Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection and Eligibility Criteria
- Reviews with or without meta-analysis comparing the cyclic fatigue strength of different rotating Ni-Ti instruments, including in vivo and in vitro studies.
- Reviews that have been published within the past ten years.
- Reviews published in the English language only.
- Randomized controlled trial published within the past ten years.
- Reviews that did not aim to assess fatigue in rotating Ni-Ti instruments.
- Case reports.
- Reviews with a publication date before ten years ago.
- Reviews published in languages other than English.
2.4. Data Extraction and Collection
- The first author of the journal, the year of publication, the type of journal, and funding.
- The number and design of studies included in each systematic review and sample size.
- Alloy.
- Kinematics.
- Diameter/Conicity.
- Conclusions.
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
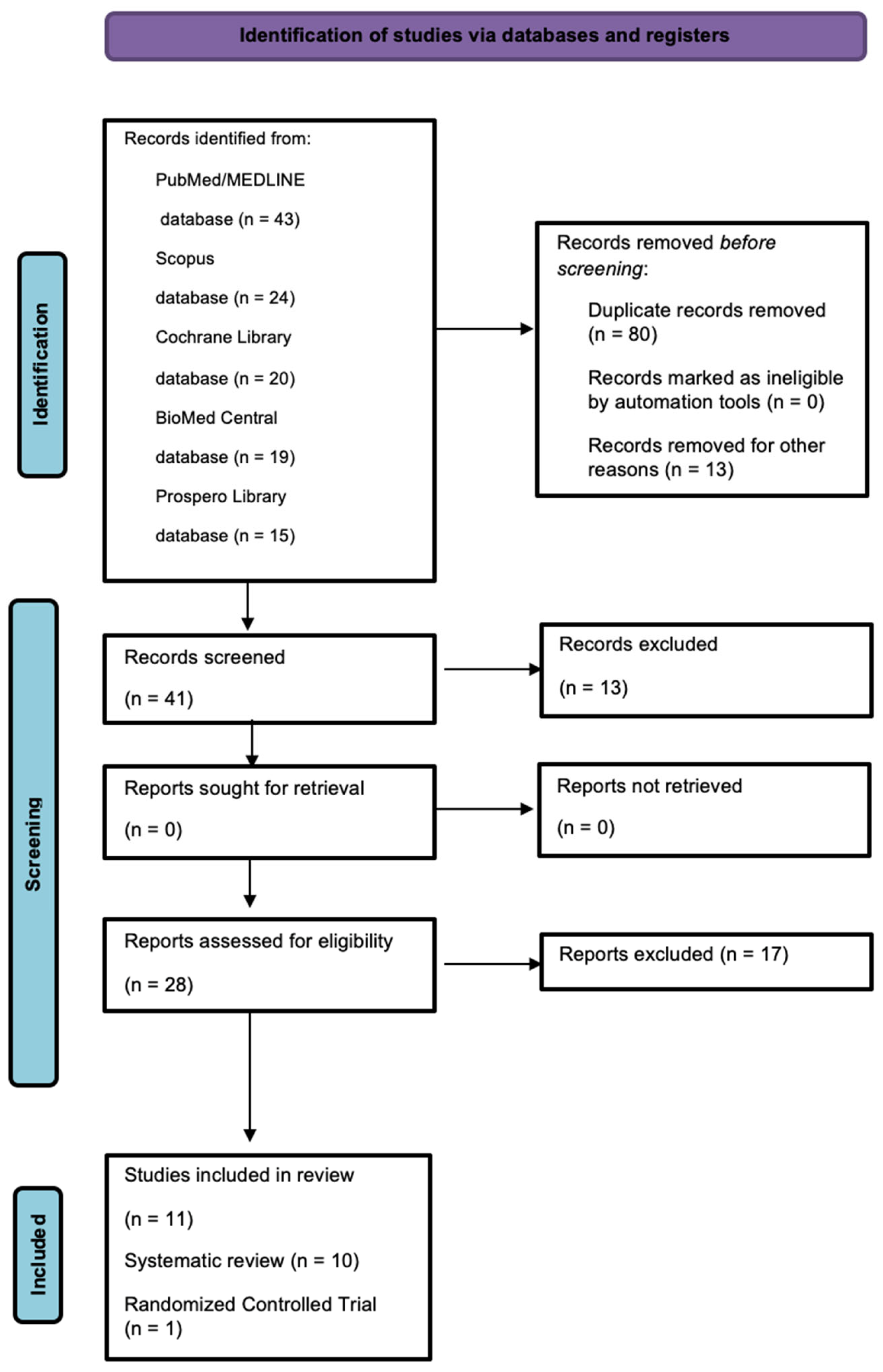
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics and Qualitative Synthesis
4. Quality Assessment
5. Discussion
- The cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated files.
