Enhanced Nuclei Segmentation and Classification via Category Descriptors in the SAM Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce category descriptors to perform automatic nuclei segmentation and classification via prompting the SAM model.
- We align the low-level features of histopathology images with the distribution of natural scenes features to exploit the high-level representation of the SAM model for accurate nuclei segmentation and classification.
- We also show that the inherent ability of the SAM model is still preserved after domain alignment and can use manual point prompts (not used during training) on histopathology images for further interactive refinement during inference.
2. Related Works
2.1. Nuclei Segmentation
2.2. Segment Anything Model (SAM)
3. Method
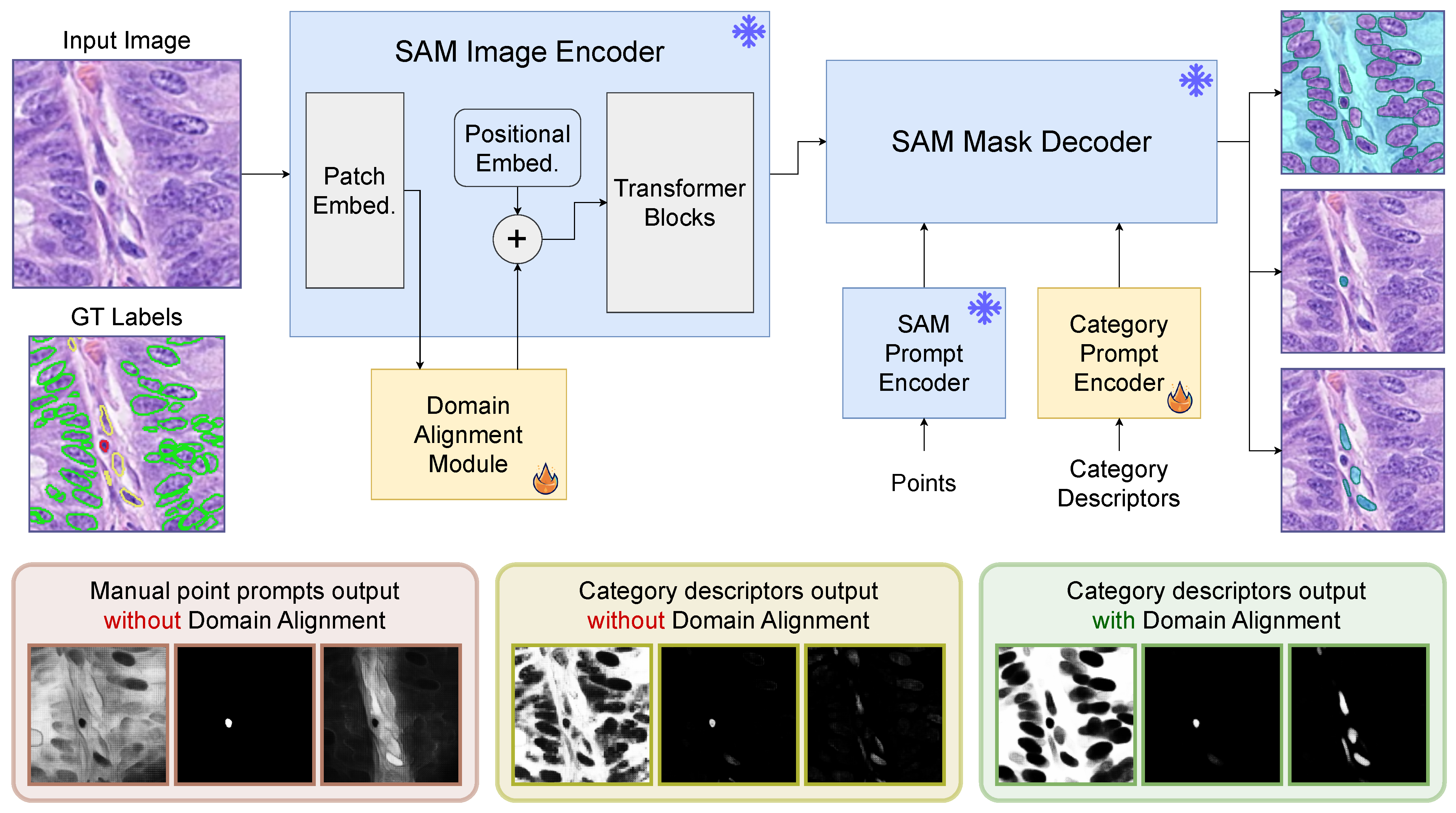
3.1. Category Descriptors
3.2. Domain Alignment
3.3. Training Objective
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Comparison Methods
4.5. Implementation Details
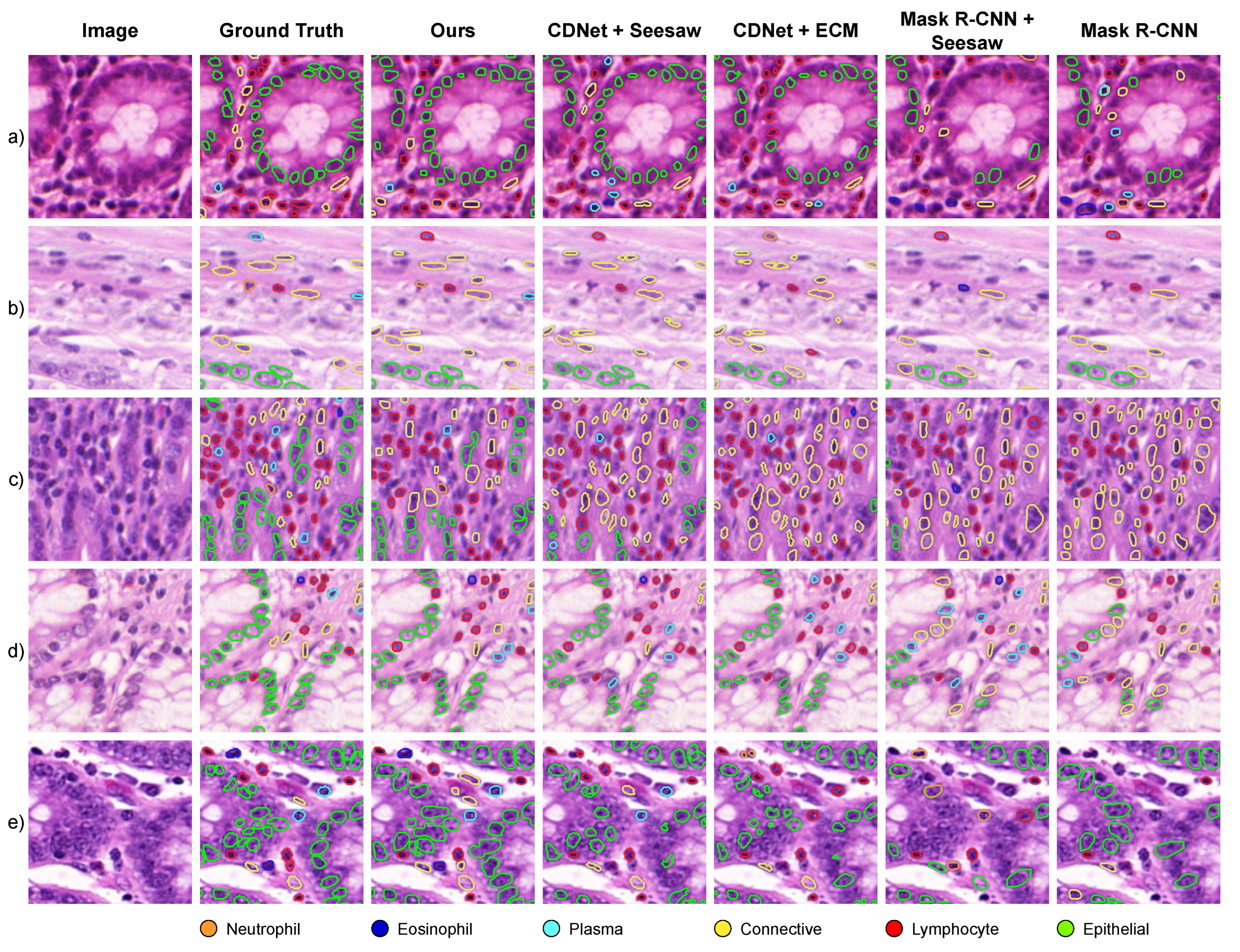
5. Results
| Method | F1mean | F1category | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rare | Frequent | ||||||
| Neutrophil | Eosinophil | Plasma | Connective | Lymphocyte | Epithelial | ||
| CDNet [12] + [54] | 0.624 | 0.304 | 0.627 | 0.509 | 0.729 | 0.757 | 0.814 |
| CDNet [12] + [53] | 0.671 | 0.443 | 0.690 | 0.574 | 0.725 | 0.768 | 0.824 |
| Mask R-CNN [9] | 0.665 | 0.382 | 0.646 | 0.564 | 0.781 | 0.788 | 0.827 |
| MRCNN [9] + [53] | 0.668 | 0.382 | 0.676 | 0.556 | 0.78 | 0.782 | 0.829 |
| Ours | 0.733 | 0.540 | 0.797 | 0.645 | 0.785 | 0.789 | 0.844 |
| Method | mAP | mAP50 | mAPcategory | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rare | Frequent | |||||||
| Neutrophil | Eosinophil | Plasma | Connective | Lymphocyte | Epithelial | |||
| CDNet [12] + [54] | 0.225 | 0.423 | 0.064 | 0.171 | 0.19 | 0.236 | 0.385 | 0.303 |
| CDNet [12] + [53] | 0.295 | 0.545 | 0.123 | 0.238 | 0.268 | 0.374 | 0.415 | 0.350 |
| Mask R-CNN [9] | 0.240 | 0.459 | 0.110 | 0.201 | 0.224 | 0.226 | 0.384 | 0.296 |
| MRCNN [9] + [53] | 0.292 | 0.536 | 0.109 | 0.231 | 0.248 | 0.384 | 0.422 | 0.355 |
| Ours | 0.321 | 0.594 | 0.238 | 0.319 | 0.274 | 0.373 | 0.38 | 0.342 |
| Method | F1mean | F1category | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rare | Frequent | ||||||
| Neutrophil | Eosinophil | Plasma | Connective | Lymphocyte | Epithelial | ||
| CDNet [12] + [54] | 0.507 | 0.154 | 0.334 | 0.418 | 0.656 | 0.689 | 0.789 |
| CDNet [12] + [53] | 0.565 | 0.236 | 0.460 | 0.465 | 0.699 | 0.710 | 0.819 |
| Mask R-CNN [9] | 0.533 | 0.244 | 0.394 | 0.482 | 0.619 | 0.722 | 0.739 |
| MRCNN [9] + [53] | 0.521 | 0.219 | 0.371 | 0.478 | 0.616 | 0.714 | 0.730 |
| Ours | 0.639 | 0.371 | 0.590 | 0.565 | 0.735 | 0.731 | 0.839 |
| Method | mAP | mAP50 | APcategory | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rare | Frequent | |||||||
