The Influence of Kinematics on Tennis Serve Speed: An In-Depth Analysis Using Xsens MVN Biomech Link Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
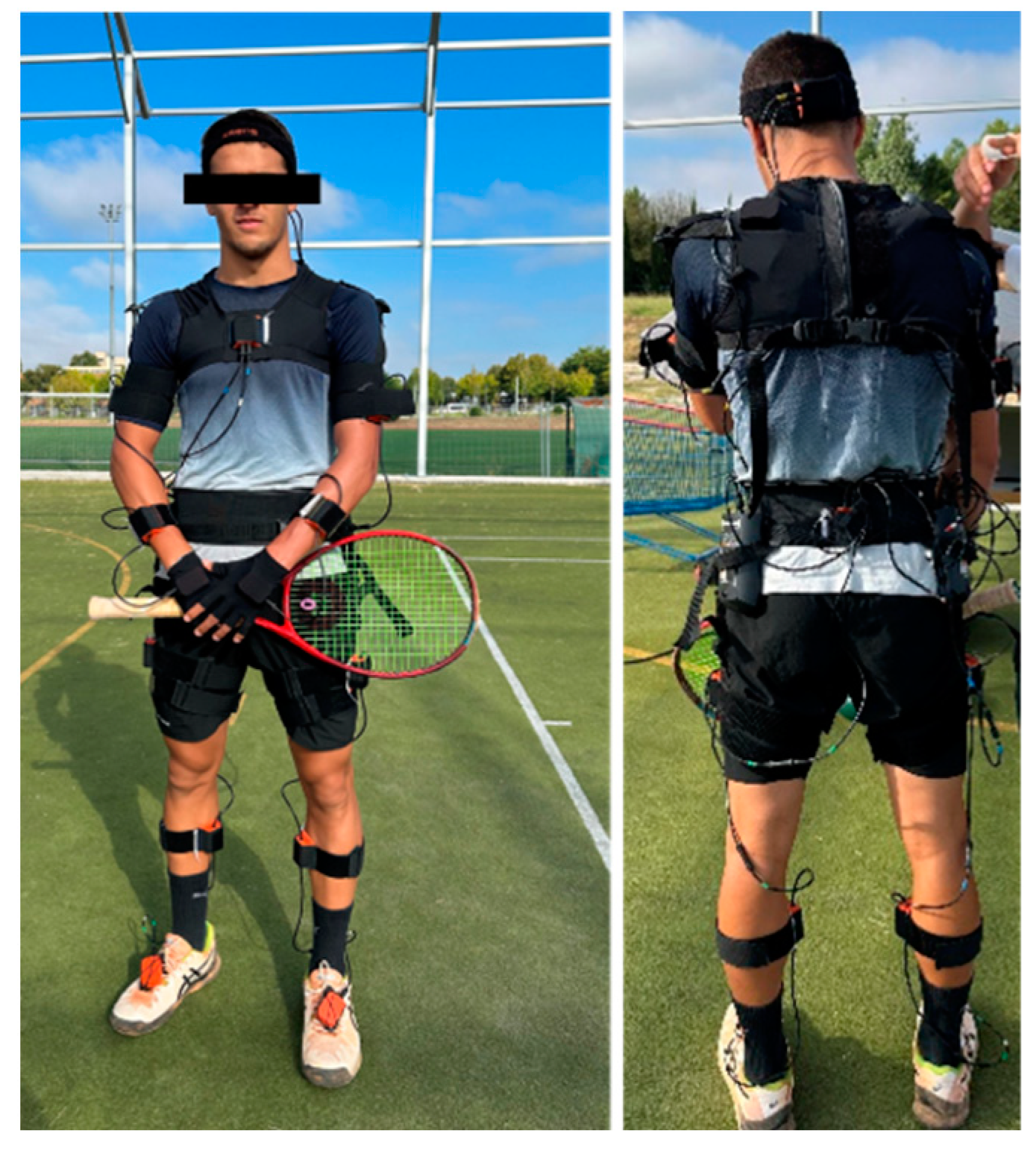
2.1. Participants
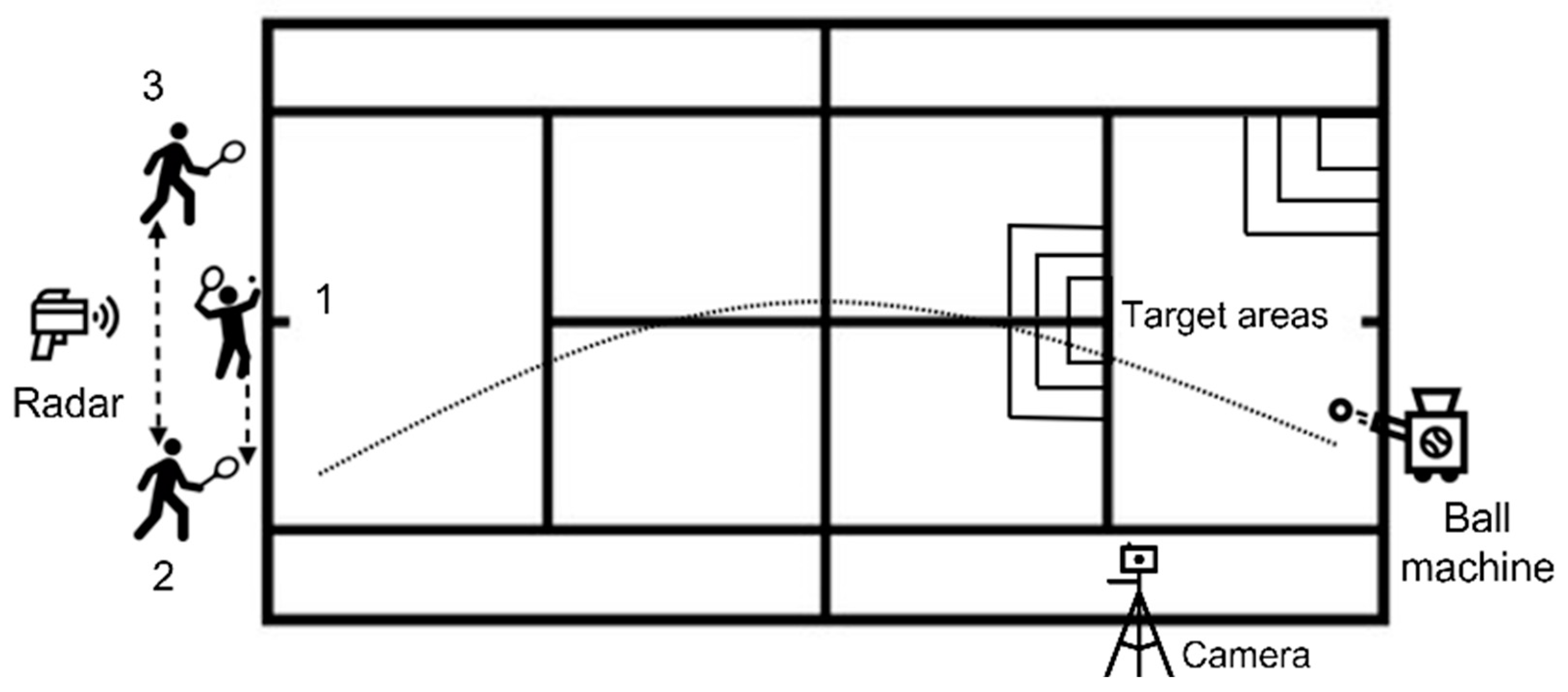
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambrich, J.; Muehlbauer, T. Physical fitness and stroke performance in healthy tennis players with different competition levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, M.S. Tennis physiology: Training the competitive athlete. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, S.; Chadwick, S.; Dignall, R.; Goodwill, S.; Rose, P. Engineering tennis-Slowing the game down. Sports Eng. 2001, 3, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgans, L.F.; Jordan, D.L.; Baeyens, D.A.; Franciosa, J.A. Heart rate responses during singles and doubles tennis competition. Physician Sportsmed. 1987, 15, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, J.; Sanz-Rivas, D.; Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. Match activity and physiological load during a clay-court tennis tournament in elite female players. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Villanueva, A.; Fernandez-Fernandez, J.; Bishop, D.; Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Terrados, N. Activity patterns, blood lactate concentrations and ratings of perceived exertion during a professional singles tennis tournament. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 296–300; discussion 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Soh, K.G.; Abdullah, B.; Huang, D.; Sun, H.; Xiao, W. Effects of physical training programs on female tennis players’ performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1234114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, O.; Micallef, J.P.; Millet, G.P. Lower-limb activity during the power serve in tennis: Effects of performance level. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, M.; Whiteside, D.; Elliott, B. Effect of skill decomposition on racket and ball kinematics of the elite junior tennis serve. Sports Biomech. 2010, 9, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, M.; Ellenbecker, T. An 8-Stage Model for Evaluating the Tennis Serve:Implications for Performance Enhancement and Injury Prevention. Sports Health 2011, 3, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I.T.Federation. ITF Rules of Tennis. 2023. Available online: https://www.itftennis.com/media/7221/2023-rules-of-tennis-english.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Keller, M.; Kuhn, Y.-A.; Lüthy, F.; Taube, W. How to Serve Faster in Tennis: The Influence of an Altered Focus of Attention and Augmented Feedback on Service Speed in Elite Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fett, J.; Oberschelp, N.; Vuong, J.L.; Wiewelhove, T.; Ferrauti, A. Kinematic characteristics of the tennis serve from the ad and deuce court service positions in elite junior players. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, A.V.; Afonso, J.; Silva, G.; Fernandez-Fernandez, J.; Fernandes, R.J. Biophysical characterization of the tennis serve: A systematic scoping review with evidence gap map. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2024, 27, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, B. Biomechanics and tennis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, B. Spin and the power serve in tennis. J. Hum. Mov. Stud. 1983, 9, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.W.; Carlton, L.G.; Lim, Y.T.; Chae, W.S.; Shim, J.H.; Kuenster, A.F.; Kokubun, K. Comparing the pre- and post-impact ball and racquet kinematics of elite tennis players’ first and second serves: A preliminary study. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Ying, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, J. Comparison and analysis of the biomechanics of the lower limbs of female tennis players of different levels in foot-up serve. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1125240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C. Should players serve using the foot-up or foot-back technique? ITF Coach. Sport Sci. Rev. 2015, 23, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrich, J.; Muehlbauer, T. Biomechanical analyses of different serve and groundstroke techniques in tennis: A systematic scoping review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacek, J.; Vagner, M.; Cleather, D.J.; Stastny, P. A Systematic Review of Spatial Differences of the Ball Impact within the Serve Type at Professional and Junior Tennis Players. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocherie, F.; Dinu, D. Biomechanical estimation of tennis serve using inertial sensors: A case study. Front. Sports Act. Living 2022, 4, 962941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubez, F.; Schwartz, C.; Croisier, J.L.; Brüls, O.; Denoël, V.; Paulus, J.; Forthomme, B. Evolution of the trophy position along the tennis serve player’s development. Sports Biomech. 2021, 20, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, B.; Fleisig, G.; Nicholls, R.; Escamilia, R. Technique effects on upper limb loading in the tennis serve. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2003, 6, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleisig, G.; Nicholls, R.; Elliott, B.; Escamilla, R. Kinematics used by world class tennis players to produce high-velocity serves. Sports Biomech. 2003, 2, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, R. Joint Power Production During the Flat and Slice Tennis Serves. In Proceedings of the 15 International Symposium on Biomechanics in Sports (1997), Denton, TX, USA, 21–25 June 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tubez, F.; Forthomme, B.; Croisier, J.L.; Brüls, O.; Denoël, V.; Paulus, J.; Schwartz, C. Inter-Session Reliability of the Tennis Serve and Influence of the Laboratory Context. J. Hum. Kinet. 2019, 66, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Bideau, B.; Delamarche, P.; Kulpa, R. Influence of a Prolonged Tennis Match Play on Serve Biomechanics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.; Richter, C.; Franklyn-Miller, A.; Daniels, K.; Wadey, R.; Jackson, M.; Moran, R.; Strike, S. Biomechanical but not timed performance asymmetries persist between limbs 9 months after ACL reconstruction during planned and unplanned change of direction. J. Biomech. 