- The fracture resistance of files used with different kinematics.
- The effects of sterilisation cycles on the degree of fracture of Ni-Ti instruments.
5.1. Heat-Treated Files
5.2. Continuous Rotation vs. Reciprocating Motion
5.3. Effects of Sterilisation Cycles on Ni-Ti Files
5.4. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Spirito, F.; Pisano, M.; Caggiano, M.; Bhasin, P.; Lo Giudice, R.; Abdellatif, D. Root Canal Cleaning after Different Irrigation Techniques: An Ex Vivo Analysis. Medicina 2022, 58, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fransson, H.; Dawson, V. Tooth survival after endodontic treatment. Int. Endod. J. 2023, 56 (Suppl. S2), 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, L.E.; Kim, J.; Wu, Y.; Alzwaideh, R.; McGowan, R.; Sigurdsson, A. Outcomes of primary root canal therapy: An updated systematic review of longitudinal clinical studies published between 2003 and 2020. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pantaleo, G.; Amato, A.; Iandolo, A.; Abdellatif, D.; Di Spirito, F.; Caggiano, M.; Pisano, M.; Blasi, A.; Fornara, R.; Amato, M. Two-Year Healing Success Rates after Endodontic Treatment Using 3D Cleaning Technique: A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abdellatif, D.; Amato, A.; Calapaj, M.; Pisano, M.; Iandolo, A. A novel modified obturation technique using biosealers: An ex vivo study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2021, 24, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Jafarzadeh, H.; Shalavi, S.; Sahebalam, R.; Kinoshita, J.I. Laser-based Disinfection of the Root Canal System: An Update. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2017, 18, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, O.A. Current challenges and concepts in the preparation of root canal systems: A review. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotinus, G.; Nagendrababu, V.; Bukiet, F.; Grande, N.M.; Veettil, S.K.; De-Deus, G.; Aly Ahmed, H.M. Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping-Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 707–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovarruscio, M.; Khajanka, E.; Isufi, A.; Feghali, M.; Pacifici, L.; Donfrancesco, O.; Bhandi, S.; Pacifici, A.; Obino, F.V. New Strategies and Instruments for Root Canal Shaping Procedure: An Overview. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2021, 22, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvaniya, J.; Agarwal, K.; Mehta, D.N.; Parmar, N.; Shyamal, R.; Patel, J. Minimal Invasive Endodontics: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e25984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gavini, G.; Santos, M.D.; Caldeira, C.L.; Machado, M.E.L.; Freire, L.G.; Iglecias, E.F.; Peters, O.A.; Candeiro, G.T.M. Nickel-titanium instruments in endodontics: A concise review of the state of the art. Braz. Oral Res. 2018, 32 (Suppl. S1), e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoch, L.; Marending, M.; Hofpeter, K.; Attin, T.; Zehnder, M. The Impact of Changing from First- to Fifth-Generation Nickel-Titanium Rotaries on Root-Filling Quality in a Clinical Undergraduate Course. Swiss Dent. J. 2022, 132, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, G.F.; Hilleman, T.B. An evaluation of 55 cobalt substituted Nitinol wire for use in orthodontics. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1971, 82, 1373–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, G.; Jordan, L. Fatigue and mechanical properties of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamoudi, R.A.; Alharbi, A.H.; Farie, G.A.; Fahim, O. The value of assessing case difficulty and its effect on endodontic iatrogenic errors: A retrospective cross-sectional study. Libyan J. Med. 2020, 15, 1688916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Elayouti, A.; Chu, A.L.; Kimionis, I.; Klein, C.; Weiger, R.; Löst, C. Efficacy of rotary instruments with greater taper in preparing oval root canals. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.A. An overview of nickel-titanium alloys used in dentistry. Int. Endod. J. 2000, 33, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.N.R.; Silva, E.J.N.L.; Marques, D.; Ajuz, N.; Rito Pereira, M.; Pereira da Costa, R.; Braz Fernandes, F.M.; Versiani, M.A. Characterization of the file-specific heat-treated ProTaper Ultimate rotary system. Int. Endod. J. 2023, 56, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, I.F.; Pereira, É.S.; Aun, D.P.; Buono, V.T.; Bahia, M.G. Constant Insertion Rate Methodology for Measuring Torque and Apical Force in 3 Nickel-Titanium Instruments with Different Cross-sectional Designs. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1540–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluskin, A.H.; Brown, D.C.; Buchanan, L.S. A reconstructed computerized tomographic comparison of Ni-Ti rotary GT files versus traditional instruments in canals shaped by novice operators. Int. Endod. J. 2001, 34, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfouzan, K.; Jamleh, A. Fracture of nickel titanium rotary instrument during root canal treatment and re-treatment: A 5-year retrospective study. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, D.; Sinha, D.J.; Singh, S.; Verma, N.; Rani, P.; Parvez, B. Comparison of single and multiple file rotary endodontic instruments for debris and irrigant extrusion: An in vitro study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2023, 26, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ikogou, T.; Chai, F.; Verriest, B.; Sy, K.; Delattre, J.; Deveaux, E.; Robberecht, L. Shaping Ability of F6 SkyTaper®, Hyflex® EDM One File, and One Curve®: A Micro-computed Tomographic Evaluation in Curved Root Canals. Eur. Endod. J. 2023, 8, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khan, L.K.; Kunz, R.; Kleijnen, J.; Antes, G. Systematic reviews to support evidence-based medicine. How to review and apply findings of healthcare research. Kahn, K.S.; Kunz, R.; Kleijnen J, Antes, G.170 × 240 mm. Pp.136. Illustrated.2003. Royal Society of Medicine Press: London, UK. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 375. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, W.S.; Wilson, M.C.; Nishikawa, J.; Hayward, R.S. The well-built clinical question: A key to evidence-based decisions. ACPJ Club 1995, 123, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkar, I.; Sanz, J.L.; Forner, L. Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Glide Path Rotary Files: A Systematic Review of in Vitro Studies. Materials 2022, 15, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferreira, F.; Adeodato, C.; Barbosa, I.; Aboud, L.; Scelza, P.; Zaccaro Scelza, M. Movement kinematics and cyclic fatigue of NiTi rotary instruments: A systematic review. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitha, S.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, V.; Chawla, A.; Vanamail, P.; Logani, A. Effect of body temperature on the cyclic fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies. J. Conserv. Dent. 2022, 25, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dioguardi, M.; Arena, C.; Sovereto, D.; Aiuto, R.; Laino, L.; Illuzzi, G.; Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Dioguardi, A.; et al. Influence of sterilization procedures on the physical and mechanical properties of rotating endodontic instruments: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 1697–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Aiuto, R.; Laino, L.; Illuzzi, G.; Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Dioguardi, A.; Zhurakivska, K.; et al. Effects of Hot Sterilization on Torsional Properties of Endodontic Instruments: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Silva, E.J.N.L.; Zanon, M.; Hecksher, F.; Belladonna, F.G.; de Vasconcelos, R.A.; Fidalgo, T.K.D.S. Influence of autoclave sterilization procedures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated nickel-titanium instruments: A systematic review. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2020, 45, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, E. Kinematic Effects of Nickel-Titanium Instruments with Reciprocating or Continuous Rotation Motion: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsilani, R.; Jadu, F.; Bogari, D.F.; Jan, A.M.; Alhazzazi, T.Y. Single file reciprocating systems: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature: Comparison of reciproc and WaveOne. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dioguardi, M.; Laneve, E.; Di Cosola, M.