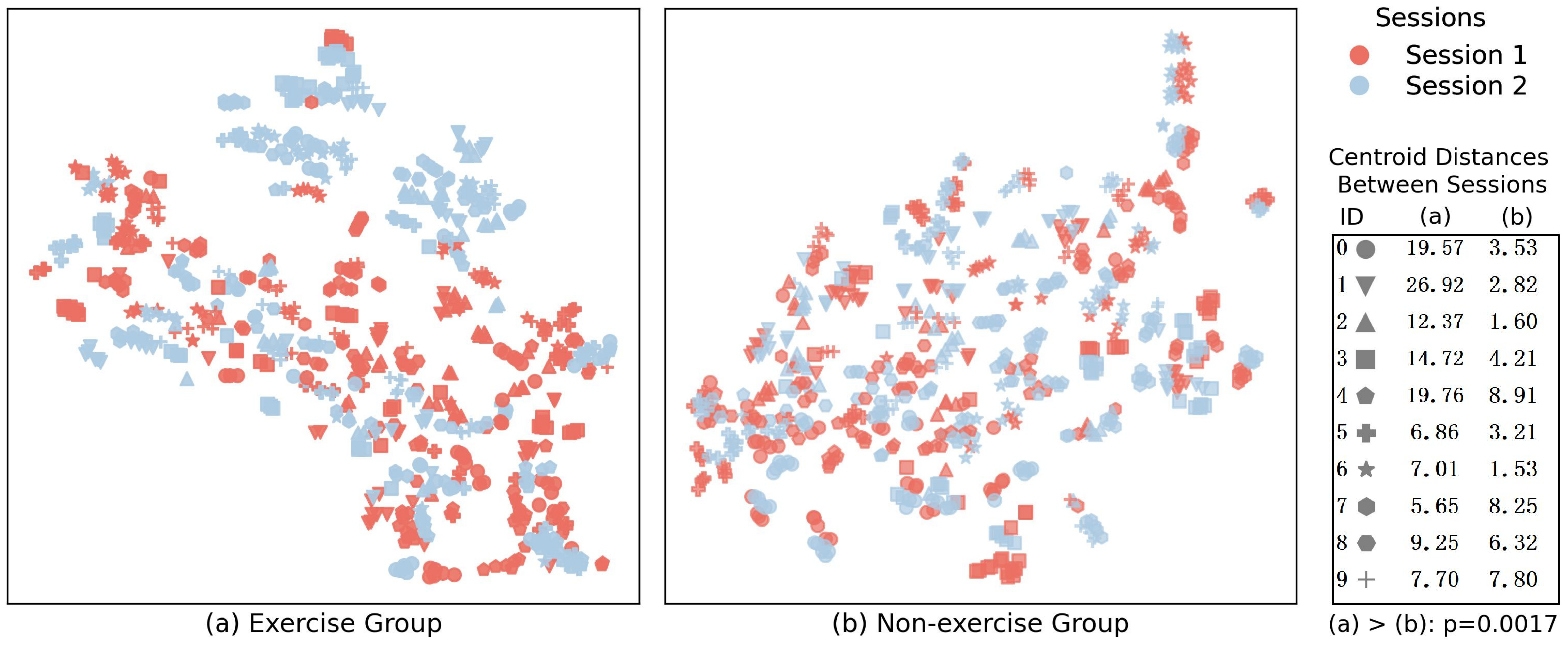
3.3. Inter-Session Recognition Accuracy of Exercise and Non-Exercise Groups
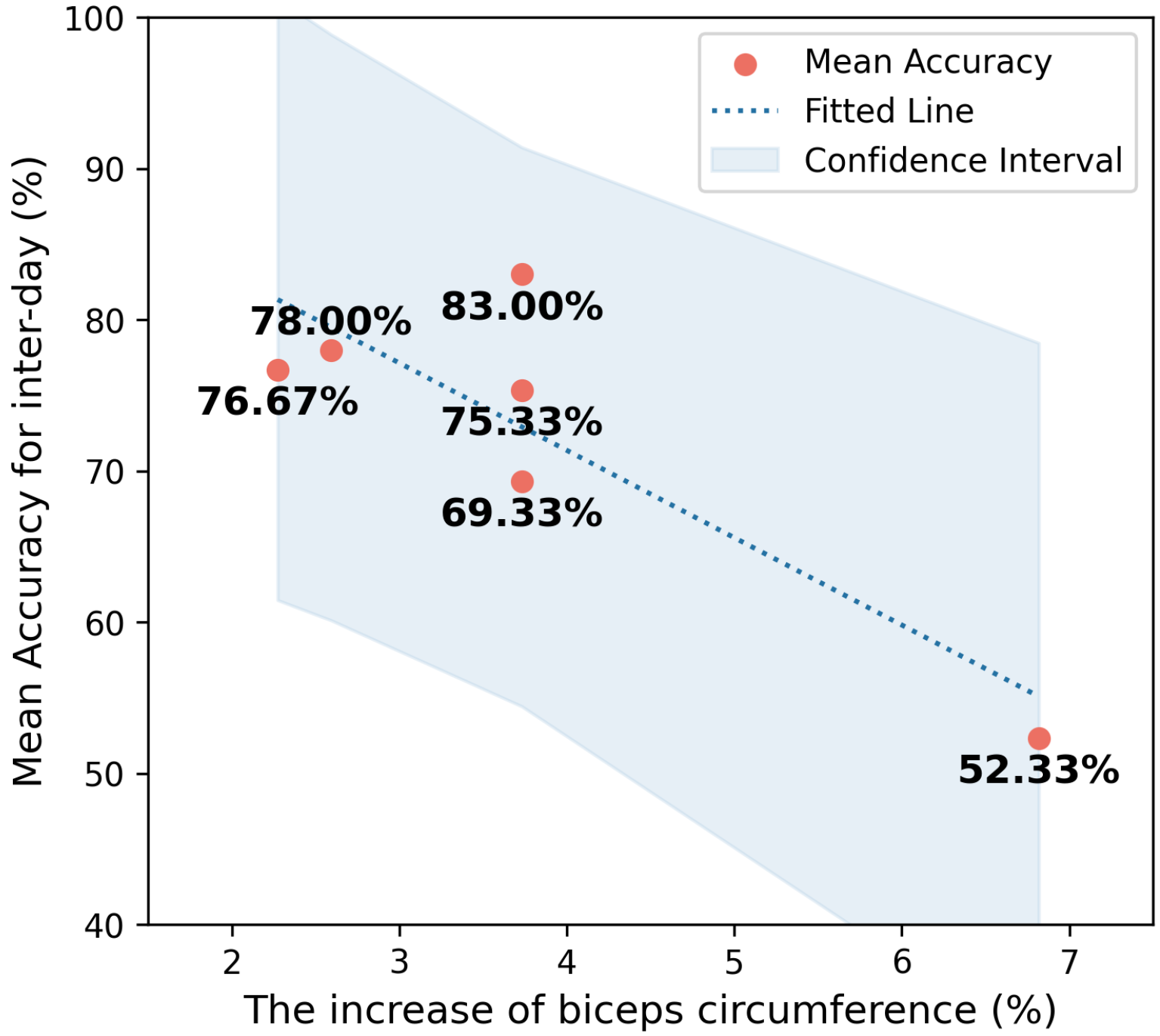
3.4. Trends in Recognition Accuracy and Biceps Circumference
4. Discussion
- Exploring the sEMG features insensitive to muscle fiber changes, such as motoneuron discharge information or frequency domain information.
