HEAL: High-Frequency Enhanced and Attention-Guided Learning Network for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
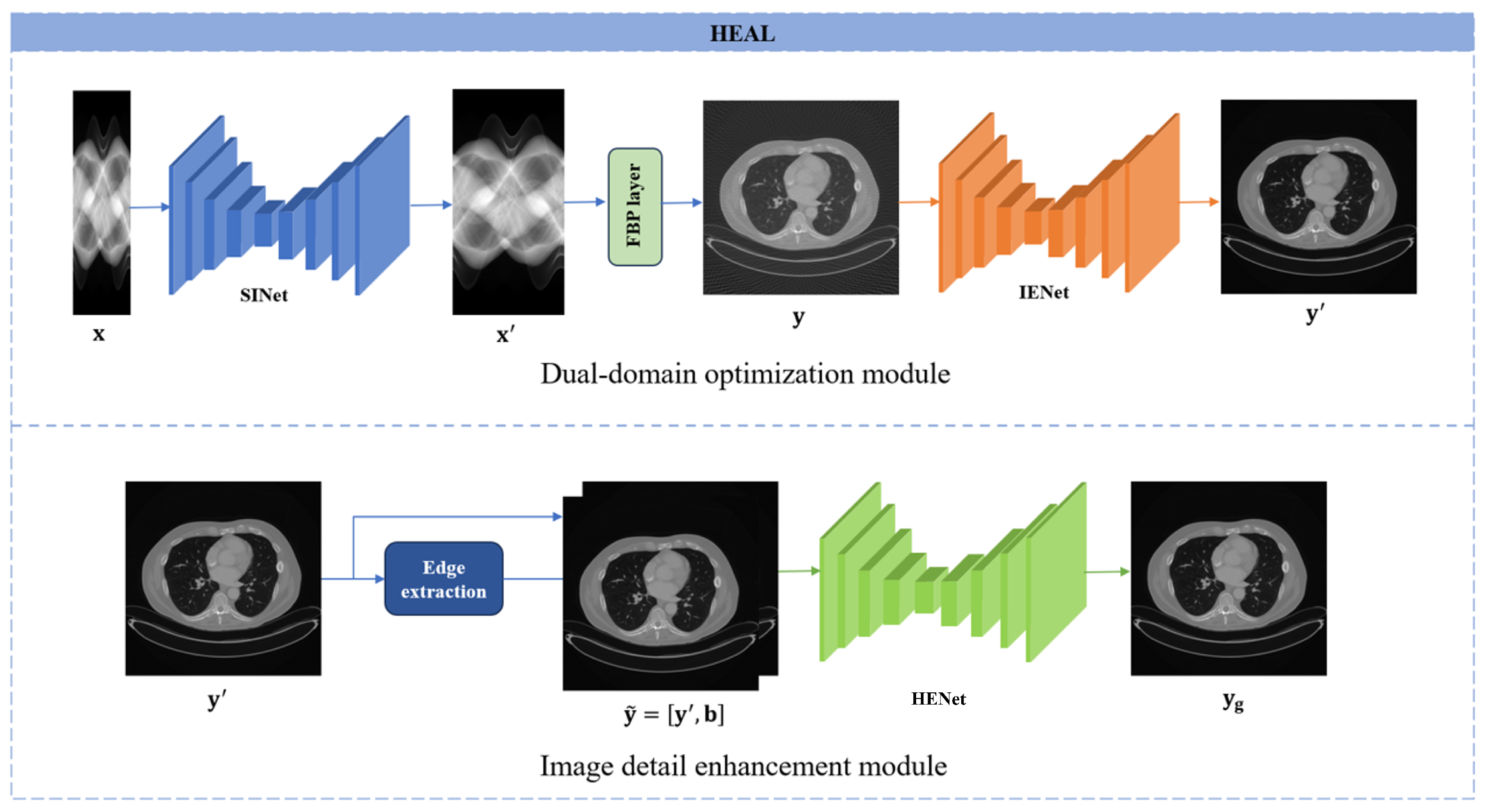
2.1. Overall Structure of HEAL Network
2.1.1. Dual-Domain Optimization Module
2.1.2. Image Detail Enhancement Module
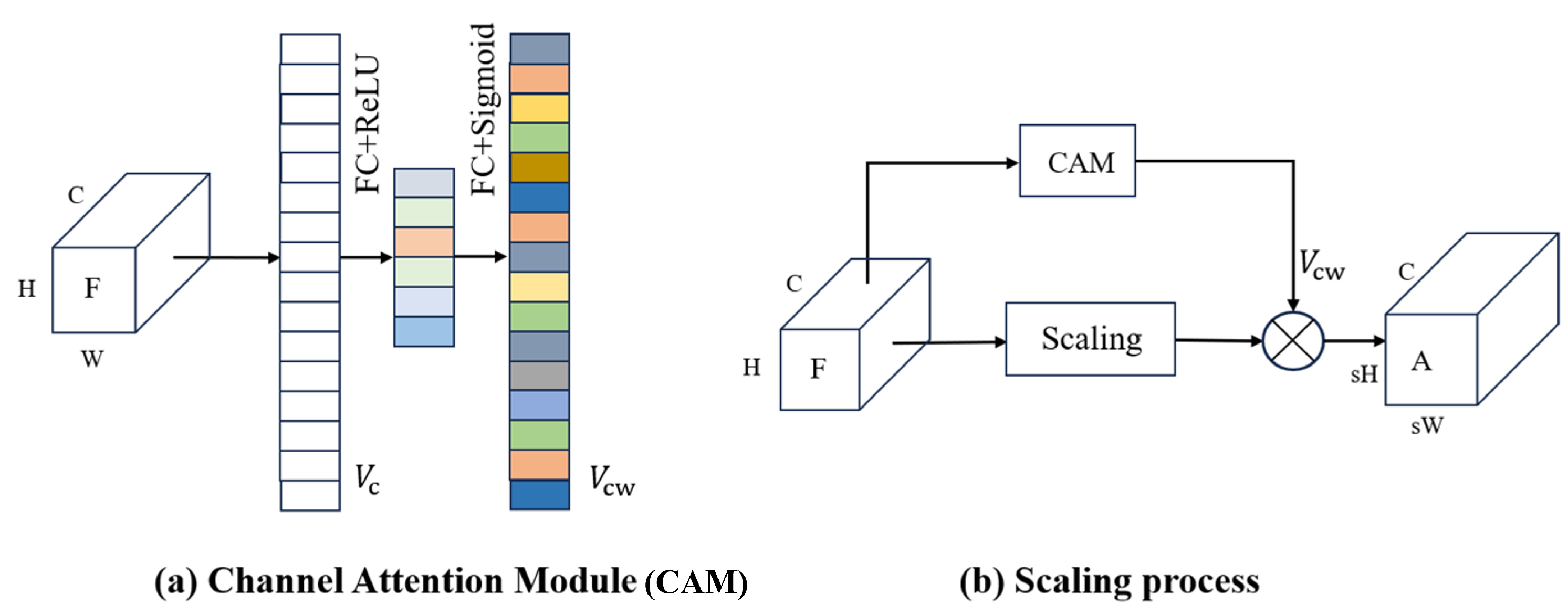
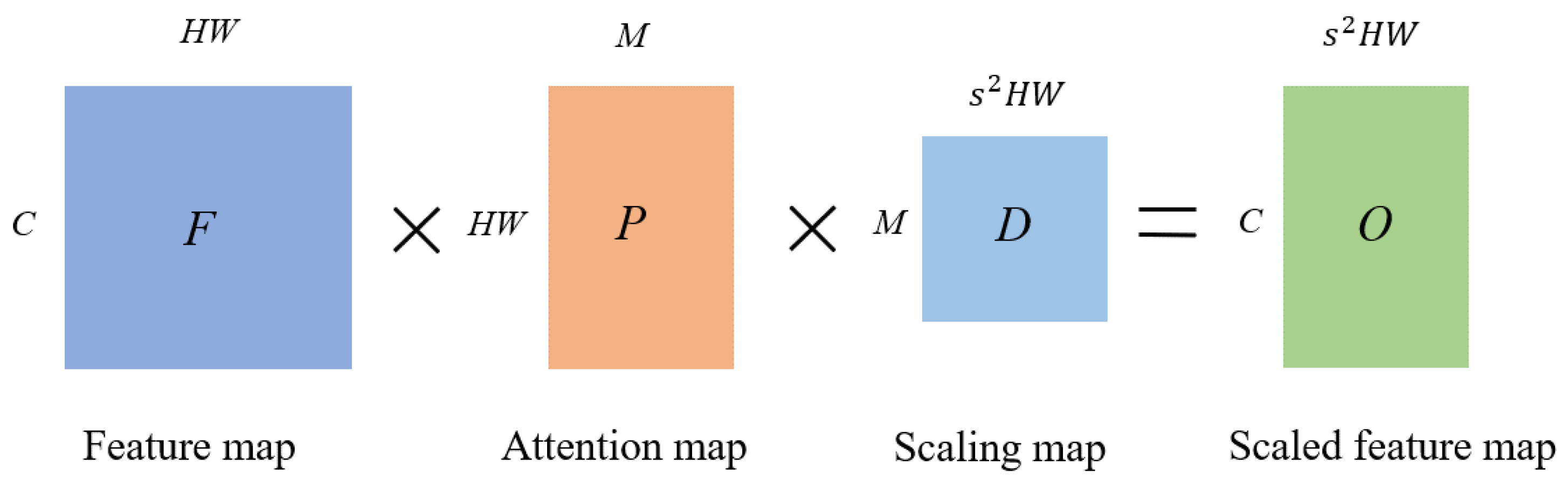
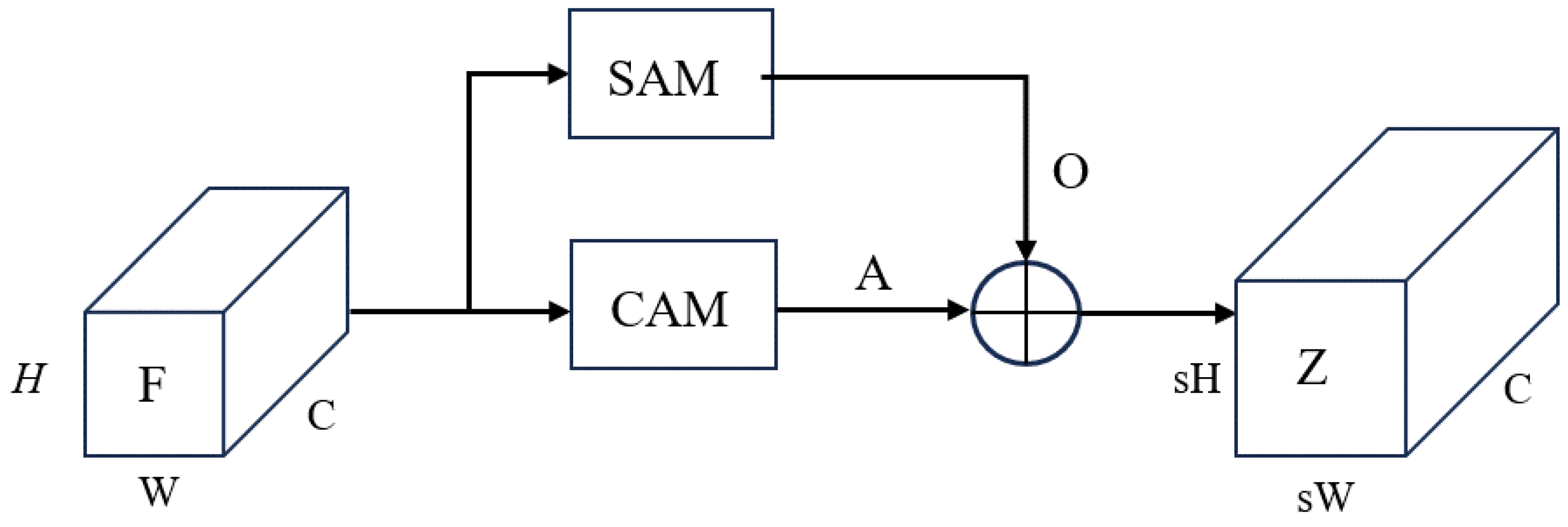
2.2. Feature Scaling with Attention Mechanism
2.3. High-Frequency Enhancement Constraints Based on Direction-Weighted Total Variation
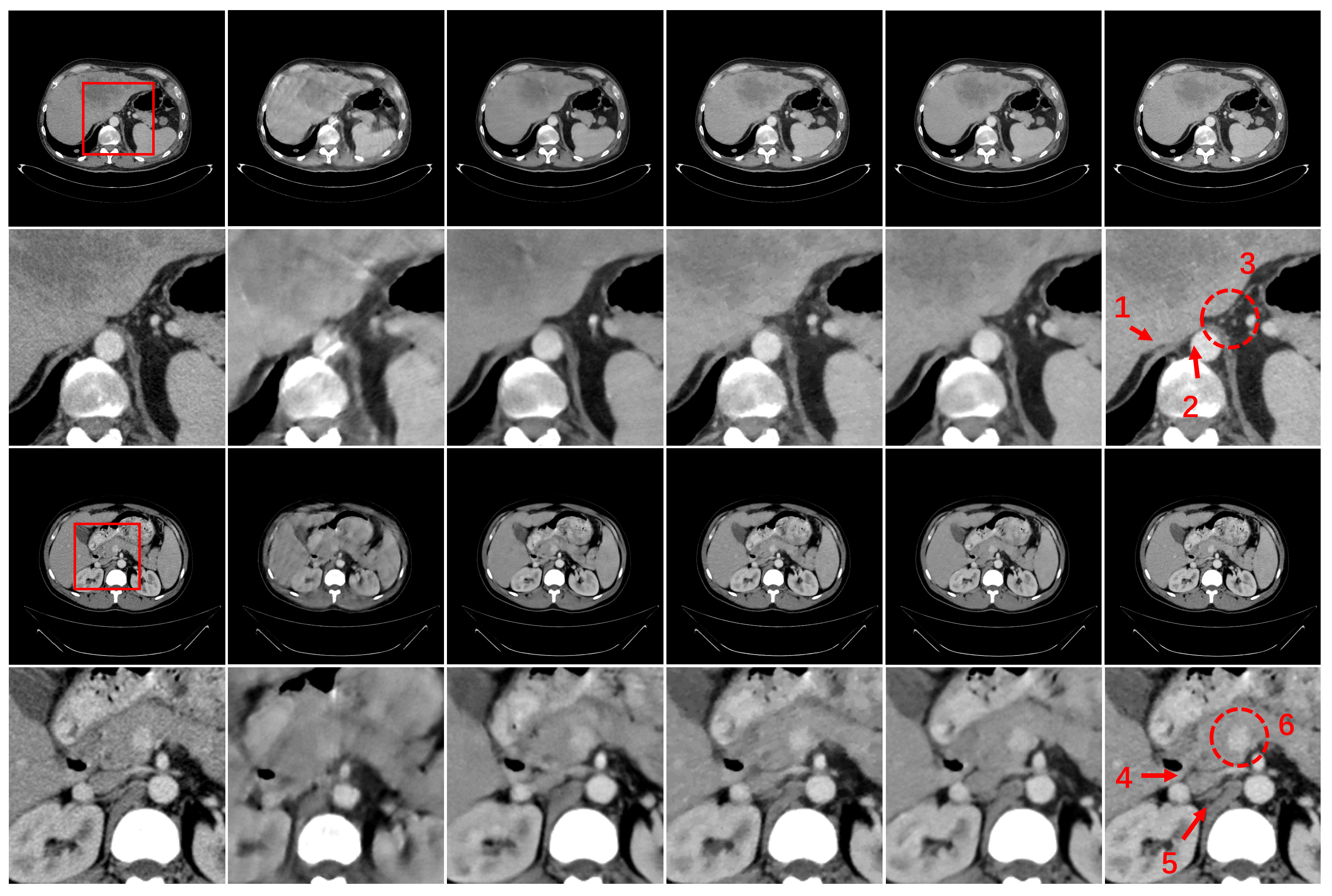
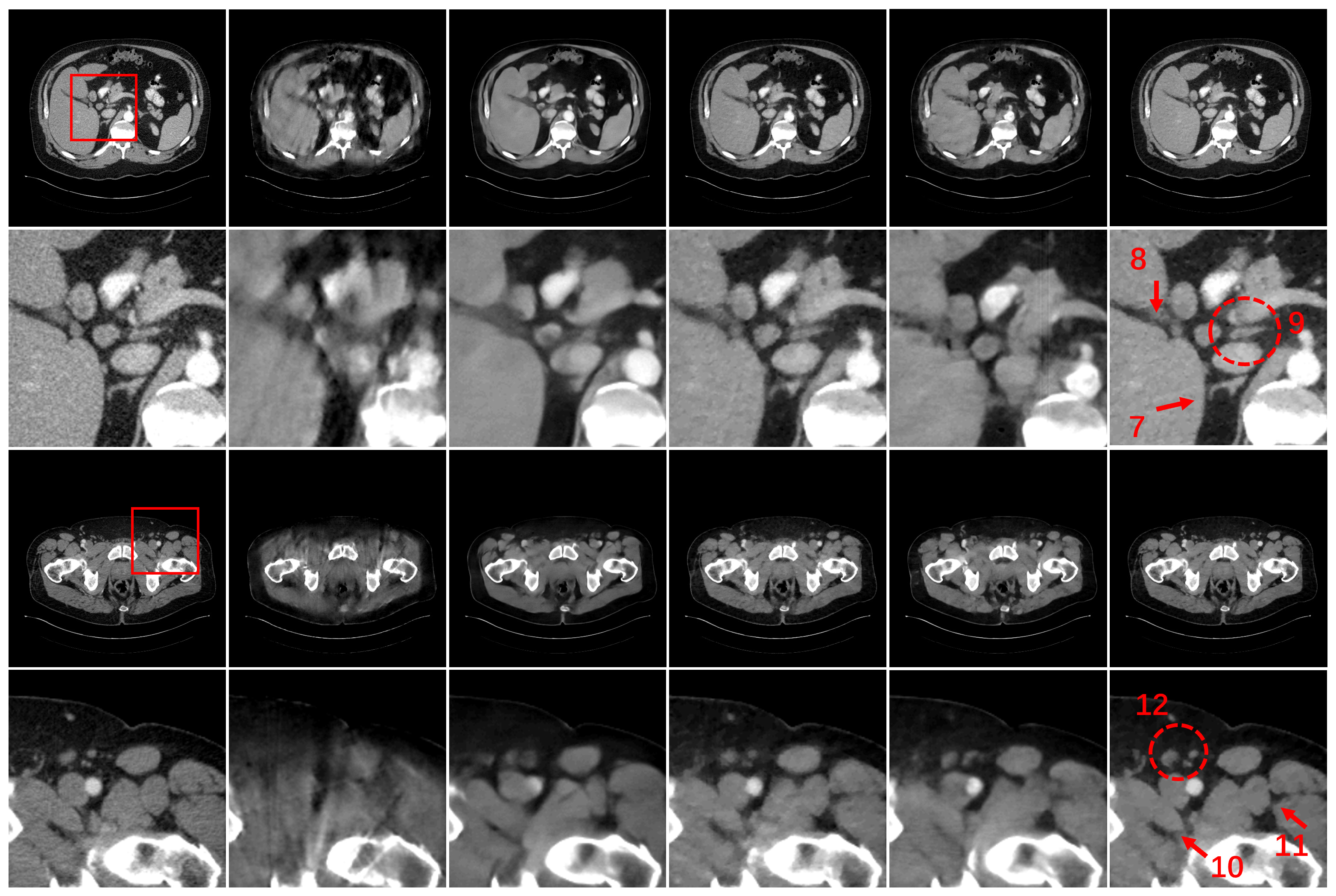
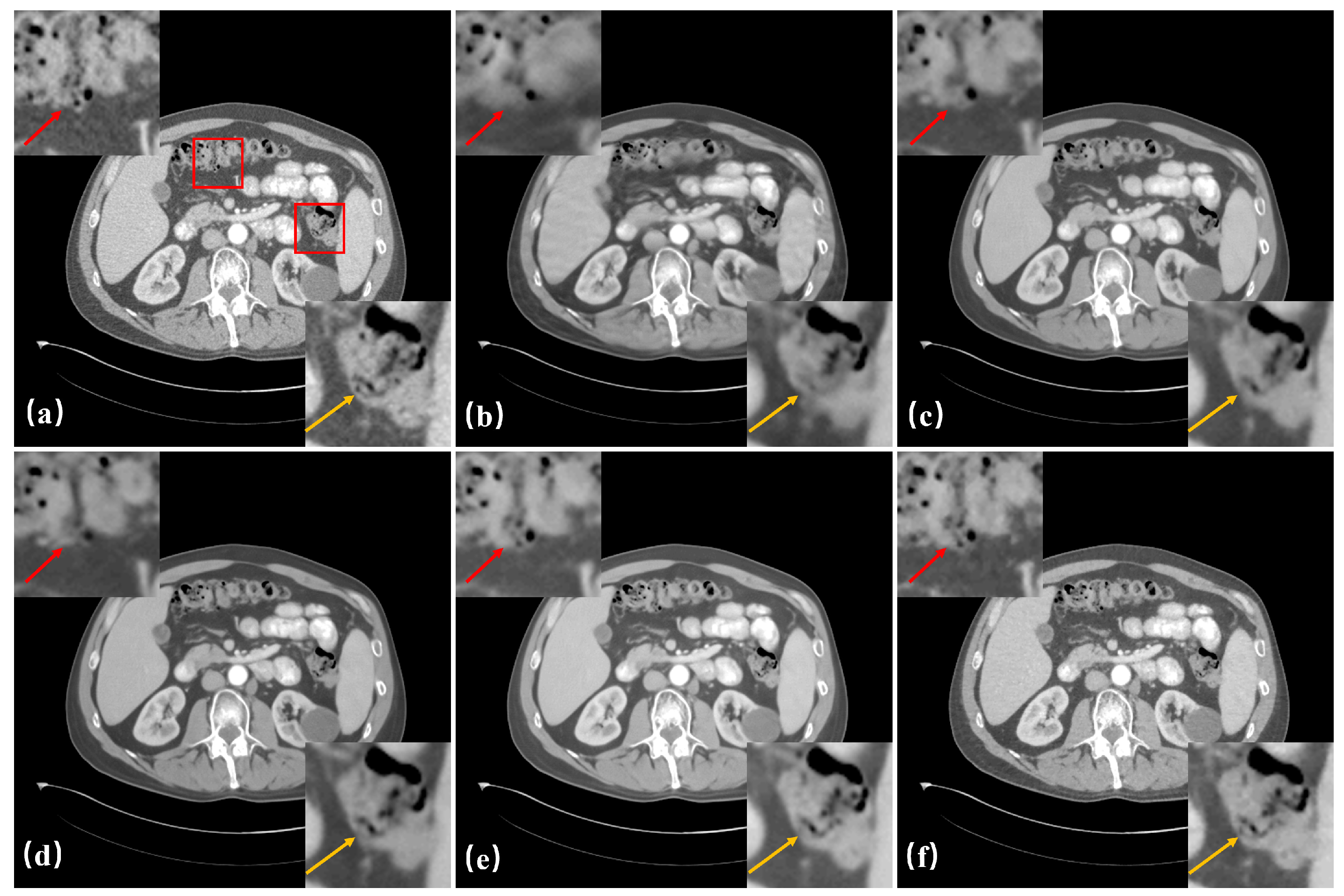
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Implementation and Training Details
3.2. Experimental Data Preparation
3.3. Results
3.4. Ablation Study
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gengsheng, L.Z. Medical Image Reconstruction: A Conceptual Tutorial; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shinbane, J.S.; Girsky, M.J.; Saxon, L.A.; Cao, M.K.; Cesario, D.A.; Budoff, M.J. CT imaging: Cardiac electrophysiology applications. In Cardiac CT Imaging: Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q. Image reconstruction for hybrid true-color micro-CT. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1711. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, E.C. Radiation Risk From Medical Imaging. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 1142–1146, quiz 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L. Donoho. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Tang, J.; Leng, S. Prior image constrained compressed sensing (PICCS): A method to accurately reconstruct dynamic CT images from highly undersampled projection data sets. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sidky, E.Y.; Kao, C.M.; Pan, X. Accurate image reconstruction from few-views and limited-angle data in divergent-beam CT. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2006, 14, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sidky, E.Y.; Pan, X. Image reconstruction in circular cone-beam computed tomography by constrained, total-variation minimization. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yu, H.Y.; Mou, X.Q. Low-Dose X-ray CT Reconstruction via Dictionary Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 1682–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K.H.; Mccann, M.T. Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Inverse Problems in Imaging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 4509–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kalra, M.K.; Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Liao, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Low-Dose CT with a Residual Encoder-Decoder Convolutional Neural Network (RED-CNN). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2524–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Huang, X.; Huang, X.; Zong, Y.; Luo, S. PIDNET: Polar Transformation Based Implicit Disentanglement Network for Truncation Artifacts. Entropy 2024, 26, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ji, L.; You, C.; Gao, S.; Zhou, L.; Bai, K.; Luo, S.; Gu, N. MARGANVAC: Metal artifact reduction method based on generative adversarial network with variable constraints. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 205005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Dong, X.; Xie, Y.; Cao, G. A Sparse-View CT Reconstruction Method Based on Combination of DenseNet and Deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Y. Artifact Removal using Improved GoogLeNet for Sparse-view CT Reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.; Yang, H.; Kang, K.; Xing, Y. Improve angular resolution for sparse-view CT with residual convolutional neural network. Med. Imaging 2018, 10573, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyeon, L.; Jongha, L.; Hyeongseok, K.; Byungchul, C.; Seungryong, C. Deep-neural-network based sinogram synthesis for sparse-view CT image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2018, 3, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Ye, J.C. Framing U-Net via Deep Convolutional Framelets: Application to Sparse-View CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J. Sparse-view CT reconstruction based on multi-level wavelet convolution neural