Tetracalcium Phosphate/Monetite/Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate Biocement for Alveolar Bone Augmentation After Tooth Extraction in Pig Mandible
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of TTCP/Monetite/Calcium Sulfhate Hemihydrate Cement
2.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing of CAS Cement Extracts
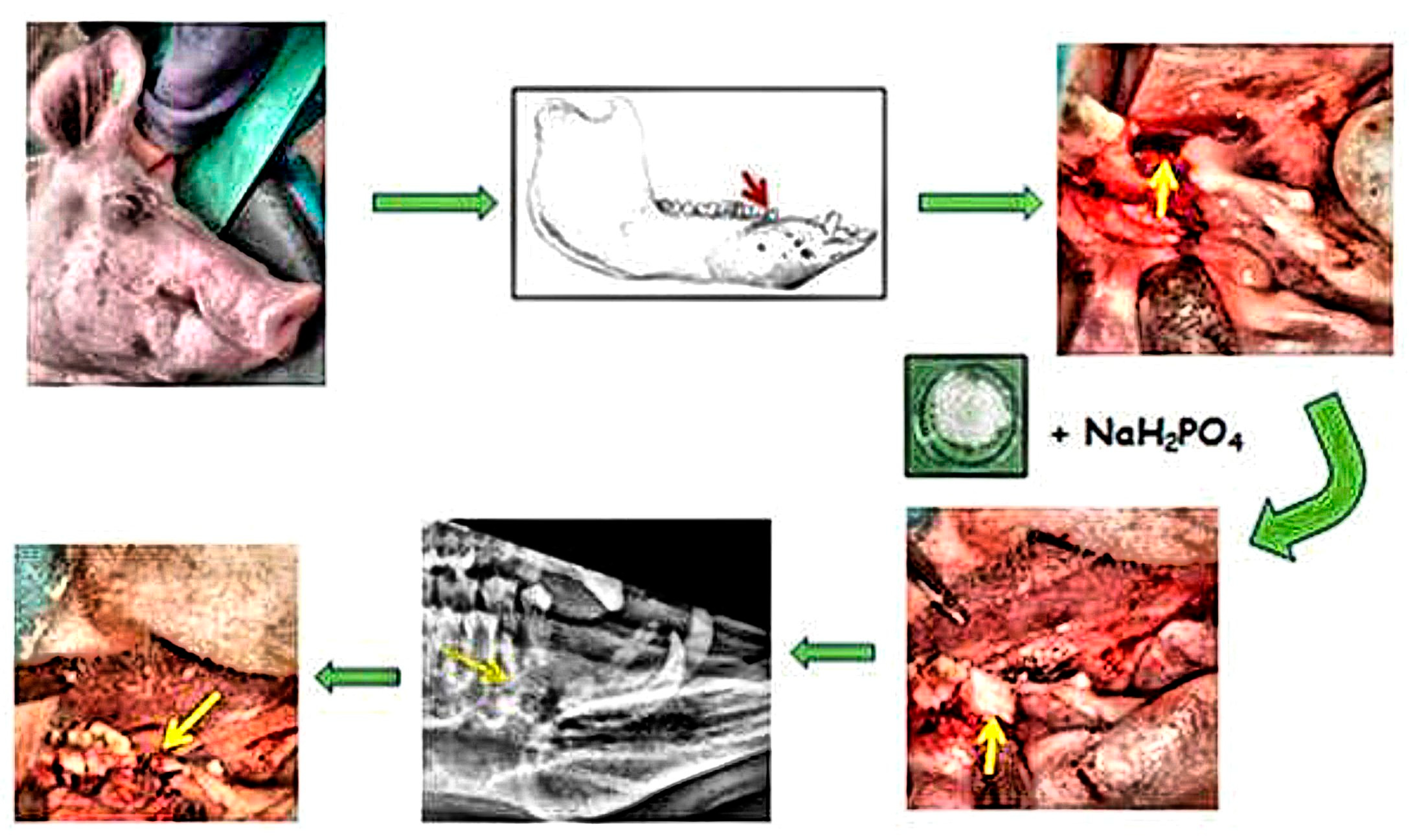
2.3. Experimental Animal Model
2.3.1. Premedication and General Anesthesia
2.3.2. Tooth Extraction and Filling of the Alveolar Bone Defect
2.3.3. Post-Operative Care
2.3.4. Animal Euthanasia and Specimen Retrieval
2.4. Assessment of Alveolar Bone Tissue Regeneration
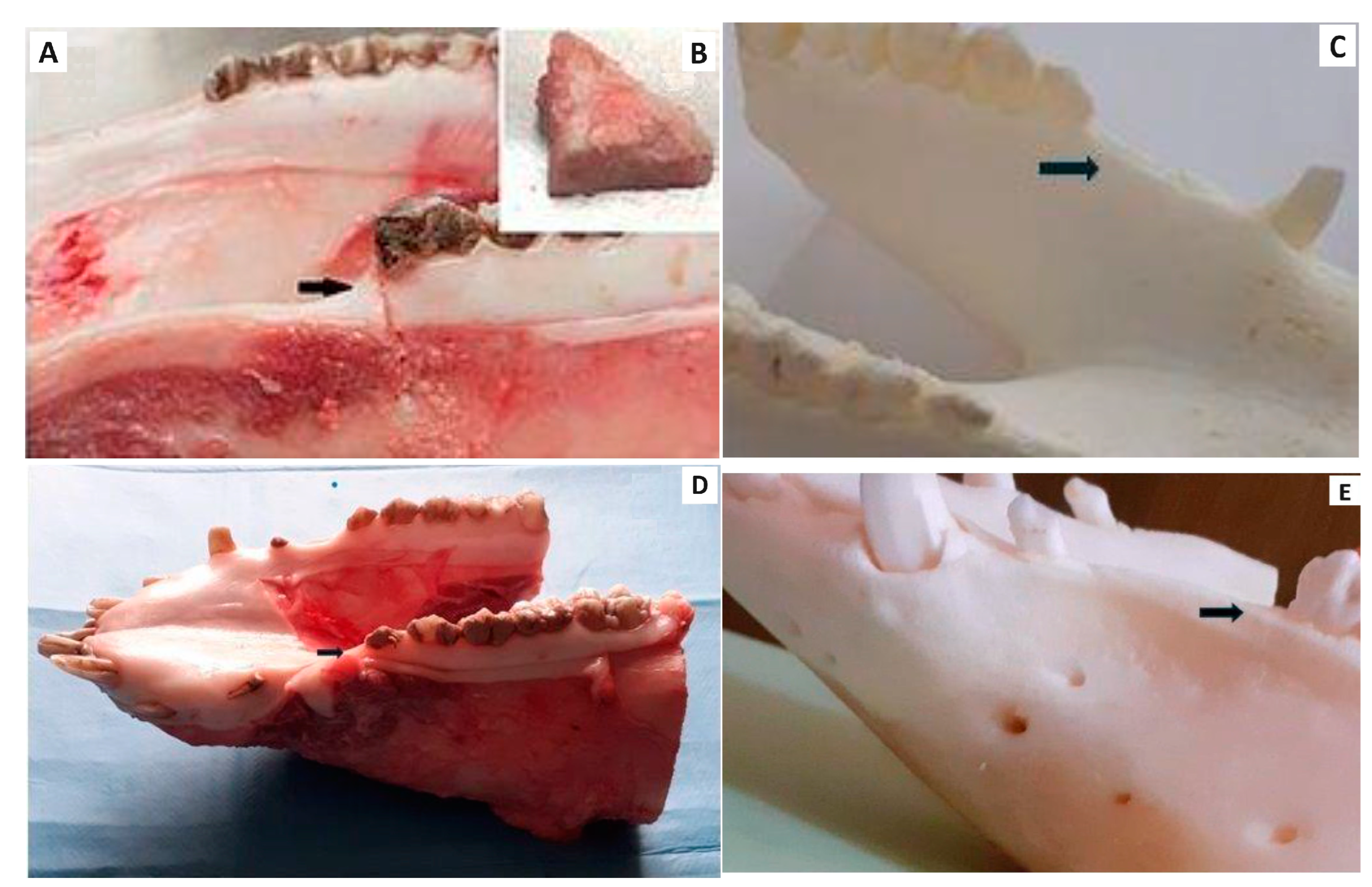
2.4.1. Macroscopic Evaluation
2.4.2. Histological Examination
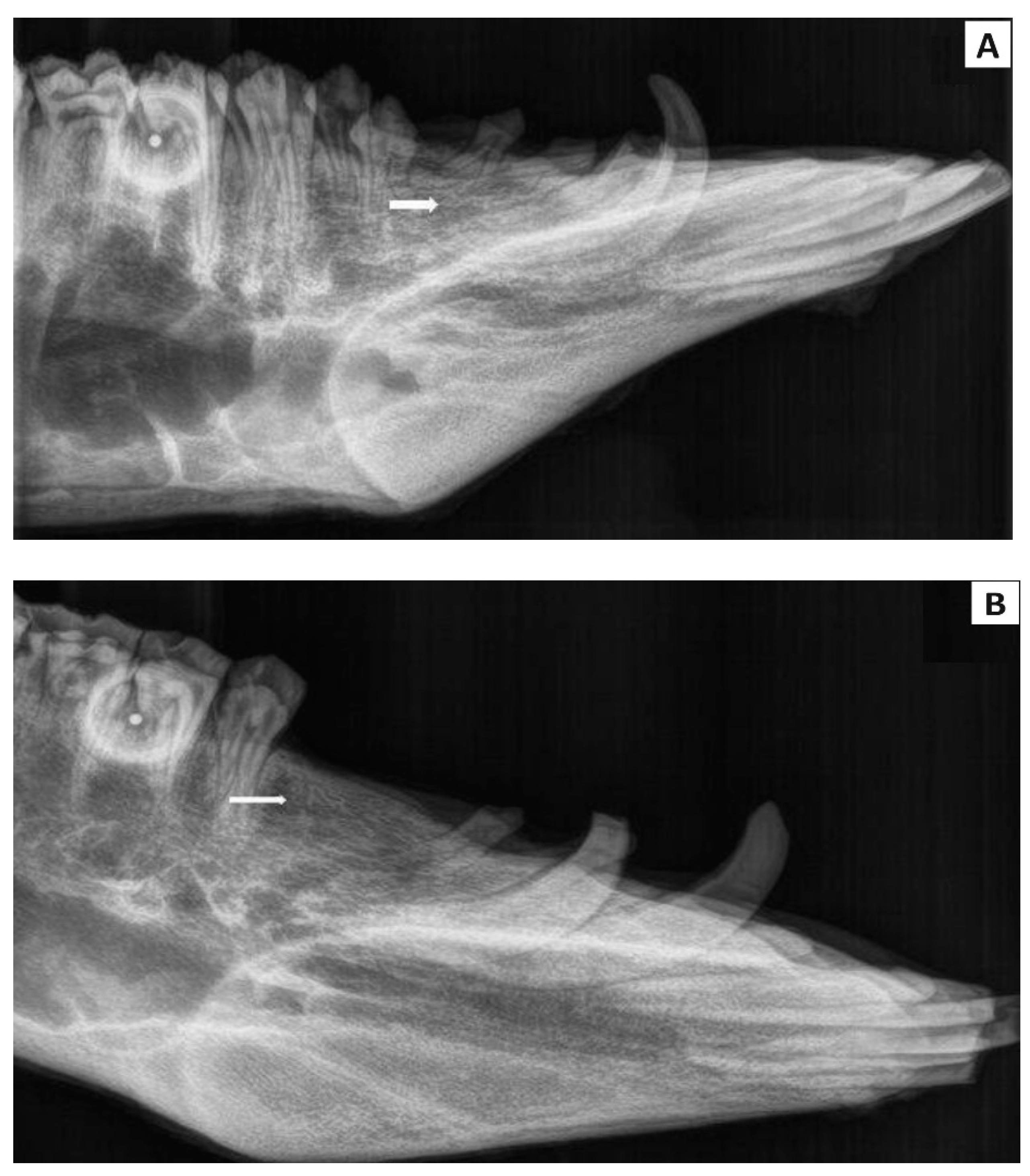
2.4.3. Radiological Examination
3. Results
3.1. Mechanical and Physico-Chemical Properties of CAS Cement
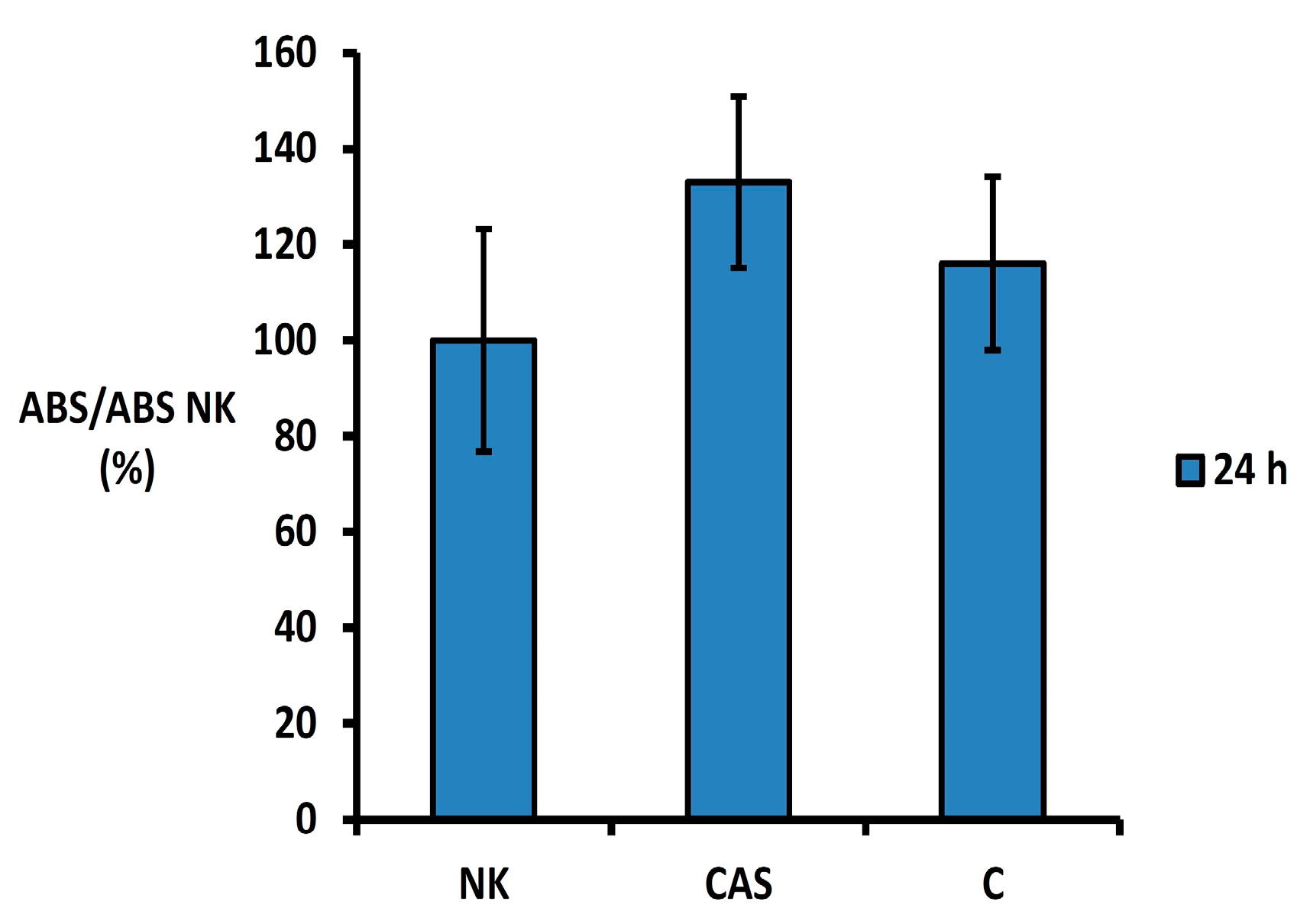
3.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Testing
3.3. Experimental Animal Model and Macroscopic Evaluation of Treated Defect
3.4. Histological Evaluation
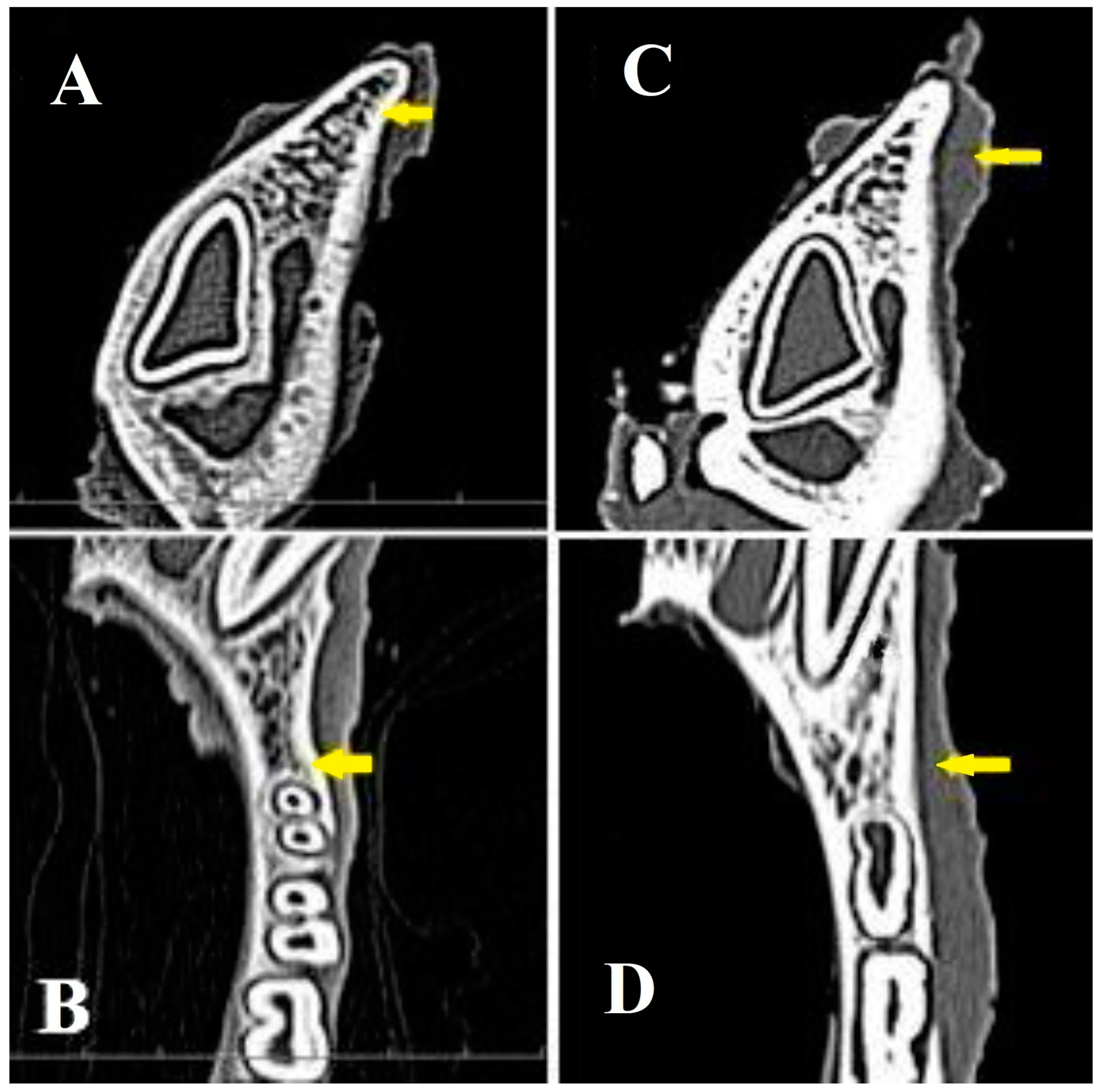