- Utilizing advanced machine learning algorithms. Recent algorithms, such as transfer learning may provide solutions. This algorithm can train a model based on non-exercise data and then fine-tune it with a small amount of exercise data to improve recognition accuracy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mourtzis, D.; Angelopoulos, J.; Panopoulos, N. The future of the human–machine interface (HMI) in society 5.0. Future Internet 2023, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, U.; Ayaz, Y.; Taiar, R. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) in brain computer interface (BCI) and Industry 4.0 for human machine interaction (HMI). Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1320536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Bao, S. A review of the key technologies for sEMG-based human–robot interaction systems. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Ye, X.; Dai, C.; Akay, M.; Chen, W. Cancelable HD-SEMG biometric identification via deep feature learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 26, 1782–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, K.; Liu, X.; Dai, C.; Clifton, D.A.; Clancy, E.A.; Akay, M.; Chen, W. Cancelable HD-sEMG-based biometrics for cross-application discrepant personal identification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Han, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. sEMG based human motion intention recognition. J. Robot. 2019, 2019, 3679174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, R.M.; Bastos-Filho, T.; Costa, R.M.; Frizera-Neto, A.; Arjunan, S.; Kumar, D. Towards sEMG classification based on Bayesian and k-NN to control a prosthetic hand. In Proceedings of the 2013 ISSNIP Biosignals and Biorobotics Conference: Biosignals and Robotics for Better and Safer Living (BRC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 18–20 February 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, A.; Kumari, B.; Sharma, S. A low-cost, wearable sEMG sensor for upper limb prosthetic application. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2019, 43, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benatti, S.; Casamassima, F.; Milosevic, B.; Farella, E.; Schönle, P.; Fateh, S.; Burger, T.; Huang, Q.; Benini, L. A versatile embedded platform for EMG acquisition and gesture recognition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2015, 9, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Jiang, G.; Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Tao, B. Surface EMG hand gesture recognition system based on PCA and GRNN. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 6343–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Z. Hand gesture recognition using sEMG signals based on support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 8th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 24–26 May 2019; pp. 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Jia, F.; Dai, C. Optimizing the feature set and electrode configuration of high-density electromyogram via interpretable deep forest. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 87, 105445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.R.; Waris, A.; Gilani, S.O.; Jamil, M.; Ashraf, H.; Shafique, M.; Niazi, I.K. Performance evaluation of convolutional neural network for hand gesture recognition using EMG. Sensors 2020, 20, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Espino, J.A.; Zamudio-Lara, A.; Marbán-Salgado, J.A.; Escobedo-Alatorre, J.J.; Palillero-Sandoval, O.; Velásquez-Aguilar, J.G. Selection of the best set of features for sEMG-based hand gesture recognition applying a CNN architecture. Sensors 2022, 22, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Fan, J.; Ren, H.; Guo, Y.; Diao, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Dai, C.; et al. User-tailored hand gesture recognition system for wearable prosthesis and armband based on surface electromyogram. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Fan, J.; Ye, X.; Dai, C.; Clancy, E.A.; Farina, D.; Chen, W. Optimization of HD-sEMG-based cross-day hand gesture classification by optimal feature extraction and data augmentation. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2022, 52, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jin, W.; Wei, W.; Hu, Y.; Geng, W. Surface EMG-based inter-session gesture recognition enhanced by deep domain adaptation. Sensors 2017, 17, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q. Hand gesture recognition with flexible capacitive wristband using triplet network in inter-day applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 2876–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Fan, J.; Dai, C.; Clancy, E.A.; Chen, W. Random channel masks for regularization of least squares-based finger EMG-force modeling to improve cross-day performance. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, X. Adaptive calibration of electrode array shifts enables robust myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 67, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, H. Fatigue-sensitivity comparison of sEMG and A-mode ultrasound based hand gesture recognition. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 26, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.; Liang, S.; Yan, T.; Hou, R.; Zheng, Z.; Ryu, J. Overcoming the effect of muscle fatigue on gesture recognition based on sEMG via generative adversarial networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Fan, J.; Ye, X.; Dai, C.; Clancy, E.A.; Akay, M.; Chen, W. Open access dataset, toolbox and benchmark processing results of high-density surface electromyogram recordings. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Bardizbanian, B.; Clancy, E.A. Comparison of constant-posture force-varying EMG-force dynamic models about the elbow. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 25, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Meng, L.; Jia, F.; Dai, C. Surface EMG feature disentanglement for robust pattern recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y. A comparative study on PCA and LDA based EMG pattern recognition for anthropomorphic robotic hand. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 4850–4855. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yue, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.; Zhao, H.; Wu, B.; Krishna, R.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A.L.; Seshia, S.A.; et al. A review of single-source deep unsupervised visual domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 33, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Jiang, X.; Dai, C.; Chen, W. EMG-based Multi-User Hand Gesture Classification via Unsupervised Transfer Learning Using Unknown Calibration Gestures. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, N.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Improving robustness against electrode shift of high density EMG for myoelectric control through common spatial patterns. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Dai, C.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y. Effects of Exercise on the Inter-Session Accuracy of sEMG-Based Hand Gesture Recognition. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080811
Liu X, Dai C, Liu J, Yuan Y. Effects of Exercise on the Inter-Session Accuracy of sEMG-Based Hand Gesture Recognition. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080811
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiangyu, Chenyun Dai, Jionghui Liu, and Yangyang Yuan. 2024. "Effects of Exercise on the Inter-Session Accuracy of sEMG-Based Hand Gesture Recognition" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080811
APA StyleLiu, X., Dai, C., Liu, J., & Yuan, Y. (2024). Effects of Exercise on the Inter-Session Accuracy of sEMG-Based Hand Gesture Recognition. Bioengineering, 11(8), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080811