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Sovereto, D.; Aiuto, R.; Laino, L.; Leanza, T.; Alovisi, M.; Troiano, G.; et al. The Effects of Sterilization Procedures on the Cutting Efficiency of Endodontic Instruments: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Materials 2021, 14, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Herbst, S.R.; Krois, J.; Schwendicke, F. Comparator Choice in Studies Testing Endodontic Instrument Fatigue Resistance: A Network Analysis. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambarini, G.; Miccoli, G.; Seracchiani, M.; Morese, A.; Piasecki, L.; Gaimari, G.; Di Nardo, D.; Testarelli, L. Fatigue Resistance of New and Used Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments: A Comparative Study. Clin. Ter. 2018, 169, e96–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, S.; Zafar, K.; Umer, F. Nickel-Titanium Rotary File Systems: What’s New? Eur. Endod. J. 2019, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parashos, P.; Gordon, I.; Messer, H.H. Factors influencing defects of nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments in postclinical use. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, P.; Liu, Y. Thermodynamic analysis of martensitic transformation in NiTi-II. Effect of the transformation cycle. Acta Metall. Mater. 1994, 42, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, S.; Pisano, M.; Amato, A.; Abdellatif, D.; Iandolo, A. Modern rotary files in minimally invasive endodontics: A case report. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2021, 13, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, M.; Di Spirito, F.; Martina, S.; Sangiovanni, G.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Iandolo, A. Intentional Replantation of Single-Rooted and Multi-Rooted Teeth: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2022, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iandolo, A.; Amato, A.; Martina, S.; Abdellatif, D.A.; Pantaleo, G. Management of severe curvatures in root canal treatment with the new generation of rotating files using a safe and predictable protocol. Open Dent. J. 2020, 14, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-C.; Kwa, S.-W.; Cheung, G.S.-P.; Ko, D.-H.; Chung, S.-M.; Lee, W.C. Cyclic Fatigue and Torsional Resistance of Two New Nickel-Titanium Instruments Used in Reciprocation Motion: Reciproc Versus WaveOne. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, R.; Nivedhitha, M.S. Effectiveness of rotary and reciprocating systems on microbial reduction: A systematic review. J. Conserv. Dent. 2019, 22, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Author | Study/Purpose | Type of Study | No. Studies | Sample Size | League | Kinematics | Diameter/Taper | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Israa Ashkar Materials (Basel) 26 September 2022 [27]. | A review of in vitro studies. The aim of this systematic review was to provide a summary of in vitro studies analysing the cyclic fatigue strength of rotating files used for glide path. | Systematic review | 20 | 1025 | M-wire, Conventional Ni-Ti, Gold-wire, CM-wire, and Heat-treated firewire Ni-Ti | Continuous rotation and reciprocating motion. | 10, 12, 13, 15, 16, 19, 20/2% 12/4% 12, 14, 17/3% 10/15% | The cyclic fatigue strength of files used for glide path can be influenced by intrinsic factors such as taper, cross-section, alloy properties, and kinematics, and external factors such as channel curvature, irrigation, lubricant use, and temperature. In addition, reciprocating motion results in a higher cyclic fatigue strength. |
| F. Ferreira Int. Endod. J. February 2017 [28]. | A systematic review of in vitro studies. The aim is to analyse the correlation between different motion kinematics and the cyclic fatigue strength of Ni-Ti files. | Systematic review | 32 | 1923 | Conventional Ni-Ti, Gold Wire, and CM-wire | Continuous rotation and reciprocating motion. | 19/4% 18/2% 20/4% 20/7% 25/8% 25/6% 30/6% 40/4% | The literature reviewed suggests that reciprocating motion improves the cyclic fatigue strength of Ni-Ti instruments regardless of the intrinsic and extrinsic file factors. However, the scientific evidence is not unbiased due to the lack of sample standardisation. |
