Investigating the Influence of Varying Surface Conditions on Human Postural Control and Sensory Integration Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
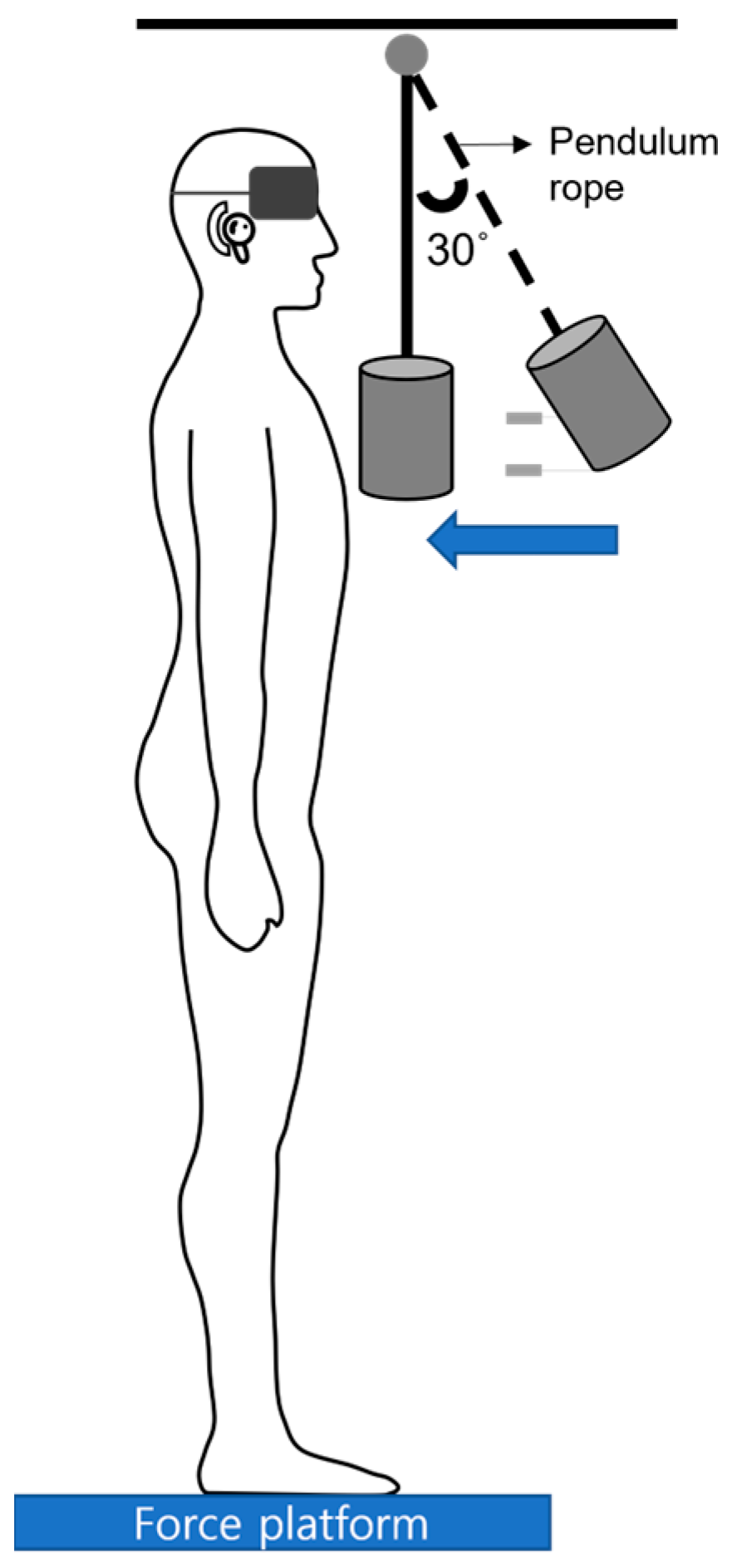
2.2. Balance Measurement
2.3. Support Surfaces
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
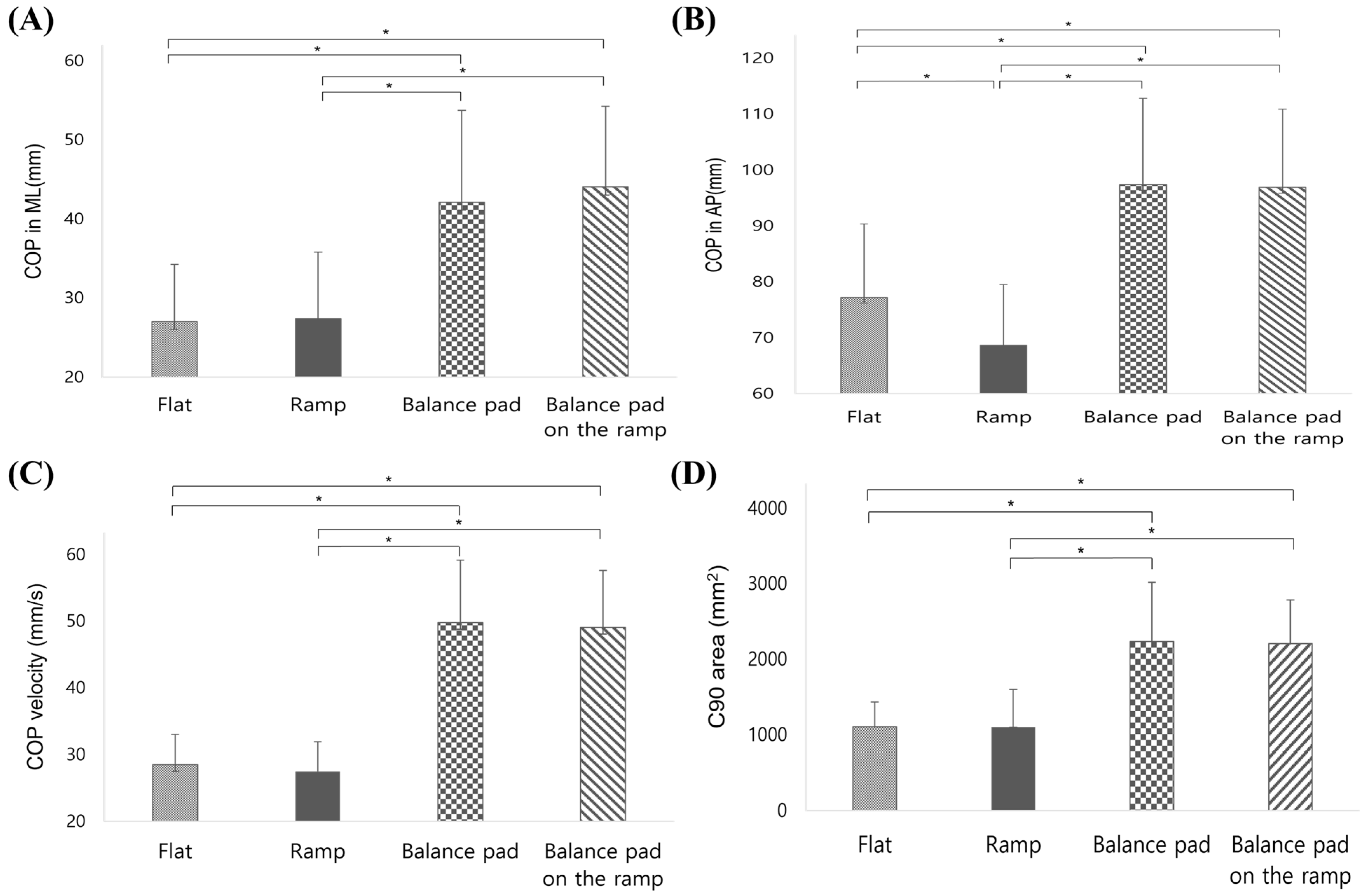
3.2. COP Displacement
- (1)
- Mediolateral COP X axis displacement
- (2)
- Anteroposterior COP Y axis displacement
- (3)
- COP Velocity during Anteroposterior Perturbations
- (4)
- C90 Area during Anteroposterior Perturbations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lugade, V.; Lin, V.; Chou, L.-S. Center of mass and base of support interaction during gait. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abatzides, G.J.; Kitsios, A. The role of rehabilitation in the treatment of balance disorders. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 1999, 12, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, H. Posture, balance and movement: Role of the vestibular system in balance control during stance and movements. Neurophysiol. Clin./Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 46, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Horak, F.B. Assessing the influence of sensory interaction on balance: Suggestion from the field. Phys. Ther. 1986, 66, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35, ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, H.-G.; Strobel, J.; Achatz, G.; von Luebken, F.; Friemert, B. The role and interaction of visual and auditory afferents in postural stability. Gait Posture 2009, 30, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mademli, L.; Mavridi, D.; Bohm, S.; Patikas, D.A.; Santuz, A.; Arampatzis, A. Standing on unstable surface challenges postural control of tracking tasks and modulates neuromuscular adjustments specific to task complexity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Succop, P.; Kincl, L.; Lu, M.L.; Bagchee, A. Postural stability during task performance on elevated and/or inclined surfaces. Occup. Ergon. 2003, 3, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.B., III; Murray, N.G.; Powell, D.W. Athletes who train on unstable compared to stable surfaces exhibit unique postural control strategies in response to balance perturbations. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wall, C., III; Kentala, E. Control of sway using vibrotactile feedback of body tilt in patients with moderate and severe postural control deficits. J. Vestib. Res. 2005, 15, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindl, R.; Kunz, K.; Schrott-Fischer, A.; Scholtz, A. Effect of age and sex on maturation of sensory systems and balance control. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterka, R.J. Sensorimotor integration in human postural control. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 1097–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, R.; Almeida, G. The effect of galvanic vestibular stimulation on postural response of Down syndrome individuals on the seesaw. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, H.-C.; Dichgans, J. On the role of vestibular, visual and somatosensory information for dynamic postural control in humans. Prog. Brain Res. 1988, 76, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bieć, E.; Zima, J.; Wojtowicz, D.; Wojciechowska-Maszkowska, B.; Kręcisz, K.; Kuczyński, M. Postural stability in young adults with Down syndrome in challenging conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laessoe, U.; Voigt, M. Anticipatory postural control strategies related to predictive perturbations. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaim, C.; Pérennou, D.A.; Villy, J.; Rousseaux, M.; Pelissier, J.Y. Validation of a standardized assessment of postural control in stroke patients: The Postural Assessment Scale for Stroke Patients (PASS). Stroke 1999, 30, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouisset, S.; Zattara, M. Biomechanical study of the programming of anticipatory postural adjustments associated with voluntary movement. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, N.W.; Brauer, S.G.; Hodges, P.W. Hip strategy for balance control in quiet standing is reduced in people with low back pain. Spine 2004, 29, E107–E112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bozec, S.; Bouisset, S.; Ribreau, C. Postural control in isometric ramp pushes: The role of Consecutive Postural Adjustments (CPAs). Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 448, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, T.E.; Myklebust, J.B.; Hoffmann, R.G.; Lovett, E.G.; Myklebust, B.M. Measures of postural steadiness: Differences between healthy young and elderly adults. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1996, 43, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetake, T.; Tanaka, H.; Shindo, M.; Okada, M. Two new methods applicable to center of pressure swing analysis. Anthropol. Sci. 2004, 112, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zang, Y.; Gu, B.; Qian, Q.; Wang, Y. Objective measurement of the balance dysfunction in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder children. Chin. J. Clin. Rehabil. 2002, 6, 1372–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Preuss, R.; Fung, J. A simple method to estimate force plate inertial components in a moving surface. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Participants | 30 (20 males, 10 females) |
| Age (years) | 24.10 ± 1.84 |
| Height (cm) | 169.30 ± 6.55 |
| Body mass (kg) | 63.15 ± 8.82 |
| Variables | Condition | Mean ± SD | F | p-Value | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COP velocity (mm/s) | Flat | 28.47 ± 4.50 | 89.177 | <0.001 * | 2.89 |
| Ramp | 27.48 ± 4.38 | ||||
| Balance pad | 49.76 ± 9.38 | ||||
| Balance pad on the ramp | 49.03 ± 8.55 | ||||
| COP area (mm2) | Flat | 1104.07 ± 330.22 | 52.659 | <0.001 * | 2.15 |
| Ramp | 1100.20 ± 500.79 | ||||
| Balance pad | 2232.97 ± 778.91 | ||||
| Balance pad on the ramp | 2202.30 ± 578.87 | ||||
| COP ML (mm) | Flat | 27.03 ± 7.23 | 38.272 | <0.001 * | 1.96 |
| Ramp | 27.38 ± 8.43 | ||||
| Balance pad | 42.10 ± 11.61 | ||||
| Balance pad on the ramp | 44.03 ± 10.22 | ||||
| COP AP (mm) | Flat | 28.47 ± 4.50 | 89.177 | <0.001 * | 2.89 |
| Ramp | 27.48 ± 4.38 | ||||
| Balance pad | 49.76 ± 9.38 | ||||
| Balance pad on the ramp | 49.03 ± 8.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-Y.; Yeo, S.-S.; Kang, T.-W.; Koo, D.-K. Investigating the Influence of Varying Surface Conditions on Human Postural Control and Sensory Integration Strategies. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060618
Park S-Y, Yeo S-S, Kang T-W, Koo D-K. Investigating the Influence of Varying Surface Conditions on Human Postural Control and Sensory Integration Strategies. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060618
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seo-Yoon, Sang-Seok Yeo, Tae-Woo Kang, and Dong-Kyun Koo. 2024. "Investigating the Influence of Varying Surface Conditions on Human Postural Control and Sensory Integration Strategies" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060618
APA StylePark, S.-Y., Yeo, S.-S., Kang, T.-W., & Koo, D.-K. (2024). Investigating the Influence of Varying Surface Conditions on Human Postural Control and Sensory Integration Strategies. Bioengineering, 11(6), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060618