2018, 81, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, J.B.; Paul, D.J.; Graham-Smith, P.; Read, P.J. Change of Direction Assessment Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Review of Current Practice and Considerations to Enhance Practical Application. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.; Giblin, G.; Whiteside, D. A kinematic comparison of the overhand throw and tennis serve in tennis players: How similar are they really? J. Sports Sci. 2014, 33, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ae, M.; Takenaka, S.; Fujii, N. Comparison of support leg kinetics between side-step and cross-step cutting techniques. Sports Biomech. 2014, 13, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condello, G.; Kernozek, T.W.; Tessitore, A.; Foster, C. Biomechanical Analysis of a Change-of-Direction Task in Collegiate Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, E.; Leroy, D.; Thouvarecq, R.; Stein, J.F. A notational analysis of elite tennis serve and serve-return strategies on slow surface. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgrò, F. Analysis of Knee Joint Motion in Tennis Flat Serve Using Low-Cost Technological Approach. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Workshop on Computer Science in Sports, Wuhan, China, 1–2 August 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-de-Villa, S.; Casillas-Pérez, D.; Jiménez-Martín, A.; García-Domínguez, J.J. Inertial sensors for human motion analysis: A comprehensive review. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 4006439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornestam, J.F.; Souza, T.R.; Magalhães, F.A.; Begon, M.; Santos, T.R.T.; Fonseca, S.T. The Effects of Knee Flexion on Tennis Serve Performance of Intermediate Level Tennis Players. Sensors 2021, 21, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, S.; Morel, B.; Saboul, D.; Rogowski, I.; Hautier, C. Influence of fatigue on upper limb muscle activity and performance in tennis. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.; Carvalho, D.; Fonseca, P.; Monteiro, A.S.; Fernandes, A.; Fernandez-Fernandez, J.; Fernandes, R. Shoulder Torque Production and Muscular Balance after Long and Short Tennis Points. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.; Lee, C.-H. World Tennis Number: The new gold standard, or a failure? ITF Coach. Sport Sci. Rev. 2023, 32, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.; Duffield, R.; Dawson, B.; Baker, J.; Crespo, M. Quantification of the physiological and performance characteristics of on-court tennis drills. Br. J. Sports Med. 2008, 42, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijmeijer, E.; Heuvelmans, P.; Bolt, R.; Gokeler, A.; Otten, E.; Benjaminse, A. Concurrent validation of the Xsens IMU system of lower-body kinematics in jump-landing and change-of-direction tasks. J. Biomech. 2023, 154, 111637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatsidis, A.; Bellusci, G.; Schepers, H.M.; De Zee, M.; Andersen, M.S.; Veltink, P.H. Estimation of Ground Reaction Forces and Moments During Gait Using Only Inertial Motion Capture. Sensors 2017, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leva, P. Adjustments to Zatsiorsky-Seluyanov’s segment inertia parameters. J. Biomech. 