3.5. Radiological Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Checchi, V.; Savarino, L.; Montevecchi, M.; Felice, P.; Checchi, L. Clinical radiographic and histological evaluation of two hydroxyapatites in human extraction sockets: A pilot study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, I.; Chen, S.; De Poi, R. Ridge preservation: What is it and when should it be Considered. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardaropoli, G.; Araujo, M.; Lindhe, J. Dynamics of bone tissue formation in tooth extraction sites. An experimental study in dogs. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2003, 30, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, C.; Nakamoto, T.; Mukaibo, T.; Kondo, Y.; Hosokawa, R. Strategies for alveolar ridge reconstruction and preservation for implant therapy. Review. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2015, 59, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fee, L. Retraction Note: Socket preservation. Br. Dent. J. 2017, 222, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Zhang, H.; Ren, A.; Li, Y.; Fu, G.; Cannon, R.D.; Ji, P.; Wu, X.; Yang, S. Nano-hydroxyapatite mineralized silk fibroinporous scaffold for tooth extraction sitepreservation. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yewale, M.; Bhat, S.; Kamath, A.; Tamrakar, A.; Patil, V.; Algal, A.S. Advanced platelet-rich fibrin plus and osseous bone graft for socket preservation and ridge augmentation—A randomized control clinical trial. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2021, 11, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçen-Röhlig, B.; Meriç, U.; Keskin, H. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of implants immediately placed in fresh extraction sockets. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 109, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijartorn, P.; Wongpairojpanich, J.; Thammarakcharoen, F.; Suwanprateeb, J.; Buranawat, B. Clinical evaluation of 3D printed nano-porous hydroxyapatite bone graft for alveolar ridge preservation: A randomized controlled trial. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aribau-Guma, C.; Jorba-Garcıa, A.; Sanchez-Torres, A.; Sanchez-Garces, M.A. Alveolar ridge preservation: An overview of systematic reviews. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 51, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schropp, L.; Wenzel, A.; Kostopoulos, L.; Karring, T. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: A clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2003, 23, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hammerle, C.H.F.; Araujo, M.G.; Simion, M. On Behalf of the Osteology Consensus Group 2011. Evidence-based knowledge on the biology and treatment of extraction sockets. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranes, D.; Kurtzman, G.M. Biphasic Calcium Sulfate as an Alternative Grafting Material in Various Dental Applications. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 45, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, N.; Ishikawa, K.; Miyamoto, Y. Alveolar ridge preservation in beagle dogs using carbonate apatite bone substitute. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, T.; Cheah, C.H.W.; Ibrahim, N.B.; Asif, M.K.; Vaithilingam, R.D. Three-dimensional assessment of the extraction sockets, augmented with platelet-rich fibrin and calcium sulfate: A clinical pilot study. J. Dent. 2020, 101, 103455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesmas, S.; Swasdison, S.; Yodsanga, S.; Sessirisombat, S.; Jansisyanont, P. Esthetic alveolar ridge preservation with calcium phosphate and collagen membrane: Preliminary report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 110, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alissa, R.; Esposito, M.; Horner, K.; Oliver, R. The influence of platelet-rich plasma on the healing of extraction