Analysis of Umbilical Artery Hemodynamics in Development of Intrauterine Growth Restriction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics with Doppler Ultrasound
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
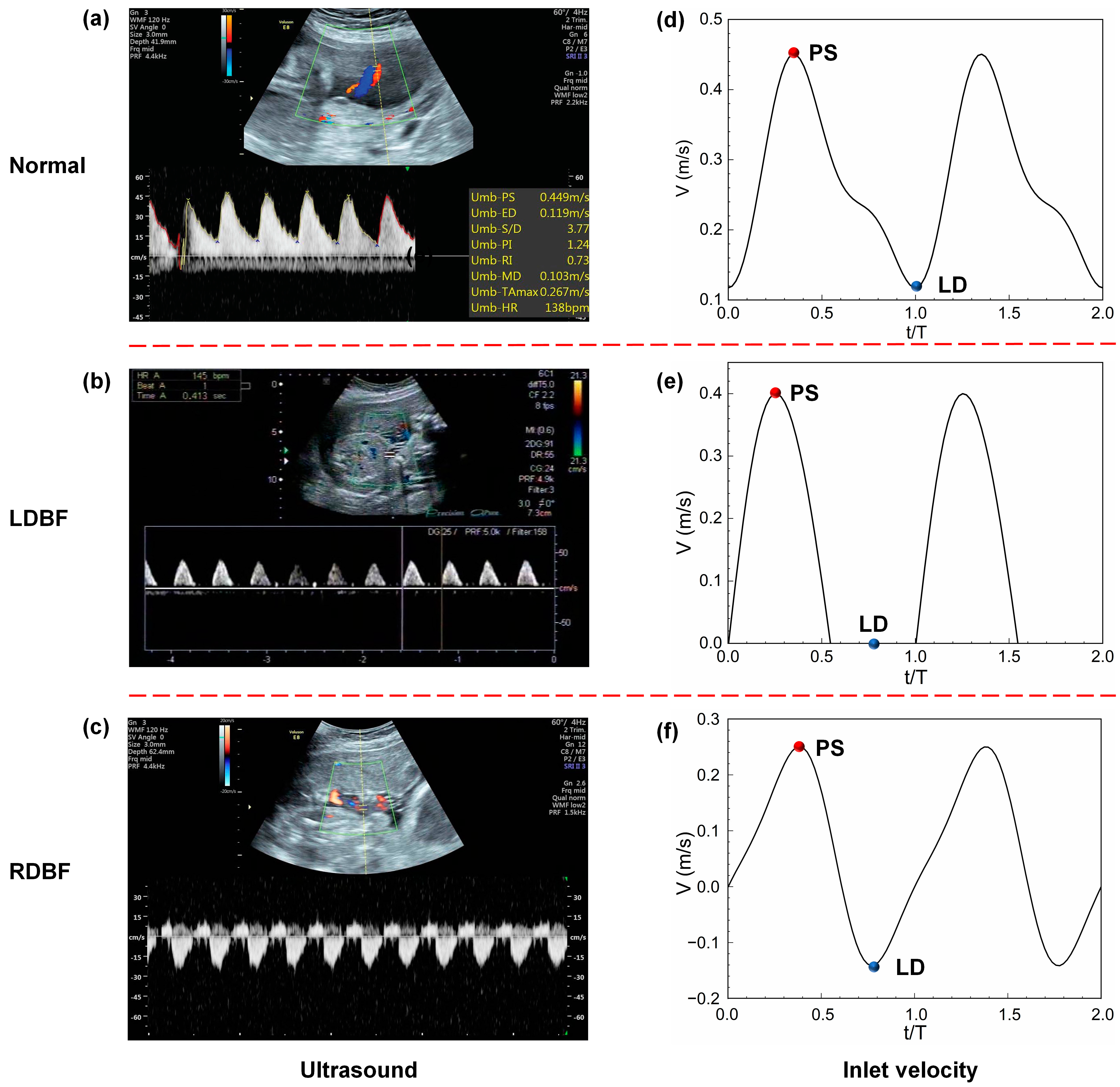
2.2. Ultrasound Image Acquisition
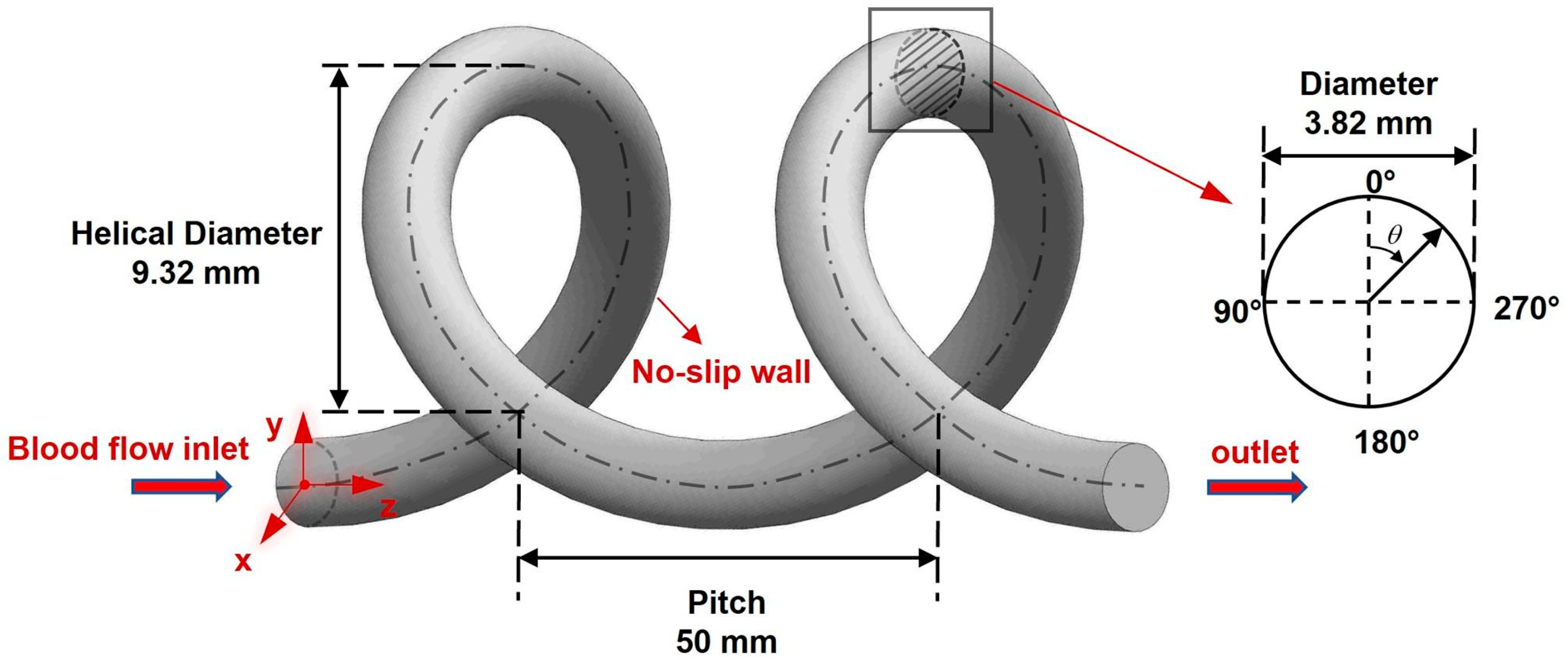
2.3. UA Model Reconstruction
2.4. CFD Methods
2.4.1. Governing Equations
2.4.2. Simulation Conditions and Solver
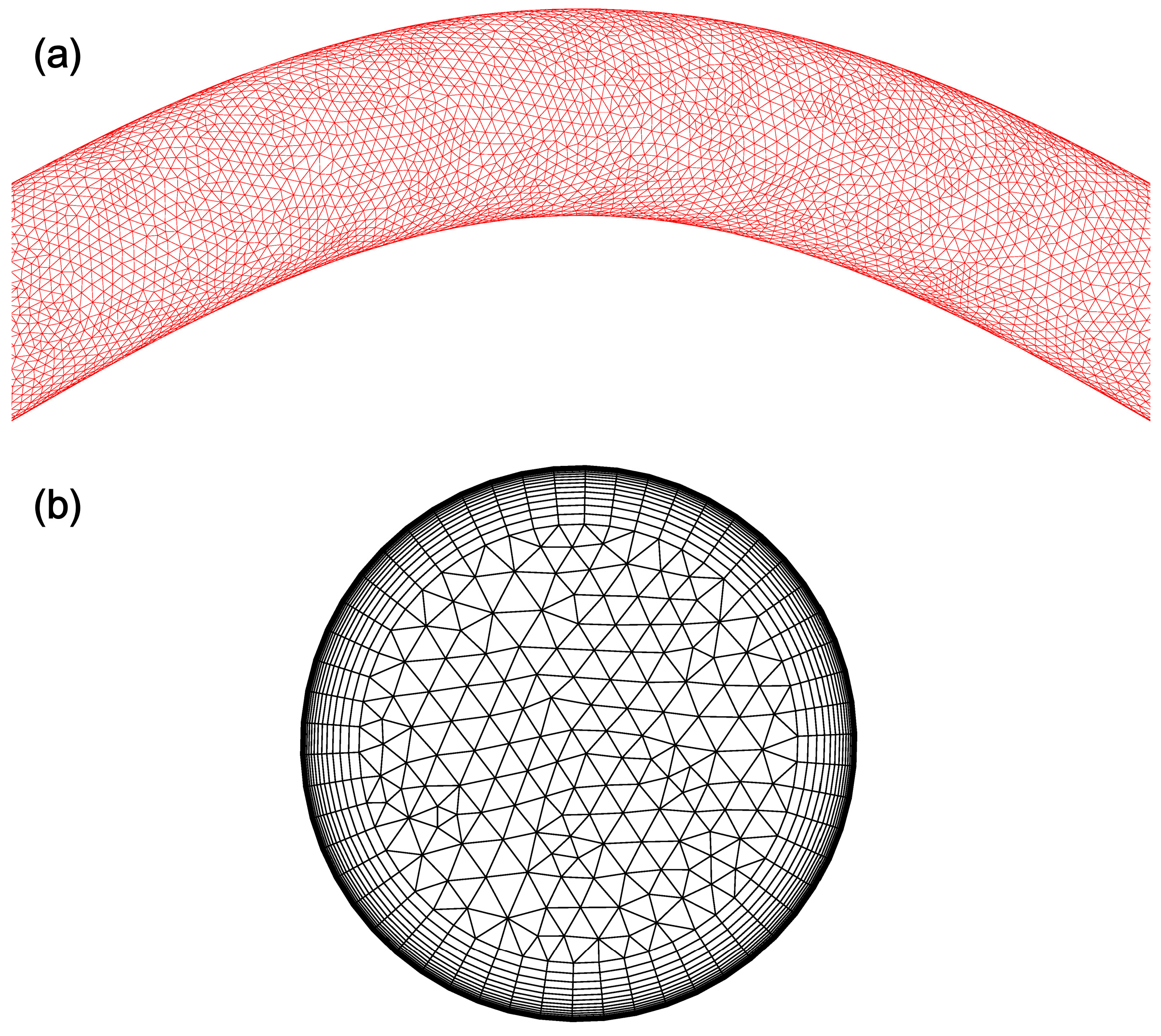
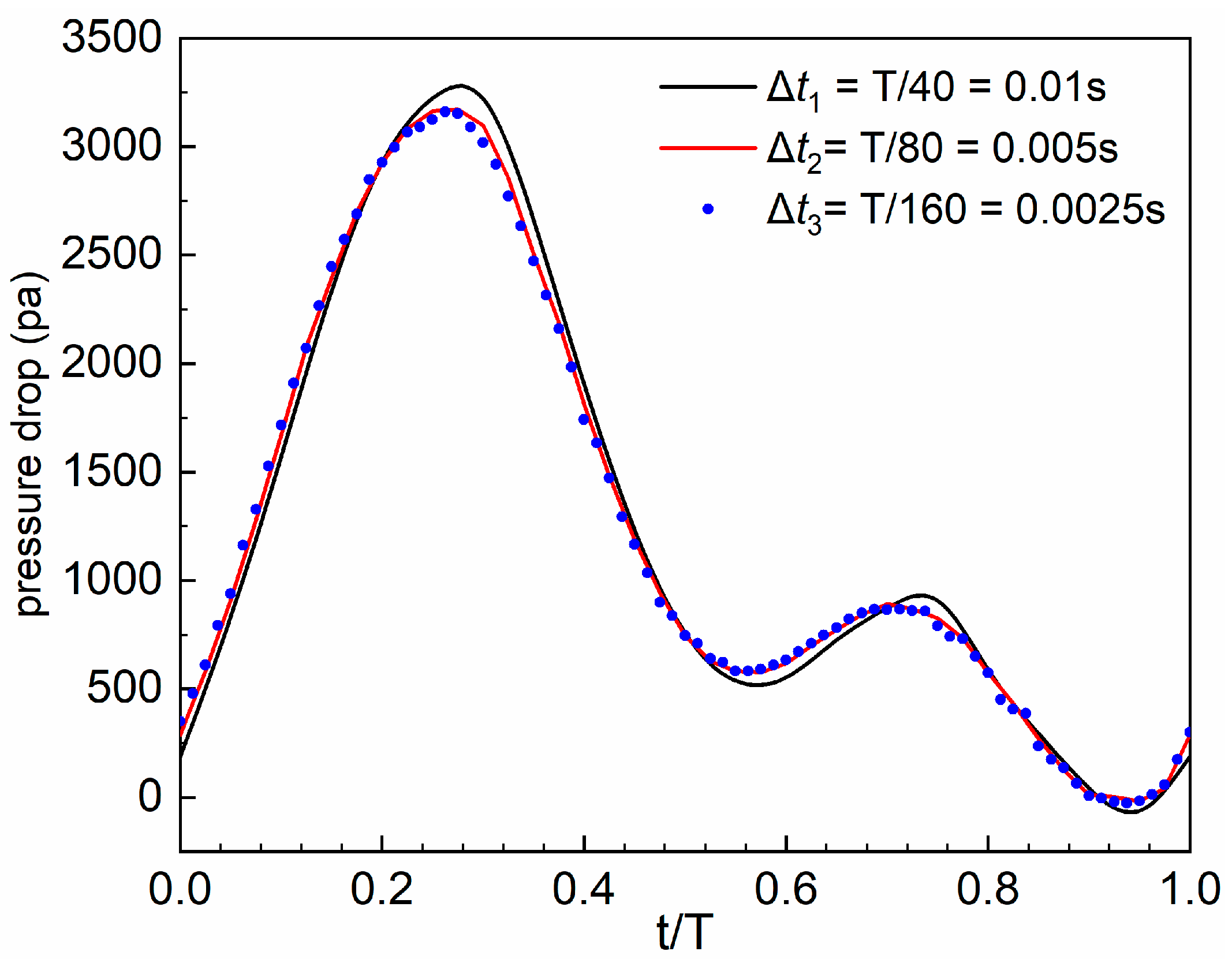
2.4.3. Grid and Time Marching Independence Analysis
2.4.4. CFD Validation
3. Results
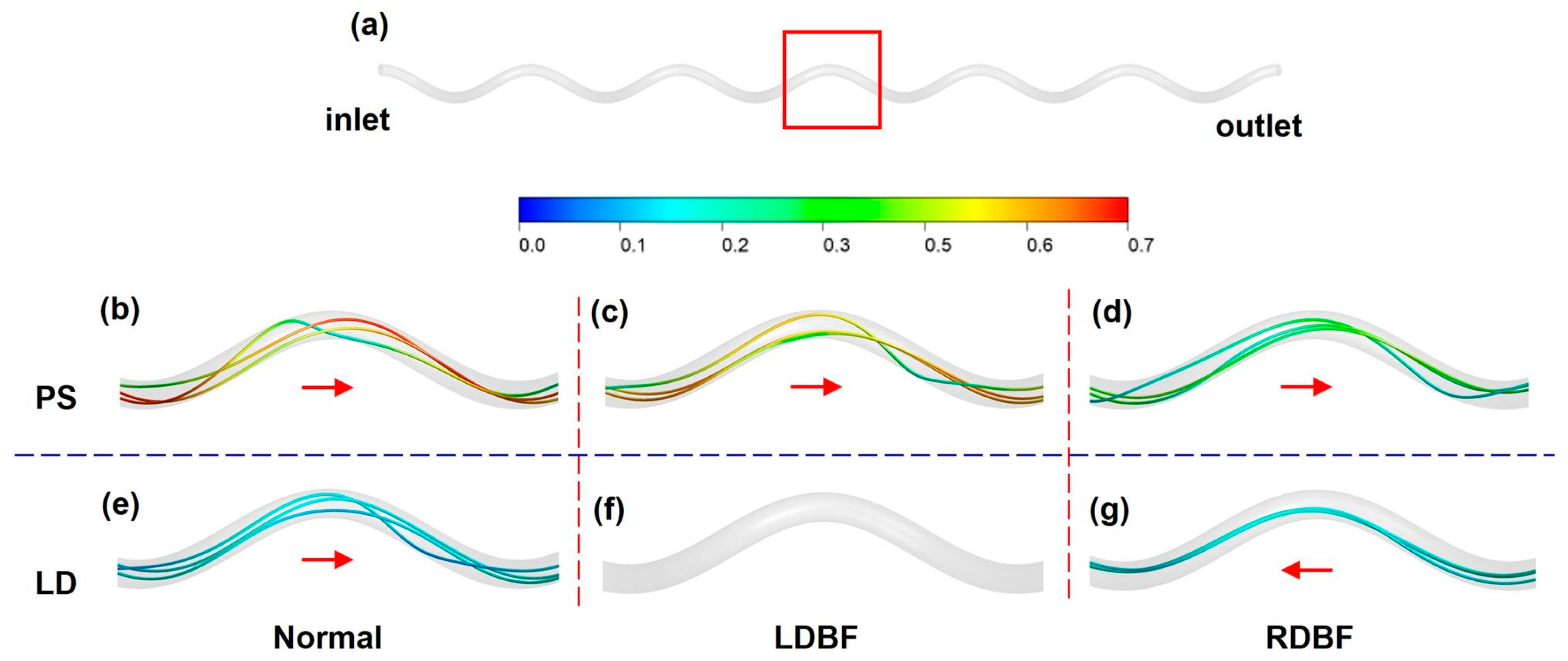
3.1. Blood Flow Velocity
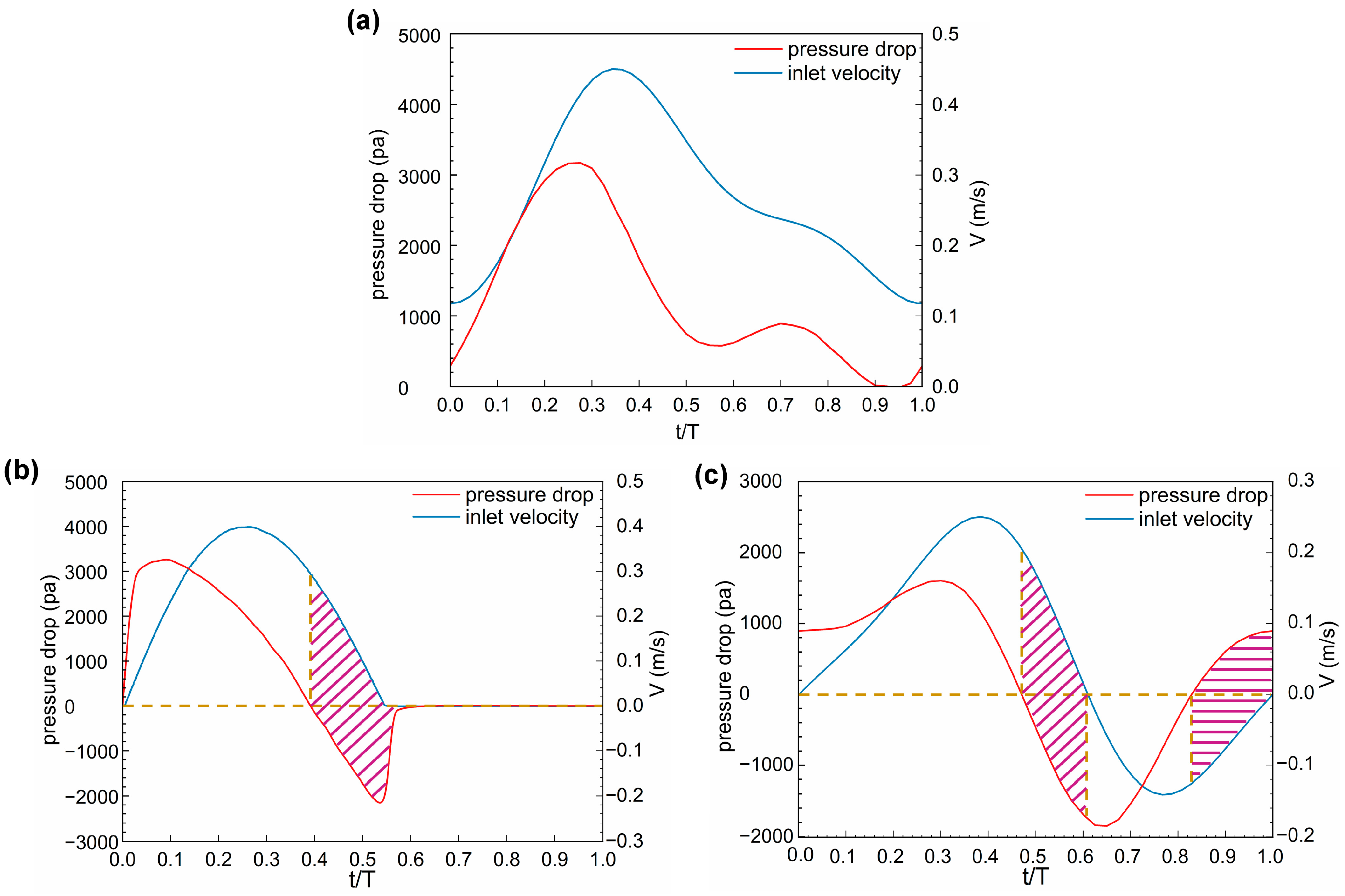
3.2. Pressure
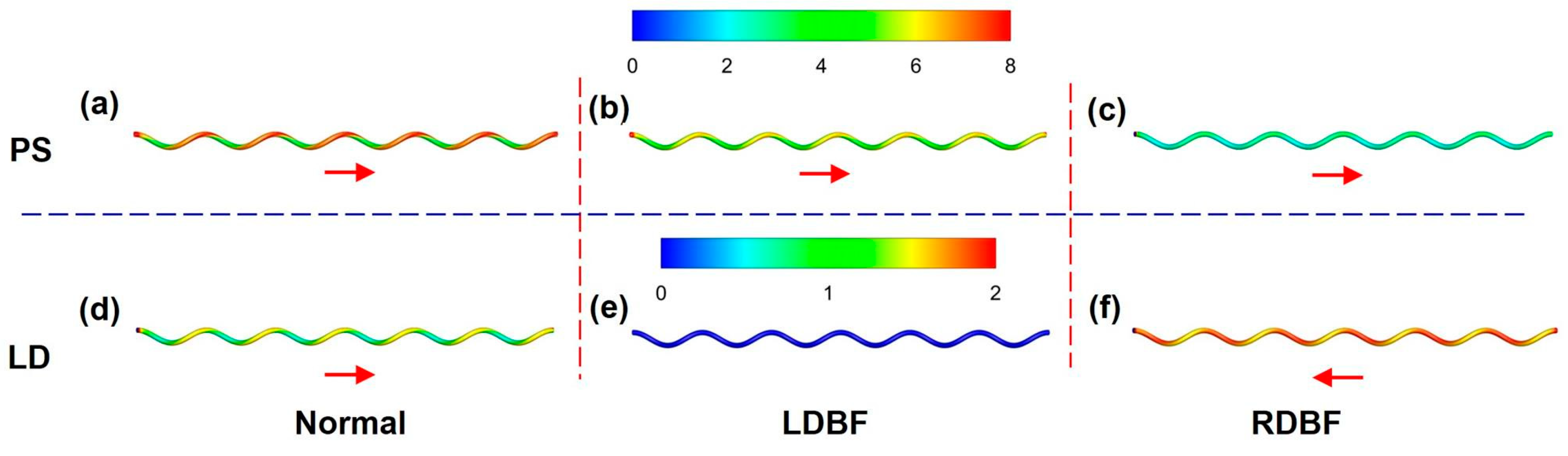
3.3. Wall Shear Stress
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| IUGR | intrauterine growth restriction |
| UA | umbilical artery |
| Normal | normal blood flow |
| LDBF | loss of end diastolic blood flow |
| RDBF | reversal of end diastolic blood flow |
| CFD | computational fluid dynamics |
| WSS | wall shear stress |
| PS | peak systolic |
| LD | least diastolic |
| UC | umbilical cord |
| UV | umbilical vein |
| UCI | umbilical cord index |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| Rr | spiral radius of the UA, m |
| RA | radius of the UA, m |
| RV | radius of the UV, m |
| U | number of UA spirals |
| L | length of the UC, cm |
| Ph | UA pitch, cm |
| x, y, z | Cartesian coordinate system coordinate variables |
| fluid velocity vector, m/s | |
| p | pressure, Pa |
| ρ | blood density, kg/m3 |
| viscous stress tensor, Pa | |
| μ | blood viscosity, pa·s |
| γ | local shear rate, s−1 |
| λ | time constant, s |
| n | power exponent |
| μ0 | zero shear viscosity, Pa·s |
| μ∞ | infinite shear viscosity, Pa·s |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| Rem | maximum of Reynolds number |
| R | tube radius, m |
| D | diameter of UA, m |
| Um | maximum average speed of blood flow, m/s |
| μa | average dynamic viscosity of blood, Pa·s |
| T | cardiac cycle, s |
| Δti | time marching step for simulation, s, i = 1, 2, 3 |
| Dn | Dean number |