1996, 29, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetenberg, D.; Luinge, H.; Slycke, P. Xsens MVN: Full 6DOF human motion tracking using miniature inertial sensors. Xsens Motion Technol. BV Tech. Rep. 2009, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gillet, B.; Begon, M.; Berger-Vachon, C.; Rogowski, I. Kinematics of Shoulder joints during tennis serve in young female athletes: Influence of history of shoulder pain. ISBS Proc. Arch. 2017, 35, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, H.; Pfusterschmied, J.; Tilp, M.; Landlinger, J.; von Duvillard, S.P.; Müller, E. Upper-body kinematics in team-handball throw, tennis serve, and volleyball spike. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataky, T.C. One-dimensional statistical parametric mapping in Python. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 2012, 15, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, M.; Penny, W.; Kiebel, S. An Introduction to Random Field Theory. In Human Brain Function, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquier-Bret, J.; Gorce, P. Kinematics of the Tennis Serve Using an Optoelectronic Motion Capture System: Are There Correlations between Joint Angles and Racket Velocity? Sensors 2024, 24, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, S.; Attaallah, M. Kinematic Analysis of the whole body Center of Gravity Trajectory and Time Structure of the Tennis Serve Performance. J. Appl. Sports Sci. 2015, 5, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside, D.; Elliott, B.; Lay, B.; Reid, M. A kinematic comparison of successful and unsuccessful tennis serves across the elite development pathway. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2013, 32, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.; McMurtrie, D.; Crespo, M. Title: The relationship between match statistics and top 100 ranking in professional men’s tennis. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport. 2010, 10, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, W.B.; Chandler, T.J.; Shapiro, R.; Conuel, M. Muscle activation in coupled scapulohumeral motions in the high performance tennis serve. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López de Subijana, C.; Navarro, E. Kinetic energy transfer during the Tennis serve. Biol. Sport. 2010, 27, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamkrajang, P.; Robinson, M.A.; Limroongreungrat, W.; Vanrenterghem, J. How do tennis players control their balance during the serve? ISBS Proc. Arch. 2017, 35, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Tornero-Aguilera, J.; Jimenez Morcillo, J.; Rubio-Zarapuz, A.; Clemente-Suárez, V. Central and Peripheral Fatigue in Physical Exercise Explained: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingül, B.M.; Aydin, M.; Bulgan, Ç.; Gelen, E.; Özbek, A. Upper extremity kinematics of flat serve in tennis. S. Afr. J. Res. Sport Phys. Educ. Recreat. 2016, 38, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fleisig, G.; Nicholls, R.; Escamilla, R.; Elliott, B. Kinematics and Kinetics of the High Velocity Tennis Serve. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzard, P.; Kulpa, R.; Bideau, B.; Montalvan, B.; Martin, C. Biomechanical analysis of the “waiter’s serve” on upper limb loads in young elite tennis players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göktepe, A.; Ak, E.; Söğüt, M.; Karabörk, H.; Korkusuz, F. Joint angles during successful and unsuccessful tennis serves kinematics of tennis serve. Eklem Hastalik. Cerrahisi 2009, 20, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, M.; Middleton, K.; Spence, G.; Cant, O.; Reid, M. Effects of Lumbar Spine Abnormality and Serve Types on Lumbar Kinematics in Elite Adolescent Tennis Players. Sports Med.-Open 2021, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pay, A.; Ramón-Llin, J.; Martínez-Gallego, R.; Sanz, D.; Sánchez-Alcaraz Martínez, B.; Frutos, S. Fitness testing in tennis: Influence of anthropometric characteristics, physical performance, and functional test on serve velocity in professional players. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fett, J.; Ulbricht, A.; Ferrauti, A. Impact of Physical Performance and Anthropometric Characteristics on Serve Velocity in Elite Junior Tennis Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomar, J.; Corbi, F.; Brich, Q.; Baiget, E. Determinant Physical Factors of Tennis Serve Velocity: A Brief Review. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2022, 17, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, J.; Nakamura, F.Y.; Moreno-Perez, V.; Lopez-Valenciano, A.; Del Coso, J.; Gallo-Salazar, C.; Barbado, D.; Ruiz-Perez, I.; Sanz-Rivas, D. Age and sex-related upper body performance differences in competitive young tennis players. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, M.J.; Spits, D.R.; Watts, D.G.; Kelly, V.G. Relationship Between Tennis Serve Velocity and Select Performance Measures. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilić, Z.; Martić, P.; Barbaros, P.; Sinković, F.; Novak, D. Neuromuscular Fitness Is Associated with Serve Speed in Young Female Tennis Players. Sports 2024, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksrud, O.; Ghelem, A.; Henrikson, F.; Englund, J.; Brodin, N. Upper and lower body power tests predict serve performance in national and international level male tennis players. Sport Perform. Sci. Rep. 2018, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mavvidis, A.; Manousaridou, A.; Grivas, N.; Evagelidis, T.; Laios, A. The effectiveness of serve in tennis depending on the placement of palm across the racket grip inwards or outwards. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2014, 14, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söğüt, M. A Comparison of Serve Speed and Motor Coordination between Elite and Club Level Tennis Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 55, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboch, J.; Süss, V. Toss differences between the slice serve and the kick serve in tennis. Acta Gymnica 2015, 45, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertwonghattakul, T.; Sriramatr, S. Analysis of kinetic chain mechanism affecting energy flow in kick topspin tennis serve in elite and amateur tennis players. Ann. Appl. Sport Sci. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

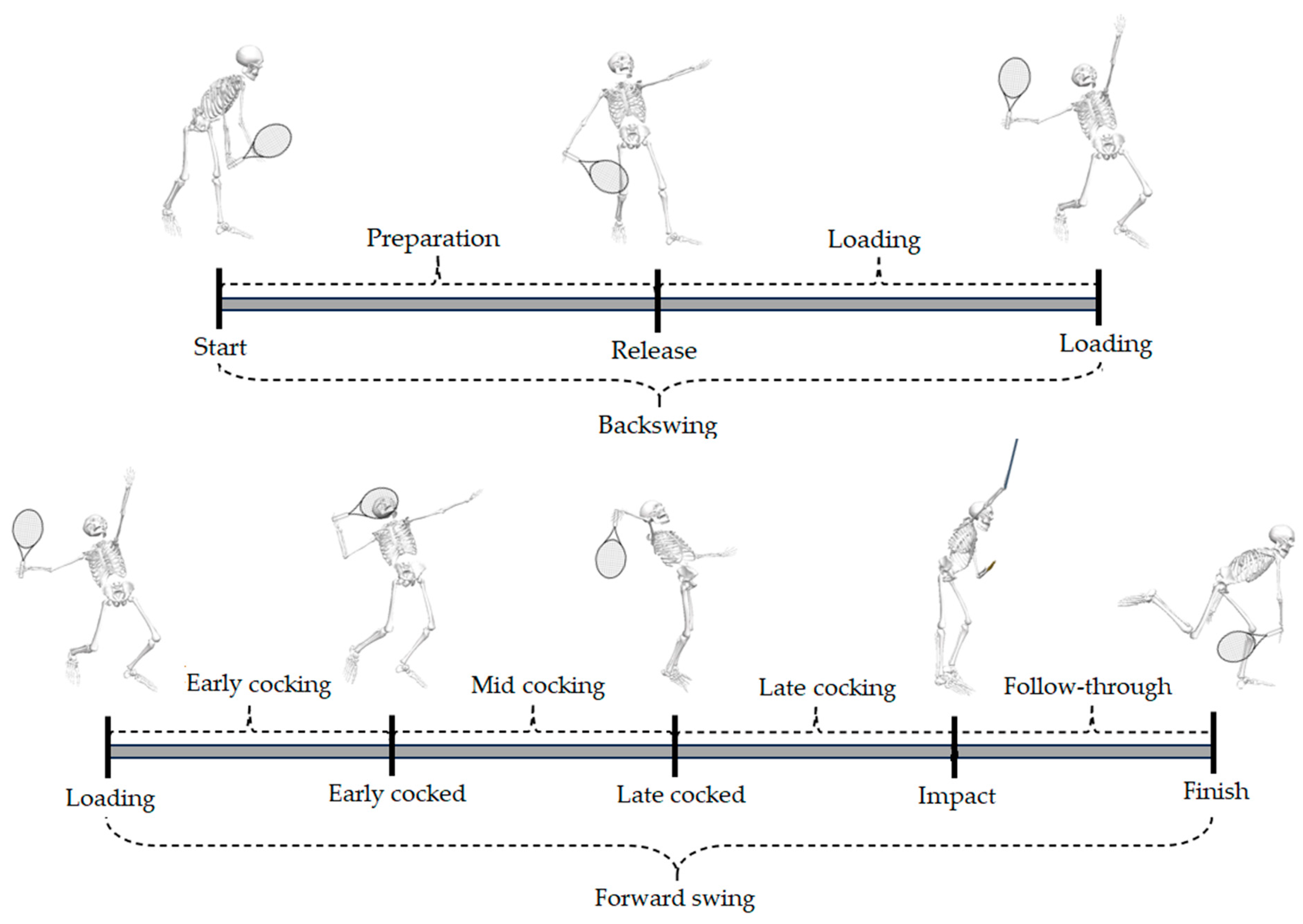