network. Phys. Medica 2020, 80, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Niu, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, Q. Generative Modeling in Sinogram Domain for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2024, 8, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Feng, R.; Wei, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y. Self-Supervised Coordinate Projection Network for Sparse-View Computed Tomography. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2023, 9, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Lv, Y.; Liao, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. LEARN: Learned Experts’ Assessment-based Reconstruction Network for Sparse-data CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Montoya, J.C.; Chen, G.H. Learning to Reconstruct Computed Tomography (CT) Images Directly from Sinogram Data under A Variety of Data Acquisition Conditions. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2469–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J. Radon Inversion via Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Huibin, L.; Zongben, X.; Jian, S. Deep ADMM-Net for compressive sensing MRI. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. RegFormer: A Local–Nonlocal Regularization-Based Model for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2024, 8, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, J. Deep embedding-attention-refinement for sparse-view CT reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Liu, J.; Lv, T.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, L. Hybrid-Domain Neural Network Processing for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2020, 5, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.J. High quality imaging from sparsely sampled computed tomography data with deep learning and wavelet transform in various domains. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hu, D.; Niu, C.; Yu, H.; Vardhanabhuti, V.; Wang, G. DRONE: Dual-domain Residual-based Optimization NEtwork for Sparse-view CT Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 3002–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xing, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z. Sam’s Net: A Self-Augmented Multistage Deep-Learning Network for End-to-End Reconstruction of Limited Angle CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 2912–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhao, Q.; Quan, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Coatrieux, G.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H. CLEAR: Comprehensive Learning Enabled Adversarial Reconstruction for Subtle Structure Enhanced Low-Dose CT Imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheslerean-Boghiu, T.; Hofmann, F.C.; Schultheiß, M.; Pfeiffer, F.; Pfeiffer, D.; Lasser, T. WNet: A Data-Driven Dual-Domain Denoising Model for Sparse-View Computed Tomography With a Trainable Reconstruction Layer. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2023, 9, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hu, D.; Niu, C.; Broeke, L.V.; Butler, A.P.; Cao, P.; Atlas, J.; Chernoglazov, A.; Vardhanabhuti, V.; Wang, G. Deep learning based spectral CT imaging. Neural Netw. 2021, 144, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Shi, Y.; Mou, X.; Kalra, M.K.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, G. Low-Dose CT Image Denoising Using a Generative Adversarial Network With Wasserstein Distance and Perceptual Loss. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A. Improved training of wasserstein GANs. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, r NIPS’17, Red Hook, NY, USA, 4–9 December; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 5769–5779. [Google Scholar]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net Architecture for Multimodal Biomedical Image Segmentation. Neural Netw. 2019, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G.; Albanie, S. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. A2-Nets: Double attention networks. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’18, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Sun, G.; Fu, Y. Accurate and Fast Image Denoising via Attention Guided Scaling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 6255–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, H.; Ge, Y.; Liang, D. Artifact removal using a hybrid-domain convolutional neural network for limited-angle computed tomography imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 155010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudh, R.; Kim, H.; Thiagarajan, J.J.; Mohan, K.A.; Champley, K.; Bremer, T. Lose The Views: Limited Angle CT Reconstruction via Implicit Sinogram Completion. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 6343–6352. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.; Rioux, J.; Clarke, S.E.; Costa, A.; Schmidt, M.; Keough, V.; Huynh, T.; Beyea, S. Comparison of objective image quality metrics to expert radiologists’ scoring of diagnostic quality of MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A.C. Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Views | Metrics | DDNet | FBPConvNet | DRONE | RegFormer | Ours |
| 60 views | SSIM | 0.9549 | 0.9736 | 0.9797 | 0.9814 | 0.9853 |
| PSNR | 39.88 | 43.76 | 45.29 | 45.92 | 47.21 | |
| VIF | 0.5857 | 0.7011 | 0.7536 | 0.7674 | 0.8012 | |
| RMSE | 6.981 | 2.856 | 1.990 | 1.718 | 1.231 | |
| GMSD | 0.0385 | 0.0185 | 0.0095 | 0.0086 | 0.0071 | |
| 30 views | SSIM | 0.9248 | 0.9587 | 0.9734 | 0.9663 | 0.9802 |
| PSNR | 36.23 | 41.13 | 43.83 | 42.09 | 45.60 | |
| VIF | 0.4976 | 0.6255 | 0.6576 | 0.6354 | 0.7043 | |
| RMSE | 16.36 | 5.248 | 3.030 | 4.216 | 1.854 | |
| GMSD | 0.0595 | 0.0312 | 0.0198 | 0.0266 | 0.0122 |
