RMCNet: A Liver Cancer Segmentation Network Based on 3D Multi-Scale Convolution, Attention, and Residual Path
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We integrated multi-scale convolutions with different receptive fields into the encoding part of the model to enable the extraction of fine-grained features, allowing the model to capture tumor characteristics of various sizes and improve segmentation efficiency.
- (2)
- By utilizing 3D CBAM for spatial feature encoding and channel importance evaluation, the model is guided to focus on the location and shape information of liver cancer during the learning process, thereby improving the overall segmentation performance of the model.
- (3)
- We designed residual paths for each encoder in the network to capture more high-resolution advanced features, guiding the segmentation model to accurately locate the boundaries of liver cancer.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Structure
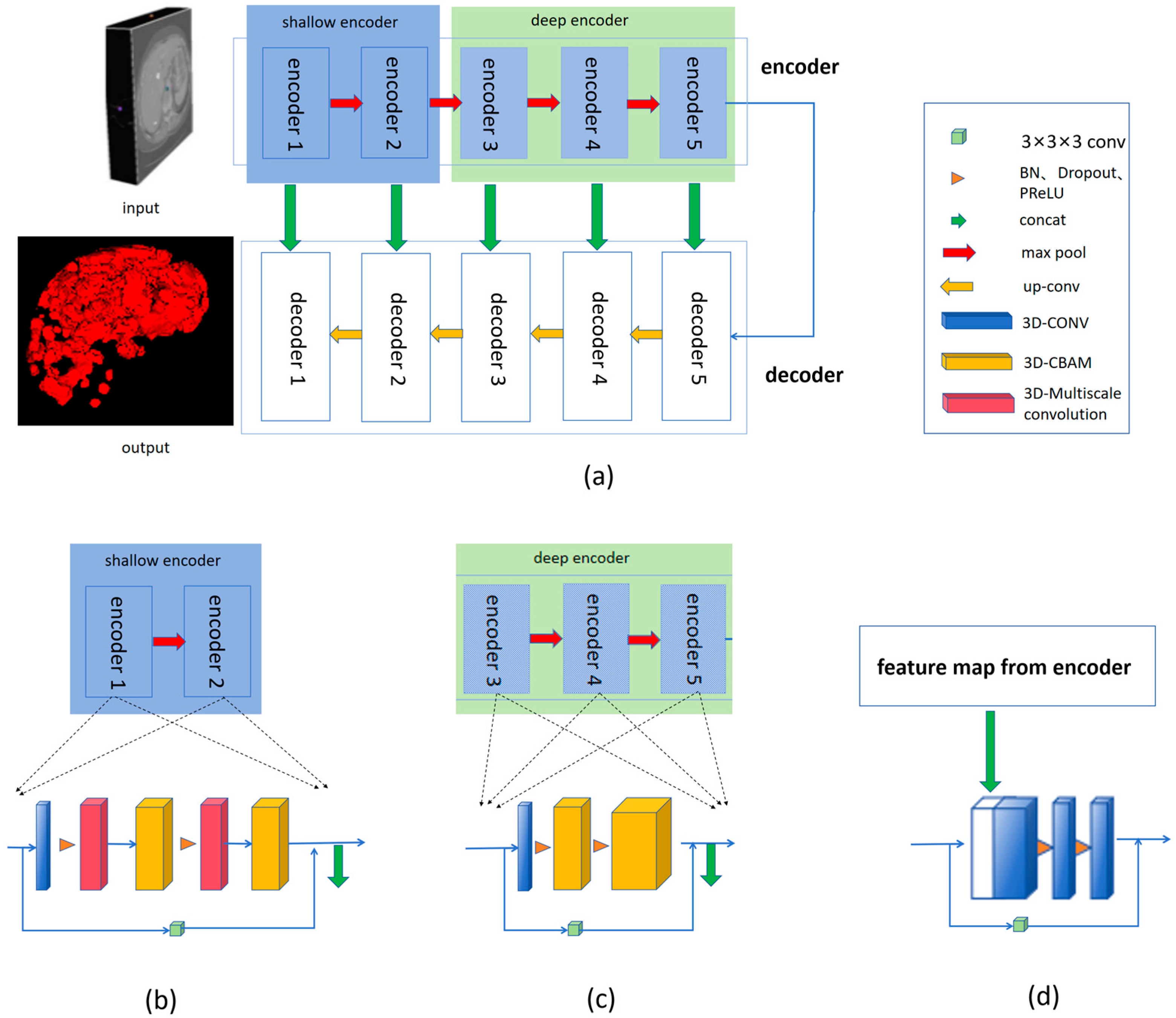
2.1.1. Overview of the Model Structure
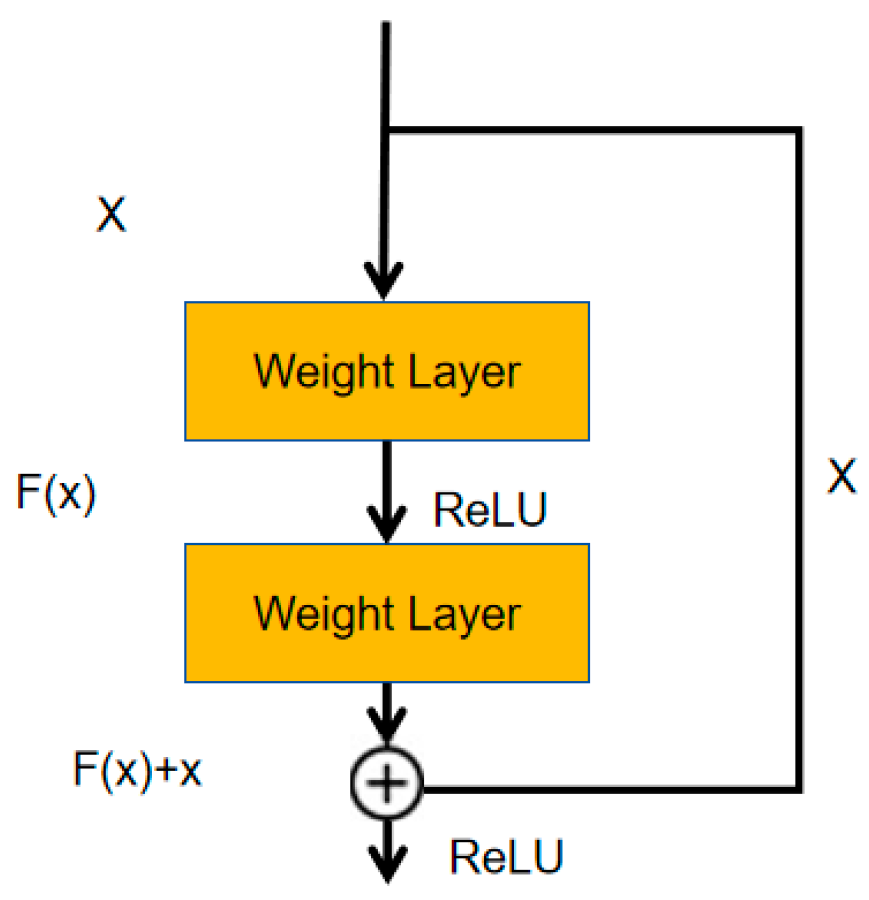
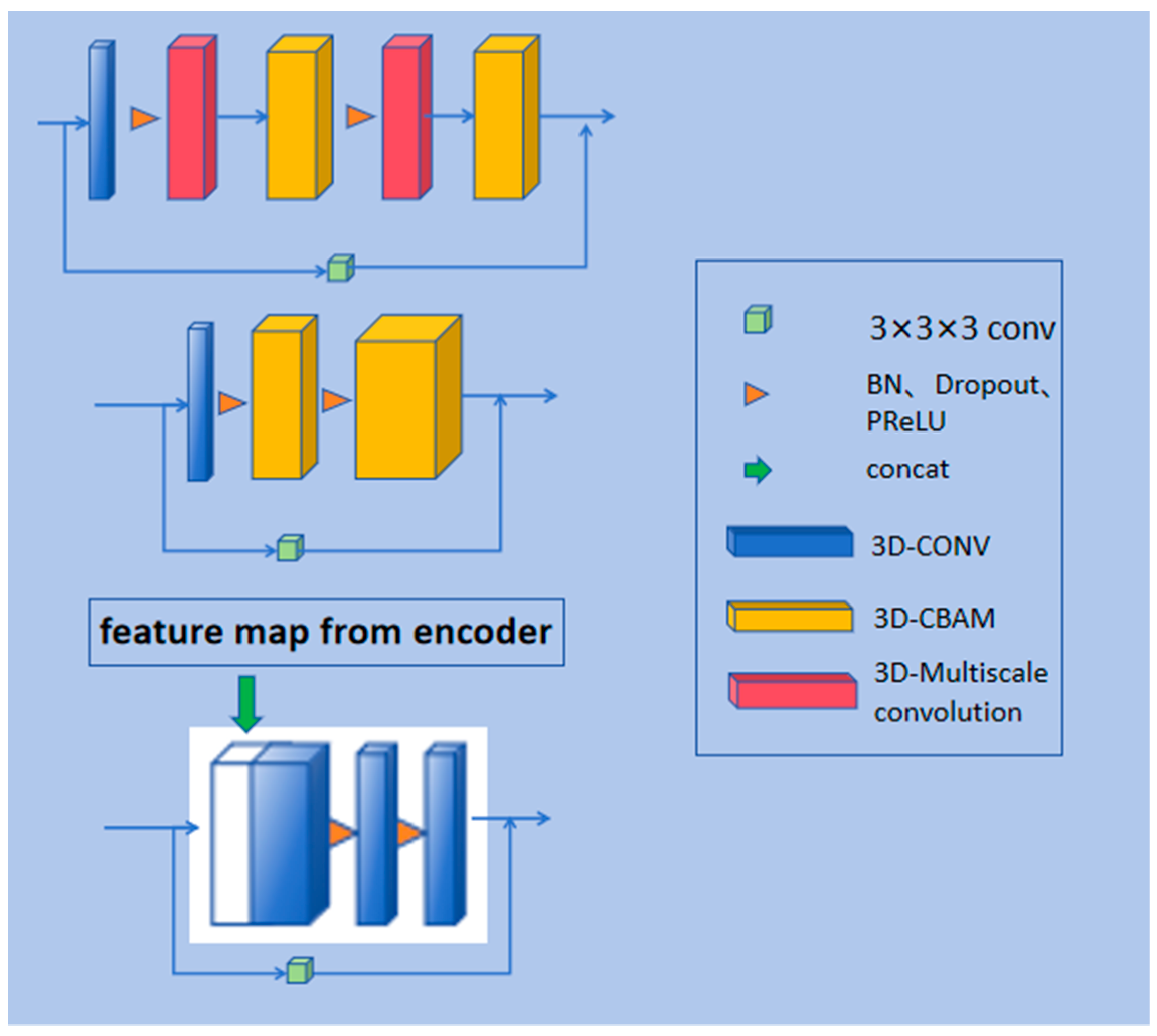
2.1.2. Residual Path
2.1.3. Multi-Scale 3D Convolution
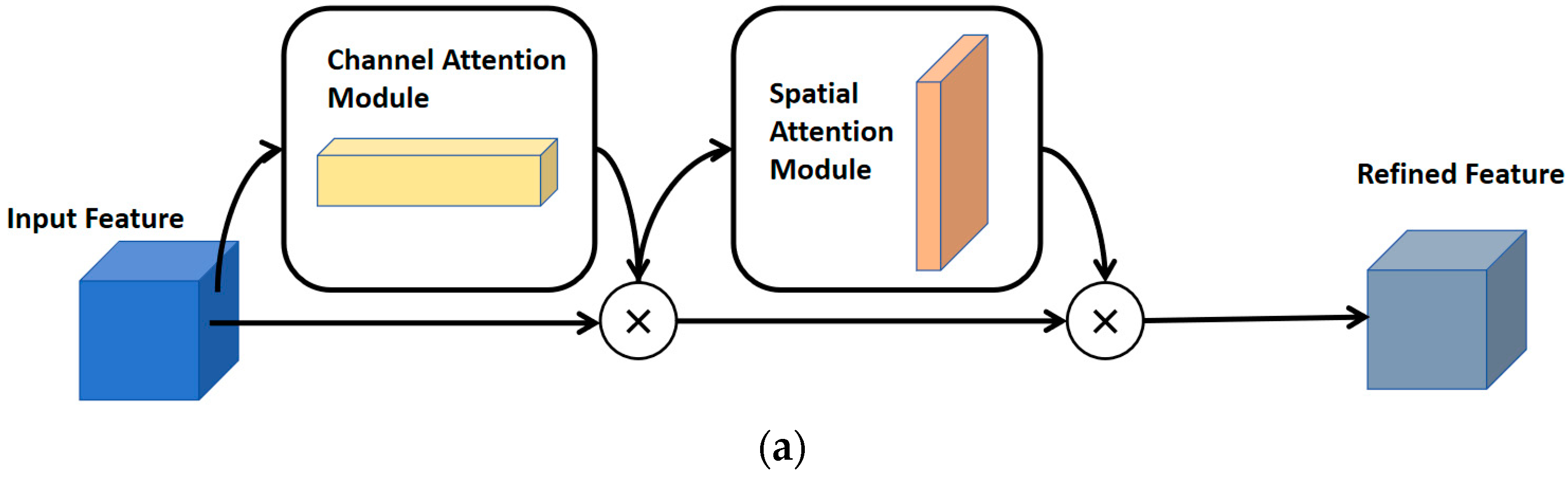
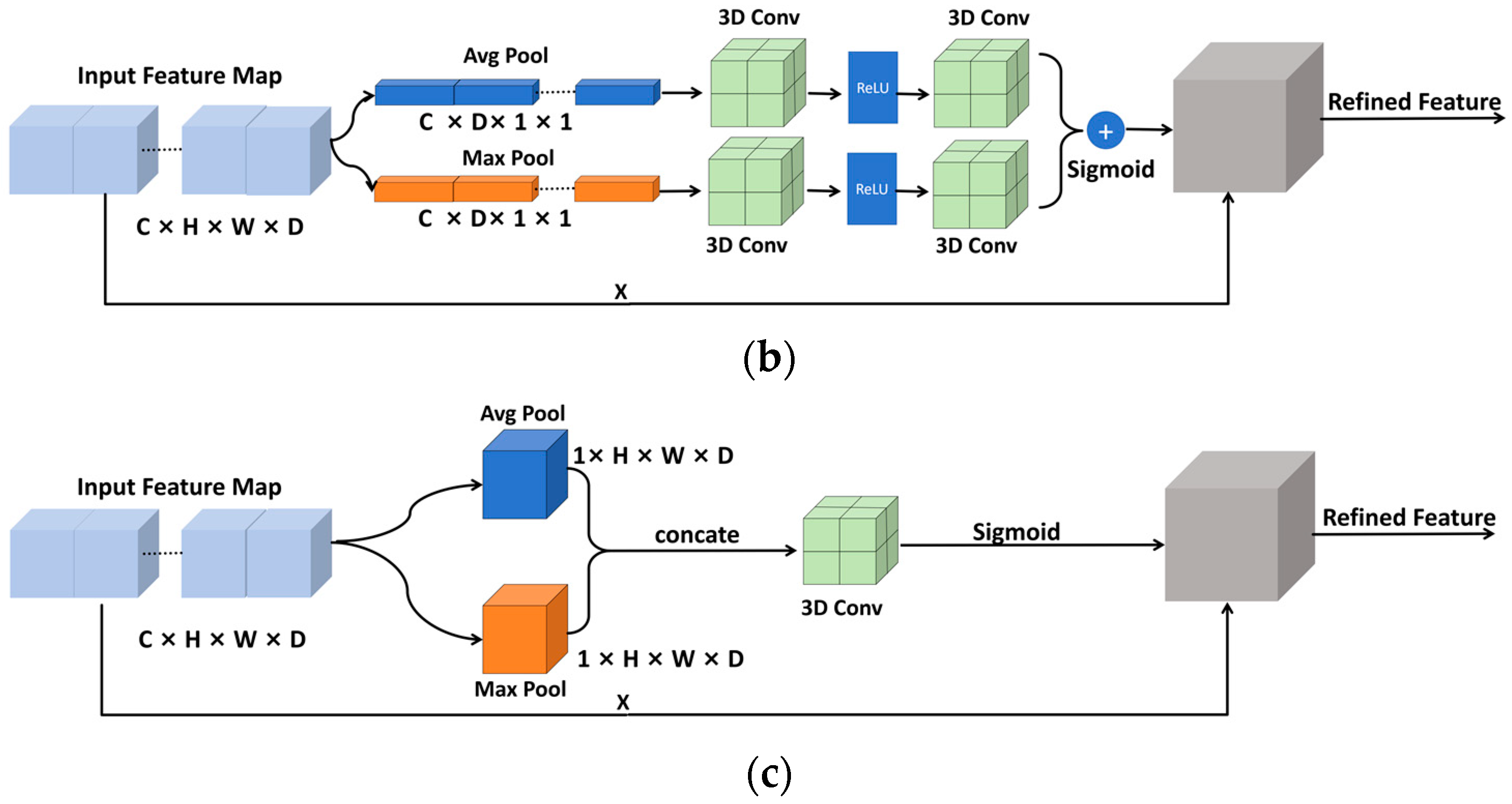
2.1.4. Convolutional Block Attention Module
2.1.5. Loss Function
2.2. Dataset and Data Preparation
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
2.4. Experimental Details
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Parameters and FLOPs
3.2. Results
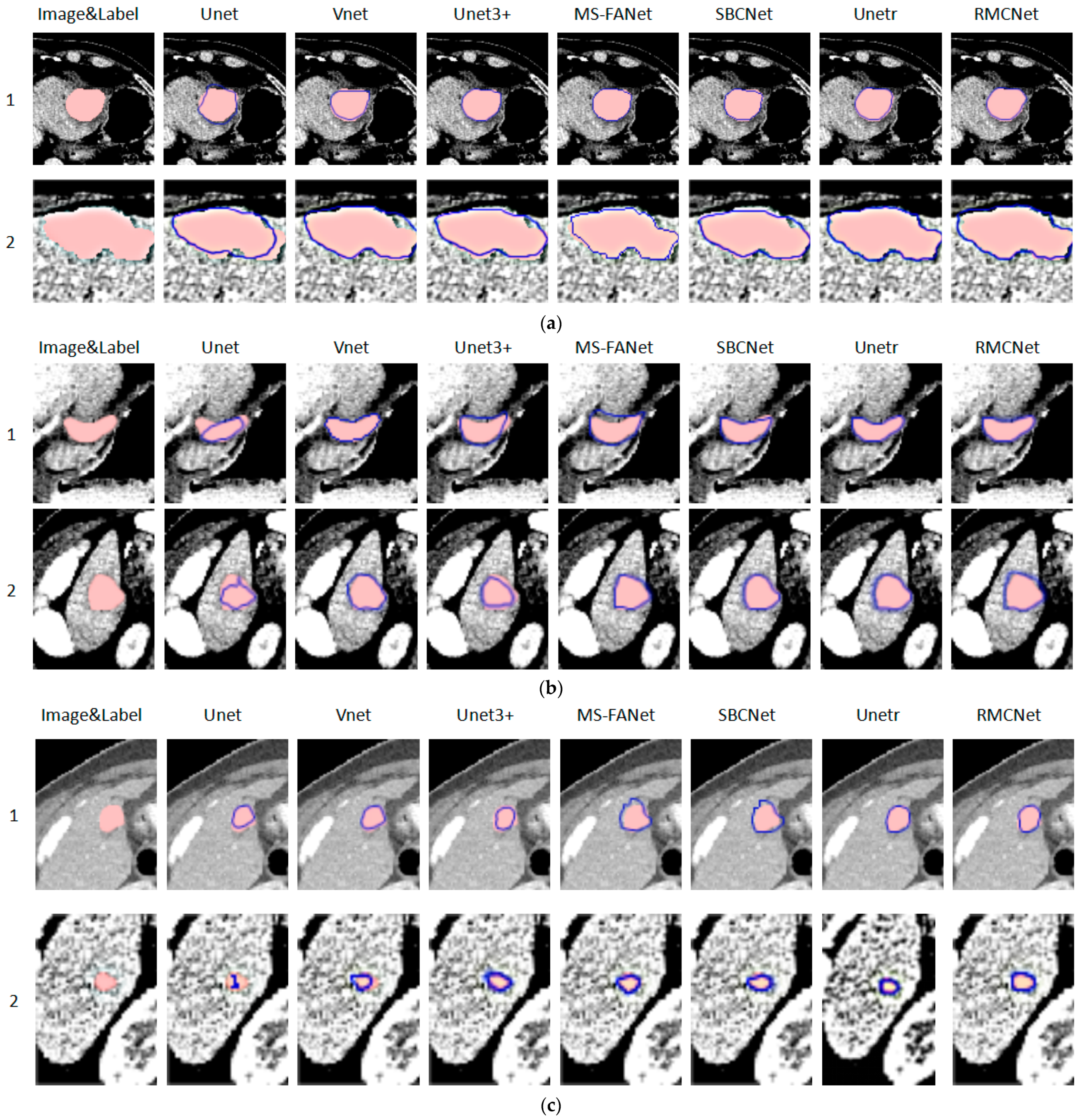