| Neutrophil | Eosinophil | Plasma | Connective | Lymphocyte | Epithelial | |||
| CDNet [12] + [54] | 0.162 | 0.309 | 0.021 | 0.038 | 0.128 | 0.223 | 0.320 | 0.246 |
| CDNet [12] + [53] | 0.171 | 0.336 | 0.021 | 0.048 | 0.141 | 0.245 | 0.319 | 0.251 |
| Mask R-CNN [9] | 0.225 | 0.396 | 0.086 | 0.126 | 0.196 | 0.281 | 0.384 | 0.276 |
| MRCNN [9]+ [53] | 0.220 | 0.390 | 0.081 | 0.115 | 0.205 | 0.277 | 0.378 | 0.263 |
| Ours | 0.269 | 0.470 | 0.108 | 0.171 | 0.239 | 0.348 | 0.393 | 0.350 |
5.1. Ablation Studies
5.2. Manual Prompts
6. Limitations
7. Generalizability
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, J.; Zhu, X.; Jonnagaddala, J.; Hawkins, N.; Huang, J. Whole slide images based cancer survival prediction using attention guided deep multiple instance learning networks. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 65, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lim, S.; Shin, H.K.; Uhm, K.H.; Lu, Y.; Jung, S.W.; Ko, S.J. Risk-aware survival time prediction from whole slide pathological images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikontwe, P.; Sung, H.J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, M.; Go, H.; Nam, S.J.; Park, S.H. Weakly supervised segmentation on neural compressed histopathology with self-equivariant regularization. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 80, 102482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M. Recent Advancements in Deep Learning Using Whole Slide Imaging for Cancer Prognosis. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Lucarini, V.; Marone, G.; Mattei, F.; Marone, G.; Schiavoni, G. Eosinophils: The unsung heroes in cancer? Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1393134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; McNamara, M.G.; Šeruga, B.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Aneja, P.; Ocaña, A.; Leibowitz-Amit, R.; Sonpavde, G.; Knox, J.J.; Tran, B.; et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wu, B.; Cheng, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Li, C. Prognostic role of pretreatment blood lymphocyte count in patients with solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berek, C.; Manz, R.A. Long-lived plasma cells. In Activation of the Immune System; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Chikontwe, P.; Kim, M.; Nam, S.J.; Go, H.; Park, S.H. Multiple instance learning with center embeddings for histopathology classification. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.; Jeong, J.; Luna, M.; Chikontwe, P.; Park, S.H. PROnet: Point Refinement Using Shape-Guided Offset Map for Nuclei Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023; pp. 528–538. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Huang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Song, G.; Wang, L.; Ren, Q.; Wei, P.; Gao, Z.; Chen, J. Cdnet: Centripetal direction network for nuclear instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 4026–4035. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; An, S.; Chikontwe, P.; Kang, M.; Adeli, E.; Pohl, K.M.; Park, S. Few Shot Part Segmentation Reveals Compositional Logic for Industrial Anomaly Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.13783. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M. Empowering deep learning based organizational decision making: A Survey. Sustain. Mach. Intell. J. 2023, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kim, S.; Jin, K.H.; Adeli, E.; Pohl, K.M.; Park, S.H. FedNN: Federated learning on concept drift data using weight and adaptive group normalizations. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 149, 110230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikontwe, P.; Nam, S.J.; Go, H.; Kim, M.; Sung, H.J.; Park, S.H. Feature re-calibration based multiple instance learning for whole slide image classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 420–430. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M. Agricultural Sustainability in the Age of Deep Learning: Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Trajectories. Sustain. Mach. Intell. J. 2023, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Verma, R.; Anand, D.; Zhou, Y.; Onder, O.F.; Tsougenis, E.; Chen, H.; Heng, P.A.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; et al. A multi-organ nucleus segmentation challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, Q.D.; Graham, S.; Kurc, T.; To, M.N.N.; Shaban, M.; Qaiser, T.; Koohbanani, N.A.; Khurram, S.A.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Zhao, T.; et al. Methods for segmentation and classification of digital microscopy tissue images. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, P.; Laé, M.; Reyal, F.; Walter, T. Segmentation of nuclei in histopathology images by deep regression of the distance map. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, A.; Pavlov, M.; Goh, G.; Gray, S.; Voss, C.; Radford, A.; Chen, M.; Sutskever, I. Zero-shot text-to-image generation. In Proceedings of the International conference on Machine Learning PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8821–8831. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Kadavath, S.; Kundu, S.; Askell, A.; Kernion, J.; Jones, A.; Chen, A.; Goldie, A.; Mirhoseini, A.; McKinnon, C.; et al. Constitutional ai: Harmlessness from ai feedback. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.08073. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment anything. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.02643. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Verma, R.; Sharma, S.; Bhargava, S.; Vahadane, A.; Sethi, A. A dataset and a technique for generalized nuclear segmentation for computational pathology. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, M.; Kwon, M.; Park, S.H. Precise separation of adjacent nuclei using a Siamese neural network. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Q.; Lao, Q.; Fevens, T. Nuclei segmentation in histopathological images using two-stage learning. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 703–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Onder, O.F.; Dou, Q.; Tsougenis, E.; Chen, H.; Heng, P.A. Cia-net: Robust nuclei instance segmentation with contour-aware information aggregation. In Proceedings of the Information Processing in Medical Imaging: 26th International Conference, IPMI 2019, Hong Kong, China, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 682–693. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; Jia, H.; Zheng, L.; Wang, F.; Xu, F. ClassWise-SAM-Adapter: Parameter Efficient Fine-tuning Adapts Segment Anything to SAR Domain for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.02326. [Google Scholar]
- Houlsby, N.; Giurgiu, A.; Jastrzebski, S.; Morrone, B.; De Laroussilhe, Q.; Gesmundo, A.; Attariyan, M.; Gelly, S. Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 2790–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chang, H.; Barner, K.E.; Parvin, B. Nuclei segmentation via sparsity constrained convolutional regression. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Brooklyn, NY, USA, 16-19 April 2015; pp. 1284–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Raza, S.E.A.; Tsang, Y.W.; Snead, D.R.; Cree, I.A.; Rajpoot, N.M. Locality sensitive deep learning for detection and classification of nuclei in routine colon cancer histology images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, M.; Chikontwe, P.; Nam, S.; Park, S.H. Attention guided multi-scale cluster refinement with extended field of view for amodal nuclei segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 108015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, P.; Laé, M.; Reyal, F.; Walter, T. Nuclei segmentation in histopathology images using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 18–21 April 2017; pp. 933–936. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, S.; Vu, Q.D.; Raza, S.E.A.; Azam, A.; Tsang, Y.W.; Kwak, J.T.; Rajpoot, N. Hover-net: Simultaneous segmentation and classification of nuclei in multi-tissue histology images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, S.; Liang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.Z. Input augmentation with sam: Boosting medical image segmentation with segmentation foundation model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2023; pp. 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Han, L.; You, C.; Wang, B. Segment anything in medical images. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurowski, M.A.; Dong, H.; Gu, H.; Yang, J.; Konz, N.; Zhang, Y. Segment anything model for medical image analysis: An experimental study. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 89, 102918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H.; Chang, A.; Zhou, X.; Chen, R.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; et al. Segment anything model for medical images? Med. Image Anal. 2024, 92, 103061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Li, G. Mammo-sam: Adapting foundation segment anything model for automatic breast mass segmentation in whole mammograms. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8 October 2023; pp. 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Zhu, L.; Deng, C.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Zang, Y.; Mao, P. Sam-adapter: Adapting segment anything in underperformed scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 3367–3375. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Fu, R.; Fang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Arbel, T. Medical sam adapter: Adapting segment anything model for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.12620. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Koltun, V.; Krähenbühl, P. Probabilistic two-stage detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.07461. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, S.; Jahanifar, M.; Azam, A.; Nimir, M.; Tsang, Y.W.; Dodd, K.; Hero, E.; Sahota, H.; Tank, A.; Benes, K.; et al. Lizard: A large-scale dataset for colonic nuclear instance segmentation and classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 684–693. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, S.; Chen, H.; Gamper, J.; Dou, Q.; Heng, P.A.; Snead, D.; Tsang, Y.W.; Rajpoot, N. MILD-Net: Minimal information loss dilated network for gland instance segmentation in colon histology images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 52, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, Q.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Xu, D.; Hu, Z.; et al. DigestPath: A benchmark dataset with challenge review for the pathological detection and segmentation of digestive-system. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 80, 102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Pluim, J.P.; Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Heng, P.A.; Guo, Y.B.; Wang, L.Y.; Matuszewski, B.J.; Bruni, E.; Sanchez, U.; et al. Gland segmentation in colon histology images: The glas challenge contest. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamper, J.; Alemi Koohbanani, N.; Benet, K.; Khuram, A.; Rajpoot, N. Pannuke: An open pan-cancer histology dataset for nuclei instance segmentation and classification. In Proceedings of the Digital Pathology: 15th European Congress, ECDP 2019, Warwick, UK, 10–13 April 2019; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Pang, J.; Gong, T.; Chen, K.; Liu, Z.