| k | normalized curvature |
| b | parameter indicating pitch, cm |
| t | time, s |
References
- Mascherpa, M.; Pegoire, C.; Meroni, A.; Minopoli, M.; Thilaganathan, B.; Frick, A.; Bhide, A. Prenatal prediction of adverse outcome using different charts and definitions of fetal growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 63, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchi, C.; Marino, C.; Nosarti, C.; Vieno, A.; Visentin, S.; Simonelli, A. Association of Intrauterine Growth Restriction and Small for Gestational Age Status With Childhood Cognitive Outcomes. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeste, N.; Gómez, N.; Vázquez-Gómez, M.; García-Contreras, C.; Pumarola, M.; González-Bulnes, A.; Bassols, A. Polyphenols and IUGR pregnancies: Intrauterine growth restriction and hydroxytyrosol affect the development and neurotransmitter profile of the hippocampus in a pig model. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaie, R.S.; Dehghan, N.; Mojibian, M.; Lookzadeh, M.H.; Namiranian, N.; Javaheri, A.; Hajisafari, M. The relationship between postnatal hypoglycemia and umbilical artery Doppler ultrasonography in neonates with intrauterine growth restriction: A longitudinal follow-up study. Int. J. Reprod. BioMed. 2022, 20, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digal, K.C.; Singh, P.; Srivastava, Y.; Chaturvedi, J.; Tyagi, A.K.; Basu, S. Effects of delayed cord clamping in intrauterine growth-restricted neonates: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, C.; Singh, P.; Shrivastava, Y.; Priyadarshi, M.; Chaurasia, S.; Chaturvedi, J.; Basu, S. Effects of umbilical cord milking versus delayed cord clamping on systemic blood flow in intrauterine growth-restricted neonates: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoong, M.F.; Chao, A.-S.; Chang, S.-D.; Lien, R.; Chang, Y.-L. Association between respiratory distress syndrome of newborns and fetal growth restriction evaluated using a dichorionic twin pregnancy model. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 2022, 51, 102383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starodubtseva, N.L.; Tokareva, A.O.; Volochaeva, M.V.