sockets: An explorative randomised clinical trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 3, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, R.; Bressan, E.; Taut, A.; Cucchi, A.; Trombelli, L. Plasma rich in growth factors in human extraction sockets: A radiographic and histomorphometric study on early bone deposition. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 2013, 24, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraschini, V.; Barboza, E.S.P. Effect of autologous platelet concentrates for alveolar socket preservation: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.A.; Imanian, M.; Alkaabi, S.; Al-sabri, G.; Forouzanfar, T.; Helder, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the use of regenerative graft materials for socket preservation in randomized clinical trials. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, N.; Saifi, A.M.; Giraddi, G.B. Clinical use of the resorbable bioscaffold poly lactic co-glycolic acid (PLGA) in post-extraction socket for maintaining the alveolar height: A prospective study. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2016, 6, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burguera, E.F.; Guitián, F.; Chow, L.C. A water setting tetracalcium phosphate–dicalcium phosphate dihydrate cement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2004, 71A, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ene, R.; Nica, M.; Ene, D.; Cursaru, A.; Cirstoiu, C. Review of calcium-sulphate-based ceramics and synthetic bone substitutes used for antibiotic delivery in PJI and osteomyelitis treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.V.; Puleo, D.A. Calcium sulfate: Properties and clinical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 88, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespi, R.; Cappare, P.; Gherlone, E. Magnesium-Enriched Hydroxyapatite Compared to Calcium Sulfate in the Healing of Human Extraction Sockets: Radiographic and Histomorphometric Evaluation at 3 Months. J. Periodont. 2009, 80, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvecky, L.; Giretova, M.; Stulajterova, R.; Luptakova, L.; Sopcak, T. Tetracalcium Phosphate/Monetite/Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate Biocement Powder Mixtures Prepared by the One-Step Synthesis for Preparation of Nanocrystalline Hydroxyapatite Biocement-Properties and In Vitro Evaluation. Materials 2021, 14, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-12:2012; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2012.