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Sirlin, C.B. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: Part I. Development, growth, and spread: Key pathologic and imaging aspects. Radiology 2014, 272, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, D.; Alksas, A.; Elnakib, A.; Mahmoud, A.; Kandil, H.; Khalil, A.; Ghazal, M.; van Bogaert, E.; Contractor, S.; El-Baz, A. The Role of Radiomics and AI Technologies in the Segmentation, Detection, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Ma, X.-H.; Wang, S.; Cai, W.; Liu, X.-B.; Zhao, X.-M. Application of artificial intelligence in preoperative imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: Current status and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5341–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häme, Y. Liver tumor segmentation using implicit surface evolution. Midas J. 2008, 1–10. Available online: https://www.columbia.edu/~yh2475/publ/ltsTKKBecs20080811.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Moltz, J.H.; Bornemann, L.; Dicken, V.; Peitgen, H. Segmentation of liver metastases in CT scans by adaptive thresholding and morphological processing. In Proceedings of the MICCAI Workshop, New York, NY, USA, 6–10 September 2008; Volume 41, p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Li, N.; Lin, Z.; Huang, G.B.; Zong, W.; Zhou, J.; Duan, Y. Liver tumor detection and segmentation using kernel-based extreme learning machine. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 3662–3665. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Huang, G.B.; Zhou, J.; Duan, Y.; Xiong, W. Random feature subspace ensemble based Extreme Learning Machine for liver tumor detection and segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 4675–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jia, F.; Hu, Q. Automatic segmentation of liver tumor in CT images with deep convolutional neural networks. J. Comput. Commun. 