| Stages | Events | Criteria | Segments | Movement Axis and Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backswing | Start | The distance between hands increases prior to ball release. |  |
|
| Release | Dominant shoulder with 52° of abduction, 8° of extension or 20° of external rotation. | |||
| Loading | Maximum knee flexion or minimum center of mass height. | |||
| Forward swing | Early cocked | Maximum shoulder external rotation, without thoracic rotation. | ||
| Late cocked | Maximum shoulder external rotation caused by inertia of the thoracic rotation. | |||
| Impact | Maximum elbow extension angle. | |||
| Finish | Vertical center of mass velocity reaches zero. |
| Phase Duration | ||||||||||||||||
| Preparation (%) | Loading (%) | Cocking (%) | Follow-through (%) | Total serve duration (s) | ||||||||||||
| Early | Mid | Late | ||||||||||||||
| Group A | 25.3 (6.7) | 30.4 (6.0) | 10.7 (4.6) | 7.8 (3.1) | 5.5 (1.2) ** | 20.0 (3.1) | 1.69 (0.14) | |||||||||
| Group B | 26.5 (10.2) | 32.6 (8.0) | 7.9 (4.9) | 5.9 (3.8) | 7.9 (2.4) | 19.0 (3.1) | 1.70 (0.18) | |||||||||
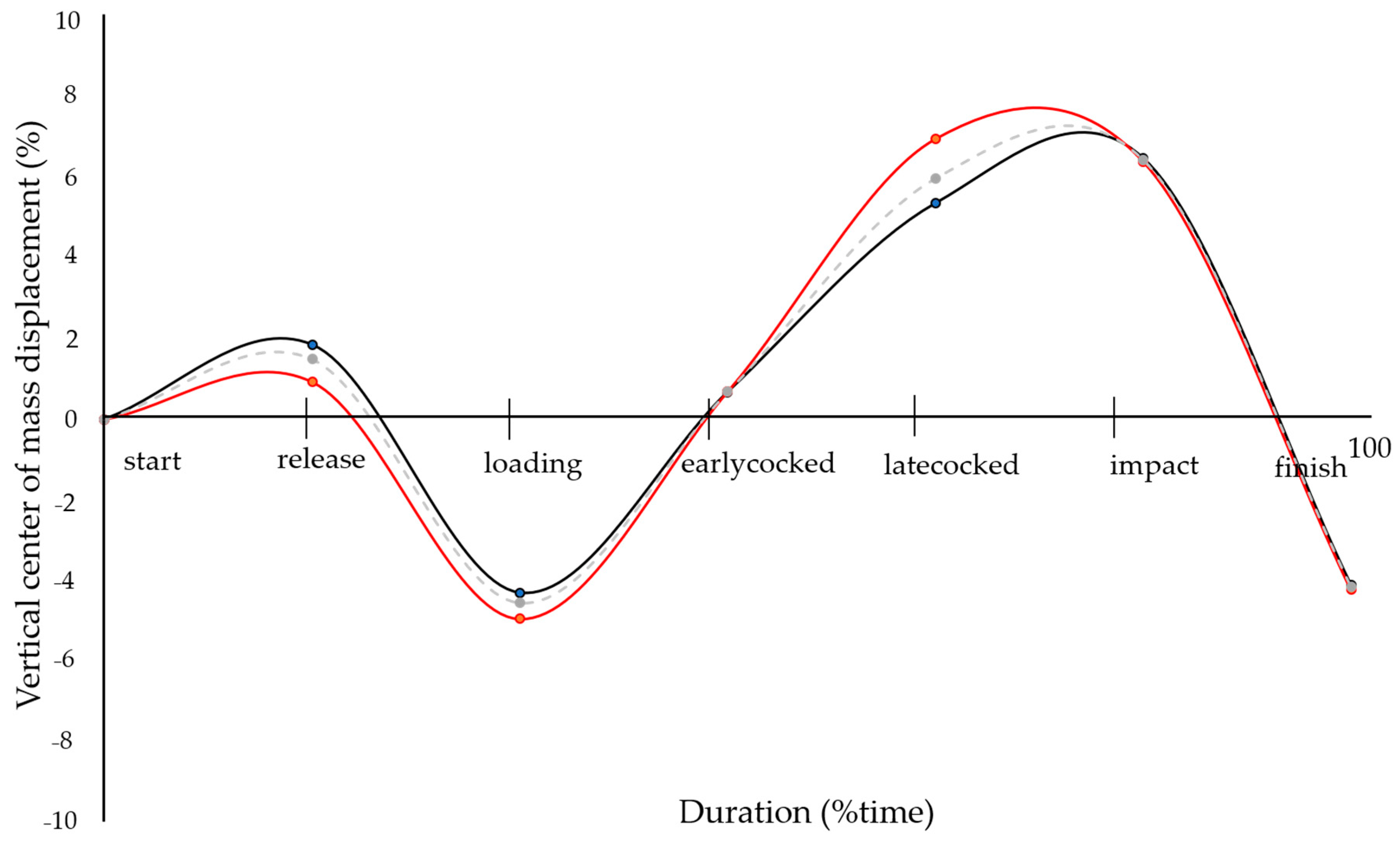
| Event | Group A | Group B | ||||||||||||||
| Instance (%) | Center of mass displacement | Instance (%) | Center of mass displacement | |||||||||||||
| Horizontal | Vertical | Horizontal | Vertical | |||||||||||||
| % | m | % | m | % | m | % | m | |||||||||
| Start | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.01 (0.03) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.98 (0.04) | ||||||
| Release | 25.1 (6.5) | −1.3 (1.7) | −0.03 (0.2) | 0.9 (1.7) | 1.03 (0.04) | 26.1 (9.0) | −1.8 (3.6) | −0.05 (0.06) | 1.8 (0.4) | 1.01 (0.04) | ||||||
| Loading | 55.5 (4.7) | 5.7 (4.9) | 0.2 (0.05) | −4.9 (3.5) | 0.92 (0.05) | 58.9 (2.6) * | 10.0 (7.0) | 0.1 (0.1) | −4.3 (2.7) | 0.90 (0.05) | ||||||
| Cocked | Early | 66.0 (5.3) | 12.0 (4.3) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.6 (2.5) | 1.02 (0.05) | 67.7 (4.5) | 14.0 (7.4) | 0.2 (0.09) | 0.6 (3.6) | 0.99 (0.06) | |||||
| Late | 70.6 (3.2) | 17.2 [4.1] | 0.3 (0.1) | 6.9 (1.9) * | 1.14 (0.02) * | 73.2 (2.2) | 18.4 (6.8) | 0.3 (0.1) | 5.3 (1.6) | 1.07 (0.05) | ||||||
| Impact | 79.8 (3.3) | 21.8 (6.4) | 0.4 (0.1) | 6.4 (2.3) | 1.13 (0.03) | 81.3 (2.8) | 23.6 (7.2) | 0.3 (0.1) | 6.5 (3.5) | 1.09 (0.08) | ||||||
| Finish | 100 | 32.5 (11.3) | 0.6 (0.1) | −4.2 (2.5) | 0.93 (0.05) | 100 | 31.9 (9.6) | 0.5 (0.1) | −4.1 (2.9) | 0.91 (0.05) | ||||||
| Events | Motion | Upper Limbs | Lower Limbs | Thorax | Pelvis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant | Non-Dominant | Front | Back | ||||||||
| Shoulder | Elbow | Wrist | Shoulder | Knee | Hip | Knee | Hip | ||||
| Loading | Frontal | −67.3 (33.6) | NR | 4.7 (12.9) | −128.4 (14.1) | NR | 1.4 (13.7) | NR | −15.9 (9.9) | 13.9 (7.1) | −20.4 (3.7) ** |
| Sagittal | −10.3 (9.5) | −58.2 (11.4) | 0.3 (21.5) * | −32.5 (14.8) | 64.3 (10.4) | −11.0 (11.3) | 64.2 (10.8) | −11.4 (9.7) | 1.9 (11.5) | −0.1 (4.7) | |
| Transverse | −46.5 (14.9) | NR | NR | NR | NR | −13.1 (4.6) | NR | 0.8 (14.9) | −13.4 (8.5) | −109.1 (15.0) | |
| Early cocked | Frontal | −77.4 (17.4) | NR | −4.2 (7.1) ** | NR | NR | 2.8 (9.2) | NR | −6.7 (7.8) | 4.8 (14.0) | −19.0 (1.9) * |
| Sagittal | −19.8 (13.7) | −67.2 (11.0) | 18.7 (18.8) | NR | 39.1 (13.8) | 5.7 (7.2) | 39.2 (12.3) | 9.4 (8.0) * | −9.5 (6.5) | NR | |