| Phase | DDNet | FBPConvNet | DRONE | RegFormer | Ours |
| Training (h) | 10.5 | 22.4 | 34 | 102 | 61 |
| Inference (s) | 0.01 | 0.03 | 96 | 0.28 | 0.08 |
| DDPM | FSAM | HFER | HENet | SSIM | PSNR | RMSE |
| - | - | - | - | 0.9744 | 44.14 | 2.643 |
| ✓ | - | - | - | 0.9791 | 44.63 | 2.345 |
| ✓ | ✓ | - | - | 0.9812 | 45.50 | 1.937 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | 0.9833 | 47.07 | 1.336 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.9853 | 47.21 | 1.231 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Deng, Z.; Ge, Y.; Luo, S. HEAL: High-Frequency Enhanced and Attention-Guided Learning Network for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070646
Li G, Deng Z, Ge Y, Luo S. HEAL: High-Frequency Enhanced and Attention-Guided Learning Network for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(7):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070646
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guang, Zhenhao Deng, Yongshuai Ge, and Shouhua Luo. 2024. "HEAL: High-Frequency Enhanced and Attention-Guided Learning Network for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction" Bioengineering 11, no. 7: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070646
APA StyleLi, G., Deng, Z., Ge, Y., & Luo, S. (2024). HEAL: High-Frequency Enhanced and Attention-Guided Learning Network for Sparse-View CT Reconstruction. Bioengineering, 11(7), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070646