2015, 3, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Dou, Q.; Fu, C.; Heng, P. H-DenseUNet: Hybrid Densely Connected UNet for Liver and Tumor Segmentation From CT Volumes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2663–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeshwaran, M.; Ahila, A. Segmentation of Liver Cancer Using SVM Techniques. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Inf. Syst. (IJCCIS) 2014, 6, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- El-Regaily, S.A.; Salem, M.A.M.; Aziz, M.H.A.; Roushdy, M.I. Lung nodule segmentation and detection in computed tomography. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Information Systems (ICICIS), Cairo, Egypt, 5–7 December 2017; pp. 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Vorontsov, E.; Abi-Jaoudeh, N.; Kadoury, S. Metastatic Liver Tumor Segmentation Using Texture-Based Omni-Directional Deformable Surface Models. In Abdominal Imaging. Computational and Clinical Applications, Proceedings of the ABD-MICCAI 2014, Cambridge, MA, USA, 14 September 2014; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Yoshida, H., Näppi, J., Saini, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8676. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, S.M.; Sruthi, A.N.; Jothi, S.C. MRI Liver Tumor Classification Using Machine Learning Approach and Structure Analysis. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2018, 11, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the NIPS, Harrahs and Harveys, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–8 December 2012; pp. 1106–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net (r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06955. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Proceedings 4; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Le Folgoc, L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Petersen, J.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Jäger, P.F.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnu-net: Breaking the spell on successful medical image segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08128. [Google Scholar]
- Chlebus, G.; Meine, H.; Moltz, J.H.; Schenk, A. Neural network-based automatic liver tumor segmentation with random forest-based candidate filtering. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.00842. [Google Scholar]
- Christ, P.F.; Ettlinger, F.; Grün, F.; Elshaera, M.E.A.; Lipkova, J.; Schlecht, S.; Ahmaddy, F.; Tatavarty, S.; Bickel, M.; Bilic, P.; et al. Automatic liver and tumor segmentation of CT and MRI volumes using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.05970. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y. Hierarchical convolutional-deconvolutional neural networks for automatic liver and tumor segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.04540. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Han, S.; Chen, Y.; Vasconcelos, N. Volumetric attention for 3D medical image segmentation and detection. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Proceedings, Part VI 22. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, C.; Xia, Y. Cotr: Efficiently bridging cnn and transformer for 3d medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2021: 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Proceedings, Part III 24. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Tang, Y.; Nath, V.; Yang, D.; Myronenko, A.; Landman, B.; Roth, H.R.; Xu, D. Unetr: Transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 574–584. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Nath, V.; Tang, Y.; Yang, D.; Roth, H.; Xu, D. Swin unetr: Swin transformers for semantic segmentation of brain tumors in mri images. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Strasbourg, France, 27 September– 1 October 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 272–284. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, A.M.; Maaz, M.; Rasheed, H.; Khan, S.; Yang, M.-H.; Khan, F.S. UNETR++: Delving into efficient and accurate 3D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024, 43, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Huang, C.; Bassenne, M.; Xiao, R.; Xing, L. Modified U-Net (mU-Net) with incorporation of object-dependent high level features for improved liver and liver-tumor segmentation in CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, X.; Wang, T.; Li, N. CPAD-Net: Contextual parallel attention and dilated network for liver tumor segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, F.; Mei, K.; Zhang, G. Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 517–532. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Targ, S.; Almeida, D.; Lyman, K. Resnet in resnet: Generalizing residual architectures. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08029. [Google Scholar]
- LiTS-Liver Tumor Segmentation Challenge. Available online: https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/17094 (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Liver Segmentation 3D-IRCADb-01. Available online: https://www.ircad.fr/research/data-sets/liver-segmentation-3d-ircadb-01 (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Varma, R.; Salpekar, O.; Noordhuis, P.; Li, T.; Paszke, A.; Smith, J.; Vaughan, B.; Damania, P.; et al. PyTorch distributed: Experiences on accelerating data parallel training. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.15704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Lin, L.; Tong, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.-W.; Wu, J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, G.; Xu, G.; Wu, F. MS-FANet: Multi-scale feature attention network for liver tumor segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 163, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.-N.; Li, S.-X.; Bu, Z.; Zhao, F.-X.; Zhou, G.-Q.; Zhou, S.-J.; Chen, Y. SBCNet: Scale and boundary context attention dual-branch network for liver tumor segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 28, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Model | Params (M) | Training Time (s) | FLOPs (G) | Inference Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unet | 1.981 | 18.10 | 5.239 | 0.542 |
| Vnet | 45.598 | 79.42 | 213.633 | 5.864 |
| Unet3+ | 22.403 | 90.82 | 251.056 | 7.067 |
| MS-FANet | 10.330 | 30.11 | 43.198 | 4.873 |
| Unetr | 92.618 | 60.25 | 55.024 | 1.412 |