| Transverse | −85.1 (15.3) * | NR | NR | NR | NR | −10.1 (7.5) | NR | 1.1 (10.6) | −26.1 (5.7) | −92.1 (16.6) | |
| Late cocked | Frontal | −110.8 (16.5) | NR | −20.1 (17.0) | NR | NR | −15.2 (6.4) | NR | 13.1 (3.4) | −26.6 (5.0) ** | −13.9 (3.4) |
| Sagittal | −29.0 (13.2) * | −48.1 (17.3) ** | 47.5 (10.6) | NR | 18.6 (8.0) | −0.5 (11.0) | 4.3 [5.3] ** | 5.5 (6.8) * | −7.0 (9.5) | NR | |
| Transverse | −121.8 (19.5) | NR | −26.4 (8.2) | NR | NR | −0.2 (9.5) | NR | −11.6 (7.4) | −13.9 (7.8) | −52.8 (10.0) | |
| Impact | Frontal | −108.6 [9.1] | −8.8 (5.2) | 6.1 (6.4) | NR | NR | −23.2 (10.0) | 0.03 (1.5) | 13.2 (5.8) | −28.9 (6.3) | −16.7 (6.5) |
| Sagittal | −28.3 (15.4) | −4.4 (5.2) | 18.5 [8.1] | NR | 24.8 (11.1) | −28.1 (10.3) | 2.8 (5.9) * | −8.5 (9.2) | 15.1 (7.4) | 17.3 (4.2) | |
| Transverse | −77.6 (19.1) | 59.9 (4.8) | −22.6 (8.5) | NR | NR | −4.3 (12.1) | −6.7 (4.1) | −14.9 (6.9) | 3.4 (7.4) | −26.9 (15.3) | |
| Finish | Frontal | 18.2 (16.2) | 16.3 (7.3) | 27.7 [12.6] | NR | NR | −8.4 (12.1) | NR | −14.8 (5.2) | −12.6 (12.1) | −6.3 (9.3) |
| Sagittal | −34.9 (10.9) | −27.6 (10.5) | 8.6 (8.6) | NR | 50.4 (6.5) | −54.6 (13.1) | 60.6 (15.7) | −12.0 (12.5) | 24.1 (8.4) | 25.1 (8.1) | |
| Transverse | 41.1 (21.6) | 110.3 (5.0) | 25.5 (9.7) | NR | NR | 0.2 (10.1) | NR | −11.7 (9.1) | 23.7 (10.0) | −1.2 (19.4) | |
| Event | Motion | Upper Limbs | Lower Limbs | Thorax | Pelvis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant | Non-Dominant | Front | Back | ||||||||
| Shoulder | Elbow | Wrist | Shoulder | Knee | Hip | Knee | Hip | ||||
| Loading | Frontal | −88.8 (29.1) | NR | 0.07 (15.7) | −119.5 [15.7] | NR | 1.9 (11.9) | NR | −16.7 (14.1) | 9.4 (8.8) | −13.0 (6.4) |
| Sagittal | −16.7 (15.8) | −58.1 (18.5) | 14.5 [10.4] | −30.5 (14.3) | 66.9 (9.9) | −18.2 (13.7) | 66.7 (7.1) | −16.7 (9.4) | −3.1 (8.6) | −5.4 (5.9) | |
| Transverse | −74.3 (27.3) | NR | NR | NR | NR | −15.7 (6.5) | NR | 2.8 (8.0) | −13.9 (10.5) | −98.3 (13.2) | |
| Early cocked | Frontal | −88.3 (27.3) | NR | −18.0 (18.7) | NR | NR | −1.6 (8.6) | NR | −4.6 (11.6) | 1.7 (11.6) | −13.8 (5.7) |
| Sagittal | −23.4 (9.8) | −69.7 (8.3) | 32.7 (16.2) | NR | 44.7 (23.1) | −2.5 (14.9) | 42.5 (16.6) | −1.9 (9.8) | −11.0 (12.2) | NR | |
| Transverse | −104.4 (23.8) | NR | NR | NR | NR | −13.1 (10.0) | NR | 3.0 (9.1) | −20.7 [8.8] | −83.1 (21.3) | |
| Late cocked | Frontal | −103.2 (12.6) | NR | −31.7 (13.3) | NR | NR | −12.8 (9.4) | NR | 7.8 (9.4) | −16.6 [8.7] | −16.1 (6.8) |
| Sagittal | −31.7 (8.0) | −66.6 (6.4) | 47.6 (9.7) | NR | 20.0 (11.5) | 7.4 (8.1) | 20.0 (10.0) | 9.1 (4.4) | −14.8 (10.2) | NR | |
| Transverse | −126.2 (13.7) | NR | −18.3 (18.0) | NR | NR | −8.1 (12.0) | NR | −4.9 (10.2) | −16.4 (10.2) | −59.4 (15.2) | |
| Impact | Frontal | −107.7 (11.8) | −6.8 (3.7) | 6.2 (6.4) | NR | −1.8 (3.5) | −26.4 (11.4) | 1.0 (3.7) | 13.8 (6.4) | −28.0 (7.3) | −21.1 (6.8) |
| Sagittal | −35.5 (13.5) | −0.1 (8.8) | 16.6 (12.2) | NR | 27.3 (12.6) | −23.5 (10.3) | 14.3 (13.0) | −3.8 (5.8) | 10.5 (10.2) | 11.7 (7.4) | |
| Transverse | −72.6 (13.1) | 62.8 (14.6) | −22.2 (17.6) | NR | 0.4 (4.6) | −10.0 (12.4) | −8.7 (5.0) | −11.2 (7.8) | 2.7 (8.8) | −13.8 (21.5) | |