| Selventhra S. J. Conserv. Dent. July–August 2022 [29]. | A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies. The analysis of the effect of body temperature, compared to room temperature, on the cyclic fatigue strength of Ni-Ti instruments. | Systematic review | 21 | 215 | Heat-treated Ni-Ti and Conventional Ni-Ti | Continuous rotation, reciprocating motion, and adaptive. | 20/0.04 25/0.04 30/0.04 35/0.04 40/0.04 20/04 25/0.08 25/0.06 30/0.05 30/0.01 25/0.08 25/0.06 25/0.07 25/0.08 10/0.02 25/0.6 40/0.06 | At body temperature, the cyclic fatigue strength of heat-treated Ni-Ti files is significantly reduced compared to room temperature. |
| Dioguardi M. Materials (Basel). 8 July 2019 [30]. | Systematic review with meta-analysis. The aim is to analyse whether and how disinfection and sterilisation procedures alter the cutting efficiency of endodontic instruments. | Systematic review | 12 | Conventional Ni-Ti, Nitiflex, Profile, R-face, and K-file | Continuous rotation. | 30/02 25/06 25/04 35/04 | New generation instruments such as those made of M wire, CM wire, and EDM alloys are more reliable after sterilisation than older generation instruments. | |
| Dioguardi M. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed). 30 December 2021 [31] | A systematic review and network meta-analysis of in vitro and in vivo studies. In the following review, the effects of heat sterilisation on the torsional properties of steel and Ni-Ti alloy instruments are analysed. | Systematic review | 51 | 368 | Gold Wire, CM-wire, Conventional Ni-Ti, M-wire, and Heat-treated Ni-Ti | Continuous rotation. | 10, 12, 13, 15, 16, 19, 20/2% 12/4% 12, 14, 17/3% 10/15% | The literature reports conflicting results on the effects of sterilisation procedures, which certainly produce changes in the physical and mechanical properties of instruments. In summary, the cutting capacity after five autoclaving cycles is significantly reduced. Hypochlorite disinfectants cause a corrosive effect after hot sterilisation. In some studies, a potential recovery of shape and increased resistance to torsional fatigue after sterilisation is contemplated. |
| Silva E.J.N.L. Restor. Dent. Endod. 31 March 2020 [32]. | A systematic review of in vitro studies. The aim is to evaluate the effect of autoclave sterilisation procedures on the cyclic fatigue strength of heat-treated Ni-Ti instruments. | Systematic review | 5 | 174 | R-phase, CM-wire, M-wire, and Gold-wire | Continuous rotation. | 25/0.06 20/0.06 20/0.04 25/0.04 40/0.04 25/0.08 30/0.06 | Considering the limited scientific evidence and the considerable risk of bias, it is possible to conclude that autoclaving procedures appear to influence the cyclic fatigue strength of heat-treated Ni-Ti instruments. |
| Ahn S.Y.J. Endod. July 2016 [33] | A systematic review of in vitro and ex vivo studies. The purpose of this review is to make a comparison, in terms of cyclic fatigue strength, modelling capability, debris extrusion, cracks, and dentin defects, between reciprocating motion and continuous rotation. | Systematic review | 58 | 1923 | M-wire, Heat-treated, R-face, Ni-Ti conventional, and CM-wire | Continuous rotation, reciprocating motion, and adaptive motion. | 25/8% 40/6% 50/5% 21/6% 40/8% 25/0.06 20/0.06 20/0.04 25/0.04 40/0.04 30/0.06 | The reciprocating movement leads to better resistance to cyclic fatigue and less canal transport compared to instruments used with a continuous movement. |
| Alsilani R. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. September–October 2016 [34] | A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature of in vitro and in vivo studies. In this study, Reciproc and WaveOne are compared through a meta-analysis with different parameters. | Systematic review | 26 | 707 | M-wire, Heat-treated, and Wave one | Continuous rotation and reciprocating motion. | 25/8% 40/6% 50/5% 21/6% 25/8% 40/8% | Reciproc has a higher cyclic fatigue than WaveOne. Further studies are needed, in particular randomised clinical trials comparing remodelling, clinical efficiency, and the possibility to reuse Reciproc and WaveOne with standardised samples. |
| Dioguardi M. Materials (Basel). 22 March 2021 [35]. | Systematic review and network meta-analysis. The aim is to analyse changes in file cutting efficiency after disinfection and sterilisation procedures. | Systematic review | 56 | 367 | Flexofile, Ni-Ti conventional, CM-Wire, and M-wire | Continuous rotation and reciprocating motion. | Disinfection and sterilisation processes cause changes in the files, such as a reduction in cutting capacity after five cycles. Due to the heterogeneity of the measurement methods used, it is complex to perform a meta-analysis. | |