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests For In Vitro Cytotoxicity. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Lodoso-Torrecilla, I.; van den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Jansen, J.A. Calcium phosphate cements: Optimization toward biodegradability. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.C.; Lee, J.W.; Ju, C.P.; Chern Lin, J.H. Physical/Chemical Properties and Resorption Behavior of a Newly Developed Ca/P/S-Based Bone Substitute Material. Materials 2020, 13, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Tägil, M.; Isaksson, H.; Boström, M.; Lidgren, L. Tissue reaction and material biodegradation of a calcium sulfate/apatitebiphasic bone substitute in rat muscle. J. Orthop. Transl. 2015, 6, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Cheng, X.R. Alveolar ridge preservation prior to implant placement with surgical-grade calcium sulfate and platelet-rich plasma: A pilot study in a canine model. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2007, 22, 656–665. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, G.S.; Greenwell, H.; Miller, R.L.; Hill, M.; Johnston, H.; Scheetz, J.P. Comparison of an allograft in an experimental putty carrier and a bovine-derived xenograft used in ridge preservation: A clinical and histologic study in humans. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2004, 19, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beuerlein, M.J.; McKee, M.D. Calcium sulfates: What is the evidence? J. Orthop. Trauma 2010, 24, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brkovic, B.; Radulovic, M. Calcium sulfate for ridge preservation prior to implant placement. A case report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 34, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.I.S.; Chang, Y.-C. Clinical application of calcium sulfate for the augmentation of extraction socket with an oro-antral communication. J. Dent. Sci. 2024, 19, 2425–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.M.; Wilkins, R.M.; Gitelis, S.; Hartjen, C.; Watson, J.T.; Kim, P.T. The use of a surgical grade calcium sulfate as a bone graft substitute: Results of a multicenter trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 382, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Ibrahim, F.M.; El-Meadawy, S.M.; Youssef, J.M. Biological effect of the nanocrystalline calcium sulfate bone graft in the periodontal regeneration. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2021, 11, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, D.; Rubey, T.; Krizan, K.; Keller, J.C. Use of hydroxyapatite cement to support implants in extraction sockets. Implant Dent. 2000, 9, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothamel, D.; Schwarz, F.; Herten, M.; Engelhardt, E.; Donath, K.; Kuehn, P.; Becker, J. Dimensional ridge alterations following socket preservation using a nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite paste: A histomorphometrical study in dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 37, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaita, P.; Chokethawai, K.; Randorn, C.; Boonsri, K.; Pringproa, K.; Thongkorn, K.; Watcharapasorn, A.; Jarupoom, P. Enhancing bioactivity and mechanical performances of hydroxyapatite–calcium sulfate bone cements for bone repair: In vivo histological evaluation in rabbit femurs. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 23286–23302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmagnola, D.; Adriaens, P.; Berglundh, T. Healing of human extraction sockets filled with Bio-Oss. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 2003, 14, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artzi, Z.; Tal, H.; Dayan, D. Porous bovine bone mineral in healing of human extraction sockets. Part 1: Histomorphometric evaluations at 9 months. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, W.; Clokie, C.; Sennerby, L.; Urist, M.R.; Becker, B.E. Histologic findings after implantation and evaluation of different grafting materials and titanium micro screws into extraction sockets: Case reports. J. Periodontol. 1998, 69, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froum, S.; Cho, S.C.; Rosenberg, E.; Rohrer, M.; Tarnow, D. Histological comparison of healing extraction sockets implanted with bioactive glass or demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft: A pilot study. J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vdoviaková, K.; Krešáková, L.; Humeník, F.; Danko, J.; Čurgali, K.; Jenča, A.; Jenča, A., Jr.; Petrášová, A.; Jenčová, J.; Vrzgula, M.; et al. Tetracalcium Phosphate/Monetite/Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate Biocement for Alveolar Bone Augmentation After Tooth Extraction in Pig Mandible. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111057
Vdoviaková K, Krešáková L, Humeník F, Danko J, Čurgali K, Jenča A, Jenča A Jr., Petrášová A, Jenčová J, Vrzgula M, et al. Tetracalcium Phosphate/Monetite/Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate Biocement for Alveolar Bone Augmentation After Tooth Extraction in Pig Mandible. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(11):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111057
Chicago/Turabian StyleVdoviaková, Katarína, Lenka Krešáková, Filip Humeník, Ján Danko, Kristína Čurgali, Andrej Jenča, Andrej Jenča, Jr., Adriána Petrášová, Janka Jenčová, Marko Vrzgula, and et al. 2024. "Tetracalcium Phosphate/Monetite/Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate Biocement for Alveolar Bone Augmentation After Tooth Extraction in Pig Mandible" Bioengineering 11, no. 11: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111057
APA StyleVdoviaková, K., Krešáková, L., Humeník, F., Danko, J., Čurgali, K., Jenča, A., Jenča, A., Jr., Petrášová, A., Jenčová, J., Vrzgula, M., Giretová, M., Štulajterová, R., & Medvecký, Ľ. (2024). Tetracalcium Phosphate/Monetite/Calcium Sulfate Hemihydrate Biocement for Alveolar Bone Augmentation After Tooth Extraction in Pig Mandible. Bioengineering, 11(11), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111057