| Finish | Frontal | 6.0 (13.5) | 23.1 (17.0) | 19.4 (6.8) | NR | NR | −7.0 (16.0) | NR | −15.3 (8.9) | −10.0 (5.6) | −14.1 (12.8) |
| Sagittal | −40.4 (9.9) | −19.6 (10.8) | 11.1 (11.7) | NR | 49.4 (10.8) | −54.2 (15.9) | 63.0 (10.1) | −16.5 (17.6) | 22.5 (7.7) | 21.6 (12.1) | |
| Transverse | 31.4 (22.1) | 108.3 (19.5) | 28.5 (16.7) | NR | NR | −2.3 (13.7) | NR | −11.7 (9.1) | 24.5 (9.4) | −15.0 (25.5) | |
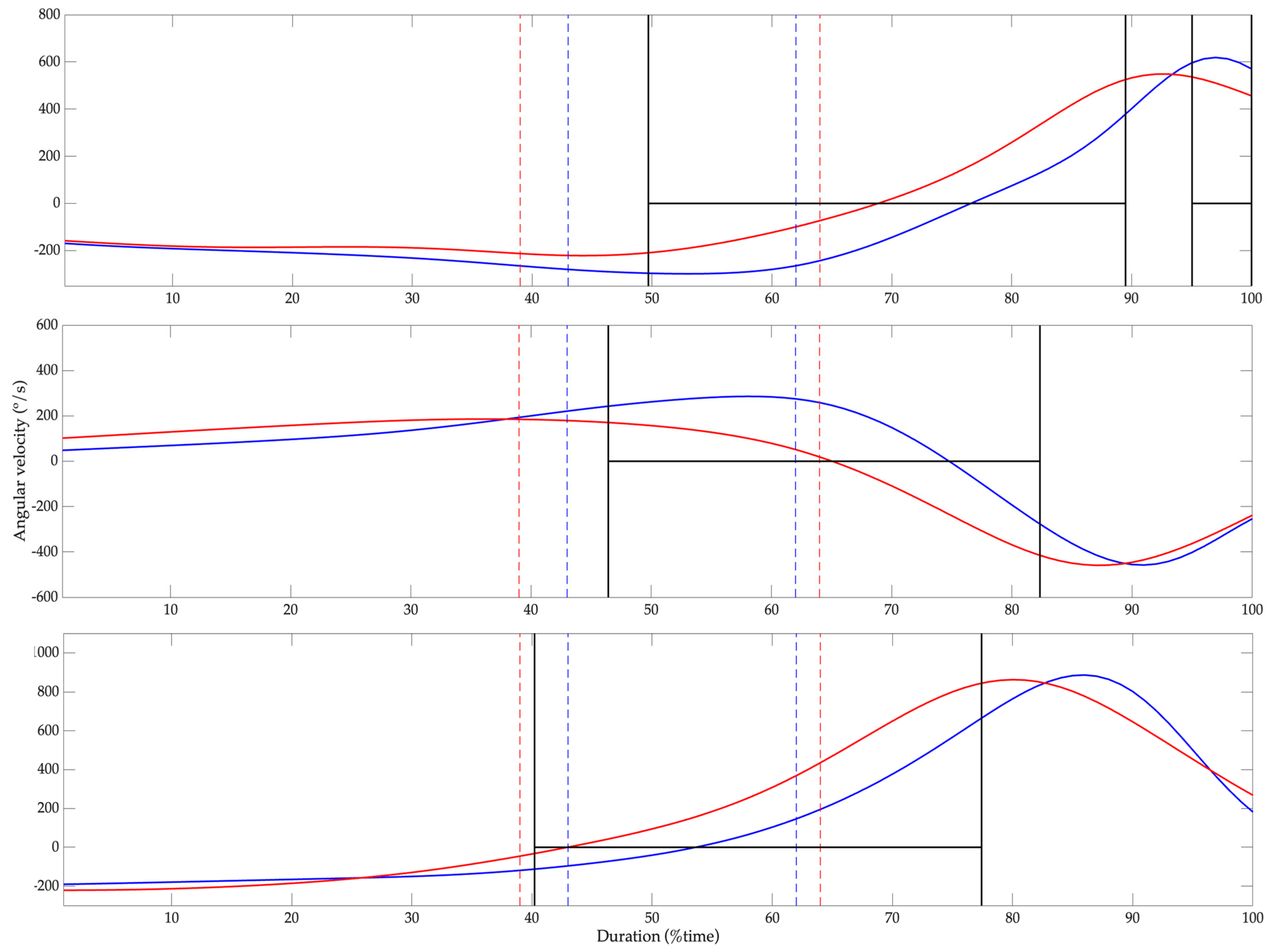
| Cocking phase | Segments | Motion | Maximal Angular Velocity (°/s) | Minimal Angular Velocity (°/s) | ||
| Group A | Group B | Group A | Group B | |||
| Shoulder | Sagittal | 653.9 (127.4) | 629.7 (127.4) | −394.5 (114.7) | −321.3 (103.5) | |
| Transverse | 194.0 (47.3) | 188.6 [122.5] | −274.9 (92.1) | −258.8 (151.6) | ||
| Elbow | Sagittal | 920.6 (254.9) | 1015.2 (122.5) | −245.8 (115.3) | −276.8 (153.1) | |
| Wrist | Frontal | 522.0 (126.2) | 554.7 (133.4) | −257.5 (112.1) | −266.8 (89.3) | |
| Sagittal | 427.0 (99.8) * | 308.3 (111.7) | −555.6 (169.8) | −592.8 (131.7) | ||
| Thorax | Frontal | 162.4 (81.7) * | 81.1 (49.7) | −381.7 (68.7) | −342.4 (80.4) | |
| Sagittal | 394.2 (73.2) | 344.6 (104.9) | −159.3 (80.8) | −144.7 (80.4) | ||
| Transverse | 134.4 (64.6) | 113.8 (53.7) | −115.0 (45.4) | −349.7 [103.5] | ||
| Pelvis | Transverse | 360.2 (61.2) | 407.8 (78.8) | 0.1 (23.8) | 0.2 (51.8) | |
| Back hip | Frontal | 205.4 (9.7) ** | 227.8 (77.0) | −84.2 (35.7) | −112.7 (39.8) | |
| Sagittal | 193.5 (43.8) ** | 240.8 (99.8) | −247.8 (107.1) | −170.8 (77.2) | ||
| Transverse | 43.6 (37.4) | 66.0 (39.6) | −212.7 (77.2) | −236.8 (55.0) | ||
| Front hip | Frontal | 64.2 (49.4) | 87.7 (51.6 | −205.8 (64.2) | −257.8 (89.1) | |
| Sagittal | 200.6 (67.2) | 256.1 (65.1) | −403.1 (49.2) | −342.3 (65.0) | ||
| Transverse | 197.2 (43.1) | 215.5 (73.6) | −72.6 (44.7) | −87.5 (53.6) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brito, A.V.; Fonseca, P.; Costa, M.J.; Cardoso, R.; Santos, C.C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, J.; Fernandes, R.J. The Influence of Kinematics on Tennis Serve Speed: An In-Depth Analysis Using Xsens MVN Biomech Link Technology. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100971
Brito AV, Fonseca P, Costa MJ, Cardoso R, Santos CC, Fernandez-Fernandez J, Fernandes RJ. The Influence of Kinematics on Tennis Serve Speed: An In-Depth Analysis Using Xsens MVN Biomech Link Technology. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(10):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100971
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrito, André V., Pedro Fonseca, Mário J. Costa, Ricardo Cardoso, Catarina C. Santos, Jaime Fernandez-Fernandez, and Ricardo J. Fernandes. 2024. "The Influence of Kinematics on Tennis Serve Speed: An In-Depth Analysis Using Xsens MVN Biomech Link Technology" Bioengineering 11, no. 10: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100971
APA StyleBrito, A. V., Fonseca, P., Costa, M. J., Cardoso, R., Santos, C. C., Fernandez-Fernandez, J., & Fernandes, R. J. (2024). The Influence of Kinematics on Tennis Serve Speed: An In-Depth Analysis Using Xsens MVN Biomech Link Technology. Bioengineering, 11(10), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100971