| Herbst S.R. A Network Analysis. J. Endod. June 2019 [36]. | A network analysis of in vitro studies. The objective of the study is to evaluate the networks of cyclic fatigue strength studies with the assumption that the intrinsic and extrinsic properties of the instruments guide the comparison. | Systematic review | 85 | / | Conventional Ni-Ti, M-wire, CM-wire, and Reciproc | Continuous rotation and reciprocating motion. | The comparator used leads to a moderate risk of bias. Factors such as sponsorship should be explored for more certain results. | |
| Gambarini G. Clin. Ter. May–June 2018 [37] | First, to evaluate in vitro the performance of two different Ni-Ti rotary instruments in one molar case; then, to evaluate their resistance to cyclic fatigue, compared to new ones | Randomized controlled trial | / | 25 | ProTaper Next | Continuous rotation. | 17/04 25/06 | Since in previous studies ProTaper Next demonstrated a better resistance to cyclic fatigue than most nickel–titanium instruments, Horizen’s performance put them in a high rank amongst the most resistant nickel–titanium rotary instruments |
| Author | The Total Number of Involved Study | Participants Clinical Studies Included |
|---|---|---|
| Ashkar I. [27] | 1025 | 20 |
| Ferreira F. [28] | 1923 | 32 |
| Selventhra S. [29]. | 215 | 21 |
| Dioguardi M. [30] | / | 12 |
| Dioguardi M. [31] | 368 | 51 |
| Silva E.J.N.L. [32] | 174 | 5 |
| Ahn S.Y. [33] | 1923 | 58 |
| Alsilani R. [34] | 707 | 26 |
| Dioguardi M. [35] | 367 | 56 |
| Herbst S.R. [36] | / | 85 |
| Authors | Main Results | Statistical Analysis | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selventhra S. [29]. | The cyclic fatigue resistance of heat-treated Ni-Ti endodontic instruments is significantly reduced at body temperature compared with room temperature. | full rotary motion: [SMD]: 4.80; 95% CI: 3.04–6.56 reciprocating motion: [SMD]: 6.37; 95% CI: 3.63–9.11 | p-value = 0.346 |
| Dioguardi M. [31] | The cutting capacity of Ni-Ti instruments decreases after the 5 sterilisation cycles. | SMD value of 0.80 CI: [0.05, 1.55]. | p-value = 0.04 |
| Alsilani R. [34] | Reciprocs resist cyclic fatigue better than WaveOne | MD value of 0.95 CI: 5.25–13.14 | p-value < 0.001 |
| Studies Selected | Question and Inclusion | Protocol | Study Design | Comprehensive Search | Study Selection | Data Extraction | Excluded Studies Justification | Included Study Details | Risk of Bias | Funding Sources | Statistical Methods | Risk of Bias in Meta-Analysis | Risk of Bias in Individual Studies | Explanation of Heterogeneity | Publication Bias | Conflict of Interest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashkar I. 2022 [27] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ferreira F. 2017 [28] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Selventhra S. 2022 [29] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dioguardi M. 2019 [30] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dioguardi M. 2021 [31] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Silva E.J.N.L. 2020 [32] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ahn S.Y. 2016 [33] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Alsilani R. 2016 [34] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dioguardi M. 2021 [35] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Herbst S.R. 2019 [36] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdellatif, D.; Iandolo, A.; Scorziello, M.; Sangiovanni, G.; Pisano, M. Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050499
Abdellatif D, Iandolo A, Scorziello M, Sangiovanni G, Pisano M. Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(5):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050499
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdellatif, Dina, Alfredo Iandolo, Michela Scorziello, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, and Massimo Pisano. 2024. "Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review" Bioengineering 11, no. 5: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050499
APA StyleAbdellatif, D., Iandolo, A., Scorziello, M., Sangiovanni, G., & Pisano, M. (2024). Cyclic Fatigue of Different Ni-Ti Endodontic Rotary File Alloys: A Comprehensive Review. Bioengineering, 11(5), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050499