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D. Seesaw loss for long-tailed instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9695–9704. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun Cho, J.; Krähenbühl, P. Long-tail detection with effective class-margins. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 698–714. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Lvis: A dataset for large vocabulary instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–19 June 2019; pp. 5356–5364. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, J.; Yu, B.; Maybank, S.J.; Tao, D. Knowledge distillation: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1789–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | CDNet [12] + [54] | CDNet [12] + [53] | Mask R-CNN [9] | MRCNN [9] + [53] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value |
| # Residual Layers | # Category Descriptors | F1 | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8 | 0.226 | 0.046 |
| 0 | 32 | 0.285 | 0.060 |
| 0 | 128 | 0.308 | 0.069 |
| 0 | 512 | 0.309 | 0.079 |
| 4 | 32 | 0.498 | 0.161 |
| 8 | 32 | 0.628 | 0.237 |
| 12 | 32 | 0.638 | 0.240 |
| 16 | 32 | 0.643 | 0.244 |
| 12 | 8 | 0.629 | 0.235 |
| 12 | 16 | 0.630 | 0.230 |
| 12 | 32 | 0.638 | 0.240 |
| 12 | 64 | 0.645 | 0.242 |
| 12 | 128 | 0.647 | 0.246 |
| # of Prompts | F1mean | F1category | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rare | Frequent | ||||||
| Neutrophil | Eosinophil | Plasma | Connective | Lymphocyte | Epithelial | ||
| 0 | 0.638 | 0.621 | 0.565 | 0.412 | 0.694 | 0.751 | 0.783 |
| 1 | 0.699 | 0.758 | 0.667 | 0.488 | 0.717 | 0.779 | 0.788 |
| 2 | 0.725 | 0.806 | 0.731 | 0.504 | 0.728 | 0.787 | 0.792 |
| 4 | 0.747 | 0.866 | 0.755 | 0.528 | 0.738 | 0.799 | 0.794 |
| 8 | 0.754 | 0.866 | 0.764 | 0.542 | 0.749 | 0.809 | 0.796 |
| 16 | 0.762 | 0.879 | 0.771 | 0.556 | 0.756 | 0.814 | 0.796 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luna, M.; Chikontwe, P.; Park, S.H. Enhanced Nuclei Segmentation and Classification via Category Descriptors in the SAM Model. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030294
Luna M, Chikontwe P, Park SH. Enhanced Nuclei Segmentation and Classification via Category Descriptors in the SAM Model. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(3):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030294
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuna, Miguel, Philip Chikontwe, and Sang Hyun Park. 2024. "Enhanced Nuclei Segmentation and Classification via Category Descriptors in the SAM Model" Bioengineering 11, no. 3: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030294
APA StyleLuna, M., Chikontwe, P., & Park, S. H. (2024). Enhanced Nuclei Segmentation and Classification via Category Descriptors in the SAM Model. Bioengineering, 11(3), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030294