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Brzhozovskiy, A.G.; Bugrova, A.E.; Timofeeva, A.V.; Kukaev, E.N.; Tyutyunnik, V.L.; Kan, N.E. Quantitative Proteomics of Maternal Blood Plasma in Isolated Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan-Martinez, D.H.; Bosquez-Mendoza, V.M.; Ruiz-Noa, Y.; Ibarra-Reynoso, L.d.R.; Barbosa-Sabanero, G.; Lazo-de-la-Vega-Monroy, M.-L. Nutritional, pharmacological, and environmental programming of NAFLD in early life. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2023, 324, G99–G114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Singh-Gryzbon, S.; Frankini, E.; Wei, Z.; Yoganathan, A.P. Clinical impact of computational heart valve models. Materials 2022, 15, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; Paules, C.; Noell, G.; Youssef, L.; Paternina-Caicedo, A.; Crovetto, F.; Cañellas, N.; Garcia-Martín, M.L.; Amigó, N.; Eixarch, E. Similarity network fusion to identify phenotypes of small-for-gestational-age fetuses. Iscience 2023, 26, 107620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.-H.; Gerdroodbary, M.B.; Valipour, P.; Faraji, M.; Abu-Hamdeh, N.H. CFD investigations of the blood hemodynamic inside internal cerebral aneurysm (ICA) in the existence of coiling embolism. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 66, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Song, H.; Chen, L.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Evaluating Short-Term and Long-Term Risks Associated with Renal Artery Stenosis Position and Severity: A Hemodynamic Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, D.; Jiang, J.; Xia, L. Effect of microcirculatory dysfunction on coronary hemodynamics: A pilot study based on computational fluid dynamics simulation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, A.; Pakravan, H.A.; Bazrafshan Drissi, H. Competitive flow of bilateral internal thoracic artery Y-graft: Insights from hemodynamics and transit time flow measurement parameters. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 091910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.A.U.; Ekici, Ö. Comparative analysis of mechanical wall shear stress and hemodynamics to study the influence of asymmetry in abdominal aortic aneurysm and descending thoracic aortic aneurysm. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 071904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlin-Premrl, D.; Boopathy, S.R.; Nemes, A.; Mohammadzadeh, M.; Monajemi, S.; Ko, B.S.; Campbell, B.C. Computational fluid dynamics in intracranial atherosclerosis-lessons from cardiology: A review of cfd in intracranial atherosclerosis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candreva, A.; De Nisco, G.; Rizzini, M.L.; D’Ascenzo, F.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Gallo, D.; Morbiducci, U.; Chiastra, C. Current and future applications of computational fluid dynamics in coronary artery disease. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramigna, V.; Palumbo, A.; Rossi, M.; Fragomeni, G. A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study to Compare Two Types of Arterial Cannulae for Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Fluids 2023, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Hussain, Z.; Khan, Z.A.; Nadeem, S.; Alzabut, J. Endoscopic balloon dilation of a stenosed artery stenting via CFD tool open-foam: Physiology of angioplasty and stent placement. Chin. J. Phys. 2023, 85, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Han, F.; Ke, D.; Lee, C. Hemodynamic analysis of VenaTech convertible vena cava filter using computational fluid dynamics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 556110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Song, X. Evaluation of hemodynamic effects of different inferior vena cava filter heads using computational fluid dynamics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1034120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, J.P.; Martínez-Castillo, J.; Cardenas, D.; Delgado-Alvarado, E.; Vigueras-Zuñiga, M.O.; Herrera-May, A.L. Simplified Models to Assess the Mechanical Performance Parameters of Stents. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, N.; Karmonik, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J. Wall enhancement, hemodynamics, and morphology in unruptured intracranial aneurysms with high rupture risk. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etli, M.; Canbolat, G.; Karahan, O.; Koru, M. Numerical investigation of patient-specific thoracic aortic aneurysms and comparison with normal subject via computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2021, 59, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, T.; Rasani, M.R. Pulsatile CFD Numerical Simulation to investigate the effect of various degree and position of stenosis on carotid artery hemodynamics. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 26, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, P.N.; Docherty, P.D.; Yazdi, S.G.; Khanafer, A.; Kabaliuk, N.; Jermy, M.; Geoghegan, P.H. Review of the development of hemodynamic modeling techniques to capture flow behavior in arteries affected by aneurysm, atherosclerosis, and stenting. J. Biomech. Eng. 2022, 144, 040802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Wu, W.; Fang, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Ji, L.; Yang, M.; Lei, Z.; Gao, F.; Wang, J. Patient-specific computational fluid dynamics for hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 389, 131263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albadawi, M.; Abuouf, Y.; Elsagheer, S.; Sekiguchi, H.; Ookawara, S.; Ahmed, M. Influence of Rigid–Elastic Artery Wall of Carotid and Coronary Stenosis on Hemodynamics. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Azriff Basri, A.; Ismail, N.B.; Arifin Ahmad, K. Hemodynamic Effects of Subaortic Stenosis on Blood Flow Characteristics of a Mechanical Heart Valve Based on OpenFOAM Simulation. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzini, M.L.; Candreva, A.; Chiastra, C.; Gallinoro, E.; Calò, K.; D’Ascenzo, F.; De Bruyne, B.; Mizukami, T.; Collet, C.; Gallo, D. Modelling coronary flows: Impact of differently measured inflow boundary conditions on vessel-specific computational hemodynamic profiles. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 221, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Ghista, D.; Zhang, D.; Shi, C.; Huang, W. Assessment of boundary conditions for CFD simulation in human carotid artery. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2018, 17, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.G.; Girardi, T.; Merz, G.; Necaise, P.; Salafia, C.M. Hemodynamic analysis of blood flow in umbilical artery using computational modeling. Placenta 2017, 57, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, D.J.; Denier, J.P.; Khong, T.Y.; Mattner, T.W. Pressure and flow in the umbilical cord. J. Biomech. 2018, 79, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.D.; Jaffa, A.J.; Timor, I.E.; Elad, D. Hemodynamic analysis of arterial blood flow in the coiled umbilical cord. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 17, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Tang, J.; Ran, S.; Ho, H. Computational modelling for the spiral flow in umbilical arteries with different systole/diastole flow velocity ratios. Med. Eng. Phys. 2020, 84, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, S.N.; Poh, Y.W.; Chia, D.; Biswas, A.; Mattar, C.N.Z.; Yap, C.H. Characterization of the hemodynamic wall shear stresses in human umbilical vessels from normal and intrauterine growth restricted pregnancies. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2018, 17, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlock, F.P.; Harrist, R.; Sharman, R.S.; Deter, R.L.; Park, S.K. Estimation of fetal weight with the use of head, body, and femur measurements—A prospective study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1985, 151, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, T.H., Jr.; Jarles, D.L.; Vega, J.S.; Feldman, D.B. The umbilical coiling index. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1994, 170, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiteropoulou, D.; Topalidou, A.; Downe, S. A computational fluid dynamics modelling of maternal-fetal heat exchange and blood flow in the umbilical cord. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Issakhov, A.; Khan, S.U.-D.; Assad, M.E.H.; Hani, E.H.B.; Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, S.U.-D. The effects of zero and high shear rates viscosities on the transportation of heat and mass in boundary layer regions: A non-Newtonian fluid with Carreau model. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 317, 113991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, G.; Sonesson, S.E.; Flo, K.; Räsänen, J.; Odibo, A. Hemodynamic aspects of normal human feto-placental (umbilical) circulation. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2016, 95, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisk, N.; Ronderos-Dumit, D.; Tannirandorn, Y.; Nicolini, U.; Talbert, D.; Rodeck, C. Normal amniotic pressure throughout gestation. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1992, 99, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lee, C. Simulation study of hemodynamic commonality of umbrella-shaped inferior vena cava filter using computational fluid dynamics. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 081913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, G.; Bonfanti, M.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Diaz-Zuccarini, V.; Balabani, S. Experimental evaluation of the patient-specific haemodynamics of an aortic dissection model using particle image velocimetry. J. Biomech. 2022, 134, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabakova, S.; Nikolova, E.; Radev, S. Carreau model for oscillatory blood flow in a tube. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1629, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Valizadeh, K.; Farahbakhsh, S.; Bateni, A.; Zargarian, A.; Davarpanah, A.; Alizadeh, A.; Zarei, M. A parametric study to simulate the non-Newtonian turbulent flow in spiral tubes. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangam, S.; Hur, N. Laminar secondary flows in curved rectangular ducts. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 217, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, L.; Debant, M.; Walker, J.; Beech, D.; Simpson, N. Placental blood flow sensing and regulation in fetal growth restriction. Placenta 2021, 113, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, J.; Suzuki, N. SMI for imaging of placental infarction. Placenta 2016, 47, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.S.; Andrade, A.R.A.; Moleiro, M.L.; Guedes-Martins, L. Doppler