| SBCNet | 9.140 | 41.77 | 39.716 | 4.460 |
| RMCNet | 5.192 | 21.45 | 20.397 | 0.728 |
| Model | DSC (%) | JCC (%) | HD (mm) | ASD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unet | 60.113 ± 1.08 | 63.780 ± 1.29 | 28.56 ± 14.58 | 8.16 ± 6.08 |
| Vnet | 66.563 ± 1.41 | 67.320 ± 1.45 | 47.48 ± 18.91 | 11.69 ± 11.85 |
| Unet3+ | 65.014 ± 1.15 | 69.890 ± 1.32 | 40.79 ± 14.88 | 9.34 ± 6.10 |
| MS-FANet | 71.913 ± 0.61 | 72.184 ± 1.42 | 15.38 ± 6.47 | 5.27 ± 1.95 |
| Unetr | 74.151 ± 0.68 | 73.274 ± 0.54 | 11.03 ± 5.26 | 2.32 ± 1.02 |
| SBCNet | 73.225 ± 0.83 | 72.616 ± 0.53 | 13.75 ± 5.12 | 3.84 ± 1.55 |
| RMCNet | 76.566 ± 0.32 | 75.820 ± 0.4 | 11.07 ± 4.89 | 2.54 ± 1.78 |
| Metric | DSC (%) | JCC (%) | HD (mm) | ASD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMCNet and Unetr | 1.91 × 10−21 | 4.03 × 10−28 | 0.973 | 0.553 |
| RMCNet and Unet | 1.10 × 10−41 | 1.51 × 10−34 | 2.31 × 10−7 | 1.91 × 10−5 |
| RMCNet and Vnet | 4.60 × 10−29 | 5.15 × 10−27 | 4.47 × 10−12 | 0.0001 |
| RMCNet and Unet3+ | 5.56 × 10−35 | 1.77 × 10−23 | 1.22 × 10−12 | 8.70 × 10−7 |
| RMCNet and MS-FANet | 7.77 × 10−36 | 1.37 × 10−15 | 0.004 | 3.19 × 10−7 |
| RMCNet and SBCNet | 1.06 × 10−22 | 1.31 × 10−33 | 0.039 | 0.004 |
| Model | DSC (%) | JCC (%) | HD (mm) | ASD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMCNet | 72.961 ± 0.47 | 71.246 ± 0.57 | 15.03 ± 4.47 | 10.21 ± 1.53 |
| Model | Small-Scale Tumors | Medium-Scale Tumors | Large-Scale Tumors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC (%) | JCC (%) | DSC (%) | JCC (%) | DSC (%) | JCC (%) | |
| Unet | 49.639 ± 0.33 | 50.65 ± 0.42 | 69.63 ± 0.32 | 73.83 ± 0.46 | 75.100 ± 0.34 | 77.86 ± 0.22 |
| Vnet | 51.870 ± 0.49 | 52.93 ± 0.37 | 73.151 ± 0.51 | 79.37 ± 0.45 | 86.617 ± 0.58 | 81,86 ± 0.47 |
| Unet3+ | 51.221 ± 0.29 | 55.81 ± 0.33 | 81.525 ± 0.36 | 80.59 ± 0.41 | 84.293 ± 0.47 | 85.67 ± 0.46 |
| MS-FANet | 53.500 ± 0.25 | 54.30 ± 0.22 | 83.111 ± 0.32 | 82.60 ± 0.28 | 91.623 ± 0.18 | 89.95 ± 0.16 |
| Unetr | 54.481 ± 0.19 | 54.02 ± 0.15 | 84.170 ± 0.26 | 83.95 ± 0.29 | 95.802 ± 0.10 | 94.65 ± 0.09 |
| SBCNet | 56.340 ± 0.21 | 57.01 ± 0.19 | 83.764 ± 0.27 | 83.17 ± 0.24 | 92.711 ± 0.12 | 91.23 ± 0.11 |
| RMCNet | 61.491 ± 0.11 | 62.21 ± 0.09 | 84.880 ± 0.15 | 84.34 ± 0.13 | 95.330 ± 0.07 | 92.91 ± 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H. RMCNet: A Liver Cancer Segmentation Network Based on 3D Multi-Scale Convolution, Attention, and Residual Path. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111073
Zhang Z, Gao J, Li S, Wang H. RMCNet: A Liver Cancer Segmentation Network Based on 3D Multi-Scale Convolution, Attention, and Residual Path. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(11):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111073
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zerui, Jianyun Gao, Shu Li, and Hao Wang. 2024. "RMCNet: A Liver Cancer Segmentation Network Based on 3D Multi-Scale Convolution, Attention, and Residual Path" Bioengineering 11, no. 11: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111073
APA StyleZhang, Z., Gao, J., Li, S., & Wang, H. (2024). RMCNet: A Liver Cancer Segmentation Network Based on 3D Multi-Scale Convolution, Attention, and Residual Path. Bioengineering, 11(11), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111073