ultrasound of the umbilical artery: Clinical application. Rev. Bras. De Ginecol. E Obs. 2022, 44, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-K. Computational fluid dynamics in cardiovascular disease. Korean Circ. J. 2011, 41, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Total Number of Grids | Pressure Drop (Pa) | Difference (%) | WSSavg (Pa) | Difference (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh 1 | 440,000 | 3403.38 | 1.29 | 9.35 | 1.28 |
| Mesh 2 | 790,000 | 3359.35 | 0.05 | 9.23 | 0.11 |
| Mesh 3 | 1,420,000 | 3357.62 | - | 9.22 | - |
| Normal | LDBF | RDBF | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Large | Ratio | Small | Large | Ratio | Small | Large | Ratio | |
| PS | 0.2D | 0.6D | 0.3 | 0.2D | 0.6D | 0.3 | 0.4D | 0.5D | 0.8 |
| LD | 0.3D | 0.6D | 0.5 | - | - | - | 0.2D | 0.6D | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Lee, C. Analysis of Umbilical Artery Hemodynamics in Development of Intrauterine Growth Restriction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics with Doppler Ultrasound. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111169
Song X, Wang J, Sun K, Lee C. Analysis of Umbilical Artery Hemodynamics in Development of Intrauterine Growth Restriction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics with Doppler Ultrasound. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(11):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111169
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xue, Jingying Wang, Ke Sun, and Chunhian Lee. 2024. "Analysis of Umbilical Artery Hemodynamics in Development of Intrauterine Growth Restriction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics with Doppler Ultrasound" Bioengineering 11, no. 11: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111169
APA StyleSong, X., Wang, J., Sun, K., & Lee, C. (2024). Analysis of Umbilical Artery Hemodynamics in Development of Intrauterine Growth Restriction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics with Doppler Ultrasound. Bioengineering, 11(11), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111169









